| Revision as of 23:21, 17 September 2011 editKangaroopower (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers3,819 editsm Reverted edits by Alberto0022 to last version by Kangaroopower (GLOO)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:44, 9 January 2025 edit undoWikiCleanerBot (talk | contribs)Bots928,066 editsm v2.05b - Bot T20 CW#61 - Fix errors for CW project (Reference before punctuation)Tag: WPCleaner | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Country in Central America}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | |||
| {{other uses|Nicaragua (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| {{pp-pc|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=November 2021}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=August 2024}} <!-- | Reason=It is in Central America... --> | |||
| {{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| |conventional_long_name |
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Nicaragua | ||
| | |
| common_name = Nicaragua | ||
| | |
| native_name = {{lang|es|República de Nicaragua}} (]) | ||
| |image_flag |
| image_flag = Flag of Nicaragua.svg | ||
| |image_coat |
| image_coat = Coat of arms of Nicaragua.svg | ||
| | national_motto = {{native phrase|es|En Dios confiamos}}<br />{{raise|0.2em|{{small|"]"}}{{lower|0.2em|{{efn|As shown on the ] (bank notes and coins).<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100924020620/http://bcn.gob.ni/billetes_monedas/index.html?&val=1 |date=24 September 2010 }}</ref>}}}}}} | |||
| |image_map = Nicaragua (orthographic projection).svg | |||
| | national_anthem = {{native name|es|]|italics=on|nolink=yes}}<br />{{small|"Hail to Thee, Nicaragua"}}<br />{{center|]}}{{center| }} | |||
| |national_motto = ''En Dios Confiamos'' {{Spaces|2}}<small>{{es icon}}<br/>"]"</small><ref name=cordoba>As shown on the ] (bank notes and coins); see for example </ref> | |||
| | image_map = NIC orthographic.svg | |||
| |national_anthem = {{lang|es|"]"}}</sup>{{spaces|2}}<small>(])<br />"Hail to Thee, Nicaragua"<br/> | |||
| | image_map2 = | |||
| |official_languages = ] | |||
| | capital = ] | |||
| |regional_languages = ], ], ], ], ], ] | |||
| | coordinates = {{Coord|12|6|N|86|14|W|type:city_region:NI-MN}} | |||
| |ethnic_groups =49% ]<br/>37% ] (majority being of Western European ancestry)<br/>5% ]<br/>9% ]<ref name=indexmundi>{{cite web|author=|title=Nicaragua Demographics Profile 2011|work=Nicaragua|publisher=Index Mundi|year=2011|url=http://www.indexmundi.com/nicaragua/demographics_profile.html|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| | largest_city = capital | |||
| |demonym = ], ], ] | |||
| | official_languages = ] | |||
| |capital = ] ] | |||
| | ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | |||
| |latd=12 |latm=9 |latNS=N |longd=86 |longm=16 |longEW=W | |||
| | 69% ] (mixed ] and ]) | |||
| |largest_city = capital | |||
| | 17% ] | |||
| |government_type = ] ] | |||
| | 9% ] | |||
| |leader_title1 = ] | |||
| | 5% ] | |||
| |leader_name1 = ] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| |leader_title2 = ] | |||
| | ethnic_groups_year = 2023<ref>{{cite web |title=Nicaragua |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua/#people-and-society |website=The World Factbook |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |access-date=4 July 2023 |language=en |date=19 June 2023 |archive-date=20 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210320071255/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua#people-and-society |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |leader_name2 = ] | |||
| | demonym = {{hlist|]|Pinolero/Pinolera (colloquial)}} | |||
| |sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| | religion_year = 2015 | |||
| |sovereignty_note = {{nobold|from ] and ]}} | |||
| | religion_ref = <ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180112003048/http://www.prolades.com/ |date=12 January 2018 }} PROLADES Religion in America by country</ref><ref name="Census2015">{{cite web|title=CENSO DE POBLACIÓN 2005|url=http://www.inide.gob.ni/censos2015/ResumenCensal/Resumen2.pdf|access-date=4 April 2015|date=2015}}{{Dead link|date=January 2021 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | |||
| |established_event1 = Declared | |||
| | religion = {{unbulleted list | |||
| |established_date1 = 15 September 1821 | |||
| | | |||
| |established_event2 = Recognized | |||
| {{Tree list}} | |||
| |established_date2 = 25 July 1850 | |||
| *84.4% ] | |||
| |established_event3 = from the ] | |||
| **55.0% ] | |||
| |established_date3 = July 1, 1823 | |||
| **27.2% ] | |||
| |established_event4 = Revolution | |||
| **2.2% other ] | |||
| |established_date4 = 19 July 1979 | |||
| {{Tree list/end}} | |||
| |established_event5 = Current constitution | |||
| |14.7% ]|0.9% other}} | |||
| |established_date5 = 9 January 1987<ref name=CIA2011>{{cite web|author=Central Intelligence Agency|title=Nicaragua|work=The World Factbook|publisher=Central Intelligence Agency|location=Langley, Virginia|year=2011|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/nu.html|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| | government_type = Unitary ] under an ] dictatorship<ref name="Awadalla 2023 pp. 701–723">{{cite journal | last=Awadalla | first=Cristina | title=Authoritarian Populism and Patriarchal Logics: Nicaragua's Engendered Politics | journal=Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society | publisher=Oxford University Press (OUP) | volume=30 | issue=2 | date=March 23, 2023 | issn=1072-4745 | doi=10.1093/sp/jxad006 | pages=701–723| doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name="Córdoba 2022 h955">{{cite web | last=Córdoba | first=José de | title=U.S. Imposes Sanctions on Nicaragua's Authoritarian Regime | website=WSJ | date=October 25, 2022 | url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-imposes-sanctions-on-nicaraguas-authoritarian-regime-11666657991 | access-date=September 3, 2023 | archive-date=3 September 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230903155100/https://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-imposes-sanctions-on-nicaraguas-authoritarian-regime-11666657991 | url-status=live |url-access=subscription}}</ref><ref name="Freedom House 2019 j906">{{cite web | title=Nicaragua: Freedom in the World 2023 Country Report | website=Freedom House | date=May 30, 2019 | url=https://freedomhouse.org/country/nicaragua/freedom-world/2023 | access-date=September 3, 2023 | archive-date=3 September 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230903155102/https://freedomhouse.org/country/nicaragua/freedom-world/2023 | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |area_rank = 97th | |||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |area_magnitude = 1 E11 | |||
| | |
| leader_name1 = {{nowrap|]}} | ||
| | |
| leader_title2 = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_name2 = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_title3 = | ||
| | leader_name3 = | |||
| |population_estimate_rank = 110th | |||
| | legislature = ] | |||
| |population_estimate_year = 2010 Census | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] {{nobold|from ], ] and the ]}} | |||
| |population_census = 5,666,301 | |||
| | established_event1 = Declared | |||
| |population_census_year = 2005 | |||
| | established_date1 = 15 September 1821 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 42 | |||
| | established_event2 = Recognized | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = 114 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | established_date2 = 25 July 1850 | |||
| |population_density_rank = 133rd | |||
| | established_event3 = From the ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP = $17.711 billion<ref name=IMF2011>{{cite web|author=International Monetary Fund|title=Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: Nicaragua|work=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2011|publisher=International Monetary Fund|location=Washington, D.C.|year=2011|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2008&ey=2011&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=278&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=43&pr.y=13|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| | established_date3 = 1 July 1823 | |||
| |GDP_PPP_rank = 132nd | |||
| | established_event4 = From the ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP_year = 2010 | |||
| | established_date4 = 31 May 1838 | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $3,045<ref name=IMF2011/> | |||
| | established_event5 = ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 167th | |||
| | established_date5 = 19 July 1979 | |||
| |GDP_nominal = $6.551 billion<ref name=IMF2011/> | |||
| | established_event6 = ] | |||
| |GDP_nominal_year = 2010 | |||
| | |
| established_date6 = 9 January 1987<ref name=cia/> | ||
| | area_km2 = 130,375 | |||
| |HDI = {{increase}} 0.565<ref name=UNHDI2010>{{cite web|author=United Nations Development Programme|title=Table 1: Human Development Index and its components|work=Human Development Report 2010 (20th Anniversary Edition) The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development|year=2010|publisher=United Nations|location=New York|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDR_2010_EN_Tables_reprint.pdf|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| | area_rank = 96th <!-- Area rank should match List of countries and dependencies by area --> | |||
| |HDI_rank = 115th | |||
| | |
| area_sq_mi = 50,193 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | ||
| | percent_water = 7.14 | |||
| |HDI_category = <span style="color:#fc0;">medium</span> | |||
| | population_estimate = 6,359,689<ref>{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Nicaragua|access-date=22 June 2023|year=2023}}</ref> | |||
| |Gini = 40.1 | |||
| | population_estimate_year = 2023 | |||
| |Gini_year = 2007 | |||
| | population_estimate_rank = 110th | |||
| |Gini_category = <span style="color:#fc0;">medium</span> | |||
| | population_density_km2 = 51 | |||
| |currency = ] | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 114 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |currency_code = NIO | |||
| | population_density_rank = 155th | |||
| |country_code = | |||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $56.697 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.NI">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=278,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=1980&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Nicaragua) |publisher=] |website=IMF.org |date=10 October 2024 |access-date=9 November 2024 }}</ref> | |||
| |time_zone = | |||
| | |
| GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | ||
| | |
| GDP_PPP_rank = 115th | ||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $8,492<ref name="IMFWEO.NI" /> | |||
| |utc_offset_DST = | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 129th | |||
| |drives_on = Right | |||
| | |
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $17.843 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.NI" /> | ||
| | |
| GDP_nominal_rank = 127th | ||
| | |
| GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | ||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $2,673<ref name="IMFWEO.NI" /> | |||
| |footnote1 = English and indigenous languages on Caribbean coast are also spoken. | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 134th | |||
| |footnote2 = Significant proportion of information obtained from | |||
| | Gini = 46.2 <!--number only--> | |||
| | Gini_year = 2014 | |||
| | Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=NI |title=GINI index (World Bank estimate) |publisher=] |website=data.worldbank.org |access-date=7 March 2019 |archive-date=22 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200522170529/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=NI |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | Gini_rank = | |||
| | HDI = 0.669 <!--number only--> | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref>{{Cite web |date=13 March 2024 |title=Human Development Report 2023/2024 |url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf |archive-date=13 March 2024 |access-date=13 March 2024 |publisher=] |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 130th | |||
| | currency = ] | |||
| | currency_code = NIO | |||
| | time_zone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = −6 | |||
| | drives_on = right | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | cctld = ] | |||
| <!--- ORPHANED: | |||
| |footnote_a = English and indigenous languages on Caribbean coast are also spoken. | |||
| |footnote_b = Significant proportion of information obtained from | |||
| ---->| regional_languages = {{unbulleted list |] |] |] |] |{{nowrap|]}} |] |]}} | |||
| | country_code = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Nicaragua''',{{efn|{{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Nicaragua.ogg|ˌ|n|ɪ|k|ə|ˈ|r|ɑː|ɡ|w|ə|,_|-|ˈ|r|æ|ɡ|-|,_|-|g|j|u|ə}}; {{IPA|es|nikaˈɾaɣwa|lang|ES-pe - Nicaragua.ogg}}}} officially the '''Republic of Nicaragua''',{{efn|{{langx|es|{{audio|ES-pe - República de Nicaragua.ogg|República de Nicaragua}}}}<!-- {{IPA|es|reˈpuβlika ðe nikaˈɾaɣwa|}}-->}} is the geographically largest ] in ], comprising {{cvt|130,370|km2}}. With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024,<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.macrotrends.net/global-metrics/countries/NIC/nicaragua/population | title=Nicaragua Population 1950-2024 }}</ref> it is the third-most populous country in Central America after ] and ]. | |||
| <!-- Geography --> | |||
| '''Nicaragua''' ({{IPAc-en|US|En-us-Nicaragua.ogg|ˌ|n|ɪ|k|ə|ˈ|r|ɑː|ɡ|w|ə}} {{respell|nik-ə|RAH|gwə}}) officially the ''' Republic of Nicaragua''' ({{lang-es|República de Nicaragua}}, {{IPA-es|reˈpuβlika ðe nikaˈɾaɣwa|pron|República_de_Nicaragua.ogg}}), is the largest country in ]. Nicaragua is bordered by ] to the north and ] to the south. Nicaragua is located at the center of the ] that forms a ] between North and South America. The country is situated between ] and ] degrees north of the ] in the ], which places it entirely within the ]. The ] lies to the west, and the ] to the east; Nicaragua's Caribbean coast is part of the ]. The country's ] divides it into three major zones: Pacific lowlands, wet, cooler central highlands, and the ]. On the Pacific side of the country are the two largest ] lakes in Central America—] and ]. Surrounding these lakes and extending to their northwest along the ] of the ] are fertile lowland plains, whose soil is highly enriched with ] from nearby ]es. Nicaragua's abundance of biologically significant and unique ]s contribute to ]'s designation as a ]. The ] runs through the spine of the country, earning Nicaragua its notably famous nickname: ''The Land of Lakes and Volcanoes.''<ref name=INDT2010>{{cite web|author=Instituto Nicaragüense de Turismo|title=About Nicaragua|work=Nicaragua|publisher=Instituto Nicaragüense de Turismo|location=Managua|year=2010|url=http://www.visitanicaragua.com/ingles/nicaragua.php|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the ] to the east, ] to the south, and the ] and shares maritime borders with ] to the west and ] to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is ], the ], with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.yara.com/news-and-media/news/archive/2016/yara-expands-presence-in-central-america/|title= Yara expands presence in Central America|date= 23 February 2018}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://time.com/archive/6943284/nicaraguas-great-leap-forward/|title= Nicaragua's Great Leap Forward|date= 8 May 2008}}</ref> Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is ], though indigenous tribes on the ] speak their own languages and ]. The mixture of cultural traditions has generated substantial diversity in folklore, cuisine, music, and literature, including contributions by Nicaraguan poets and writers such as ]. | |||
| <!-- History --> | |||
| The ] conquered the region in the 16th century and the territory became associated with the ] and later the ]. Alongside the Spanish, the British established a ] on the eastern seaboard beginning in the middle of the 17th century, and ending roughly two centuries later with the rise of the Spanish ] in the coast. The eastern seaboard retains its ]; English and ] are commonly spoken and the culture in the Atlantic region identifies as being more Caribbean. In 1821, Nicaragua achieved its independence from Spain and joined the ] in 1823, later leaving the Federal Republic in 1838.<ref name=Smith1963>{{cite journal|last1=Smith|first1=RS|title=Financing the Central American federation, 1821-1838 (abstract)|journal=The Hispanic American Historical Review|volume=43|issue=4|pages=483–510|year=1963|pmc=|pmid=|doi=|jstor=2509898}}</ref> Nicaragua increasingly became a subject of substantial interest because of its geographic position for a ] that would service the ].<ref name=Colquhoun1895>{{cite book|last=Colquhoun|first=AR|title=The key of the Pacific: the Nicaragua canal|publisher=Archibald Constable and Company|location=Westminster, England|year=1895|url=http://www.archive.org/stream/keypacificnicar02colqgoog#page/n6/mode/2up}}</ref> Roughly a century after operations of the ] commenced and one hundred and eighty five years after the initial plans for the ] waterway, the prospect of a Nicaraguan ] has remained the subject of interest, with its construction in progress.<ref name=Munoz2001>{{cite web|author=Néfer Muñoz|title=An 'Eco-Canal' across Nicaragua|work=Accents|publisher=Tierramérica|location=Granada, Nicaragua|year=2001|url=http://www.tierramerica.net/2001/0506/iacentos.shtml|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref><ref name=EPN2009>{{cite web|author=Empresa Portuaria Nacional|title=Proyecto "Construcción del Puerto Monkey Point"|work=Proyectos|publisher=Empresa Portuaria Nacional|location=Managua|language=Spanish|year=2009|url=http://www.epn.com.ni/Puerto-mp.aspx|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref><ref name=Alvarez2008>{{cite news|author=Gustavo Alvarez|title=Empresas de seis países interesadas en Monkey Point|newspaper=elnuevodiario.com.ni|publisher=]|location=Managua|date=2008-02-18|language=Spanish|url=http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/economia/8704|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref><ref name=Hidalgo2010>{{cite news|author=Wendy Álvarez Hidalgo|title=Harán puerto Monkey Point|newspaper=laprensa.co.ni|publisher=]|location=Managua|date=2010-07-07|language=Spanish|url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/07/07/economia/30625|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref> Eighteen years after leaving the federal Republic it also became the center of ] ] filibustering in Central America.<ref name=Walker1860>{{cite book|last=Walker|first=W|title=The War in Nicaragua|publisher=S.H. Goetzel & Company|location=New York|year=1860|url=http://www.archive.org/stream/warinnicaragua00walkgoog#page/n6/mode/2up}}</ref><ref name=Juda1919>{{cite journal|last=Juda|first=F|title=California Filibusters: A History of their Expeditions into Hispanic America (excerpt)|journal=The Grizzly Bear (official organ Native sons and native daughters Golden West)|volume=XXI|issue=4|pages=3–6, 15, 19|year=1919|url=http://www.sfmuseum.org/hist1/walker.html|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref><ref name=Baker2001>{{cite book|last=Baker|first=CP|title=Moon Handbooks: Costa Rica|edition=4th|chapter=The William Walker Saga|page=67|publisher=Avalon Travel Publishing|location=New York|year=2001|isbn=978-1566916080|url=http://www.amazon.com/Moon-Handbooks-Costa-Christopher-Baker/dp/1566916089#reader_1566916089|accessdate=2011-07-20}}</ref> Since its independence, Nicaragua has undergone periods of political unrest, ], ] and fiscal crisis—the most notable causes that lead to the ]. Although the ] ruled the country in the form of a dictatorship for forty years, Nicaragua was among the first countries to sign the ] in 1945.<ref name=UNCharter1945>{{cite document|author=United Nations|title=Charter of the United Nations and Statute of the International Court of Justice|page=49|publisher=United Nations|location=San Francisco|date=1945-06-26|url=http://treaties.un.org/doc/Publication/CTC/uncharter.pdf}}</ref> Prior to the revolution, Nicaragua was one of Central America's wealthiest and most developed countries. The revolutionary conflict, paired with ] reversed the country's prior economic standing. Despite the harsh economic effects of both phenomena, Nicaragua is a ] republic which has experienced economic growth and political stability in recent years. In 1990, Nicaragua elected ] as its president, making it the first country in the Americas and in ] to democratically elect a ] and the second country in the Western Hemisphere to do so, following ]'s democratic election of ]. | |||
| Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the ] in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part was transferred to ] in 1960. Since its independence, Nicaragua has undergone periods of political unrest, dictatorship, occupation and fiscal crisis, including the ] of the 1960s and 1970s and the ]{{Broken anchor|date=2024-07-21|bot=User:Cewbot/log/20201008/configuration|target_link=Nicaraguan Revolution#Contra War|reason= The anchor (Contra War) ].}} of the 1980s. | |||
| <!-- Demographics --> | |||
| The population in Nicaragua, hovering at approximately 6 million, is ]. Roughly one quarter of the nation's population lives in the capital city, ], making Managua the second largest city and ] in Central America (following ]). Other major cities include ], ], ], ] and ]. Segments of the population include ] native tribes from the ], Europeans, Africans, Asians and people of Middle Eastern origin. The main language is Spanish, although native tribes on the eastern coast speak their native languages, such as Miskito, Sumo and Rama, as well as English Creole. Of the Spanish-speaking countries in Central America, Nicaragua is where the use of the '']'' form of address is most widespread. The mixture of cultural traditions has generated substantial diversity in art, cuisine, literature, and music. Nicaragua has earned recognition and various colloquial names in reference to its geographic location, cultural achievements and recent economic development. Nicaragua's biological diversity, warm tropical climate, and active volcanoes make it an increasingly popular destination for tourists, surfers, biologists, and volcanologists.<ref name=Dicum2006>{{cite web|last=Dicum|first=G|title=The Rediscovery of Nicaragua|work=Travel Section|publisher=TraveThe New York Times|location=New York|date=2006-12-17|url=http://travel.nytimes.com/2006/12/17/travel/17Nicaragua.html?ref=travel|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref><ref name=MNN2010>{{cite web|last=Davis|first=LS|title=Nicaragua: The next Costa Rica?|work=Mother Nature Network|publisher=MNN Holdings, LLC|date=2009-04-22|url=http://www.mnn.com/lifestyle/eco-tourism/stories/nicaragua-the-next-costa-rica|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> The country has also been dubbed ''The Land of Poets'', due to various literary contributions of renown Nicaraguan writers, including ], ] and ].<ref name=elcomercio2008>{{cite web|url=http://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&layout=2&eotf=1&sl=es&tl=en&u=http://elcomercio.pe/edicionimpresa/Html/2008-01-20/nicaragua-eterna-tierra-poetas.html&act=url|title=Nicaragua, Eternal Land of Poets|publisher=Elcomercio.pe|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| Though nominally a unitary presidential republic, Nicaragua has experienced significant ] following the ] and subsequent crackdown{{citation needed|date=January 2025}}. Following the ], it has descended into an ] ].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Mendoza |first=Yubelka |last2=Kitroeff |first2=Natalie |date=2021-11-07 |title=Nicaragua Descends Into Autocratic Rule as Ortega Crushes Dissent |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/07/world/americas/nicaragua-election-ortega.html |access-date=2025-01-05 |work=The New York Times |language=en-US |issn=0362-4331}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Córdoba |first=José de |date=2021-11-06 |title=Nicaragua Veers to Dictatorship as President Holds Election the U.S. Calls ‘Sham’ |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/nicaragua-veers-to-dictatorship-as-president-holds-election-the-u-s-calls-sham-11636201160 |access-date=2025-01-05 |work=Wall Street Journal |language=en-US |issn=0099-9660}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Naím |first=Moisés |date=2021-11-19 |title=Why dictators love elections |url=https://english.elpais.com/opinion/the-global-observer/2021-11-19/why-dictators-love-elections.html |access-date=2025-01-05 |website=EL PAÍS English |language=en}}</ref> It is a developing country and has the ] and ] among Latin American and Caribbean countries. In 2023, Nicaragua was ranked as the second most corrupt country in Latin America, after Venezuela, by the ]. Known as the "land of lakes and volcanoes",<ref name="Brierley">{{cite news|last1=Brierley|first1=Jan|title=Sense of wonder: Discover the turbulent past of Central America|url=http://www.express.co.uk/travel/beach/865185/Discover-the-turbulent-past-Central-America-travel|access-date=October 27, 2017|work=Daily Express|date=October 15, 2017|language=en|archive-date=18 June 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220618135750/https://www.express.co.uk/travel/beach/865185/Discover-the-turbulent-past-Central-America-travel|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Wallace">{{cite news|author=Wallace, Will |author2=Wallace, Camilla|title=Traveller's Guide: Nicaragua|url=https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/americas/travellers-guide-nicaragua-1940000.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220618/https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/americas/travellers-guide-nicaragua-1940000.html |archive-date=18 June 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|access-date=October 27, 2017|work=The Independent|date=April 10, 2010}}</ref> Nicaragua is also home to the ], the second-largest rainforest of the Americas.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Peter|date=2019-02-16|title=12 largest rainforests in the world and where to find them|url=https://www.atlasandboots.com/travel-blog/largest-rainforests-in-the-world/|access-date=2021-06-03|website=Atlas & Boots|language=en-GB|archive-date=3 June 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210603203457/https://www.atlasandboots.com/travel-blog/largest-rainforests-in-the-world/|url-status=live}}</ref> The biological diversity, warm tropical climate and active volcanoes have made Nicaragua an increasingly popular ].<ref>{{Cite news|last=Dicum|first=G|title=The Rediscovery of Nicaragua|work=Travel Section|publisher=TraveThe New York Times|location=New York|date=2006-12-17|url=http://travel.nytimes.com/2006/12/17/travel/17Nicaragua.html?ref=travel|access-date=2010-06-26|archive-date=10 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110510020955/http://travel.nytimes.com/2006/12/17/travel/17Nicaragua.html?ref=travel|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Davis|first=LS|title=Nicaragua: The next Costa Rica?|work=Mother Nature Network|publisher=MNN Holdings, LLC|date=2009-04-22|url=http://www.mnn.com/lifestyle/eco-tourism/stories/nicaragua-the-next-costa-rica|access-date=2010-06-26|archive-date=11 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511082141/http://www.mnn.com/lifestyle/eco-tourism/stories/nicaragua-the-next-costa-rica|url-status=live}}</ref> Nicaragua co-founded the ]<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kurtas |first=Susan |title=Research Guides: UN Membership: Founding Members |url=https://research.un.org/en/unmembers/founders |access-date=2022-06-26 |website=research.un.org |language=English |archive-date=4 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190704121608/https://research.un.org/en/unmembers/founders |url-status=live }}</ref> and is also a member of the ],<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Vanden |first1=Harry E. |last2=Morales |first2=Waltraud Queiser |date=1985 |title=Nicaraguan Relations with the Nonaligned Movement |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/165603 |journal=Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=141–161 |doi=10.2307/165603 |jstor=165603 |issn=0022-1937 |access-date=26 June 2022 |archive-date=26 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220626221431/https://www.jstor.org/stable/165603 |url-status=live }}</ref> ],<ref>{{Cite web |title=A Guide to ALBA |url=https://www.americasquarterly.org/a-guide-to-alba/ |access-date=2022-06-26 |website=Americas Quarterly |language=en-US |archive-date=26 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220626221430/https://www.americasquarterly.org/a-guide-to-alba/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2018-02-16 |title=CELAC {{!}} CELAC INTERNATIONAL |url=https://celacinternational.org/celac-2-2/ |access-date=2022-06-26 |language=en-US |archive-date=11 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220711223056/https://celacinternational.org/celac-2-2/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| The origin of the name "Nicaragua" is somewhat unclear; one theory is that it is a ] coined by Spanish colonists based on the name '']'', chief of the most populous indigenous tribe and ''agua'', the ] word for water.<ref name=questconnect>{{cite web|url=http://www.questconnect.org/ca_nicaragua.htm|title=Background notes on Nicaragua|publisher=Questconnect.org|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> Another theory is that it may have meant "surrounded by water" or "sweet sea" in an indigenous language.<ref name=britannica>{{cite web|work=Enyclopædia Britannica|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/413907/Lake-Nicaragua|title=Lake Nicaragua, Britannica Online|publisher=Britannica.com|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> The surrounding water might refer to the country's two largest lakes, ]—which is the largest in Central America and ]—and ]. Alternatively, it might refer to its being bounded on the east and the west by oceans. | |||
| == Etymology ==<!-- Linked to by another article. --> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{Main|History of Nicaragua|Spanish colonization of the Americas|Political history of Nicaragua}} | |||
| It was previously believed that the name ''Nicaragua'' was coined by Spanish colonists based on the name ],<ref name="Ideal">{{cite news|title=¿Por qué los países de América Latina se llaman como se llaman?|url=http://www.ideal.es/sociedad/201507/29/paises-america-latina-llaman-20150727134054.html|access-date=April 12, 2017|work=Ideal|date=July 29, 2015|trans-title=Why do Latin American countries call themselves as they are called?|language=es|archive-date=25 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225183349/https://www.ideal.es/sociedad/201507/29/paises-america-latina-llaman-20150727134054.html|url-status=live}}</ref> who was a ] of a powerful ] tribe encountered by the Spanish ] ] during his entry into southwestern Nicaragua in 1522. This theory held that the etymology of Nicaragua was formed from Nicarao and {{lang|es|agua}} (Spanish for 'water'), to refer to the fact that there are two large lakes and several other bodies of water within the country.<ref name="Pueblo">{{cite news|last1=Sánchez|first1=Edwin|title=El origen de "Nicarao-agua": la Traición y la Paz|url=http://www.elpueblopresidente.com/noticias/ver/titulo:35129-el-origen-de-nicarao-agua-la-traicion-y-la-paz|access-date=July 3, 2017|work=El Pueblo Presidente|date=October 16, 2016|language=es|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170801080334/http://www.elpueblopresidente.com/noticias/ver/titulo:35129-el-origen-de-nicarao-agua-la-traicion-y-la-paz|archive-date=2017-08-01|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ===Pre-Columbian history=== | |||
| ] preserved in volcanic mud near ]]] | |||
| However, this etymology is considered to be outdated by most historians as in 2002 it was discovered that the real name of the cacique was Macuilmiquiztli and not Nicarao.<ref>"Nicarao" </ref><ref>"Encuentro" </ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Sánchez|first1=Edwin|title=De Macuilmiquiztli al Güegüence pasando por Fernando Silva|url=https://www.el19digital.com/articulos/ver/titulo:47267-de-macuilmiquiztli-al-gueguence-pasando-por-fernando-silva|access-date=April 12, 2017|work=El 19|date=October 3, 2016|trans-title=From Macuilmiquizli to Güegüence through Fernando Silva|language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Silva|first1=Fernando|title=Macuilmiquiztli|url=http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/cultural/118693-macuilmiquiztli/|access-date=April 12, 2017|work=El Nuevo Diario|date=March 15, 2003|language=es|archive-date=12 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170412143935/http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/cultural/118693-macuilmiquiztli/|url-status=dead}}</ref> In addition, the ] referred to their land as Nicānāhuac, which most historians now believe is the true etymology of "Nicaragua". It means "here lies Anahuac" in Nahuatl and is a combination of the words "Nican" (here),<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://nahuatl.wired-humanities.org/content/nican|title= Nahuatl Dictionary: Nican}}</ref> and "]", which in turn is a combination of the words "atl" (water) and "nahuac", a locative meaning "surrounded". Therefore the literal translation of ''Nicanahuac'' is "here surrounded by water", fitting the theory that the etymology refers to the large bodies of water in and around the country, the ], lakes ] and ], and the rivers and lagoons.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://planlea.edu.do/2017/02/origen-de-los-nombres-de-los-paises-de-latinoamaerica/|title= Origin of the names of the Latin American countries|date= 8 February 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://elcafelatino.org/es/latinoamerica-origen-nombre-paises/|title= The curious story of the origin of the names of Latin American countries|date= 16 February 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cclec.org/membership/nicaragua/|title= Nicaragua|date= 4 November 2024}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Nahuatl Dictionary |url=https://www.vocabulario.com.mx/nahuatl/diccionario_nahuatl_n.html}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://etimologias.dechile.net/?Nicaragua|title= Etymology of Nicaragua}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.mined.gob.ni/biblioteca/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Libro-Toponimia-Octubre-2022.pdf|title=Nicaraguan place names|access-date=19 October 2024|archive-date=10 June 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240610042123/https://www.mined.gob.ni/biblioteca/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Libro-Toponimia-Octubre-2022.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://telegrafi.com/en/nga-brazili-ne-bolivi-e-kosta-rike-disa-shpjegime-ne-lidhje-emrat-e-vendeve-te-amerikes-latine/amp/|title= From Brazil to Bolivia and Costa Rica: Explanations about Latin American country names}}</ref> | |||
| In ] times, in what is now known as Nicaragua, the ] were part of the ] located between the ]n and ] cultural regions and within the influence of the ] area. It was the point where the Mesoamerican and South American native cultures met. This is confirmed by the ], along with other ] evidence, mainly in the form of ] and statues made of volcanic stone, such as the ones found on the island of ] in ] and ]s found on ] island. The '']'' migrated to Nicaragua from central Mexico after 500 B.C.<ref name=Fowler1985>{{cite journal|author=Fowler Jr|first=WR|year=1985|title=Ethnohistoric Sources on the Pipil Nicarao: A Critical Analysis|journal=Ethnohistory|volume=32|issue=1|pages=37–62|location=Columbus, Ohio|publisher=American Indian Ethnohistoric Conference|oclc=62217753|doi=10.2307/482092|jstor=482092}}:38; {{cite journal|author={{aut|Kaufman, Terrence}}|authorlink=Terrence Kaufman|year=2001|title=The history of the Nawa language group from the earliest times to the sixteenth century: some initial results|url=http://www.albany.edu/anthro/maldp/Nawa.pdf|format=PDF|version=Revised March 2001|publisher=Project for the Documentation of the Languages of Mesoamerica|accessdate=2007-10-07}}</ref> | |||
| Additional theories about the country's name comes from any of the following Nahuatl words: {{lang|nci|nican-nahua}}, which means "here are the Nahuas"; and {{lang|nci|nic-atl-nahuac}}, the longer form of Nicanahuac meaning "here by the water" or "surrounded by water".<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cclec.org/membership/nicaragua/|title= Nicaragua|date= 4 November 2024}}</ref><ref name="Ideal" /><ref name="Pueblo" /><ref name="Choque">{{cite web |last1=Solórzano |first1=Carla Torres |title=Choque de lenguas o el mestizaje de nuestro idioma |url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/09/18/espectaculo/38089-choque-de-lenguas-o-el-mestizaje-de-nuestro-idioma |website=La Prensa |access-date=July 26, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170412143717/http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/09/18/espectaculo/38089-choque-de-lenguas-o-el-mestizaje-de-nuestro-idioma |archive-date=April 12, 2017 |trans-title=Clash of languages or the mixing of our language |language=es |date=September 18, 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=La raíz nahuatl de nuestro lenguaje|url=http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/cultural/132502-raiz-nahuatl-nuestro-lenguaje/|access-date=July 3, 2017|work=El Nuevo Diario|date=August 10, 2004|trans-title=The Nahuatl root of our language|language=es|archive-date=12 August 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170812052335/http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/cultural/132502-raiz-nahuatl-nuestro-lenguaje/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| By the end of the 15th century, western Nicaragua was inhabited by several indigenous peoples related by culture to the Mesoamerican civilizations, such as the ] and ], and by language to the ].<ref name=LOC1>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Precolonial Period|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0013)|work=Library of Congress Country Studies|accessdate=2007-06-29}}, interpretation of statement: "the native peoples were linguistically and culturally similar to the ] and the ]"</ref> They were primarily farmers who lived in towns, organized into small kingdoms. | |||
| == History == | |||
| Meanwhile, the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua was inhabited by other peoples, mostly ] groups. They had coalesced in Central America and migrated also to present-day northern Colombia and nearby areas.<ref name=ipsnews>, ''Colombia'', ''Inter Press Service (IPS) News'', 30 Nov 2007, accessed 9 Nov 2010</ref> | |||
| {{Main|History of Nicaragua}} | |||
| They lived a life based primarily on hunting and gathering.<ref name= webcitation>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: VI History|url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761577584_8/Nicaragua.html|work=Encarta|accessdate=2007-06-13|archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/query?id=1257037551111387|archivedate=2009-11-01|deadurl=yes}}</ref> Joined by waters, the people of eastern Nicaragua traded with, and were influenced by, other native peoples of the Caribbean. Round thatched huts and canoes, both typical of the Caribbean, were commonly crafted and used in eastern Nicaragua. | |||
| === Pre-Columbian history === | |||
| In the west and ] areas, occupying the territory between Lake Nicaragua and the Pacific Coast, the '']'' were governed by ] '']'', or ''Nicaragua''. The wealthy ruler lived in '']'', site of the present-day city of ]. The '']'' lived in the central region of Nicaragua. Without women in their parties, the Spanish conquerors took Niquirano and Chorotega wives and partners, beginning the multi-ethnic mix of native and European stock now known as ], which constitutes the great majority of population in western Nicaragua.<ref name=LOC2>Nicaragua: Precolonial Period</ref> Within three decades after European contact, what had been an estimated Indian population of one million plummeted. Scientists and historians estimate approximately half of the indigenous people in western Nicaragua died from the rapid spread of new ]s carried by the Spaniards, such as ] and ], to which the Indians had no ]. The indigenous people of the Caribbean coast escaped the ] due to the remoteness of their area. Their societies continued more culturally intact as a result.<ref name=LOC2/> | |||
| ] on ]]] | |||
| ] first inhabited what is now known as Nicaragua as far back as 12,000 BCE.<ref name="Dall2005">{{cite book|last=Dall|first=Christopher|title=Nicaragua in Pictures|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vUP3hLbq6DEC&pg=PA66|date=October 1, 2005|publisher=Twenty-First Century Books|isbn=978-0-8225-2671-1|pages=66–67}}</ref> In later ] times, Nicaragua's ] were part of the ],<ref name="Brief">{{cite book|last1=Pérez-Brignoli|first1=Héctor|last2=translated by Sawrey A.|first2=Ricardo B.|last3=Sawrey|first3=Susana Stettri de|title=A Brief History of Central America|url=https://archive.org/details/briefhistoryofce00pr|url-access=registration|date=1989|publisher=University of California Press|location=Berkeley|isbn=978-0520060494|edition=2nd}}</ref>{{rp|33}} between the ]n and ] cultural regions, and within the influence of the ]. Nicaragua's central region and its Caribbean coast were inhabited by ] ethnic groups such as the ], ], ], and ].<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|20}} They had coalesced in Central America and migrated both to and from present-day northern Colombia and nearby areas.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120220131907/http://ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=40290 |date=2012-02-20 }}, ''Colombia'', ''Inter Press Service (IPS) News'', 30 Nov 2007, accessed 9 Nov 2010</ref> Their food came primarily from hunting and gathering, but also fishing and ] agriculture.<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|33}}<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Nicaragua: VI History|encyclopedia=Encarta|date=2007-06-13}}</ref><ref name="Newson">{{cite book|last1=Newson|first1=Linda A.|title=Indian survival in colonial Nicaragua|date=1987|publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|location=Norman |isbn=978-0806120089|edition=1st}}</ref>{{rp|65}} | |||
| At the end of the 15th century, western Nicaragua was inhabited by several indigenous peoples related by culture to the Mesoamerican civilizations of the ] and ], and by language to the ].<ref name=LOC1>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Precolonial Period|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0013)|work=Library of Congress Country Studies|access-date=2007-06-29|archive-date=22 September 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080922145600/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0013)|url-status=live}}, interpretation of statement: "the native peoples were linguistically and culturally similar to the Aztec and the Maya"</ref> The Chorotegas were ] ethnic groups who had arrived in Nicaragua from what is now the Mexican state of ] sometime around 800 CE.<ref name="Choque" /><ref name="Newson" />{{rp|26–33}} The ] were a branch of ] who spoke the ] dialect and also came from Chiapas, around 1200 CE.<ref name="Campbell1985">{{cite book|last=Campbell|first=Lyle|title=The Pipil Language of El Salvador|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N5bmUh7jproC&pg=PA10|date=January 1, 1985|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|isbn=978-3-11-088199-8|pages=10–12}}</ref> Prior to that, the Nicaraos had been associated with the ] civilization.<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|26–33}}<ref name="Campbell1985" /><ref>{{cite journal|last=Fowler|first=WR Jr.|year=1985|title=Ethnohistoric Sources on the Pipil Nicarao: A Critical Analysis|journal=Ethnohistory|volume=32|issue=1|pages=37–62|place=Columbus, Ohio|oclc=62217753|doi=10.2307/482092|jstor=482092 | issn = 0014-1801}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Brinton|first1=Daniel G.|title=Were the Toltecs an Historic Nationality?|journal=Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society|date=1887|volume=24|issue=126|pages=229–230|jstor=983071}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author1=von Humboldt, Alexander|author2=Poynter, J. Ryan |author3=Altamirano Rayo, Giorleny D |author4=Kraft, Tobias |title=Views of the Cordilleras and Monuments of the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas: A Critical Edition|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=G7Pt35axXEkC&pg=PA92|date=January 25, 2013|publisher=University of Chicago Press|isbn=978-0-226-86509-6|page=92}}</ref> Both Chorotegas and Nicaraos originated in Mexico's ] valley,<ref name="Campbell1985" /> and migrated south.<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|26–33}} A third group, the ]s, were an ] people who migrated from the Mexican state of ] around 1200 CE.<ref name="Campbell1997">{{cite book |last1=Campbell |first1=Lyle |title=American Indian languages : the historical linguistics of Native America |date=1997 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |isbn=0-19-509427-1}}</ref>{{rp|159}} Additionally, there were trade-related colonies in Nicaragua set up by the Aztecs starting in the 14th century.<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|26–33}} | |||
| ===The Spanish conquest=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| === Spanish era (1523–1821) === | |||
| In 1502, ] was the first European known to have reached what is now Nicaragua as he sailed southeast toward the ]. On his fourth voyage, Columbus explored the Misquitos Coast on the Atlantic side of Nicaragua.<ref name= americanjourneys>{{cite news|title=Letter of Columbus on the Fourth Voyage|publisher=American Journey|url=http://www.americanjourneys.org/aj-068/summary/index.asp|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> The first attempt to conquer what is now known as Nicaragua was by ],<ref name=EBH>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: History|url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-214487/Nicaragua|work=Encyclopædia Britannica|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> who arrived in ] in January 1520. | |||
| {{Further|Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spanish conquest of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] near ], one of the most visited sites in ]]] | |||
| In 1502, on his fourth voyage, ] became the first European known to have reached what is now Nicaragua as he sailed southeast toward the ].<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|193}}<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|92}} Columbus explored the ] on the Atlantic side of Nicaragua<ref>{{cite news|title=Letter of Columbus on the Fourth Voyage|publisher=American Journey|url=http://www.americanjourneys.org/aj-068/summary/index.asp|access-date=2007-05-09|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070403152053/http://americanjourneys.org/aj-068/summary/index.asp|archive-date=2007-04-03}}</ref> but did not encounter any indigenous people. 20 years later, the Spaniards returned to Nicaragua, this time to its southwestern part. The first attempt to conquer Nicaragua was by the conquistador ],<ref name=EBH>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Nicaragua: History|url=https://www.britannica.com/eb/article-214487/Nicaragua|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=10 June 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080610194232/http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-214487/Nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> who had arrived in Panama in January 1520. In 1522, González Dávila ventured to the area that later became the ] of Nicaragua.<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|35}}<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|92}} There he encountered an indigenous Nahua tribe led by chief Macuilmiquiztli, whose name has sometimes been erroneously referred to as "]" or "Nicaragua". The tribe's capital was Quauhcapolca.<ref name="Encuentro">{{cite news|title=Encuentro del cacique y el conquistador|url=http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/especiales/44697-encuentro-cacique-conquistador/|access-date=May 17, 2017|work=El Nuevo Diario|date=April 4, 2009|trans-title=Encounter of the cacique and the conqueror|language=es|archive-date=7 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170507054414/http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/especiales/44697-encuentro-cacique-conquistador/|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="HealyPohl1980">{{cite book|author1=Healy, Paul |author2=Pohl, Mary |title=Archaeology of the Rivas Region, Nicaragua|url=https://archive.org/details/archaeologyofriv0001heal|url-access=registration |year=1980|publisher=Wilfrid Laurier Univ. Press|isbn=978-0-88920-094-4|page=}}</ref><ref name="Dyck2015">{{cite book|author1=Dyck, Erika |author2=Fletcher, Christopher |title=Locating Health: Historical and Anthropological Investigations of Place and Health|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m-c5CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA107|date=October 6, 2015|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-317-32278-8|page=107}}</ref> González Dávila conversed with Macuilmiquiztli thanks to two indigenous interpreters who had learned Spanish, whom he had brought along.<ref name="Sanchez">{{cite news|last1=Sánchez|first1=Edwin|title=No hubo Nicarao, todo es invento|work=El Nuevo Diario|date=September 16, 2002|trans-title=There was no Nicarao, it's all invented|language=es}}</ref> After exploring and gathering gold<ref name="Encuentro" /><ref name="Brief" />{{rp|35}}<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|55}} in the fertile western valleys, González Dávila and his men were attacked and driven off by the Chorotega, led by chief ].<ref name="Encuentro" /><ref>{{cite news|title=The Spanish Conquest|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0014)|work=Library of Congress|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=22 September 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080922150135/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0014)|url-status=live}}</ref> The Spanish tried to convert the tribes to Christianity; Macuilmiquiztli's tribe was baptized,<ref name="Encuentro" /><ref name="Newson" />{{rp|86}} but Diriangén was openly hostile to the Spaniards. Western Nicaragua, at the Pacific Coast, became a port and shipbuilding facility for the Galleons plying the waters between Manila, Philippines and Acapulco, Mexico.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211117122328/https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/bitstream/10125/100380/1/Peterson_Andrew_r.pdf |date=17 November 2021 }} Citing Andre Gschaedler, "Mexico and the Pacific, 1540 - 1565: The Voyage of Villabos and Legazpi and the Preparations Made for Them," (Ph.D. dissertation, Columbia University, 1954), 40.</ref> | |||
| The first Spanish permanent settlements were founded in 1524.<ref name=EBH/> That year, the conquistador ] founded two of Nicaragua's main cities: ] on ], and then ], west of ].<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|35, 193}}<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|92}} Córdoba soon built defenses for the cities and fought against incursions by other conquistadors.<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|92}} Córdoba was later publicly ] for having defied his superior, ].<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|35}} Córdoba's tomb and remains were discovered in 2000 in the ].<ref name=ET>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua Briefs: An Historic Find|publisher=Central American University – UCA|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/1418|work=Envío|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=12 July 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170712083309/http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/1418|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| González claimed to have converted some 30,000 indigenous peoples and discovered a possible transisthmian water link. After exploring and gathering ] in the fertile western valleys, González was attacked by the indigenous people, some of whom were commanded by Nicarao and an estimated 3,000 led by chief ].<ref name= Conquest>{{cite news|title=The Spanish Conquest|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0014)|work=Library of Congress|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> González later returned to Panama where Governor ] tried to arrest him and confiscate his treasure, some 90,000 pesos of gold. González escaped to ]. | |||
| The clashes among Spanish forces did not impede their destruction of the indigenous people and their culture. The series of battles came to be known as the "War of the Captains".<ref>{{cite book|last=Duncan|first=David Ewing|title=Hernando de Soto – A Savage Quest in the Americas – Book II: Consolidation|publisher=Crown Publishers|location=New York|year=1995}}</ref> Pedro Arias Dávila was a winner;<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|35}} although he lost control of Panama, he moved to Nicaragua and established his base in León.<ref name="Whisnant2000">{{cite book|last=Whisnant|first=David E.|title=Rascally Signs in Sacred Places: The Politics of Culture in Nicaragua|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qK8TBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA30|date=November 9, 2000|publisher=Univ of North Carolina Press|isbn=978-0-8078-6626-9|pages=30–32|access-date=24 May 2017|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140444/https://books.google.com/books?id=qK8TBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA30#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1527, León became the capital of the colony.<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|93}}<ref name="Whisnant2000" /> Through diplomacy, Arias Dávila became the colony's first governor.<ref name=ET/> | |||
| It was not until 1524 that the first Spanish permanent settlements were founded.<ref name=EBH/> ] ] founded two of Nicaragua's principal towns in 1524: ] on Lake Nicaragua was the first settlement, followed by ] at a location east of ]. Córdoba soon built defenses for the cities and attacked against incursions by the other conquistadors. Córdoba was later publicly ] following a power struggle with ]. His tomb and remains were discovered in 2000 in the ].<ref name=ET>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua Briefs: An Historic Find|publisher=Central American University – UCA|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/1418|work=Envío|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| Without women in their parties,<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|123}} the Spanish conquerors took Nahua and Chorotega wives and partners, beginning the multiethnic mix of indigenous and European stock now known as "'']''", which constitutes the great majority of the population in western Nicaragua.<ref name=LOC1/> Many indigenous people were killed by European ]s, compounded by neglect by the Spaniards, who controlled their subsistence.<ref name=EBH/> Many other indigenous peoples were captured and transported as slaves to Panama and Peru between 1526 and 1540.<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|193}}<ref name="Newson" />{{rp|104–105}} | |||
| The clash among Spanish forces did not impede their devastation of the indigenous population and civilization. The series of battles came to be known as ''The War of the Captains''.<ref name= Duncan1995>Duncan, David Ewing, ''Hernando de Soto – A Savage Quest in the Americas – Book II: Consolidation'', Crown Publishers, Inc., New York, 1995</ref> By 1529, the conquest of Nicaragua was complete. Several conquistadors came out winners, while they executed or murdered others. Pedrarias Dávila was a winner—although he had lost control of Panama, he moved to Nicaragua and successfully established his base in León. Through adroit diplomatic machinations, he became the first governor of the colony.<ref name=ET/> | |||
| In 1610, the ] volcano erupted, destroying the city of León.<ref name="Geomorph">{{cite book|last=Bergoeing|first=Jean Pierre|title=Geomorphology of Central America: A Syngenetic Perspective|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TWwZBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA68|date=May 18, 2015|publisher=Elsevier Science|isbn=978-0-12-803185-8|pages=68–69|access-date=25 May 2017|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140445/https://books.google.com/books?id=TWwZBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA68#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> The city was rebuilt northwest of the original,<ref name="Whisnant2000" /><ref name="Geomorph" /> which is now known as the ]. During the ], Central America was subject to conflict between Britain and Spain. British navy admiral ] led expeditions in the ] in 1779 and on the ], the latter of which had temporary success before being abandoned due to disease. | |||
| The land was parceled out to the conquistadors, who were most interested in the western portion. They enslaved many indigenous people as labor to develop and maintain estates there. Others were put to work in ] in northern Nicaragua, some were killed in warfare. The great majority were sold as slaves, whipped, and shipped to other Spanish colonies in the New World, at a significant profit to the newly landed aristocracy. Many of the indigenous people died as a result of infectious disease, compounded by neglect by the Spaniards, who controlled their subsistence.<ref name=EBH/> | |||
| === Independent Nicaragua from 1821 to 1909 === | |||
| ===Colonization to independence=== | |||
| ] in 1830]] | |||
| ] off the Atlantic Coast was a ] until it was ceded along with the rest of the ] to Nicaragua]] | |||
| ] during the ]]] | |||
| ] was constructed in the late 17th century to protect locals in neighboring ] from ] attacks. Today, it is one of the country's main tourist attractions.]] | |||
| The ] dissolved the ] in September 1821, and Nicaragua soon ] of the ]. In July 1823, after the overthrow of the Mexican monarchy in March of the same year, Nicaragua joined the newly formed ], a country later known as the Federal Republic of Central America. Nicaragua definitively became an independent republic in 1838.<ref>{{cite journal|last1= Smith|first1= RS|title= Financing the Central American federation, 1821–1838|journal= The Hispanic American Historical Review|volume= 43|issue= 4|pages= 483–510|year= 1963|doi= 10.2307/2509898|jstor= 2509898}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The early years of independence were characterized by rivalry between the ] elite of León and the ] elite of Granada, which often degenerated into civil war, particularly during the 1840s and 1850s. ] rose to undisputed preeminence as the nation's capital in 1852 to allay the rivalry between the two feuding cities.<ref name="Capital">{{cite book|last= Cybriwsky|first= Roman Adrian|title= Capital Cities around the World: An Encyclopedia of Geography, History, and Culture|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=qb6NAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA177|date= May 23, 2013|publisher= ABC-CLIO|isbn= 978-1-61069-248-9|page= 177|access-date= 27 May 2017|archive-date= 5 February 2024|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140429/https://books.google.com/books?id=qb6NAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA177|url-status= live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title= Managua|url= http://archivo.laprensa.com.ni/archivo/2006/marzo/09/servicios/guiaturistica/|access-date= May 24, 2017|work= La Prensa|date= March 9, 2006|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131111081208/http://archivo.laprensa.com.ni/archivo/2006/marzo/09/servicios/guiaturistica/|language= es|archive-date= November 11, 2013 | quote = Fue elevada a ciudad en 1846 y salomónicamente declarada capital de la República en 1852, para dirimir el viejo conflicto entre las urbes coloniales de León (occidente) y Granada (oriente) que rivalizaban por ejercer la hegemonía política de Nicaragua.}}</ref> Following the start of the ] in 1848, Nicaragua provided a route for travelers from the eastern United States to journey to ] by sea, via the ] and Lake Nicaragua.<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|81}} Invited by the Liberals in 1855 to join their struggle against the Conservatives, the American adventurer and ] ] set himself up as ] after conducting a farcical election in 1856; his presidency lasted less than a year.<ref name="mined">{{cite web|url= http://www.mined.gob.ni/gobernant4.php|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121009181920/http://www.mined.gob.ni/gobernant4.php|url-status= dead|archive-date= 9 October 2012|title= Gobernantes de Nicaragua|date= 9 December 2012|publisher= Ministerio de Educación|access-date= 29 August 2020}}</ref> Military forces from Costa Rica, Honduras, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Nicaragua itself united to drive Walker out of Nicaragua in 1857,<ref>{{cite book|last= Walker|first= W|title= The War in Nicaragua|publisher= S.H. Goetzel & Company|place= New York|year= 1860|url= https://archive.org/stream/warinnicaragua00walkgoog#page/n6/mode/2up}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last= Juda|first= F|title= California Filibusters: A History of their Expeditions into Hispanic America (excerpt)|journal= The Grizzly Bear|volume= XXI|issue= 4|pages= 3–6, 15, 19|year= 1919|url= http://www.sfmuseum.org/hist1/walker.html|access-date= 2011-07-20|archive-date= 2 August 2009|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090802063416/http://www.sfmuseum.org/hist1/walker.html|url-status= live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last= Baker|first= CP|title= Moon Handbooks: Costa Rica|edition= 4th|chapter= The William Walker Saga|page= |publisher= Avalon Travel Publishing|place= New York|year= 2001|isbn= 978-1-56691-608-0|chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/costarica00bake_2/page/67}}</ref> bringing three decades of Conservative rule. | |||
| In 1536, the ] was established. By 1570, the southern part of New Spain was designated the ]. The area of Nicaragua was divided into administrative "parties" with León as the capital. In 1610, the ] volcano erupted, destroying the capital. It was rebuilt northwest of what is now known as the ]. | |||
| Great Britain, which had claimed the ] as a ] since 1655, delegated the area to Honduras in 1859 before transferring it to Nicaragua in 1860. The Mosquito Coast remained an ] until 1894. ], President of Nicaragua from 1893 to 1909, negotiated the integration of the Mosquito Coast into Nicaragua. In his honor, the region became "]". | |||
| During the ], Central America was subject to conflict between ] and ], as Britain sought to expand its influence beyond coastal logging and fishing communities in present-day ], ] and Nicaragua. ] led expeditions against ] in 1779 and the ], which had temporary success before being abandoned due to disease. In turn, the Spanish colonial leaders could not completely eliminate British influences along the Mosquito Coast. | |||
| Throughout the late 19th-century, the United States and several European powers considered various schemes to link the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic by building a ].<ref> | |||
| The Captaincy General of Guatemala was dissolved in September 1821 with the ], and Nicaragua became part of the ]. After the monarchy of the First Mexican Empire was overthrown in 1823, Nicaragua joined the newly formed United Provinces of Central America, which was later renamed as the ]. Nicaragua finally became an independent republic in 1838.<ref name=Smith1963/> | |||
| {{cite book | |||
| |last= Colquhoun|first= AR|title= The key of the Pacific: the Nicaragua canal | |||
| |publisher= Archibald Constable and Company | |||
| |place= Westminster, England|year= 1895 | |||
| |url= https://archive.org/stream/keypacificnicar02colqgoog#page/n6/mode/2up | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| === United States occupation (1909–1933) === | |||
| Rivalry between the ] elite of León and the ] elite of Granada characterized the early years of independence and often degenerated into ], particularly during the 1840s and 1850s. Invited by the Liberals in 1855 to join their struggle against the Conservatives, a United States adventurer and ] named ] set himself up as president of Nicaragua, after conducting a farcical election in 1856.<ref name=Walker1860/> Costa Rica, Honduras and other Central American countries united to drive Walker out of Nicaragua in 1857,<ref name=Walker1860/><ref name=Juda1919/><ref name=Baker2001/> after which a period of three decades of Conservative rule ensued. | |||
| {{See also|United States occupation of Nicaragua}} | |||
| In 1909, the United States supported the forces rebelling against President Zelaya. U.S. motives included differences over the proposed ], Nicaragua's potential to destabilize the region, and Zelaya's attempts to regulate foreign access to Nicaraguan natural resources. On November 18, 1909, U.S. warships were sent to the area after 500 revolutionaries (including two Americans) were executed by order of Zelaya. The U.S. justified the intervention by claiming to protect U.S. lives and property. Zelaya resigned later that year. | |||
| In August 1912, the President of Nicaragua, ], requested the secretary of war, General ], to resign for fear he was leading an insurrection. Mena fled Managua with his brother, the chief of police of Managua, to start an insurrection. After Mena's troops captured steam boats of an American company, the U.S. delegation asked President Díaz to ensure the safety of American citizens and property during the insurrection. He replied he could not, and asked the U.S. to intervene in the conflict.<ref>{{cite book|title=Foreign Relations of the United States|year=1912|page=1032}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Langley|first=Lester D.|title=The Banana Wars: United States Intervention in the Caribbean, 1898-1934|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xc1RBfZd3pcC&pg=PA64|year=2002|publisher=SR Books|location=Wilmington|isbn=978-0-8420-5047-0|page=64|access-date=5 February 2024|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140307/https://books.google.com/books?id=Xc1RBfZd3pcC&pg=PA64#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Great Britain, which had claimed the Mosquito Coast as a ] since 1655, delegated the area to Honduras in 1859 before transferring it to Nicaragua in 1860. The Mosquito Coast remained an ] until 1894. ], president of Nicaragua from 1893{{ndash}}1909, negotiated the annexation of the Mosquito Coast to the rest of Nicaragua. In his honor, the region was named ]. | |||
| ] occupied Nicaragua from 1912 to 1933,<ref name="Brief" />{{rp|111, 197}}<ref>{{cite news|title=US violence for a century: Nicaragua: 1912–33|url=http://www.socialistworker.co.uk/art.php?id=12191|work=Socialist Worker|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=27 September 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927213236/http://www.socialistworker.co.uk/art.php?id=12191|url-status=dead}}</ref> except for a nine-month period beginning in 1925. In 1914, the ] was signed, giving the U.S. control over a proposed canal through Nicaragua, as well as leases for potential canal defenses.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Bryan–Chamorro Treaty|url=https://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9016820/Bryan-Chamorro-Treaty|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=27 February 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080227005939/http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9016820/Bryan-Chamorro-Treaty|url-status=live}}</ref> After the U.S. Marines left, another ] between Liberals and Conservatives in 1926 resulted in the return of U.S. Marines.<ref>{{cite news|title=General Augusto C. Sandino: The Constitutional War|url=http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/16-augusto-sandino.html|work=ViaNica|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=22 August 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070822222208/http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/16-augusto-sandino.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In the 19th century, Nicaragua attracted many immigrants, primarily from Europe. In particular, families from Germany, Italy, Spain, France and Belgium emigrated to set up businesses with money they brought from Europe. They established many agricultural businesses, such as ] and ] ], and also newspapers, hotels and banks. | |||
| ] (center) in June 1929]] | |||
| Throughout the late 19th century, the United States (and several European powers) considered a scheme to build a ], linking the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic.<ref name=Colquhoun1895/> A bill was put before the U.S. Congress in 1899 to build the canal, which failed to pass it; construction of the ] was begun instead. | |||
| From 1927 to 1933, rebel general ] led a sustained guerrilla war against the regime and then against the ], whom he fought for over five years.<ref>{{cite news|last=Vukelich|first=D|title=A Disaster Foretold|publisher=The Advocacy Project|url=http://www.advocacynet.org/news_view/news_141.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070403231532/http://www.advocacynet.org/news_view/news_141.html|archive-date=April 3, 2007|access-date=2007-05-09|url-status=dead}}</ref> When the Americans left in 1933, they set up the '']'' (national guard),<ref name=SY>{{cite encyclopedia|title=The Somoza years|url=https://www.britannica.com/eb/article-40992/Nicaragua|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=19 June 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080619204204/http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-40992/Nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> a combined military and police force trained and equipped by the Americans and designed to be loyal to U.S. interests. | |||
| After the U.S. Marines withdrew from Nicaragua in January 1933, Sandino and the newly elected administration of President ] reached an agreement that Sandino would cease his guerrilla activities in return for amnesty, a land grant for an agricultural colony, and retention of an armed band of 100 men for a year.<ref>{{cite news|title=Biographical Notes |url=http://www.sandino.org/bio_en.htm |access-date=2007-05-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061231171221/http://www.sandino.org/bio_en.htm |archive-date=December 31, 2006 }}</ref> However, due to a growing hostility between Sandino and National Guard director ] and a fear of armed opposition from Sandino, Somoza García ordered his assassination.<ref name=SY/><ref>{{cite news|title=History of U.S. Violence Across the Globe: Washington's War Crimes (1912–33)|date=2001-12-16|url=http://www.bulatlat.com/news/2-5/2-5-reader-arnove.html|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=14 November 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061114023101/http://www.bulatlat.com/news/2-5/2-5-reader-arnove.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|first=T|last=Solo|title=Nicaragua: From Sandino to Chavez|date=2005-10-07|publisher=Dissident Voice|url=http://www.dissidentvoice.org/Oct05/solo1007.htm|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=5 April 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070405114858/http://www.dissidentvoice.org/Oct05/solo1007.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Sacasa invited Sandino for dinner and to sign a peace treaty at the Presidential House on the night of February 21, 1934. After leaving the Presidential House, Sandino's car was stopped by National Guard soldiers and they kidnapped him. Later that night, Sandino was assassinated by National Guard soldiers. Later, hundreds of men, women, and children from Sandino's agricultural colony were murdered.<ref name=SomozaDynasty>{{cite news |title=The Somoza Dynasty |publisher=University of Pittsburgh |url=http://www.ucis.pitt.edu/clas/nicaragua_proj/history/somoza/Hist-Somoza-dinasty.pdf |page=1 |access-date=2007-05-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061110033552/http://www.ucis.pitt.edu/clas/nicaragua_proj/history/somoza/Hist-Somoza-dinasty.pdf |archive-date=November 10, 2006 }}</ref> | |||
| ===United States intervention (1909–1933)=== | |||
| {{See also|United States occupation of Nicaragua|Nicaragua Canal}} | |||
| === Somoza dynasty (1927–1979) === | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] (left) with ] President ] in 1952]] | |||
| In 1909, the United States provided political support to conservative-led forces rebelling against President Zelaya. U.S. motives included differences over the proposed ], Nicaragua's potential as a destabilizing influence in the region, and Zelaya's attempts to regulate foreign access to Nicaraguan natural resources. On November 18, 1909, U.S. warships were sent to the area after 500 revolutionaries (including two Americans) were executed by order of Zelaya. The U.S. justified the intervention by claiming to protect U.S. lives and property. Zelaya resigned later that year. | |||
| ] (center) with U.S. president ] in 1971]] | |||
| Nicaragua has experienced several military dictatorships, the longest being the hereditary dictatorship of the ], who ruled for 43 nonconsecutive years during the 20th century.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Colburn|first=Forrest D.|title=Nicaragua, Forlorn|journal=World Policy Journal|issue=Spring 2012|url=http://www.worldpolicy.org/journal/spring2012/nicaragua-forlorn|access-date=31 May 2012|date=2012-03-26|volume=29|pages=91–100|doi=10.1177/0740277512443806|archive-date=6 May 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120506221638/http://www.worldpolicy.org/journal/spring2012/nicaragua-forlorn|url-status=dead}}</ref> The Somoza family came to power in 1937 partly as a result of a U.S.-engineered pact in 1927 that stipulated the formation of the ''Guardia Nacional'' to replace the marines who had long reigned in the country.<ref>{{cite book|title=Lying for Empire: How to Commit War Crimes With a Straight Face|first=David|last=Model|publisher=Common Courage Press|year=2005}}</ref> Somoza García slowly eliminated officers in the national guard who might have stood in his way, and then deposed Sacasa and became president on January 1, 1937, in a ].<ref name=SY/> | |||
| In 1941, during the ], Nicaragua declared war on ] (8 December), ] (11 December), ] (11 December), ] (19 December), ] (19 December) and ] (19 December). Only Romania reciprocated, declaring war on Nicaragua on the same day (19 December 1941).<ref>Goldstein, Erik (2005) ''Wars and Peace Treaties: 1816 to 1991''. Routledge. p. 218. {{ISBN|9781134899111}}</ref> No soldiers were sent to the war, but Somoza García confiscated properties held by ] residents.<ref>{{cite news|title=El asalto de Somoza a los alemanes |date=6 January 2005 |url=http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/2005/enero/06-enero-2005/nacional/nacional-20050106-04.html |access-date=2007-07-13 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071012011055/http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/2005/enero/06-enero-2005/nacional/nacional-20050106-04.html |archive-date=October 12, 2007 }}</ref> In 1945, Nicaragua was among the first countries to ratify the United Nations Charter.<ref>{{cite web|title=Charter of the United Nations and Statute of the International Court of Justice|page=49|publisher=United Nations|place=San Francisco|date=1945-06-26|url=http://treaties.un.org/doc/Publication/CTC/uncharter.pdf|access-date=21 July 2011|archive-date=16 January 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116214749/http://treaties.un.org/doc/Publication/CTC/uncharter.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In August 1912 the President of Nicaragua, ], requested that the Secretary of War, General ], resign for fear that he was leading an insurrection. Mena fled Managua with his brother, the Chief of Police of Managua, to start an insurrection. When the U.S. Legation asked President Díaz to ensure the safety of American citizens and property during the insurrection he replied that he could not and that... {{cquote|In consequence my Government desires that the Government of the United States guarantee with its forces security for the property of American Citizens in Nicaragua and that it extend its protection to all the inhabitants of the Republic.<ref name=ForeignRelations>{{cite news|title=Foreign Relations of the United States 1912, pg. 1032ff}}</ref>}} ] occupied Nicaragua from 1912 to 1933,<ref name= socialistworker>{{cite news|title=US violence for a century: Nicaragua: 1912–33|url=http://www.socialistworker.co.uk/art.php?id=12191|work=Socialist Worker|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> except for a nine month period beginning in 1925. From 1910 to 1926, the conservative party ruled Nicaragua. The ], which had long dominated the party, effectively controlled the government during that period. In 1914, the ] was signed, giving the U.S. control over the proposed canal, as well as leases for potential canal defenses.<ref name= BryanChamorro>{{cite news|title=Bryan–Chamorro Treaty|url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9016820/Bryan-Chamorro-Treaty|work=Encyclopædia Britannica|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> Following the evacuation of U.S. Marines, another violent conflict between liberals and conservatives took place in 1926, known as the Constitutionalist War, which resulted in a coalition government and the return of U.S. Marines.<ref name= Sandino>{{cite news|title=General Augusto C. Sandino: The Constitutional War|url=http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/16-augusto-sandino.html|work=ViaNica|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| On September 29, 1956,<ref>{{Cite web|date=September 30, 1956|title=SOMOZA'S NATION CALLED HIS FIEF; Rule of Nicaraguan General, Beginning With 1935 Coup, Was Seldom Challenged PRESIDENT FIRST IN '37 Graduate of Business School in U.S., He Acquired Great Wealth During Regime|url=http://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1956/09/30/88469093.html|access-date=2021-11-08|website=New York Times TimesMachine|language=en|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140309/https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1956/09/30/88469093.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Somoza García was shot to death by ], a 27-year-old Liberal Nicaraguan poet. ], the eldest son of the late president, was appointed president by the congress and officially took charge of the country.<ref name=SY/> He is remembered by some as moderate, but after only a few years in power died of a heart attack. His successor as president was ], whom most Nicaraguans viewed "as nothing more than a puppet of the Somozas".<ref>{{cite news|last=Leonard |first=TM |title=Against all odds: U.S. policy and the 1963 Central America Summit Conference |year=2003 |publisher=Journal of Third World Studies |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3821/is_200304/ai_n9173383/pg_11 |archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20090628115503/http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3821/is_200304/ai_n9173383/pg_11 |url-status=dead |archive-date=2009-06-28 |page=11 |access-date=2007-05-09 }}</ref> Somoza García's youngest son, ], often referred to simply as "Somoza", became president in 1967. | |||
| From 1927 until 1933, Gen. ] led a sustained ] war first against the Conservative regime and subsequently against the U.S. Marines, who withdrew upon the establishment of a new Liberal government. Sandino was the only Nicaraguan general to refuse to sign the ''el tratado del Espino Negro'' agreement and then headed up to the northern mountains of Las Segovias, where he fought the U.S. Marines for over five years.<ref name= Vukelich>{{cite news |last=Vukelich|first=D|title=A Disaster Foretold|publisher=The Advocacy Project|url=http://www.advocacynet.org/news_view/news_141.html|accessdate=2007-05-09|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070403231532/http://www.advocacynet.org/news_view/news_141.html|archivedate=April 3, 2007}}</ref> When the Americans left in 1933, they set up the ] (National Guard),<ref name=SY>{{cite news|title=The Somoza years|url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-40992/Nicaragua|work=Encyclopædia Britannica|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> a combined military and police force trained and equipped by the Americans and designed to be loyal to U.S. interests. ], a close friend of the American government, was put in charge. He was one of the three rulers of the country, the others being Sandino and the President ]. | |||
| An ] destroyed nearly 90% of Managua, including much of its infrastructure.<ref>{{cite news|title=Headline: Nicaragua Earthquake |date=1972-12-16 |publisher=Vanderbilt Television News Archive |url=http://tvnews.vanderbilt.edu/program.pl?ID=221286 |access-date=2007-05-24 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110510035404/https://tvnews.vanderbilt.edu/program.pl?ID=221286 |archive-date=2011-05-10 }}</ref> Instead of helping to rebuild the city, Somoza siphoned off relief money. The mishandling of relief money also prompted ] star ] to personally fly to Managua on December 31, 1972, but he died ''en route'' in an airplane accident.<ref>{{cite web |title=Roberto Clemente |url=https://baseballhall.org/hall-of-famers/clemente-roberto |website=National Baseball Hall of Fame |access-date=8 March 2022 |archive-date=8 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220308052248/https://baseballhall.org/hall-of-famers/clemente-roberto |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Roberto Clemente – Bio|publisher=The National Baseball Hall of Fame|url=http://baseballhalloffame.org/hofers_and_honorees/hofer_bios/clemente_roberto.htm|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070427145215/http://www.baseballhalloffame.org/hofers_and_honorees/hofer_bios/clemente_roberto.htm|archive-date=April 27, 2007|url-status=dead}}</ref> Even the economic elite were reluctant to support Somoza, as he had acquired monopolies in industries that were key to rebuilding the nation.<ref>{{cite news|title=A Battle Ends, a War Begins|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,946048-1,00.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930135935/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,946048-1,00.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=September 30, 2007|magazine=TIME|access-date=2007-08-21|date=1978-09-11}}</ref> | |||
| After the U.S. Marines withdrew from Nicaragua in January 1933, Sandino and the newly elected Sacasa government reached an agreement by which he would cease his guerrilla activities in return for amnesty, a grant of land for an agricultural colony, and retention of an armed band of 100 men for a year.<ref name= BiographicalNotes>{{cite news|title=Biographical Notes|url=http://www.sandino.org/bio_en.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> But a growing hostility between Sandino and Somoza led Somoza to order the assassination of Sandino.<ref name=SY/><ref name= bulatlat>{{cite news|title=History of U.S. Violence Across the Globe: Washington's War Crimes (1912–33)|date=2001-12-16|url=http://www.bulatlat.com/news/2-5/2-5-reader-arnove.html|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref><ref name= Solo2005>{{cite news|first=T|last=Solo|title=Nicaragua: From Sandino to Chavez|date=2005-10-07|publisher=Dissident Voice|url=http://www.dissidentvoice.org/Oct05/solo1007.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Fearing future armed opposition from Sandino, Somoza invited him to a meeting in Managua, where Sandino was assassinated on February 21 of 1934 by soldiers of the National Guard. Hundreds of men, women, and children from Sandino's agricultural colony were executed later.<ref name=SomozaDynasty>{{cite news|title=The Somoza Dynasty|publisher=University of Pittsburgh|url=http://www.ucis.pitt.edu/clas/nicaragua_proj/history/somoza/Hist-Somoza-dinasty.pdf|format=PDF|page=1|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> | |||
| The Somoza family was among a few families or groups of influential firms which reaped most of the benefits of the country's growth from the 1950s to the 1970s. When Somoza was deposed by the Sandinistas in 1979, the family's worth was estimated to be between $500 million and $1.5 billion.<ref>{{cite news|last=Annis|first=B|title=Nicaragua: Diversification and Growth, 1945–77|year=1993|publisher=The Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0047)|access-date=2012-09-25|archive-date=7 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230407221029/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0047)|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===The Somoza Dynasty (1936–1979)=== | |||
| ] and his sons ] (left) and ] (right).]] | |||
| Nicaragua has experienced several military dictatorships, the longest one being the ] of the ] for much of the 20th century. The Somoza family came to power as part of a US-engineered pact in 1927 that stipulated the formation of the Guardia Nacional, or the National Guard, to replace the U.S. marines that had long reigned in the country.<ref name= Model2005>Lying for Empire: How to Commit War Crimes With a Straight Face" David Model, Common Courage Press, 2005</ref> Somoza slowly eliminated officers in the National Guard who might have stood in his way, and then deposed Sacasa and became president on January 1, 1937 in a ].<ref name=SY/> Somoza was 35 at the time. | |||
| === Nicaraguan Revolution (1960s–1990) === | |||
| Nicaragua declared war on Germany on December 8, 1941, during World War II.<ref name= nytimesGermany>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua Declares War on Germany and Her Allies|url=http://query.nytimes.com/mem/archive-free/pdf?_r=1&res=9E03E0D61F3FE433A2575BC0A9639C946996D6CF|work=The New York Times|accessdate=2009-04-20|format=PDF|date=1918-05-08}}</ref> Although war was formally declared, no soldiers were sent to the war, but ] did seize the occasion to confiscate attractive properties held by German-Nicaraguans, the best-known of which was the ] estate which today operates as a privately owned luxury resort and casino.<ref name= elnuevodiario20050106>{{cite news|title=El asalto de Somoza a los alemanes|date=6 January 2005|url=http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/2005/enero/06-enero-2005/nacional/nacional-20050106-04.html|accessdate=2007-07-13|language=Spanish}}</ref> In 1945 Nicaragua was among the first countries to ratify the United Nations Charter.<ref name=UNCharter1945/> | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan Revolution}} | |||
| ] rebels in 1987]] | |||
| ] in ] in 1989]] | |||
| In 1961, ] looked back to the historical figure of Sandino, and along with two other people, one of whom was believed to be Casimiro Sotelo, who was later assassinated, founded the ] (FSLN).<ref name=SY/> After the 1972 earthquake and Somoza's apparent corruption, the ranks of the Sandinistas were flooded with young disaffected Nicaraguans who no longer had anything to lose.<ref name=Grinnell2007>{{cite news|title=The Sandinistas and the Revolution|publisher=Grinnell College|url=http://web.grinnell.edu/LatinAmericanStudies/this.html|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070206200536/http://web.grinnell.edu/LatinAmericanStudies/this.html|archive-date=2007-02-06|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In December 1974, a group of the FSLN, in an attempt to kidnap U.S. ambassador Turner Shelton, held some Managuan partygoers hostage after killing the party's host, former agriculture minister Jose Maria Castillo, until the Somoza government met their demands for a large ransom and free transport to ]. Somoza granted the demand, and then subsequently sent his national guard out into the countryside to look for the kidnappers, who were described by opponents as terrorists.<ref>{{cite book|first1=Pamela |last1=Constable |author-link=Pamela Constable |first2=Arturo |last2=Valenzuela |year=1991 |title=A Nation of Enemies: Chile Under Pinochet |page= |publisher=W. W. Norton & Company |isbn=978-0-393-30985-0 |url=https://archive.org/details/nationofenemiesc00cons/page/150}}</ref> | |||
| Throughout his years as dictator, "Tacho" Somoza 'ruled Nicaragua with a strong arm'.<ref name=SomozaDynasty/> He had three main sources for his power: control of Nicaraguan economy, military support, and support from the U.S. | |||
| On January 10, 1978, ], the editor of the national newspaper '']'' and ardent opponent of Somoza, was assassinated.<ref name=AC>{{cite news|title=History of Nicaragua: The Beginning of the End|publisher=American Nicaraguan School|url=http://www.ans.edu.ni/Academics/history/somozatachito.html|access-date=2007-08-04|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060520223517/http://www.ans.edu.ni/Academics/history/somozatachito.html|archive-date=May 20, 2006|url-status=dead}}</ref> It is alleged that the planners and perpetrators of the murder were at the highest echelons of the Somoza regime.<ref name=AC/> | |||
| The Sandinistas forcefully took power in July 1979, ousting Somoza, and prompting the exodus of the majority of Nicaragua's middle class, wealthy landowners, and professionals, many of whom settled in the United States.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Nordheimer|first1=Jon|title=Nicaraguan Exiles Find A Place In The Sun: Miami|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/29/us/nicaraguan-exiles-find-a-place-in-the-sun-miami.html|access-date=May 27, 2017|work=The New York Times|date=July 29, 1987|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024123311/https://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/29/us/nicaraguan-exiles-find-a-place-in-the-sun-miami.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Wilkinson|first1=Tracy|title=Families Struggle to Maintain Life Style : Sandinista Rule Not Easy on Middle Class|url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1988-08-07-mn-373-story.html|access-date=May 27, 2017|work=Los Angeles Times|date=August 7, 1988|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140400/https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1988-08-07-mn-373-story.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Wicker|first1=Tom|title=In The Nation; The Sandinista Puzzle|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1983/07/29/opinion/in-the-nation-the-sandinista-puzzle.html|access-date=May 27, 2017|work=The New York Times|date=July 29, 1983|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024123644/https://www.nytimes.com/1983/07/29/opinion/in-the-nation-the-sandinista-puzzle.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The Carter administration decided to work with the new government, while attaching a provision for aid forfeiture if it was found to be assisting insurgencies in neighboring countries.<ref>{{cite book|last=Pastor|first=Robert|title=Exiting the Whirlpool: U.S. Foreign Policy Toward Latin America and the Caribbean|publisher=Westview Press|year=2001|isbn=978-0-8133-3811-8|url=https://archive.org/details/exitingwhirlpool00past}}</ref> Somoza fled the country, and eventually ended up in ], where he was assassinated in September 1980, allegedly by members of the Argentinian Revolutionary Workers' Party.<ref>{{cite web|title=Timeline: Nicaragua|publisher=Stanford University|url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/timeline/|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=26 April 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060426233326/http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/timeline/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Despite his complete control, on September 21, 1956, Somoza was shot by ], a 27-year-old liberal Nicaraguan poet. Somoza was attending a PLN party to celebrate his nomination for the Presidency. He died eight days later. After his father's death, ], the eldest son of the late dictator, was appointed President by the congress and officially took charge of the country.<ref name=SY/> | |||
| ] | |||
| He is remembered by some for being moderate, but was in power only for a few years and then died of a ]. Then came president ] whom most Nicaraguans viewed "as nothing more than a ] of the Somozas".<ref name=Leonard2003>{{cite news|last=Leonard|first=TM|title=Against all odds: U.S. policy and the 1963 Central America Summit Conference|year=2003|publisher=Journal of Third World Studies|url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3821/is_200304/ai_n9173383/pg_11|page=11|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Somoza's brother, Anastasio Somoza Debayle, a ] graduate, succeeded his father in charge of the National Guard, controlled the country, and officially took the presidency after Schick. | |||
| In 1980, the ] provided $60 million in aid to Nicaragua under the Sandinistas, but the aid was suspended when the administration obtained evidence of Nicaraguan shipment of arms to El Salvadoran rebels.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024122802/https://www.nytimes.com/1981/04/02/world/us-halts-economic-aid-to-nicaragua.html |date=24 October 2023 }}, New York Times, 2 April 1981</ref> {{Clarify span|Most people sided with Nicaragua against the Sandinistas.|date=May 2024}}<ref>Mary C. Waters, et al. ''The New Americans : A Guide to Immigration Since 1965''. Harvard University Press, 2007. ''EBSCOhost'', https://search-ebscohost-com.lpclibrary.idm.oclc.org/login.aspx?direct=true&db=nlebk&AN=282331&site=ehost-live {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140334/https://clpccd.idaccessmanage.com/idp/profile/SAML2/POST/SSO?execution=e1s1 |date=5 February 2024 }}.</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua experienced economic growth during the 1960s and 1970s largely as a result of industrialization,<ref name=Annis1993>{{cite news|last=Annis|first=B|title=Nicaragua: Diversification and Growth, 1945–77|year=1993|publisher=The Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0047)|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> and became one of Central America's most developed nations. Due to its stable and high growth economy, foreign investments grew, primarily from U.S. companies such as Citigroup, Sears, Westinghouse, Coca Cola, Bank of America, Chase Manhattan Bank, "Morgan Guaranty Trust and Wells Fargo Bank.{{Citation needed|date=July 2010}} Other investors included London Bank and the Bank of Montreal.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} | |||
| ===Contras=== | |||
| The capital city of Managua suffered a ] in 1972 which destroyed nearly 90% of the city, creating major losses,<ref name=vanderbilt>{{cite news|title=Headline: Nicaragua Earthquake|date=1972-12-16|publisher=Vanderbilt Television News Archive|url=http://tvnews.vanderbilt.edu/program.pl?ID=221286|accessdate=2007-05-24}}</ref> and leveling a 600-square block area in the heart of Managua. Some Nicaraguan historians see the 1972 earthquake that devastated Managua as the final 'nail in the coffin' for Somoza. Instead of helping to rebuild Managua, Somoza siphoned off relief money to help pay for National Guard luxury homes, while the homeless poor had to make do with hastily constructed wooden shacks. The mishandling of relief money also prompted ] star ] to personally fly to Managua on 31 December 1972, but he died enroute in an airplane accident.<ref name=baseballhalloffame>{{cite news|title=Roberto Clemente – Bio|publisher=The National Baseball Hall of Fame|url=http://baseballhalloffame.org/hofers_and_honorees/hofer_bios/clemente_roberto.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070427145215/http://www.baseballhalloffame.org/hofers_and_honorees/hofer_bios/clemente_roberto.htm|archivedate=April 27, 2007}}</ref> Even the economic elite were reluctant to support Somoza, as he had acquired monopolies in industries that were key to rebuilding the nation,<ref name=TIME1978>{{cite news|title=A Battle Ends, a War Begins|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,946048-1,00.html|work=TIME|accessdate=2007-08-21|date=1978-09-11}}</ref> and did not allow the businessmen to compete with the profits that would result. | |||
| {{Main|Contras}} | |||
| In response to the Sandinistas, various rebel groups collectively known as the "]" were formed to oppose the new government. The ] ultimately authorized the ] to ] with funding, weapons, and training.<ref name=CA>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Growth of Opposition, 1981–83|url=http://www.ciaonet.org/atlas/countries/ni_data_loc.html|work=Ciao Atlas|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=12 January 2013|archive-url=https://archive.today/20130112154844/http://www.ciaonet.org/atlas/countries/ni_data_loc.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The Contras operated from camps in the neighboring countries of Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south.<ref name=CA/> | |||
| They engaged in a systematic campaign of terror among rural Nicaraguans to disrupt the social reform projects of the Sandinistas. Several historians have criticized the Contra campaign and the ], citing the brutality and numerous human rights violations of the Contras, alleging that health centers, schools, and cooperatives were destroyed by rebels,<ref>{{cite book|author=LaRamee, Pierre |author2=Polakoff, Erica|isbn=9780333751992|title=The Undermining of the Sandinista Revolution|year=1999|publisher=Palgrave Macmillan|location=New York|pages=141–205}}</ref> and that murder, rape, and torture occurred on a large scale in Contra-dominated areas.<ref>{{cite book|last=Chomsky|first=Noam|title=Turning the Tide|url=https://archive.org/details/turningtideusint00chom|url-access=registration|year=1985|publisher=South End Press|location=Boston, MA}}</ref> The U.S. also carried out a campaign of economic sabotage, and disrupted shipping by planting underwater mines in Nicaragua's port of ],<ref>{{cite news |last=Truver |first=SC |title=Mines and Underwater IEDs in U.S. Ports and Waterways... |url=http://www.mast.udel.edu/873/Spring%202007/ScottTruves.pdf |page=4 |access-date=2007-08-21 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080428050841/http://www.mast.udel.edu/873/Spring%202007/ScottTruves.pdf |archive-date=2008-04-28 }}</ref> an action ] by the ] as illegal.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071107024852/http://www.icj-cij.org/docket/index.php?sum=360&code=nus&p1=3&p2=3&case=70&k=66&p3=5 |date=2007-11-07 }} of the ] of 10 May 1984</ref> The court also found that the U.S. encouraged acts contrary to humanitarian law by producing the manual '']'' and disseminating it to the Contras.<ref>"...Finds that the United States of America, by producing in 1983 a manual entitled "Operaciones sicológicas en guerra de guerrillas", and disseminating it to Contra forces, has encouraged the commission by them of acts contrary to general principles of humanitarian law." As seen at: International Court of Justice 1986, (9)</ref> The manual, among other things, advised on how to rationalize killings of civilians.<ref name="ReferenceC">"In the case of shooting "a citizen who was trying to leave the town or city in which the guerrillas are carrying out armed propaganda or political proselytism," the manual suggests that the Contras "...explain that if that citizen had managed to escape, he would have alerted the enemy." As seen at: Sklar 1988, p. 179</ref> The U.S. also sought to place economic pressure on the Sandinistas, and the Reagan administration imposed a full trade embargo.<ref>{{cite news|title=US Policy: Economic Embargo: The War Goes On|publisher=Central American University – UCA|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/2695|work=Envío|access-date=2007-08-21|archive-date=21 June 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070621163831/http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/2695|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In 1973, the year of reconstruction, many new buildings were built, but the level of corruption in the government prevented further growth. Strikes and demonstrations developed as citizens became increasingly angry and politically mobilized. The elite were angry that Somoza was asking them to pay new emergency taxes to further his own ends. As a result, more of the young elite joined the Sandinista Liberation Front (FSLN). The ever increasing tensions and anti-government uprisings slowed growth in the last two years of the Somoza dynasty. | |||
| The Sandinistas were also accused of human rights abuses including torture, disappearances and mass executions.<ref>Moore, John Norton (1987) ''The Secret War in Central America''. University Publications of America. p. 143. {{ISBN|978-0890939611}}</ref><ref>Miranda, Roger and Ratliff, William (1993) ''The Civil War in Nicaragua''. Transaction. p. 193. {{ISBN|9781412819688}}</ref> The ] investigated abuses by Sandinista forces, including an execution of 35 to 40 ] in December 1981,<ref>{{Cite news|title=OAS Study Says Miskito Indians Suffered Abuse From Sandinistas|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/politics/1984/06/08/oas-study-says-miskito-indians-suffered-abuse-from-sandinistas/5a034db2-11ad-4142-80d8-2c4fe611c8a6/|access-date=2021-07-21|newspaper=The Washington Post|language=en|archive-date=2 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201202123333/https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/politics/1984/06/08/oas-study-says-miskito-indians-suffered-abuse-from-sandinistas/5a034db2-11ad-4142-80d8-2c4fe611c8a6/|url-status=live}}</ref> and an execution of 75 people in November 1984.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cidh.oas.org/annualrep/92eng/chap.4b.htm|title=Annual Report 1992–1993|date=1993-03-12|publisher=Inter-American Commission on Human Rights|access-date=2009-03-30|archive-date=12 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131112024022/http://www.cidh.oas.org/annualrep/92eng/chap.4b.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Nicaraguan Revolution=== | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan Revolution|FSLN|Junta of National Reconstruction}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1961 ] turned back to the historical figure of Sandino, and along with 2 others founded the ] (FSLN).<ref name=SY/> Fonseca turned to the KGB and Cuba's DGI for arms and assistance. The FSLN was a tiny party throughout most of the 1960s, but Somoza's utter hatred of it and his heavy-handed treatment of anyone he suspected to be a ] sympathizer gave many ordinary Nicaraguans the idea that the Sandinistas were much stronger. | |||
| In the ], which were judged by at least one visiting 30-person delegation of NGO representatives to have been free and fair,<ref>{{cite news |title=NICARAGUAN VOTE:'FREE, FAIR, HOTLY CONTESTED' |page=30 |work=The New York Times |date=16 November 1984 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1984/11/16/opinion/l-nicaraguan-vote-free-fair-hotly-contested-089345.html |access-date=2 December 2023 |archive-date=1 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170701011437/http://www.nytimes.com/1984/11/16/opinion/l-nicaraguan-vote-free-fair-hotly-contested-089345.html |url-status=live }}</ref> the Sandinistas won the parliamentary election and their leader ] won the presidential election.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/november/5/newsid_2538000/2538379.stm|title=1984: Sandinistas claim election victory|work=BBC News|date=November 5, 1984|access-date=18 May 2012|archive-date=29 June 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190629081613/http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/november/5/newsid_2538000/2538379.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> The Reagan administration criticized the elections as a "sham" based on the claim that ], the candidate nominated by the ], comprising three right wing political parties, did not participate in the elections. However, the administration privately argued against Cruz's participation for fear that his involvement would legitimize the elections, and thus weaken the case for American aid to the Contras.<ref>{{cite news|last=Taubman|first=Philip|title=KEY AIDES DISPUTE U.S. ROLE IN NICARAGUAN VOTE|work=The New York Times|page=12|date=21 October 1984|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1984/10/21/world/key-aides-dispute-us-role-in-nicaraguan-vote.html|access-date=2 December 2023|archive-date=31 May 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230531075251/https://www.nytimes.com/1984/10/21/world/key-aides-dispute-us-role-in-nicaraguan-vote.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| After the 1972 earthquake and Somoza's brazen corruption, mishandling of relief aid, and refusal to rebuild Managua, the ranks of the Sandinistas were flooded with young disaffected Nicaraguans who no longer had anything to lose.<ref name=Grinnell2007>{{cite news|title=The Sandinistas and the Revolution|publisher=Grinnell College|url=http://web.grinnell.edu/LatinAmericanStudies/this.html|accessdate=2007-05-09|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070206200536/http://web.grinnell.edu/LatinAmericanStudies/this.html|archivedate=2007-02-06}}</ref> These economic problems propelled the Sandinistas in their struggle against Somoza by leading many middle- and upper-class Nicaraguans to see the Sandinistas as the only hope for removing the brutal Somoza regime. | |||
| In 1983 the U.S. Congress prohibited federal funding of the Contras, but the Reagan administration illegally continued to back them by covertly selling arms to ] and channeling the proceeds to the Contras in the ], for which several members of the Reagan administration were convicted of felonies.<ref>{{cite book|last=Baker|first=D|title=The United States since 1980 (The World Since 1980)|publisher=Cambridge University Press|place=Cambridge, UK|page=|isbn=978-0-521-86017-8|date=2007-03-05|url=https://archive.org/details/unitedstatessinc00bake/page/101}}</ref> The ], in regard to the case of ] in 1986, found, "the United States of America was under an obligation to make reparation to the Republic of Nicaragua for all injury caused to Nicaragua by certain breaches of obligations under customary international law and treaty-law committed by the United States of America".<ref name="icj-cij">{{cite web|title=Case concerning military and paramilitary activities in and against Nicaragua (Nicaragua v. United States of America), International Court of Justice, Order of 26 september 1991|url=http://www.icj-cij.org/docket/files/70/6483.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924063157/http://www.icj-cij.org/docket/files/70/6483.pdf|archive-date=24 September 2015|access-date=5 November 2008}}</ref> During the war between the Contras and the Sandinistas, 30,000 people were killed.<ref> by Bethany Lacina</ref> | |||
| In December 1974, a group of FSLN, in an attempt to kidnap U.S. Ambassador Tuner Shelton, held some Managuan partygoers hostage (after killing the host, former Agriculture Minister Jose Maria Castillo), until the Somozan government met their demands for a large ransom and free transport to Cuba. Somoza granted this, then subsequently sent his National Guard out into the countryside to look for the perpetrators of the kidnapping that were described by opponents of this kidnapping as 'terrorists'. While searching, the National Guard pillaged villages and imprisoned, tortured, raped, and executed hundreds of villagers. This led to the Roman Catholic Church withdrawing any and all support of the Somoza regime. Around this time, ]an president ] was removed from power in a military coup that prompted Allende to take his own life, as the presidential palace came under fire. With right-wing ] in power in Chile, several hundred committed Chilean revolutionaries joined the Sandinista army in Nicaragua.<ref name=Constable1991>Pamela Constable and Arturo Valenzuela (1991). A Nation of Enemies: Chile Under Pinochet, P. 150</ref> | |||
| === Post-war (1990–2018) === | |||
| On January 10, 1978, ], the editor of the national newspaper '']'' and ardent opponent of Somoza, was assassinated.<ref name=AC>{{cite news|title=History of Nicaragua: The Beginning of the End|publisher=American Nicaraguan School|url=http://www.ans.edu.ni/Academics/history/somozatachito.html|accessdate=2007-08-04|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060520223517/http://www.ans.edu.ni/Academics/history/somozatachito.html|archivedate=May 20, 2006}}</ref> This is believed to have led to the extreme general disappointment with Somoza. The planners and perpetrators of the murder were at the highest echelons of the Somoza regime and included the dictator's son, "El Chiguin" ("The Kid"), the President of Housing, Cornelio Hueck, the Attorney General, and Pedro Ramos, a Cuban expatriate and close ally, who commercialized ].<ref name=AC/> | |||
| ] war, ] became the first woman president democratically elected in the history of the ].]] | |||
| ] in 1998]] | |||
| ] in May 2018]] | |||
| In the ], a coalition of anti-Sandinista parties from both the left and right of the political spectrum led by ], the widow of Pedro Joaquín Chamorro Cardenal, defeated the Sandinistas. The defeat shocked the Sandinistas, who had expected to win.<ref>{{cite news|last=O'Grady |first=M |title=Ortega's Comeback Schemes Roil Nicaragua |url=http://www.mre.gov.br/portugues/noticiario/internacional/selecao_detalhe.asp?ID_RESENHA=154683&Imprime=on |access-date=2007-05-09 }}{{dead link|date=June 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> | |||
| Exit polls of Nicaraguans reported Chamorro's victory over ] was achieved with a 55% majority.<ref>{{cite news|title=Was February 25 a 'triumph'? National Review v. 42|publisher=Tulane University|url=http://lal.tulane.edu/RESTRICTED/CABIB/nicabib_.txt|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060901190113/http://lal.tulane.edu/RESTRICTED/CABIB/nicabib_.txt|archive-date=September 1, 2006}}</ref> Chamorro was the first woman president of Nicaragua. Ortega vowed he would govern ''desde abajo'' (from below).<ref>{{cite news|title=El Sandinista Daniel Ortega se convierte de nuevo en presidente de Nicaragua|date=2006-11-08|url=http://www.elmundo.es/elmundo/2006/11/08/internacional/1162945503.html|work=El Mundo|access-date=2007-05-09|language=es|archive-date=1 November 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231101160122/https://www.elmundo.es/elmundo/2006/11/08/internacional/1162945503.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Chamorro came to office with an economy in ruins, primarily because of the financial and social costs of the Contra War with the Sandinista-led government.<ref>{{cite news|last=Dennis|first=G|title=Social conditions of Nicaragua|date=December 1993|publisher=The Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0035)|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=22 September 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080922150151/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0035)|url-status=live}}</ref> In the ], Daniel Ortega and the Sandinistas of the FSLN lost again, this time to ] of the ] (PLC). | |||
| The Sandinistas, supported by some of the populace, elements of the Catholic Church, and regional governments (including Panama, Mexico, Costa Rica, and Venezuela), took power in July 1979. The Carter administration, refusing to act unilaterally, decided to work with the new government, while attaching a provision for aid forfeiture if it was found to be assisting insurgencies in neighboring countries.<ref name=Pastor2001>Pastor, Robert. ''Exiting the Whirlpool: U.S. Foreign Policy Toward Latin America and the Caribbean''. (Westview Press, 2001).</ref> A group of prominent citizens known as ], "the Twelve", denounced the Somoza regime and said that "there can be no dialogue with Somoza...because he is the principal obstacle to all rational understanding...through the long dark history of ''Somocismo'', dialogues with the dictatorship have only served to strengthen it..." Somoza fled the country and eventually ended up in ], where he was assassinated in September 1980, allegedly by members of the Argentinian Revolutionary Workers Party.<ref name=Stanfordtimeline>{{cite news|title=Timeline: Nicaragua|publisher=Stanford University|url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/timeline/|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> | |||
| In ], the PLC again defeated the FSLN, with Alemán's Vice President ] succeeding him as president. However, Alemán was convicted and sentenced in 2003 to 20 years in prison for ], ], and corruption;<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Political profile|url=http://www.alertnet.org/printable.htm?URL=/db/cp/nicaragua.htm|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=18 September 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060918221221/http://www.alertnet.org/printable.htm?URL=/db/cp/nicaragua.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> liberal and Sandinista parliament members combined to strip the presidential powers of President Bolaños and his ministers, calling for his resignation and threatening ]. The Sandinistas said they no longer supported Bolaños after U.S. Secretary of State ] told Bolaños to distance from the FSLN.<ref>{{cite news |last=Thompson |first=G |title=Old Foe of U.S. Trying for a Comeback in Nicaragua |date=2005-04-05 |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2005/04/05/world/americas/old-foe-of-us-trying-for-a-comeback-in-nicaragua.html |access-date=2023-04-02 |archive-date=24 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024122152/https://www.nytimes.com/2005/04/05/world/americas/old-foe-of-us-trying-for-a-comeback-in-nicaragua.html |url-status=live }}</ref> This "slow motion ''coup d'état''" was averted partially by pressure from the Central American presidents, who vowed not to recognize any movement that removed Bolaños; the U.S., the OAS, and the ] also opposed the action.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua 'creeping coup' warning|date=2005-09-30|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/4296818.stm|work=BBC News|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=10 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230410155830/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/4296818.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| To begin the task of establishing a new government, the Sandinistas created a Council (or {{lang|es|''junta''}}) of National Reconstruction, made up of five members: Sandinista militants ] and Moises Hassan, novelist ] (a member of Los Doce), businessman ], and Violeta Barrios de Chamorro (the widow of ]). Sandinista supporters thus comprised three of the five members of the junta. | |||
| Nicaragua briefly participated in the ] in 2004 as part of the ], a military contingent of mixed personnel.<ref name="AP 2004-04-29">{{cite web |agency=Associated Press |title=Spanish defense minister: No more troops for Iraq |website=Deseret News |date=2004-04-29 |url=https://www.deseret.com/2004/4/29/19826018/spanish-defense-minister-no-more-troops-for-iraq |access-date=2024-01-17 |archive-date=17 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240117214140/https://www.deseret.com/2004/4/29/19826018/spanish-defense-minister-no-more-troops-for-iraq |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The non-Sandinistas, Robelo and Chamorro, later resigned because they had little actual power in the junta. Sandinista mass organizations were also powerful: including the Sandinista Workers' Federation ({{lang|es|''Central Sandinista de Trabajadores''}}), the ] ({{lang|es|''Asociación de Mujeres Nicaragüenses Luisa Amanda Espinoza''}}), and the National Union of Farmers and Ranchers ({{lang|es|''Unión Nacional de Agricultores y Ganaderos''}}). | |||
| Before ], the ] passed a bill further restricting ].<ref>{{cite news|last=Frazier|first=JB|title=Nicaraguan President Signs Abortion Ban|date=2006-11-18|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/11/18/AR2006111800351.html|newspaper=]|access-date=2007-05-25|archive-date=18 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210718132940/https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/11/18/AR2006111800351.html|url-status=live}}</ref> As a result, Nicaragua is one of five countries in the world where abortion is illegal with no exceptions.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/society/sarah-boseley-global-health/2010/jun/11/abortion-nicaragua|title=Nicaragua refuses to lift abortion ban|last=Boseley|first=S|newspaper=The Guardian|date=2010-06-11|access-date=15 December 2016|archive-date=25 February 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170225094013/https://www.theguardian.com/society/sarah-boseley-global-health/2010/jun/11/abortion-nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> Legislative and presidential elections took place on November 5, 2006. Ortega returned to the presidency with 37.99% of the vote. This percentage was enough to win the presidency outright, because of a change in electoral law which lowered the percentage requiring a runoff election from 45% to 35% (with a 5% margin of victory).<ref>{{cite news|title=Bolaños Will Move To The National Assembly After All|year=2006|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/3439|work=Envío Magazine|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=4 February 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070204105521/http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/3439|url-status=live}}</ref> ] resulted in the re-election of Ortega, with a landslide 62.46% of the vote. In 2014 the National Assembly approved changes to the constitution allowing Ortega to run for a third successive term.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua's Revolution Heads Toward Dictatorship|last=Gibney|first=James|publisher=Bloomberg|date=2014-01-30|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-30/nicaragua-s-revolution-heads-toward-dictatorship-.html|access-date=2014-02-04|archive-date=22 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140222145224/http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-30/nicaragua-s-revolution-heads-toward-dictatorship-.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| On the Atlantic Coast a small uprising also occurred in support of the Sandinistas. This event is often overlooked in histories about the Sandinista revolution. A group of Creoles led by a native of ], Dexter Hooker (known as Commander Abel), raided a Somoza-owned business to gain access to food, guns and money before heading off to join Sandinista fighters who had liberated the city of ]. The 'Black Sandinistas' returned to Bluefields on July 19, 1979 and took the city without a fight. The Black Sandinistas were challenged by a group of mestizo Sandinista fighters. | |||
| In November 2016, ] (his fourth overall). International monitoring of the elections was initially prohibited, and as a result the validity of the ] has been disputed, but observation by the ] was announced in October.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Geoff|first1=Thale|title=As Nicaragua's Election Draws Near, Concerns Grow Over Abuse of Power|url=https://www.wola.org/analysis/nicaraguas-election-draws-near-concerns-grow-abuse-power/|access-date=13 January 2018|publisher=WOLA|archive-date=13 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180113203631/https://www.wola.org/analysis/nicaraguas-election-draws-near-concerns-grow-abuse-power/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=OAS Mission in Nicaragua Recommends Integral Electoral Reform|url=http://www.oas.org/en/media_center/press_release.asp?sCodigo=E-079/17|access-date=13 January 2018|agency=Organization of American States|date=November 7, 2016|archive-date=14 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180114020252/http://www.oas.org/en/media_center/press_release.asp?sCodigo=E-079/17|url-status=live}}</ref> Ortega was reported by Nicaraguan election officials as having received 72% of the vote. However, the ] (FAD), having promoted boycotts of the elections, claimed that 70% of voters had abstained (while election officials claimed 65.8% participation).<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-37892477|title=Nicaragua's Ortega re-elected president|date=2016-11-07|work=BBC News|access-date=2017-09-12|language=en-GB|archive-date=25 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171225142817/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-37892477|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ensuing standoff between the two groups, with the Black Sandinistas occupying the National Guard barracks (the cuartel) and the mestizo group occupying the Town Hall (Palacio) gave the revolution on the Atlantic Coast a racial dimension which was absent from other parts of the country. The Black Sandinistas were assisted in their power struggle with the Palacio group by the arrival of the ] from Costa Rica. | |||
| In April 2018, ] were held to oppose a decree increasing taxes and reducing benefits in the country's pension system. Local independent press organizations documented at least 19 dead and over 100 missing in the ensuing conflict.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://confidencial.com.ni/quienes-son-muertos-de-las-protestas-en-nicaragua/|title=Los muertos de la represión que Daniel Ortega oculta|last=Cerda|first=Arlen|date=2018-04-22|work=Confidencial|access-date=2018-04-25|language=es-NI|archive-date=26 April 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180426012028/https://confidencial.com.ni/quienes-son-muertos-de-las-protestas-en-nicaragua/|url-status=live}}</ref> A reporter from NPR spoke to protestors who explained that while the initial issue was the pension reforms, the uprisings that spread across the country reflected many grievances about the government's time in office, and that the fight is for President Ortega and his vice president, his wife, to step down.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Kahn|first1=Carrie|title=Nicaragua Withdraws Social Security Changes That Sparked Unrest|url=https://www.npr.org/2018/04/23/604854250/nicaragua-withdraws-social-security-changes-that-sparked-unrest|access-date=31 May 2018|publisher=NPR|date=April 23, 2018|language=en|archive-date=6 June 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180606075104/https://www.npr.org/2018/04/23/604854250/nicaragua-withdraws-social-security-changes-that-sparked-unrest|url-status=live}}</ref> April 24, 2018 marked the day of the greatest march in opposition of the Sandinista party. On May 2, 2018, university-student leaders made a public announcement giving the government seven days to set a date and time for a dialogue that was promised to the people due to the recent events of repression. The students also scheduled another peaceful protest march on that same day. As of May 2018, estimates of the death toll were as high as 63, many of them student protesters, and the wounded totalled more than 400.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Garvin|first1=Glenn|title=In Nicaragua, the political battle is moving from the streets to the negotiating table|url=http://www.miamiherald.com/latest-news/article210129639.html|access-date=May 2, 2018|work=Miami Herald|date=May 2, 2018|language=en|archive-date=14 June 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180614020016/http://www.miamiherald.com/latest-news/article210129639.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Following a working visit from May 17 to 21, the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights adopted precautionary measures aimed at protecting members of the student movement and their families after testimonies indicated the majority of them had suffered acts of violence and death threats for their participation.<ref>{{cite news|title=CIDH condena nuevos hechos de violencia en Nicaragua|url=http://www.oas.org/es/cidh/prensa/comunicados/2018/116.asp|access-date=26 May 2018|work=www.oas.org|agency=Inter-American Commission on Human Rights|publisher=Organization of American States|date=25 May 2018|language=es|archive-date=28 May 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180528043043/https://www.oas.org/es/cidh/prensa/comunicados/2018/116.asp|url-status=live}}</ref> In the last week of May, thousands who accuse Mr. Ortega and his wife of acting like dictators joined in resuming anti-government rallies after attempted peace talks have remained unresolved.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaraguan protesters call on Ortega to go|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-44269498|access-date=27 May 2018|work=BBC News|publisher=BBC|date=27 May 2018|archive-date=27 May 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180527062610/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-44269498|url-status=live}}</ref> Open suppression of political dissent and more militarized policing began in April 2018, but the onset of repression was gradual.<ref>Dammert, Lucía, and Mary Fran T. Malone. “From Community Policing to Political Police in Nicaragua.” ''European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies / Revista Europea de Estudios Latinoamericanos y Del Caribe'', no. 110, 2020, pp. 79–99. JSTOR, https://www.jstor.org/stable/26979875 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231125012623/https://www.jstor.org/stable/26979875 |date=25 November 2023 }}. Accessed 25 Nov. 2023.</ref> | |||
| One of the brigade's members, an Afro-Costa Rican called Marvin Wright (known as Kalalu) became known for the rousing speeches he made, which included elements of ] ideology in his attempts to unite all the black militias that had formed in Bluefields. The introduction of a racial element into the revolution was not welcomed by the Sandinista National Directorate, which expelled Kalalu and the rest of the brigade from Nicaragua and sent them to Panama.<ref name=Baracco2007>Baracco, L. (2007) Wadabagei: A Journal of the Caribbean and its Diaspora, Vol. 10, No. 1, pp. 4–23.</ref> | |||
| == |
== Geography and climate == | ||
| {{Main| |
{{Main|Geography of Nicaragua|Climate of Nicaragua}} | ||
| {{See also|Volcanoes of Nicaragua|}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Upon assuming office in 1981, ] ] condemned the FSLN for joining with Cuba in supporting Marxist revolutionary movements in other Latin American countries such as ]. Reagan was also concerned about the growing Soviet and Cuban presence in Nicaragua, and the Soviet hope to turn Nicaragua into a "second Cuba". Under the ], his administration authorized the ] to have paramilitary officers from their elite ] begin financing, arming and training rebels, some of whom were the remnants of Somoza's National Guard, as anti-Sandinista guerrillas that were branded "counter-revolutionary" by leftists ({{lang|es|''contrarrevolucionarios''}} in Spanish).<ref name=CA>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Growth of Opposition, 1981–83|url=http://www.ciaonet.org/atlas/countries/ni_data_loc.html|work=Ciao Atlas|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> This was shortened to '']'', a label the anti-socialist forces chose to embrace. ] and many of the indigenous guerrilla forces unassociated with the "Somozistas" also resisted the Sandinistas. The Contras operated out of camps in the neighboring countries of Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south.<ref name=CA/> As was typical in guerrilla warfare, they were engaged in a campaign of economic sabotage in an attempt to combat the Sandinista government and disrupted shipping by planting underwater mines in Nicaragua's Port of ],<ref name=Truver2007>{{cite news|last=Truver|first=SC|title=Mines and Underwater IEDs in U.S. Ports and Waterways...|url=http://www.mast.udel.edu/873/Spring%202007/ScottTruves.pdf|format=PDF|page=4|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> an action condemned by the ] as illegal.<ref name=icjdocket> of the ] of 10 May 1984</ref> The U.S. also sought to place economic pressure on the Sandinistas, and the Reagan administration imposed a full trade ].<ref name=UCA2695>{{cite news|title=US Policy: Economic Embargo: The War Goes On|publisher=Central American University – UCA|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/2695|work=Envío|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua occupies a landmass of {{convert|130967|km2|0|abbr=on}}, which makes it slightly larger than England. Nicaragua has three distinct geographical regions: the Pacific lowlands – fertile valleys which the Spanish colonists settled, the ] (North-central highlands), and the Mosquito Coast (Atlantic lowlands/]). | |||
| The low plains of the Atlantic Coast are {{convert|97|km|0|abbr=on}} wide in areas. They have long been exploited for their natural resources. | |||
| U.S. support for this Nicaraguan insurgency continued in spite of the fact that impartial observers from international groupings such as the ], religious groups sent to monitor the election, and observers from democratic nations such as Canada and the ] concluded that the ] were completely free and fair. The Reagan administration disputed these results, despite the fact that the government of the United States never had any observers in Nicaragua at the time. | |||
| On the Pacific side of Nicaragua are the two largest freshwater lakes in Central America—] and ]. Surrounding these lakes and extending to their northwest along the ] of the ] are fertile lowland plains, with soil highly enriched by ] from nearby ]es of the central highlands. Nicaragua's abundance of biologically significant and unique ]s contribute to ]'s designation as a ]. Nicaragua has made efforts to become less dependent on fossil fuels, and it expects to acquire 90% of its energy from renewable resources by 2020.<ref name="bbc">{{Cite news|title=Why isn't Nicaragua in the Paris agreement?|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-40135819|newspaper=BBC News|access-date=October 27, 2017|date=June 3, 2017|archive-date=10 October 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181010132459/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-40135819|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Nicaragua: a renewable energy paradise in Central America|url=http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2013/10/25/energias-renovables-nicaragua|website=World Bank|access-date=October 27, 2017|language=en|date=October 25, 2013|archive-date=28 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171028092850/http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2013/10/25/energias-renovables-nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> Nicaragua was one of the few countries that did not enter an ] at ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-12-08/after-two-decades-of-stumbles-carbon-market-pioneers-revving-up#media-2|title=Carbon Markets Are Making a Slow, But Steady, Comeback|first1=Alex|last1=Nussbaum|first2=Ewa|last2=Krukowska|first3=Mathew|last3=Carr|date=8 December 2015|work=Bloomberg.com|access-date=17 February 2016|archive-date=2 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171002070611/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-12-08/after-two-decades-of-stumbles-carbon-market-pioneers-revving-up#media-2|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www4.unfccc.int/submissions/indc/Submission%20Pages/submissions.aspx|title=INDCs as communicated by Parties|publisher=unfccc.int|access-date=9 December 2015|archive-date=13 February 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160213114249/http://www4.unfccc.int/submissions/indc/Submission%20Pages/submissions.aspx|url-status=live}}</ref> Nicaragua initially chose not to join the Paris Climate Accord because it felt that "much more action is required" by individual countries on restricting global temperature rise.<ref name="bbc" /> However, in October 2017, Nicaragua made the decision to join the agreement.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua to join Paris climate accord, leaving US and Syria isolated|url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2017/oct/23/nicaragua-joins-paris-climate-accord-us-trump-syria|access-date=December 4, 2017|work=The Guardian|date=October 23, 2017|archive-date=21 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171121110757/https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2017/oct/23/nicaragua-joins-paris-climate-accord-us-trump-syria|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Stack|first1=Liam|title=Only U.S. and Syria Now Oppose Paris Climate Deal, as Nicaragua Joins|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/10/24/world/americas/nicaragua-paris-climate-agreement-us.html|access-date=December 4, 2017|work=The New York Times|date=October 24, 2017|archive-date=5 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171205043817/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/10/24/world/americas/nicaragua-paris-climate-agreement-us.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Noack|first1=Rick|title=Being outside the Paris climate deal: Something now only the U.S. and Syria agree on|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2017/10/24/not-being-part-of-the-paris-climate-deal-something-only-the-u-s-and-syria-agree-on/|access-date=December 4, 2017|newspaper=]|date=October 24, 2017|archive-date=11 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171211054805/https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2017/10/24/not-being-part-of-the-paris-climate-deal-something-only-the-u-s-and-syria-agree-on/|url-status=live}}</ref> It ratified this agreement on November 22, 2017.<ref>{{cite web|title=Paris Agreement – Status of Ratification|url=http://unfccc.int/paris_agreement/items/9444.php|publisher=United Nations|access-date=13 January 2018|archive-date=14 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180114073512/http://unfccc.int/paris_agreement/items/9444.php|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The elections were not also recognized as legitimate because ], the candidate nominated by the ], comprising three rightwing political parties, did not participate in the elections.<ref name=Ryan1995>{{cite book|last=Ryan|first=P|title=The fall and rise of the market in Sandinista Nicaragua|page=151|year=1995|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=3vjWxkl_mqYC|isbn=9780773513594}}</ref> He withdrew from the elections due to the government's lack of response to the document "A Step Toward Democracy, Free Elections" issued in 1982. The document was asking the government to re-establish all civil rights: freedom of speech, freedom of organization, release of all political prisoners, cease of hostilities against the opposition, lifting the censorship on the media and abolishing all the laws violating human rights.<ref name=envio2578>{{cite web|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/2578|title=Election archive|publisher=Envio.org.ni|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref><ref name=lcweb2>{{cite web|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0027|title=The library of Congress Country Studies|publisher=Lcweb2.loc.gov|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| Nearly one fifth of Nicaragua is designated as ] like national parks, nature reserves, and biological reserves. The country had a 2019 ] mean score of 3.63/10, ranking it 146th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal|last1=Grantham|first1=H. S.|last2=Duncan|first2=A.|last3=Evans|first3=T. D.|last4=Jones|first4=K. R.|last5=Beyer|first5=H. L.|last6=Schuster|first6=R.|last7=Walston|first7=J.|last8=Ray|first8=J. C.|last9=Robinson|first9=J. G.|last10=Callow|first10=M.|last11=Clements|first11=T.|last12=Costa|first12=H. M.|last13=DeGemmis|first13=A.|last14=Elsen|first14=P. R.|last15=Ervin|first15=J.|last16=Franco|first16=P.|last17=Goldman|first17=E.|last18=Goetz|first18=S.|last19=Hansen|first19=A.|last20=Hofsvang|first20=E.|last21=Jantz|first21=P.|last22=Jupiter|first22=S.|last23=Kang|first23=A.|last24=Langhammer|first24=P.|last25=Laurance|first25=W. F.|last26=Lieberman|first26=S.|last27=Linkie|first27=M.|last28=Malhi|first28=Y.|last29=Maxwell|first29=S.|last30=Mendez|first30=M.|last31=Mittermeier|first31=R.|last32=Murray|first32=N. J.|last33=Possingham|first33=H.|last34=Radachowsky|first34=J.|last35=Saatchi|first35=S.|last36=Samper|first36=C.|last37=Silverman|first37=J.|last38=Shapiro|first38=A.|last39=Strassburg|first39=B.|last40=Stevens|first40=T.|last41=Stokes|first41=E.|last42=Taylor|first42=R.|last43=Tear|first43=T.|last44=Tizard|first44=R.|last45=Venter|first45=O.|last46=Visconti|first46=P.|last47=Wang|first47=S.|last48=Watson|first48=J. E. M.|display-authors=1|title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material|journal=Nature Communications|volume=11|issue=1|year=2020|page=5978|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3|pmid=33293507|pmc=7723057|bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G |doi-access=free}}</ref> ]ly, Nicaragua is surrounded by the ], an ] ] underlying Central America, and the ]. Since Central America is a major ] zone, Nicaragua hosts most of the ]. On 9 June 2021, Nicaragua launched a new volcanic supersite research in strengthening the monitoring and surveillance of the country's 21 active volcanoes. | |||
| As the Sandinistas moved further in the direction of creating a Marxist state and repressing political opposition, opposition to the regime increased. Heavy-handed tactics by the Ministry of Interior, guided by Soviet, Cuban, Bulgarian and East German advisers,security forces in the countryside, also added recruits to the contra numbers. Inept economic policies, which resulted in hyperinflation and food shortages, also contributed to discontent. Large Soviet arms shipments, including T-55 tanks, other armored vehicles, and Hind helicopters, were used in an increasingly violent counterinsurgency campaign. | |||
| === Pacific lowlands === | |||
| After the U.S. Congress prohibited federal funding of the Contras in 1983, the Reagan administration continued to back the Contras by covertly selling arms to ] and channeling the proceeds to the Contras (the ]).<ref name=Baker>{{cite book|last=Baker|first=D|title=The United States since 1980 (The World Since 1980)|publisher=Cambridge University Press|location=Cambridge, UK|page=101|isbn=0-521-86017-2}}</ref> When this scheme was revealed, Reagan admitted that he knew about the Iranian "arms for hostages" dealings but professed ignorance about the proceeds funding the Contras; for this, ] aide ] ] took much of the blame. | |||
| ], seen from ].]] | |||
| ] and located northeast of ] in northeastern Nicaragua, is the second-largest rainforest in the ] after the Amazonian Rainforest in ]]] | |||
| In the west of the country, these lowlands consist of a broad, hot, fertile plain. Punctuating this plain are several large volcanoes of the ] mountain range, including ] just outside Granada, and ] near León. The lowland area runs from the ] to Nicaragua's Pacific border with Costa Rica south of ]. Lake Nicaragua is the largest freshwater lake in Central America (20th largest in the world),<ref>{{cite news|title=Large Lakes of the World|url=http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0001777.html|access-date=2007-05-25|work=factmonster.com|archive-date=29 March 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170329213828/http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0001777.html|url-status=live}}</ref> and is home to some of the world's rare freshwater sharks (]).<ref>{{cite news|work=nature.org|title=The Nature Conservancy in Nicaragua|url=http://www.nature.org/wherewework/centralamerica/nicaragua/|access-date=2007-05-25|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070405074947/http://www.nature.org/wherewework/centralamerica/nicaragua/|archive-date=2007-04-05|url-status=dead}}</ref> The Pacific lowlands region is the most populous, with over half of the nation's population. | |||
| The eruptions of western Nicaragua's 40 volcanoes, many of which are still active, have sometimes devastated settlements but also have enriched the land with layers of fertile ash. The geologic activity that produces vulcanism also breeds powerful earthquakes. Tremors occur regularly throughout the Pacific zone, and earthquakes have nearly destroyed the capital city, Managua, more than once.<ref name="gr1">{{Dead link|date=August 2019|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}} ''Encyclopedia Americana''. Grolier Online. (200-11-20){{date?}} {{Dead link|date=August 2019|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}}{{subscription required}}</ref> | |||
| Senator ]'s 1988 ] report on Contra-drug links concluded that "senior U.S. policy makers were not immune to the idea that drug money was a perfect solution to the Contras' funding problems."<ref name='ONF'>{{cite news|title=The Oliver North File|url=http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB113/index.htm|work=National Security Archive|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> According to the ], Oliver North had been in contact with ], a Panamanian ] and the ] military ] of Panama from 1983 to 1989 when he was overthrown and captured by a U.S. invading force.<ref name=SERRILL1989> MICHAEL S. SERRILL, Reported by Jonathan Beaty and Ricardo Chavira/Washington, '50th birthday last week' written February 1989</ref> He was taken to the United States, tried for drug trafficking, and imprisoned in 1992.<ref name=CNN2004>{{cite web|author=|title=Noriega suffers mild stroke, hospitalized in Miami|work=|publisher=CNN|year=2004|url=http://www.cnn.com/2004/US/12/04/noriega.stroke/index.html|accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
| Most of the Pacific zone is '']'', the "hot land" of tropical Spanish America at elevations under {{convert|2000|ft|m|0|order=flip}}. Temperatures remain virtually constant throughout the year, with highs ranging between {{convert|85|and|90|°F|°C|1|abbr=on|order=flip}}. After a dry season lasting from November to April, rains begin in May and continue to October, giving the Pacific lowlands {{convert|40|to|60|in|mm|0|order=flip}} of precipitation. Good soils and a favourable climate combine to make western Nicaragua the country's economic and demographic centre. The southwestern shore of Lake Nicaragua lies within {{convert|15|mi|km|0|order=flip}} of the Pacific Ocean. Thus the lake and the San Juan River were often proposed in the 19th century as the longest part of a canal route across the Central American isthmus. Canal proposals were periodically revived in the 20th and 21st centuries.<ref name=gr1/><ref>{{cite web|title=TED CASE: Nicaragua Canal Proposal|publisher=american.edu|url=http://www1.american.edu/TED/nicanal.htm|access-date=2011-07-16|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111151730/http://www1.american.edu/TED/nicanal.htm|archive-date=2012-01-11}}</ref> Roughly a century after the opening of the ], the prospect of a Nicaraguan ] remains a topic of interest.<ref>{{cite web |author=Muñoz, Néfer |title=An 'Eco-Canal' across Nicaragua |work=Accents |publisher=Tierramérica |location=Granada, Nicaragua |year=2001 |url=http://www.tierramerica.net/2001/0506/iacentos.shtml |access-date=2011-07-20 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110510015252/http://www.tierramerica.net/2001/0506/iacentos.shtml |archive-date=May 10, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Proyecto "Construcción del Puerto Monkey Point" |work=Proyectos |publisher=Empresa Portuaria Nacional |location=Managua |language=es |year=2009 |url=http://www.epn.com.ni/Puerto-mp.aspx |access-date=2011-07-20 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511094605/http://www.epn.com.ni/Puerto-mp.aspx |archive-date=May 11, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=Alvarez, Gustavo|title=Empresas de seis países interesadas en Monkey Point|newspaper=elnuevodiario.com.ni|publisher=]|place=Managua|date=2008-02-18|language=es|url=http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/economia/8704|access-date=2011-07-20|archive-date=13 July 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100713163014/http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/economia/8704|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=Álvarez Hidalgo, Wendy|title=Harán puerto Monkey Point|newspaper=laprensa.co.ni|publisher=]|place=Managua|date=2010-07-07|language=es|url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/07/07/economia/30625|access-date=2011-07-20|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110813073852/http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/07/07/economia/30625|archive-date=2011-08-13}}</ref> | |||
| In August 1996, '']'' reporter ] published a series titled ''Dark Alliance'', linking the origins of ] in California to the Contras.<ref name=darkalliance>, ''San Jose Mercury News'', now hosted by narconews.com</ref> ] inquiries by the National Security Archive and other investigators unearthed a number of documents showing that White House officials, including Oliver North, knew about and supported using money raised via ] to fund the Contras. Sen. John Kerry's report in 1988 led to the same conclusions; major media outlets, the Justice Department, and Reagan denied the allegations.<ref name=Crockett2006>{{cite news|last=Crockett|first=S|title=Bush and Republicans vs. rule of law|url=http://www.freepress.org/departments/display/20/2006/1713|work=The Free Press|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| In addition to its beach and resort communities, the Pacific lowlands contains most of Nicaragua's Spanish colonial architecture and artifacts. Cities such as León and ] abound in colonial architecture; founded in 1524, Granada is the oldest colonial city in the Americas.<ref>{{cite news|last=White|first=RL|title=Pittsburghers find once war-ravaged country is a good place to invest|date=2004-08-24|url=http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/04237/366377.stm|work=Post Gazette|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=16 May 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070516145838/http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/04237/366377.stm|url-status=live}}</ref>{{update inline|date=January 2024}} | |||
| The ], in regard to the case of ] in 1984, found; "the United States of America was under an obligation to make reparation to the Republic of Nicaragua for all injury caused to Nicaragua by certain breaches of obligations under customary international law and treaty-law committed by the United States of America".<ref name=docket6483>{{cite web|author=|title=Case concerning military and paramilitary activities in and against Nicaragua (Nicaragua v. United States of America)], International Court of Justice, Order of 26 september 1991|work=|publisher=|year=|url=http://www.icj-cij.org/docket/files/70/6483.pdf|accessdate=}}</ref> United States however rejected and did not comply with the judgement under the 'Connally Amendment' (part of the conditional participation of USA in the International court of Justice, which excludes from ICJ's jurisdiction "disputes with regard to matters that are essentially within the jurisdiction of the United States of America, as determined by the United States of America").<ref name=ICLQ1958>''International and Comparative Law Quarterly'' (1958), 7:758–762. Cambridge University Press</ref> | |||
| === |
=== North central highlands === | ||
| ] in ] in the ] in northern Nicaragua]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Northern Nicaragua is the most diversified region producing coffee, cattle, milk products, vegetables, wood, gold, and flowers. Its extensive forests, rivers and geography are suited for ecotourism. | |||
| The ] saw the defeat of the Sandinistas by a coalition of anti-Sandinista (from the left and right of the political spectrum) parties led by Violeta Chamorro, the widow of Pedro Joaquín Chamorro. The defeat shocked the Sandinistas, as numerous pre-election polls had indicated a sure Sandinista victory, and their pre-election rallies had attracted crowds of several hundred thousand people.<ref name=OGrady>{{cite news|last=O'Grady|first=M|title=Ortega's Comeback Schemes Roil Nicaragua|url=http://www.mre.gov.br/portugues/noticiario/internacional/selecao_detalhe.asp?ID_RESENHA=154683&Imprime=on|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> The unexpected result was subject to extensive analysis and comment. Commentators such as ] and ] attributed the outcome to the U.S./Contra threats to continue the war if the Sandinistas retained power, the general war-weariness of the Nicaraguan population, and the abysmal Nicaraguan economic situation. | |||
| The central highlands are a significantly less populated and economically developed area in the north, between Lake Nicaragua and the Caribbean. Forming the country's ], or "temperate land", at elevations between {{convert|2000|and|5000|ft|m|0|order=flip}}, the highlands enjoy mild temperatures with daily highs of {{convert|75|to|80|°F|°C|1|abbr=on|order=flip}}. This region has a longer, wetter rainy season than the Pacific lowlands, making erosion a problem on its steep slopes. Rugged terrain, poor soils, and low population density characterize the area as a whole, but the northwestern valleys are fertile and well settled.<ref name=gr1/> | |||
| ] countered the US-centered criticism in his book ''Give War a Chance'', saying "the unfair advantages of using state resources for party ends, about how Sandinista control of the transit system prevented ] supporters from attending rallies, how Sandinista domination of the army forced soldiers to vote for Ortega and how Sandinista bureaucracy kept $3.3 million of U.S. campaign aid from getting to UNO while Daniel Ortega spent millions donated by overseas people and millions and millions more from the Nicaraguan treasury ..."<ref name=ORourke1990>P. J. O'Rourke, "The Return of the Death of Communism: Nicaragua, February 1990", in ''Give War a Chance...'', New York: Grove Press; reprint edition (November 2003, ISBN 0-8021-4031-9).</ref> | |||
| The area has a cooler climate than the Pacific lowlands. About a quarter of the country's agriculture takes place in this region, with coffee grown on the higher slopes. ]s, ]s, ], ]s and ] are abundant in the ]s of the region. | |||
| Exit polls of Nicaraguans reported Chamorro's victory over Ortega was achieved with 55% majority.<ref name=Tulane>{{cite news|title=Was February 25 a 'triumph'? National Review v. 42|publisher=Tulane University|url=http://lal.tulane.edu/RESTRICTED/CABIB/nicabib_.txt|accessdate=2007-05-09|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060901190113/http://lal.tulane.edu/RESTRICTED/CABIB/nicabib_.txt|archivedate=September 1, 2006}}</ref> Violeta Chamorro was the first female ] of Nicaragua, and also the first woman to be popularly elected for this position in any American nation. Exit polling convinced Daniel Ortega that the election results were legitimate, and were instrumental in his decision to accept the vote of the people and step down rather than void the election. Ortega vowed that he would govern ''desde abajo'' (from below);<ref name=elmundo20061108>{{cite news|title=El Sandinista Daniel Ortega se convierte de nuevo en presidente de Nicaragua|date=2006-11-08|url=http://www.elmundo.es/elmundo/2006/11/08/internacional/1162945503.html|work=El Mundo|accessdate=2007-05-09|language=Spanish}}</ref> in other words due to his widespread control of institutions and Sandinista individuals in all government agencies, he would still be able to maintain control and govern even without being president. | |||
| Bird life in the forests of the central region includes ]s, ], ]s, ]s and ]. | |||
| Chamorro came to office with an economy in ruins. The ''per capita'' income of Nicaragua had been reduced by over 80% during the 1980s, and a huge government debt had ascended to US$12 billion, primarily due to the financial and social costs of the Contra war with the Sandinista-led government.<ref name=Dennis1993>{{cite news|last=Dennis|first=G|title=Social conditions of Nicaragua|date=December 1993|publisher=The Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0035)|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Much to the surprise of the U.S. and the contra forces, Chamorro did not dismantle the ], although the name was changed to the Nicaraguan Army. Chamorro's main contribution to Nicaragua was the ] of groups in the northern and central areas of the country. This provided the stability which the country had lacked for over ten years. | |||
| === Caribbean lowlands === | |||
| In the next election, the ], Daniel Ortega and the Sandinistas of the FSLN were again defeated, this time by ] of the ] (PLC). | |||
| This large ] region is irrigated by several large rivers and is sparsely populated. The area has 57% of the territory of the nation and most of its mineral resources. It has been heavily exploited, but much natural diversity remains. The ] is the largest river in Central America; it forms the border with Honduras. The Caribbean coastline is much more sinuous than its generally straight Pacific counterpart; lagoons and deltas make it very irregular.{{citation needed|date=November 2014}} | |||
| Nicaragua's ] is in the Atlantic lowlands, part of which is located in the municipality of ]; it protects {{convert|1800000|acre|km2|order=flip}} of ] forest – almost 7% of the country's area – making it the largest rainforest north of the ] in Brazil.<ref>{{cite news|title=Bosawas Bioreserve Nicaragua|url=http://www.abc.net.au/rn/scienceshow/stories/2006/1718459.htm|access-date=2007-05-25|archive-date=11 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511122659/http://www.abc.net.au/rn/scienceshow/stories/2006/1718459.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ], in 2008]] | |||
| The municipalities of ], ], and ], known as the "Mining Triangle", are located in the region known as the ], in the Caribbean lowlands. Bonanza still contains an active gold mine owned by HEMCO. Siuna and Rosita do not have active mines but panning for gold is still very common in the region.{{citation needed|date=November 2014}} | |||
| In ], the PLC again defeated the FSLN, with ] winning the Presidency. President Bolaños subsequently brought forward allegations of money laundering, theft and ] against former President Alemán. The ex-president was convicted and sentenced to 20 years in prison for ], ], and corruption.<ref name=alertnet>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Political profile|url=http://www.alertnet.org/printable.htm?URL=/db/cp/nicaragua.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Liberal members who were loyal to Alemán and also members of congress reacted angrily, and along with Sandinista parliament members, stripped the presidential powers of President Bolaños and his ministers, calling for his resignation and threatening ]. | |||
| Nicaragua's tropical east coast is very different from the rest of the country. The climate is predominantly tropical, with high temperature and high humidity. Around the area's principal city of Bluefields, English is widely spoken along with the official Spanish. The population more closely resembles that found in many typical Caribbean ports than the rest of Nicaragua.<ref>{{cite book|title=Alternative Histories of English|editor1 =Trudgill, Peter |editor2=Watts, Richard J.|isbn=9780415233569 |publisher=Routledge|year= 2002|page=35|quote=English-speaking protestants formed the majority of the population until about 1900...indigenous anglophones still form about 85 per cent of the population, which also includes non-anglophone Black Caribs...At least at the level of arolectal Whites, the accent is rhotic though obviously Caribbean....England established a protectorate over the local Miskito Indians, who the region is named after, and the area was a British dependency from 1740 to 1786. In Nicaragua the British founded the principal Miskito coast city of Bluefields... There are about 30,000 native speakers of English in this area of Nicaragua who look to Bluefields as their centre... The English of the anglophone Corn Islands is also typically Caribbean.}}</ref> | |||
| The Sandinistas alleged that their support for Bolaños was lost when U.S. Secretary of State ] told Bolaños to keep his distance from the FSLN.<ref name=Thompson2005>{{cite news|last=Thompson|first=G|title=U.S. fears comeback of an old foe in Nicaragua|date=2005-04-06|work=International Herald Tribune|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/04/05/news/nica.php|page=3|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> This "slow motion ]" was averted partially due to pressure from the Central American presidents, who vowed not to recognize any movement that removed Bolaños; the U.S., the OAS, and the ] also opposed the "slow motion ]".<ref name=bbc4296818>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua 'creeping coup' warning|date=2005-09-30|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/4296818.stm|work=BBC News|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> The proposed constitutional changes, to be introduced in 2005 against the Bolaños administration, were delayed until January 2007 after the entrance of the new government. One day before they were due to be enforced, the National Assembly postponed their enforcement until January 2008. | |||
| A great variety of birds can be observed including ]s, ]s, ]s and ]s. Other animal life in the area includes different species of ]s, ]s, white-tailed ] and ]s.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://vianica.com/animals|title=Nicaraguan Animal Guide|website=Vianica|access-date=August 17, 2018|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024123152/https://vianica.com/animals|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Before ], the ] passed a bill further restricting ] 52-0 (9 abstaining, 29 absent). President ] supported this measure, and signed the bill into law on 17 November 2006.<ref name=Frazier2006>{{cite news|last=Frazier|first=JB|title=Nicaraguan President Signs Abortion Ban|date=2006-11-18|url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/11/18/AR2006111800351.html|work=Washington Post|accessdate=2007-05-25}}</ref> As a result, Nicaragua is one of five countries in the world where ] is ] with no exceptions, along with Chile, ], ],<ref name=four>{{cite web|title=Nicaragua refuses to lift abortion ban|last=Boseley|first=S|publisher=The Guardian|date=2010-06-11}}</ref> and the ]. | |||
| === Flora and fauna === | |||
| ] took place on November 5, 2006. Daniel Ortega returned to the presidency with 37.99% of the vote. This percentage was enough to win the presidency outright, due to a change in electoral law which lowered the percentage requiring a runoff election from 45% to 35% (with a 5% margin of victory).<ref name=envio3439>{{cite news|title=Bolaños Will Move To The National Assembly After All|year=2006|url=http://www.envio.org.ni/articulo/3439|work=Envío Magazine|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Fauna of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] ("ravine-guard") is Nicaragua's national bird.]] | |||
| Nicaragua is home to a rich variety of plants and animals. Nicaragua is located in the middle of the Americas and this privileged location has enabled the country to serve as host to a great biodiversity. This factor, along with the weather and light altitudinal variations, allows the country to harbor 248 species of amphibians and reptiles, 183 species of mammals, 705 bird species, 640 fish species, and about 5,796 species of plants. | |||
| The region of great forests is located on the eastern side of the country. Rainforests are found in the ] and in the autonomous regions of ] and ]. This biome groups together the greatest biodiversity in the country and is largely protected by the ] in the south and the ] in the north. The Nicaraguan jungles, which represent about {{convert|2.4|e6acre|km2|order=flip|abbr=off}}, are considered the lungs of Central America and comprise the second largest-sized rainforest of the Americas.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Rogers|first1=Tim|title=In Latin America's Second Largest Rainforest, an Indigenous Tribe Fights for Its Land|url=https://world.time.com/2013/05/15/the-battle-over-latin-americas-second-largest-rainforest/|access-date=August 3, 2017|magazine=Time|date=May 15, 2013|archive-date=26 April 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180426220455/http://world.time.com/2013/05/15/the-battle-over-latin-americas-second-largest-rainforest/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Connor|first1=Liz|title=10 reasons why you should visit Nicaragua|url=https://www.standard.co.uk/lifestyle/travel/10-reasons-why-you-should-visit-nicaragua-in-2017-a3398571.html|access-date=August 3, 2017|work=Evening Standard|date=November 17, 2016|archive-date=5 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201205060812/https://www.standard.co.uk/lifestyle/travel/10-reasons-why-you-should-visit-nicaragua-in-2017-a3398571.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| There are currently 78 protected areas in Nicaragua, covering more than {{convert|22000|km2}}, or about 17% of its landmass. These include ]s and ]s that shelter a wide range of ]s. There are more than 1,400 animal species classified thus far in Nicaragua. Some 12,000 species of plants have been ] thus far in Nicaragua, with an estimated 5,000 species not yet classified.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://centralamerica.com/nicaragua/parks/nationalpark.htm|title=National Parks and Protected Areas of Nicaragua|access-date=17 February 2016|archive-date=2 August 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170802185044/http://centralamerica.com/nicaragua/parks/nationalpark.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The ] is a species of shark that can survive for an extended period of time in fresh water. It can be found in ] and the ], where it is often referred to as the "Nicaragua shark".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nature.org/wherewework/centralamerica/nicaragua/|title=Nicaragua|publisher=The Nature Conservancy|access-date=17 February 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070405074947/http://www.nature.org/wherewework/centralamerica/nicaragua/|archive-date=5 April 2007|url-status=dead|df=dmy-all}}</ref> Nicaragua has recently banned freshwater fishing of the Nicaragua shark and the ] in response to the declining populations of these animals.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.underwatertimes.com/news.php?article_id=05437210968|title=Nicaragua bans freshwater shark fishing amid dwindling population numbers|work=UnderwaterTimes.com|access-date=17 February 2016|archive-date=24 February 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160224085133/http://www.underwatertimes.com/news.php?article_id=05437210968|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| == Government == | |||
| {{Main|Politics of Nicaragua}} | {{Main|Politics of Nicaragua}} | ||
| {{more citations needed|section|date=September 2017}}<!--only 2 footnotes in entire section--> | |||
| ] with then ] ] in ] in 2008]] | |||
| Politics of Nicaragua takes place in a framework of a ] ] republic, whereby the ] is both ] and ], and of a ]. ] is exercised by the government. ] is vested in both the government and the ]. The ] makes up the third branch of government. | |||
| Between 2007 and 2009, Nicaragua's major political parties discussed the possibility of going from a presidential system to a parliamentary system. Their reason: there would be a clear differentiation between the ] (prime minister) and the ] (president). Nevertheless, it was argued that the true reason for this proposal was to find a legal way for President Ortega to stay in power after January 2012, when his second and last government period was expected to end. Ortega was ], and ]; both elections were tainted by credible reports of large-scale fraud, voter intimidation, and politically motivated arrests of opposition party leaders. Independent observers were barred from the polls. The ], United States, and European Union all described the 2021 election as a "sham" due to these issues.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Sesin |first1=Carmen |title='Rigged': Criticism mounts of Nicaragua's 'sham' elections under Ortega |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/news/latino/rigged-criticism-mounts-nicaraguas-sham-elections-ortega-rcna4820 |access-date=7 May 2022 |publisher=NBC News |date=8 November 2021 |archive-date=12 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230512031653/http://www.nbcnews.com/news/latino/rigged-criticism-mounts-nicaraguas-sham-elections-ortega-rcna4820 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Blinken |first1=Anthony |title=New Sanctions Following Sham Elections in Nicaragua |url=https://www.state.gov/new-sanctions-following-sham-elections-in-nicaragua/ |publisher=White House |access-date=7 May 2022 |archive-date=23 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220523053054/https://www.state.gov/new-sanctions-following-sham-elections-in-nicaragua/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Politics of Nicaragua takes place in a framework of a ] ] republic, whereby the ] is both ] and ], and of a ]. ] is exercised by the government. ] is vested in both the ] and the ]. The ] is independent of the executive and the legislature. | |||
| Since ]'s election in 2006, liberal democratic norms and individual rights in practice have deteriorated. Parties other than the ruling ] have been repressed through arbitrary arrest and detention of opposition candidates and activists. Most government jobs ''de facto'' require membership in the FSLN. Opposition media has been repressed through arrests of journalists and seizure of broadcasting and printing materials.<ref>{{cite web |title=Freedom in the World 2024: Nicaragua |url=https://freedomhouse.org/country/nicaragua/freedom-world/2024 |publisher=Freedom House |access-date=8 August 2024|archive-date=19 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240619060319/https://freedomhouse.org/country/nicaragua/freedom-world/2024 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Between 2007–2009, Nicaragua's major political parties discussed the possibility of going from a presidential system to a parliamentary system. Their reason: there would be a clear differentiation between the ] (Prime Minister) and the ] (President). Nevertheless, it was later known the true reason behind this proposal was to find a legal way for current President Ortega to stay in power after January 2012 (this is when his second and last government period ends). | |||
| === Foreign relations === | |||
| ===Presidential election=== | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of Nicaragua}} | |||
| '''Cid Gallup''' | |||
| Nicaragua pursues an independent foreign policy. ] with Colombia over the ] and ] and with Costa Rica over a boundary dispute involving the ]. | |||
| On 12 October 2022, Nicaragua voted against condemning ] for ].<ref>{{cite magazine |title=A New U.N. Vote Shows Russia Isn't as Isolated as the West May Like to Think |url=https://time.com/6222005/un-vote-russia-ukraine-allies/ |magazine=] |date=13 October 2022 |access-date=2 December 2023 |archive-date=11 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230811053026/https://time.com/6222005/un-vote-russia-ukraine-allies/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| !colspan=2|Party | |||
| !Candidate | |||
| !January 2011<ref>http://www.nicanet.org/?p=1000</ref> | |||
| !May 2011<ref>http://incakolanews.blogspot.com/2011/05/nicaragua-polling-for-2011-presidential.html</ref> | |||
| !September 2011<ref>http://www.lajornadanet.com/diario/archivo/2011/septiembre/9/1.php</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |bgcolor=darkblue| | |||
| |FSLN | |||
| |] | |||
| |36% | |||
| |38% | |||
| |44% | |||
| |- | |||
| |bgcolor=yellow| | |||
| |PLI | |||
| |] | |||
| |17% | |||
| |28% | |||
| |32% | |||
| |- | |||
| |bgcolor=red| | |||
| |PLC | |||
| |] | |||
| |23% | |||
| |14% | |||
| |13% | |||
| |- | |||
| |bgcolor=green| | |||
| |Other | |||
| |''Other parties'' | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |4% | |||
| |1% | |||
| |- | |||
| |bgcolor=gray| | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |''No answer'' | |||
| |24% | |||
| |16% | |||
| |10% | |||
| |} | |||
| Since 2019, ] have been rated ]. | |||
| ==Military== | |||
| {{Main|Military of Nicaragua}} | |||
| === Military === | |||
| The ] consists of various military contingencies. Nicaragua has an ], ] and ]. There are roughly 14,000 active duty personnel, which is much less compared to the numbers seen during the ]. Although the army has had a rough military history, a portion of its forces, which were known as the ] became integrated with what is now the ]. In essence, the police became a ]. The National Police of Nicaragua are rarely, if ever, labeled as a ]. The other elements and manpower that were not devoted to the National Police were sent over to cultivate the new Army of Nicaragua. The Nicaraguan army often uses monkey skins to cover their weapons when in combat. This works as a great camouflage for the soldiers. | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan Armed Forces}} | |||
| The ] consist of various military contingents. Nicaragua has an ], ] and an ]. There are roughly 14,000 active duty personnel, which is much less compared to the numbers seen during the ]. Although the army has had a rough military history, a portion of its forces, which were known as the ], became integrated with what is now the ]. In essence, the police became a '']''. The National Police of Nicaragua are rarely, if ever, labeled as a '']''. The other elements and manpower that were not devoted to the national police were sent over to cultivate the new Army of Nicaragua. | |||
| The age to serve in the armed forces is 17 and ] is not imminent. As of |
The age to serve in the armed forces is 17 and ] is not imminent. {{As of|2006}}, the military budget was roughly 0.7% of Nicaragua's expenditures. | ||
| In 2017, Nicaragua signed the UN ].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |title=Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons |publisher=United Nations Treaty Collection |date=7 July 2017 |access-date=2 December 2023 |archive-date=6 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190806220546/https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Departments and municipalities== | |||
| {{Main|Departments of Nicaragua|Municipalities of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] | |||
| === Law enforcement === | |||
| Nicaragua is a ] republic. For administrative purposes it is divided into 15 ] (''departamentos'') and two self-governing regions (autonomous communities) based on the Spanish model. The departments are then subdivided into 153 municipios (]). The two autonomous regions are 'Región Autónoma Atlántico Norte' | |||
| {{main|Law enforcement in Nicaragua}} | |||
| and 'Región Autónoma Atlántico Sur', often referred to as ''RAAN'' and ''RAAS'', respectively; until they were granted autonomy in 1985 they formed the single department of ].<ref name=stellent>{{cite news|title=Background and socio-economic context|url=http://documents.wfp.org/stellent/groups/public/documents/vam/wfp073961.pdf|format=PDF|page=9|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The ] Force (in Spanish: La Policía Nacional Nicaragüense) is the national police of Nicaragua. The force is in charge of regular police functions and, at times, works in conjunction with the Nicaraguan military, making it an indirect and rather subtle version of a gendarmerie.{{citation needed|date=July 2015}} However, the Nicaraguan National Police work separately and have a different established set of norms than the nation's military.{{citation needed|date=July 2015}} According to a recent US Department of State report, corruption is endemic, especially within law enforcement and the judiciary, and arbitrary arrests, torture, and harsh prison conditions are the norm.<ref name="Nicaragua">{{Cite web|title=Nicaragua|url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2019-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/nicaragua/|access-date=2020-06-22|website=United States Department of State|language=en-US|archive-date=30 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231030023818/https://www.state.gov/reports/2019-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/nicaragua/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua has one of the lowest intentional homicide rates in Central America, according to the ], with a homicide rate of 11 per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2021.<ref name="Intentional homicides (per 100,000 people) - Nicaragua">{{Cite web|title=Intentional homicides (per 100,000 people) - Nicaragua|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/VC.IHR.PSRC.P5?locations=NI|access-date=22 May 2024|archive-date=22 May 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240522045626/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/VC.IHR.PSRC.P5?locations=NI|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {|style="background:none;" | |||
| === Administrative divisions === | |||
| {{Main|Departments of Nicaragua|}} | |||
| Nicaragua is a ] republic. For administrative purposes it is divided into 15 ] (''departamentos'') and two self-governing regions (autonomous communities) based on the Spanish model. The departments are then ] (municipalities). The two autonomous regions are the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region | |||
| and South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region, often referred to as RACCN and RACCS, respectively.<ref>{{cite news|title=Background and socio-economic context |url=http://documents.wfp.org/stellent/groups/public/documents/vam/wfp073961.pdf |page=9 |access-date=2007-05-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061015212525/http://documents.wfp.org/stellent/groups/public/documents/vam/wfp073961.pdf |archive-date=October 15, 2006 }}</ref> | |||
| {| | |||
| |- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| |<!--First column:--> | |<!--First column:--> | ||
| Line 306: | Line 330: | ||
| |'''1'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''1'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''2'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''3'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''3'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''4'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''4'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''5'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''5'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''6'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''6'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''7'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''7'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''8'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''8'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''9'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''{{Spaces|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''9'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''{{Spaces|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |} | |||
| |<!--Second column:--> | |||
| {|class="wikitable" | |||
| |||{{Spaces|1}}'''Department'''||{{Smaller|'''Capital city'''}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''10'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''{{nbsp|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''10'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''{{nbsp|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| Line 330: | Line 350: | ||
| |'''11'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''11'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''12'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''12'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''13'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''13'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| Line 336: | Line 356: | ||
| |'''14'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''14'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''15'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''15'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''16'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''16'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''17'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | |'''17'''||]{{Spaces|1}}'''{{Smaller|]}}'''||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| == |
== Economy == | ||
| {{Main|Economy of Nicaragua}} | |||
| {{Main|Geography of Nicaragua|Climate of Nicaragua}} {{See also|Volcanoes of Nicaragua|Wildlife of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] per capita in Nicaragua]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is one of the Nicaragua's largest exports. It is grown in ], ], ], ], and ], and exported worldwide through North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. ] and ] buy Nicaraguan coffee.]] | |||
| Nicaragua occupies a landmass of {{convert|130967|km²|0|abbr=on}}, comparable to that of Greece or the state of ]. It lies between latitudes ] and ], and longitudes ] and ]. | |||
| Nicaragua is one of the poorest countries in the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/LACEXT/NICARAGUAEXTN/0,,contentMDK:22255024~pagePK:1497618~piPK:217854~theSitePK:258689,00.html|title=Nicaragua - Country Brief|website=web.worldbank.org|access-date=18 March 2010|archive-date=3 October 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141003113427/http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/LACEXT/NICARAGUAEXTN/0,,contentMDK:22255024%7EpagePK:1497618%7EpiPK:217854%7EtheSitePK:258689,00.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Rank Order – GDP – per capita (PPP)|publisher=CIA World Factbook|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2004rank.html|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=24 April 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130424075526/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2004rank.html|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Social indicators: Per capita GDP|publisher=United Nations|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/socind/inc-eco.htm|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=30 April 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070430044658/http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/socind/inc-eco.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Its gross domestic product (GDP) in ] (PPP) in 2008 was estimated at US$17.37 billion.<ref name=cia>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua|publisher=CIA World Factbook|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua/|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=20 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210320071255/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> Agriculture represents 15.5% of GDP, the highest percentage in Central America.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/214.html#NU|title=Field Listing :: GDP - composition, by sector of origin — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency|website=www.cia.gov|access-date=2019-05-05|archive-date=11 November 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201111214540/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/214.html#NU|url-status=dead}}</ref> Remittances account for over 15% of the Nicaraguan GDP. Close to one billion dollars are sent to the country by Nicaraguans living abroad.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.migrationinformation.org/Feature/display.cfm?id=393|title=Migration Information Source – Remittance Trends in Central America|publisher=Migrationinformation.org|access-date=2010-06-26|date=April 2006|archive-date=10 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140210034140/http://www.migrationinformation.org/Feature/display.cfm?ID=393|url-status=live}}</ref> The economy grew at a rate of about 4% in 2011.<ref name=cia/> By 2019, given restrictive taxes and a civil conflict, it recorded a negative growth of - 3.9%; the International Monetary Fund forecast for 2020 is a further decline of 6% due to COVID-19.<ref>{{cite web |publisher=Nordea |date=2020 |title=Nicaragua: Economic Outline |url=https://www.nordeatrade.com/en/explore-new-market/nicaragua/economy |url-access=subscription |access-date=22 June 2020 |archive-date=25 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200625222218/https://www.nordeatrade.com/en/explore-new-market/nicaragua/economy |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The restrictive tax measures put in place in 2019 and a political crisis over social security negatively affected the country's weak public spending and investor confidence in sovereign debt. According to the update IMF forecasts from 14 April 2020, due to the COVID-19 outbreak, GDP growth is expected to fall to -6% in 2020.{{citation needed|date=April 2021}}{{update inline|date=April 2021}} | |||
| Nearly one fifth of the territory is designated as ] like national parks, nature reserves, and biological reserves. The country is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ]ly, Nicaragua is surrounded by the ], an ] ] underlying Central America and the ]. Since Central America is a major ] zone, Nicaragua hosts most of the ]. | |||
| According to the ], 48% of the population of Nicaragua live below the poverty line,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.pnud.org.ni/noticias/343 |title=Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo – Noticias – La pobreza se arraiga en el país |publisher=Pnud.org.ni |access-date=2010-06-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511101524/http://www.pnud.org.ni/noticias/343 |archive-date=May 11, 2011 }}</ref> 79.9% of the population live with less than $2 per day,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hdrstats.undp.org/indicators/24.html |title=Human Development Report 2009 – Countries' shares of total stock of migrants in Africa (%) |publisher=Hdrstats.undp.org |access-date=2010-06-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090221190342/http://hdrstats.undp.org/indicators/24.html |archive-date=2009-02-21 }}</ref> According to UN figures, 80% of the ] (who make up 5% of the population) live on less than $1 per day.<ref>{{cite news|last=Silva |first=JA |title=NICARAGUA: Name and Identity for Thousands of Indigenous Children |url=http://ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=43760 |work=IPS |access-date=2008-09-12 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080911133236/http://www.ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=43760 |archive-date=September 11, 2008 }}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua has three distinct geographical regions: the Pacific Lowlands, fertile valleys which the Spanish colonists settled, the ] (North-Central Highlands), and the Mosquito Coast (Atlantic Lowlands). The low plains of the Atlantic Coast are 60 miles wide in areas. They have long been exploited for their natural resources. | |||
| According to the World Bank, Nicaragua ranked as the 123rd out of 190 best economy for starting a business.<ref>{{cite news|title=Economy Rankings: Doing Business|publisher=World Bank|url=http://www.doingbusiness.org/rankings/|access-date=2014-01-04|archive-date=10 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201210072629/https://www.doingbusiness.org/rankings|url-status=dead}}</ref> In 2007, Nicaragua's economy was labelled "62.7% free" by the conservative ] ], with high levels of fiscal, government, labor, investment, financial, and trade freedom.<ref>{{cite news|title=Index Of Economic Freedom: Nicaragua|url=http://www.heritage.org/research/features/index/country.cfm?id=Nicaragua|work=Heritage.org|access-date=2007-11-02|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071026050611/http://www.heritage.org/research/features/index/country.cfm?ID=Nicaragua|archive-date=2007-10-26}}</ref> It ranked as the 61st ], and 14th (of 29) in the Americas. Nicaragua was ranked 124th in the ] in 2024.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/|title=Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship|access-date=2024-10-22|author=]|year=2024|isbn=978-92-805-3681-2|doi= 10.34667/tind.50062|website=www.wipo.int|location=Geneva|page=18}}</ref> | |||
| ===Pacific Lowlands=== | |||
| ] located on ].]]Located in the west of the country, these lowlands consist of a broad, hot, fertile plain. Punctuating this plain are several large volcanoes of the ] mountain range, including ] just outside Granada, and ] near León. The lowland area runs from the ] to Nicaragua's Pacific border with Costa Rica south of ]. Lake Nicaragua is the largest freshwater lake in Central America (20th largest in the world),<ref name=factmonster>{{cite news|title=Large Lakes of the World|url=http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0001777.html|accessdate=2007-05-25}}</ref> and is home to some of the world's only freshwater sharks (]).<ref name=wherewework>{{cite news|title=The Nature Conservancy in Nicaragua|url=http://www.nature.org/wherewework/centralamerica/nicaragua/|accessdate=2007-05-25}}</ref> The Pacific lowlands region is the most populous, with over half of the nation's population. The capital city of Managua is the most populous and is the only city with over 1.5 million inhabitants. | |||
| In March 2007, ] and Nicaragua signed an agreement to write off 30.6 million dollars, which was borrowed by the Nicaraguan government in the 1980s.<ref>{{cite news|title=Poland forgives nearly 31 million dollars of debt owed by Nicaragua|date=2007-03-21|url=http://english.people.com.cn/200703/31/eng20070331_362713.html|work=People's Daily Online|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=16 January 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116214745/http://english.people.com.cn/200703/31/eng20070331_362713.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Inflation reduced from 33,500% in 1988 to 9.45% in 2006, and the foreign debt was cut in half.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua:Economy|url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|work=U.S. State Department|access-date=2007-11-02|archive-date=21 January 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170121153233/https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The eruptions of western Nicaragua's 40 volcanoes, many of which are still active, have sometimes devastated settlements but also have enriched the land with layers of fertile ash. The geologic activity that produces vulcanism also breeds powerful ]. Tremors occur regularly throughout the Pacific zone, and earthquakes have nearly destroyed the capital city, Managua, more than once.<ref name=grolier1> ''Encyclopedia Americana''. 2009. Grolier Online. 20 Nov. 2009 </ref> | |||
| Nicaragua is primarily an agricultural country; agriculture constitutes 60% of its total exports which annually yield approximately US$300 million.<ref>{{cite news|title=General Information – Nicaragua: Economy|url=http://centralamerica.com/nicaragua/info/general.htm#economy|access-date=2014-01-04|archive-date=2011-08-28|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110828041455/http://centralamerica.com/nicaragua/info/general.htm#economy|url-status=dead}}</ref> Nearly two-thirds of the coffee crop comes from the northern part of the central highlands, in the area north and east of the town of Estelí.<ref name=gr1/> Tobacco, grown in the same northern highlands region as coffee, has become an increasingly important cash crop since the 1990s, with annual exports of leaf and cigars in the neighborhood of $200 million per year.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Tobacco_Sector_Exceeds_Expectations|title=Tobacco Sector Exceeds Expectations – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal|website=www.centralamericadata.com|access-date=22 December 2017|archive-date=22 April 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220422003628/https://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Tobacco_Sector_Exceeds_Expectations|url-status=live}}</ref> Soil erosion and pollution from the heavy use of pesticides have become serious concerns in the cotton district. Yields and exports have both been declining since 1985.<ref name=gr1/> Today most of Nicaragua's bananas are grown in the northwestern part of the country near the port of Corinto; sugarcane is also grown in the same district.<ref name=gr1/> ], a root crop somewhat similar to the potato, is an important food in tropical regions. Cassava is also the main ingredient in tapioca pudding.<ref name=gr1/> Nicaragua's agricultural sector has benefited because of the country's strong ties to ]. It is estimated that Venezuela will import approximately $200 million in agricultural goods.<ref>{{cite web|last=Sánchez|first=E|url=http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Nicaragua_Plans_to_Sell_Over_200_Million_to_Venezuela/925161|title=Nicaragua Plans to Sell Over $200 Million to Venezuela – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal|publisher=CentralAmericaData|date=2010-03-29|access-date=2010-06-26|archive-date=11 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511101523/http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Nicaragua_Plans_to_Sell_Over_200_Million_to_Venezuela/925161|url-status=live}}</ref> In the 1990s, the government initiated efforts to diversify agriculture. Some of the new export-oriented crops were peanuts, ], melons, and onions.<ref name=gr1/> | |||
| Most of the Pacific zone is '']'', the "hot land" of tropical Spanish America at elevations under {{convert|2000|ft|m|0}}. Temperatures remain virtually constant throughout the year, with highs ranging between {{convert|85|and|90|°F|°C|1|abbr=on}}. After a dry season lasting from November to April, rains begin in May and continue to October, giving the Pacific Lowlands {{convert|40|to|60|in|mm|0}} of precipitation. Good soils and a favorable climate combine to make western Nicaragua the country's economic and demographic center. The southwestern shore of Lake Nicaragua lies within {{convert|15|mi|km|0}} of the Pacific Ocean. Thus the lake and the San Juan River were often proposed in the 19th century as the longest part of a canal route across the Central American isthmus. Canal proposals were periodically revived in the 20th and 21st centuries.<ref name=grolier1/><ref name=american>{{cite web|author=|title=TED CASE: Nicaragua Canal Proposal|work=|publisher=american.edu|year=|url=http://www1.american.edu/TED/nicanal.htm|accessdate=2011-07-16}}</ref> Roughly a century after the opening of the ], the prospect of a Nicaraguan ] remains a topic of interest.<ref name=Munoz2001/><ref name=EPN2009/><ref name=Alvarez2008/><ref name=Hidalgo2010/> | |||
| Fishing boats on the Caribbean side bring shrimp as well as lobsters into processing plants at Puerto Cabezas, Bluefields, and Laguna de Perlas.<ref name=gr1/> A turtle fishery thrived on the Caribbean coast before it collapsed from ].<ref name=gr1/> | |||
| In addition to its beach and resort communities, the Pacific Lowlands contains most of Nicaragua's Spanish colonial architecture and artifacts. Cities such as León and ] abound in colonial architecture; founded in 1524, Granada is the oldest colonial city in the Americas.<ref name=White2004>{{cite news|last=White|first=RL|title=Pittsburghers find once war-ravaged country is a good place to invest|date=2004-08-24|url=http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/04237/366377.stm|work=Post Gazette|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> | |||
| Mining is becoming a major industry in Nicaragua,<ref>Dan Oancea: {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116212655/http://magazine.mining.com/Issues/0901/MiningCentralAmerica.pdf |date=January 16, 2013 }}</ref> contributing less than 1% of gross domestic product (GDP). Restrictions are being placed on lumbering due to increased environmental concerns about destruction of the rain forests. But lumbering continues despite these obstacles; indeed, a single hardwood tree may be worth thousands of dollars.<ref name=gr1/> | |||
| ===North-Central Highlands=== | |||
| The Central Highlands are a significantly less populated and economically developed area located in the north but narrow southeastward between Lake Nicaragua and the Caribbean. Forming the country's ], or "temperate land", at elevations between {{convert|2000|and|5000|ft|m|0}}, the highlands enjoy mild temperatures with daily highs of <br />{{convert|75|to|80|°F|°C|1|abbr=on}}. This region has a longer, wetter rainy season than the Pacific Lowlands, making erosion a problem on its steep slopes. Rugged terrain, poor soils, and low population density characterize the area as a whole, but the northwestern valleys are fertile and well settled.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| During the war between the US-backed Contras and the government of the ] in the 1980s, much of the country's infrastructure was damaged or destroyed.<ref>{{cite news|last=Tartter|first=JR|title=The Nicaraguan Resistance|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/D?cstdy:10:./temp/~frd_famN::|work=Country Studies|access-date=2007-11-02|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024123358/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/D?cstdy:10:./temp/~frd_famN::|url-status=live}}</ref> Transportation throughout the nation is often inadequate. For example, it was until recently impossible to travel all the way by highway from Managua to the Caribbean coast. A new road between Nueva Guinea and Bluefields was completed in 2019 and allows regular bus service to the capital.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.bnamericas.com/en/news/nicaragua-completes-bluefields-nueva-guinea-highway |title=Nicaragua completes Bluefields-Nueva Guinea highway |work=Bnamericas |date=2 May 2019 |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=7 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220407073143/https://www.bnamericas.com/en/news/nicaragua-completes-bluefields-nueva-guinea-highway |url-status=live }}</ref> The Centroamérica power plant on the ] in the Central highlands has been expanded, and other hydroelectric projects have been undertaken to help provide electricity to the nation's newer industries.<ref name=gr1/> Nicaragua has long been considered as a possible site for a ] that could supplement the Panama Canal, connecting the Caribbean Sea (and therefore the Atlantic Ocean) with the Pacific Ocean. | |||
| The area has a cooler climate than the Pacific Lowlands. About a quarter of the country's agriculture takes place in this region, with ] grown on the higher slopes. ]s, ]s, ], ]s and ] are abundant in the ]s of the region. | |||
| Nicaragua's minimum wage is among the lowest in the Americas and in the world.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130308021701/http://www.pbs.org/now/politics/cafta.pdf |date=8 March 2013 }}. (PDF). Retrieved on 2012-05-02.</ref><ref>Raphaelidis, Leia . Multinational Monitor. September 1, 1997</ref><ref>Sarah Anderson . wakeupwalmart.com. April 15, 2005</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://asiapacific.anu.edu.au/frontpage|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100705112448/http://rspas.anu.edu.au/~anita/pdf/AChancp461.pdf|url-status=dead|title=Home|first=ANU College of Asia & the Pacific|last=Dean|archive-date=July 5, 2010|website=ANU College of Asia & the Pacific|access-date=3 May 2019}}</ref> Remittances are equivalent to roughly 15% of the country's gross domestic product.<ref name=cia/> Growth in the ''maquila'' sector slowed in the first decade of the 21st century with rising competition from Asian markets, particularly China.<ref name=gr1/> Land is the traditional basis of wealth in Nicaragua, with great fortunes coming from the export of staples such as coffee, cotton, beef, and sugar. Almost all of the upper class and nearly a quarter of the middle class are substantial landowners. | |||
| Bird life in the forests of the central region includes ], ], ]s, ]s and ]. | |||
| ] is a common bird in Nicaragua´s Rainforests]] | |||
| A 1985 government study classified 69.4 percent of the population as poor on the basis that they were unable to satisfy one or more of their basic needs in housing, sanitary services (water, sewage, and garbage collection), education, and employment. The defining standards for this study were very low; housing was considered substandard if it was constructed of discarded materials with dirt floors or if it was occupied by more than four persons per room. | |||
| ===Caribbean Lowlands=== | |||
| This large ] region is irrigated by several large rivers and is sparsely populated. The area has 57% of the territory of the nation and most of its mineral resources. It has been heavily exploited, but much natural diversity remains. The ] is the largest river in Central America; it forms the border with Honduras. The Caribbean coastline is much more sinuous than its generally straight Pacific counterpart; lagoons and deltas make it very irregular. | |||
| Rural workers are dependent on agricultural wage labor, especially in coffee and cotton. Only a small fraction hold permanent jobs. Most are migrants who follow crops during the harvest period and find other work during the off-season. The "lower" peasants are typically smallholders without sufficient land to sustain a family; they also join the harvest labor force. The "upper" peasants have sufficient resources to be economically independent. They produce enough surplus, beyond their personal needs, to allow them to participate in the national and world markets. | |||
| Nicaragua's ] is located in the Atlantic lowlands; it protects {{convert|1800000|acre|ha|0|lk=on}} of ] forest – almost seven percent of the country's area – making it the largest rainforest north of the ] in Brazil.<ref name=Bosawas>{{cite news|title=Bosawas Bioreserve Nicaragua|url=http://www.abc.net.au/rn/scienceshow/stories/2006/1718459.htm|accessdate=2007-05-25}}</ref> | |||
| ] at night]] | |||
| Nicaragua's ] east coast is very different from the rest of the country. The climate is predominantly tropical, with high temperature and high humidity. Around the area's principal city of Bluefields, English is widely spoken along with the official Spanish. The population more closely resembles that found in many typical Caribbean ports than the rest of Nicaragua. | |||
| The urban lower class is characterized by the informal sector of the economy. The informal sector consists of small-scale enterprises that utilize traditional technologies and operate outside the legal regime of labor protections and taxation. Workers in the informal sector are self-employed, unsalaried family workers or employees of small-enterprises, and they are generally poor. | |||
| Nicaragua's informal sector workers include tinsmiths, mattress makers, seamstresses, bakers, shoemakers, and carpenters; people who take in laundry and ironing or prepare food for sale in the streets; and thousands of peddlers, owners of small businesses (often operating out of their own homes), and market stall operators. Some work alone, but others labor in the small talleres (workshops/factories) that are responsible for a large share of the country's industrial production. Because informal sector earnings are generally very low, few families can subsist on one income.<ref name="Nicaragua – SOCIETY">{{cite web |title=Nicaragua – SOCIETY |quote=CITATION: Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. The Country Studies Series. Published 1988–1999. |url=http://www.mongabay.com/reference/country_studies/nicaragua/GEOGRAPHY.html |access-date=2014-05-03 |website=Mongabay.com |location=Menlo Park, CA, US |publisher=] |archive-date=27 April 2013 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130427041957/http://www.mongabay.com/reference/country_studies/nicaragua/GEOGRAPHY.html |url-status=live }}<br />Original source: {{cite book |title=Nicaragua |series=Country Studies |first=Tim |last=Merrill |publisher=], U.S. ] |access-date=2014-05-03 |url=https://archive.org/details/nicaraguacountry00merr |location=Washington, DC |date=1994 |website=lcweb2.loc.gov |isbn=978-0-8444-0831-6 |oclc=30623751 }}</ref> Like most Latin American nations Nicaragua is also characterized by a very small upper-class, roughly 2% of the population, that is very wealthy and wields the political and economic power in the country that is not in the hands of foreign corporations and private industries. These families are oligarchical in nature and have ruled Nicaragua for generations and their wealth is politically and economically horizontally and vertically integrated. | |||
| A great variety of birds can be observed including ]s, ], ]s, ]s and ]s. Animal life in the area includes different species of ]s, ]s, white-tailed ] and ]s. | |||
| Nicaragua is currently a member of the ], also known as ALBA. ALBA has proposed creating a new currency, the ], for use among its members. In essence, this means that the Nicaraguan córdoba will be replaced with the Sucre. Other nations that will follow a similar pattern include: ], Ecuador, ], Honduras, ], Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2009/12/13/nacionales/10246 |title=Primera prueba del sucre en enero – LA PRENSA — EL Diario de los Nicaragüenses |publisher=Laprensa.com.ni |date=2010-06-16 |access-date=2010-06-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100116202832/http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2009/12/13/nacionales/10246 |archive-date=2010-01-16 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Flora and fauna== | |||
| ] is the largest ] in Nicaragua]] | |||
| The '''Flora and Fauna of Nicaragua''' is characterized by a very high level of ]. Much of ]'s wildlife lives in ]. There are currently 78 protected areas in Nicaragua, covering more than {{convert|22000|km2|sp=us}}, or about 17% of its landmass. These protected areas encompass a wide variety of ]s, including ]s, lakes, mountains, and volcanoes throughout the country. For example, ] covers {{convert|7300|km2|sp=us}}, making it the second largest rainforest in the ] after the ] in ]. | |||
| Nicaragua is considering construction of a canal linking the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean, which President Daniel Ortega has said will give Nicaragua its "economic independence".<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-25607757|title=Nicaragua canal construction 'will not begin until 2015'|publisher=bbc.co.uk|date=2014-01-04|access-date=2014-01-04|newspaper=BBC News|archive-date=5 January 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140105010930/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-25607757|url-status=live}}</ref> Scientists have raised concerns about environmental impacts, but the government has maintained that the canal will benefit the country by creating new jobs and potentially increasing its annual growth to an average of 8% per year.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Howard|first1=Brian Clark|title=Nicaraguan Canal Could Wreck Environment, Scientists Say|url=https://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/02/140220-nicaraguan-canal-environment-conservation/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140302024223/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/02/140220-nicaraguan-canal-environment-conservation/|url-status=dead|archive-date=2 March 2014|website=National Geographic|publisher=National Geographic Society|access-date=26 May 2018|date=22 February 2014}}</ref> The project was scheduled to begin construction in December 2014,<ref>{{cite magazine|url=http://www.nation.com.pk/business/13-Jan-2014/nicaragua-chinese-tycoon-say-canal-work-to-start-in-2014|title=Nicaragua, Chinese tycoon say canal work to start in 2014|magazine=The Nation|date=2014-01-13|access-date=2014-01-14|archive-date=13 January 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140113073406/http://www.nation.com.pk/business/13-Jan-2014/nicaragua-chinese-tycoon-say-canal-work-to-start-in-2014|url-status=live}}</ref> however the ] has yet to be started.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://panampost.com/adriana-peralta/2017/05/08/four-years-later-china-backed-nicaragua-canal-struggles-to-take-off-the-ground/ |title=Four Years Later, China-Backed Nicaragua Canal Struggles to Take Off the Ground |date=2017-05-08 |website=PanAm Post |language=en-US |access-date=2017-12-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170823160624/https://panampost.com/adriana-peralta/2017/05/08/four-years-later-china-backed-nicaragua-canal-struggles-to-take-off-the-ground/ |archive-date=2017-08-23 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Mammals=== | |||
| ] monkey]] | |||
| === Tourism === | |||
| Nicaragua is home to several species of ]s, including the ], which is currently listed by the ] (IUCN) as an ].<ref name=iucn>{{IUCN2008|assessors=Cuarón, A.D., Morales, A., Shedden, A., Rodriguez-Luna, E. & de Grammont, P.C.|year=2008|id=2279|title=Ateles geoffroyi|downloaded=7 October 2008}} Database entry includes justification for why this species is endangered</ref> The ] is the largest ] that is ] to Nicaragua. Other species include the ], ], ], and ]. There are a number of unusual mammals found in Nicaragua, including the ], ] (lesser anteater), and two species of ].<ref name="nicaragua.com"></ref> | |||
| {{Main|Tourism in Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] ] docked near the beach at ] in southern Nicaragua]] | |||
| ], called "Huellas de Acahualinca" and preserved in volcanic mud near ]]] | |||
| ], a nature reserve located between the departments of ] and ]]] | |||
| ], tropical islands in ], which are home to 76 bird species and are a growing ecotourism destination]] | |||
| By 2006, tourism became the second-largest industry in Nicaragua.<ref>{{cite news|title=Travel And Tourism in Nicaragua|publisher=Euromonitor International|url=http://www.euromonitor.com/Travel_And_Tourism_in_Nicaragua|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=14 June 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100614011500/http://www.euromonitor.com/Travel_And_Tourism_in_Nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> Previously, tourism had grown about 70% nationwide during a period of 7 years, with rates of 10%–16% annually.<ref name=C2>{{cite news |first=G |last=Alemán |title=Turismo en Nicaragua: aportes y desafios parte I |url=http://www.canal2tv.com/Noticias/Marzo%202007/turismo%20con%20gran%20empuje%20en%20Nicaragua.html |work=Canal 2 |access-date=2007-07-29 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070717184332/http://www.canal2tv.com/Noticias/Marzo%202007/turismo%20con%20gran%20empuje%20en%20Nicaragua.html |archive-date=2007-07-17 }}</ref> The increase and growth led to the income from tourism to rise more than 300% over a period of 10 years.<ref>{{cite news |title=A Dynamic Economy: Dynamic Sectors of the Economy; Tourism |url=http://www.pronicaragua.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=25&Itemid=98 |work=ProNicaragua |access-date=2007-08-01 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927210500/http://www.pronicaragua.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=25&Itemid=98 |archive-date=2007-09-27 }}</ref> The growth in tourism has also positively affected the agricultural, commercial, and finance industries, as well as the construction industry. President ] has stated his intention to use tourism to combat poverty throughout the country.<ref name="Nica">{{cite news|first=Rory |last=Carroll |title=Ortega banks on tourism to beat poverty |date=2007-01-07 |url=http://observer.guardian.co.uk/world/story/0,,1984401,00.html |work=Guardian Unlimited |access-date=2007-08-12 |location=London |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070607065504/https://observer.guardian.co.uk/world/story/0%2C%2C1984401%2C00.html |archive-date=2007-06-07 }}</ref> The results for Nicaragua's tourism-driven economy have been significant, with the nation welcoming one million tourists in a calendar year for the first time in its history in 2010.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.sify.com/news/nicaragua-exceeds-one-mn-foreign-tourists-for-first-time-news-international-km4ladiidea.html|title=Nicaragua exceeds one mn foreign tourists for first time|website=]|language=en|access-date=2019-01-18|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181017082140/http://www.sify.com/news/nicaragua-exceeds-one-mn-foreign-tourists-for-first-time-news-international-km4ladiidea.html|archive-date=2018-10-17|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Every year about 60,000 U.S. citizens visit Nicaragua, primarily business people, tourists, and those visiting relatives.<ref>{{cite news|title=Background Note: Nicaragua; Economy|publisher=U.S. State Department|url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=21 January 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170121153233/https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Some 5,300 people from the U.S. reside in Nicaragua. The majority of tourists who visit Nicaragua are from the U.S., Central or South America, and Europe. According to the Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua (INTUR),<ref>{{cite news|title=Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua|publisher=INTUR|url=http://www.intur.gob.ni/|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070513114726/http://www.intur.gob.ni/|archive-date=2007-05-13|url-status=dead}}</ref> the colonial cities of ] and ] are the preferred spots for tourists. Also, the cities of ], ] and the likes of ], ], the ], ], the ] volcano, and the ] among other locations are the main tourist attractions. In addition, ], ] and ] attract many tourists to Nicaragua. | |||
| ===Birds=== | |||
| ], ''Blue-crowned Motmot'') is the national bird of Nicaragua]] | |||
| {{main|List of birds of Nicaragua}} | |||
| According to the ''TV Noticias'' news program, the main attractions in Nicaragua for tourists are the beaches, the scenic routes, the architecture of cities such as León and Granada, ], and ] particularly in northern Nicaragua.<ref name=C2/> As a result of increased tourism, Nicaragua has seen its ] increase by 79.1% from 2007 to 2009.<ref>{{cite web|author=Acan-Efe|url=http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Foreign_investment_Increases_by_791_in_Nicaragua/378984|title=Foreign investment Increases by 79.1% in Nicaragua – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal|publisher=CentralAmericaData|date=2009-03-27|access-date=2010-06-26|archive-date=11 May 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511101528/http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Foreign_investment_Increases_by_791_in_Nicaragua/378984|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] includes a total of 698 species. Eight of these species, including the ] (''Dendroica chrysoparia'') and the ] (''Ara ambigua''), are currently listed by the IUCN as ]. Many of Nicaragua's birds are brilliantly colored, including various species of ], ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]s. The ] is the ] of Nicaragua. | |||
| Nicaragua is referred to as ''"the land of lakes and volcanoes"'' due to the number of lagoons and lakes, and the chain of volcanoes that runs from the north to the south along the country's Pacific side.<ref name="Brierley" /><ref name="Wallace" /><ref name="CNNTravel">{{cite web|last1=Parker|first1=Nick|title=Can Nicaragua deliver on huge potential?|url=http://www.cnn.com/travel/article/nicaragua-tourism/index.html|website=CNN Travel|access-date=October 27, 2017|date=August 1, 2012|archive-date=22 April 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220422013811/http://www.cnn.com/travel/article/nicaragua-tourism/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Today, only 7 of the 50 volcanoes in Nicaragua are considered active. Many of these volcanoes offer some great possibilities for tourists with activities such as ], ], ], and ] in crater lakes. | |||
| ===Reptiles=== | |||
| ] on the beach in Nicaragua]] | |||
| The ] was created by the eruption of the Apoyo Volcano about 23,000 years ago, which left a huge 7 km-wide crater that gradually filled with water. It is surrounded by the old crater wall.<ref>{{cite news | title =Volcanoes in Nicaragua: Apoyo Volcano | url =http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/9-nicaragua-volcanoes.html | work =ViaNica | access-date =2007-08-12 | archive-date =29 October 2012 | archive-url =https://web.archive.org/web/20121029112723/http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/9-nicaragua-volcanoes.html | url-status =live }}</ref> The rim of the lagoon is lined with restaurants, many of which have ] available. Besides exploring the forest around it, many water sports are practiced in the lagoon, most notably ].<ref>{{cite news | title =Activities in and around the Apoyo Lagoon | url =http://www.vianica.com/activity/17/activities-in-and-around-the-apoyo-lagoon | work =ViaNica | access-date =2007-08-12 | archive-date =22 August 2007 | archive-url =https://web.archive.org/web/20070822223958/http://www.vianica.com/activity/17/activities-in-and-around-the-apoyo-lagoon | url-status =live }}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua is home to many nesting populations of ]s, including the ], ], ], ], and the ] (''Chelonia mydas agassisi''). All of these are endangered or ] species, with declining global populations. ] are currently underway to preserve them as much as possible.<ref name=Actionatlas></ref><ref>http://www.fauna-flora.org/americas/turtles.html</ref> | |||
| Sand skiing has become a popular attraction at the ] volcano in ]. Both dormant and active volcanoes can be climbed. Some of the most visited volcanoes include the ], ], ], ] and ]'s ] and ]. | |||
| ===Fishes=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] aims to be ecologically and socially conscious; it focuses on local culture, wilderness, and adventure. Nicaragua's ecotourism is growing with every passing year.<ref>{{cite news | title =Nicaraguan Ecotourism | url =http://www.nicaragua.com/ecotourism/ | work =Nicaragua.com | access-date =2007-08-12 | archive-date =16 July 2007 | archive-url =https://web.archive.org/web/20070716120324/http://www.nicaragua.com/ecotourism/ | url-status =live }}</ref> It boasts a number of ecotourist tours and perfect places for adventurers. Nicaragua has three eco-regions (the Pacific, Central, and Atlantic) which contain volcanoes, tropical rainforests, and agricultural land.<ref>{{cite news| title=Nicaragua Travel Guide – Overview| url=http://www.worldtravelguide.net/country/198/country_guide/Central-America/Nicaragua.html| work=World Travel Guide| access-date=2007-08-12| url-status=dead| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070807210850/http://www.worldtravelguide.net/country/198/country_guide/Central-America/Nicaragua.html| archive-date=2007-08-07}}</ref> The majority of the eco-lodges and other environmentally-focused touristic destinations are found on Ometepe Island,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://ometepeislandinfo.com/|title=Ometepe Island Information – Everything About Traveling To Ometepe Island In One Place!|website=ometepeislandinfo.com|language=en|access-date=2017-03-05|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170306132130/http://ometepeislandinfo.com/|archive-date=2017-03-06|url-status=dead}}</ref> located in the middle of Lake Nicaragua just an hour's boat ride from Granada. While some are foreign-owned, others are owned by local families. | |||
| The ] is a species of shark that can survive for an extended period of time in fresh water. It can be found in ] and the ], where it is often referred to as the "Nicaragua shark".<ref></ref> Nicaragua has recently banned freshwater fishing of the Nicaragua shark and the ] in response to the declining populations of these animals.<ref></ref> | |||
| == |
== Demographics == | ||
| {{Main|Nicaraguans|Demographics of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ===Molluscs=== | |||
| {|class="wikitable" style="float: right; margin-left: 10px" | |||
| {{See|List of non-marine molluscs of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ! colspan="4" style="text-align:center; background:#cfb;"|Population{{UN_Population|ref}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#cfb;"|Year | |||
| ! style="background:#cfb;"|Million | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|1950 ||style="text-align:right;"|1.3 | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|2000 ||style="text-align:right;"|5.0 | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|{{UN_Population|Year}} ||style="text-align:right;"|{{#expr:{{formatnum:{{UN_Population|Nicaragua}}|R}}/1e6 round 1}} | |||
| |} | |||
| ] | |||
| According to a 2014 research published in the journal ''Genetics and Molecular Biology'', European ancestry predominates in 69% of Nicaraguans, followed by African ancestry in 20%, and lastly ] in 11%.<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Mauro Salzano, Francisco |author2=Sans, Mónica |title=Interethnic admixture and the evolution of Latin American populations|journal=Genetics and Molecular Biology|date=2014|volume=37|issue=1 (suppl)|pages=151–170|doi=10.1590/s1415-47572014000200003|pmid=24764751 |pmc=3983580}}</ref> A Japanese research of "Genomic Components in America's demography" demonstrated that, on average, the ancestry of Nicaraguans is 58–62% European, 28% Native American, and 14% African, with a very small Near Eastern contribution.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://c1.staticflickr.com/5/4307/35125440893_3566ed7714_o.jpg|title=Genomic Components in America's demography|access-date=January 8, 2018|archive-date=7 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210307232735/https://c1.staticflickr.com/5/4307/35125440893_3566ed7714_o.jpg|url-status=live}}</ref> Non-genetic data from the '']'' establish that from Nicaragua's 2016 population of 5,966,798, around 69% are ], 17% ], 5% Native American, and 9% ] and other races.<ref name=cia/> This fluctuates with changes in migration patterns. The population is 58% urban {{As of|2013|lc=y}}.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS|title=Urban population (% of total)|publisher=]|access-date=2015-06-26|archive-date=2 March 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170302054104/http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The capital ] is the biggest city, with an estimated population of 1,042,641 in 2016.<ref>{{cite report |url=http://www.inide.gob.ni/Anuarios/Anuario%20Estadistico%202015.pdf |title=Anuario Estadístico 2015 |page=52 |publisher=] |date=February 2016 |access-date=2017-12-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171215012047/http://www.inide.gob.ni/Anuarios/Anuario%20Estadistico%202015.pdf |archive-date=2017-12-15 |url-status=dead }}</ref> In 2005, over 5 million people lived in the Pacific, Central and North regions, and 700,000 in the Caribbean region.<ref name=CN>{{cite news |title=VIII Censo de Poblacion y IV de Vivienda |date=October 2005 |url=http://www.inec.gob.ni/censos2005/ResumenCensal/RESUMENCENSAL.pdf |work=Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos |access-date=2007-07-07 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070824192548/http://www.inec.gob.ni/censos2005/ResumenCensal/RESUMENCENSAL.pdf |archive-date=2007-08-24 }}</ref> | |||
| Many species of ] are indigenous to Nicaragua, including at least 79 species of terrestrial ].<ref name="Pérez 2008">{{sp icon}} Pérez A. M., Sotelo M., Arana I. & López A. (2008). "Diversidad de moluscos gasterópodos terrestres en la región del Pacífico de Nicaragua y sus preferencias de hábitat". '']'' '''56'''(1): 317-332,. </ref> | |||
| There is a growing expatriate community,<ref>{{cite news|title=Expatriates of Nicaragua|url=http://www.nicaragua.com/expatriates/|work=Nicaragua.com|access-date=2007-07-30|archive-date=14 July 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070714201243/http://www.nicaragua.com/expatriates/|url-status=live}}</ref> the majority of whom move for business, investment or retirement from across the world, such as from the US, Canada, ], and European countries; the majority have settled in Managua, ] and ]. | |||
| ===Flora=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The flora of Nicaragua is very rich with their more than 10,000 species of plants and vascular trees. Biosfera BOSAWAS'S Reservation constitutes the physical area where the flora and fauna of North and South America converge. Therefore, the botanical diversity of the Reservation is very high although one ignores the number of species exactly. The vegetation of BOSAWAS is even unknown but judging for the preliminary data of the last inventories, she/he is considered in thousands of species arbustivas and vascular. | |||
| The botanical diversity of the reservation is very high, being considered in thousands the species arbustivas and vascular. The arboreal composition of the forests of the region doesn't present significant changes, due to the high levels of humidity. they are | |||
| ], National Park and Biological Reservation.]] | |||
| distinguished six types of forests: | |||
| *Low forest sub-perennifolio and forest low perennifolio. | |||
| *Medium forest sub-perennifolio. | |||
| *Forest medium perennifolio. | |||
| *High forest sub-perennifolio. | |||
| *Forest high perennifolio. | |||
| According to some experts, the vast vegetable wealth of BOSAWAS presents three economic potentials | |||
| *Nutritious | |||
| *Ornamental | |||
| *Medicinal | |||
| Many ], particularly in Costa Rica, the United States, Spain, Canada, and other Central American countries.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140215015815/http://www.migrationinformation.org/Profiles/display.cfm?ID=636 |date=15 February 2014 }}. Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.</ref>{{failed verification|date=September 2023}} | |||
| ===Protected areas=== | |||
| {{main|National System of Protected Areas (Nicaragua)|Protected areas of Nicaragua}} | |||
| There are currently 78 protected areas in Nicaragua, covering more than {{convert|22000|km2|sp=us}}, or about 17% of its landmass. These include ]s and ]s that shelter a wide range of ]s. There are more than 1,400 animal species classified thus far in Nicaragua. Some 12,000 species of plants have been ] thus far in Nicaragua, with an estimated 5,000 species not yet classified.<ref></ref> | |||
| Nicaragua has a population growth rate of 1.5% {{As of|2013|lc=y}}.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.GROW/countries/NI?display=graph|title=Population growth (annual %)|publisher=]|access-date=26 June 2015|archive-date=19 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160619233907/http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.GROW/countries/NI?display=graph|url-status=live}}</ref> This is the result of one of the highest ]s in the ]:{{citation needed|reason=Is this still correct as of 2017?|date=January 2019}} 17.7 per 1,000 as of 2017.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.indexmundi.com/nicaragua/birth_rate.html|title=Nicaragua Birth rate - Demographics|website=www.indexmundi.com|access-date=2 December 2023|archive-date=7 April 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220407073226/https://www.indexmundi.com/nicaragua/birth_rate.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The death rate was 4.7 per 1,000 during the same period according to the United Nations.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=PopDiv&f=variableID%3A65|title=Crude death rate – the United Nations|publisher=]|access-date=26 June 2015|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150627055521/https://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=PopDiv&f=variableID%3A65|archive-date=27 June 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| {{Main|Economy of Nicaragua}} | |||
| === |
=== Ethnic groups === | ||
| ] man]] | |||
| ] in ] is the country's only deep-water port capable of handling ] and ]]] | |||
| The majority of the Nicaraguan population is composed of mestizos, roughly 69%, while 17% of Nicaragua's population is white,<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua/#people-and-society |title=Nicaragua – People and Society |work=The World Factbook |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=20 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210320071255/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua#people-and-society |url-status=live }}</ref> with the majority of them being of Spanish descent, while others are of German, Italian, English, Turkish, Danish or French ancestry. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ====Black Creoles==== | |||
| Nicaragua is primarily an agricultural country; agriculture constitutes 60% of its total exports which annually yield approximately US $2.0 billion.<ref name=centralamericaeconomy>{{cite news|title=General Information – Nicaragua: Economy|url=http://centralamerica.com/nicaragua/info/general.htm#economy|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> In addition, Nicaragua's ] rum is renowned as among the best in Latin America, and its tobacco and beef are also well regarded. Nicaragua's agrarian economy has historically been based on the export of ]s such as ]s, coffee, ], ] and ]. Light industry (maquila), tourism, banking, mining, fisheries, and general commerce are expanding. | |||
| About 9% of Nicaragua's population is ] and mainly resides on the country's Caribbean (or Atlantic) coast. The black population is mostly composed of black English-speaking Creoles who are the descendants of escaped or shipwrecked slaves; many carry the name of ] who brought slaves with them, such as ], ], ], and ]. Although many Creoles supported Somoza because of his close association with the United States, they rallied to the Sandinista cause in July 1979, only to reject the revolution soon afterwards in response to a new phase of "westernization" and imposition of central rule from Managua.<ref>{{cite book|last=Baracco |first=L|year=2005|title=Nicaragua: The Imagining of a Nation. From Nineteenth-Century Liberals to Twentieth-Century Sandinistas |place=New York|publisher=Algora Publishing|chapter=From Acquiescence to Ethnic Militancy: Costeno Responses to Sandinista Anti-Imperialist Nationalism}}</ref> There is a smaller number of ], a people of mixed ], ] and ] descent. In the mid-1980s, the government divided the ] – consisting of the eastern half of the country – into two autonomous regions and granted the black and indigenous people of this region limited self-rule within the republic. | |||
| Nicaragua also depends heavily on remittances from Nicaraguans living abroad, which totaled $655.5 million in 2006. | |||
| {{Anchor|Amerindians}} | |||
| Nicaragua has always been a predominantly agricultural country. On the Pacific side, coffee and cotton are by far the most important commercial crops. In 1992, more land was devoted to coffee than to any other crop, and it is the nation's leading export in terms of value. Nearly two-thirds of the coffee crop comes from the northern part of the Central Highlands, in the area north and east of the town of Estelí.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| ==== Indigenous population ==== | |||
| In the early 1980s, cotton became Nicaragua's second-largest export earner. Production is centered on large farms along the central Pacific coast. Unfortunately, the growth of the cotton industry has created serious problems. Soil erosion and pollution from the heavy use of pesticides have become serious concerns in the cotton district. Yields and exports have both been declining since 1985.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| The remaining 5% of Nicaraguans are indigenous, the descendants of the country's original inhabitants. Nicaragua's ] population consisted of many indigenous groups. In the western region, the Nahuas (]) were present along with other groups such as the Chorotega people and the ]s (also known as Maribios or Hokan Xiu). The central region and the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua were inhabited by indigenous peoples who were ] groups that had migrated to and from South America in ancient times, primarily what is now ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://ticotimes.net/2008/01/11/vestiges-of-ancient-indigenous-language-still-found-today-in-matagalpa-s-northern-highlands |title=Vestiges of Ancient Indigenous Language Still Found Today in Matagalpa's Northern Highlands |work=The Tico Times |last=Zúñiga |first=Alejandro |date=11 January 2008 |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=22 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220422031324/https://ticotimes.net/2008/01/11/vestiges-of-ancient-indigenous-language-still-found-today-in-matagalpa-s-northern-highlands |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.mundoalfal.org/CDAnaisXVII/trabalhos/R0839-1.pdf |title=¿La Costa Pacífica de América Central y América del sur Como Zona de Difusión Lexical?: Primeras Aproximaciones |last=Urban |first=Matthias |publisher=ALFAL 2014 |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=30 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220130215833/https://www.mundoalfal.org/CDAnaisXVII/trabalhos/R0839-1.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> These groups include the present-day ], ], ], as well as Mayangnas and Ulwas who are also known as ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://iwgia.org/en/nicaragua/4237-iw-2021-nicaragua.html |title=Indigenous peoples in Nicaragua |publisher=IWGIA |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=27 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220427101921/https://iwgia.org/en/nicaragua/4237-iw-2021-nicaragua.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Brief" />{{rp|20}} In the 19th century, there was a substantial indigenous minority, but this group was largely assimilated culturally into the mestizo majority. The ] are also present, mainly on the Caribbean Coast. They are a people of mixed African and Indigenous descent.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://minorityrights.org/minorities/garifuna/ |title=Garifuna |work=World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples |date=19 June 2015 |publisher=Minority Rights Group International |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=28 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220128032203/https://minorityrights.org/minorities/garifuna/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Languages === | |||
| Plantation crops are significant in the Caribbean lowlands. After disease wiped out most of the region's banana plants in the years before 1945, attempts were made to diversify crops. Today most of Nicaragua's bananas are grown in the northwestern part of the country near the port of Corinto; sugarcane is also grown in the same district.<ref name=grolier1/> Subsistence farms, where food is grown mainly for the consumption of the farm family instead of for sale, are found throughout Nicaragua. Favorite food crops grown on such farms include rice, beans, maize, citrus fruits, and cassava. Cassava, a root crop somewhat similar to the potato, is an important food in tropical regions. The plant's roots can be eaten boiled and sliced, or ground into flour. Cassava is also the main ingredient in tapioca pudding.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| {{Main|Languages of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] (middle), and ] (bottom)]] | |||
| ] has many indigenous influences and several distinguishing characteristics. For example, some Nicaraguans have a tendency to replace ] with ] when speaking. Although Spanish is spoken throughout, the country has great variety: vocabulary, accents and colloquial language can vary between towns and departments.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FLCnGxUR8K4| archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211028/FLCnGxUR8K4| archive-date=2021-10-28|title=Aqui Nicaragua Documentary, Program by Carlos Fernando Chamorro. Programa Inaugural de Aqui Nicaragua, Idiosincracia Nicaragüense | date=27 February 2008|language=es|publisher=YouTube|access-date=2010-06-26}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| ] emerged in the 1970s and 1980s among deaf children as the first special education schools brought them together, and its emergence became of particular interest to linguists as an opportunity to directly observe the creation of a language.<ref>{{cite web|access-date=2022-04-24|title=LADR About NSL|url=http://www.columbia.edu/~as1038/about-nsl.html|website=www.columbia.edu|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024122152/http://www.columbia.edu/~as1038/about-nsl.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|access-date=2022-04-24|title=Evolution: Library: Birth of a Language|url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/07/2/l_072_04.html|website=www.pbs.org|archive-date=7 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230407221031/https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/07/2/l_072_04.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Kocab |first1=Annemarie |last2=Senghas |first2=Ann |last3=Snedeker |first3=Jesse |date=November 2016 |title=The emergence of temporal language in Nicaraguan Sign Language |journal=Cognition |language=en |volume=156 |pages=147–163 |doi=10.1016/j.cognition.2016.08.005 |pmc=5027136 |pmid=27591549}}</ref> | |||
| The Pacific lowlands and the middle and southern parts of the Central Highlands are the principal cattle-grazing areas. An especially large number of cattle are found to the east of Lake Nicaragua. | |||
| On the ] coast, indigenous languages, ], and Spanish are spoken. The ], spoken by the ] as a first language and some other indigenous and Afro-descendants people as a second, third, or fourth language, is the most commonly spoken indigenous language. The indigenous ] of Mayangna and Ulwa are spoken by the respective peoples of the same names. Many Miskito, Mayangna, and Sumo people also speak ], and a large majority also speak Spanish. Fewer than three dozen of nearly 2,000 ] speak their ] ] fluently, with nearly all Ramas speaking ] and the vast majority speaking Spanish. Linguists have attempted to document and revitalize the language over the past three decades.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.turkulka.net/ |title=Turkulka |access-date=2015-04-23 |archive-date=27 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150427220123/http://www.turkulka.net/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Beginning in the 1960s, shrimp became big business on both the Pacific and Caribbean coasts. The main shrimping centers on the Pacific coast are Corinto and San Juan del Sur. Fishing boats on the Caribbean side bring shrimp as well as lobsters into processing plants at Puerto Cabezas, Bluefields, and Laguna de Perlas.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| The ], descendants of indigenous and Afro-descendant people who came to Nicaragua from Honduras in the early twentieth century, have recently attempted to revitalize their ] ]. The majority speak Miskito Coast Creole as their first language and Spanish as their second. The Creole or Kriol people, descendants of enslaved Africans brought to the ] during the British colonial period and European, Chinese, Arab, and British West Indian immigrants, also speak Miskito Coast Creole as their first language and Spanish as their second.<ref>{{cite news|title=Languages of Nicaragua|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=NI|work=Ethnologue|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=15 January 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130115100732/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=NI|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The lumber industry, concentrated mainly in the eastern third of the country, has been lethargic since 1980, with its activities limited by several problems. First, the best trees in the most accessible places have already been cut down. In addition, pure groves of trees are uncommon in tropical forests. Hundreds of species per acre are generally the rule, complicating the task of harvesting. Moreover, the most valuable dense ]s will not float. As a result, these trees must be trucked out of the forest rather than floated downriver to a sawmill. Finally, more restrictions are being placed on lumbering due to increased environmental concerns about destruction of the rain forests. But lumbering continues despite these obstacles; indeed, a single hardwood tree may be worth thousands of dollars.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| === Largest cities === | |||
| Political turmoil has had a severe impact on the mining industry. Exports of gold are down, and little effort has been made to develop the large ] deposits of the northeast. Fighting during the revolution destroyed nearly one-third of Nicaragua's industry. As it rebuilds, the government is trying to change the industrial mix of the country and achieve decentralization. Before the revolution, more than 60 percent of the nation's industrial production, by value, was concentrated in Managua. The industrial-decentralization policy may help to slow the growth of the largest cities, while assisting in the redistribution of income and development of economies in impoverished areas. Major industries include food processing, cement production, metal fabrication, and oil refining. The Centroamérica power plant on the ] in the Central Highlands has been expanded, and other hydroelectric projects have been undertaken to help provide electricity to the nation's newer industries.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| {{Largest cities | |||
| | country = Nicaragua | |||
| | kind = ] | |||
| | stat_ref = (2016 projections) | |||
| | list_by_pop = | |||
| | div_name = Department | |||
| | div_link = | |||
| |city_1 = Managua | |||
| The economic core of Nicaragua is located in the Pacific zone, and the railway and highway network reflects that concentration of activity. The government-owned rail system—an inefficient money loser—is gradually being replaced by truck transport. Transportation throughout the rest of the nation is often inadequate. For example, one cannot travel all the way by highway from Managua to the Caribbean coast. The road ends at the town of ]. Travelers have to transfer and make the rest of the trip by ] down the ]—a five-hour journey.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| |div_1 = Managua Department{{!}}Managua | |||
| |pop_1 = 1,042,641 | |||
| |img_1 = | |||
| |city_2 = León, Nicaragua{{!}}León | |||
| ] is the only modern deepwater port in Nicaragua. It handles both agricultural exports and general-cargo imports. Petroleum is unloaded at ], from which it travels by pipeline to a refinery in Managua. Trade with other nations in Central America has increased in recent years. Nicaragua has long been considered as a possible site for a new sea-level canal that could supplement the Panama Canal.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| |div_2 = León Department{{!}}León | |||
| |pop_2 = 206,264 | |||
| |img_2 = Catedral de León Nicaragua2.JPG | |||
| |city_3 = Masaya | |||
| ===Components of the economy=== | |||
| |div_3 = Masaya Department{{!}}Masaya | |||
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in ] (PPP) in 2008 was estimated at $17.37 billion USD.<ref name=cia>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: Economy|publisher=CIA World Factbook|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/nu.html|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> The service sector is the largest component of GDP at 56.9%, followed by the industrial sector at 26.1% (2006 est.). Agriculture represents 17% of GDP, the highest percentage in Central America <ref name=ciagdp>, CIA World Factbook</ref> (2008 est.). Remittances account for over 15% of the Nicaraguan GDP. Close to one billion dollars are sent to the country by Nicaraguans living abroad.<ref name=migrationinformation>{{cite web|url=http://www.migrationinformation.org/Feature/display.cfm?id=393|title=Migration Information Source – Remittance Trends in Central America|publisher=Migrationinformation.org|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> Nicaraguan labor force is estimated at 2.322 million of which 29% is occupied in agriculture, 19% in the industrial sector and 52% in the service sector (est. 2008). | |||
| |pop_3 = 176,344 | |||
| |img_3 = Masaya_Market,_Nicaragua.jpg | |||
| |city_4 = Matagalpa | |||
| ====Agriculture==== | |||
| |div_4 = Matagalpa Department{{!}}Matagalpa | |||
| ] | |||
| |pop_4 = 158,095 | |||
| After 1950 the scope of capital-intensive modern agriculture increased greatly. This growth was concentrated in export crops, while crops destined for domestic use continued to be produced by traditional labor-intensive methods. The shift to industrialized agriculture also significantly reduced the proportion of the population directly dependent on agriculture. | |||
| |img_4 = Matagalpa080408c.jpg | |||
| |city_5 = Tipitapa | |||
| Commercial agriculture thrives in the Pacific Lowlands, where ] and ] are the staple crops. Although coffee is grown in the Pacific zone at elevations over 1,000 feet (300 meters), the most important coffee zone is the northwestern part of the Central Highlands, from ] to ]. Cattle for the export of beef are raised in the southeastern part of the highlands. The overall expansion of export production by large landholders pushed the smallholders who produced the country's ], ], and other dietary staples onto marginal lands, with the result that food production could not keep up with population increase. | |||
| |div_5 = Managua Department{{!}}Managua | |||
| |pop_5 = 140,569 | |||
| |city_6 = Chinandega | |||
| In the 1990s the government initiated efforts to diversify agriculture. Some of the new export-oriented crops were ], ], ], and ].<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| |div_6 = Chinandega Department{{!}}Chinandega | |||
| |pop_6 = 135,154 | |||
| |city_7 = Jinotega | |||
| Nicaragua's agricultural sector has benefited because of the country's strong ties to ]. It is estimated that Venezuela will import approximately $200 million in agricultural goods.<ref name=Sanchez2010>{{cite web|last=Sánchez|first=E|url=http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Nicaragua_Plans_to_Sell_Over_200_Million_to_Venezuela/925161|title=Nicaragua Plans to Sell Over $200 Million to Venezuela – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal|publisher=CentralAmericaData|date=2010-03-29|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| |div_7 = Jinotega Department{{!}}Jinotega | |||
| |pop_7 = 133,705 | |||
| |city_8 = Granada, Nicaragua{{!}}Granada | |||
| ====Fishing and forestry==== | |||
| |div_8 = Granada Department{{!}}Granada | |||
| ] | |||
| |pop_8 = 127,892 | |||
| Forestry and fishing are the bases of the eastern seaboard's commercial economy. In national terms, neither sector was important until the take-off of the fishing industry in the late 20th century. ] was harvested commercially on the Atlantic coast beginning early in the 19th century. In the 20th century ] stands began to be exploited. In neither case, though, was the resource managed so as to ensure a sustained yield. | |||
| |city_9 = Estelí | |||
| Nicaragua's fishing industry operates off both coasts and in freshwater Lake Nicaragua. The lake also has an aquaculture industry. The most valuable catches are ] and ]. The government expanded the size of the fishing fleet in the 1980s, which permitted a rapid expansion of shrimp and lobster exports in the 1990s. A ] fishery thrived on the Caribbean coast before it collapsed from ].<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| |div_9 = Estelí Department{{!}}Estelí | |||
| |pop_9 = 126,290 | |||
| |city_10 = Puerto Cabezas | |||
| ====Mining and the production of energy==== | |||
| |div_10 = North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region{{!}}RACCN | |||
| Mining is not a major industry in Nicaragua,<ref name=Oancea>Dan Oancea: </ref> contributing less than 1% of gross domestic product (GDP). Still, gold and silver mines in the north-central and northeastern parts of the country are important elements of regional economies and constitute sources of revenue. Important domestic sources of electrical energy are hydropower and ], the latter from the volcano Momotombo, near Managua. But most commercial electricity is generated by imported petroleum. | |||
| |pop_10 = 113,534 | |||
| }} | |||
| ====Manufacturing==== | |||
| Although the manufacturing sector of the economy contributes somewhat more to GDP than agriculture, it employs far fewer people. It was traditionally concerned largely with the processing of agricultural products, and it supplied the domestic market with foods, beverages, edible oils, cigarettes, and textile goods. Also manufactured were light metal goods, construction materials, wood and paper products, and chemicals such as fertilizers and pesticides. | |||
| === Religion === | |||
| The manufacturing sector was expanded beyond these areas in the 1990s with the introduction of maquila industries, in which imported parts are assembled for reexport. The principal products were garments, footwear, aluminum frames, and jewelry. Growth in the ''maquila'' sector slowed in the first decade of the 21st century with rising competition from ], particularly China.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| {{Main|Religion in Nicaragua}} | |||
| ], one of Nicaragua's ]s]] | |||
| Religion plays a significant role in Nicaraguan culture and is afforded special protections in its ]. ] (which has been guaranteed since 1939) and ] are officially promoted by the government, but, in recent years, the ] and the regime led by ] have been in open conflict. The latter has been accused of using the police to harass clergy (including bishops),<ref>{{Cite web |last=ACN |date=2022-05-24 |title=Nicaragua bishop on hunger strike to protest police harassment |url=https://acninternational.org/police-harassment-nicaraguan-bishop/ |access-date=2022-11-21 |website=ACN International |language=en-US |archive-date=21 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221121112532/https://acninternational.org/police-harassment-nicaraguan-bishop/ |url-status=live }}</ref> closing down Catholic media outlets, and arresting members of the clergy (including ] of the ]). | |||
| Nicaragua has no official ]. Catholic bishops are expected to lend their authority to important state occasions, and their pronouncements on national issues are closely followed. They can be called upon to mediate between contending parties at moments of political crisis.<ref name=LOCR>{{cite news|first=G|last=Dennis|title=Nicaragua: Religion|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0040)|work=Country Studies|access-date=2007-10-30|archive-date=2 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200102130553/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0040)|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1979, Miguel D'Escoto Brockman, a priest who had embraced ], served in the government as foreign minister when the Sandinistas came to power. The largest denomination, and traditionally the religion of the majority, is the ]. It came to Nicaragua in the 16th century with the Spanish conquest and remained, until 1939, the ]. | |||
| ====Economic development in the 21st century==== | |||
| Nicaragua has widespread underemployment and the second lowest per capita income in the Americas. The ] (CAFTA) has been in effect since April 2006 and has expanded export opportunities for many agricultural and manufactured goods. Textiles and apparel account for nearly 60% of Nicaragua's exports, but recent increases in the minimum wage have a strong possibility of eroding Nicaragua's ] in this industry. Nicaragua's minimum wage is among the lowest in the Americas and in the World.<ref name=PBSCAFTA></ref><ref name=allbusiness></ref><ref></ref><ref name=rspas></ref> | |||
| The number of practicing Roman Catholics has been declining, while membership of ] groups and ] (LDS Church) has been growing rapidly since the 1990s. There is a significant LDS missionary effort in Nicaragua. There are two missions and 95,768 members of the LDS Church (1.54% of the population).<ref>{{cite web|title=Nicaragua – Facts and Statistics|url=https://newsroom.churchofjesuschrist.org/facts-and-statistics/country/nicaragua|website=Mormon Newsroom|access-date=26 May 2017|archive-date=28 June 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190628004621/https://newsroom.churchofjesuschrist.org/facts-and-statistics/country/nicaragua|url-status=live}}</ref> There are also strong ] and ] communities on the Caribbean coast in what once constituted the sparsely populated ] colony. It was under British influence for nearly three centuries. ] was brought to the ] mainly by British and German colonists in forms of ] and the ]. Other kinds of Protestant and other ]s were introduced to the rest of Nicaragua during the 19th century. | |||
| Nicaragua relies on international economic assistance to meet internal and external debt financing obligations. In early 2004, Nicaragua secured some $4.5 billion in foreign debt reduction under the ] initiative. In October 2007, the ] (IMF) approved a new ] program. Despite the support, severe budget shortfalls resulting from the suspension of large amounts of direct budget support from foreign donors concerned with recent political developments has caused a slowdown in PRGF disbursements. | |||
| Popular religion revolves around the saints, who are perceived as intercessors between human beings and God. Most localities, from the capital of Managua to small rural communities, honor ]s, selected from the Roman Catholic calendar, with annual ''fiestas''. In many communities, a rich lore has grown up around the celebrations of patron saints, such as Managua's Saint Dominic (Santo Domingo), honored in August with two colorful, often riotous, day-long processions through the city. The high point of Nicaragua's religious calendar for the masses is neither Christmas nor Easter, but La Purísima, a week of festivities in early December dedicated to the ], during which elaborate altars to the ] are constructed in homes and workplaces.<ref name=LOCR/> | |||
| Similarly, private sector concerns surrounding Daniel Ortega's handling of economic issues have dampened investment. Economic growth has slowed in 2009, due to decreased export demand from the US and Central American markets from the overall recession, lower commodity prices for key ] ], and low ] growth. Remittances are equivalent to roughly 15% of the country's ].<ref name=cia/> | |||
| ] has increased with a steady influx of immigration.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110513110733/http://archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni/2004/octubre/24-octubre-2004/mundo_oculto/mundo_oculto-20041020-01.html |date=2011-05-13 }}. Archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.</ref> | |||
| ===Poverty=== | |||
| Nicaragua is among one of the poorer countries in the ].<ref name=worldbank22255024>{{cite news|title=World Bank Country Profiles, Nicaragua|url=http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/LACEXT/NICARAGUAEXTN/0,,contentMDK:22255024~pagePK:1497618~piPK:217854~theSitePK:258689,00.html}}</ref><ref name=Factbook>{{cite news|title=Rank Order – GDP – per capita (PPP)|publisher=CIA World Factbook|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2004rank.html|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref><ref name=unstats>{{cite news|title=Social indicators: Per capita GDP|publisher=United Nations|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/socind/inc-eco.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Nicaragua's nominal GDP stands at 6.554 for 2009 and increasing to 8.532 by 2014.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} Nicaragua's ] 16.709 billion and the ] per capita is $1,028 for Nicaragua.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} | |||
| Although ] have been living in Nicaragua since the 18th century, the ] is small, numbering less than 200 people in 2017. Of these, 112 were recent converts who claimed ] Jewish ancestry.<ref name="Dolsten">{{cite news |last1=Dolsten |first1=Josefin |title=Tiny Nicaraguan Community Doubles in Size as 112 Convert |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/tiny-nicaragua-jewish-community-doubles-in-size-as-114-convert/ |access-date=30 December 2021 |publisher=Times of Israel |date=2 August 2017 |archive-date=30 December 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211230134726/https://www.timesofisrael.com/tiny-nicaragua-jewish-community-doubles-in-size-as-114-convert/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| According to the ], 48% of the population in Nicaragua live below the poverty line,<ref name=pnud>{{cite web|url=http://www.pnud.org.ni/noticias/343|title=Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo – Noticias – La pobreza se arraiga en el país|publisher=Pnud.org.ni|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> 79.9% of the population live with less than $2 per day,<ref name=hdrstats>{{cite web|url=http://hdrstats.undp.org/indicators/24.html|title=Human Development Report 2009 – Countries' shares of total stock of migrants in Africa (%)|publisher=Hdrstats.undp.org|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> unemployment is 3.9%, and another 46.5% are ] (2008 est.). As in many other ], a large segment of the economically poor in Nicaragua are women. In addition, a relatively high proportion of Nicaragua's homes have a woman as head of household: 39% of ] homes and 28% of rural homes. According to UN figures, 80% of the ] (who make up 5% of the population) live on less than $1 per day.<ref name=Silva>{{cite news|last=Silva|first=JA|title=NICARAGUA: Name and Identity for Thousands of Indigenous Children|url=http://ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=43760|work=IPS|accessdate=2008-09-12}}</ref> According to the ], 27% of all ] are suffering from ]; the highest percentage in Central America. | |||
| As of 2007, approximately 1,200 to 1,500 Nicaraguan residents practiced ], most of them ] who are ] or ] from ], ], and ] or natural-born Nicaraguan descendants of the two groups.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080724182039/http://nicaragua.usembassy.gov/religious_2007.html |date=24 July 2008 }} (Released October 2007, covers period of June 2006 to May 2007)</ref> | |||
| ===Infrastructure=== | |||
| During the war between the US-backed Contras and the government of the ] in the 1980s, much of the country's infrastructure was damaged or destroyed.<ref name=Tartter>{{cite news|last=Tartter|first=JR|title=The Nicaraguan Resistance|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/D?cstdy:10:./temp/~frd_famN::|work=Country Studies|accessdate=2007-11-02}}</ref> ] averaged 30% throughout the 1980s. After the United States imposed a trade embargo in 1985, which lasted 5 years, Nicaragua's inflation rate rose dramatically. The 1985 annual rate of 220% tripled the following year and rose to more than 13,000% in 1988, the highest rate for any country in the ] in that year. | |||
| === Immigration === | |||
| The country is still a recovering economy and it continues to implement further reforms to improve profits for foreign businesses, on which aid from the ] is conditional. In 2005 finance ministers of the leading eight industrialized nations (]) agreed to forgive some of Nicaragua's foreign debt, as part of the ] program. According to the ], Nicaragua's ] was around $4.9 billion US dollars. In March 2007, Poland and Nicaragua signed an agreement to write off 30.6 million dollars which was borrowed by the Nicaraguan government in the 1980s.<ref name=Poland>{{cite news|title=Poland forgives nearly 31 million dollars of debt owed by Nicaragua|date=2007-03-21|url=http://english.people.com.cn/200703/31/eng20070331_362713.html|work=People's Daily Online|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Since the end of the war almost two decades ago, more than 350 state enterprises have been ]. Inflation reduced from 33,500% in 1988 to 9.45% in 2006, and the foreign debt was cut in half.<ref name=state1850>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua:Economy|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|work=U.S. State Department|accessdate=2007-11-02}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Immigration to Nicaragua}} | |||
| Relative to its population, Nicaragua has not experienced large waves of immigration. The number of immigrants in Nicaragua, from other Latin American countries or other countries, never surpassed 1% of its total population before 1995. The 2005 census showed the foreign-born population at 1.2%, having risen a mere 0.06% in 10 years.<ref name=CN/> | |||
| In the 19th century, Nicaragua experienced modest waves of immigration from Europe. In particular, families from Germany, Italy, Spain, France and Belgium immigrated to Nicaragua, particularly the departments in the Central and Pacific region. | |||
| According to the World Bank, Nicaragua ranked as the 62nd best economy for starting a business: making it the second best in Central America, after Panama.<ref>{{cite news|title=Economy Rankings: Doing Business|publisher=World Bank|url=http://www.doingbusiness.org/EconomyRankings/|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Nicaragua's economy is "62.7% free" with high levels of fiscal, government, labor, investment, financial, and trade freedom.<ref name=heritage>{{cite news|title=Index Of Economic Freedom: Nicaragua|url=http://www.heritage.org/research/features/index/country.cfm?id=Nicaragua|work=Heritage.org|accessdate=2007-11-02}}</ref> It ranks as the 61st ], and 14th (of 29) in the Americas. | |||
| Also present is a small Middle Eastern-Nicaraguan community of ], ], ], and ] people in Nicaragua. This community numbers about 30,000. There is an East Asian community mostly consisting of ]. The ] population is estimated at 12,000.<ref>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: People groups|url=http://www.joshuaproject.net/countries.php?rog3=NU|work=Joshua Project|access-date=2007-03-26|archive-date=13 February 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070213010531/http://www.joshuaproject.net/countries.php?rog3=NU|url-status=live}}</ref> The Chinese arrived in the late 19th century but were unsubstantiated until the 1920s. | |||
| ===Currency=== | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan córdoba}}] in its circulated currency. Illustrated here is a 50 córdoba banknote.]] | |||
| === Diaspora === | |||
| During the era of the Spanish colonial rule, and for more than 50 years afterward, Nicaragua used Spanish coins that were struck for use in the "New World". The first unique coins for Nicaragua were issued in 1878 in the '']'' denomination. The ] became Nicaragua's currency in 1912 and was initially equal in value to the U.S. dollar. The ] was named after ], the national founder. The front of each of Nicaragua's circulating coins features the national coat of arms. The five volcanoes represent the five Central American countries at the time of Nicaragua's independence; the rainbow at the top symbolizes peace; and the cap in the center is a symbol of freedom. The design is contained within a triangle to indicate equality. The back of each coin features the denomination, with the inscription ''En Dios Confiamos'' (In God We Trust). | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan diaspora}} | |||
| The Civil War forced many Nicaraguans to start lives outside of their country. Many people emigrated during the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century due to the lack of employment opportunities and poverty. The majority of the ] migrated to the United States and ]. Today one in six Nicaraguans live in these two countries.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thedialogue.org/PublicationFiles/The%20Nicaragua%20case_M%20Orozco2%20REV.pdf |title=The Nicaragua case_M Orozco2 REV.doc |access-date=2010-06-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511104117/http://www.thedialogue.org/PublicationFiles/The%20Nicaragua%20case_M%20Orozco2%20REV.pdf |archive-date=2011-05-11 }}</ref> | |||
| The diaspora has seen Nicaraguans settling around in smaller communities in other parts of the world, particularly Western Europe. Small communities of Nicaraguans are found in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Communities also exist in Australia and New Zealand. Canada, Brazil and Argentina host small groups of these communities. In Asia, Japan hosts a small Nicaraguan community. | |||
| Nicaragua is the first country in the Americas to successfully overhaul production of its paper currency in favor of ]. Polymer banknotes were issued in 2009 to reduce the need to reprint banknotes, combat counterfeiting and introduce a more hygienic currency. The previously issued banknotes are still accepted as legal tender. However, unlike previous banknote series, the current series does not have any illustration of politicians. Rather, the current currency series celebrates the country's landmarks, history and culture. | |||
| Due to extreme poverty at home, many Nicaraguans are now living and working in neighboring ], a country that has the ] as its currency.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/internacionales/102550|title=El Salvador inicia plan para regularizar a nicaragüenses residentes|newspaper=]|date=May 18, 2011|access-date=February 19, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120706204153/http://www.elnuevodiario.com.ni/internacionales/102550|archive-date=July 6, 2012|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.laprensagrafica.com/el-salvador/departamentos/214132-nicaragueenses-se-acogen-a-programa.html|title=Nicaragüenses se acogen a programa|author=Lazo, Flor|work=]|date=August 28, 2011|access-date=February 19, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140427034529/http://www.laprensagrafica.com/el-salvador/departamentos/214132-nicaragueenses-se-acogen-a-programa.html|archive-date=April 27, 2014}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (MARENA) | |||
| == |
=== Healthcare === | ||
| {{Main|Healthcare in Nicaragua}}Although Nicaragua's health outcomes have improved over the past few decades with the efficient utilization of resources relative to other Central American nations, ] still confronts challenges responding to its populations' diverse healthcare needs.<ref name=":0">Angel-Urdinola D, Cortez R, Tanabe K. (2008). Equity, Access to Health Care Services and Expenditures on Health in Nicaragua. Health, Nutrition and Population of the World Bank.</ref> | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| The ] guarantees universal free ] for its citizens.<ref name=":1">Sequeira M, Espinoza H, Amador JJ, Domingo G, Quintanilla M, and de los Santos T. (2011). The Nicaraguan Health System. PATH.</ref> However, limitations of current delivery models and unequal distribution of resources and medical personnel contribute to the persistent lack of quality care in more remote areas of Nicaragua, especially among rural communities in the Central and Atlantic region.<ref name=":0"/> To respond to the dynamic needs of localities, the government has adopted a decentralized model that emphasizes community-based preventive and primary medical care.<ref>Birn AE, Zimmerman S, Garfield R. (2000). To decentralize or not to decentralize, is that the question? Nicaraguan health policy under structural adjustment in the 1990s. I''nternational Journal of Health Services,'' ''30,'' 111–28.</ref> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * on Wildlife | |||
| * Article on endangered shark in Nicaragua. | |||
| * Adopt-a-turtle fund | |||
| * Information about National Parks | |||
| * on reserves | |||
| * Wildlife of Laguna de Apoyo Nature Reserve | |||
| === Education === | |||
| {{North America topic|Fauna of}} | |||
| {{Main|Education in Nicaragua}} | |||
| The adult literacy rate in 2005 was 78.0%, the lowest ] rate in Central America.<ref name=unescolit>{{cite web|title=National adult literacy rates (15+), youth literacy rates (15–24) and elderly literacy rates (65+)|url=http://stats.uis.unesco.org/unesco/TableViewer/tableView.aspx?ReportId=210|publisher=UNESCO Institute for Statistics|access-date=2013-07-22|archive-date=2013-10-29|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029183908/http://stats.uis.unesco.org/unesco/TableViewer/tableView.aspx?ReportId=210|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Primary education is free in Nicaragua. A system of private schools exists, many of which are religiously affiliated and often have more robust English programs.<ref>{{cite news|last=Liu|first=D|title=Nicaragua's new gov't to enforce free education|date=2006-12-06|url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2006-12/06/content_5442752.htm|work=CHINA VIEW|access-date=2007-05-09|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061228223949/http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2006-12/06/content_5442752.htm|archive-date=2006-12-28}}</ref> As of 1979, the educational system was one of the poorest in Latin America.<ref name=NE>{{cite news|first=D|last=Gilbert|title=Nicaragua: Education|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0036)|work=Country Studies|access-date=2007-07-02|archive-date=2 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200102104512/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0036)|url-status=live}}</ref> One of the first acts of the newly elected Sandinista government in 1980 was an extensive and successful literacy campaign, using secondary school students, university students and teachers as volunteer teachers: it reduced the overall illiteracy rate from 50.3% to 12.9% within only five months.<ref name=NLC>{{cite news|first=U|last=Hanemann|title=Nicaragua's Literacy Campaign|url=http://portal.unesco.org/education/en/file_download.php/67b39f3aaf8f20da06be3c6a4e4c6dfeHanemann_U.doc|work=UNESCO|access-date=2007-07-02|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070703020810/http://portal.unesco.org/education/en/file_download.php/67b39f3aaf8f20da06be3c6a4e4c6dfeHanemann_U.doc|archive-date=July 3, 2007}}</ref> This was one of a number of large-scale programs which received international recognition for their gains in ], health care, education, ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite news|title=Historical Background of Nicaragua|publisher=Stanford University|url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/history/background.html|access-date=2007-05-09|archive-date=22 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170422185323/http://stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/history//background.html|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Nicaragua Pre-election Delegation Report |publisher=Global Exchange |url=http://www.globalexchange.org/tours/NicaraguaReportOct2001.html |access-date=2007-05-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060930032055/http://www.globalexchange.org/tours/NicaraguaReportOct2001.html |archive-date=September 30, 2006 }}</ref> The Sandinistas also added a leftist ideological content to the curriculum, which was removed after 1990.<ref name=gr1/> In September 1980, ] awarded Nicaragua the ] sponsored ] for the literacy campaign.<ref>{{cite news|last=Arrien|first=JB|title=Literacy in Nicaragua|publisher=UNESCO|url=http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001459/145937e.pdf|access-date=2007-08-01|archive-date=19 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171019150639/http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001459/145937e.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| === Gender equality === | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Gender equality in Nicaragua}} | |||
| Nicaragua's gender equality ranks high among countries in ].<ref name=":02">{{Cite journal|last=Piper|first=Alan T.|date=May 2018|title=An investigation into the reported closing of the Nicaraguan gender gap|journal=Mpra Paper|url=https://ideas.repec.org/p/pra/mprapa/86769.html|language=en|access-date=31 October 2018|archive-date=1 November 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181101095420/https://ideas.repec.org/p/pra/mprapa/86769.html|url-status=live}}</ref> When it came to global rankings regarding gender equality, the World Economic Forum ranked Nicaragua at number twelve in 2015,<ref name=":02" /> and in its 2020 report Nicaragua ranked number five, behind only northern European countries.<ref>{{cite web |publisher=World Economic Forum |date=2020 |title=Global Gender Gap Report |page=9 |location=Geneva |url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GGGR_2020.pdf |access-date=20 August 2021 |archive-date=17 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191217140602/http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GGGR_2020.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua was among the many countries in Latin America and the Caribbean to ratify the ], which aimed to promote women's rights.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.unwomen.org/en/where-we-are/americas-and-the-caribbean|title=Americas and the Caribbean|work=UN Women|access-date=2018-11-27|language=en|archive-date=29 November 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181129100444/http://www.unwomen.org/en/where-we-are/americas-and-the-caribbean|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Conversion to the SUCRE=== | |||
| {{Main|Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas|SUCRE (currency)}} | |||
| In 2009, a Special Ombudsman for Sexual Diversity position was created within its Office of the Human Rights Ombudsman. And, in 2014, the Health Ministry in 2014 banned discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2018-12-18|title=Nicaragua's rainbow revolutionaries|url=https://www.washingtonblade.com/2018/12/18/nicaraguas-rainbow-revolutionaries/|access-date=2020-06-22|website=Washington Blade: Gay News, Politics, LGBT Rights|language=en-US|archive-date=26 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200626015421/https://www.washingtonblade.com/2018/12/18/nicaraguas-rainbow-revolutionaries/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Nevertheless, discrimination against LGBTQ individuals is common, particularly in housing, education, and the workplace.<ref name="Nicaragua"/> | |||
| Nicaragua is currently a member of the ], which is also known as ALBA. ALBA has proposed creating a new currency, the ] for use among its members. In essence, this means that the Nicaraguan córdoba will be replaced with the Sucre. Members must make their local currency deposits in ], to enter into force on sucre. The ] first will be virtual, to be used only among the states for inter-regional trade. It will then be used in print form. The ALBA-Sucre union is similar to that of the ] of the ]. | |||
| ] ranked Nicaragua 106 out of 160 countries in the ] in 2017. It reflects gender-based inequalities in three dimensions - reproductive health, empowerment, and economic activity.<ref>{{Cite journal|title=Human development indices and indicators: 2018 statistical update|date=2018-09-19|doi=10.18356/9a42b856-en|s2cid=240203402|url=http://www.gbv.de/dms/zbw/1041186428.pdf|access-date=14 November 2022|archive-date=21 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221121042557/https://www.gbv.de/dms/zbw/1041186428.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Other nations that will follow a similar pattern include: ], ], ], Honduras, ], ], ] and ].<ref name=laprensa20100616>{{cite web|url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2009/12/13/nacionales/10246|title=Primera prueba del sucre en enero – LA PRENSA — EL Diario de los Nicaragüenses|publisher=Laprensa.com.ni|date=2010-06-16|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| == |
== Culture == | ||
| <!-- Commented out: ], Nicaragua]] --> | |||
| {{Main|Tourism in Nicaragua}} | |||
| By 2006, tourism in Nicaragua had become the second largest industry in the nation,<ref name=Euromonitor>{{cite news|title=Travel And Tourism in Nicaragua|publisher=Euromonitor International|url=http://www.euromonitor.com/Travel_And_Tourism_in_Nicaragua|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> over the last 7 years ] has grown about 70% nationwide with rates of 10%–16% annually.<ref name=C2>{{cite news|first=G|last=Alemán|title=Turismo en Nicaragua: aportes y desafios parte I|url=http://www.canal2tv.com/Noticias/Marzo%202007/turismo%20con%20gran%20empuje%20en%20Nicaragua.html|work=Canal 2|accessdate=2007-07-29|language=Spanish}}</ref> Nicaragua had seen positive growth in the tourism sector over the last decade, and it became the first largest industry in 2007. The increase and growth led to the ] from tourism to rise more than 300% over a period of 10 years.<ref>{{cite news|title=A Dynamic Economy: Dynamic Sectors of the Economy; Tourism|url=http://www.pronicaragua.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=25&Itemid=98|work=ProNicaragua|accessdate=2007-08-01}}</ref> The growth in tourism has also positively affected the agricultural, commercial, and finance industries, as well as the construction industry. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Every year about 60,000 U.S. citizens visit Nicaragua, primarily business people, tourists, and those visiting relatives.<ref>{{cite news|title=Background Note: Nicaragua; Economy|publisher=U.S. State Department|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/1850.htm|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Some 5,300 people from the U.S. reside in the country now. The majority of tourists who visit Nicaragua are from the U.S., Central or South America, and Europe. According to the Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua (INTUR),<ref>{{cite news|title=Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua|publisher=INTUR|url=http://www.intur.gob.ni/|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> the colonial city of ] is the preferred spot for tourists. Also, the cities of León, Masaya, Rivas and the likes of ], San Juan River, ], Mombacho Volcano, the ], and others are main tourist attractions. In addition, ] and ] attract many tourists to Nicaragua. | |||
| According to ''TV Noticias'' (news program) on ], a Nicaragua television station, the main attractions in Nicaragua for tourists are the beaches, scenic routes, the architecture of cities such as León and Granada, and most recently ] and ], particularly in Northern Nicaragua.<ref name=C2/> As a result of increased tourism, Nicaragua has seen its ] increase by 79.1% from 2007 to 2009.<ref>{{cite web|author=By Acan-Efe|url=http://www.centralamericadata.com/en/article/home/Foreign_investment_Increases_by_791_in_Nicaragua/378984|title=Foreign investment Increases by 79.1% in Nicaragua – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal|publisher=CentralAmericaData|date=2009-03-27|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguans|Demographics of Nicaragua}} | |||
| ===Population=== | |||
| According to the ], Nicaragua has a population of 5,891,199; comprising mainly 69% mestizo, 17% ], 5% ], 9.0% ] and this fluctuates with changes in migration patterns. The population is 84% urban. | |||
| ] | |||
| According to the CIA World Factbook, Nicaragua's life expectancy was 71.5 years in 2009,<ref>, CIA World Factbook</ref> a figure roughly equivalent to that of ] and ]. The infant mortality rate stood at 25.5, roughly equivalent to that of the ] and ].<ref>, CIA World Handbook</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua appears ranked 91st in the international mortality rate, which places it between the world average and Panama.<ref>, CIA World Factbook</ref> | |||
| The most populous city in Nicaragua is the capital, Managua, with a population of 1.8 million (2005) and an estimated 2.2 by 2010 and more than 2.5 mill for the metro area. As of 2005, over 7.0 million inhabitants live in the Pacific, Central and North regions, 5.5 in the Pacific region alone, while inhabitants in the Caribbean region reached an estimated 700,000.<ref name=CN>{{cite news|title=VIII Censo de Poblacion y IV de Vivienda|date=October 2005|url=http://www.inec.gob.ni/censos2005/ResumenCensal/RESUMENCENSAL.pdf|format=PDF|work=Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos|accessdate=2007-07-07|language=Spanish}}</ref> | |||
| There is a growing ] community<ref>{{cite news|title=Expatriates of Nicaragua|url=http://www.nicaragua.com/expatriates/|work=Nicaragua.com|accessdate=2007-07-30}}</ref> the majority of whom move for business, investment or retirement from United States, Canada, Europe, ], and other countries; the majority have settled in Managua, ] and ]. | |||
| Many ], particularly in the United States, Mexico, Costa Rica, Canada and El Salvador.<ref>. Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua has a ] of 1.8% as of 2008.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} This is the result of one of the highest ]s in the ]: 24.9X1,000 according to the ] for the period 2005–2010.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} The death rate is 4.1X1,000 during the same period according to the ].{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} | |||
| ===Ethnic groups=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The majority of the Nicaraguan population, (86% or approximately 5.06 million people), is either Mestizo or White. 69% are Mestizos (mixed Amerindian and ]) and 17% are White with the majority being of Spanish, German, Italian, English or French ancestry. Mestizos and Whites mainly reside in the western region of the country. | |||
| About 9% of Nicaragua's population are black, and mainly reside on the country's sparsely populated Caribbean or Atlantic coast. The black population is mostly composed of black English-speaking Creoles who are the descendents of escaped or shipwrecked slaves; many carry the name of Scottish settlers who brought slaves with them, such as Campbell, Gordon, Downs and Hodgeson. Although many Creoles supported Somoza because of his close association with the US, they rallied to the Sandinista cause in July 1979 only to reject the revolution soon afterwards in response to a new phase of 'westernization' and imposition of central rule from Managua.<ref name=Baracco2005>{{cite book|last=Baracco|first=L|year=2005|title=Nicaragua: The Imagining of a Nation. From Nineteenth-Century Liberals to Twentieth-Century Sandinistas|location=New York|publisher=Algora Publishing|chapter=From Acquiescence to Ethnic Militancy: Costeno Responses to Sandinista Anti-Imperialist Nationalism}}</ref> Nicaragua has the largest ] population in Central America. There is also a smaller number of ], a people of mixed ], ] and ] descent. In the mid-1980s, the government divided the department of ] – consisting of the eastern half of the country – into two autonomous regions and granted the black and indigenous people of this region limited self-rule within the Republic. | |||
| The remaining 5% of Nicaraguans are Amerindians, the unmixed descendants of the country's indigenous inhabitants. Nicaragua's ] population consisted of many indigenous groups. In the western region the Nicarao people, after whom the country is named, were present along with other groups related by culture and language to the ]. The Caribbean coast of Nicaragua was inhabited by indigenous peoples who were mostly ] related groups that had migrated from South America, primarily present day ] and ]. These groups include the ]s, ] and ]. In the 19th century, there was a substantial ] minority, but this group was also largely assimilated culturally into the mestizo majority. | |||
| ===Immigration=== | |||
| ]s celebrating the 10th anniversary of the Nicaraguan revolution in Managua waving Palestinian and ] flags]] | |||
| Relative to its overall population, Nicaragua has never experienced any large-scale immigrant waves. The total number of immigrants to Nicaragua, both originating from other Latin American countries and all other countries, never surpassed 1% of its total population prior to 1995. The 2005 census showed the foreign-born population at 1.2%, having risen a mere .06% in 10 years.<ref name=CN/> | |||
| In the 19th century Nicaragua experienced modest waves of immigration from Europe. In particular, families from Germany, Italy, Spain, France and Belgium immigrated to Nicaragua, particularly the departments in the Central and Pacific region. As a result, the Northern cities of ], ] and ] have significant communities of fourth generation Germans. They established many agricultural businesses such as coffee and sugar cane plantations, newspapers, hotels and banks. | |||
| Also present is a small Middle Eastern-Nicaraguan community of ], ], ]s, ], and ] people in Nicaragua with a total population of about 30,000. There is also an East Asian community mostly consisting of ], ]ese, and Japanese. The ] population is estimated at around 12,000.<ref name=joshuaproject>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua: People groups|url=http://www.joshuaproject.net/countries.php?rog3=NU|work=Joshua Project|accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> The Chinese arrived in the late 19th century but were unsubstantiated until the 1920s. | |||
| ===Diaspora=== | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan Diaspora}} | |||
| The Civil War forced many Nicaraguans to start lives outside of their country. Although many Nicaraguans returned after the end of the war, many people emigrated during the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century due to the lack of employment opportunities and poverty. The majority of the ] migrated to ] and the United States, and today one in six Nicaraguans live in these two countries.<ref name=thedialogue>{{cite web|url=http://www.thedialogue.org/PublicationFiles/The%20Nicaragua%20case_M%20Orozco2%20REV.pdf|title=Microsoft Word - The Nicaragua case_M Orozco2 REV.doc|format=PDF|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| The diaspora has also seen Nicaraguans settling around in smaller communities in other parts of the world, particularly Western Europe. Small communities of Nicarguans are found in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Communities also exist in Australia and New Zealand. Canada, Brazil and Argentina in the Americas also host small groups of these communities. In Asia, Japan also hosts a small Nicaraguan community. | |||
| == Maternal and Child Health Care == | |||
| In June 2011, the ] released a report on . It contained new data on the midwifery workforce and policies relating to newborn and maternal mortality for 58 countries. The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Nicaragua is 100. This is compared with 102.6 in 2008 and 100.8 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 27 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 46. The aim of this report is to highlight ways in which the ] can be achieved, particularly Goal 4 – Reduce child mortality and Goal 5 – improve maternal death. In Nicaragua the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 7 and 1 in 300 shows us the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women.<ref name="SOWMY">{{cite web|url=http://www.unfpa.org/sowmy/report/home.html|title=The State Of The World's Midwifery|publisher=United Nations Population Fund|date=Accessed August 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| {{Main|Culture of Nicaragua}} | {{Main|Culture of Nicaragua}} | ||
| ], a ], was the first literary work of post-Columbian Nicaragua and is regarded as one of ]'s most distinctive colonial-era expressions and as Nicaragua's signature folkloric masterpiece combining music, dance, and theatre.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by ] but also including Native American sounds and flavors. Nicaraguan culture can further be defined in several distinct strands. The Pacific coast has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by ]. It was colonized by Spain and has a similar culture to other Spanish-speaking Latin American countries. The indigenous groups that historically inhabited the Pacific coast have largely been assimilated into the ] culture. | |||
| The Caribbean coast of Nicaragua was once a British protectorate. English is still predominant in this region and spoken domestically along with Spanish and ]. Its culture is similar to that of Caribbean nations that were or are British possessions, such as ], Belize, the ], etc. Unlike on the west coast, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean coast have maintained distinct identities, and some still speak their native languages as first languages. | |||
| ] has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by ] but enriched with Amerindian sounds and flavors. Nicaraguan culture can further be defined in several distinct strands. The Pacific coast has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by ]. It was colonized by Spain and has a similar culture to other Spanish-speaking Latin American countries. The indigenous groups that historically inhabited the Pacific coast have largely been assimilated into the ] culture. | |||
| === Music === | |||
| The Caribbean coast of the country, on the other hand, was once a British ]. English is still predominant in this region and spoken domestically along with Spanish and ]. Its culture is similar to that of Caribbean nations that were or are British possessions, such as ], ], the ], etc. Unlike on the west coast, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean coast have maintained distinct identities, and some still speak their native languages as first languages. | |||
| ===Music=== | |||
| {{Main|Music of Nicaragua}} | {{Main|Music of Nicaragua}} | ||
| ] costume, which is a traditional costume worn to dance the Mestizaje dance. The costume demonstrates the Spanish influence upon Nicaraguan clothing.<ref>{{cite news|title=Traditional Nicaraguan Costumes: Mestizaje Costume|url=http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/19-traditional-nicaraguan-costumes.html|work=ViaNica.com|access-date=2007-11-21|archive-date=24 October 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231024123152/https://www.vianica.com/go/specials/19-traditional-nicaraguan-costumes.html|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] is a mixture of indigenous and Spanish influences. Musical instruments include the ] and others common across Central America. The marimba of Nicaragua is played by a sitting performer holding the instrument on his knees. He is usually accompanied by a bass ], guitar and guitarrilla (a small guitar like a ]). This music is played at social functions as a sort of background music. | |||
| The marimba is made with hardwood plates placed over bamboo or metal tubes of varying lengths. It is played with two or four ]s. The Caribbean coast of Nicaragua is known for a lively, sensual form of ] called '']'' which is popular throughout the country. It is especially loud and celebrated during the Palo de Mayo festival in May. The ] community (Afro-Native American) is known for its popular music called '']''. | |||
| Nicaragua has international influence in music. ], ], ] and ] have gained prominence in cultural centres such as Managua, Leon and ]. Cumbia dancing has grown popular with the introduction of Nicaraguan artists, including Gustavo Leyton, on ] and in Managua. ] has become extremely popular in Managua's nightclubs. With various influences, the form of salsa dancing varies in Nicaragua. New York style and Cuban Salsa (Salsa Casino) elements have gained popularity across the country. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Nicaragua enjoys a variety of international influence in the music arena. ], ], ] and ] have gained prominence in cultural centers such as Managua, Leon and ]. Cumbia dancing has grown popular with the introduction of Nicaraguan artists, including Gustavo Leyton, on ] and in Managua. ] has become extremely popular in Managua's nightclubs. With various influences, the form of salsa dancing varies in Nicaragua. New York style and Cuban Salsa (Salsa Casino) elements have gained popularity across the country. | |||
| === Dance === | |||
| ] has also gained popularity in Nicaragua. Combinations of styles from the ] and the United States can be found throughout the country. The nature of the dance in Nicaragua varies depending on the region. Rural areas tend to have a stronger focus on movement of the hips and turns. Urbanized cities, on the other hand, focus primarily on more sophisticated footwork in addition to movement and turns. A considerable amount of Bachata dancing influence comes from Nicaraguans living abroad, in cities that include ], ] and, to a much lesser extent, ]. ] has also surfaced recently in cultural cities and ballroom dance occasions. | |||
| {{Further|Dance in Nicaragua}} | |||
| Dance in Nicaragua varies depending upon the region. Rural areas tend to have a stronger focus on movement of the hips and turns. The dance style in cities focuses primarily on more sophisticated footwork in addition to movement and turns. Combinations of styles from the ] and the United States can be found throughout Nicaragua. ] is popular in Nicaragua. A considerable amount of Bachata dancing influence comes from Nicaraguans living abroad, in cities that include Miami, Los Angeles and, to a much lesser extent, New York City. ] has also surfaced recently in cultural cities and ballroom dance occasions. | |||
| ===Literature=== | === Literature === | ||
| {{Main|Literature of Nicaragua}} | {{Main|Literature of Nicaragua}} | ||
| ], founder of ]'s ] literary movement]] | |||
| The origin of ] can arguably be traced to ] times. The myths and ] formed the cosmogenic view of the world of the indigenous people. Some of these stories are still known in Nicaragua. Like many Latin American countries, the Spanish conquerors have had the most effect on both the culture and the literature. Nicaraguan literature has historically been an important source of poetry in the Spanish-speaking world, with internationally renowned contributors such as ] who is regarded as the most important literary figure in Nicaragua. He is called the "Father of Modernism" for leading the '']'' literary movement at the end of the 19th century.<ref name=NI/> Other literary figures include ], ], Alberto Cuadra Mejia, Manolo Cuadra, Pablo Alberto Cuadra Arguello, Orlando Cuadra Downing, Alfredo Alegría Rosales, ], ], ], ] and ], among others.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&layout=2&eotf=1&sl=es&tl=en&u=http://elcomercio.pe/edicionimpresa/Html/2008-01-20/nicaragua-eterna-tierra-poetas.html&act=url|title=Nicaragua, Eternal Land of Poets|publisher=Elcomercio.pe|access-date=2010-06-26|archive-date=25 February 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160225083118/http://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&layout=2&eotf=1&sl=es&tl=en&u=http://elcomercio.pe/edicionimpresa/Html/2008-01-20/nicaragua-eterna-tierra-poetas.html&act=url|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The satirical drama '']'' was the first literary work of post-Columbian Nicaragua. It was written in both ] and Spanish.<ref name="Campbell1997" />{{rp|21}} It's regarded as one of Latin America's most distinctive colonial-era expressions and as Nicaragua's signature folkloric masterpiece. El Güegüense is a work of resistance to Spanish colonialism that combined music, dance and theatre.<ref name='NI'>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Showcasing Nicaragua's Folkloric Masterpiece – El Gueguense – and Other Performing and Visual Arts |url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-150984344.html |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia.com |access-date=2007-08-03 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071216041440/http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-150984344.html |archive-date=December 16, 2007 }}</ref> The ] play was written by an anonymous author in the 16th century, making it one of the oldest ] theatrical/dance works of the ]. In 2005 it was recognized by ] as "a patrimony of humanity".<ref>{{cite news|title=Native Theatre: El Gueguense|publisher=Smithsonian Institution|url=http://www.nmai.si.edu/calendar/index.asp?month=10&year=2006&day=22|access-date=2007-08-03|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071206171831/http://www.nmai.si.edu/calendar/index.asp?month=10&year=2006&day=22|archive-date=December 6, 2007}}</ref> After centuries of popular performance, the play was first published in a book in 1942.<ref>{{cite news|title=El Güegüense o Macho Ratón|url=http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/21-el-gueguense-macho-raton.html|work=ViaNica|access-date=2007-08-03|archive-date=21 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210221194255/https://vianica.com/go/specials/21-el-gueguense-macho-raton.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ], the founder of the ] literary movement in ].]]The ] can be traced to ] times; the myths and ] formed the cosmogonic view of the world of the indigenous people. Some of these stories are still known in Nicaragua. Like many Latin American countries, the Spanish conquerors have had the most effect on both the culture and the literature. Nicaraguan literature has historically been an important source of ] in the Spanish-speaking world, with internationally renowned contributors such as ], who is regarded as the most important literary figure in Nicaragua. He is called the "Father of Modernism" for leading the '']'' literary movement at the end of the 19th century.<ref name=NI/> Other literary figures include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ], among others. | |||
| === Cuisine === | |||
| The ] ] '']'' was the first literary work of post-Columbian Nicaragua. It is regarded as one of Latin America's most distinctive colonial-era expressions and as Nicaragua's signature folkloric masterpiece, combining music, dance and theater.<ref name='NI'>{{cite news|title=Showcasing Nicaragua's Folkloric Masterpiece – El Gueguense – and Other Performing and Visual Arts|url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-150984344.html|work=Encyclopedia.com|accessdate=2007-08-03}}</ref> The ] ] was written by an anonymous author in the 16th century, making it one of the oldest ] theatrical/dance works of the ].<ref name=Smithsonian2006>{{cite news|title=Native Theatre: El Gueguense|publisher=Smithsonian Institution|url=http://www.nmai.si.edu/calendar/index.asp?month=10&year=2006&day=22|accessdate=2007-08-03|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20071206171831/http://www.nmai.si.edu/calendar/index.asp?month=10&year=2006&day=22|archivedate=December 6, 2007}}</ref> After centuries of popular performance, the play was first published in a book in 1942.<ref name=gueguense>{{cite news|title=El Güegüense o Macho Ratón|url=http://www.vianica.com/go/specials/21-el-gueguense-macho-raton.html|work=ViaNica|accessdate=2007-08-03}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Nicaraguan cuisine}} | |||
| ], a Nicaraguan dish served with boiled yuca and chicharrones (fried pork with skin) and topped with a cabbage salad]] | |||
| ], a traditional Nicaraguan dish made with rice and beans]] | |||
| ] is a mixture of Spanish food and dishes of a pre-Columbian origin.<ref name=NICA>{{cite web|title=Try the culinary delights of Nicaragua cuisine|publisher=Nicaragua.com|url=http://www.nicaragua.com/cuisine/|access-date=2006-05-08|archive-date=16 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151016015343/http://www.nicaragua.com/cuisine/|url-status=live}}</ref> Traditional cuisine changes from the Pacific to the Caribbean coast. The Pacific coast's main staple revolves around local fruits and corn, the Caribbean coast cuisine makes use of seafood and the coconut. | |||
| As in many other Latin American countries, ] is a ] and is used in many of the widely consumed dishes, such as the ], ], and '']''. Maize is also an ingredient for drinks such as ] and ] as well as sweets and desserts. In addition to corn, rice and beans are eaten very often. | |||
| ===Language=== | |||
| {{Main|Languages of Nicaragua|Central American Spanish|Nicaraguan Spanish|Voseo}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ], Nicaragua's ], is made with white rice and small red beans that are cooked individually and then fried together. The dish has several variations including the addition of ] or grated ] on the Caribbean coast. Most Nicaraguans begin their day with gallo pinto. Gallo pinto is most usually served with ''carne asada'', a salad, fried cheese, ] or maduros. | |||
| ] has many indigenous influences and several distinguishing characteristics. Until the 19th century, a hybrid form of Nahuat-Spanish was the common language of Nicaragua. Today ], ], and ] words and syntax can be found in everyday speech.<ref name=everyculture></ref> The Nicaraguan accent dates back to the 16th century in ], and the relative isolation of Nicaragua meant that the accent did not change in the same ways that the Andalusian accent has. For example, some Nicaraguans have a tendency to replace the "s" sound with an "h"" sound when speaking.<ref name=everyculture/> Other Nicaraguans pronounce the word ''vos'' with a strong ''s'' sound at the end. In the central part of the country, regions such as ] pronounce ''vos'' without the ''s'' sound at the end. The result is ''vo'', similar to ''vous'' in ] and ''voi'' in ]. | |||
| Many of Nicaragua's dishes include indigenous fruits and vegetables such as ], ], ], ]o, pipian, banana, ], ], and herbs such as ], ] and ].<ref name=NICA/> | |||
| ], ] and ], where ] Spanish is spoken.]] ] is spoken by about 90% of Nicaragua's population. In Nicaragua, the '']'' form of address is dominant in both speech and publications. The same is true for the ] region of South America. Nicaraguan Spanish can be understood everywhere in the ]. | |||
| Nicaraguans, unlike most Spanish-speaking groups, cannot be categorized uniformly in terms of accent and word usage. Although Spanish is spoken throughout the country, the country has great variety: vocabulary, accents and colloquial language can vary between towns and departments.<ref name=Chamorro>{{cite web|author=|url=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FLCnGxUR8K4|title=Aqui Nicaragua Documentary, Program by Carlos Fernando Chamorro. Programa Inaugural de Aqui Nicaragua, Idiosincracia Nicaragüense|language=Spanish|publisher=Youtube.com|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| Traditional street food snacks found in Nicaragua include "]", a thick tortilla with soft cheese and cream, "tajadas" (deep-fried plantain chips), "maduros" (a sautéed ripe plantain), and "fresco" (fresh juices such as hibiscus and tamarind commonly served in a plastic bag with a straw).<ref>{{cite web|last1=Gleeson|first1=Bridget|title=How to eat like a Nicaraguan|url=https://www.lonelyplanet.com/nicaragua/travel-tips-and-articles/how-to-eat-like-a-nicaraguan/40625c8c-8a11-5710-a052-1479d276db80|website=Lonely Planet|access-date=27 May 2018|language=en|date=15 April 2016|archive-date=29 May 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180529204450/https://www.lonelyplanet.com/nicaragua/travel-tips-and-articles/how-to-eat-like-a-nicaraguan/40625c8c-8a11-5710-a052-1479d276db80|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In the Caribbean coast, many Afro-Nicaraguans and creoles speak English and ] as their first language, but as a second language, they speak a fluent Spanish. The language in the North and South Atlantic Regions are influenced by English, Dutch, Portuguese, Spanish and French roots. In addition, many of the indigenous people speak their native languages, such as the ], ], ] and ].<ref name=ethnologue>{{cite news|title=Languages of Nicaragua|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=NI|work=Ethnologue|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> In addition, many ]s in Nicaragua have maintained ancestral languages, while also speaking Spanish or English; these include Chinese, Arabic, German, and Italian. | |||
| Nicaraguans have been known to eat ]s,<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gpEjzy6njwwC&q=nicaragua+guinea+pig|title=Nicaragua|last=Gritzner|first=Charles F.|date=2010|publisher=Infobase Publishing|isbn=9781604136197|language=en|access-date=27 October 2020|archive-date=5 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205140326/https://books.google.com/books?id=gpEjzy6njwwC&q=nicaragua+guinea+pig#v=snippet&q=nicaragua%20guinea%20pig&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> known as ''cuy''. Tapirs, iguanas, turtle eggs, armadillos and boas are also sometimes eaten, but because of extinction threats to these wild creatures, there are efforts to curb this custom.<ref name="NICA" /> | |||
| Spanish is taught as the principal language. English is taught to students during their high school years and tends to be the national second language. Other languages, particularly ], can also be found sporadically, particularly within ] communities. | |||
| === Media === | |||
| Nicaragua was home to three ]s, one of which was never classified. ] is also of particular interest to ] as the world's youngest language.<ref name=indiana1999>{{cite web|url=http://www.indiana.edu/~langacq/E105/Nicaragua.html|title=Nicaragua|publisher=Indiana.edu|date=1999-10-24|accessdate=2010-06-26}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Media of Nicaragua}} | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| For most Nicaraguans radio and TV are the main sources of news. There are more than 100 radio stations and several TV networks. Cable TV is available in most urban areas.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1225218.stm#leaders|work=BBC News|title=Country profile: Nicaragua|date=2009-09-02|access-date=2010-05-20|archive-date=3 June 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100603034458/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1225218.stm#leaders|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The Nicaraguan print media are varied and partisan, representing pro and anti-government positions. Publications include ], ], ], Hoy, and Mercurio. Online news publications include Confidencial and ]. | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{Main|Religion in Nicaragua}} | |||
| ] is growing in diversity, the majority of Nicaraguans identify themselves as observers of the ] faith. Pictured above is the ], which is among one of the nation's ]s and an active place of religious worship in ].]]Religion is a significant part of the culture of Nicaragua and is referred to in the ]. Religious freedom, which has been guaranteed since 1939, and religious tolerance are promoted by both the Nicaraguan government and the constitution. | |||
| === Sports === | |||
| Nicaragua has no official religion. Catholic ]s are expected to lend their authority to important state occasions, and their pronouncements on national issues are closely followed. They can also be called upon to mediate between contending parties at moments of political crisis.<ref name=LOCR>{{cite news|first=G|last=Dennis|title=Nicaragua: Religion|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0040)|work=Country Studies|accessdate=2007-10-30}}</ref> | |||
| ], Nicaragua's main outdoor stadium]] | |||
| ] is the most popular sport in Nicaragua. Although some professional Nicaraguan baseball teams have recently folded, the country still enjoys a strong tradition of American-style baseball. | |||
| Baseball was introduced to Nicaragua during the 19th century. In the Caribbean coast, locals from Bluefields were taught how to play baseball in 1888 by Albert Addlesberg, a retailer from the United States.<ref name=BB>{{cite news |first=B |last=Villa |title=LA HISTORIA DEL BÉISBOL EN LATINOAMERICA: Nicaragua |url=http://latinobaseball.com/cwb-history.php |work=Latino Baseball |access-date=2007-07-29 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070702032726/http://www.latinobaseball.com/cwb-history.php |archive-date=July 2, 2007 }}</ref> Baseball did not catch on in the Pacific coast until 1891 when a group of mostly college students from the United States formed "La Sociedad de Recreo" (Society of Recreation) where they played various sports, baseball being the most popular.<ref name=BB/> | |||
| The largest denomination, and traditionally the religion of the majority, is ]. The numbers of practicing Roman Catholics have been declining, while members of ] ] groups and ] have been rapidly growing in numbers since the 1990s. There are also strong ] and ] communities on the Caribbean coast. | |||
| Nicaragua has had its share of ] players, including shortstop ], pitcher ], and pitcher ], but the most notable is ], who was the first baseball player from Nicaragua to play in ].<ref>{{cite news|last=Washburn |first=G |title='El Presidente' happy in new job |url=http://baltimore.orioles.mlb.com/news/article.jsp?ymd=20050220&content_id=946722&vkey=news_bal&fext=.jsp&c_id=bal |work=Major League Baseball |access-date=2007-08-21 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071012205044/http://baltimore.orioles.mlb.com/news/article.jsp?ymd=20050220&content_id=946722&vkey=news_bal&fext=.jsp&c_id=bal |archive-date=2007-10-12 }}</ref> He became the first Latin-born pitcher to throw a ], and the 13th in the major league history, when he played with the ] against the ] at Dodger Stadium in 1991.<ref>{{cite news|title=Baseball's Perfect Games: Dennis Martinez, Montreal Expos|. Also, Everth Cabrera who MLB debut was in 2009 season with San Diego Padres |publisher=The BASEBALL Page.com |url=http://www.thebaseballpage.com/stats/lists_feats/perfect_games.htm |archive-url=https://archive.today/20061113020621/http://www.thebaseballpage.com/stats/lists_feats/perfect_games.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=2006-11-13 |access-date=2007-08-21 }}</ref> | |||
| Roman Catholicism came to Nicaragua in the 16th century with the Spanish conquest and remained, until 1939, the established faith. ] and other ]s came to Nicaragua during the 19th century, but only gained large followings in the Caribbean Coast during the 20th century. | |||
| ] is the second most popular sport in Nicaragua.<ref>{{cite news|title=Salon de la Fama: Deportes en Nicaragua|url=http://www.manfut.org/museos/deportes1.html|access-date=2007-07-30|language=es|archive-date=26 September 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070926234154/http://www.manfut.org/museos/deportes1.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The country has had world champions such as ] and ] as well as ]. Recently, ] has gained popularity. The ] has served as a venue for both baseball and football. The first ever national football-only stadium in Managua, the ], was completed in 2011.<ref>{{cite news|title=Building for tomorrow in Belize and Nicaragua|publisher=FIFA|url=https://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/organisation/president/news/newsid=1418832/index.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110624001931/http://www.fifa.com/aboutfifa/organisation/president/news/newsid=1418832/index.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=June 24, 2011|access-date=2014-01-04}}</ref> | |||
| Popular religion revolves around the saints, who are perceived as intercessors (but not mediators) between human beings and God. Most localities, from the capital of Managua to small rural communities, honor ]s, selected from the Roman Catholic calendar, with annual ''fiestas''. In many communities, a rich lore has grown up around the celebrations of patron saints, such as Managua's Saint Dominic (Santo Domingo), honored in August with two colorful, often riotous, day-long processions through the city. The high point of Nicaragua's religious calendar for the masses is neither ] nor ], but La Purísima, a week of festivities in early December dedicated to the ], during which elaborate altars to the ] are constructed in homes and workplaces.<ref name=LOCR/> | |||
| ] had some recent success as it won the silver medal at the ].<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220321133108/https://www.insidethegames.biz/articles/1058880/panama-win-mens-basketball-gold-at-central-american-games-in-managua |date=21 March 2022 }} Michael Pavitt (insidethegames.biz), 7 December 2017. Accessed 14 August 2020.</ref> They will be taking part in the ] for the first time when Nicaragua hosts in ]. | |||
| The country's close political ties have also encouraged religious ties. ] has increased with a steady influx of immigration.<ref name=elnuevodiario20041024>. Archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.</ref> | |||
| Nicaragua featured national teams in ] that competed at the ] in both the women's and the men's sections.<ref>{{cite news |title=Continental Cup Finals start in Africa |url=https://www.fivb.com/en/about/news/continental-cup-finals-start-in-africa?id=94414 |accessdate=7 August 2021 |work=] |date=22 June 2021 |archive-date=7 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210807141038/https://www.fivb.com/en/about/news/continental-cup-finals-start-in-africa?id=94414 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Cuisine=== | |||
| {{Main|Cuisine of Nicaragua}} | |||
| == See also == | |||
| The Cuisine of Nicaragua is a mixture of criollo food and dishes of pre-Columbian origin. The ] found that the ] had incorporated local foods available in the area into their ].<ref name=NICA>{{cite web|title=Try the culinary delights of Nicaragua cuisine|publisher=Nicaragua.com|url=http://www.nicaragua.com/cuisine/|accessdate=2006-05-08}}</ref> Traditional cuisine changes from the Pacific to the Caribbean coast; while the Pacific coast's main staple revolves around local fruits and corn, the Caribbean coast cuisine makes use of ] and the ]. | |||
| {{portal|Nicaragua|Latin America}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| As in many other Latin American countries, ] is a main staple. Corn is used in many of the widely consumed dishes, such as the ], and ]. Corn is also an ingredient for drinks such as ] and ] as well as sweets and desserts. In addition to corn, rice and beans are eaten very often. | |||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| ], Nicaragua's ], is made with white rice and red beans that are cooked separately and then fried together. The dish has several variations including the addition of ] and/or grated ] on the Caribbean coast. Most Nicaraguans begin their day with Gallopinto. Gallopinto is most usually served with carne asada, a salad, fried cheese, platains or maduros. | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == Additional sources == | |||
| Many of Nicaragua's dishes include indigenous fruits and vegetables such as ], ], ], ]o, pipian, ], ], ], and herbs such as ], ] and ].<ref name=NICA/> | |||
| * {{StateDept}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| Nicaraguans also have been known to eat guinea pigs, tapirs, iguanas, turtle eggs, armadillos and boas but efforts are currently underway to curb this tendency.{{Citation needed|date=July 2011}} | |||
| {{sister project links|voy=Nicaragua}} | |||
| === |
===Government=== | ||
| * | |||
| ] of the ], a ] team]] | |||
| ;General information | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210320071255/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/nicaragua |date=20 March 2021 }}. '']''. ]. | |||
| * from the Business Anti-Corruption Portal | |||
| * at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100603034458/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1225218.stm |date=3 June 2010 }} from the ] | |||
| * {{Wikiatlas|Nicaragua}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081028145010/http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/namerica/camerica/ni.htm |date=28 October 2008 }} from WorldAtlas.com | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141107102704/http://www.nicaraguaportal.de/ |date=7 November 2014 }}: Official information of the Honorary Consulate of Nicaragua | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121216103743/http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=NI |date=16 December 2012 }} from ] | |||
| ===Other=== | |||
| ] is the most popular sport played in Nicaragua. Although some professional Nicaraguan baseball teams have folded in the recent past, Nicaragua enjoys a strong tradition of American-style Baseball. Baseball was introduced to Nicaragua at different years during the 19th century. In the Caribbean coast locals from Bluefields were taught how to play baseball in 1888 by Albert Addlesberg, a retailer from the United States.<ref name=BB>{{cite news|first=B|last=Villa|title=LA HISTORIA DEL BÉISBOL EN LATINOAMERICA: Nicaragua|url=http://latinobaseball.com/cwb-history.php|work=Latino Baseball|accessdate=2007-07-29|language=Spanish}}</ref> Baseball did not catch on in the Pacific coast until 1891 when a group of mostly students originating from universities of the United States formed "La Sociedad de Recreo" (Society of Recreation) where they played various sports, baseball being the most popular among them.<ref name=BB/> There are five teams that compete amongst themselves: Indios del Boer (Managua), Chinandega, Tiburones (Sharks) of Granada, León and Masaya. Players from these teams comprise the ] when Nicaragua competes internationally. The country has had its share of ] players (including current ] pitcher ] and ] pitcher ]), but the most notable is ], who was the first baseball player from Nicaragua to play in ].<ref name=Washburn2005>{{cite news|last=Washburn|first=G|title='El Presidente' happy in new job|url=http://baltimore.orioles.mlb.com/news/article.jsp?ymd=20050220&content_id=946722&vkey=news_bal&fext=.jsp&c_id=bal|work=Major League Baseball|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> He became the first Latin-born pitcher to throw a ], and the 13th in major league history, when he played with the Montreal Expos against the ] at Dodger Stadium in 1991.<ref name=thebaseballpage>{{cite news|title=Baseball's Perfect Games: Dennis Martinez, Montreal Expos|. Also, Everth Cabrera who MLB debut was in 2009 season with San Diego Padres publisher=The BASEBALL Page.com|url=http://www.thebaseballpage.com/stats/lists_feats/perfect_games.htm|accessdate=2007-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070928160120/http://www.visitanicaragua.com/ |date=28 September 2007 }} | |||
| * The State of the World's Midwifery – {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130512152957/http://www.unfpa.org/sowmy/resources/docs/country_info/profile/en_Nicaragua_SoWMy_Profile.pdf |date=12 May 2013 }} | |||
| {{Nicaragua topics}} | |||
| ] is the second most popular sport in Nicaragua.<ref name=deportes1>{{cite news|title=Salon de la Fama: Deportes en Nicaragua|url=http://www.manfut.org/museos/deportes1.html|accessdate=2007-07-30|language=Spanish}}</ref> The country has had world champions such as ] and ] among others. Recently, ] has gained popularity, especially with the younger population. The ] has served as a venue for both baseball and football but the first ever national football stadium in Managua is currently under construction.<ref name=FIFA2007>{{cite news|title=Like clockwork in Nicaragua|publisher=FIFA|url=http://www.fifa.com/en/development/goal/index/0,1223,104011,00.html?articleid=104011|accessdate=2007-05-09|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070407061947/http://www.fifa.com/en/development/goal/index/0,1223,104011,00.html?articleid=104011|archivedate=April 7, 2007}}</ref>{{Clear}} | |||
| {{navboxes | |||
| |list= | |||
| ==Education== | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| {{Main|Education in Nicaragua}}{{See also|Universities in Nicaragua|List of Schools in Nicaragua}} | |||
| |title= Geographic locale | |||
| ] Propaganda Poster]] | |||
| Nicaragua's first public primary school opened in 1837. By the late 1860s public grade schools existed in most of the larger cities. In 1877, Nicaraguan authorities accepted the principle that such schools should be nationally funded, and that attendance should be free and compulsory. In 1881 education was formally removed from religious control and turned over to government, but church-run schools continued to operate alongside the public system. Subsequently shortages of facilities and teachers, especially in rural areas, hampered educational development. The Sandinista government sharply increased spending on education and reduced illiteracy significantly, but shortages of facilities and personnel remained a problem. The Sandinistas also added a leftist ideological content to the curriculum, which was removed after 1990.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| Higher education dates from 1818 when the National Autonomous University of Nicaragua (UNAN) was founded in León. A major reform, begun in 1980, reorganized the country's postsecondary system into two universities: the UNAN, with campuses in León and Managua, and the Central American University in Managua. It also restructured the curriculum, giving more emphasis to science and technology, and less to law and commerce. Nicaragua also has several more specialized institutions, with a focus on education that will promote economic development.<ref name=grolier1/> | |||
| Education is paid via taxes for all Nicaraguans.<ref name=Liu2006>{{cite news|last=Liu|first=D|title=Nicaragua's new gov't to enforce free education|date=2006-12-06|url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2006-12/06/content_5442752.htm|work=CHINA VIEW|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Elementary education is free and compulsory, but many children in rural areas are unable to attend due to lack of schools and other reasons. Communities located on the Caribbean coast have access to education in their native languages. | |||
| The majority of higher education institutions are located in Managua, higher education has financial, organic and administrative autonomy, according to the law. Also, freedom of subjects is recognized.<ref name=education>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua Education|url=http://www.nicaragua.com/culture/education/|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> Nicaragua's higher education system consists of 48 ], and 113 ]s and technical institutes in the areas of ], ] and ], ], ] and ]-related services.<ref name=ProNicaragua>{{cite news|title=Human Capital: Educationand Training|url=http://www.pronicaragua.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=27&Itemid=87|work=ProNicaragua|accessdate=2007-08-01}}</ref> The educational system includes 1 ] English-language university, 3 ], 5 Bilingual secondary schools and dozens of ]s. In 2005, almost 400,000 (7%) of Nicaraguans held a ].<ref name=FTD>{{cite news|title=Central American Countries of the Future 2005/2006|date=2005-08-01|url=http://www.pronicaragua.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=27&Itemid=87|accessdate=2007-08-01}}</ref> 18% of Nicaragua's total budget is invested in primary, secondary and higher education. University level institutions account for 6% of 18%. | |||
| As of 1979, the educational system was one of the poorest in Latin America.<ref name=NE>{{cite news|first=D|last=Gilbert|title=Nicaragua: Education|publisher=Library of Congress|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+ni0036)|work=Country Studies|accessdate=2007-07-02}}</ref> Under the Somoza dictatorships, limited spending on education and generalized poverty, which forced many adolescents into the labor market, constricted educational opportunities for Nicaraguans. One of the first acts of the newly elected Sandinista government in 1980 was an extensive and successful literacy campaign, using secondary school students, university students and teachers as volunteer teachers: it reduced the overall ] rate from 50.3% to 12.9% within only five months.<ref name=NLC>{{cite news|first=U|last=Hanemann|title=Nicaragua's Literacy Campaign|url=http://portal.unesco.org/education/en/file_download.php/67b39f3aaf8f20da06be3c6a4e4c6dfeHanemann_U.doc|work=UNESCO|accessdate=2007-07-02|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070703020810/http://portal.unesco.org/education/en/file_download.php/67b39f3aaf8f20da06be3c6a4e4c6dfeHanemann_U.doc|archivedate=July 3, 2007}}</ref> This was one of a number of large scale programs which received international recognition for their gains in ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name=Stanford>{{cite news|title=Historical Background of Nicaragua|publisher=Stanford University|url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/discovery_eng/history/background.html|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref><ref name=globalexchange2001>{{cite news|title=Nicaragua Pre-election Delegation Report|publisher=Global Exchange|url=http://www.globalexchange.org/tours/NicaraguaReportOct2001.html|accessdate=2007-05-09}}</ref> In September 1980, ] awarded Nicaragua the '']'' award for the literacy campaign. This was followed by the literacy campaigns of 1982, 1986, 1987, 1995 and 2000, all of which were also awarded by UNESCO.<ref name=Arrien>{{cite news|last=Arrien|first=JB|title=Literacy in Nicaragua|publisher=UNESCO|url=http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001459/145937e.pdf|format=PDF|accessdate=2007-08-01}}</ref> | |||
| ==Communications and Media== | |||
| For most Nicaraguans radio and TV are the main sources of news. There are more than 100 radio stations, many of them in the capital, and several TV networks. Cable TV is available in most urban areas.<ref name=bbc1225218>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1225218.stm#leaders|work=BBC News|title=Country profile: Nicaragua|date=2009-09-02|accessdate=2010-05-20}}</ref> | |||
| The print media are varied and partisan, representing pro and anti-government positions. | |||
| ===Print=== | |||
| La Prensa; El Nuevo Diario; Confidencial Varies; Hoy; Mercurio | |||
| ===Television=== | |||
| Televicentro Canal 2; Multinoticias Canal 4; Telenica Canal 8; Canal 9; Canal 10; TVRED canal 11; Nicavision Canal 12; Viva Nicaragua Canal 13; VosTV Canal 14; 100% Noticias canal 15; CDNN Canal 23; Extraplus Canal 37 | |||
| ===Radio=== | |||
| Radio Corporacion; Radio Mundial; Radio Nicaragua (Government-owned); Radio Sandino; Radio Pirata; Radio Maranata:; Estacion X; Radio joya; Radio Romantica; Radio Pachanguera; Radio Buenisima; Radio Disney: Radio Oldis | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{satop|Geography|North America|Central America|Latin America|Nicaragua}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| <!-- *] --> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| *{{StateDept}} | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| *Asleson, Vern. (2004) ''Nicaragua: Those Passed By''. Galde Press ISBN 1-931942-16-1 | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Babb|first=FE|title=After revolution: mapping gender and cultural politics in neoliberal Nicaragua|publisher=University of Texas Press|location=Austin|year=2001|isbn=0-292-70900-5}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Bayard de Volo|first=L|title=Mothers of heroes and martyrs: gender identity politics in Nicaragua, 1979–1999|publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press|location=Baltimore|year=2001|isbn=0-8018-6764-9}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Belli|first=G|authorlink=Gioconda Belli|title=The Country Under My Skin : A Memoir of Love and War|publisher=Anchor|location=Garden City, N.Y|isbn=1-4000-3216-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Bermann|first=K|title=Under the big stick: Nicaragua and the United States since 1848|publisher=]|location=Boston|year=1986|isbn=0-89608-323-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Bermúdez|first=E|authorlink=Enrique Bermúdez|title=The Contras' Valley Forge: How I View the Nicaraguan Crisis|date=Summer 1988|publisher=The Heritage Foundation|work=Policy Review magazine}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Borge|first=T|title=The patient impatience: from boyhood to guerilla: a personal narrative of Nicaragua's struggle for liberation|publisher=Curbstone Press|location=Willimantic, Connecticut|year=1992|isbn=0-915306-97-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Brown|first=TX|title=The real Contra War: highlander peasant resistance in Nicaragua|publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|location=Norman|year=2001|isbn=0-8061-3252-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Brunnegger|first=S|title=From Conflict to Autonomy in Nicaragua: Lessons Learnt|publisher=Minority Rights Group International|location=London|year=2007|isbn=1904584616}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Bugajski|first=J|title=Sandinista communism and rural Nicaragua|publisher=Praeger|location=New York|year=1990|isbn=0-275-93536-1}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Charlip|first=JA|title=Cultivating Coffee: The Farmers of Carazo, Nicaragua, 1880–1930 (Ohio RIS Latin America Series)|publisher=Ohio University Press|location=Athens, Ohio|isbn=0-89680-227-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|author=]; Herman, Edward S.|title=Manufacturing consent: the political economy of the mass media|publisher=Pantheon Books|location=New York|year=2002|isbn=0-375-71449-9}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Christian|first=S|title=Nicaragua, revolution in the family|publisher=Vintage Books|location=New York|year=1986|isbn=0-394-74457-8}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Clark|first=GC|title=With the Old Corps in Nicaragua|publisher=Presidio Press|location=Novato, California|year=2001|isbn=0-89141-737-0}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Colburn|first=FD|title=My car in Managua|publisher=University of Texas Press|location=Austin|year=1991|isbn=0-292-75124-9}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last1=Cox|first1=Jack|last2=Somoza|first2=A|authorlink2=Anastasio Somoza Debayle|last3=Earle|first3=P|title=]|publisher=Western Islands|location=Boston|year=1980|isbn=0-88279-235-0}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Field|first=LW|title=The grimace of Macho Ratón: artisans, identity, and nation in late-twentieth century western Nicaragua|publisher=Duke University Press|location=Durham, N.C|year=1999|isbn=0-8223-2288-9}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Gilbert|first=DL|title=Sandinistas: The Party And The Revolution|publisher=Blackwell Publishers|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts|isbn=1-55786-006-8}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Gobat|first=M|title=Confronting the American Dream: Nicaragua under U.S. Imperial Rule (American Encounters/Global Interactions)|publisher=Duke University Press|location=Durham, N.C|isbn=0-8223-3634-0}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Gordon|first=EW|title=Disparate diasporas: identity and politics in an African Nicaraguan community|publisher=University of Texas Press, Austin, Institute of Latin American Studies|location=Austin, Tex|year=1998|isbn=0-292-72819-0}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Gould|first=JL|title=To die in this way: Nicaraguan Indians and the myth of mestizaje, 1880–1965|publisher=Duke University Press|location=Durham, N.C|year=1998|isbn=0-8223-2098-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Hale|first=CR|title=Resistance and Contradiction: Miskitu Indians and the Nicaraguan State, 1894–1987|publisher=Stanford University Press|location=Stanford, Calif|isbn=0-8047-2800-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Heyck|first=DLD|title=Life stories of the Nicaraguan revolution|publisher=Routledge|location=New York|year=1990|isbn=0-415-90211-8}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Horton|first=L|title=Peasants In Arms: War & Peace in the Mountains of Nicaragua, 1979–1994 (Ohio RIS Latin America Series)|publisher=Ohio University Press|location=Athens, Ohio|isbn=0-89680-204-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Kagan|first=RA|title=A twilight struggle: American power and Nicaragua, 1977–1990|publisher=Free Press|location=New York|year=1996|isbn=0-02-874057-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Kinzer|first=S|authorlink=Stephen Kinzer|title=]|publisher=Putnam|location=New York|year=1991|isbn=0-399-13594-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Kinzer|first=S|title=Overthrow: America's Century of Regime Change from Hawaii to Iraq|publisher=Times Books|location=New York|isbn=0-8050-7861-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Kruckewitt|first=J|title=The Death of ]: The Story of a North American in Sandinista Nicaragua|publisher=Seven Stories Press|location=New York|isbn=1-58322-068-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Lancaster|first=RN|title=Life is hard: machismo, danger, and the intimacy of power in Nicaragua|publisher=University of California Press|location=Berkeley|year=1992|isbn=0-520-08929-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Macaulay|first=N|title=The Sandino Affair|publisher=Wacahoota Pr|isbn=0-9653864-4-9}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Morley|first=MH|title=Washington, Somoza and the Sandinistas: State and Regime in US Policy toward Nicaragua 1969–1981|publisher=Cambridge University Press|location=Cambridge, UK|isbn=0-521-52335-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Pardo-Maurer|first=R|title=The Contras, 1980–1989: a special kind of politics|publisher=Praeger|location=New York|year=1990|isbn=0-275-93818-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Plunkett|first=H|title=In Focus Nicaragua a Guide to the People, Politics and Culture (In Focus Guides)|publisher=Interlink Publishing Group|isbn=1-56656-438-7}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Randall|first=M|title=Sandino's daughters: testimonies of Nicaraguan women in struggle|publisher=Rutgers University Press|location=New Brunswick, N.J|year=1995|isbn=0-8135-2214-5}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|author=Ratliff, William E.; Miranda, Roger|title=Civil War in Nicaragua: Inside the Sandinistas|publisher=Transaction Publishers|location=New Brunswick, N.J., U.S.A|isbn=1-56000-761-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Rushdie|first=S|title=The Jaguar Smile: A Nicaraguan Journey|publisher=Owl Books|location=Clearwater, Fla|isbn=0-8050-5311-5}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Sabia|first=D|title=Contradiction and conflict: the popular church in Nicaragua|publisher=University of Alabama Press|location=University|year=1997|isbn=0-8173-0873-3}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Sirias|first=S|title=Bernardo and the Virgin: A Novel|publisher=Northwestern University Press|location=Evanston, Ill|isbn=0-8101-2427-0}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Sklar|first=H|title=Washington's war on Nicaragua|publisher=]|location=Boston|year=1988|isbn=0-89608-295-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|author=Taber, Michael; Bishop, Maurice; Marcus, Bruce|title=Maurice Bishop speaks: the Grenada Revolution, 1979–83|publisher=Pathfinder Press|location=New York|year=1983|isbn=0-87348-619-6}} | |||
| *{{Cite report|author=United Nations Development Programme|title=Regional Human Development Report for Latin America and the Caribbean 2010: Acting on the future: breaking the intergenerational transmission of inequality|year=2010|publisher=United Nations|location=New York|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/reports/regional/latinamericathecaribbean/idhalc_en_2010.pdf}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Walker|first=TG|title=Nicaragua, 4th Edition|publisher=Westview Press|location=Boulder, Colo|isbn=0-8133-3882-4}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Walker|first=WJ|title=The war in Nicaragua|publisher=University of Arizona Press|location=Tucson|year=1985|isbn=0-8165-0882-8}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|authorlink=Gary Webb|last=Webb|first=G|title=Dark Alliance : The CIA, the Contras, and the Crack Cocaine Explosion|publisher=Seven Stories Press|location=New York|isbn=1-888363-68-1}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Zimmermann|first=M|title=Sandinista: Carlos Fonseca and the Nicaraguan revolution|publisher=Duke University Press|location=Durham, N.C|year=2000|isbn=0-8223-2595-0}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * | |||
| * Visit Nicaragua | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ; Government | |||
| * | |||
| ; General information | |||
| *{{CIA_World_Factbook link|nu|Nicaragua}} | |||
| * at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| *{{dmoz|Regional/Central_America/Nicaragua}} | |||
| *{{Wikiatlas|Nicaragua}} | |||
| * from WorldAtlas.com | |||
| *: Official information of the Honorary Consulate of Nicaragua | |||
| ; | |||
| ; Volunteer | |||
| * A US based non-profit Organization connecting Nicaraguan youths with US students in more than 100 schools. Sales of handwoven bracelets made by former street children raise funds for projects in Nicaragua. | |||
| * A quaker organization dedicated to empowering the people of Nicaragua. Student groups volunteer annually. | |||
| ;Other | |||
| *{{Wikitravel|Nicaragua}} | |||
| * The State of the World's Midwifery - | |||
| {{Coord|13|-85|type:country|display=title}} | |||
| {{Nicaragua topics|state=uncollasped}} | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| |title=<!-- ] --> Geographic locale | |||
| |list= | |list= | ||
| {{Departments of Nicaragua}} | {{Departments of Nicaragua}} | ||
| Line 799: | Line 686: | ||
| {{North America topic}} | {{North America topic}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| |title=International membership | |title=International membership | ||
| |list= | |list= | ||
| {{Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA)}} | |||
| {{Organization of American States}} | |||
| {{World Trade Organization}} | {{World Trade Organization}} | ||
| {{Latin Union}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Coord|13|N|85|W|region:NI_type:country|display=title}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| <!--please leave the empty space as standard--> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{link FA|os}} | |||
| <!--Other languages--> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:44, 9 January 2025
Country in Central America For other uses, see Nicaragua (disambiguation).
| Republic of NicaraguaRepública de Nicaragua (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: En Dios confiamos (Spanish) "In God We Trust" | |
| Anthem: Salve a ti, Nicaragua (Spanish) "Hail to Thee, Nicaragua" | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Managua 12°6′N 86°14′W / 12.100°N 86.233°W / 12.100; -86.233 |
| Official languages | Spanish |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2023) |
|
| Religion (2015) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary presidential republic under an authoritarian dictatorship |
| • President | Daniel Ortega |
| • Vice President | Rosario Murillo |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence from Spain, Mexico and the Federal Republic of Central America | |
| • Declared | 15 September 1821 |
| • Recognized | 25 July 1850 |
| • From the First Mexican Empire | 1 July 1823 |
| • From the Federal Republic of Central America | 31 May 1838 |
| • Nicaraguan Revolution | 19 July 1979 |
| • Current constitution | 9 January 1987 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 130,375 km (50,338 sq mi) (96th) |
| • Water (%) | 7.14 |
| Population | |
| • 2023 estimate | 6,359,689 (110th) |
| • Density | 51/km (132.1/sq mi) (155th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2014) | 46.2 high inequality |
| HDI (2022) | medium (130th) |
| Currency | Córdoba (NIO) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +505 |
| ISO 3166 code | NI |
| Internet TLD | .ni |
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest country in Central America, comprising 130,370 km (50,340 sq mi). With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America after Guatemala and Honduras.
Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean and shares maritime borders with El Salvador to the west and Colombia to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is Managua, the fourth-largest city in Central America, with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is Spanish, though indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English. The mixture of cultural traditions has generated substantial diversity in folklore, cuisine, music, and literature, including contributions by Nicaraguan poets and writers such as Rubén Darío.
Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part was transferred to Honduras in 1960. Since its independence, Nicaragua has undergone periods of political unrest, dictatorship, occupation and fiscal crisis, including the Nicaraguan Revolution of the 1960s and 1970s and the Contra War of the 1980s.
Though nominally a unitary presidential republic, Nicaragua has experienced significant democratic backsliding following the 2018 protests and subsequent crackdown. Following the 2021 election, it has descended into an authoritarian dictatorship. It is a developing country and has the second lowest GDP per capita (nominal) and third lowest GDP per capita (PPP) among Latin American and Caribbean countries. In 2023, Nicaragua was ranked as the second most corrupt country in Latin America, after Venezuela, by the Corruption Perceptions Index. Known as the "land of lakes and volcanoes", Nicaragua is also home to the Bosawás Biosphere Reserve, the second-largest rainforest of the Americas. The biological diversity, warm tropical climate and active volcanoes have made Nicaragua an increasingly popular tourist destination. Nicaragua co-founded the United Nations and is also a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America, and Community of Latin American and Caribbean States.
Etymology
It was previously believed that the name Nicaragua was coined by Spanish colonists based on the name Nicarao, who was a cacique of a powerful nahua tribe encountered by the Spanish conquistador Gil González Dávila during his entry into southwestern Nicaragua in 1522. This theory held that the etymology of Nicaragua was formed from Nicarao and agua (Spanish for 'water'), to refer to the fact that there are two large lakes and several other bodies of water within the country.
However, this etymology is considered to be outdated by most historians as in 2002 it was discovered that the real name of the cacique was Macuilmiquiztli and not Nicarao. In addition, the Nicaraos referred to their land as Nicānāhuac, which most historians now believe is the true etymology of "Nicaragua". It means "here lies Anahuac" in Nahuatl and is a combination of the words "Nican" (here), and "Ānāhuac", which in turn is a combination of the words "atl" (water) and "nahuac", a locative meaning "surrounded". Therefore the literal translation of Nicanahuac is "here surrounded by water", fitting the theory that the etymology refers to the large bodies of water in and around the country, the Pacific Ocean, lakes Nicaragua and Xolotlan, and the rivers and lagoons.
Additional theories about the country's name comes from any of the following Nahuatl words: nican-nahua, which means "here are the Nahuas"; and nic-atl-nahuac, the longer form of Nicanahuac meaning "here by the water" or "surrounded by water".
History
Main article: History of NicaraguaPre-Columbian history

Paleo-Indians first inhabited what is now known as Nicaragua as far back as 12,000 BCE. In later pre-Columbian times, Nicaragua's indigenous people were part of the Intermediate Area, between the Mesoamerican and Andean cultural regions, and within the influence of the Isthmo-Colombian Area. Nicaragua's central region and its Caribbean coast were inhabited by Macro-Chibchan language ethnic groups such as the Miskito, Rama, Mayangna, and Matagalpas. They had coalesced in Central America and migrated both to and from present-day northern Colombia and nearby areas. Their food came primarily from hunting and gathering, but also fishing and slash-and-burn agriculture.
At the end of the 15th century, western Nicaragua was inhabited by several indigenous peoples related by culture to the Mesoamerican civilizations of the Aztec and Maya, and by language to the Mesoamerican language area. The Chorotegas were Mangue language ethnic groups who had arrived in Nicaragua from what is now the Mexican state of Chiapas sometime around 800 CE. The Nicarao people were a branch of Nahuas who spoke the Nawat dialect and also came from Chiapas, around 1200 CE. Prior to that, the Nicaraos had been associated with the Toltec civilization. Both Chorotegas and Nicaraos originated in Mexico's Cholula valley, and migrated south. A third group, the Subtiabas, were an Oto-Manguean people who migrated from the Mexican state of Guerrero around 1200 CE. Additionally, there were trade-related colonies in Nicaragua set up by the Aztecs starting in the 14th century.
Spanish era (1523–1821)
Further information: Spanish colonization of the Americas and Spanish conquest of Nicaragua

In 1502, on his fourth voyage, Christopher Columbus became the first European known to have reached what is now Nicaragua as he sailed southeast toward the Isthmus of Panama. Columbus explored the Mosquito Coast on the Atlantic side of Nicaragua but did not encounter any indigenous people. 20 years later, the Spaniards returned to Nicaragua, this time to its southwestern part. The first attempt to conquer Nicaragua was by the conquistador Gil González Dávila, who had arrived in Panama in January 1520. In 1522, González Dávila ventured to the area that later became the Rivas Department of Nicaragua. There he encountered an indigenous Nahua tribe led by chief Macuilmiquiztli, whose name has sometimes been erroneously referred to as "Nicarao" or "Nicaragua". The tribe's capital was Quauhcapolca. González Dávila conversed with Macuilmiquiztli thanks to two indigenous interpreters who had learned Spanish, whom he had brought along. After exploring and gathering gold in the fertile western valleys, González Dávila and his men were attacked and driven off by the Chorotega, led by chief Diriangén. The Spanish tried to convert the tribes to Christianity; Macuilmiquiztli's tribe was baptized, but Diriangén was openly hostile to the Spaniards. Western Nicaragua, at the Pacific Coast, became a port and shipbuilding facility for the Galleons plying the waters between Manila, Philippines and Acapulco, Mexico.
The first Spanish permanent settlements were founded in 1524. That year, the conquistador Francisco Hernández de Córdoba founded two of Nicaragua's main cities: Granada on Lake Nicaragua, and then León, west of Lake Managua. Córdoba soon built defenses for the cities and fought against incursions by other conquistadors. Córdoba was later publicly beheaded for having defied his superior, Pedro Arias Dávila. Córdoba's tomb and remains were discovered in 2000 in the ruins of León Viejo.
The clashes among Spanish forces did not impede their destruction of the indigenous people and their culture. The series of battles came to be known as the "War of the Captains". Pedro Arias Dávila was a winner; although he lost control of Panama, he moved to Nicaragua and established his base in León. In 1527, León became the capital of the colony. Through diplomacy, Arias Dávila became the colony's first governor.
Without women in their parties, the Spanish conquerors took Nahua and Chorotega wives and partners, beginning the multiethnic mix of indigenous and European stock now known as "mestizo", which constitutes the great majority of the population in western Nicaragua. Many indigenous people were killed by European infectious diseases, compounded by neglect by the Spaniards, who controlled their subsistence. Many other indigenous peoples were captured and transported as slaves to Panama and Peru between 1526 and 1540.
In 1610, the Momotombo volcano erupted, destroying the city of León. The city was rebuilt northwest of the original, which is now known as the ruins of León Viejo. During the American Revolutionary War, Central America was subject to conflict between Britain and Spain. British navy admiral Horatio Nelson led expeditions in the Battle of San Fernando de Omoa in 1779 and on the San Juan River in 1780, the latter of which had temporary success before being abandoned due to disease.
Independent Nicaragua from 1821 to 1909
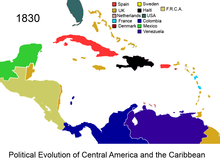

The Act of Independence of Central America dissolved the Captaincy General of Guatemala in September 1821, and Nicaragua soon became part of the First Mexican Empire. In July 1823, after the overthrow of the Mexican monarchy in March of the same year, Nicaragua joined the newly formed United Provinces of Central America, a country later known as the Federal Republic of Central America. Nicaragua definitively became an independent republic in 1838.
The early years of independence were characterized by rivalry between the Liberal elite of León and the Conservative elite of Granada, which often degenerated into civil war, particularly during the 1840s and 1850s. Managua rose to undisputed preeminence as the nation's capital in 1852 to allay the rivalry between the two feuding cities. Following the start of the California Gold Rush in 1848, Nicaragua provided a route for travelers from the eastern United States to journey to California by sea, via the San Juan River and Lake Nicaragua. Invited by the Liberals in 1855 to join their struggle against the Conservatives, the American adventurer and filibuster William Walker set himself up as President of Nicaragua after conducting a farcical election in 1856; his presidency lasted less than a year. Military forces from Costa Rica, Honduras, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Nicaragua itself united to drive Walker out of Nicaragua in 1857, bringing three decades of Conservative rule.
Great Britain, which had claimed the Mosquito Coast as a protectorate since 1655, delegated the area to Honduras in 1859 before transferring it to Nicaragua in 1860. The Mosquito Coast remained an autonomous area until 1894. José Santos Zelaya, President of Nicaragua from 1893 to 1909, negotiated the integration of the Mosquito Coast into Nicaragua. In his honor, the region became "Zelaya Department".
Throughout the late 19th-century, the United States and several European powers considered various schemes to link the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic by building a canal across Nicaragua.
United States occupation (1909–1933)
See also: United States occupation of NicaraguaIn 1909, the United States supported the forces rebelling against President Zelaya. U.S. motives included differences over the proposed Nicaragua Canal, Nicaragua's potential to destabilize the region, and Zelaya's attempts to regulate foreign access to Nicaraguan natural resources. On November 18, 1909, U.S. warships were sent to the area after 500 revolutionaries (including two Americans) were executed by order of Zelaya. The U.S. justified the intervention by claiming to protect U.S. lives and property. Zelaya resigned later that year.
In August 1912, the President of Nicaragua, Adolfo Díaz, requested the secretary of war, General Luis Mena, to resign for fear he was leading an insurrection. Mena fled Managua with his brother, the chief of police of Managua, to start an insurrection. After Mena's troops captured steam boats of an American company, the U.S. delegation asked President Díaz to ensure the safety of American citizens and property during the insurrection. He replied he could not, and asked the U.S. to intervene in the conflict.
U.S. Marines occupied Nicaragua from 1912 to 1933, except for a nine-month period beginning in 1925. In 1914, the Bryan–Chamorro Treaty was signed, giving the U.S. control over a proposed canal through Nicaragua, as well as leases for potential canal defenses. After the U.S. Marines left, another violent conflict between Liberals and Conservatives in 1926 resulted in the return of U.S. Marines.

From 1927 to 1933, rebel general Augusto César Sandino led a sustained guerrilla war against the regime and then against the U.S. Marines, whom he fought for over five years. When the Americans left in 1933, they set up the Guardia Nacional (national guard), a combined military and police force trained and equipped by the Americans and designed to be loyal to U.S. interests.
After the U.S. Marines withdrew from Nicaragua in January 1933, Sandino and the newly elected administration of President Juan Bautista Sacasa reached an agreement that Sandino would cease his guerrilla activities in return for amnesty, a land grant for an agricultural colony, and retention of an armed band of 100 men for a year. However, due to a growing hostility between Sandino and National Guard director Anastasio Somoza García and a fear of armed opposition from Sandino, Somoza García ordered his assassination. Sacasa invited Sandino for dinner and to sign a peace treaty at the Presidential House on the night of February 21, 1934. After leaving the Presidential House, Sandino's car was stopped by National Guard soldiers and they kidnapped him. Later that night, Sandino was assassinated by National Guard soldiers. Later, hundreds of men, women, and children from Sandino's agricultural colony were murdered.
Somoza dynasty (1927–1979)


Nicaragua has experienced several military dictatorships, the longest being the hereditary dictatorship of the Somoza family, who ruled for 43 nonconsecutive years during the 20th century. The Somoza family came to power in 1937 partly as a result of a U.S.-engineered pact in 1927 that stipulated the formation of the Guardia Nacional to replace the marines who had long reigned in the country. Somoza García slowly eliminated officers in the national guard who might have stood in his way, and then deposed Sacasa and became president on January 1, 1937, in a rigged election.
In 1941, during the Second World War, Nicaragua declared war on Japan (8 December), Germany (11 December), Italy (11 December), Bulgaria (19 December), Hungary (19 December) and Romania (19 December). Only Romania reciprocated, declaring war on Nicaragua on the same day (19 December 1941). No soldiers were sent to the war, but Somoza García confiscated properties held by German Nicaraguan residents. In 1945, Nicaragua was among the first countries to ratify the United Nations Charter.
On September 29, 1956, Somoza García was shot to death by Rigoberto López Pérez, a 27-year-old Liberal Nicaraguan poet. Luis Somoza Debayle, the eldest son of the late president, was appointed president by the congress and officially took charge of the country. He is remembered by some as moderate, but after only a few years in power died of a heart attack. His successor as president was René Schick Gutiérrez, whom most Nicaraguans viewed "as nothing more than a puppet of the Somozas". Somoza García's youngest son, Anastasio Somoza Debayle, often referred to simply as "Somoza", became president in 1967.
An earthquake in 1972 destroyed nearly 90% of Managua, including much of its infrastructure. Instead of helping to rebuild the city, Somoza siphoned off relief money. The mishandling of relief money also prompted Pittsburgh Pirates star Roberto Clemente to personally fly to Managua on December 31, 1972, but he died en route in an airplane accident. Even the economic elite were reluctant to support Somoza, as he had acquired monopolies in industries that were key to rebuilding the nation.
The Somoza family was among a few families or groups of influential firms which reaped most of the benefits of the country's growth from the 1950s to the 1970s. When Somoza was deposed by the Sandinistas in 1979, the family's worth was estimated to be between $500 million and $1.5 billion.
Nicaraguan Revolution (1960s–1990)
Main article: Nicaraguan Revolution

In 1961, Carlos Fonseca looked back to the historical figure of Sandino, and along with two other people, one of whom was believed to be Casimiro Sotelo, who was later assassinated, founded the Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN). After the 1972 earthquake and Somoza's apparent corruption, the ranks of the Sandinistas were flooded with young disaffected Nicaraguans who no longer had anything to lose.
In December 1974, a group of the FSLN, in an attempt to kidnap U.S. ambassador Turner Shelton, held some Managuan partygoers hostage after killing the party's host, former agriculture minister Jose Maria Castillo, until the Somoza government met their demands for a large ransom and free transport to Cuba. Somoza granted the demand, and then subsequently sent his national guard out into the countryside to look for the kidnappers, who were described by opponents as terrorists.
On January 10, 1978, Pedro Joaquín Chamorro Cardenal, the editor of the national newspaper La Prensa and ardent opponent of Somoza, was assassinated. It is alleged that the planners and perpetrators of the murder were at the highest echelons of the Somoza regime.
The Sandinistas forcefully took power in July 1979, ousting Somoza, and prompting the exodus of the majority of Nicaragua's middle class, wealthy landowners, and professionals, many of whom settled in the United States. The Carter administration decided to work with the new government, while attaching a provision for aid forfeiture if it was found to be assisting insurgencies in neighboring countries. Somoza fled the country, and eventually ended up in Paraguay, where he was assassinated in September 1980, allegedly by members of the Argentinian Revolutionary Workers' Party.
In 1980, the Carter administration provided $60 million in aid to Nicaragua under the Sandinistas, but the aid was suspended when the administration obtained evidence of Nicaraguan shipment of arms to El Salvadoran rebels. Most people sided with Nicaragua against the Sandinistas.
Contras
Main article: ContrasIn response to the Sandinistas, various rebel groups collectively known as the "Contras" were formed to oppose the new government. The Reagan administration ultimately authorized the CIA to help the Contra rebels with funding, weapons, and training. The Contras operated from camps in the neighboring countries of Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south.
They engaged in a systematic campaign of terror among rural Nicaraguans to disrupt the social reform projects of the Sandinistas. Several historians have criticized the Contra campaign and the Reagan administration's support for the Contras, citing the brutality and numerous human rights violations of the Contras, alleging that health centers, schools, and cooperatives were destroyed by rebels, and that murder, rape, and torture occurred on a large scale in Contra-dominated areas. The U.S. also carried out a campaign of economic sabotage, and disrupted shipping by planting underwater mines in Nicaragua's port of Corinto, an action condemned by the International Court of Justice as illegal. The court also found that the U.S. encouraged acts contrary to humanitarian law by producing the manual Psychological Operations in Guerrilla Warfare and disseminating it to the Contras. The manual, among other things, advised on how to rationalize killings of civilians. The U.S. also sought to place economic pressure on the Sandinistas, and the Reagan administration imposed a full trade embargo.
The Sandinistas were also accused of human rights abuses including torture, disappearances and mass executions. The Inter-American Commission on Human Rights investigated abuses by Sandinista forces, including an execution of 35 to 40 Miskitos in December 1981, and an execution of 75 people in November 1984.
In the Nicaraguan general elections of 1984, which were judged by at least one visiting 30-person delegation of NGO representatives to have been free and fair, the Sandinistas won the parliamentary election and their leader Daniel Ortega won the presidential election. The Reagan administration criticized the elections as a "sham" based on the claim that Arturo Cruz, the candidate nominated by the Coordinadora Democrática Nicaragüense, comprising three right wing political parties, did not participate in the elections. However, the administration privately argued against Cruz's participation for fear that his involvement would legitimize the elections, and thus weaken the case for American aid to the Contras.
In 1983 the U.S. Congress prohibited federal funding of the Contras, but the Reagan administration illegally continued to back them by covertly selling arms to Iran and channeling the proceeds to the Contras in the Iran–Contra affair, for which several members of the Reagan administration were convicted of felonies. The International Court of Justice, in regard to the case of Nicaragua v. United States in 1986, found, "the United States of America was under an obligation to make reparation to the Republic of Nicaragua for all injury caused to Nicaragua by certain breaches of obligations under customary international law and treaty-law committed by the United States of America". During the war between the Contras and the Sandinistas, 30,000 people were killed.
Post-war (1990–2018)



In the 1990 Nicaraguan general election, a coalition of anti-Sandinista parties from both the left and right of the political spectrum led by Violeta Chamorro, the widow of Pedro Joaquín Chamorro Cardenal, defeated the Sandinistas. The defeat shocked the Sandinistas, who had expected to win.
Exit polls of Nicaraguans reported Chamorro's victory over Ortega was achieved with a 55% majority. Chamorro was the first woman president of Nicaragua. Ortega vowed he would govern desde abajo (from below). Chamorro came to office with an economy in ruins, primarily because of the financial and social costs of the Contra War with the Sandinista-led government. In the 1996 general election, Daniel Ortega and the Sandinistas of the FSLN lost again, this time to Arnoldo Alemán of the Constitutional Liberal Party (PLC).
In the 2001 elections, the PLC again defeated the FSLN, with Alemán's Vice President Enrique Bolaños succeeding him as president. However, Alemán was convicted and sentenced in 2003 to 20 years in prison for embezzlement, money laundering, and corruption; liberal and Sandinista parliament members combined to strip the presidential powers of President Bolaños and his ministers, calling for his resignation and threatening impeachment. The Sandinistas said they no longer supported Bolaños after U.S. Secretary of State Colin Powell told Bolaños to distance from the FSLN. This "slow motion coup d'état" was averted partially by pressure from the Central American presidents, who vowed not to recognize any movement that removed Bolaños; the U.S., the OAS, and the European Union also opposed the action.
Nicaragua briefly participated in the Iraq War in 2004 as part of the Plus Ultra Brigade, a military contingent of mixed personnel.
Before the general elections on November 5, 2006, the National Assembly passed a bill further restricting abortion in Nicaragua. As a result, Nicaragua is one of five countries in the world where abortion is illegal with no exceptions. Legislative and presidential elections took place on November 5, 2006. Ortega returned to the presidency with 37.99% of the vote. This percentage was enough to win the presidency outright, because of a change in electoral law which lowered the percentage requiring a runoff election from 45% to 35% (with a 5% margin of victory). Nicaragua's 2011 general election resulted in the re-election of Ortega, with a landslide 62.46% of the vote. In 2014 the National Assembly approved changes to the constitution allowing Ortega to run for a third successive term.
In November 2016, Ortega was elected for his third consecutive term (his fourth overall). International monitoring of the elections was initially prohibited, and as a result the validity of the elections has been disputed, but observation by the OAS was announced in October. Ortega was reported by Nicaraguan election officials as having received 72% of the vote. However, the Broad Front for Democracy (FAD), having promoted boycotts of the elections, claimed that 70% of voters had abstained (while election officials claimed 65.8% participation).
In April 2018, demonstrations were held to oppose a decree increasing taxes and reducing benefits in the country's pension system. Local independent press organizations documented at least 19 dead and over 100 missing in the ensuing conflict. A reporter from NPR spoke to protestors who explained that while the initial issue was the pension reforms, the uprisings that spread across the country reflected many grievances about the government's time in office, and that the fight is for President Ortega and his vice president, his wife, to step down. April 24, 2018 marked the day of the greatest march in opposition of the Sandinista party. On May 2, 2018, university-student leaders made a public announcement giving the government seven days to set a date and time for a dialogue that was promised to the people due to the recent events of repression. The students also scheduled another peaceful protest march on that same day. As of May 2018, estimates of the death toll were as high as 63, many of them student protesters, and the wounded totalled more than 400. Following a working visit from May 17 to 21, the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights adopted precautionary measures aimed at protecting members of the student movement and their families after testimonies indicated the majority of them had suffered acts of violence and death threats for their participation. In the last week of May, thousands who accuse Mr. Ortega and his wife of acting like dictators joined in resuming anti-government rallies after attempted peace talks have remained unresolved. Open suppression of political dissent and more militarized policing began in April 2018, but the onset of repression was gradual.
Geography and climate
Main articles: Geography of Nicaragua and Climate of Nicaragua See also: Volcanoes of Nicaragua
Nicaragua occupies a landmass of 130,967 km (50,567 sq mi), which makes it slightly larger than England. Nicaragua has three distinct geographical regions: the Pacific lowlands – fertile valleys which the Spanish colonists settled, the Amerrisque Mountains (North-central highlands), and the Mosquito Coast (Atlantic lowlands/Caribbean lowlands).
The low plains of the Atlantic Coast are 97 km (60 mi) wide in areas. They have long been exploited for their natural resources.
On the Pacific side of Nicaragua are the two largest freshwater lakes in Central America—Lake Managua and Lake Nicaragua. Surrounding these lakes and extending to their northwest along the rift valley of the Gulf of Fonseca are fertile lowland plains, with soil highly enriched by ash from nearby volcanoes of the central highlands. Nicaragua's abundance of biologically significant and unique ecosystems contribute to Mesoamerica's designation as a biodiversity hotspot. Nicaragua has made efforts to become less dependent on fossil fuels, and it expects to acquire 90% of its energy from renewable resources by 2020. Nicaragua was one of the few countries that did not enter an INDC at COP21. Nicaragua initially chose not to join the Paris Climate Accord because it felt that "much more action is required" by individual countries on restricting global temperature rise. However, in October 2017, Nicaragua made the decision to join the agreement. It ratified this agreement on November 22, 2017.
Nearly one fifth of Nicaragua is designated as protected areas like national parks, nature reserves, and biological reserves. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 3.63/10, ranking it 146th globally out of 172 countries. Geophysically, Nicaragua is surrounded by the Caribbean Plate, an oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America, and the Cocos Plate. Since Central America is a major subduction zone, Nicaragua hosts most of the Central American Volcanic Arc. On 9 June 2021, Nicaragua launched a new volcanic supersite research in strengthening the monitoring and surveillance of the country's 21 active volcanoes.
Pacific lowlands


In the west of the country, these lowlands consist of a broad, hot, fertile plain. Punctuating this plain are several large volcanoes of the Cordillera Los Maribios mountain range, including Mombacho just outside Granada, and Momotombo near León. The lowland area runs from the Gulf of Fonseca to Nicaragua's Pacific border with Costa Rica south of Lake Nicaragua. Lake Nicaragua is the largest freshwater lake in Central America (20th largest in the world), and is home to some of the world's rare freshwater sharks (Nicaraguan shark). The Pacific lowlands region is the most populous, with over half of the nation's population.
The eruptions of western Nicaragua's 40 volcanoes, many of which are still active, have sometimes devastated settlements but also have enriched the land with layers of fertile ash. The geologic activity that produces vulcanism also breeds powerful earthquakes. Tremors occur regularly throughout the Pacific zone, and earthquakes have nearly destroyed the capital city, Managua, more than once.
Most of the Pacific zone is tierra caliente, the "hot land" of tropical Spanish America at elevations under 610 metres (2,000 ft). Temperatures remain virtually constant throughout the year, with highs ranging between 29.4 and 32.2 °C (85 and 90 °F). After a dry season lasting from November to April, rains begin in May and continue to October, giving the Pacific lowlands 1,016 to 1,524 millimetres (40 to 60 in) of precipitation. Good soils and a favourable climate combine to make western Nicaragua the country's economic and demographic centre. The southwestern shore of Lake Nicaragua lies within 24 kilometres (15 mi) of the Pacific Ocean. Thus the lake and the San Juan River were often proposed in the 19th century as the longest part of a canal route across the Central American isthmus. Canal proposals were periodically revived in the 20th and 21st centuries. Roughly a century after the opening of the Panama Canal, the prospect of a Nicaraguan ecocanal remains a topic of interest.
In addition to its beach and resort communities, the Pacific lowlands contains most of Nicaragua's Spanish colonial architecture and artifacts. Cities such as León and Granada abound in colonial architecture; founded in 1524, Granada is the oldest colonial city in the Americas.
North central highlands

Northern Nicaragua is the most diversified region producing coffee, cattle, milk products, vegetables, wood, gold, and flowers. Its extensive forests, rivers and geography are suited for ecotourism.
The central highlands are a significantly less populated and economically developed area in the north, between Lake Nicaragua and the Caribbean. Forming the country's tierra templada, or "temperate land", at elevations between 610 and 1,524 metres (2,000 and 5,000 ft), the highlands enjoy mild temperatures with daily highs of 23.9 to 26.7 °C (75 to 80 °F). This region has a longer, wetter rainy season than the Pacific lowlands, making erosion a problem on its steep slopes. Rugged terrain, poor soils, and low population density characterize the area as a whole, but the northwestern valleys are fertile and well settled.
The area has a cooler climate than the Pacific lowlands. About a quarter of the country's agriculture takes place in this region, with coffee grown on the higher slopes. Oaks, pines, moss, ferns and orchids are abundant in the cloud forests of the region.
Bird life in the forests of the central region includes resplendent quetzals, goldfinches, hummingbirds, jays and toucanets.
Caribbean lowlands
This large rainforest region is irrigated by several large rivers and is sparsely populated. The area has 57% of the territory of the nation and most of its mineral resources. It has been heavily exploited, but much natural diversity remains. The Rio Coco is the largest river in Central America; it forms the border with Honduras. The Caribbean coastline is much more sinuous than its generally straight Pacific counterpart; lagoons and deltas make it very irregular.
Nicaragua's Bosawás Biosphere Reserve is in the Atlantic lowlands, part of which is located in the municipality of Siuna; it protects 7,300 square kilometres (1,800,000 acres) of La Mosquitia forest – almost 7% of the country's area – making it the largest rainforest north of the Amazon in Brazil.
The municipalities of Siuna, Rosita, and Bonanza, known as the "Mining Triangle", are located in the region known as the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region, in the Caribbean lowlands. Bonanza still contains an active gold mine owned by HEMCO. Siuna and Rosita do not have active mines but panning for gold is still very common in the region.
Nicaragua's tropical east coast is very different from the rest of the country. The climate is predominantly tropical, with high temperature and high humidity. Around the area's principal city of Bluefields, English is widely spoken along with the official Spanish. The population more closely resembles that found in many typical Caribbean ports than the rest of Nicaragua.
A great variety of birds can be observed including eagles, toucans, parakeets and macaws. Other animal life in the area includes different species of monkeys, anteaters, white-tailed deer and tapirs.
Flora and fauna
Main article: Fauna of Nicaragua
Nicaragua is home to a rich variety of plants and animals. Nicaragua is located in the middle of the Americas and this privileged location has enabled the country to serve as host to a great biodiversity. This factor, along with the weather and light altitudinal variations, allows the country to harbor 248 species of amphibians and reptiles, 183 species of mammals, 705 bird species, 640 fish species, and about 5,796 species of plants.
The region of great forests is located on the eastern side of the country. Rainforests are found in the Río San Juan Department and in the autonomous regions of RAAN and RAAS. This biome groups together the greatest biodiversity in the country and is largely protected by the Indio Maíz Biological Reserve in the south and the Bosawás Biosphere Reserve in the north. The Nicaraguan jungles, which represent about 9,700 square kilometres (2.4 million acres), are considered the lungs of Central America and comprise the second largest-sized rainforest of the Americas.
There are currently 78 protected areas in Nicaragua, covering more than 22,000 square kilometres (8,500 sq mi), or about 17% of its landmass. These include wildlife refuges and nature reserves that shelter a wide range of ecosystems. There are more than 1,400 animal species classified thus far in Nicaragua. Some 12,000 species of plants have been classified thus far in Nicaragua, with an estimated 5,000 species not yet classified.
The bull shark is a species of shark that can survive for an extended period of time in fresh water. It can be found in Lake Nicaragua and the San Juan River, where it is often referred to as the "Nicaragua shark". Nicaragua has recently banned freshwater fishing of the Nicaragua shark and the sawfish in response to the declining populations of these animals.
Government
Main article: Politics of Nicaragua| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Nicaragua" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Politics of Nicaragua takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Nicaragua is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the national assembly. The judiciary makes up the third branch of government.
Between 2007 and 2009, Nicaragua's major political parties discussed the possibility of going from a presidential system to a parliamentary system. Their reason: there would be a clear differentiation between the head of government (prime minister) and the head of state (president). Nevertheless, it was argued that the true reason for this proposal was to find a legal way for President Ortega to stay in power after January 2012, when his second and last government period was expected to end. Ortega was reelected to a third term in November 2016, and a fourth in 2021; both elections were tainted by credible reports of large-scale fraud, voter intimidation, and politically motivated arrests of opposition party leaders. Independent observers were barred from the polls. The OAS, United States, and European Union all described the 2021 election as a "sham" due to these issues.
Since Daniel Ortega's election in 2006, liberal democratic norms and individual rights in practice have deteriorated. Parties other than the ruling FSLN have been repressed through arbitrary arrest and detention of opposition candidates and activists. Most government jobs de facto require membership in the FSLN. Opposition media has been repressed through arrests of journalists and seizure of broadcasting and printing materials.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of NicaraguaNicaragua pursues an independent foreign policy. Nicaragua is in territorial disputes with Colombia over the Archipelago de San Andrés y Providencia and Quita Sueño Bank and with Costa Rica over a boundary dispute involving the San Juan River.
On 12 October 2022, Nicaragua voted against condemning Russia for its invasion of Ukraine.
Since 2019, human rights in Nicaragua have been rated not free.
Military
Main article: Nicaraguan Armed ForcesThe Nicaraguan Armed Forces consist of various military contingents. Nicaragua has an army, navy and an air force. There are roughly 14,000 active duty personnel, which is much less compared to the numbers seen during the Nicaraguan Revolution. Although the army has had a rough military history, a portion of its forces, which were known as the national guard, became integrated with what is now the National Police of Nicaragua. In essence, the police became a gendarmerie. The National Police of Nicaragua are rarely, if ever, labeled as a gendarmerie. The other elements and manpower that were not devoted to the national police were sent over to cultivate the new Army of Nicaragua.
The age to serve in the armed forces is 17 and conscription is not imminent. As of 2006, the military budget was roughly 0.7% of Nicaragua's expenditures.
In 2017, Nicaragua signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Law enforcement
Main article: Law enforcement in Nicaragua
The National Police of Nicaragua Force (in Spanish: La Policía Nacional Nicaragüense) is the national police of Nicaragua. The force is in charge of regular police functions and, at times, works in conjunction with the Nicaraguan military, making it an indirect and rather subtle version of a gendarmerie. However, the Nicaraguan National Police work separately and have a different established set of norms than the nation's military. According to a recent US Department of State report, corruption is endemic, especially within law enforcement and the judiciary, and arbitrary arrests, torture, and harsh prison conditions are the norm.
Nicaragua has one of the lowest intentional homicide rates in Central America, according to the United Nations Development Program, with a homicide rate of 11 per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2021.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Departments of NicaraguaNicaragua is a unitary republic. For administrative purposes it is divided into 15 departments (departamentos) and two self-governing regions (autonomous communities) based on the Spanish model. The departments are then subdivided into 153 municipios (municipalities). The two autonomous regions are the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region and South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region, often referred to as RACCN and RACCS, respectively.
|
Economy
Main article: Economy of Nicaragua

Nicaragua is one of the poorest countries in the Americas. Its gross domestic product (GDP) in purchasing power parity (PPP) in 2008 was estimated at US$17.37 billion. Agriculture represents 15.5% of GDP, the highest percentage in Central America. Remittances account for over 15% of the Nicaraguan GDP. Close to one billion dollars are sent to the country by Nicaraguans living abroad. The economy grew at a rate of about 4% in 2011. By 2019, given restrictive taxes and a civil conflict, it recorded a negative growth of - 3.9%; the International Monetary Fund forecast for 2020 is a further decline of 6% due to COVID-19.
The restrictive tax measures put in place in 2019 and a political crisis over social security negatively affected the country's weak public spending and investor confidence in sovereign debt. According to the update IMF forecasts from 14 April 2020, due to the COVID-19 outbreak, GDP growth is expected to fall to -6% in 2020.
According to the United Nations Development Programme, 48% of the population of Nicaragua live below the poverty line, 79.9% of the population live with less than $2 per day, According to UN figures, 80% of the indigenous people (who make up 5% of the population) live on less than $1 per day.
According to the World Bank, Nicaragua ranked as the 123rd out of 190 best economy for starting a business. In 2007, Nicaragua's economy was labelled "62.7% free" by the conservative think tank Heritage Foundation, with high levels of fiscal, government, labor, investment, financial, and trade freedom. It ranked as the 61st freest economy, and 14th (of 29) in the Americas. Nicaragua was ranked 124th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
In March 2007, Poland and Nicaragua signed an agreement to write off 30.6 million dollars, which was borrowed by the Nicaraguan government in the 1980s. Inflation reduced from 33,500% in 1988 to 9.45% in 2006, and the foreign debt was cut in half.
Nicaragua is primarily an agricultural country; agriculture constitutes 60% of its total exports which annually yield approximately US$300 million. Nearly two-thirds of the coffee crop comes from the northern part of the central highlands, in the area north and east of the town of Estelí. Tobacco, grown in the same northern highlands region as coffee, has become an increasingly important cash crop since the 1990s, with annual exports of leaf and cigars in the neighborhood of $200 million per year. Soil erosion and pollution from the heavy use of pesticides have become serious concerns in the cotton district. Yields and exports have both been declining since 1985. Today most of Nicaragua's bananas are grown in the northwestern part of the country near the port of Corinto; sugarcane is also grown in the same district. Cassava, a root crop somewhat similar to the potato, is an important food in tropical regions. Cassava is also the main ingredient in tapioca pudding. Nicaragua's agricultural sector has benefited because of the country's strong ties to Venezuela. It is estimated that Venezuela will import approximately $200 million in agricultural goods. In the 1990s, the government initiated efforts to diversify agriculture. Some of the new export-oriented crops were peanuts, sesame, melons, and onions.
Fishing boats on the Caribbean side bring shrimp as well as lobsters into processing plants at Puerto Cabezas, Bluefields, and Laguna de Perlas. A turtle fishery thrived on the Caribbean coast before it collapsed from overexploitation.
Mining is becoming a major industry in Nicaragua, contributing less than 1% of gross domestic product (GDP). Restrictions are being placed on lumbering due to increased environmental concerns about destruction of the rain forests. But lumbering continues despite these obstacles; indeed, a single hardwood tree may be worth thousands of dollars.
During the war between the US-backed Contras and the government of the Sandinistas in the 1980s, much of the country's infrastructure was damaged or destroyed. Transportation throughout the nation is often inadequate. For example, it was until recently impossible to travel all the way by highway from Managua to the Caribbean coast. A new road between Nueva Guinea and Bluefields was completed in 2019 and allows regular bus service to the capital. The Centroamérica power plant on the Tuma River in the Central highlands has been expanded, and other hydroelectric projects have been undertaken to help provide electricity to the nation's newer industries. Nicaragua has long been considered as a possible site for a new canal that could supplement the Panama Canal, connecting the Caribbean Sea (and therefore the Atlantic Ocean) with the Pacific Ocean.
Nicaragua's minimum wage is among the lowest in the Americas and in the world. Remittances are equivalent to roughly 15% of the country's gross domestic product. Growth in the maquila sector slowed in the first decade of the 21st century with rising competition from Asian markets, particularly China. Land is the traditional basis of wealth in Nicaragua, with great fortunes coming from the export of staples such as coffee, cotton, beef, and sugar. Almost all of the upper class and nearly a quarter of the middle class are substantial landowners.
A 1985 government study classified 69.4 percent of the population as poor on the basis that they were unable to satisfy one or more of their basic needs in housing, sanitary services (water, sewage, and garbage collection), education, and employment. The defining standards for this study were very low; housing was considered substandard if it was constructed of discarded materials with dirt floors or if it was occupied by more than four persons per room.
Rural workers are dependent on agricultural wage labor, especially in coffee and cotton. Only a small fraction hold permanent jobs. Most are migrants who follow crops during the harvest period and find other work during the off-season. The "lower" peasants are typically smallholders without sufficient land to sustain a family; they also join the harvest labor force. The "upper" peasants have sufficient resources to be economically independent. They produce enough surplus, beyond their personal needs, to allow them to participate in the national and world markets.

The urban lower class is characterized by the informal sector of the economy. The informal sector consists of small-scale enterprises that utilize traditional technologies and operate outside the legal regime of labor protections and taxation. Workers in the informal sector are self-employed, unsalaried family workers or employees of small-enterprises, and they are generally poor.
Nicaragua's informal sector workers include tinsmiths, mattress makers, seamstresses, bakers, shoemakers, and carpenters; people who take in laundry and ironing or prepare food for sale in the streets; and thousands of peddlers, owners of small businesses (often operating out of their own homes), and market stall operators. Some work alone, but others labor in the small talleres (workshops/factories) that are responsible for a large share of the country's industrial production. Because informal sector earnings are generally very low, few families can subsist on one income. Like most Latin American nations Nicaragua is also characterized by a very small upper-class, roughly 2% of the population, that is very wealthy and wields the political and economic power in the country that is not in the hands of foreign corporations and private industries. These families are oligarchical in nature and have ruled Nicaragua for generations and their wealth is politically and economically horizontally and vertically integrated.
Nicaragua is currently a member of the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas, also known as ALBA. ALBA has proposed creating a new currency, the Sucre, for use among its members. In essence, this means that the Nicaraguan córdoba will be replaced with the Sucre. Other nations that will follow a similar pattern include: Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Honduras, Cuba, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Dominica and Antigua and Barbuda.
Nicaragua is considering construction of a canal linking the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean, which President Daniel Ortega has said will give Nicaragua its "economic independence". Scientists have raised concerns about environmental impacts, but the government has maintained that the canal will benefit the country by creating new jobs and potentially increasing its annual growth to an average of 8% per year. The project was scheduled to begin construction in December 2014, however the Nicaragua Canal has yet to be started.
Tourism
Main article: Tourism in Nicaragua



By 2006, tourism became the second-largest industry in Nicaragua. Previously, tourism had grown about 70% nationwide during a period of 7 years, with rates of 10%–16% annually. The increase and growth led to the income from tourism to rise more than 300% over a period of 10 years. The growth in tourism has also positively affected the agricultural, commercial, and finance industries, as well as the construction industry. President Daniel Ortega has stated his intention to use tourism to combat poverty throughout the country. The results for Nicaragua's tourism-driven economy have been significant, with the nation welcoming one million tourists in a calendar year for the first time in its history in 2010.
Every year about 60,000 U.S. citizens visit Nicaragua, primarily business people, tourists, and those visiting relatives. Some 5,300 people from the U.S. reside in Nicaragua. The majority of tourists who visit Nicaragua are from the U.S., Central or South America, and Europe. According to the Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua (INTUR), the colonial cities of León and Granada are the preferred spots for tourists. Also, the cities of Masaya, Rivas and the likes of San Juan del Sur, El Ostional, the Fortress of the Immaculate Conception, Ometepe Island, the Mombacho volcano, and the Corn Islands among other locations are the main tourist attractions. In addition, ecotourism, sport fishing and surfing attract many tourists to Nicaragua.
According to the TV Noticias news program, the main attractions in Nicaragua for tourists are the beaches, the scenic routes, the architecture of cities such as León and Granada, ecotourism, and agritourism particularly in northern Nicaragua. As a result of increased tourism, Nicaragua has seen its foreign direct investment increase by 79.1% from 2007 to 2009.
Nicaragua is referred to as "the land of lakes and volcanoes" due to the number of lagoons and lakes, and the chain of volcanoes that runs from the north to the south along the country's Pacific side. Today, only 7 of the 50 volcanoes in Nicaragua are considered active. Many of these volcanoes offer some great possibilities for tourists with activities such as hiking, climbing, camping, and swimming in crater lakes.
The Apoyo Lagoon Natural Reserve was created by the eruption of the Apoyo Volcano about 23,000 years ago, which left a huge 7 km-wide crater that gradually filled with water. It is surrounded by the old crater wall. The rim of the lagoon is lined with restaurants, many of which have kayaks available. Besides exploring the forest around it, many water sports are practiced in the lagoon, most notably kayaking.
Sand skiing has become a popular attraction at the Cerro Negro volcano in León. Both dormant and active volcanoes can be climbed. Some of the most visited volcanoes include the Masaya Volcano, Momotombo, Mombacho, Cosigüina and Ometepe's Maderas and Concepción.
Ecotourism aims to be ecologically and socially conscious; it focuses on local culture, wilderness, and adventure. Nicaragua's ecotourism is growing with every passing year. It boasts a number of ecotourist tours and perfect places for adventurers. Nicaragua has three eco-regions (the Pacific, Central, and Atlantic) which contain volcanoes, tropical rainforests, and agricultural land. The majority of the eco-lodges and other environmentally-focused touristic destinations are found on Ometepe Island, located in the middle of Lake Nicaragua just an hour's boat ride from Granada. While some are foreign-owned, others are owned by local families.
Demographics
Main articles: Nicaraguans and Demographics of Nicaragua| Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Million | ||
| 1950 | 1.3 | ||
| 2000 | 5.0 | ||
| 2021 | 6.9 | ||

According to a 2014 research published in the journal Genetics and Molecular Biology, European ancestry predominates in 69% of Nicaraguans, followed by African ancestry in 20%, and lastly indigenous ancestry in 11%. A Japanese research of "Genomic Components in America's demography" demonstrated that, on average, the ancestry of Nicaraguans is 58–62% European, 28% Native American, and 14% African, with a very small Near Eastern contribution. Non-genetic data from the CIA World Factbook establish that from Nicaragua's 2016 population of 5,966,798, around 69% are mestizo, 17% white, 5% Native American, and 9% black and other races. This fluctuates with changes in migration patterns. The population is 58% urban as of 2013.
The capital Managua is the biggest city, with an estimated population of 1,042,641 in 2016. In 2005, over 5 million people lived in the Pacific, Central and North regions, and 700,000 in the Caribbean region.
There is a growing expatriate community, the majority of whom move for business, investment or retirement from across the world, such as from the US, Canada, Taiwan, and European countries; the majority have settled in Managua, Granada and San Juan del Sur.
Many Nicaraguans live abroad, particularly in Costa Rica, the United States, Spain, Canada, and other Central American countries.
Nicaragua has a population growth rate of 1.5% as of 2013. This is the result of one of the highest birth rates in the Western Hemisphere: 17.7 per 1,000 as of 2017. The death rate was 4.7 per 1,000 during the same period according to the United Nations.
Ethnic groups

The majority of the Nicaraguan population is composed of mestizos, roughly 69%, while 17% of Nicaragua's population is white, with the majority of them being of Spanish descent, while others are of German, Italian, English, Turkish, Danish or French ancestry.
Black Creoles
About 9% of Nicaragua's population is black and mainly resides on the country's Caribbean (or Atlantic) coast. The black population is mostly composed of black English-speaking Creoles who are the descendants of escaped or shipwrecked slaves; many carry the name of Scottish settlers who brought slaves with them, such as Campbell, Gordon, Downs, and Hodgson. Although many Creoles supported Somoza because of his close association with the United States, they rallied to the Sandinista cause in July 1979, only to reject the revolution soon afterwards in response to a new phase of "westernization" and imposition of central rule from Managua. There is a smaller number of Garifuna, a people of mixed West African, Carib and Arawak descent. In the mid-1980s, the government divided the Zelaya Department – consisting of the eastern half of the country – into two autonomous regions and granted the black and indigenous people of this region limited self-rule within the republic.
Indigenous population
The remaining 5% of Nicaraguans are indigenous, the descendants of the country's original inhabitants. Nicaragua's pre-Columbian population consisted of many indigenous groups. In the western region, the Nahuas (Nicarao people) were present along with other groups such as the Chorotega people and the Subtiabas (also known as Maribios or Hokan Xiu). The central region and the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua were inhabited by indigenous peoples who were Macro-Chibchan language groups that had migrated to and from South America in ancient times, primarily what is now Colombia and Venezuela. These groups include the present-day Matagalpas, Miskitos, Ramas, as well as Mayangnas and Ulwas who are also known as Sumos. In the 19th century, there was a substantial indigenous minority, but this group was largely assimilated culturally into the mestizo majority. The Garifuna are also present, mainly on the Caribbean Coast. They are a people of mixed African and Indigenous descent.
Languages
Main article: Languages of Nicaragua
Nicaraguan Spanish has many indigenous influences and several distinguishing characteristics. For example, some Nicaraguans have a tendency to replace /s/ with /h/ when speaking. Although Spanish is spoken throughout, the country has great variety: vocabulary, accents and colloquial language can vary between towns and departments.
Nicaraguan Sign Language emerged in the 1970s and 1980s among deaf children as the first special education schools brought them together, and its emergence became of particular interest to linguists as an opportunity to directly observe the creation of a language.
On the Caribbean coast, indigenous languages, English-based creoles, and Spanish are spoken. The Miskito language, spoken by the Miskito people as a first language and some other indigenous and Afro-descendants people as a second, third, or fourth language, is the most commonly spoken indigenous language. The indigenous Misumalpan languages of Mayangna and Ulwa are spoken by the respective peoples of the same names. Many Miskito, Mayangna, and Sumo people also speak Miskito Coast Creole, and a large majority also speak Spanish. Fewer than three dozen of nearly 2,000 Rama people speak their Chibchan language fluently, with nearly all Ramas speaking Rama Cay Creole and the vast majority speaking Spanish. Linguists have attempted to document and revitalize the language over the past three decades.
The Garifuna people, descendants of indigenous and Afro-descendant people who came to Nicaragua from Honduras in the early twentieth century, have recently attempted to revitalize their Arawakan language. The majority speak Miskito Coast Creole as their first language and Spanish as their second. The Creole or Kriol people, descendants of enslaved Africans brought to the Mosquito Coast during the British colonial period and European, Chinese, Arab, and British West Indian immigrants, also speak Miskito Coast Creole as their first language and Spanish as their second.
Largest cities
| Largest municipalities in Nicaragua Anuario Estadístico 2015, pp. 50–53 (2016 projections) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Department | Pop. | ||||||
 León |
1 | Managua | Managua | 1,042,641 |  Masaya  Matagalpa | ||||
| 2 | León | León | 206,264 | ||||||
| 3 | Masaya | Masaya | 176,344 | ||||||
| 4 | Matagalpa | Matagalpa | 158,095 | ||||||
| 5 | Tipitapa | Managua | 140,569 | ||||||
| 6 | Chinandega | Chinandega | 135,154 | ||||||
| 7 | Jinotega | Jinotega | 133,705 | ||||||
| 8 | Granada | Granada | 127,892 | ||||||
| 9 | Estelí | Estelí | 126,290 | ||||||
| 10 | Puerto Cabezas | RACCN | 113,534 | ||||||
Religion
Main article: Religion in Nicaragua
Religion plays a significant role in Nicaraguan culture and is afforded special protections in its constitution. Religious freedom (which has been guaranteed since 1939) and religious tolerance are officially promoted by the government, but, in recent years, the Catholic Church and the regime led by Daniel Ortega have been in open conflict. The latter has been accused of using the police to harass clergy (including bishops), closing down Catholic media outlets, and arresting members of the clergy (including Bishop Rolando Alvarez of the Diocese of Matagalpa).
Nicaragua has no official state religion. Catholic bishops are expected to lend their authority to important state occasions, and their pronouncements on national issues are closely followed. They can be called upon to mediate between contending parties at moments of political crisis. In 1979, Miguel D'Escoto Brockman, a priest who had embraced Liberation Theology, served in the government as foreign minister when the Sandinistas came to power. The largest denomination, and traditionally the religion of the majority, is the Roman Catholic Church. It came to Nicaragua in the 16th century with the Spanish conquest and remained, until 1939, the established faith.
The number of practicing Roman Catholics has been declining, while membership of evangelical Protestant groups and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) has been growing rapidly since the 1990s. There is a significant LDS missionary effort in Nicaragua. There are two missions and 95,768 members of the LDS Church (1.54% of the population). There are also strong Anglican and Moravian communities on the Caribbean coast in what once constituted the sparsely populated Mosquito Coast colony. It was under British influence for nearly three centuries. Protestantism was brought to the Mosquito Coast mainly by British and German colonists in forms of Anglicanism and the Moravian Church. Other kinds of Protestant and other Christian denominations were introduced to the rest of Nicaragua during the 19th century.
Popular religion revolves around the saints, who are perceived as intercessors between human beings and God. Most localities, from the capital of Managua to small rural communities, honor patron saints, selected from the Roman Catholic calendar, with annual fiestas. In many communities, a rich lore has grown up around the celebrations of patron saints, such as Managua's Saint Dominic (Santo Domingo), honored in August with two colorful, often riotous, day-long processions through the city. The high point of Nicaragua's religious calendar for the masses is neither Christmas nor Easter, but La Purísima, a week of festivities in early December dedicated to the Immaculate Conception, during which elaborate altars to the Virgin Mary are constructed in homes and workplaces.
Buddhism has increased with a steady influx of immigration.
Although Jews have been living in Nicaragua since the 18th century, the Jewish population is small, numbering less than 200 people in 2017. Of these, 112 were recent converts who claimed Sephardic Jewish ancestry.
As of 2007, approximately 1,200 to 1,500 Nicaraguan residents practiced Islam, most of them Sunnis who are resident aliens or naturalized citizens from Palestine, Libya, and Iran or natural-born Nicaraguan descendants of the two groups.
Immigration
Main article: Immigration to NicaraguaRelative to its population, Nicaragua has not experienced large waves of immigration. The number of immigrants in Nicaragua, from other Latin American countries or other countries, never surpassed 1% of its total population before 1995. The 2005 census showed the foreign-born population at 1.2%, having risen a mere 0.06% in 10 years.
In the 19th century, Nicaragua experienced modest waves of immigration from Europe. In particular, families from Germany, Italy, Spain, France and Belgium immigrated to Nicaragua, particularly the departments in the Central and Pacific region.
Also present is a small Middle Eastern-Nicaraguan community of Syrians, Armenians, Jewish Nicaraguans, and Lebanese people in Nicaragua. This community numbers about 30,000. There is an East Asian community mostly consisting of Chinese. The Chinese Nicaraguan population is estimated at 12,000. The Chinese arrived in the late 19th century but were unsubstantiated until the 1920s.
Diaspora
Main article: Nicaraguan diasporaThe Civil War forced many Nicaraguans to start lives outside of their country. Many people emigrated during the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century due to the lack of employment opportunities and poverty. The majority of the Nicaraguan Diaspora migrated to the United States and Costa Rica. Today one in six Nicaraguans live in these two countries.
The diaspora has seen Nicaraguans settling around in smaller communities in other parts of the world, particularly Western Europe. Small communities of Nicaraguans are found in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Communities also exist in Australia and New Zealand. Canada, Brazil and Argentina host small groups of these communities. In Asia, Japan hosts a small Nicaraguan community.
Due to extreme poverty at home, many Nicaraguans are now living and working in neighboring El Salvador, a country that has the US dollar as its currency.
Healthcare
Main article: Healthcare in NicaraguaAlthough Nicaragua's health outcomes have improved over the past few decades with the efficient utilization of resources relative to other Central American nations, healthcare in Nicaragua still confronts challenges responding to its populations' diverse healthcare needs.
The Nicaraguan government guarantees universal free health care for its citizens. However, limitations of current delivery models and unequal distribution of resources and medical personnel contribute to the persistent lack of quality care in more remote areas of Nicaragua, especially among rural communities in the Central and Atlantic region. To respond to the dynamic needs of localities, the government has adopted a decentralized model that emphasizes community-based preventive and primary medical care.
Education
Main article: Education in NicaraguaThe adult literacy rate in 2005 was 78.0%, the lowest literacy rate in Central America.
Primary education is free in Nicaragua. A system of private schools exists, many of which are religiously affiliated and often have more robust English programs. As of 1979, the educational system was one of the poorest in Latin America. One of the first acts of the newly elected Sandinista government in 1980 was an extensive and successful literacy campaign, using secondary school students, university students and teachers as volunteer teachers: it reduced the overall illiteracy rate from 50.3% to 12.9% within only five months. This was one of a number of large-scale programs which received international recognition for their gains in literacy, health care, education, childcare, unions, and land reform. The Sandinistas also added a leftist ideological content to the curriculum, which was removed after 1990. In September 1980, UNESCO awarded Nicaragua the Soviet Union sponsored Nadezhda Krupskaya award for the literacy campaign.
Gender equality
Main article: Gender equality in NicaraguaNicaragua's gender equality ranks high among countries in Latin America. When it came to global rankings regarding gender equality, the World Economic Forum ranked Nicaragua at number twelve in 2015, and in its 2020 report Nicaragua ranked number five, behind only northern European countries.
Nicaragua was among the many countries in Latin America and the Caribbean to ratify the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women, which aimed to promote women's rights.
In 2009, a Special Ombudsman for Sexual Diversity position was created within its Office of the Human Rights Ombudsman. And, in 2014, the Health Ministry in 2014 banned discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation. Nevertheless, discrimination against LGBTQ individuals is common, particularly in housing, education, and the workplace.
The Human Development Report ranked Nicaragua 106 out of 160 countries in the Gender Inequality Index (GII) in 2017. It reflects gender-based inequalities in three dimensions - reproductive health, empowerment, and economic activity.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Nicaragua
Nicaraguan culture has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by European culture but also including Native American sounds and flavors. Nicaraguan culture can further be defined in several distinct strands. The Pacific coast has strong folklore, music and religious traditions, deeply influenced by Europeans. It was colonized by Spain and has a similar culture to other Spanish-speaking Latin American countries. The indigenous groups that historically inhabited the Pacific coast have largely been assimilated into the mestizo culture.
The Caribbean coast of Nicaragua was once a British protectorate. English is still predominant in this region and spoken domestically along with Spanish and indigenous languages. Its culture is similar to that of Caribbean nations that were or are British possessions, such as Jamaica, Belize, the Cayman Islands, etc. Unlike on the west coast, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean coast have maintained distinct identities, and some still speak their native languages as first languages.
Music
Main article: Music of Nicaragua
Nicaraguan music is a mixture of indigenous and Spanish influences. Musical instruments include the marimba and others common across Central America. The marimba of Nicaragua is played by a sitting performer holding the instrument on his knees. He is usually accompanied by a bass fiddle, guitar and guitarrilla (a small guitar like a mandolin). This music is played at social functions as a sort of background music.
The marimba is made with hardwood plates placed over bamboo or metal tubes of varying lengths. It is played with two or four hammers. The Caribbean coast of Nicaragua is known for a lively, sensual form of dance music called Palo de Mayo which is popular throughout the country. It is especially loud and celebrated during the Palo de Mayo festival in May. The Garifuna community (Afro-Native American) is known for its popular music called Punta.
Nicaragua has international influence in music. Bachata, Merengue, Salsa and Cumbia have gained prominence in cultural centres such as Managua, Leon and Granada. Cumbia dancing has grown popular with the introduction of Nicaraguan artists, including Gustavo Leyton, on Ometepe Island and in Managua. Salsa dancing has become extremely popular in Managua's nightclubs. With various influences, the form of salsa dancing varies in Nicaragua. New York style and Cuban Salsa (Salsa Casino) elements have gained popularity across the country.
Dance
Further information: Dance in NicaraguaDance in Nicaragua varies depending upon the region. Rural areas tend to have a stronger focus on movement of the hips and turns. The dance style in cities focuses primarily on more sophisticated footwork in addition to movement and turns. Combinations of styles from the Dominican Republic and the United States can be found throughout Nicaragua. Bachata dancing is popular in Nicaragua. A considerable amount of Bachata dancing influence comes from Nicaraguans living abroad, in cities that include Miami, Los Angeles and, to a much lesser extent, New York City. Tango has also surfaced recently in cultural cities and ballroom dance occasions.
Literature
Main article: Literature of Nicaragua
The origin of Nicaraguan literature can arguably be traced to pre-Columbian times. The myths and oral literature formed the cosmogenic view of the world of the indigenous people. Some of these stories are still known in Nicaragua. Like many Latin American countries, the Spanish conquerors have had the most effect on both the culture and the literature. Nicaraguan literature has historically been an important source of poetry in the Spanish-speaking world, with internationally renowned contributors such as Rubén Darío who is regarded as the most important literary figure in Nicaragua. He is called the "Father of Modernism" for leading the modernismo literary movement at the end of the 19th century. Other literary figures include Carlos Martinez Rivas, Pablo Antonio Cuadra, Alberto Cuadra Mejia, Manolo Cuadra, Pablo Alberto Cuadra Arguello, Orlando Cuadra Downing, Alfredo Alegría Rosales, Sergio Ramirez Mercado, Ernesto Cardenal, Gioconda Belli, Claribel Alegría and José Coronel Urtecho, among others.
The satirical drama El Güegüense was the first literary work of post-Columbian Nicaragua. It was written in both Nicarao and Spanish. It's regarded as one of Latin America's most distinctive colonial-era expressions and as Nicaragua's signature folkloric masterpiece. El Güegüense is a work of resistance to Spanish colonialism that combined music, dance and theatre. The theatrical play was written by an anonymous author in the 16th century, making it one of the oldest indigenous theatrical/dance works of the Western Hemisphere. In 2005 it was recognized by UNESCO as "a patrimony of humanity". After centuries of popular performance, the play was first published in a book in 1942.
Cuisine
Main article: Nicaraguan cuisine

Nicaraguan cuisine is a mixture of Spanish food and dishes of a pre-Columbian origin. Traditional cuisine changes from the Pacific to the Caribbean coast. The Pacific coast's main staple revolves around local fruits and corn, the Caribbean coast cuisine makes use of seafood and the coconut.
As in many other Latin American countries, maize is a staple food and is used in many of the widely consumed dishes, such as the nacatamal, güirila, and indio viejo. Maize is also an ingredient for drinks such as pinolillo and chicha as well as sweets and desserts. In addition to corn, rice and beans are eaten very often.
Gallo pinto, Nicaragua's national dish, is made with white rice and small red beans that are cooked individually and then fried together. The dish has several variations including the addition of coconut milk or grated coconut on the Caribbean coast. Most Nicaraguans begin their day with gallo pinto. Gallo pinto is most usually served with carne asada, a salad, fried cheese, plantains or maduros.
Many of Nicaragua's dishes include indigenous fruits and vegetables such as jocote, mango, papaya, tamarindo, pipian, banana, avocado, yuca, and herbs such as cilantro, oregano and achiote.
Traditional street food snacks found in Nicaragua include "quesillo", a thick tortilla with soft cheese and cream, "tajadas" (deep-fried plantain chips), "maduros" (a sautéed ripe plantain), and "fresco" (fresh juices such as hibiscus and tamarind commonly served in a plastic bag with a straw).
Nicaraguans have been known to eat guinea pigs, known as cuy. Tapirs, iguanas, turtle eggs, armadillos and boas are also sometimes eaten, but because of extinction threats to these wild creatures, there are efforts to curb this custom.
Media
Main article: Media of NicaraguaFor most Nicaraguans radio and TV are the main sources of news. There are more than 100 radio stations and several TV networks. Cable TV is available in most urban areas.
The Nicaraguan print media are varied and partisan, representing pro and anti-government positions. Publications include La Prensa, El Nuevo Diario, Confidencial, Hoy, and Mercurio. Online news publications include Confidencial and The Nicaragua Dispatch.
Sports

Baseball is the most popular sport in Nicaragua. Although some professional Nicaraguan baseball teams have recently folded, the country still enjoys a strong tradition of American-style baseball.
Baseball was introduced to Nicaragua during the 19th century. In the Caribbean coast, locals from Bluefields were taught how to play baseball in 1888 by Albert Addlesberg, a retailer from the United States. Baseball did not catch on in the Pacific coast until 1891 when a group of mostly college students from the United States formed "La Sociedad de Recreo" (Society of Recreation) where they played various sports, baseball being the most popular.
Nicaragua has had its share of MLB players, including shortstop Everth Cabrera, pitcher Vicente Padilla, and pitcher Jonathan Loáisiga, but the most notable is Dennis Martínez, who was the first baseball player from Nicaragua to play in Major League Baseball. He became the first Latin-born pitcher to throw a perfect game, and the 13th in the major league history, when he played with the Montreal Expos against the Dodgers at Dodger Stadium in 1991.
Boxing is the second most popular sport in Nicaragua. The country has had world champions such as Alexis Argüello and Ricardo Mayorga as well as Román González. Recently, football has gained popularity. The Dennis Martínez National Stadium has served as a venue for both baseball and football. The first ever national football-only stadium in Managua, the Nicaragua National Football Stadium, was completed in 2011.
Nicaragua's national basketball team had some recent success as it won the silver medal at the 2017 Central American Games. They will be taking part in the FIBA AmeriCup for the first time when Nicaragua hosts in 2025.
Nicaragua featured national teams in beach volleyball that competed at the 2018–2020 NORCECA Beach Volleyball Continental Cup in both the women's and the men's sections.
See also
- Nicaraguan nationality law
- Bibliography of Nicaragua
- Index of Nicaragua-related articles
- Outline of Nicaragua
Notes
- As shown on the Córdoba (bank notes and coins).
- /ˌnɪkəˈrɑːɡwə, -ˈræɡ-, -ɡjuə/ ; Spanish: [nikaˈɾaɣwa]
- Spanish: República de Nicaragua
References
- Banco Central de Nicaragua Archived 24 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- "Nicaragua". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 19 June 2023. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 4 July 2023.
- The Latin American Socio-Religious Studies Program / Programa Latinoamericano de Estudios Sociorreligiosos (PROLADES) Archived 12 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine PROLADES Religion in America by country
- "CENSO DE POBLACIÓN 2005" (PDF). 2015. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- Awadalla, Cristina (23 March 2023). "Authoritarian Populism and Patriarchal Logics: Nicaragua's Engendered Politics". Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society. 30 (2). Oxford University Press (OUP): 701–723. doi:10.1093/sp/jxad006. ISSN 1072-4745.
- Córdoba, José de (25 October 2022). "U.S. Imposes Sanctions on Nicaragua's Authoritarian Regime". WSJ. Archived from the original on 3 September 2023. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- "Nicaragua: Freedom in the World 2023 Country Report". Freedom House. 30 May 2019. Archived from the original on 3 September 2023. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- ^ "Nicaragua". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Nicaragua". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 22 June 2023. (Archived 2023 edition.)
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Nicaragua)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2024. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- "GINI index (World Bank estimate)". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Archived from the original on 22 May 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
- "Human Development Report 2023/2024" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- "Nicaragua Population 1950-2024".
- "Yara expands presence in Central America". 23 February 2018.
- "Nicaragua's Great Leap Forward". 8 May 2008.
- Mendoza, Yubelka; Kitroeff, Natalie (7 November 2021). "Nicaragua Descends Into Autocratic Rule as Ortega Crushes Dissent". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 5 January 2025.
- Córdoba, José de (6 November 2021). "Nicaragua Veers to Dictatorship as President Holds Election the U.S. Calls 'Sham'". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved 5 January 2025.
- Naím, Moisés (19 November 2021). "Why dictators love elections". EL PAÍS English. Retrieved 5 January 2025.
- ^ Brierley, Jan (15 October 2017). "Sense of wonder: Discover the turbulent past of Central America". Daily Express. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ^ Wallace, Will; Wallace, Camilla (10 April 2010). "Traveller's Guide: Nicaragua". The Independent. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- Peter (16 February 2019). "12 largest rainforests in the world and where to find them". Atlas & Boots. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- Dicum, G (17 December 2006). "The Rediscovery of Nicaragua". Travel Section. New York: TraveThe New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- Davis, LS (22 April 2009). "Nicaragua: The next Costa Rica?". Mother Nature Network. MNN Holdings, LLC. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- Kurtas, Susan. "Research Guides: UN Membership: Founding Members". research.un.org. Archived from the original on 4 July 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- Vanden, Harry E.; Morales, Waltraud Queiser (1985). "Nicaraguan Relations with the Nonaligned Movement". Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs. 27 (3): 141–161. doi:10.2307/165603. ISSN 0022-1937. JSTOR 165603. Archived from the original on 26 June 2022. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- "A Guide to ALBA". Americas Quarterly. Archived from the original on 26 June 2022. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- "CELAC | CELAC INTERNATIONAL". 16 February 2018. Archived from the original on 11 July 2022. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ^ "¿Por qué los países de América Latina se llaman como se llaman?" [Why do Latin American countries call themselves as they are called?]. Ideal (in Spanish). 29 July 2015. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Sánchez, Edwin (16 October 2016). "El origen de "Nicarao-agua": la Traición y la Paz". El Pueblo Presidente (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- "Nicarao"
- "Encuentro"
- Sánchez, Edwin (3 October 2016). "De Macuilmiquiztli al Güegüence pasando por Fernando Silva" [From Macuilmiquizli to Güegüence through Fernando Silva]. El 19 (in Spanish). Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- Silva, Fernando (15 March 2003). "Macuilmiquiztli". El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- "Nahuatl Dictionary: Nican".
- "Origin of the names of the Latin American countries". 8 February 2017.
- "The curious story of the origin of the names of Latin American countries". 16 February 2022.
- "Nicaragua". 4 November 2024.
- "Nahuatl Dictionary".
- "Etymology of Nicaragua".
- "Nicaraguan place names" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- "From Brazil to Bolivia and Costa Rica: Explanations about Latin American country names".
- "Nicaragua". 4 November 2024.
- ^ Solórzano, Carla Torres (18 September 2010). "Choque de lenguas o el mestizaje de nuestro idioma" [Clash of languages or the mixing of our language]. La Prensa (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 26 July 2021.
- "La raíz nahuatl de nuestro lenguaje" [The Nahuatl root of our language]. El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish). 10 August 2004. Archived from the original on 12 August 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- Dall, Christopher (1 October 2005). Nicaragua in Pictures. Twenty-First Century Books. pp. 66–67. ISBN 978-0-8225-2671-1.
- ^ Pérez-Brignoli, Héctor; translated by Sawrey A., Ricardo B.; Sawrey, Susana Stettri de (1989). A Brief History of Central America (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520060494.
- Gloria Helena Rey, "The Chibcha Culture – Forgotten, But Still Alive" Archived 2012-02-20 at the Wayback Machine, Colombia, Inter Press Service (IPS) News, 30 Nov 2007, accessed 9 Nov 2010
- "Nicaragua: VI History". Encarta. 13 June 2007.
- ^ Newson, Linda A. (1987). Indian survival in colonial Nicaragua (1st ed.). Norman : University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0806120089.
- ^ "Nicaragua: Precolonial Period". Library of Congress Country Studies. Archived from the original on 22 September 2008. Retrieved 29 June 2007., interpretation of statement: "the native peoples were linguistically and culturally similar to the Aztec and the Maya"
- ^ Campbell, Lyle (1 January 1985). The Pipil Language of El Salvador. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 10–12. ISBN 978-3-11-088199-8.
- Fowler, WR Jr. (1985). "Ethnohistoric Sources on the Pipil Nicarao: A Critical Analysis". Ethnohistory. 32 (1). Columbus, Ohio: 37–62. doi:10.2307/482092. ISSN 0014-1801. JSTOR 482092. OCLC 62217753.
- Brinton, Daniel G. (1887). "Were the Toltecs an Historic Nationality?". Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society. 24 (126): 229–230. JSTOR 983071.
- von Humboldt, Alexander; Poynter, J. Ryan; Altamirano Rayo, Giorleny D; Kraft, Tobias (25 January 2013). Views of the Cordilleras and Monuments of the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas: A Critical Edition. University of Chicago Press. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-226-86509-6.
- ^ Campbell, Lyle (1997). American Indian languages : the historical linguistics of Native America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509427-1.
- "Letter of Columbus on the Fourth Voyage". American Journey. Archived from the original on 3 April 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ "Nicaragua: History". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 10 June 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- ^ "Encuentro del cacique y el conquistador" [Encounter of the cacique and the conqueror]. El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish). 4 April 2009. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 17 May 2017.
- Healy, Paul; Pohl, Mary (1980). Archaeology of the Rivas Region, Nicaragua. Wilfrid Laurier Univ. Press. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-88920-094-4.
- Dyck, Erika; Fletcher, Christopher (6 October 2015). Locating Health: Historical and Anthropological Investigations of Place and Health. Routledge. p. 107. ISBN 978-1-317-32278-8.
- Sánchez, Edwin (16 September 2002). "No hubo Nicarao, todo es invento" [There was no Nicarao, it's all invented]. El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish).
- "The Spanish Conquest". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 22 September 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Making the First Global Trade Route: The Southeast Asian Foundations of the Acapulco–Manila Galleon Trade, 1519-1650 (Page 163) Archived 17 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine Citing Andre Gschaedler, "Mexico and the Pacific, 1540 - 1565: The Voyage of Villabos and Legazpi and the Preparations Made for Them," (Ph.D. dissertation, Columbia University, 1954), 40.
- ^ "Nicaragua Briefs: An Historic Find". Envío. Central American University – UCA. Archived from the original on 12 July 2017. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Duncan, David Ewing (1995). Hernando de Soto – A Savage Quest in the Americas – Book II: Consolidation. New York: Crown Publishers.
- ^ Whisnant, David E. (9 November 2000). Rascally Signs in Sacred Places: The Politics of Culture in Nicaragua. Univ of North Carolina Press. pp. 30–32. ISBN 978-0-8078-6626-9. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ Bergoeing, Jean Pierre (18 May 2015). Geomorphology of Central America: A Syngenetic Perspective. Elsevier Science. pp. 68–69. ISBN 978-0-12-803185-8. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 25 May 2017.
- Smith, RS (1963). "Financing the Central American federation, 1821–1838". The Hispanic American Historical Review. 43 (4): 483–510. doi:10.2307/2509898. JSTOR 2509898.
- Cybriwsky, Roman Adrian (23 May 2013). Capital Cities around the World: An Encyclopedia of Geography, History, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. p. 177. ISBN 978-1-61069-248-9. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2017.
- "Managua". La Prensa (in Spanish). 9 March 2006. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
Fue elevada a ciudad en 1846 y salomónicamente declarada capital de la República en 1852, para dirimir el viejo conflicto entre las urbes coloniales de León (occidente) y Granada (oriente) que rivalizaban por ejercer la hegemonía política de Nicaragua.
- "Gobernantes de Nicaragua". Ministerio de Educación. 9 December 2012. Archived from the original on 9 October 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- Walker, W (1860). The War in Nicaragua. New York: S.H. Goetzel & Company.
- Juda, F (1919). "California Filibusters: A History of their Expeditions into Hispanic America (excerpt)". The Grizzly Bear. XXI (4): 3–6, 15, 19. Archived from the original on 2 August 2009. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- Baker, CP (2001). "The William Walker Saga". Moon Handbooks: Costa Rica (4th ed.). New York: Avalon Travel Publishing. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-56691-608-0.
- Colquhoun, AR (1895). The key of the Pacific: the Nicaragua canal. Westminster, England: Archibald Constable and Company.
- Foreign Relations of the United States. 1912. p. 1032.
- Langley, Lester D. (2002). The Banana Wars: United States Intervention in the Caribbean, 1898-1934. Wilmington: SR Books. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-8420-5047-0. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- "US violence for a century: Nicaragua: 1912–33". Socialist Worker. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "Bryan–Chamorro Treaty". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 27 February 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "General Augusto C. Sandino: The Constitutional War". ViaNica. Archived from the original on 22 August 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Vukelich, D. "A Disaster Foretold". The Advocacy Project. Archived from the original on 3 April 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ "The Somoza years". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 19 June 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "Biographical Notes". Archived from the original on 31 December 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "History of U.S. Violence Across the Globe: Washington's War Crimes (1912–33)". 16 December 2001. Archived from the original on 14 November 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Solo, T (7 October 2005). "Nicaragua: From Sandino to Chavez". Dissident Voice. Archived from the original on 5 April 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "The Somoza Dynasty" (PDF). University of Pittsburgh. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 November 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Colburn, Forrest D. (26 March 2012). "Nicaragua, Forlorn". World Policy Journal. 29 (Spring 2012): 91–100. doi:10.1177/0740277512443806. Archived from the original on 6 May 2012. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- Model, David (2005). Lying for Empire: How to Commit War Crimes With a Straight Face. Common Courage Press.
- Goldstein, Erik (2005) Wars and Peace Treaties: 1816 to 1991. Routledge. p. 218. ISBN 9781134899111
- "El asalto de Somoza a los alemanes" (in Spanish). 6 January 2005. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2007.
- "Charter of the United Nations and Statute of the International Court of Justice" (PDF). San Francisco: United Nations. 26 June 1945. p. 49. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "SOMOZA'S NATION CALLED HIS FIEF; Rule of Nicaraguan General, Beginning With 1935 Coup, Was Seldom Challenged PRESIDENT FIRST IN '37 Graduate of Business School in U.S., He Acquired Great Wealth During Regime". New York Times TimesMachine. 30 September 1956. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- Leonard, TM (2003). "Against all odds: U.S. policy and the 1963 Central America Summit Conference". Journal of Third World Studies. p. 11. Archived from the original on 28 June 2009. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Headline: Nicaragua Earthquake". Vanderbilt Television News Archive. 16 December 1972. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2007.
- "Roberto Clemente". National Baseball Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 8 March 2022. Retrieved 8 March 2022.
- "Roberto Clemente – Bio". The National Baseball Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 27 April 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "A Battle Ends, a War Begins". TIME. 11 September 1978. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Annis, B (1993). "Nicaragua: Diversification and Growth, 1945–77". The Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- "The Sandinistas and the Revolution". Grinnell College. Archived from the original on 6 February 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Constable, Pamela; Valenzuela, Arturo (1991). A Nation of Enemies: Chile Under Pinochet. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 150. ISBN 978-0-393-30985-0.
- ^ "History of Nicaragua: The Beginning of the End". American Nicaraguan School. Archived from the original on 20 May 2006. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- Nordheimer, Jon (29 July 1987). "Nicaraguan Exiles Find A Place In The Sun: Miami". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2017.
- Wilkinson, Tracy (7 August 1988). "Families Struggle to Maintain Life Style : Sandinista Rule Not Easy on Middle Class". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2017.
- Wicker, Tom (29 July 1983). "In The Nation; The Sandinista Puzzle". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2017.
- Pastor, Robert (2001). Exiting the Whirlpool: U.S. Foreign Policy Toward Latin America and the Caribbean. Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-8133-3811-8.
- "Timeline: Nicaragua". Stanford University. Archived from the original on 26 April 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- U.S. HALTS ECONOMIC AID TO NICARAGUA Archived 24 October 2023 at the Wayback Machine, New York Times, 2 April 1981
- Mary C. Waters, et al. The New Americans : A Guide to Immigration Since 1965. Harvard University Press, 2007. EBSCOhost, https://search-ebscohost-com.lpclibrary.idm.oclc.org/login.aspx?direct=true&db=nlebk&AN=282331&site=ehost-live Archived 5 February 2024 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Nicaragua: Growth of Opposition, 1981–83". Ciao Atlas. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- LaRamee, Pierre; Polakoff, Erica (1999). The Undermining of the Sandinista Revolution. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 141–205. ISBN 9780333751992.
- Chomsky, Noam (1985). Turning the Tide. Boston, MA: South End Press.
- Truver, SC. "Mines and Underwater IEDs in U.S. Ports and Waterways..." (PDF). p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 April 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Summary of the Order Archived 2007-11-07 at the Wayback Machine of the International Court of Justice of 10 May 1984
- "...Finds that the United States of America, by producing in 1983 a manual entitled "Operaciones sicológicas en guerra de guerrillas", and disseminating it to Contra forces, has encouraged the commission by them of acts contrary to general principles of humanitarian law." As seen at: International Court of Justice 1986, (9)
- "In the case of shooting "a citizen who was trying to leave the town or city in which the guerrillas are carrying out armed propaganda or political proselytism," the manual suggests that the Contras "...explain that if that citizen had managed to escape, he would have alerted the enemy." As seen at: Sklar 1988, p. 179
- "US Policy: Economic Embargo: The War Goes On". Envío. Central American University – UCA. Archived from the original on 21 June 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Moore, John Norton (1987) The Secret War in Central America. University Publications of America. p. 143. ISBN 978-0890939611
- Miranda, Roger and Ratliff, William (1993) The Civil War in Nicaragua. Transaction. p. 193. ISBN 9781412819688
- "OAS Study Says Miskito Indians Suffered Abuse From Sandinistas". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- "Annual Report 1992–1993". Inter-American Commission on Human Rights. 12 March 1993. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2009.
- "NICARAGUAN VOTE:'FREE, FAIR, HOTLY CONTESTED'". The New York Times. 16 November 1984. p. 30. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- "1984: Sandinistas claim election victory". BBC News. 5 November 1984. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- Taubman, Philip (21 October 1984). "KEY AIDES DISPUTE U.S. ROLE IN NICARAGUAN VOTE". The New York Times. p. 12. Archived from the original on 31 May 2023. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- Baker, D (5 March 2007). The United States since 1980 (The World Since 1980). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 101. ISBN 978-0-521-86017-8.
- "Case concerning military and paramilitary activities in and against Nicaragua (Nicaragua v. United States of America), International Court of Justice, Order of 26 september 1991" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- The PRIO Battle Deaths Dataset, 1946–2008, Version 3.0: Documentation of Coding Decisions by Bethany Lacina
- O'Grady, M. "Ortega's Comeback Schemes Roil Nicaragua". Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Was February 25 a 'triumph'? National Review v. 42". Tulane University. Archived from the original on 1 September 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "El Sandinista Daniel Ortega se convierte de nuevo en presidente de Nicaragua". El Mundo (in Spanish). 8 November 2006. Archived from the original on 1 November 2023. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Dennis, G (December 1993). "Social conditions of Nicaragua". The Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 22 September 2008. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Nicaragua: Political profile". Archived from the original on 18 September 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Thompson, G (5 April 2005). "Old Foe of U.S. Trying for a Comeback in Nicaragua". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- "Nicaragua 'creeping coup' warning". BBC News. 30 September 2005. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Spanish defense minister: No more troops for Iraq". Deseret News. Associated Press. 29 April 2004. Archived from the original on 17 January 2024. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- Frazier, JB (18 November 2006). "Nicaraguan President Signs Abortion Ban". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 18 July 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2007.
- Boseley, S (11 June 2010). "Nicaragua refuses to lift abortion ban". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 25 February 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- "Bolaños Will Move To The National Assembly After All". Envío Magazine. 2006. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Gibney, James (30 January 2014). "Nicaragua's Revolution Heads Toward Dictatorship". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- Geoff, Thale. "As Nicaragua's Election Draws Near, Concerns Grow Over Abuse of Power". WOLA. Archived from the original on 13 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- "OAS Mission in Nicaragua Recommends Integral Electoral Reform". Organization of American States. 7 November 2016. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- "Nicaragua's Ortega re-elected president". BBC News. 7 November 2016. Archived from the original on 25 December 2017. Retrieved 12 September 2017.
- Cerda, Arlen (22 April 2018). "Los muertos de la represión que Daniel Ortega oculta". Confidencial (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 26 April 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- Kahn, Carrie (23 April 2018). "Nicaragua Withdraws Social Security Changes That Sparked Unrest". NPR. Archived from the original on 6 June 2018. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- Garvin, Glenn (2 May 2018). "In Nicaragua, the political battle is moving from the streets to the negotiating table". Miami Herald. Archived from the original on 14 June 2018. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- "CIDH condena nuevos hechos de violencia en Nicaragua". www.oas.org (in Spanish). Organization of American States. Inter-American Commission on Human Rights. 25 May 2018. Archived from the original on 28 May 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- "Nicaraguan protesters call on Ortega to go". BBC News. BBC. 27 May 2018. Archived from the original on 27 May 2018. Retrieved 27 May 2018.
- Dammert, Lucía, and Mary Fran T. Malone. “From Community Policing to Political Police in Nicaragua.” European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies / Revista Europea de Estudios Latinoamericanos y Del Caribe, no. 110, 2020, pp. 79–99. JSTOR, https://www.jstor.org/stable/26979875 Archived 25 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed 25 Nov. 2023.
- ^ "Why isn't Nicaragua in the Paris agreement?". BBC News. 3 June 2017. Archived from the original on 10 October 2018. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- "Nicaragua: a renewable energy paradise in Central America". World Bank. 25 October 2013. Archived from the original on 28 October 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- Nussbaum, Alex; Krukowska, Ewa; Carr, Mathew (8 December 2015). "Carbon Markets Are Making a Slow, But Steady, Comeback". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- "INDCs as communicated by Parties". unfccc.int. Archived from the original on 13 February 2016. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- "Nicaragua to join Paris climate accord, leaving US and Syria isolated". The Guardian. 23 October 2017. Archived from the original on 21 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Stack, Liam (24 October 2017). "Only U.S. and Syria Now Oppose Paris Climate Deal, as Nicaragua Joins". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Noack, Rick (24 October 2017). "Being outside the Paris climate deal: Something now only the U.S. and Syria agree on". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 11 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Paris Agreement – Status of Ratification". United Nations. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- "Large Lakes of the World". factmonster.com. Archived from the original on 29 March 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2007.
- "The Nature Conservancy in Nicaragua". nature.org. Archived from the original on 5 April 2007. Retrieved 25 May 2007.
- ^ "Nicaragua." Encyclopedia Americana. Grolier Online. (200-11-20) (subscription required)
- "TED CASE: Nicaragua Canal Proposal". american.edu. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- Muñoz, Néfer (2001). "An 'Eco-Canal' across Nicaragua". Accents. Granada, Nicaragua: Tierramérica. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- "Proyecto "Construcción del Puerto Monkey Point"". Proyectos (in Spanish). Managua: Empresa Portuaria Nacional. 2009. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- Alvarez, Gustavo (18 February 2008). "Empresas de seis países interesadas en Monkey Point". elnuevodiario.com.ni (in Spanish). Managua: El Nuevo Diario. Archived from the original on 13 July 2010. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- Álvarez Hidalgo, Wendy (7 July 2010). "Harán puerto Monkey Point". laprensa.co.ni (in Spanish). Managua: La Prensa. Archived from the original on 13 August 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- White, RL (24 August 2004). "Pittsburghers find once war-ravaged country is a good place to invest". Post Gazette. Archived from the original on 16 May 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Bosawas Bioreserve Nicaragua". Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 25 May 2007.
- Trudgill, Peter; Watts, Richard J., eds. (2002). Alternative Histories of English. Routledge. p. 35. ISBN 9780415233569.
English-speaking protestants formed the majority of the population until about 1900...indigenous anglophones still form about 85 per cent of the population, which also includes non-anglophone Black Caribs...At least at the level of arolectal Whites, the accent is rhotic though obviously Caribbean....England established a protectorate over the local Miskito Indians, who the region is named after, and the area was a British dependency from 1740 to 1786. In Nicaragua the British founded the principal Miskito coast city of Bluefields... There are about 30,000 native speakers of English in this area of Nicaragua who look to Bluefields as their centre... The English of the anglophone Corn Islands is also typically Caribbean.
- "Nicaraguan Animal Guide". Vianica. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- Rogers, Tim (15 May 2013). "In Latin America's Second Largest Rainforest, an Indigenous Tribe Fights for Its Land". Time. Archived from the original on 26 April 2018. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- Connor, Liz (17 November 2016). "10 reasons why you should visit Nicaragua". Evening Standard. Archived from the original on 5 December 2020. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- "National Parks and Protected Areas of Nicaragua". Archived from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- "Nicaragua". The Nature Conservancy. Archived from the original on 5 April 2007. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- "Nicaragua bans freshwater shark fishing amid dwindling population numbers". UnderwaterTimes.com. Archived from the original on 24 February 2016. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- Sesin, Carmen (8 November 2021). "'Rigged': Criticism mounts of Nicaragua's 'sham' elections under Ortega". NBC News. Archived from the original on 12 May 2023. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Blinken, Anthony. "New Sanctions Following Sham Elections in Nicaragua". White House. Archived from the original on 23 May 2022. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- "Freedom in the World 2024: Nicaragua". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 19 June 2024. Retrieved 8 August 2024.
- "A New U.N. Vote Shows Russia Isn't as Isolated as the West May Like to Think". Time. 13 October 2022. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- ^ "Nicaragua". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 30 October 2023. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- "Intentional homicides (per 100,000 people) - Nicaragua". Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- "Background and socio-economic context" (PDF). p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Nicaragua - Country Brief". web.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 3 October 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2010.
- "Rank Order – GDP – per capita (PPP)". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Social indicators: Per capita GDP". United Nations. Archived from the original on 30 April 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Field Listing :: GDP - composition, by sector of origin — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- "Migration Information Source – Remittance Trends in Central America". Migrationinformation.org. April 2006. Archived from the original on 10 February 2014. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "Nicaragua: Economic Outline". Nordea. 2020. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- "Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo – Noticias – La pobreza se arraiga en el país". Pnud.org.ni. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "Human Development Report 2009 – Countries' shares of total stock of migrants in Africa (%)". Hdrstats.undp.org. Archived from the original on 21 February 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- Silva, JA. "NICARAGUA: Name and Identity for Thousands of Indigenous Children". IPS. Archived from the original on 11 September 2008. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- "Economy Rankings: Doing Business". World Bank. Archived from the original on 10 December 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "Index Of Economic Freedom: Nicaragua". Heritage.org. Archived from the original on 26 October 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. Geneva. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Poland forgives nearly 31 million dollars of debt owed by Nicaragua". People's Daily Online. 21 March 2007. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Nicaragua:Economy". U.S. State Department. Archived from the original on 21 January 2017. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- "General Information – Nicaragua: Economy". Archived from the original on 28 August 2011. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "Tobacco Sector Exceeds Expectations – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal". www.centralamericadata.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2022. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- Sánchez, E (29 March 2010). "Nicaragua Plans to Sell Over $200 Million to Venezuela – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal". CentralAmericaData. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- Dan Oancea: "Mining In Central America" Archived January 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Tartter, JR. "The Nicaraguan Resistance". Country Studies. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- "Nicaragua completes Bluefields-Nueva Guinea highway". Bnamericas. 2 May 2019. Archived from the original on 7 April 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- PBS Now Politics CAFTA Archived 8 March 2013 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF). Retrieved on 2012-05-02.
- Raphaelidis, Leia Sewing Discontent in Nicaragua: The Harsh Regime of Asian Garment Companies in Nicaragua. Multinational Monitor. September 1, 1997
- Sarah Anderson Walmart Pay Gap. wakeupwalmart.com. April 15, 2005
- Dean, ANU College of Asia & the Pacific. "Home" (PDF). ANU College of Asia & the Pacific. Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- "Nicaragua – SOCIETY". Mongabay.com. Menlo Park, CA, US: Mongabay. Archived from the original on 27 April 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
CITATION: Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. The Country Studies Series. Published 1988–1999.
Original source: Merrill, Tim (1994). Nicaragua. Country Studies. Washington, DC: Federal Research Division, U.S. Library of Congress. ISBN 978-0-8444-0831-6. OCLC 30623751. Retrieved 3 May 2014.{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - "Primera prueba del sucre en enero – LA PRENSA — EL Diario de los Nicaragüenses". Laprensa.com.ni. 16 June 2010. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "Nicaragua canal construction 'will not begin until 2015'". BBC News. bbc.co.uk. 4 January 2014. Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- Howard, Brian Clark (22 February 2014). "Nicaraguan Canal Could Wreck Environment, Scientists Say". National Geographic. National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- "Nicaragua, Chinese tycoon say canal work to start in 2014". The Nation. 13 January 2014. Archived from the original on 13 January 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- "Four Years Later, China-Backed Nicaragua Canal Struggles to Take Off the Ground". PanAm Post. 8 May 2017. Archived from the original on 23 August 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
- "Travel And Tourism in Nicaragua". Euromonitor International. Archived from the original on 14 June 2010. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ Alemán, G. "Turismo en Nicaragua: aportes y desafios parte I". Canal 2 (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 17 July 2007. Retrieved 29 July 2007.
- "A Dynamic Economy: Dynamic Sectors of the Economy; Tourism". ProNicaragua. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- Carroll, Rory (7 January 2007). "Ortega banks on tourism to beat poverty". Guardian Unlimited. London. Archived from the original on 7 June 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- "Nicaragua exceeds one mn foreign tourists for first time". Sify. Archived from the original on 17 October 2018. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- "Background Note: Nicaragua; Economy". U.S. State Department. Archived from the original on 21 January 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Ministry of Tourism of Nicaragua". INTUR. Archived from the original on 13 May 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Acan-Efe (27 March 2009). "Foreign investment Increases by 79.1% in Nicaragua – CentralAmericaData :: The Regional Business Portal". CentralAmericaData. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- Parker, Nick (1 August 2012). "Can Nicaragua deliver on huge potential?". CNN Travel. Archived from the original on 22 April 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- "Volcanoes in Nicaragua: Apoyo Volcano". ViaNica. Archived from the original on 29 October 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- "Activities in and around the Apoyo Lagoon". ViaNica. Archived from the original on 22 August 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- "Nicaraguan Ecotourism". Nicaragua.com. Archived from the original on 16 July 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- "Nicaragua Travel Guide – Overview". World Travel Guide. Archived from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- "Ometepe Island Information – Everything About Traveling To Ometepe Island In One Place!". ometepeislandinfo.com. Archived from the original on 6 March 2017. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- Mauro Salzano, Francisco; Sans, Mónica (2014). "Interethnic admixture and the evolution of Latin American populations". Genetics and Molecular Biology. 37 (1 (suppl)): 151–170. doi:10.1590/s1415-47572014000200003. PMC 3983580. PMID 24764751.
- "Genomic Components in America's demography". Archived from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- "Urban population (% of total)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 2 March 2017. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- Anuario Estadístico 2015 (PDF) (Report). INIDE. February 2016. p. 52. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ^ "VIII Censo de Poblacion y IV de Vivienda" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (in Spanish). October 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2007. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- "Expatriates of Nicaragua". Nicaragua.com. Archived from the original on 14 July 2007. Retrieved 30 July 2007.
- Migration Information Source – El Salvador: Despite End to Civil War, Emigration Continues Archived 15 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.
- "Population growth (annual %)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 19 June 2016. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- "Nicaragua Birth rate - Demographics". www.indexmundi.com. Archived from the original on 7 April 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- "Crude death rate – the United Nations". UNData. Archived from the original on 27 June 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- "Nicaragua – People and Society". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- Baracco, L (2005). "From Acquiescence to Ethnic Militancy: Costeno Responses to Sandinista Anti-Imperialist Nationalism". Nicaragua: The Imagining of a Nation. From Nineteenth-Century Liberals to Twentieth-Century Sandinistas. New York: Algora Publishing.
- Zúñiga, Alejandro (11 January 2008). "Vestiges of Ancient Indigenous Language Still Found Today in Matagalpa's Northern Highlands". The Tico Times. Archived from the original on 22 April 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- Urban, Matthias. "¿La Costa Pacífica de América Central y América del sur Como Zona de Difusión Lexical?: Primeras Aproximaciones" (PDF). ALFAL 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 January 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- "Indigenous peoples in Nicaragua". IWGIA. Archived from the original on 27 April 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- "Garifuna". World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples. Minority Rights Group International. 19 June 2015. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- "Aqui Nicaragua Documentary, Program by Carlos Fernando Chamorro. Programa Inaugural de Aqui Nicaragua, Idiosincracia Nicaragüense" (in Spanish). YouTube. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "LADR About NSL". www.columbia.edu. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2022.
- "Evolution: Library: Birth of a Language". www.pbs.org. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2022.
- Kocab, Annemarie; Senghas, Ann; Snedeker, Jesse (November 2016). "The emergence of temporal language in Nicaraguan Sign Language". Cognition. 156: 147–163. doi:10.1016/j.cognition.2016.08.005. PMC 5027136. PMID 27591549.
- "Turkulka". Archived from the original on 27 April 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- "Languages of Nicaragua". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ACN (24 May 2022). "Nicaragua bishop on hunger strike to protest police harassment". ACN International. Archived from the original on 21 November 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ Dennis, G. "Nicaragua: Religion". Country Studies. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 2 January 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- "Nicaragua – Facts and Statistics". Mormon Newsroom. Archived from the original on 28 June 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2017.
- Con Todo el Poder de la Informmación – El Nuevo Diario – Managua, Nicaragua Archived 2011-05-13 at the Wayback Machine. Archivo.elnuevodiario.com.ni. Retrieved on 2011-04-29.
- Dolsten, Josefin (2 August 2017). "Tiny Nicaraguan Community Doubles in Size as 112 Convert". Times of Israel. Archived from the original on 30 December 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- International Religious Freedom 2007 Archived 24 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine (Released October 2007, covers period of June 2006 to May 2007)
- "Nicaragua: People groups". Joshua Project. Archived from the original on 13 February 2007. Retrieved 26 March 2007.
- "The Nicaragua case_M Orozco2 REV.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "El Salvador inicia plan para regularizar a nicaragüenses residentes". El Nuevo Diario. 18 May 2011. Archived from the original on 6 July 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- Lazo, Flor (28 August 2011). "Nicaragüenses se acogen a programa". La Prensa Gráfica. Archived from the original on 27 April 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ Angel-Urdinola D, Cortez R, Tanabe K. (2008). Equity, Access to Health Care Services and Expenditures on Health in Nicaragua. Health, Nutrition and Population of the World Bank.
- Sequeira M, Espinoza H, Amador JJ, Domingo G, Quintanilla M, and de los Santos T. (2011). The Nicaraguan Health System. PATH.
- Birn AE, Zimmerman S, Garfield R. (2000). To decentralize or not to decentralize, is that the question? Nicaraguan health policy under structural adjustment in the 1990s. International Journal of Health Services, 30, 111–28.
- "National adult literacy rates (15+), youth literacy rates (15–24) and elderly literacy rates (65+)". UNESCO Institute for Statistics. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- Liu, D (6 December 2006). "Nicaragua's new gov't to enforce free education". CHINA VIEW. Archived from the original on 28 December 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Gilbert, D. "Nicaragua: Education". Country Studies. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 2 January 2020. Retrieved 2 July 2007.
- Hanemann, U. "Nicaragua's Literacy Campaign". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 2 July 2007.
- "Historical Background of Nicaragua". Stanford University. Archived from the original on 22 April 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- "Nicaragua Pre-election Delegation Report". Global Exchange. Archived from the original on 30 September 2006. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- Arrien, JB. "Literacy in Nicaragua" (PDF). UNESCO. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ^ Piper, Alan T. (May 2018). "An investigation into the reported closing of the Nicaraguan gender gap". Mpra Paper. Archived from the original on 1 November 2018. Retrieved 31 October 2018.
- "Global Gender Gap Report" (PDF). Geneva: World Economic Forum. 2020. p. 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- "Americas and the Caribbean". UN Women. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 27 November 2018.
- "Nicaragua's rainbow revolutionaries". Washington Blade: Gay News, Politics, LGBT Rights. 18 December 2018. Archived from the original on 26 June 2020. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- "Human development indices and indicators: 2018 statistical update" (PDF). 19 September 2018. doi:10.18356/9a42b856-en. S2CID 240203402. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 November 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Traditional Nicaraguan Costumes: Mestizaje Costume". ViaNica.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 21 November 2007.
- ^ "Showcasing Nicaragua's Folkloric Masterpiece – El Gueguense – and Other Performing and Visual Arts". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 16 December 2007. Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- "Nicaragua, Eternal Land of Poets". Elcomercio.pe. Archived from the original on 25 February 2016. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- "Native Theatre: El Gueguense". Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 6 December 2007. Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- "El Güegüense o Macho Ratón". ViaNica. Archived from the original on 21 February 2021. Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- ^ "Try the culinary delights of Nicaragua cuisine". Nicaragua.com. Archived from the original on 16 October 2015. Retrieved 8 May 2006.
- Gleeson, Bridget (15 April 2016). "How to eat like a Nicaraguan". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 29 May 2018. Retrieved 27 May 2018.
- Gritzner, Charles F. (2010). Nicaragua. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 9781604136197. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 27 October 2020.
- "Country profile: Nicaragua". BBC News. 2 September 2009. Archived from the original on 3 June 2010. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ Villa, B. "LA HISTORIA DEL BÉISBOL EN LATINOAMERICA: Nicaragua". Latino Baseball (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2 July 2007. Retrieved 29 July 2007.
- Washburn, G. "'El Presidente' happy in new job". Major League Baseball. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "Baseball's Perfect Games: Dennis Martinez, Montreal Expos|. Also, Everth Cabrera who MLB debut was in 2009 season with San Diego Padres". The BASEBALL Page.com. Archived from the original on 13 November 2006. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "Salon de la Fama: Deportes en Nicaragua" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 26 September 2007. Retrieved 30 July 2007.
- "Building for tomorrow in Belize and Nicaragua". FIFA. Archived from the original on 24 June 2011. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- Panama win men's basketball gold at Central American Games in Managua Archived 21 March 2022 at the Wayback Machine Michael Pavitt (insidethegames.biz), 7 December 2017. Accessed 14 August 2020.
- "Continental Cup Finals start in Africa". FIVB. 22 June 2021. Archived from the original on 7 August 2021. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
Additional sources
 This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.
This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.
External links
Government
- General information
- Nicaragua Archived 20 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Nicaragua Corruption Profile from the Business Anti-Corruption Portal
- Nicaragua at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Nicaragua profile Archived 3 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Nicaragua
Wikimedia Atlas of Nicaragua- Maps Archived 28 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine from WorldAtlas.com
- Nicaraguaportal Archived 7 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine: Official information of the Honorary Consulate of Nicaragua
- Key Development Forecasts for Nicaragua Archived 16 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine from International Futures
Other
- Visit Nicaragua Archived 28 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- The State of the World's Midwifery – Nicaragua Country Profile Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
| Nicaragua articles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||||
| Geography | |||||||
| Politics | |||||||
| Economy | |||||||
| Society |
| ||||||
13°N 85°W / 13°N 85°W / 13; -85
Categories: