| Revision as of 00:08, 3 May 2018 view sourcePlyrStar93 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers46,828 editsm Reverted edits by 190.56.75.60 (talk) (HG) (3.3.5)Tags: Huggle Rollback← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:31, 8 January 2025 view source TessiDon (talk | contribs)164 edits I made copyedits | ||
| (317 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|System or group governing an organized community}} | |||
| {{other uses|Government (disambiguation)|Gov (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Redirect|Gov}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2012}} | |||
| {{pp-vandalism|small=yes}} | |||
| {{For-multi|the executive power referred to as "the government"|Executive (government)|other uses}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=September 2021}} | |||
| {{Use British English|date=January 2016}} | {{Use British English|date=January 2016}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Systems of government}} | ||
| {{Governance}} | |||
| {{Politics sidebar|expanded=Subseries}} | |||
| <!-- For future edits, consider avoid filling up the lead with unwanted, unreliable sources, because as per Misplaced Pages:Manual_of_Style/Layout#Order_of_article_elements, the lead will usually repeat information that is in the body, editors should balance the desire to avoid redundant citations in the lead with the desire to aid readers in locating sources for challengeable material. --> | |||
| A '''government''' is the system or group of people governing an organized community, often a ].<ref>{{cite web|title=government|publisher=''Oxford English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press|date=November 2010|url=http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/government}}</ref> | |||
| A '''government''' is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a ]. | |||
| In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of ], ], and ]. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining ]. Each government has a kind of ], a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. Typically the philosophy chosen is some balance between the principle of individual ] and the idea of absolute state authority (]). | |||
| In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of ], ], and ]. Government is a means by which organizational ] are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of ], a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. | |||
| While all types of organizations have governance, the word ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 ] on ], as well as subsidiary organizations.<ref name=EncycSocialSciences>{{cite book|title=International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences|year=2001|publisher=Elsevier|isbn=0-08-043076-7}}</ref> | |||
| While all types of organizations have ], the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 ] and ]. | |||
| Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, ], ], ], ], ] and ]. The main aspect of any philosophy of government is how political power is obtained, with the two main forms being ] and ]. | |||
| The main types of modern ]s recognized are ], ]s, and, sitting between these two, ] with a variety of ]s.<ref name="Dobratz 2015 p. 47">{{Cite book |last=Dobratz |first=B.A. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RoK9CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA47 |title=Power, Politics, and Society: An Introduction to Political Sociology |date=2015 |publisher=Taylor & Francis |isbn=978-1-317-34529-9 |page=47 |access-date=Apr 30, 2023 |archive-date=30 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230430083243/https://books.google.com/books?id=RoK9CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA47 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="LinzLinz2000">{{Cite book |last=Linz |first=Juan José |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8cYk_ABfMJIC&pg=PA143 |title=Totalitarian and Authoritarian Regimes |date=2000 |publisher=Lynne Rienner Publisher |isbn=978-1-55587-890-0 |pages=143 |oclc=1172052725 |author-link=Juan José Linz |access-date=20 October 2022 |archive-date=22 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230422130238/https://books.google.com/books?id=8cYk_ABfMJIC&pg=PA143 |url-status=live }}</ref> Modern classification systems also include ] as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three.<ref name="Garcia-AlexanderWooCarlson2017">{{Cite book |last1=Garcia-Alexander |first1=Ginny |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y-M8DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA137 |title=Social Foundations of Behavior for the Health Sciences |last2=Woo |first2=Hyeyoung |last3=Carlson |first3=Matthew J. |date=2017 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-3-319-64950-4 |pages=137– |oclc=1013825392}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=8 April 2016 |title=14.2 Types of Political Systems |url=https://opentextbooks.uregina.ca/sociology/chapter/14-2-types-of-political-systems/#:~:text=The%20major%20types%20of%20political,and%20instead%20rule%20through%20fear |access-date=20 October 2022 |archive-date=22 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221022061920/https://opentextbooks.uregina.ca/sociology/chapter/14-2-types-of-political-systems/#:~:text=The%20major%20types%20of%20political,and%20instead%20rule%20through%20fear |url-status=dead }}</ref> Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, ], ], ], ], ], and ]. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and ]s are common. The main aspect of any philosophy of government is how political power is obtained, with the two main forms being ] and ]. | |||
| ==Definitions and etymology== | ==Definitions and etymology== | ||
| A government is the ] to ] a ] or community. The '']'' defines government as "a system of social control under which the right to make laws, and the right to enforce them, is vested in a particular group in society".<ref>{{Cite book |title=Columbia Encyclopedia |title-link=Columbia Encyclopedia |date=2000 |publisher=Columbia University Press |edition=6th}}{{full citation needed|date=July 2022}}<!--missing the specific entry/pages and author--></ref> While all types of organizations have ], the word ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 ] on Earth, as well as their subsidiary organizations, such as ] as well as ]s.{{sfn|Smelser|Baltes|2001|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} | |||
| The word ''government'' derives from the Greek verb {{lang|grc|κυβερνάω}} meaning ''to steer'' with a ] (rudder), the metaphorical sense being attested in the literature of ], including ]'s ].{{sfn|Brock|2013|p=53–62}} In ], "government" sometimes refers to what's also known as a "]" or an "]", i.e., the policies and government officials of a particular executive or governing ]. Finally, ''government'' is also sometimes used in English as a ] for rule or governance.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Government English Definition and Meaning |url=https://www.lexico.com/en/definition/government |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220717193211/https://www.lexico.com/en/definition/government |archive-date=17 July 2022 |access-date=2022-07-17 |website=Lexico |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| A '''government''' is the ] to ] a ] or community.<ref>{{cite web|title=government|publisher=]|date=November 2010|url=http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/government}}</ref> | |||
| The word ''government'' derives, ultimately, from the Greek verb κυβερνάω (meaning ''to steer'' with ] (rudder), the metaphorical sense being attested in ]'s ]).<ref name="britannica1911">{{cite book|title=The Encyclopædia Britannica: A Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, Literature and General Information|year=1911|publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica Company}}</ref> | |||
| The Columbia Encyclopedia defines government as "a system of social control under which the right to make laws, and the right to enforce them, is vested in a particular group in society".<ref>{{cite book|publisher=Columbia University Press | title=], 6th edition |year=2000}}</ref> | |||
| In other languages, ]s may have a narrower scope, such as the ], which is more similar to the concept of ]. | |||
| While all types of organizations have governance, the word ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 ] on ], as well as their subsidiary organizations.<ref name=EncycSocialSciences>{{cite book|title=International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences|year=2001|publisher=Elsevier|isbn=0-08-043076-7}}</ref> | |||
| In the ], the word ''government'' is also used more narrowly to refer to the ], a collective group of people that exercises ] in a state{{cn|date=September 2017}} or, metonymically, to the governing ] as part of the executive. | |||
| Finally, ''government'' is also sometimes used in English as a ] for ]. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| {{main|Political history of the world|Political philosophy}} | {{main|Political history of the world|Political philosophy}} | ||
| === Earliest governments === | |||
| The moment and place that the phenomenon of human government developed is lost in time; however, history does record the formations of early governments. About 5,000 years ago, the first small city-states appeared.{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=245}} By the third to second millenniums BC, some of these had developed into larger governed areas: ], ], the ], and the ].{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=294}} | |||
| The moment and place that the phenomenon of human government developed is lost in time; however, history does record the formations of early governments. About 5,000 years ago, the first small city-states appeared.{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=245}} By the third to second millenniums BC, some of these had developed into larger governed areas: ], ], the ], and the ].{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=294}} | |||
| One reason that explains the emergence of governments includes agriculture. Since the ], agriculture has been an efficient method to create food surplus. This enabled people to specialize in non-agricultural activities. Some of them included being able to rule over others as an external authority. Others included social experimentation with diverse governance models. Both these activities formed the basis of governments.<ref name="Eagly99">{{cite journal |author1=Eagly, Alice H. |author2=Wood, Wendy |date=June 1999 |title=The Origins of Sex Differences in Human Behavior: Evolved Dispositions Versus Social Roles |url=http://www.sscnet.ucla.edu/anthro/faculty/fiske/facets/eagly&wood.htm |url-status=dead |journal=American Psychologist |volume=54 |issue=6 |pages=408–423 |doi=10.1037/0003-066x.54.6.408 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000817071347/http://www.sscnet.ucla.edu/anthro/faculty/fiske/facets/eagly&wood.htm |archive-date=17 August 2000}}</ref> These governments gradually became more complex as agriculture supported larger and denser populations, creating new ] and ] that the government needed to control. ] explains | |||
| The development of ] and ] projects were a catalyst for the development of governments.<ref name="brittanica2010">The New Encyclopædia Britannica (15th edition)</ref> For many thousands of years when people were ]s and small scale farmers, humans lived in small, non-hierarchical and ] communities.{{cn|date=October 2017}} On occasion a chief of a tribe was elected by various rituals or tests of strength to govern his tribe, sometimes with a group of elder tribesmen as a council. The human ability to precisely communicate abstract, learned information allowed humans to become ever more effective at agriculture,{{sfn|Christian|2004|pp=146–147}} and that allowed for ever increasing population densities.{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=245}} David Christian explains how this resulted in states with laws and governments:<ref name="Christian">{{cite book | |||
| |title=Maps of Time | |||
| |last=Christian | |||
| |first=David | |||
| |date=2004 | |||
| |publisher=University of California Press | |||
| |isbn=0-520-24476-1 | |||
| |ref=harv | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| {{ |
{{blockquote|As farming populations gathered in larger and denser communities, interactions between different groups increased and the social pressure rose until, in a striking parallel with star formation, new structures suddenly appeared, together with a new level of complexity. Like stars, cities and states reorganize and energize the smaller objects within their gravitational field.{{sfn|Christian|2004|p=245}}}} | ||
| Another explanation includes the need to properly manage infrastructure projects such as water infrastructure. Historically, this required centralized administration and complex social organisation, as seen in regions like Mesopotamia.<ref name="Fukuyama-2012">{{Cite book |last=Fukuyama |first=Francis |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=i9xRAQAAMAAJ&q=origins+of+political+order+amazon |title=The Origins of Political Order: From Prehuman Times to the French Revolution |date=2012-03-27 |publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux |isbn=978-0-374-53322-9 |pages=70 |language=en}}</ref> However, there is archaeological evidence that shows similar successes with more egalitarian and decentralized complex societies.<ref>{{cite book |author=Roosevelt, Anna C. |title=Cambridge history of the Native peoples of the Americas: South America, Volume 3 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-521-63075-7 |editor=Salomon, Frank |pages=266–267 |chapter=The Maritime, Highland, Forest Dynamic and the Origins of Complex Culture |editor2=Schwartz, Stuart B. |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hxqgDcCrzjkC&pg=PA266 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160624045250/https://books.google.com/books?id=hxqgDcCrzjkC&pg=PA266 |archive-date=24 June 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Starting at the end of the ], the prevalence of ] of government grew. The ] in England, the ], and the ] contributed to the growth of representative forms of government. The ] was the first large country to have a ] government.<ref name=EncycSocialSciences /> Since the fall of the ], ] has become an even more prevalent form of government.<ref name="Kuper" /> | |||
| === Modern governments === | |||
| In the nineteenth and twentieth century, there was a significant increase in the size and scale of government at the national level.<ref>{{cite|isbn=978-0-19-957967-9|title=The Oxford Handbook of State and Local Government|date=2014}}</ref> This included the regulation of ] and the development of the ].<ref name="Kuper">{{cite book|title=The Social Science Encyclopedia|editor=Adam Kuper and Jessica Kuper|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0-415-47635-5}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Starting at the end of the 17th century, the prevalence of republican forms of government grew. The ] and ] in England, the ], and the ] contributed to the growth of representative forms of government. The ] was the first large country to have a ] government.{{sfn|Smelser|Baltes|2001|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} Since the fall of the ], ] has become an even more prevalent form of government.{{sfn|Kuper|Kuper|2008|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} | |||
| In the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, there was a significant increase in the size and scale of government at the national level.{{sfn|Haider-Markel|2014|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} This included the regulation of corporations and the development of the ].{{sfn|Kuper|Kuper|2008|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} | |||
| ==Political science== | ==Political science== | ||
| {{main|Political science}} | |||
| === Classifying government === | |||
| {{Politics sidebar|expanded=Subseries}} | |||
| In political science, it has long been a goal to create a typology or taxonomy of ], as typologies of political systems are not obvious.<ref>Lewellen, Ted C. ''Political Anthropology: An Introduction Third Edition''. Praeger Publishers; 3rd edition (30 November 2003)</ref> It is especially important in the ] fields of ] and ]. Like all categories discerned within forms of government, the boundaries of government classifications are either fluid or ill-defined. | |||
| === Classification === | |||
| Superficially, all governments have an official or ideal form. The United States is a ], while the former Soviet Union was a ]. However self-identification is not objective, and as Kopstein and Lichbach argue, defining regimes can be tricky.<ref>''Comparative politics : interests, identities, and institutions in a changing global order'', Jeffrey Kopstein, Mark Lichbach (eds.), 2nd ed, Cambridge University Press, 2005, {{ISBN|0521708400}}, p. 4.</ref> For example, ]s are a defining characteristic of an electoral democracy,{{citation needed|date=October 2012}} but in practice elections in the former Soviet Union were not "free and fair" and took place in a ]. ] argued that "the ] is neither Holy, nor Roman, nor an Empire".<ref>{{cite journal | title=The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire | journal=Michigan Academician | last1=Renna | first1=Thomas | volume=42 | issue=1 | pages=60–75 | url=http://journal.themichiganacademy.org/doi/abs/10.7245/0026-2005-42.1.60?code=msal-site&journalCode=maca | doi=10.7245/0026-2005-42.1.60 | date=Sep 2015 }}</ref> Many governments that officially call themselves a "]" are not democratic, nor a republic; they are usually a dictatorship '']''. Communist dictatorships have been especially prone to use this term. For example, the official name of North Vietnam was "The Democratic Republic of Vietnam". China uses a variant, "The People's Republic of China". Thus in many practical classifications it would not be considered democratic. | |||
| In political science, it has long been a goal to create a typology or taxonomy of ], as typologies of political systems are not obvious.{{sfn|Lewellen|2003|p={{page needed|date=July 2022}}}} It is especially important in the ] fields of ] and ]. Like all categories discerned within forms of government, the boundaries of government classifications are either fluid or ill-defined. | |||
| Superficially, all governments have an official '']'' or ideal form. The United States is a federal constitutional republic, while the former ] was a federal ]. However self-identification is not objective, and as Kopstein and Lichbach argue, defining regimes can be tricky, especially '']'', when both its government and its economy deviate in practice.{{sfn|Kopstein|Lichbach|2005|p=4}} For example, ] argued that "the ] is neither Holy, nor Roman, nor an Empire".{{sfn|Renna|2015}} In practice, the Soviet Union was a centralized autocratic one-party state under ]. | |||
| Identifying a form of government is also difficult because many ] originate as socio-economic movements and are then carried into governments by ] naming themselves after those movements; all with competing political-ideologies. Experience with those movements in power, and the strong ties they may have to particular forms of government, can cause them to be considered as forms of government in themselves. | |||
| Identifying a form of government is also difficult because many ] originate as socio-economic movements and are then carried into governments by parties naming themselves after those movements; all with competing political ideologies. Experience with those movements in power, and the strong ties they may have to particular forms of government, can cause them to be considered as forms of government in themselves. | |||
| Other complications include general non-consensus or deliberate "distortion or bias" of reasonable technical definitions to political ideologies and associated forms of governing, due to the nature of politics in the modern era. For example: The meaning of "]" in the ] has little in common with the way the word's definition is used elsewhere. As Ribuffo notes, "what Americans now call conservatism much of the world calls ] or neoliberalism".<ref>Leo P. Ribuffo, "20 Suggestions for Studying the Right now that Studying the Right is Trendy," ''Historically Speaking'' Jan 2011 v.12#1 pp. 2–6, quote on p. 6</ref> Since the 1950s conservatism in the United States has been chiefly associated with the ]. However, during the era of ] many ] were conservatives, and they played a key role in the ] that controlled Congress from 1937 to 1963.<ref>Kari Frederickson, ''The Dixiecrat Revolt and the End of the Solid South, 1932–1968'', p. 12, "...conservative southern Democrats viewed warily the potential of New Deal programs to threaten the region's economic dependence on cheap labor while stirring the democratic ambitions of the disfranchised and undermining white supremacy.", The University of North Carolina Press, 2000, {{ISBN|978-0-8078-4910-1}}</ref> | |||
| Other complications include general non-consensus or deliberate "]" of reasonable technical definitions of political ideologies and associated forms of governing, due to the nature of politics in the modern era. For example: The meaning of "conservatism" in the United States has little in common with the way the word's definition is used elsewhere. As Ribuffo notes, "what Americans now call conservatism much of the world calls liberalism or ]"; a "conservative" in Finland would be labeled a "]" in the United States.{{sfn|Ribuffo|2011|pp=2–6|loc=quote on p. 6}} Since the 1950s conservatism in the United States has been chiefly associated with ] and the ]. However, during the era of ] many ] were conservatives, and they played a key role in the ] that controlled Congress from 1937 to 1963.{{sfn|Frederickson|2000|p=12}}{{efn|{{harvnb|Frederickson|2000|p=12}}, quote: "...conservative southern Democrats viewed warily the potential of New Deal programs to threaten the region's economic dependence on cheap labor while stirring the democratic ambitions of the disfranchised and undermining white supremacy."}} | |||
| ===Social-political ambiguity=== | ===Social-political ambiguity=== | ||
| Opinions vary by individuals concerning the types and properties of governments that exist. "Shades of gray" are commonplace in any government and its corresponding classification. Even the most liberal democracies limit rival political activity to one extent or another while the most tyrannical dictatorships must organize a broad base of support thereby creating difficulties for "]" governments into narrow categories. Examples include the claims of the ] rather than a democracy since some American voters believe elections are being manipulated by wealthy ].{{sfn|Freeland|2012}} Some consider that government is to be reconceptualised where in times of climatic change the needs and desires of the individual are reshaped to generate sufficiency for all.<ref>"". Deflorian, Michel (2015). Retrieved 2 October 2023</ref> | |||
| ==Measurement of governing== | |||
| === The dialectical forms of government === | |||
| The quality of a government can be measured by ], which relates to ] and ].<ref name=Guisan>{{cite journal |last1=Guisan |first1=Maria-Carmen |title=Government effectiveness, education, economic development and well-being: analysis of European countries in comparison with the United States and Canada, 2000-2007 |journal=Applied Econometrics and International Development |date=2009 |volume=9 |issue=1 |page=1 |url=http://www.usc.es/economet/reviews/aeid914.pdf |access-date=25 April 2019}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main article|Plato's five regimes}} | |||
| The ] ] ] discusses five types of regimes: ], ], ], ] and ]. Plato also assigns a man to each of these regimes to illustrate what they stand for. The tyrannical man would represent tyranny for example. These five regimes progressively degenerate starting with aristocracy at the top and tyranny at the bottom. | |||
| ==Forms |
==Forms== | ||
| {{ |
{{Main|List of forms of government}} | ||
| {{Further|Mixed government}} | |||
| {{Basic forms of government}} | |||
| One method of classifying governments is through which people have the authority to rule. This can either be one person (an autocracy, such as monarchy), a select group of people (an aristocracy), or the people as a whole (a democracy, such as a republic). | |||
| ] in his book '']'' (375 BC) divided governments into five basic types (four being existing forms and one being Plato's ideal form, which exists "only in speech"):<ref name="Abjorensen2019">{{Cite book |last=Abjorensen |first=Norman |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cNSSDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA288 |title=Historical Dictionary of Democracy |date=2019 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-5381-2074-3 |pages=288– |oclc=1081354236}}</ref> | |||
| The division of governments as monarchy, aristocracy and democracy has been used since Aristotle's ].{{citation needed|date=November 2017}} In his book ], ] expands on this classification. | |||
| * ] (rule by ], like ideal traditional "benevolent" kingdoms that are not tyrannical) | |||
| {{quote|The difference of Commonwealths consisteth in the difference of the sovereign, or the person representative of all and every one of the multitude. And because the sovereignty is either in one man, or in an assembly of more than one; and into that assembly either every man hath right to enter, or not every one, but certain men distinguished from the rest; it is manifest there can be but three kinds of Commonwealth. For the representative must needs be one man, or more; and if more, then it is the assembly of all, or but of a part. When the representative is one man, then is the Commonwealth a monarchy; when an assembly of all that will come together, then it is a democracy, or popular Commonwealth; when an assembly of a part only, then it is called an aristocracy. Other kind of Commonwealth there can be none: for either one, or more, or all, must have the sovereign power (which I have shown to be indivisible) entire.<ref name="Leviathan">{{cite wikisource|author=Hobbes, Thomas|title=Leviathan|wslink=Leviathan/The Second Part}}</ref>}} | |||
| * ] (rule by pure ] and ], like a ] citizen) | |||
| * ] (rule by wealth and market-based-ethics, like a ] capitalist state) | |||
| * ] (rule by honor and duty, like a "benevolent" military; Sparta as an example) | |||
| * ] (], like a ]) | |||
| These five regimes progressively degenerate starting with aristocracy at the top and tyranny at the bottom.{{sfn|Brill|2016}} | |||
| ===Autocracy=== | |||
| An autocracy is a system of government in which supreme ] is concentrated in the hands of one person, whose decisions are subject to neither external legal restraints nor regularized mechanisms of popular control (except perhaps for the implicit threat of a ] or mass ]).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.auburn.edu/~johnspm/gloss/autocracy |title=Autocracy: A Glossary of Political Economy Terms|author=Paul M. Johnson |publisher=Auburn.edu |date= |accessdate=2012-09-14}}</ref> | |||
| In his '']'', Aristotle elaborates on Plato's five regimes discussing them in relation to the government of one, of the few, and of the many.<ref name="Jordović2019">{{Cite book |last=Jordović |first=Ivan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=if7vxwEACAAJ |title=Taming Politics: Plato and the Democratic Roots of Tyrannical Man |date=2019 |publisher=Franz Steiner Verlag |isbn=978-3-515-12457-7 |page=intro |oclc=1107421360}}</ref> From this follows the classification of forms of government according to which people have the authority to rule: either one person (an ], such as monarchy), a select group of people (an aristocracy), or the people as a whole (a democracy, such as a republic). | |||
| A ] is a government ruled by a single entity with absolute power, whose decisions are subject to neither external legal restraints nor regular mechanisms of popular control (except perhaps for implicit threat). That entity may be an individual, as in an ], or it may be a group, as in an ]. The word despotism means to "rule in the fashion of despots".{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| ] stated on their classification: | |||
| A ] is where a family or group of families (rarely another type of group), called the ], represents national identity, with power traditionally assigned to one of its individuals, called the monarch, who mostly rule kingdoms. The actual role of the monarch and other members of royalty varies from purely symbolical (]) to partial and restricted (]) to completely despotic (]). Traditionally and in most cases, the post of the monarch is ], but there are also ] where the monarch is elected.{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| {{blockquote|The difference of ]s consisteth in the difference of the ], or the person representative of all and every one of the multitude. And because the sovereignty is either in one man, or in an assembly of more than one; and into that assembly either every man hath right to enter, or not everyone, but certain men distinguished from the rest; it is manifest there can be but three kinds of Commonwealth. For the representative must need to be one man or more; and if more, then it is the assembly of all, or but of a part. When the representative is one man, then is the Commonwealth a monarchy; when an assembly of all that will come together, then it is a democracy or popular Commonwealth; when an assembly of a part only, then it is called an aristocracy. In other kinds of Commonwealth there can be none: for either one, or more, or all, must have the sovereign power (which I have shown to be indivisible) entire.<ref name="Leviathan">{{Cite wikisource |last1=Hobbes |first1=Thomas |title=Leviathan |wslink=Leviathan/The Second Part}}</ref>}} | |||
| ===Aristocracy=== | |||
| '''Aristocracy''' (] ἀριστοκρατία ''aristokratía'', from ἄριστος '']'' "excellent", and κράτος '']'' "]") is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ].<ref name=OED>{{cite journal|last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date=December 1989 |title=Aristocracy |trans_title= |journal=] |volume= |issue= |pages= |id= |url=http://dictionary.oed.com/cgi/entry/50011987?single=1&query_type=word&queryword=aristocracy&first=1&max_to_show=10 |accessdate=December 22, 2009 |quote= |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110629022358/http://dictionary.oed.com/cgi/entry/50011987?single=1&query_type=word&queryword=aristocracy&first=1&max_to_show=10 |archivedate=June 29, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Modern basic political systems=== | |||
| An oligarchy is ruled by a small group of segregated, powerful or influential people who usually share similar interests or family relations. These people may spread power and elect candidates equally or not equally. An oligarchy is different from a true democracy because very few people are given the chance to change things. An oligarchy does not have to be hereditary or monarchic. An oligarchy does not have one clear ruler but several rulers.{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| According to ] professor ], there a three main types of ]s today: ], | |||
| ]s and, sitting between these two, ] with ]s.<ref name="LinzLinz2000" /><ref name="Michie2014">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ip_IAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA95 |title=Reader's Guide to the Social Sciences |date=3 February 2014 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-135-93226-8 |editor-last=Jonathan Michie |page=95 |access-date=20 October 2022 |archive-date=22 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230422130238/https://books.google.com/books?id=ip_IAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA95 |url-status=live }}</ref> Another modern classification system includes ] as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three.<ref name="Garcia-AlexanderWooCarlson2017" /> Scholars generally refer to a ] as either a form of authoritarianism or totalitarianism.<ref name="ToddWaller2015">{{Cite book |last1=Todd |first1=Allan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y_pfCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA10 |title=History for the IB Diploma Paper 2 AuthoritariaAuthoritarian States (20th Century) |last2=Waller |first2=Sally |date=10 September 2015 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-107-55889-2 |editor-last=Todd |editor-first=Allan |pages=10– |editor-last2=Waller |editor-first2=Sally |access-date=20 October 2022 |archive-date=22 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230422130238/https://books.google.com/books?id=y_pfCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA10 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="LinzLinz2000" /><ref name="Sondrol">{{Cite journal |last=Sondrol |first=P. C. |date=2009 |title=Totalitarian and Authoritarian Dictators: A Comparison of Fidel Castro and Alfredo Stroessner |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/157386 |journal=Journal of Latin American Studies |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=599–620 |doi=10.1017/S0022216X00015868 |jstor=157386 |s2cid=144333167 |access-date=20 October 2022 |archive-date=8 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230308100323/https://www.jstor.org/stable/157386 |url-status=live |issn=0022-216X }}</ref> | |||
| ===Autocracy=== | |||
| {{Main|Autocracy}} | |||
| An autocracy is a system of government in which supreme ] is concentrated in the hands of one person, whose decisions are subject to neither external legal restraints nor regularized mechanisms of popular control (except perhaps for the implicit threat of a ] or mass ]).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Johnson |first=Paul M. |title=Autocracy: A Glossary of Political Economy Terms |url=http://www.auburn.edu/~johnspm/gloss/autocracy |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181226063927/http://www.auburn.edu/~johnspm/gloss/autocracy%20 |archive-date=26 December 2018 |access-date=14 September 2012 |publisher=Auburn.edu}}</ref> ] is a historically prevalent form of autocracy, wherein a ] governs as a singular ] with no limitation on ]. Most absolute monarchies are ], however some, notably the ], are ] by an ] (such as the ], or ]s). Other forms of autocracy include ], ], and ]. | |||
| ===Aristocracy=== | |||
| {{Main|Aristocracy}} | |||
| Aristocracy{{efn|{{langx|grc|ἀριστοκρατία}} {{transliteration|grc|aristokratía}}, from {{lang|grc|ἄριστος}} {{transliteration|grc|]}} "excellent", and {{lang|grc|κράτος}} {{transliteration|grc|]}} "]".}} is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, ] ],<ref name="OED">{{Cite OED|aristocracy}}</ref> such as a hereditary ] or ]d ]. This class exercises ], often as a ] ], wealthy ], or ]. | |||
| Some historical examples of oligarchy are the former ]s. Some critics of ] think of ]. The ] used ] to elect candidates, almost always male, Greek, educated citizens holding a minimum of land, wealth and status.{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| Many monarchies were aristocracies, although in modern constitutional monarchies, the monarch may have little effective power. The term ''aristocracy'' could also refer to the non-], non-servant, and non-] classes in the ].{{citation needed|date=July 2022}} | |||
| A ] is rule by a religious elite; a system of governance composed of religious institutions in which the state and the church are traditionally or ]ally the same entity. ]'s (see ]), ]'s (see ]), ]'s (see ]), ]s and other ]s are historically considered ''theocracies''.{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| ===Democracy=== | ===Democracy=== | ||
| {{Main|Democracy|Types of democracy}} | |||
| In a general sense, in a ], all the people of a ] or ] are involved in making decisions about its affairs. Also refer to the rule by a government chosen by election where most of the populace are enfranchised. The key distinction between a democracy and other forms of constitutional government is usually taken to be that the right to vote is not limited by a person's wealth or race (the main qualification for enfranchisement is usually having reached a certain age). A democratic government is, therefore, one supported (at least at the time of the election) by a ] of the populace (provided the election was held fairly). A "majority" may be defined in different ways. There are many "power-sharing" (usually in countries where people mainly identify themselves by race or religion) or "electoral-college" or "constituency" systems where the government is not chosen by a simple one-vote-per-person headcount.{{citation needed|date=September 2017}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ]'' survey{{efn|Conducted by the American ] ], which is largely funded by the ].}}]] | |||
| Democracy is a system of government where ]s exercise power by ] and ]. In a ], the citizenry as a whole directly forms a ] governing body and vote directly on each issue. In ], the citizenry governs indirectly through the selection of ] or ] from among themselves, typically by ] or, less commonly, by ]. These select citizens then meet to form a governing body, such as a legislature or ]. | |||
| In democracies, large proportions of the population may vote, either to make decisions or to choose representatives to make decisions. Commonly significant in democracies are political parties, which are groups of people with similar ideas about how a country or region should be governed. Different political parties have different ideas about how the government should handle different problems.{{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| Some governments combine both direct and indirect democratic governance, wherein the citizenry selects representatives to administer day-to-day governance, while also reserving the right to govern directly through ]s, ]s (plebiscites), and the ]. In a ] the powers of the majority are exercised within the framework of representative democracy, but the constitution limits ], usually through the provision by all of certain ]s, such as ] or ].<ref>'']'': "democracy".</ref><ref name="britannica">{{Cite encyclopedia |last=Watkins |first=Frederick |date=1970 |title=Democracy |edition=Expo '70 hardcover |volume=7 |encyclopedia=] |publisher=William Benton |pages=215–223 |language=en |isbn=978-0-85229-135-1}}</ref> | |||
| ] is a variant of democracy. It is a ] in which ] operates under the principles of ]. It is characterised by fair, free, and competitive ]s between ] ], a ] into different ], the ] in everyday life as part of an ], and the protection of ] and ] for all persons. To define the system in practice, liberal democracies often draw upon a ], either formally written or ], to delineate the powers of government and enshrine the ]. After a period of sustained expansion throughout the 20th century, liberal democracy became the predominant political system in the world. A liberal democracy may take various constitutional forms: it may be a ], such as ], ], ], ], ], ], or the ]; or a ], such as ], ], or the ]. It may have a ] (], ], ], or the ]), a ] (], ], or ]), or a ] (], ], ], ], ], ], New Zealand, or the ]).{{citation needed|date=September 2017}} | |||
| ==== Republics ==== | ==== Republics ==== | ||
| {{Main|Republic}} | |||
| A republic is a form of government in which the country is considered a "public matter" (Latin: ''res publica''), not the private concern or property of the rulers, and where offices of states are subsequently directly or indirectly elected or appointed rather than inherited. The people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people.<ref name="autogenerated1">], '']'' (1748), Bk. II, ch. 1.</ref><ref name="Britannica">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Republic|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica}}</ref> A common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of state is not a monarch.<ref name="WordNet">{{Cite journal |title=republic |journal=WordNet 3.0 |publisher=Dictionary.com |accessdate=20 March 2009 |url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/republic}}</ref><ref name="M-W">{{cite encyclopedia|title=Republic|encyclopedia=Merriam-Webster|url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/republic|accessdate=14 August 2010}}</ref> ] included both ], where all the people have a share in rule, and ] or ], where only some of the people rule, as republican forms of government.<ref name="autogenerated2">Montesquieu, ''Spirit of the Laws'', Bk. II, ch. 2–3.</ref> | |||
| A republic is a form of government in which the country is considered a "public matter" ({{langx|la|res publica}}), not the private concern or property of the rulers, and where offices of states are subsequently directly or indirectly elected or appointed rather than inherited. The people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people.{{sfn|Montesquieu|1748|loc=book 2, chapters 1}}<ref name="Britannica">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Republic |encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica}}{{full citation needed|date=July 2022}}<!--Author? Edition?--></ref> | |||
| A common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of state is not a monarch.<ref name="WordNet">{{Cite journal |title=republic |url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/republic |url-status=live |journal=WordNet 3.0 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090312065659/http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/republic |archive-date=12 March 2009 |access-date=20 March 2009}}</ref><ref name="M-W">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Republic |encyclopedia=Merriam-Webster |url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/republic |access-date=14 August 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180612162708/https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/republic |archive-date=12 June 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref> ] included both ], where all the people have a share in rule, and ] or ], where only some of the people rule, as republican forms of government.{{sfn|Montesquieu|1748|loc=book 2, chapters 2–3}} | |||
| Other terms used to describe different republics include ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| Other terms used to describe different republics include ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| == Scope of government == | |||
| Rule by ] governments is identified in societies where a specific set of people possess the authority of the state in a ] or union. It is a ] controlled by unelected rulers who usually permit some degree of ]. Rule by a ] government is characterised by a highly centralised and coercive authority that regulates nearly every aspect of public and private life.{{citation needed|date=September 2017}} | |||
| ==== Federalism ==== | |||
| In contrast, a ] is rule by a government whose powers are limited by law or a formal constitution, and chosen by a vote amongst at least some sections of the populace (Ancient Sparta was in its own terms a republic, though most inhabitants were disenfranchised). Republics that exclude sections of the populace from participation will typically claim to represent all citizens (by defining people without the vote as "non-citizens"). Examples include the ], ], ], etc. {{cn|date=November 2017}} | |||
| {{Main|Federalism}} | |||
| Federalism is a political concept in which a ''group'' of members are bound together by ] with a governing ]. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of government in which ] is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and constituent political units, variously called states, provinces or otherwise. Federalism is a system based upon democratic principles and institutions in which the power to govern is shared between national and provincial/state governments, creating what is often called a ].<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Cane |first1=Peter |title=The new Oxford companion to law |last2=Conaghan |first2=Joanne |date=2008 |publisher=Oxford university press |isbn=978-0-19-929054-3 |location=Oxford |chapter=Federalism}}</ref> Proponents are often called ]s. | |||
| === Federalism === | |||
| {{Expand section|date=January 2013}} | |||
| Federalism is a political concept in which a ''group'' of members are bound together by covenant (Latin: ''foedus'', ]) with a governing ]. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of government in which ] is ]ally divided between a central governing authority and constituent political units (such as states or provinces). Federalism is a system based upon democratic rules and institutions in which the power to govern is shared between national and provincial/state governments, creating what is often called a ]. Proponents are often called ]s. | |||
| == |
== Branches == | ||
| ], demonstrating the ''trias politica'' model]] | |||
| {{further|Economic system}} | |||
| {{further|Separation of powers|Fusion of powers}} | |||
| Historically, most political systems originated as ] ]. Experience with those movements in power and the strong ties they may have to particular forms of government can cause them to be considered as forms of government in themselves. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| Governments are typically organised into distinct institutions constituting branches of government each with particular ]s, functions, duties, and responsibilities. The distribution of powers between these institutions differs between governments, as do the functions and number of branches. An independent, parallel distribution of powers between branches of government is the ]. A shared, intersecting, or overlapping distribution of powers is the ]. | |||
| |- | |||
| !Term | |||
| Governments are often organised into three branches with separate powers: a legislature, an executive, and a judiciary; this is sometimes called the {{lang|la|trias politica}} model. However, in ]ary and ]s, branches of government often intersect, having shared membership and overlapping functions. Many governments have fewer or additional branches, such as an independent ] or ] branch.{{sfn|Needler|1991|pp=–118}} | |||
| !Definition | |||
| |- | |||
| == Party system == | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system in which the ] (machines, tools, factories, etc.) are under private ownership and their use is for profit. | |||
| {{Party politics|expanded=party systems}} | |||
| |- | |||
| {{Redirect|One-party government|a state in which a single political party controls the ruling system|One-party state}} | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system in which means of production are commonly owned (either by the people directly, through the ] or by ]), and production is undertaken ], rather than ].<ref>{{cite book |last= Steele|first= David Ramsay |title= From Marx to Mises: Post Capitalist Society and the Challenge of Economic Calculation |publisher= Open Court|date=September 1999|isbn= 978-0875484495|page = 66|quote= Marx distinguishes between two phases of marketless communism: an initial phase, with labor vouchers, and a higher phase, with free access.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last= Busky|first= Donald F.|title= Democratic Socialism: A Global Survey|publisher= Praeger|date=July 20, 2000|isbn= 978-0275968861|page = 4|quote=Communism would mean free distribution of goods and services. The communist slogan, 'From each according to his ability, to each according to his needs' (as opposed to 'work') would then rule}}</ref> Communist society is thus ], ], moneyless, and ]. | |||
| {{Further|Political party|Party system}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system in which widespread ] ownership as fundamental right;<ref>Shiach, Morag (2004). ''Modernism, Labour and Selfhood in British Literature and Culture, 1890–1930''. ]. p. 224. {{ISBN|978-0-521-83459-9}}</ref> the ] are spread as widely as possible rather than being centralized under the control of the state (]), a few individuals (]), or corporations (]).<ref>Zwick, Mark and Louise (2004). ''The Catholic Worker Movement: Intellectual and Spiritual Origins ''. ]. p. 156. {{ISBN|978-0-8091-4315-3}}</ref> Distributism fundamentally opposes ] and ],<ref>Boyle, David; Simms, Andrew (2009). ''The New Economics''. ]. p. 20. {{ISBN|978-1-84407-675-8}}</ref><ref>Novak, Michael; Younkins, Edward W. (2001). ''Three in One: Essays on Democratic Capitalism, 1976–2000''. ]. p. 152. {{ISBN|978-0-7425-1171-2}}</ref> which distributists view as equally flawed and exploitative. In contrast, distributism seeks to subordinate economic activity to human life as a whole, to our spiritual life, our intellectual life, our family life".<ref>Storck, Thomas. "Capitalism and Distributism: two systems at war," in ''Beyond Capitalism & Socialism''. Tobias J. Lanz, ed. IHS Press, 2008. p. 75</ref> | |||
| Presently, most governments are administered by members of an explicitly constituted ] which coordinates the activities of associated government ]s and ]s for office. In a ] of government, multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government offices, typically by competing in ]s, although the ] may be limited. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system of land ownership and duties. Under feudalism, all the land in a kingdom was the king's. However, the king would give some of the land to the lords or nobles who fought for him. These presents of land were called manors. Then the nobles gave some of their land to vassals. The vassals then had to do duties for the nobles. The lands of vassals were called fiefs. | |||
| A ] is a government by one or more ] together holding an absolute majority of seats in the parliament, in contrast to a ] in which they have only a plurality of seats and often depend on a ] arrangement with other parties. A ] is one in which multiple parties cooperate to form a government as part of a ]. In a single-party government, a single party forms a government without the support of a coalition, as is typically the case with majority governments,{{sfn|Gallagher|Laver|Mair|2006}}{{sfn|Kettle|2015}} but even a minority government may consist of just one party unable to find a willing coalition partner at the moment.{{sfn|Duxbury|2021}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system in which ] and ] the ]<ref>{{Cite book|title = Upton Sinclair's: A Monthly Magazine: for Social Justice, by Peaceful Means If Possible|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=i0w9AQAAMAAJ|date = 1918-01-01|last = Sinclair|first = Upton|authorlink= Upton Sinclair|quote = Socialism, you see, is a bird with two wings. The definition is 'social ownership and democratic control of the instruments and means of production.'}}</ref> and the economic framework may be ], distributed or ] ] or ] in autonomous economic units.<ref>Schweickart, David. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120617235335/http://orion.it.luc.edu/~dschwei/demsoc.htm |date=17 June 2012 }}. Encyclopedia of Activism and Social Justice (2006): "Virtually all (democratic) socialists have distanced themselves from the economic model long synonymous with 'socialism,' i.e. the Soviet model of a non-market, centrally-planned economy...Some have endorsed the concept of 'market socialism,' a post-capitalist economy that retains market competition, but socializes the means of production, and, in some versions, extends democracy to the workplace. Some hold out for a non-market, participatory economy. All democratic socialists agree on the need for a democratic alternative to capitalism."</ref> ]s would be ], ], or ], such as ] and ]. | |||
| A state that continuously maintains a single-party government within a (nominally) multiparty system possesses a ]. In a (nondemocratic) ] a single ] has the (more-or-less) exclusive right to form the government, and the formation of other parties may be obstructed or illegal. In some cases, a government may have a ], as is the case with ] or ]. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system that concentrates power in the state at the expense of individual freedom. Among other variants, the term subsumes theocracy, absolute monarchy, Nazism, fascism, authoritarian socialism, and plain, unadorned dictatorship. Such variants differ on matters of form, tactics and ideology. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || A social-economic system in which the state plays a key role in the protection and promotion of the economic and social well-being of its citizens. It is based on the principles of ], equitable ], and public responsibility for those unable to avail themselves of the minimal provisions for a good life. | |||
| |} | |||
| == Maps == | == Maps == | ||
| {{see also|List of countries by system of government}} | |||
| ---- {{Form of government legend}}]] | |||
| Democracy is the most popular form of government. More than half of the nations in the world are democracies—97 of 167, as of 2021.<ref name=IDEA/> However, the world is becoming more authoritarian with a quarter of the world's population under ] governments.<ref name="IDEA"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220809193024/https://www.idea.int/gsod/sites/default/files/2021-11/the-global-state-of-democracy-2021_0.pdf |date=9 August 2022 }}, International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance</ref> | |||
| ] by the ], 2017.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://pages.eiu.com/rs/753-RIQ-438/images/Democracy_Index_2017.pdf?mkt_tok=eyJpIjoiWkRKbU1HWmxNVEUwTW1FdyIsInQiOiJPdlltVFV0blFRQzZNVERCZHhVeitZRElmUGplOHh3NWs1d2wzVzdRS1JvNU1kVmUxQVRESU9LbEVSOVwvR1F4aG1PV1NlS0ZZcng4NzBcLzVNZ09JOUxiZU5TTEVPekVHayttOTRqQkQ5TkNzWGNtRlowQTZ0UzlUK0pDdm9PVGlcLyJ9|title=Democracy Index 2017 – Economist Intelligence Unit|last=|first=|date=|website=EIU.com|access-date=17 February 2018}}</ref> | |||
| ] by the ], 2017<ref>{{Cite web |title=Democracy Index 2017 – Economist Intelligence Unit |url=http://pages.eiu.com/rs/753-RIQ-438/images/Democracy_Index_2017.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201221004840/http://pages.eiu.com/rs/753-RIQ-438/images/Democracy_Index_2017.pdf |archive-date=21 December 2020 |access-date=17 February 2018 |website=EIU.com}}</ref> | |||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| {{col-begin}} | {{col-begin}} | ||
| Line 143: | Line 152: | ||
| '''Full Democracies''' | '''Full Democracies''' | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#006837|9–10}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#1a9850|8–9}} | ||
| {{col-break}} | {{col-break}} | ||
| '''Flawed Democracies''' | '''Flawed Democracies''' | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#66bd63|7–8}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#a6d96a|6–7}} | ||
| {{col-break}} | {{col-break}} | ||
| '''Hybrid Regimes''' | '''Hybrid Regimes''' | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#fee08b|5–6}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#fdae61|4–5}} | ||
| {{col-break}} | {{col-break}} | ||
| '''Authoritarian Regimes''' | '''Authoritarian Regimes''' | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#f46d43|3–4}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#d73027|2–3}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#a50026|0–2}} | ||
| {{legend|#cccccc;|Not determined}} | |||
| {{col-end}}]] | {{col-end}}]] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ]s (<span style="color: |
]s (<span style="color: #0000b0">'''blue'''</span>) | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#0000b0|]s}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#00e000|]}}]] | ||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Politics}} | |||
| {{columnslist|colwidth=20em| | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 185: | Line 194: | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| }} | |||
| == |
==Notes== | ||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| Certain major characteristics are defining of certain types; others are historically associated with certain types of government. | |||
| * ] (unwritten ethical principles) vs. written ] | |||
| * ] or ] vs. ] | |||
| * ] vs. ] | |||
| * ] or ] vs. ] | |||
| * ] or ] vs. ] or ] with ] and ] rules to prevent ] and protect ] | |||
| * ] (]) or ] (]) vs. ], ] provision, or silence on the matter | |||
| ===Autonomy=== | |||
| This list focuses on differing approaches that political systems take to the distribution of ], and the ] of regions within the state. | |||
| * Sovereignty located exclusively at the centre of political jurisdiction. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * Sovereignty located at the centre and in peripheral areas. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] and ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * Diverging degrees of sovereignty. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** Unrecognized state | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] and ] (powers redistributed from central to regional or local governments) | |||
| == |
==References== | ||
| {{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| ==Bibliography== | ===Bibliography=== | ||
| {{Refbegin|colwidth=30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| * ''American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' (4th ed.). 222 Berkeley Street, Boston, MA 02116: Houghton Mifflin Company. {{ISBN|0-395-82517-2}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Brill |first=Sara |date=2016 |title=Political Pathology in Plato's Republic |url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/apeiron-2015-0003/html |journal=Apeiron |language=en |volume=49 |issue=2 |pages=127–161 |doi=10.1515/apeiron-2015-0003 |issn=2156-7093 |s2cid=148505083 |access-date=4 August 2022 |archive-date=27 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221027215252/https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/apeiron-2015-0003/html |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Brock |first=Roger |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QCSGircE9WwC |title=Greek Political Imagery from Homer to Aristotle |date=2013 |publisher=Bloomsbury |isbn=978-1-4725-0218-6 |location=London |oclc=1040413173 |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=9 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231109175722/https://books.google.com/books?id=QCSGircE9WwC |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Christian |first=David |url=https://archive.org/details/mapsoftimeintrod00chri |title=Maps of Time: an Introduction to Big History |date=2004 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-24476-4 |location=Berkeley, CA |oclc=966003275 |url-access=registration }} | |||
| * {{Cite news |last=Duxbury |first=Charlie |date=29 November 2021 |title=Magdalena Andersson named Swedish prime minister (again) |work=Politico |url=https://www.politico.eu/article/magdalena-andersson-sweden-prime-minister-again-resignation |url-status=live |access-date=2022-07-14 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220415130747/https://www.politico.eu/article/magdalena-andersson-sweden-prime-minister-again-resignation/ |archive-date=15 April 2022 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Frederickson |first=Kari |title=The Dixiecrat Revolt and the End of the Solid South, 1932–1968 |date=2000 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |isbn=978-0-8078-4910-1 |location=Chapel Hill |oclc=475254808}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Freeland |first=Chrystia |title=Plutocrats: the Rise of the New Global Super-Rich and the Fall of Everyone Else |title-link=Plutocrats (book) |date=2012 |publisher=Allen Lane |isbn=978-1-84614-252-9 |location=London |oclc=795857028 |author-link=Chrystia Freeland}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Gallagher |first1=Michael |title=Representative Government in Western Europe |last2=Laver |first2=M. |last3=Mair |first3=P. |date=2006 |publisher=McGraw-Hill |isbn=978-0070366848 |edition=4th |location=New York |oclc=906939909}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Haider-Markel |first=Donald P. |title=The Oxford Handbook of State and Local Government |date=2014 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-957967-9 |location=Oxford, UK |oclc=904484428}} | |||
| * {{Cite news |last=Kettle |first=Martin |date=17 April 2015 |title=Coalition and minority governments are not so unusual in UK elections; The first-past-the-post system has led to fewer one-party majority governments in Britain than might be expected -- only half of all those in the 20th century |work=Guardian |url=https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A410102999/ITOF?u=wikipedia&sid=bookmark-ITOF&xid=fe0349d5 |url-status=live |access-date=2022-07-14 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220730081416/https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=ITOF&u=wikipedia&id=GALE%7CA410102999&v=2.1&it=r&sid=bookmark-ITOF&asid=fe0349d5 |archive-date=30 July 2022 |via=Gale General OneFile }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Comparative politics: interests, identities, and institutions in a changing global order |date=2005 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=0521708400 |editor-last=Kopstein |editor-first=Jeffrey |edition=2nd |location=Cambridge, UK |oclc=1293165230 |editor-last2=Lichbach |editor-first2=Mark}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The Social Science Encyclopedia |date=2008 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-0-415-47635-5 |editor-last=Kuper |editor-first=Adam |location=London |oclc=789658928 |editor-last2=Kuper |editor-first2=Jessica}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Lewellen |first=Ted C. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gwJBNWbrXeIC |title=Political Anthropology: An Introduction |date=2003 |publisher=Praeger |isbn=978-0-89789-891-1 |edition=3rd |location=Westport, CT |oclc=936497371 |access-date=20 May 2020 |archive-date=9 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231109175725/https://books.google.com/books?id=gwJBNWbrXeIC |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Montesquieu |title=The Spirit of the Laws |title-link=The Spirit of Law |date=1748 |author-link=Montesquieu}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Needler |first=Martin C. |title=The Concepts of Comparative Politics |date=1991 |publisher=Praeger |isbn=978-0-275-93653-2 |location=New York |oclc=925042067}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Renna |first=Thomas |date=September 2015 |title=The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire |journal=Michigan Academician |volume=42 |issue=1 |pages=60–75 |doi=10.7245/0026-2005-42.1.60}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Ribuffo |first=Leo P. |date=2011 |title=20 Suggestions for Studying the Right now that Studying the Right is Trendy |journal=Historically Speaking |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=2–6 |doi=10.1353/hsp.2011.0013 |s2cid=144367661}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Smelser |first1=Neil J. |title=International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences |last2=Baltes |first2=Paul B. |date=2001 |publisher=Elsevier Science |isbn=978-0-08-043076-8 |location=New York |oclc=43548228}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | == Further reading == | ||
| * {{Cite book |last1=de Mesquita |first1=Bruce Bueno |title=The Dictator's Handbook: Why Bad Behavior Is Almost Always Good Politics |last2=Smith |first2=Alastair |date=2012 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1610390446 |location=New York |oclc=1026803822 |author-link=Bruce Bueno de Mesquita}} | |||
| * Krader, Lawrence (1968). ''Formation of the State'', in ''Foundations of Modern Anthropology Series''. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. x, 118 p. | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=de Mesquita |first1=Bruce Bueno |title=The Logic of Political Survival |title-link=The Logic of Political Survival |last2=Smith |first2=Alastair |last3=Siverson |first3=Randolph M. |last4=Morrow |first4=James D. |date=2003 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0262025461 |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |oclc=475265120 |author-link=Bruce Bueno de Mesquita |author-link4=James D. Morrow}} | |||
| * {{cite book|title=The Dictator's Handbook: Why Bad Behavior is Almost Always Good Politics|year=2011|pages=272|publisher=]|author=] and ]|isbn=9781610390446|oclc=701015473}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Dobson |first=William J. |title=The Dictator's Learning Curve: Inside the Global Battle for Democracy |date=2013 |publisher=Anchor |isbn=978-0307477552 |location=New York |oclc=849820048 |author-link=William J. Dobson}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Friedrich |first1=Carl J. |url=https://archive.org/details/totalitariandict0000frie |title=Totalitarian Dictatorship and Autocracy |last2=Brzezinski |first2=Zbigniew K. |date=1966 |publisher=Frederick A. Praeger |isbn=978-0674895652 |edition=2nd |location=New York |oclc=826626632 |author-link2=Zbigniew Brzezinski |orig-date=1965 |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bueno de Mesquita|first1=Bruce|first2=Alastair|last2=Smith|first3=Randolph M.|last3=Siverson|first4=James D.|last4=Morrow |title=The Logic of Political Survival |year=2003 |publisher=] |isbn=0-262-63315-9}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Krader |first=Lawrence |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rIyZAAAAIAAJ |title=Formation of the State |date=1968 |publisher=Prentice-Hall |isbn=0133294900 |series=Foundations of Modern Anthropology |location=Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey |oclc=266086412}} | |||
| * {{cite book|title=The Dictator's Learning Curve: Inside the Global Battle for Democracy|author=]|isbn=978-0307477552|year=2013|publisher=Anchor}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| == External links == | |||
| |title=Related Navboxes | |||
| {{Wiktionary|government}} | |||
| | titlestyle = background: lightblue | |||
| {{Wiktionary|Appendix:List of forms of government}} | |||
| |list= | |||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| {{Government}} | |||
| {{commons category}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Navboxes|list= | |||
| {{Autonomous types of first-tier administration}} | {{Autonomous types of first-tier administration}} | ||
| {{World government}} | {{World government}} | ||
| {{Political culture}} | {{Political culture}} | ||
| {{Political ideologies}} | {{Political ideologies}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Political philosophy}} | ||
| {{Political spectrum}} | {{Political spectrum}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Subject bar |auto=yes |book=Government |commons=yes |wikt=yes |wikt-search=government |n=yes |q=yes |s=yes |s-search=Portal:Government |b=yes |b-search=Subject:Government |v=yes |d=yes |d-search=Q7188}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Government, Forms of}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Government, Forms of}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:31, 8 January 2025
System or group governing an organized community "Gov" redirects here. For other uses, see Gov (disambiguation).For the executive power referred to as "the government", see Executive (government). For other uses, see Government (disambiguation).
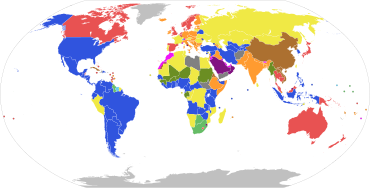
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature Constitutional monarchy with a ceremonial monarch Parliamentary republic with a ceremonial president Parliamentary republic with an executive president
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature Presidential republic
Hybrid systems: Semi-presidential republic: Executive president is independent of the legislature; head of government is appointed by the president and is accountable to the legislature Assembly-independent republic: Head of government (president or directory) is elected by the legislature, but is not accountable to it
Other systems: Theocratic republic: Supreme Leader holds significant executive and legislative power Semi-constitutional monarchy: Monarch holds significant executive or legislative power Absolute monarchy: Monarch has unlimited power One-party state: Power is constitutionally linked to a single political party Military junta: Committee of military leaders controls the government; constitutional provisions are suspended Provisional government: No constitutionally defined basis to current regime Dependent territories or places without governments
Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
| Part of a series on |
| Governance |
|---|
| Models |
| By level |
| By field |
| Measures |
| Related topics |
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy.
While all types of organizations have governance, the term government is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations.
The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also include monarchies as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governments are common. The main aspect of any philosophy of government is how political power is obtained, with the two main forms being electoral contest and hereditary succession.
Definitions and etymology
A government is the system to govern a state or community. The Columbia Encyclopedia defines government as "a system of social control under which the right to make laws, and the right to enforce them, is vested in a particular group in society". While all types of organizations have governance, the word government is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments on Earth, as well as their subsidiary organizations, such as state and provincial governments as well as local governments.
The word government derives from the Greek verb κυβερνάω meaning to steer with a gubernaculum (rudder), the metaphorical sense being attested in the literature of classical antiquity, including Plato's Ship of State. In British English, "government" sometimes refers to what's also known as a "ministry" or an "administration", i.e., the policies and government officials of a particular executive or governing coalition. Finally, government is also sometimes used in English as a synonym for rule or governance.
In other languages, cognates may have a narrower scope, such as the government of Portugal, which is more similar to the concept of "administration".
History
Main articles: Political history of the world and Political philosophyEarliest governments
The moment and place that the phenomenon of human government developed is lost in time; however, history does record the formations of early governments. About 5,000 years ago, the first small city-states appeared. By the third to second millenniums BC, some of these had developed into larger governed areas: Sumer, ancient Egypt, the Indus Valley civilization, and the Yellow River civilization.
One reason that explains the emergence of governments includes agriculture. Since the Neolithic Revolution, agriculture has been an efficient method to create food surplus. This enabled people to specialize in non-agricultural activities. Some of them included being able to rule over others as an external authority. Others included social experimentation with diverse governance models. Both these activities formed the basis of governments. These governments gradually became more complex as agriculture supported larger and denser populations, creating new interactions and social pressures that the government needed to control. David Christian explains
As farming populations gathered in larger and denser communities, interactions between different groups increased and the social pressure rose until, in a striking parallel with star formation, new structures suddenly appeared, together with a new level of complexity. Like stars, cities and states reorganize and energize the smaller objects within their gravitational field.
Another explanation includes the need to properly manage infrastructure projects such as water infrastructure. Historically, this required centralized administration and complex social organisation, as seen in regions like Mesopotamia. However, there is archaeological evidence that shows similar successes with more egalitarian and decentralized complex societies.
Modern governments

Starting at the end of the 17th century, the prevalence of republican forms of government grew. The English Civil War and Glorious Revolution in England, the American Revolution, and the French Revolution contributed to the growth of representative forms of government. The Soviet Union was the first large country to have a Communist government. Since the fall of the Berlin Wall, liberal democracy has become an even more prevalent form of government.
In the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, there was a significant increase in the size and scale of government at the national level. This included the regulation of corporations and the development of the welfare state.
Political science
Main article: Political science| Part of the Politics series |
| Politics |
|---|
| Primary topics |
| Political systems |
| Academic disciplines |
Public administration
|
| Policy |
| Government branches |
| Related topics |
| Subseries |
|
|
Classification
In political science, it has long been a goal to create a typology or taxonomy of polities, as typologies of political systems are not obvious. It is especially important in the political science fields of comparative politics and international relations. Like all categories discerned within forms of government, the boundaries of government classifications are either fluid or ill-defined.
Superficially, all governments have an official de jure or ideal form. The United States is a federal constitutional republic, while the former Soviet Union was a federal socialist republic. However self-identification is not objective, and as Kopstein and Lichbach argue, defining regimes can be tricky, especially de facto, when both its government and its economy deviate in practice. For example, Voltaire argued that "the Holy Roman Empire is neither Holy, nor Roman, nor an Empire". In practice, the Soviet Union was a centralized autocratic one-party state under Joseph Stalin.
Identifying a form of government is also difficult because many political systems originate as socio-economic movements and are then carried into governments by parties naming themselves after those movements; all with competing political ideologies. Experience with those movements in power, and the strong ties they may have to particular forms of government, can cause them to be considered as forms of government in themselves.
Other complications include general non-consensus or deliberate "distortion or bias" of reasonable technical definitions of political ideologies and associated forms of governing, due to the nature of politics in the modern era. For example: The meaning of "conservatism" in the United States has little in common with the way the word's definition is used elsewhere. As Ribuffo notes, "what Americans now call conservatism much of the world calls liberalism or neoliberalism"; a "conservative" in Finland would be labeled a "socialist" in the United States. Since the 1950s conservatism in the United States has been chiefly associated with right-wing politics and the Republican Party. However, during the era of segregation many Southern Democrats were conservatives, and they played a key role in the conservative coalition that controlled Congress from 1937 to 1963.
Social-political ambiguity
Opinions vary by individuals concerning the types and properties of governments that exist. "Shades of gray" are commonplace in any government and its corresponding classification. Even the most liberal democracies limit rival political activity to one extent or another while the most tyrannical dictatorships must organize a broad base of support thereby creating difficulties for "pigeonholing" governments into narrow categories. Examples include the claims of the United States as being a plutocracy rather than a democracy since some American voters believe elections are being manipulated by wealthy Super PACs. Some consider that government is to be reconceptualised where in times of climatic change the needs and desires of the individual are reshaped to generate sufficiency for all.
Measurement of governing
The quality of a government can be measured by Government effectiveness index, which relates to political efficacy and state capacity.
Forms
Main article: List of forms of government Further information: Mixed government| Part of the Politics series | ||||||||
| Basic forms of government | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List of forms · List of countries | ||||||||
Source of power
|
||||||||
Power ideology
|
||||||||
|
Power structure |
||||||||
|
Related |
||||||||
|
| ||||||||
Plato in his book The Republic (375 BC) divided governments into five basic types (four being existing forms and one being Plato's ideal form, which exists "only in speech"):
- Aristocracy (rule by law and order, like ideal traditional "benevolent" kingdoms that are not tyrannical)
- Democracy (rule by pure liberty and equality, like a free citizen)
- Oligarchy (rule by wealth and market-based-ethics, like a laissez-faire capitalist state)
- Timocracy (rule by honor and duty, like a "benevolent" military; Sparta as an example)
- Tyranny (rule by fear, like a despot)
These five regimes progressively degenerate starting with aristocracy at the top and tyranny at the bottom.
In his Politics, Aristotle elaborates on Plato's five regimes discussing them in relation to the government of one, of the few, and of the many. From this follows the classification of forms of government according to which people have the authority to rule: either one person (an autocracy, such as monarchy), a select group of people (an aristocracy), or the people as a whole (a democracy, such as a republic).
Thomas Hobbes stated on their classification:
The difference of Commonwealths consisteth in the difference of the sovereign, or the person representative of all and every one of the multitude. And because the sovereignty is either in one man, or in an assembly of more than one; and into that assembly either every man hath right to enter, or not everyone, but certain men distinguished from the rest; it is manifest there can be but three kinds of Commonwealth. For the representative must need to be one man or more; and if more, then it is the assembly of all, or but of a part. When the representative is one man, then is the Commonwealth a monarchy; when an assembly of all that will come together, then it is a democracy or popular Commonwealth; when an assembly of a part only, then it is called an aristocracy. In other kinds of Commonwealth there can be none: for either one, or more, or all, must have the sovereign power (which I have shown to be indivisible) entire.
Modern basic political systems
According to Yale professor Juan José Linz, there a three main types of political systems today: democracies, totalitarian regimes and, sitting between these two, authoritarian regimes with hybrid regimes. Another modern classification system includes monarchies as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three. Scholars generally refer to a dictatorship as either a form of authoritarianism or totalitarianism.
Autocracy
Main article: AutocracyAn autocracy is a system of government in which supreme power is concentrated in the hands of one person, whose decisions are subject to neither external legal restraints nor regularized mechanisms of popular control (except perhaps for the implicit threat of a coup d'état or mass insurrection). Absolute monarchy is a historically prevalent form of autocracy, wherein a monarch governs as a singular sovereign with no limitation on royal prerogative. Most absolute monarchies are hereditary, however some, notably the Holy See, are elected by an electoral college (such as the college of cardinals, or prince-electors). Other forms of autocracy include tyranny, despotism, and dictatorship.
Aristocracy
Main article: AristocracyAristocracy is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, elite ruling class, such as a hereditary nobility or privileged caste. This class exercises minority rule, often as a landed timocracy, wealthy plutocracy, or oligarchy.
Many monarchies were aristocracies, although in modern constitutional monarchies, the monarch may have little effective power. The term aristocracy could also refer to the non-peasant, non-servant, and non-city classes in the feudal system.
Democracy
Main articles: Democracy and Types of democracy
- National governments which self-identify as democracies
- National governments which do not self-identify as democracies
Democracy is a system of government where citizens exercise power by voting and deliberation. In a direct democracy, the citizenry as a whole directly forms a participatory governing body and vote directly on each issue. In indirect democracy, the citizenry governs indirectly through the selection of representatives or delegates from among themselves, typically by election or, less commonly, by sortition. These select citizens then meet to form a governing body, such as a legislature or jury.
Some governments combine both direct and indirect democratic governance, wherein the citizenry selects representatives to administer day-to-day governance, while also reserving the right to govern directly through popular initiatives, referendums (plebiscites), and the right of recall. In a constitutional democracy the powers of the majority are exercised within the framework of representative democracy, but the constitution limits majority rule, usually through the provision by all of certain universal rights, such as freedom of speech or freedom of association.
Republics
Main article: RepublicA republic is a form of government in which the country is considered a "public matter" (Latin: res publica), not the private concern or property of the rulers, and where offices of states are subsequently directly or indirectly elected or appointed rather than inherited. The people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people.
A common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of state is not a monarch. Montesquieu included both democracies, where all the people have a share in rule, and aristocracies or oligarchies, where only some of the people rule, as republican forms of government.
Other terms used to describe different republics include democratic republic, parliamentary republic, semi-presidential republic, presidential republic, federal republic, people's republic, and Islamic republic.
Federalism
Main article: FederalismFederalism is a political concept in which a group of members are bound together by covenant with a governing representative head. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of government in which sovereignty is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and constituent political units, variously called states, provinces or otherwise. Federalism is a system based upon democratic principles and institutions in which the power to govern is shared between national and provincial/state governments, creating what is often called a federation. Proponents are often called federalists.
Branches

Governments are typically organised into distinct institutions constituting branches of government each with particular powers, functions, duties, and responsibilities. The distribution of powers between these institutions differs between governments, as do the functions and number of branches. An independent, parallel distribution of powers between branches of government is the separation of powers. A shared, intersecting, or overlapping distribution of powers is the fusion of powers.
Governments are often organised into three branches with separate powers: a legislature, an executive, and a judiciary; this is sometimes called the trias politica model. However, in parliamentary and semi-presidential systems, branches of government often intersect, having shared membership and overlapping functions. Many governments have fewer or additional branches, such as an independent electoral commission or auditory branch.
Party system
| Part of the Politics series | ||||||
| Party politics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Political spectrum
|
||||||
| Major ideologies | ||||||
| Types | ||||||
| Leaders and organization | ||||||
| Internal elections | ||||||
| Party discipline | ||||||
|
Party systems |
||||||
| Coalitions between parties | ||||||
| Lists of political parties | ||||||
|
| ||||||
Presently, most governments are administered by members of an explicitly constituted political party which coordinates the activities of associated government officials and candidates for office. In a multiparty system of government, multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government offices, typically by competing in elections, although the effective number of parties may be limited.
A majority government is a government by one or more governing parties together holding an absolute majority of seats in the parliament, in contrast to a minority government in which they have only a plurality of seats and often depend on a confidence-and-supply arrangement with other parties. A coalition government is one in which multiple parties cooperate to form a government as part of a coalition agreement. In a single-party government, a single party forms a government without the support of a coalition, as is typically the case with majority governments, but even a minority government may consist of just one party unable to find a willing coalition partner at the moment.
A state that continuously maintains a single-party government within a (nominally) multiparty system possesses a dominant-party system. In a (nondemocratic) one-party system a single ruling party has the (more-or-less) exclusive right to form the government, and the formation of other parties may be obstructed or illegal. In some cases, a government may have a non-partisan system, as is the case with absolute monarchy or non-partisan democracy.
Maps
See also: List of countries by system of governmentDemocracy is the most popular form of government. More than half of the nations in the world are democracies—97 of 167, as of 2021. However, the world is becoming more authoritarian with a quarter of the world's population under democratically backsliding governments.

| Full Democracies 9–10 8–9 | Flawed Democracies 7–8 6–7 | Hybrid Regimes 5–6 4–5 | Authoritarian Regimes 3–4 2–3 0–2 |

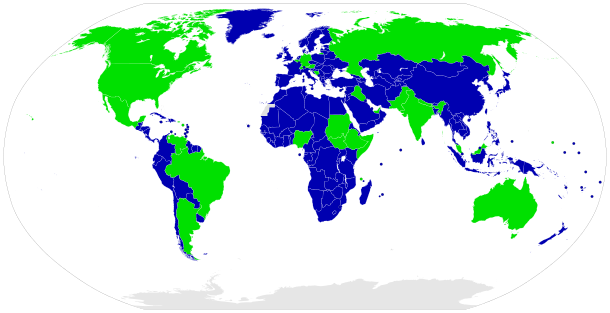
Unitary states Federations
See also
- List of forms of government
- Central government
- Civics
- Comparative government
- Constitutional economics
- Deep state
- Digital democracy
- E-Government
- History of politics
- Legal rights
- List of countries by system of government
- List of European Union member states by political system
- Local government
- Ministry
- Political economy
- Political history
- Prime ministerial government
- State (polity)
- Voting system
- World government
Notes
- Frederickson 2000, p. 12, quote: "...conservative southern Democrats viewed warily the potential of New Deal programs to threaten the region's economic dependence on cheap labor while stirring the democratic ambitions of the disfranchised and undermining white supremacy."
- Ancient Greek: ἀριστοκρατία aristokratía, from ἄριστος aristos "excellent", and κράτος kratos "power".
- Conducted by the American think tank Freedom House, which is largely funded by the US government.
References
- Dobratz, B.A. (2015). Power, Politics, and Society: An Introduction to Political Sociology. Taylor & Francis. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-317-34529-9. Archived from the original on 30 April 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ Linz, Juan José (2000). Totalitarian and Authoritarian Regimes. Lynne Rienner Publisher. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-55587-890-0. OCLC 1172052725. Archived from the original on 22 April 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- ^ Garcia-Alexander, Ginny; Woo, Hyeyoung; Carlson, Matthew J. (2017). Social Foundations of Behavior for the Health Sciences. Springer. pp. 137–. ISBN 978-3-319-64950-4. OCLC 1013825392.
- "14.2 Types of Political Systems". 8 April 2016. Archived from the original on 22 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- Columbia Encyclopedia (6th ed.). Columbia University Press. 2000.
- ^ Smelser & Baltes 2001, p. .
- Brock 2013, p. 53–62.
- "Government English Definition and Meaning". Lexico. Archived from the original on 17 July 2022. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ Christian 2004, p. 245.
- Christian 2004, p. 294.
- Eagly, Alice H.; Wood, Wendy (June 1999). "The Origins of Sex Differences in Human Behavior: Evolved Dispositions Versus Social Roles". American Psychologist. 54 (6): 408–423. doi:10.1037/0003-066x.54.6.408. Archived from the original on 17 August 2000.
- Fukuyama, Francis (27 March 2012). The Origins of Political Order: From Prehuman Times to the French Revolution. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 70. ISBN 978-0-374-53322-9.
- Roosevelt, Anna C. (1999). "The Maritime, Highland, Forest Dynamic and the Origins of Complex Culture". In Salomon, Frank; Schwartz, Stuart B. (eds.). Cambridge history of the Native peoples of the Americas: South America, Volume 3. Cambridge University Press. pp. 266–267. ISBN 978-0-521-63075-7. Archived from the original on 24 June 2016.
- ^ Kuper & Kuper 2008, p. .
- Haider-Markel 2014, p. .
- Lewellen 2003, p. .
- Kopstein & Lichbach 2005, p. 4.
- Renna 2015.
- Ribuffo 2011, pp. 2–6, quote on p. 6.
- Frederickson 2000, p. 12.
- Freeland 2012.
- "Governing the "Enough" in a Warming World The Discourse of "Sufficiency" from a Climate Governmentality Perspective". Deflorian, Michel (2015). Retrieved 2 October 2023
- Guisan, Maria-Carmen (2009). "Government effectiveness, education, economic development and well-being: analysis of European countries in comparison with the United States and Canada, 2000-2007" (PDF). Applied Econometrics and International Development. 9 (1): 1. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- Abjorensen, Norman (2019). Historical Dictionary of Democracy. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 288–. ISBN 978-1-5381-2074-3. OCLC 1081354236.
- Brill 2016.
- Jordović, Ivan (2019). Taming Politics: Plato and the Democratic Roots of Tyrannical Man. Franz Steiner Verlag. p. intro. ISBN 978-3-515-12457-7. OCLC 1107421360.
- Hobbes, Thomas. Leviathan – via Wikisource.
- Jonathan Michie, ed. (3 February 2014). Reader's Guide to the Social Sciences. Routledge. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-135-93226-8. Archived from the original on 22 April 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- Todd, Allan; Waller, Sally (10 September 2015). Todd, Allan; Waller, Sally (eds.). History for the IB Diploma Paper 2 AuthoritariaAuthoritarian States (20th Century). Cambridge University Press. pp. 10–. ISBN 978-1-107-55889-2. Archived from the original on 22 April 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- Sondrol, P. C. (2009). "Totalitarian and Authoritarian Dictators: A Comparison of Fidel Castro and Alfredo Stroessner". Journal of Latin American Studies. 23 (3): 599–620. doi:10.1017/S0022216X00015868. ISSN 0022-216X. JSTOR 157386. S2CID 144333167. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- Johnson, Paul M. "Autocracy: A Glossary of Political Economy Terms". Auburn.edu. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- "aristocracy". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Oxford English Dictionary: "democracy".
- Watkins, Frederick (1970). "Democracy". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (Expo '70 hardcover ed.). William Benton. pp. 215–223. ISBN 978-0-85229-135-1.
- Montesquieu 1748, book 2, chapters 1.
- "Republic". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- "republic". WordNet 3.0. Archived from the original on 12 March 2009. Retrieved 20 March 2009.
- "Republic". Merriam-Webster. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- Montesquieu 1748, book 2, chapters 2–3.
- Cane, Peter; Conaghan, Joanne (2008). "Federalism". The new Oxford companion to law. Oxford: Oxford university press. ISBN 978-0-19-929054-3.
- Needler 1991, pp. 116–118.
- Gallagher, Laver & Mair 2006.
- Kettle 2015.
- Duxbury 2021.
- ^ The Global State of Democracy 2021 Archived 9 August 2022 at the Wayback Machine, International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance
- "Democracy Index 2017 – Economist Intelligence Unit" (PDF). EIU.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 December 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
Bibliography
- Brill, Sara (2016). "Political Pathology in Plato's Republic". Apeiron. 49 (2): 127–161. doi:10.1515/apeiron-2015-0003. ISSN 2156-7093. S2CID 148505083. Archived from the original on 27 October 2022. Retrieved 4 August 2022.
- Brock, Roger (2013). Greek Political Imagery from Homer to Aristotle. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-4725-0218-6. OCLC 1040413173. Archived from the original on 9 November 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- Christian, David (2004). Maps of Time: an Introduction to Big History. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24476-4. OCLC 966003275.
- Duxbury, Charlie (29 November 2021). "Magdalena Andersson named Swedish prime minister (again)". Politico. Archived from the original on 15 April 2022. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- Frederickson, Kari (2000). The Dixiecrat Revolt and the End of the Solid South, 1932–1968. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-4910-1. OCLC 475254808.
- Freeland, Chrystia (2012). Plutocrats: the Rise of the New Global Super-Rich and the Fall of Everyone Else. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-1-84614-252-9. OCLC 795857028.
- Gallagher, Michael; Laver, M.; Mair, P. (2006). Representative Government in Western Europe (4th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0070366848. OCLC 906939909.
- Haider-Markel, Donald P. (2014). The Oxford Handbook of State and Local Government. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-957967-9. OCLC 904484428.
- Kettle, Martin (17 April 2015). "Coalition and minority governments are not so unusual in UK elections; The first-past-the-post system has led to fewer one-party majority governments in Britain than might be expected -- only half of all those in the 20th century". Guardian. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 14 July 2022 – via Gale General OneFile.
- Kopstein, Jeffrey; Lichbach, Mark, eds. (2005). Comparative politics: interests, identities, and institutions in a changing global order (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521708400. OCLC 1293165230.
- Kuper, Adam; Kuper, Jessica, eds. (2008). The Social Science Encyclopedia. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-47635-5. OCLC 789658928.
- Lewellen, Ted C. (2003). Political Anthropology: An Introduction (3rd ed.). Westport, CT: Praeger. ISBN 978-0-89789-891-1. OCLC 936497371. Archived from the original on 9 November 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- Montesquieu (1748). The Spirit of the Laws.
- Needler, Martin C. (1991). The Concepts of Comparative Politics. New York: Praeger. ISBN 978-0-275-93653-2. OCLC 925042067.
- Renna, Thomas (September 2015). "The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire". Michigan Academician. 42 (1): 60–75. doi:10.7245/0026-2005-42.1.60.
- Ribuffo, Leo P. (2011). "20 Suggestions for Studying the Right now that Studying the Right is Trendy". Historically Speaking. 12 (1): 2–6. doi:10.1353/hsp.2011.0013. S2CID 144367661.
- Smelser, Neil J.; Baltes, Paul B. (2001). International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. New York: Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-08-043076-8. OCLC 43548228.
Further reading
- de Mesquita, Bruce Bueno; Smith, Alastair (2012). The Dictator's Handbook: Why Bad Behavior Is Almost Always Good Politics. New York: PublicAffairs. ISBN 978-1610390446. OCLC 1026803822.
- de Mesquita, Bruce Bueno; Smith, Alastair; Siverson, Randolph M.; Morrow, James D. (2003). The Logic of Political Survival. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0262025461. OCLC 475265120.
- Dobson, William J. (2013). The Dictator's Learning Curve: Inside the Global Battle for Democracy. New York: Anchor. ISBN 978-0307477552. OCLC 849820048.
- Friedrich, Carl J.; Brzezinski, Zbigniew K. (1966) . Totalitarian Dictatorship and Autocracy (2nd ed.). New York: Frederick A. Praeger. ISBN 978-0674895652. OCLC 826626632.
- Krader, Lawrence (1968). Formation of the State. Foundations of Modern Anthropology. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0133294900. OCLC 266086412.
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity Data from Wikidata
Data from Wikidata