| Revision as of 06:03, 22 February 2020 editInternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers5,387,727 edits Bluelink 1 book for verifiability. ) #IABot (v2.0) (GreenC bot← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:35, 22 February 2020 edit undoJLMadrigal (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,267 edits With new lede paragraph - see talk pageNext edit → | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| {{economic liberalism sidebar}} | {{economic liberalism sidebar}} | ||
| <!-- What right-libertarianism is and taxonomy. --> | <!-- What right-libertarianism is and taxonomy. --> | ||
| '''Right-libertarianism''' |
'''Right-libertarianism''' <ref name="Rothbard">Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971). . ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. '''7''' (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.</ref><ref name="Goodway">Goodway, David (2006). '']''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. . "'Libertarian' and 'libertarianism' are frequently employed by anarchists as synonyms for 'anarchist' and 'anarchism', largely as an attempt to distance themselves from the negative connotations of 'anarchy' and its derivatives. The situation has been vastly complicated in recent decades with the rise of anarcho-capitalism, 'minimal statism' and an extreme right-wing laissez-faire philosophy advocated by such theorists as Rothbard and Nozick and their adoption of the words 'libertarian' and 'libertarianism'. It has therefore now become necessary to distinguish between their right libertarianism and the left libertarianism of the anarchist tradition".</ref><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565">Marshall, Peter (2008). '']''. London: Harper Perennial. p. 565. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".</ref><ref name="Carlson">Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: SAGE Publications. . {{ISBN|1412988764}}.</ref>{{sfn|Wündisch|2014}} also known as '''libertarian capitalism'''<ref name="LibertarianCapitalism">{{cite journal|url=https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/292300|title=The Fallacy of Libertarian Capitalism|last=Reiman|first=Jeffrey H.|year=2005|journal=Ethics|volume=10|issue=1|pages=85–95|doi=10.1086/292300|jstor=2380706}}</ref> or '''right-wing libertarianism''',<ref name="Rothbard"/><ref name="Newman">{{cite book|last=Newman|first=Saul|authorlink=Saul Newman|title=The Politics of Postanarchism|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SiqBiViUsOkC&pg=PA43|year=2010|publisher=Edinburgh University Press|pages=53|isbn=978-0-7486-3495-8|quote=It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism). There is a complex debate within this tradition between those like Robert Nozick, who advocate a 'minimal state', and those like Rothbard who want to do away with the state altogether and allow all transactions to be governed by the market alone. From an anarchist perspective, however, both positions—the minimal state (minarchist) and the no-state ('anarchist') positions—neglect the problem of economic domination; in other words, they neglect the hierarchies, oppressions, and forms of exploitation that would inevitably arise in a laissez-faire 'free' market. Anarchism, therefore, has no truck with this right-wing libertarianism, not only because it neglects economic inequality and domination, but also because in practice (and theory) it is highly inconsistent and contradictory. The individual freedom invoked by right-wing libertarians is only a narrow economic freedom within the constraints of a capitalist market, which, as anarchists show, is no freedom at all.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=32947|title=Libertarismo y deber. Una reflexión sobre la ética de Nozick|trans-title=Libertarianism and duty. A reflection on Nozick's ethics|journal=Revista de ciencias sociales|volume=91|pages=123–128|language=Spanish|issn=0210-0223}}</ref> | ||
| is a term used by some political scientists and writers to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital along socialist–capitalist lines. <ref>Long, Joseph. W (1996). "Toward a Libertarian Theory of Class". ''Social Philosophy and Policy''. '''15''' (2): 310. "When I speak of 'libertarianism' I mean all three of these very different movements. It might be protested that LibCap , LibSoc and LibPop are too different from one another to be treated as aspects of a single point of view. But they do share a common—or at least an overlapping—intellectual ancestry."</ref><ref>Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: SAGE Publications. . {{ISBN|1412988764}}. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism; the extent to which these represent distinct ideologies as opposed to variations on a theme is contested by scholars."</ref><ref name="Rothbard"/><ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/><ref name="Carlson"/><ref name="Newman"/><ref name="Francis">{{cite journal|last1=Francis|first1=Mark|title=Human Rights and Libertarians|journal=]|volume=29|issue=3|pages=462–472|date=December 1983|doi=10.1111/j.1467-8497.1983.tb00212.x|issn=0004-9522}}</ref> | |||
| Under this classification, right-libertarianism is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that strongly supports ], ] ] of ] and ].<ref>{{harvnb|Kymlicka|2005|p=516}}. "Right-wing libertarians argue that the right of self-ownership entails the right to appropriate unequal parts of the external world, such as unequal amounts of land".</ref> Like most forms of libertarianism, it tends to support ],<ref name="Rothbard"/> but also ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.libertarianism.org/encyclopedia/natural-law|title=Natural Law|last=Miller|first=Fred|work=The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism|date=15 August 2008|accessdate=31 July 2019}}</ref> ]<ref>Sterba, James P. (October 1994). "From Liberty to Welfare". ''Ethics''. Cambridge: Blackwell. '''105''' (1): 237–241.</ref> and a major reversal of the modern ].{{sfn|Baradat|2015|p=31}} Right-libertarianism is contrasted with ], a type of libertarianism that combines ] with an ] approach to natural resources.{{sfn|Vallentyne|2007|p=6|ps=. "The best-known versions of libertarianism are right-libertarian theories, which hold that agents have a very strong moral power to acquire full private property rights in external things. Left-libertarians, by contrast, hold that natural resources (e.g., space, land, minerals, air, and water) belong to everyone in some egalitarian manner and thus cannot be appropriated without the consent of, or significant payment to, the members of society."}} because it tends to support ownership of natural resources and the means of production.<ref name="Rothbard"/> Unlike left-libertarians, right-libertarians make no distinction between capitalism and free markets, and view any attempt to dictate the market process as counterproductive. Right-libertarians are typically referred to simply as "libertarians".<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/><ref name="Newman"/> | |||
| <!-- Term. --> | <!-- Term. --> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
| {{see also|Definition of anarchism and libertarianism}} | {{see also|Definition of anarchism and libertarianism}} | ||
| ] as right-libertarians oppose ], supporting instead '']'' economics within ]]] | ] as right-libertarians oppose ], supporting instead '']'' economics within ]]] | ||
| People described as being "left-libertarian" or "right-libertarian" generally tend to call themselves simply "libertarians" and refer to their philosophy as "libertarianism". As a result, some political scientists and writers classify the forms of ] into two groups, | |||
| People described as being "left-libertarian" or "right-libertarian" generally tend to call themselves simply "libertarians" and refer to their philosophy as "libertarianism". As a result, some political scientists and writers classify the forms of ] into two groups,<ref>Long, Joseph. W (1996). "Toward a Libertarian Theory of Class". ''Social Philosophy and Policy''. '''15''' (2): 310. "When I speak of 'libertarianism' I mean all three of these very different movements. It might be protested that LibCap , LibSoc and LibPop are too different from one another to be treated as aspects of a single point of view. But they do share a common—or at least an overlapping—intellectual ancestry."</ref><ref>Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: SAGE Publications. . {{ISBN|1412988764}}. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism; the extent to which these represent distinct ideologies as opposed to variations on a theme is contested by scholars."</ref> namely ] and right-libertarianism,<ref name="Rothbard"/><ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/><ref name="Carlson"/><ref name="Newman"/> to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of ] and ].<ref name="Francis"/> | |||
| Traditionally, "libertarian" was a term coined by the French ] ]<ref name="Graham"/><ref name="Marshall"/><ref name="Déjacque">Déjacque, Joseph (1857). (in French).</ref><ref name="LeLibertaire">{{cite web|url=http://joseph.dejacque.free.fr/libertaire/libertaire.htm|title=Le Libertaire, Journal du mouvement social|first=Jean Claude|last=Mouton|language=French|accessdate=16 July 2019}}</ref><ref name="Woodcock">Woodcock, George (1962). ''Anarchism: A History of Libertarian Ideas and Movements''. Meridian Books. p. 280. "He called himself a "social poet," and published two volumes of heavily didactic verse—Lazaréennes and Les Pyrénées Nivelées. In New York, from 1858 to 1861, he edited an anarchist paper entitled ''Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social'', in whose pages he printed as a serial his vision of the anarchist Utopia, entitled L'Humanisphére."</ref> to mean a form of ] that has been frequently used to refer to ]<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Nettlau"/><ref name="Graham"/><ref name="Marshall"/> and ]<ref name="Chomsky"/> since the mid- to late 19th century.<ref name="150Libertarian"/><ref name="160Libertarian"/> With the modern development of right-libertarian ideologies such as ] and ] co-opting<ref name="RothbardBetrayal"/><ref name="Bookchin"/><ref name="Fernandez"/> the term "libertarian" in the mid-20th century to instead advocate '']'' ] and strong ] such as in land, infrastructure and natural resources,<ref>{{cite book|last=Hussain|first=Syed B.|title=Encyclopedia of Capitalism. Vol. II : H-R.|year=2004|publisher=Facts on File Inc|location=New York|isbn=0816052247|page=492|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FbVZAAAAYAAJ|quote=In the modern world, political ideologies are largely defined by their attitude towards capitalism. Marxists want to overthrow it, liberals to curtail it extensively, conservatives to curtail it moderately. Those who maintain that capitalism is a excellent economic system, unfairly maligned, with little or no need for corrective government policy, are generally known as libertarians.}}</ref> the terms "left-libertarianism" and "right-libertarianism" have been used more often as to differentiate between the two.<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/> ]<ref>Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publications. p. 1006. {{ISBN|1412988764}}. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism. ocialist libertarians advocate for the simultaneous abolition of both government and capitalism."</ref> has been included within a broad left-libertarianism<ref>Bookchin, Murray; Biehl, Janet (1997). ''The Murray Bookchin Reader''. Cassell. p. 170 {{ISBN|0-304-33873-7}}.</ref><ref>Hicks, Steven V.; Shannon, Daniel E. (2003). ''The American Journal of Economics and Sociolology''. Blackwell Pub. p. 612.</ref><ref>"Anarchism". In Gaus, Gerald F.; D'Agostino, Fred, eds. (2012). ''The Routledge Companion to Social and Political Philosophy''. p. 227.</ref> while right-libertarianism mainly refers to ''laissez-faire'' capitalism such as ]'s anarcho-capitalism and ]'s minarchism.<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/><ref name="Newman"/> | Traditionally, "libertarian" was a term coined by the French ] ]<ref name="Graham"/><ref name="Marshall"/><ref name="Déjacque">Déjacque, Joseph (1857). (in French).</ref><ref name="LeLibertaire">{{cite web|url=http://joseph.dejacque.free.fr/libertaire/libertaire.htm|title=Le Libertaire, Journal du mouvement social|first=Jean Claude|last=Mouton|language=French|accessdate=16 July 2019}}</ref><ref name="Woodcock">Woodcock, George (1962). ''Anarchism: A History of Libertarian Ideas and Movements''. Meridian Books. p. 280. "He called himself a "social poet," and published two volumes of heavily didactic verse—Lazaréennes and Les Pyrénées Nivelées. In New York, from 1858 to 1861, he edited an anarchist paper entitled ''Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social'', in whose pages he printed as a serial his vision of the anarchist Utopia, entitled L'Humanisphére."</ref> to mean a form of ] that has been frequently used to refer to ]<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Nettlau"/><ref name="Graham"/><ref name="Marshall"/> and ]<ref name="Chomsky"/> since the mid- to late 19th century.<ref name="150Libertarian"/><ref name="160Libertarian"/> With the modern development of right-libertarian ideologies such as ] and ] co-opting<ref name="RothbardBetrayal"/><ref name="Bookchin"/><ref name="Fernandez"/> the term "libertarian" in the mid-20th century to instead advocate '']'' ] and strong ] such as in land, infrastructure and natural resources,<ref>{{cite book|last=Hussain|first=Syed B.|title=Encyclopedia of Capitalism. Vol. II : H-R.|year=2004|publisher=Facts on File Inc|location=New York|isbn=0816052247|page=492|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FbVZAAAAYAAJ|quote=In the modern world, political ideologies are largely defined by their attitude towards capitalism. Marxists want to overthrow it, liberals to curtail it extensively, conservatives to curtail it moderately. Those who maintain that capitalism is a excellent economic system, unfairly maligned, with little or no need for corrective government policy, are generally known as libertarians.}}</ref> the terms "left-libertarianism" and "right-libertarianism" have been used more often as to differentiate between the two.<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/> ]<ref>Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publications. p. 1006. {{ISBN|1412988764}}. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism. ocialist libertarians advocate for the simultaneous abolition of both government and capitalism."</ref> has been included within a broad left-libertarianism<ref>Bookchin, Murray; Biehl, Janet (1997). ''The Murray Bookchin Reader''. Cassell. p. 170 {{ISBN|0-304-33873-7}}.</ref><ref>Hicks, Steven V.; Shannon, Daniel E. (2003). ''The American Journal of Economics and Sociolology''. Blackwell Pub. p. 612.</ref><ref>"Anarchism". In Gaus, Gerald F.; D'Agostino, Fred, eds. (2012). ''The Routledge Companion to Social and Political Philosophy''. p. 227.</ref> while right-libertarianism mainly refers to ''laissez-faire'' capitalism such as ]'s anarcho-capitalism and ]'s minarchism.<ref name="Goodway"/><ref name="Marshall 2008 p. 565"/><ref name="Newman"/> | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 22 February 2020
| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (February 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Right-libertarianism also known as libertarian capitalism or right-wing libertarianism, is a term used by some political scientists and writers to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital along socialist–capitalist lines. Under this classification, right-libertarianism is a political philosophy and type of libertarianism that strongly supports property rights, market distribution of natural resources and private property. Like most forms of libertarianism, it tends to support civil liberties, but also natural law, negative rights and a major reversal of the modern welfare state. Right-libertarianism is contrasted with left-libertarianism, a type of libertarianism that combines self-ownership with an egalitarian approach to natural resources. because it tends to support ownership of natural resources and the means of production. Unlike left-libertarians, right-libertarians make no distinction between capitalism and free markets, and view any attempt to dictate the market process as counterproductive. Right-libertarians are typically referred to simply as "libertarians".
Being the most common type of libertarianism in the United States, right-libertarianism has become the most common referent of "libertarianism" there since the late 20th century while historically and elsewhere it continues to be widely used to refer to anti-state forms of socialism such as anarchism and more generally libertarian communism/libertarian Marxism and libertarian socialism. Around the time of Murray Rothbard, who popularized the term "libertarian" in the United States during the 1960s, anarcho-capitalist movements started calling themselves "libertarian", leading to the rise of the term "right-libertarian" to distinguish them. Rothbard himself acknowledged the co-opting of the term and boasted of its "capture from the enemy".
Right-libertarian political thought is characterized by the strict priority given to liberty, with the need to maximize the realm of individual freedom and minimize the scope of public authority. Right-libertarians typically see the state as the principal threat to liberty. This anti-statism differs from anarchist doctrines in that it is based upon an uncompromising individualism that places little or no emphasis upon human sociability or cooperation. Right-libertarian philosophy is also rooted in the ideas of individual rights and laissez-faire economics. The right-libertarianism theory of individual rights generally stresses that the individual is the owner of his person and that people have an absolute entitlement to the property that his labor produces. Economically, right-libertarians emphasize the self-regulating nature and mechanisms of the market, portraying government intervention and attempts to redistribute wealth as invariably unnecessary and counter-productive. Although all right-libertarians oppose government intervention, there is a division between anarcho-capitalists, who view the state as an unnecessary evil and want property rights protected without statutory law through market-generated tort, contract and property law; and minarchists, who recognize the necessary need for a minimal state, often referred to as a night-watchman state, to provide its citizens with the military, the police and courts.
While influenced by classical liberal thought, with some viewing right-libertarianism as an outgrowth or as a variant of it, there are significant differences. Edwin van de Haar argues that "confusingly, in the United States the term libertarianism is sometimes also used for or by classical liberals. But this erroneously masks the differences between them". Classical liberalism refuses to give priority to liberty over order and therefore does not exhibit the hostility to the state which is the defining feature of libertarianism. As such, right-libertarians believe classical liberals favor too much state involvement, arguing that they do not have enough respect for individual property rights and lack sufficient trust in the workings of the free market and its spontaneous order leading to support of a much larger state. Right-libertarians also disagree with classical liberals as being too supportive of central banks and monetarist policies.
Definition
See also: Definition of anarchism and libertarianism
People described as being "left-libertarian" or "right-libertarian" generally tend to call themselves simply "libertarians" and refer to their philosophy as "libertarianism". As a result, some political scientists and writers classify the forms of libertarianism into two groups,
Traditionally, "libertarian" was a term coined by the French libertarian communist Joseph Déjacque to mean a form of left-wing politics that has been frequently used to refer to anarchism and libertarian socialism since the mid- to late 19th century. With the modern development of right-libertarian ideologies such as anarcho-capitalism and minarchism co-opting the term "libertarian" in the mid-20th century to instead advocate laissez-faire capitalism and strong private property rights such as in land, infrastructure and natural resources, the terms "left-libertarianism" and "right-libertarianism" have been used more often as to differentiate between the two. Socialist libertarianism has been included within a broad left-libertarianism while right-libertarianism mainly refers to laissez-faire capitalism such as Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism and Robert Nozick's minarchism.
Right-libertarianism has been described as combining individual freedom and opposition to the state, with strong support for property rights and free markets. Property rights have been the issue that has divided libertarian philosophies. According to Jennifer Carlson, right-libertarianism is the dominant form of libertarianism in the United States. Right-libertarians "see strong private property rights as the basis for freedom and thus are—to quote the title of Brian Doherty's text on libertarianism in the United States—"radicals for capitalism".
Herbert Kitschelt and Anthony J. McGann contrast right-libertarianism—"a strategy that combines pro-market positions with opposition to hierarchical authority, support of unconventional political participation, and endorsement of feminism and of environmentalism"—with right-authoritarianism.
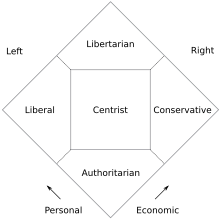
According to modern American libertarian Walter Block, left-libertarians and right-libertarians agree with certain libertarian premises, but "where differ is in terms of the logical implications of these founding axioms". Although some libertarians may reject the political spectrum, especially the left–right political spectrum, several strands of libertarianism in the United States and right-libertarianism have been described as being right-wing, New Right or radical right and reactionary.
American libertarian activist and politician David Nolan, the principal founder of the Libertarian Party, developed what is now known as the Nolan Chart to replace the traditional left–right political spectrum. The Nolan Chart has been used by several modern American libertarians and right-libertarians who reject the traditional political spectrum for its lack of inclusivity and see themselves as north-of-center. It is used in an effort to quantify typical libertarian views that support both free markets and social liberties and reject what they see as restrictions on economic and personal freedom imposed by the left and the right, respectively, although this later point has been criticized. Other libertarians reject the separation of personal and economic liberty, or that the Nolan Chart gives no weight to foreign policy.
Since the resurgence of neoliberalism in the 1970s, right-libertarianism has spread beyond North America via think tanks and political parties. In the United States, libertarianism is increasingly viewed as this capitalist free-market position.
Philosophy
Right-libertarianism developed in the United States in the mid-20th century from the works of European liberal writers like John Locke, Friedrich Hayek and Ludwig von Mises and is the most popular conception of libertarianism in the United States today. It is commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of classical liberalism. The most important of these early right-libertarian philosophers were modern American libertarians such as Robert Nozick and Murray Rothbard.
Although often sharing the left-libertarian advocacy for social freedom, right-libertarians also value the social institutions that enforce conditions of capitalism while rejecting institutions that function in opposition to these on the grounds that such interventions represent unnecessary coercion of individuals and abrogation of their economic freedom. Anarcho-capitalists seek complete elimination of the state in favor of private defense agencies while minarchists defend night-watchman states which maintain only those functions of government necessary to safeguard natural rights, understood in terms of self-ownership or autonomy.
Right-libertarians are economical liberals of the Austrian School and support laissez-faire capitalism.
Right-libertarianism and its individualism have been discussed as part of the New Right in relation to neoliberalism and Thatcherism. In the 20th century, New Right liberal conservatism influenced by right-libertarianism marginalized other forms of conservatism.
Non-aggression principle
Main article: Non-aggression principleThe non-aggression principle (NAP) is often described as the foundation of several present-day libertarian philosophies, including right-libertarianism. The NAP is a moral stance which forbids actions that are inconsistent with capitalist private property and property rights. It defines aggression and initiation of force as violation of these rights. The NAP and property rights are closely linked since what constitutes aggression depends on what it is considered to be one's property.
While the principle has been used rhetorically to oppose policies such as military drafts, taxation and victimless crime laws, use of the NAP as a justification for right-libertarianism has been criticized as circular reasoning and as a rhetorical obfuscation of the coercive nature of right-libertarian property law enforcement because the principle redefines aggression in their own terms.
Property rights
Main article: Property rights (economics)While there is debate on whether right-libertarianism and left-libertarianism or socialist libertarianism "represent distinct ideologies as opposed to variations on a theme", right-libertarianism is most in favor of capitalist private property and property rights. Right-libertarians maintain that unowned natural resources "may be appropriated by the first person who discovers them, mixes his labor with them, or merely claims them—without the consent of others, and with little or no payment to them". This contrasts with left-libertarianism in which "unappropriated natural resources belong to everyone in some egalitarian manner". Right-libertarians believe that natural resources are originally unowned and therefore private parties may appropriate them at will without the consent of, or owing to, others (e.g. a land value tax).
Right-libertarians are also referred to as propertarians as they hold that societies in which private property rights are enforced are the only ones that are both ethical and lead to the best possible outcomes. They generally support free-market capitalism and are not opposed to any concentrations of economic power, provided it occurs through non-coercive means. This has been criticized because "the holders of large amounts of property have great power to dictate the terms upon which others work for them and thus in effect the power to "force" others to be resources for them".
State
Main articles: Anarcho-capitalism and Night-watchman state
There is a debate amongst right-libertarians as to whether or not the state is legitimate. While anarcho-capitalists advocate its abolition, minarchists support minimal states, often referred to as night-watchman states. Minarchists maintain that the state is necessary for the protection of individuals from aggression, breach of contract, fraud and theft. They believe the only legitimate governmental institutions are courts, military and police, although some expand this list to include the executive and legislative branches, fire departments and prisons. These minarchists justify the state on the grounds that it is the logical consequence of adhering to the non-aggression principle and argue that anarchy is immoral because it implies that the non-aggression principle is optional and that the enforcement of laws under anarchism is open to competition. Another common justification is that private defense agencies and court firms would tend to represent the interests of those who pay them enough.
Right-libertarians such as anarcho-capitalists argue that the state violates the non-aggression principle by its nature because governments use force against those who have not stolen or vandalized private property, assaulted anyone, or committed fraud. Others argue that monopolies tend to be corrupt and inefficient and that private defense and court agencies would have to have a good reputation in order to stay in business. Linda and Morris Tannehill argue that no coercive monopoly of force can arise on a truly free market and that a government's citizenry can desert them in favor of a competent protection and defense agency.
Philosopher Moshe Kroy argues that the disagreement between anarcho-capitalists who adhere to Murray Rothbard's view of human consciousness and the nature of values and minarchists who adhere to Ayn Rand's view of human consciousness and the nature of values over whether or not the state is moral is not due to a disagreement over the correct interpretation of a mutually held ethical stance. He argues that the disagreement between these two groups is instead the result of their disagreement over the nature of human consciousness and that each group is making the correct interpretation of their differing premises. According to Kroy, these two groups are not making any errors with respect to deducing the correct interpretation of any ethical stance because they do not hold the same ethical stance.
Taxation as theft
Main article: Taxation as theftThe idea of taxation as theft is a viewpoint found in a number of political philosophies. Under this view, government transgresses property rights by enforcing compulsory tax collection. Right-libertarians see taxation as a violation of the non-aggression principle.
Schools of thought
Anarcho-capitalism
Main article: Anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism is a political philosophy which advocates the elimination of the state in favor of individual sovereignty in a free-market capitalism. In an anarcho-capitalist society, courts, law enforcement and all other security services would be provided by privately funded competitors rather than through taxation and money would be privately and competitively provided in an open market. As a result, personal and economic activities under anarcho-capitalism would be regulated by privately run law rather than through politics.
The most well-known version of anarcho-capitalism was formulated in the mid-20th century by Austrian School economist and paleolibertarian Murray Rothbard. Rothbard coined the term and is widely regarded as its founder. He combined the free market approach from the Austrian School with the human rights views and a rejection of the state he learned from 19th-century American individualist anarchists such as Lysander Spooner and Benjamin Tucker, although he rejected their anti-capitalism, along with the labor theory of value and the normative implications they derived from it.
In Rothbardian anarcho-capitalism, there would first be the implementation of a mutually agreed-upon libertarian "legal code which would be generally accepted and which the courts would pledge themselves to follow". This legal code would recognize sovereignty of the individual and the principle of non-aggression. Many writers deny that anarcho-capitalism is a form of anarchism at all, or that capitalism itself is compatible with anarchism, regarding it instead as right-libertarian.
Conservative libertarianism
Main article: Conservative libertarianism See also: FusionismConservative libertarianism is a political philosophy that combines laissez-faire economics and conservative values. Conservative libertarianism advocates the greatest possible economic liberty and the least possible government regulation of social life, but harnesses this to a belief in a more traditional and conservative social philosophy emphasizing authority and duty.
Conservative libertarianism prioritizes liberty as its main emphasis, promoting free expression, freedom of choice and laissez-faire capitalism to achieve socially and culturally conservative ends as they reject liberal social engineering, or in the opposite way yet not excluding the above conservative libertarianism could be understood as promoting civil society through conservative institutions and authority such as family, fatherland, religion and education in the quest of libertarian ends for less state power.
In American politics, fusionism is the philosophical and political combination or fusion of traditionalist and social conservatism with political and economic right-libertarianism. The philosophy is most closely associated with Frank Meyer.
Minarchism
Main article: MinarchismWithin right-libertarianism, minarchism is a political philosophy supportive of a night-watchman state, or minarchy, a model of a state whose only functions are to provide its citizens with courts, military and police, protecting them from aggression, breach of contract, fraud and theft whilst enforcing property laws. 19th-century Britain has been described by historian Charles Townshend as standard-bearer of this form of government among European countries.
As a term, night-watchman state (Template:Lang-de) was coined by German socialist Ferdinand Lassalle, an advocate of social democratic state socialism, to criticize the bourgeois state. Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises, a classical liberal who greatly influenced right-libertarianism, later opined that Lassalle tried to make limited government look ridiculous, but that it was no more ridiculous than governments that concerned themselves with "the preparation of sauerkraut, with the manufacture of trouser buttons, or with the publication of newspapers".
Robert Nozick, a right-libertarian advocate of minarchism, received a National Book Award in category Philosophy and Religion for his book Anarchy, State, and Utopia (1974), where he argued that only a minimal state limited to the narrow functions of protection against "force, fraud, theft, and administering courts of law" could be justified without violating people's rights.
Neo-classical liberalism
Not to be confused with Neoclassical liberalism See also: Classical liberalism and Neoliberalism
Traditionally, liberalism's primary emphasis was placed on securing the freedom of the individual by limiting the power of the government and maximizing the power of free market forces. As a political philosophy, it advocated civil liberties under the rule of law, with an emphasis on economic freedom. Closely related to economic liberalism, it developed in the early 19th century, emerging as a response to urbanization and to the Industrial Revolution in Europe and the United States. It advocated a limited government and held a belief in laissez-faire economic policy.
Built on ideas that had already arisen by the end of the 18th century such as selected ideas of John Locke, Adam Smith, Thomas Robert Malthus, Jean-Baptiste Say and David Ricardo, it drew on classical economics and economic ideas as espoused by Smith in The Wealth of Nations and stressed the belief in progress, natural law and utilitarianism. These liberals were more suspicious than conservatives of all but the most minimal government and adopted Thomas Hobbes's theory of government, believing government had been created by individuals to protect themselves from one another. The term classical liberalism was applied in retrospect to distinguish earlier 19th-century liberalism from the newer social liberalism.
Neoliberalism emerged in the era following World War II during which social liberalism was the mainstream form of liberalism while Keynesianism and social democracy were the dominant ideologies in the Western world. It was led by economists such as Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman, who advocated the reduction of the state and a return to classical liberalism, hence the term neo-classical liberalism. However, it did accept some aspects of social liberalism such as some degree of welfare provision by the state, but on a greatly reduced scale. Hayek and Friedman used the term classical liberalism to refer to their ideas, but others use the term to refer to all liberalism before the 20th century, not to designate any particular set of political views and therefore see all modern developments as being by definition not classical.
Right-libertarianism has been influenced by these schools of liberalism. It has been commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of classical liberalism and referred to as neo-classical liberalism.
Neolibertarianism
Main article: NeolibertarianismThe concept of neolibertarianism gained a small following within right-libertarianism in the mid-2000s among right-leaning commentators who distinguished themselves from neoconservatives by their support for individual liberties and from libertarians by their support for foreign interventionism.
Paleolibertarianism
Main article: Paleolibertarianism
Paleolibertarianism is a political philosophy developed by theorists Murray Rothbard and Lew Rockwell that combines conservative cultural values and social philosophy with a libertarian opposition to government intervention.
Paleolibertarianism is a controversial current due its connections to the Tea Party movement and the alt-right. However, these movements are united by an anti-Barack Obama stance, their support of the right to keep and bear arms and as a result an anti-gun control stance in regard to gun laws and politics instead of further ideological overlaps. In the essay "Right-Wing Populism: A Strategy for the Paleo Movement", Rothbard reflected on the ability of paleolibertarians to engage in an "outreach to rednecks" founded on social conservatism and radical libertarianism. He cited former Louisiana State Representative David Duke and former United States Senator Joseph McCarthy as models for the new movement.
In Europe, paleolibertarianism and right-wing populism have some significant overlap. Former European Union-parliamentarian Janusz Korwin-Mikke from KORWiN supports both laissez-faire economics and anti-immigration and anti-feminist positions.
Propertarianism
Main article: PropertarianismPropertarianism is an ethical philosophy that advocates the replacement of states with contractual relationships. Propertarian ideals are most commonly cited to advocate for a state or other governance body whose main or only job is to enforce contracts and private property.
Propertarianism is generally considered right-libertarian because it "reduce all human rights to rights of property, beginning with the natural right of self-ownership".
As a term, propertarian appears to have been coined in 1963 by Edward Cain, who wrote:
Since the use of the word "liberty" refers almost exclusively to property, it would be helpful if we had some other word, such as "propertarian," to describe them. Novelist Ayn Rand is not a conservative at all but claims to be very relevant. She is a radical capitalist, and is the closest to what I mean by a propertarian.
See also
- Anarcho-capitalism
- Anti-egalitarianism
- Austrian School
- Classical liberalism
- Conservative liberalism
- Constitutionalism
- Criticism of democracy
- Cultural conservatism
- Debates within libertarianism
- Economic liberalism
- Fiscal conservatism
- Freedom of association
- Free market
- Fusionism
- Laissez-faire
- Left-libertarianism
- Labor mobility
- Liberal conservatism
- Libertarian conservatism
- Libertarianism in the United States
- Market fundamentalism
- Minarchy
- Mises Institute
- Outline of libertarianism
- Paleolibertarianism
- Patriot movement
- Propertarianism
- Reaganomics
- Republican Liberty Caucus
- Ron Paul Revolution
- Taxation as theft
- Thatcherism
References
- ^ Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971). "The Left and Right Within Libertarianism". WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ Goodway, David (2006). Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. p. 4. "'Libertarian' and 'libertarianism' are frequently employed by anarchists as synonyms for 'anarchist' and 'anarchism', largely as an attempt to distance themselves from the negative connotations of 'anarchy' and its derivatives. The situation has been vastly complicated in recent decades with the rise of anarcho-capitalism, 'minimal statism' and an extreme right-wing laissez-faire philosophy advocated by such theorists as Rothbard and Nozick and their adoption of the words 'libertarian' and 'libertarianism'. It has therefore now become necessary to distinguish between their right libertarianism and the left libertarianism of the anarchist tradition".
- ^ Marshall, Peter (2008). Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism. London: Harper Perennial. p. 565. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces laissez-faire liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".
- ^ Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America. London: SAGE Publications. p. 1006. ISBN 1412988764.
- Wündisch 2014.
- ^ Reiman, Jeffrey H. (2005). "The Fallacy of Libertarian Capitalism". Ethics. 10 (1): 85–95. doi:10.1086/292300. JSTOR 2380706.
- ^ Newman, Saul (2010). The Politics of Postanarchism. Edinburgh University Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-7486-3495-8.
It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism). There is a complex debate within this tradition between those like Robert Nozick, who advocate a 'minimal state', and those like Rothbard who want to do away with the state altogether and allow all transactions to be governed by the market alone. From an anarchist perspective, however, both positions—the minimal state (minarchist) and the no-state ('anarchist') positions—neglect the problem of economic domination; in other words, they neglect the hierarchies, oppressions, and forms of exploitation that would inevitably arise in a laissez-faire 'free' market. Anarchism, therefore, has no truck with this right-wing libertarianism, not only because it neglects economic inequality and domination, but also because in practice (and theory) it is highly inconsistent and contradictory. The individual freedom invoked by right-wing libertarians is only a narrow economic freedom within the constraints of a capitalist market, which, as anarchists show, is no freedom at all.
- "Libertarismo y deber. Una reflexión sobre la ética de Nozick" [Libertarianism and duty. A reflection on Nozick's ethics]. Revista de ciencias sociales (in Spanish). 91: 123–128. ISSN 0210-0223.
- Long, Joseph. W (1996). "Toward a Libertarian Theory of Class". Social Philosophy and Policy. 15 (2): 310. "When I speak of 'libertarianism' I mean all three of these very different movements. It might be protested that LibCap , LibSoc and LibPop are too different from one another to be treated as aspects of a single point of view. But they do share a common—or at least an overlapping—intellectual ancestry."
- Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America. London: SAGE Publications. p. 1006. ISBN 1412988764. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism; the extent to which these represent distinct ideologies as opposed to variations on a theme is contested by scholars."
- Francis, Mark (December 1983). "Human Rights and Libertarians". Australian Journal of Politics & History. 29 (3): 462–472. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8497.1983.tb00212.x. ISSN 0004-9522.
- Kymlicka 2005, p. 516. "Right-wing libertarians argue that the right of self-ownership entails the right to appropriate unequal parts of the external world, such as unequal amounts of land".
- Miller, Fred (15 August 2008). "Natural Law". The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- Sterba, James P. (October 1994). "From Liberty to Welfare". Ethics. Cambridge: Blackwell. 105 (1): 237–241.
- ^ Baradat 2015, p. 31.
- Vallentyne 2007, p. 6. "The best-known versions of libertarianism are right-libertarian theories, which hold that agents have a very strong moral power to acquire full private property rights in external things. Left-libertarians, by contrast, hold that natural resources (e.g., space, land, minerals, air, and water) belong to everyone in some egalitarian manner and thus cannot be appropriated without the consent of, or significant payment to, the members of society."
- ^ Rothbard, Murray (2009) . The Betrayal of the American Right (PDF). Mises Institute. p. 83. ISBN 978-1610165013.
One gratifying aspect of our rise to some prominence is that, for the first time in my memory, we, 'our side,' had captured a crucial word from the enemy. 'Libertarians' had long been simply a polite word for left-wing anarchists, that is for anti-private property anarchists, either of the communist or syndicalist variety. But now we had taken it over.
- ^ Bookchin, Murray (January 1986). "The Greening of Politics: Toward a New Kind of Political Practice". Green Perspectives: Newsletter of the Green Program Project (1). "We have permitted cynical political reactionaries and the spokesmen of large corporations to pre-empt these basic libertarian American ideals. We have permitted them not only to become the specious voice of these ideals such that individualism has been used to justify egotism; the pursuit of happiness to justify greed, and even our emphasis on local and regional autonomy has been used to justify parochialism, insularism, and exclusivity – often against ethnic minorities and so-called deviant individuals. We have even permitted these reactionaries to stake out a claim to the word libertarian, a word, in fact, that was literally devised in the 1890s in France by Elisée Reclus as a substitute for the word anarchist, which the government had rendered an illegal expression for identifying one's views. The propertarians, in effect – acolytes of Ayn Rand, the earth mother of greed, egotism, and the virtues of property – have appropriated expressions and traditions that should have been expressed by radicals but were willfully neglected because of the lure of European and Asian traditions of socialism, socialisms that are now entering into decline in the very countries in which they originated".
- ^ Nettlau, Max (1996). A Short History of Anarchism. London: Freedom Press. p. 162. ISBN 978-0-900384-89-9. OCLC 37529250.
- ^ Fernandez, Frank (2001). Cuban Anarchism. The History of a Movement. Sharp Press. p. 9. "Thus, in the United States, the once exceedingly useful term "libertarian" has been hijacked by egotists who are in fact enemies of liberty in the full sense of the word."
- ^ "The Week Online Interviews Chomsky". Z Magazine. 23 February 2002. "The term libertarian as used in the US means something quite different from what it meant historically and still means in the rest of the world. Historically, the libertarian movement has been the anti-statist wing of the socialist movement. In the US, which is a society much more dominated by business, the term has a different meaning. It means eliminating or reducing state controls, mainly controls over private tyrannies. Libertarians in the US don't say let's get rid of corporations. It is a sort of ultra-rightism."
- Ward, Colin (2004). Anarchism: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. p. 62. "For a century, anarchists have used the word 'libertarian' as a synonym for 'anarchist', both as a noun and an adjective. The celebrated anarchist journal Le Libertaire was founded in 1896. However, much more recently the word has been appropriated by various American free-market philosophers."
- ^ Robert Graham, ed. (2005). Anarchism: A Documentary History of Libertarian Ideas. Vol. Volume One: From Anarchy to Anarchism (300 CE–1939). Montreal: Black Rose Books. §17.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ Marshall, Peter (2009). Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism. p. 641. "The word 'libertarian' has long been associated with anarchism, and has been used repeatedly throughout this work. The term originally denoted a person who upheld the doctrine of the freedom of the will; in this sense, Godwin was not a 'libertarian', but a 'necessitarian'. It came however to be applied to anyone who approved of liberty in general. In anarchist circles, it was first used by Joseph Déjacque as the title of his anarchist journal Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social published in New York in 1858. At the end of the last century, the anarchist Sebastien Faure took up the word, to stress the difference between anarchists and authoritarian socialists".
- ^ The Anarchist FAQ Editorial Collective (11 December 2008). "150 years of Libertarian". Anarchist Writers. The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- ^ The Anarchist FAQ Editorial Collective (17 May 2017). "160 years of Libertarian". Anarchist Writers. Anarchist FAQ. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- Marshall, Peter (2009). Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism. p. 641. "For a long time, libertarian was interchangable in France with anarchism but in recent years, its meaning has become more ambivalente. Some anarchists like Daniel Guérin will call themselves 'libertarian socialists', partly to avoid the negative overtones still associated with anarchism, and partly to stress the place of anarchism within the socialist tradition. Even Marxists of the New Left like E. P. Thompson call themselves 'libertarian' to distinguish themselves from those authoritarian socialists and communists who believe in revolutionary dictatorship and vanguard parties."
- ^ Heywood 2004, p. 337.
- Newman 2010, p. 43 harvnb error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFNewman2010 (help) "It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Murray Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism). There is a complex debate within this tradition between those like Robert Nozick, who advocate a 'minimal state', and those like Rothbard who want to do away with the state altogether and allow all transactions to be governed by the market alone. From an anarchist perspective, however, both positions—the minimal state (minarchist) and the no-state ('anarchist') positions—neglect the problem of economic domination; in other words, they neglect the hierarchies, oppressions, and forms of exploitation that would inevitably arise in a laissez-faire 'free' market. Anarchism, therefore, has no truck with this right-wing libertarianism, not only because it neglects economic inequality and domination, but also because in practice (and theory) it is highly inconsistent and contradictory. The individual freedom invoked by right-wing libertarians is only a narrow economic freedom within the constraints of a capitalist market, which, as anarchists show, is no freedom at all".
- ^ Goodman, John C. (20 December 2005). "What Is Classical Liberalism?". National Center for Policy Analysis. Retrieved 26 June 2019. Archived 9 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- van de Haar 2015, p. 71. sfn error: no target: CITEREFvan_de_Haar2015 (help)
- ^ van de Haar 2015, p. 42. sfn error: no target: CITEREFvan_de_Haar2015 (help)
- van de Haar 2015, p. 43. sfn error: no target: CITEREFvan_de_Haar2015 (help)
- Déjacque, Joseph (1857). "De l'être-humain mâle et femelle–Lettre à P.J. Proudhon" (in French).
- Mouton, Jean Claude. "Le Libertaire, Journal du mouvement social" (in French). Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- Woodcock, George (1962). Anarchism: A History of Libertarian Ideas and Movements. Meridian Books. p. 280. "He called himself a "social poet," and published two volumes of heavily didactic verse—Lazaréennes and Les Pyrénées Nivelées. In New York, from 1858 to 1861, he edited an anarchist paper entitled Le Libertaire, Journal du Mouvement Social, in whose pages he printed as a serial his vision of the anarchist Utopia, entitled L'Humanisphére."
- Hussain, Syed B. (2004). Encyclopedia of Capitalism. Vol. II : H-R. New York: Facts on File Inc. p. 492. ISBN 0816052247.
In the modern world, political ideologies are largely defined by their attitude towards capitalism. Marxists want to overthrow it, liberals to curtail it extensively, conservatives to curtail it moderately. Those who maintain that capitalism is a excellent economic system, unfairly maligned, with little or no need for corrective government policy, are generally known as libertarians.
- Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America. London: Sage Publications. p. 1006. ISBN 1412988764. "There exist three major camps in libertarian thought: right-libertarianism, socialist libertarianism, and left-libertarianism. ocialist libertarians advocate for the simultaneous abolition of both government and capitalism."
- Bookchin, Murray; Biehl, Janet (1997). The Murray Bookchin Reader. Cassell. p. 170 ISBN 0-304-33873-7.
- Hicks, Steven V.; Shannon, Daniel E. (2003). The American Journal of Economics and Sociolology. Blackwell Pub. p. 612.
- "Anarchism". In Gaus, Gerald F.; D'Agostino, Fred, eds. (2012). The Routledge Companion to Social and Political Philosophy. p. 227.
- ^ Kitschelt, Herbert; McGann, Anthony J. (1997) . The Radical Right in Western Europe: A Comparative Analysis. University of Michigan Press. p. 27. ISBN 9780472084418.
- ^ Mudde, Cas (11 October 2016). The Populist Radical Right: A Reader (1st ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-1138673861.
- Block, Walter (2010). "Libertarianism Is Unique and Belongs Neither to the Right Nor the Left: A Critique of the Views of Long, Holcombe, and Baden on the Left, Hoppe, Feser, and Paul on the Right". Journal of Libertarian Studies. 22. pp. 127–170.
- Read, Leonard E. (January 1956). "Neither Left Nor Right". The Freeman. 48 (2): 71–73.
- Browne, Harry (21 December 1998). "The Libertarian Stand on Abortion". HarryBrowne.Org. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- Raimondo, Justin (2000). An Enemy of the State. Chapter 4: "Beyond left and right". Prometheus Books. p. 159.
- Machan, Tibor R. (2004). "Neither Left Nor Right: Selected Columns". 522. Hoover Institution Press. ISBN 0817939822. ISBN 9780817939823.
- Robin, Corey (2011). The Reactionary Mind: Conservatism from Edmund Burke to Sarah Palin. Oxford University Press. pp. 15–16. ISBN 978-0199793747.
- Harmel, Robert; Gibson, Rachel K. (June 1995). "Right‐Libertarian Parties and the "New Values": A Re‐examination". Scandinavian Political Studies (July 1993). doi:10.1111/j.1467-9477.1995.tb00157.x.
- ^ Robinson, Emily; et al. (2017). "Telling stories about post-war Britain: popular individualism and the 'crisis' of the 1970s". Twentieth Century British History. 28 (2): 268–304.
- "About the Quiz". Advocates for Self-Government. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- Micthell, Brian Patrick (2007). Eight Ways to Run the Country: A New and Revealing Look at Left and Right. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 7–8. ISBN 978-0-275-99358-0.
- Huebert, Jacob H. (2010). Libertarianism Today. Santa Barbara, California: Praeger. pp. 22–24. ISBN 9780313377556. OCLC 655885097.
- Teles, Steven; Kenney, Daniel A. (2008). "Spreading the Word: The Diffusion of American Conservatism in Europe and Beyond". In Steinmo, Sven (2007). Growing Apart?: America and Europe in the Twenty-First Century. Cambridge University Press. pp. 136–169.
- Gregory, Anthony (24 April 2007). "Real World Politics and Radical Libertarianism". LewRockwell.com. Archived 18 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- Boaz, David (21 November 1998). "Preface for the Japanese Edition of Libertarianism: A Primer". Cato Institute. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- Silber, Kenneth (4 February 2007). "Radicals for Capitalism (Book Review)". The New York Post. Archived 8 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- Lester, J. C. (22 October 2017). "New-Paradigm Libertarianism: a Very Brief Explanation". PhilPapers. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ Boaz, David (1998). Libertarianism: A Primer. Free Press. pp. 22–26.
- ^ Conway, David (2008). "Freedom of Speech". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). Liberalism, Classical. The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; Cato Institute. pp. 295–98 at p. 296. doi:10.4135/9781412965811.n112. ISBN 978-1-4129-6580-4. LCCN 2008009151. OCLC 750831024.
Depending on the context, libertarianism can be seen as either the contemporary name for classical liberalism, adopted to avoid confusion in those countries where liberalism is widely understood to denote advocacy of expansive government powers, or as a more radical version of classical liberalism.
- "About the Libertarian Party". Libertarian Party. Retrieved 27 June 2019. "Libertarians strongly oppose any government interference into their personal, family, and business decisions. Essentially, we believe all Americans should be free to live their lives and pursue their interests as they see fit as long as they do no harm to another".
- Newman, Saul (2010). The Politics of Postanarchism. Edinburgh University Press. p. 43. ISBN 0748634959. "It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism)".
- Marshall, Peter (2008). Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism. London: Harper Perennial. p. 565. "In fact, few anarchists would accept the 'anarcho-capitalists' into the anarchist camp since they do not share a concern for economic equality and social justice, Their self-interested, calculating market men would be incapable of practicing voluntary co-operation and mutual aid. Anarcho-capitalists, even if they do reject the State, might therefore best be called right-wing libertarians rather than anarchists".
- Nozick, Robert (1974). Anarchy, State, and Utopia. Basic Books.
- Raico, Ralph (2012). Classical Liberalism and the Austrian School. Auburn, Alabama: Mises Institute. ISBN 9781610160032.
- "National Questions" (30 June 1997). National Review. 49 (12): 16–17.
- "Join the Libertarian Party". Libertarian Party. 1971. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
I certify that I oppose the initiation of force to achieve political or social goals.
- Block, Walter (17 February 2003). "The Non-Aggression Axiom of Libertarianism". Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- Barnet, Phred (14 April 2011). "The Non-Aggression Principle". Americanly Yours. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- Kinsella, Stephan (4 October 2011). "The relation between the non-aggression principle and property rights: a response to Division by Zer0". Mises Wire. Mises Institute. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Vance, Laurence M. Vance (1 October 2015). "The Morality of Libertarianism". The Future of Freedom Foundation. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- Kinsella, Stephan (21 August 2009). "What Libertarianism Is". Mises Daily. Mises Institute. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- Friedman, Jeffrey (1993). "What's Wrong with Libertarianism". Critical Review. 11 (3). p. 427.
- Sterba, James P. (October 1994). "From Liberty to Welfare". Ethics. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Blackwell. 105 (1): 237–241.
- Partridge, Ernest (2004). "With Liberty and Justice for Some". In Zimmerman, Michael; Callicott, Baird; Warren, Karen; Klaver, Irene; Clark, John. Environmental Philosophy: From Animal Rights to Radical Ecology (4th ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0-1311-2695-4.
- Wolff, Jonathan (22 October 2006). "Libertarianism, Utility, and Economic Competition" (PDF). Virginia Law Review. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Fried, Barbara (2009). The Progressive Assault on Laissez Faire: Robert Hale and the First Law and Economics Movement. Harvard University Press. p. 50. ISBN 9780674037304.
- Bruenig, Matt (28 October 2013). "Libertarians Are Huge Fans of Economic Coercion". Demos. Archived from the original on 18 February 2019. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
- Bruenig, Matt (17 November 2013). "Libertarians are Huge Fans of Initiating Force". Demos. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
- Carlson 2012, p. 1007.
- Vallentyne, Peter (20 July 2010). "Libertarianism". In Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- Becker, Lawrence C.; Becker, Charlotte B. (2001). Encyclopedia of Ethics. 3. New York: Routledge. p. 1562.
- Rothbard, Murray (1998). The Ethics of Liberty. New York: NYU Press. ISBN 978-0814775066.
- von Mises, Ludwig (2007). Human Action: A Treatise on Economics. Indianapolis: Liberty Fund. ISBN 978-0865976313.
- ^ Gregory, Anthory (10 May 2004). "The Minarchist's Dilemma". Strike The Root. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- "What role should certain specific governments play in Objectivist government?". Peikoff.com. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- "Interview with Yaron Brook on economic issues in today's world (Part 1)". Peikoff.com. 10 March 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Holcombe, Randall G. "Government: Unnecessary but Inevitable" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Long, Roderick T. (16 February 2009). "Market Anarchism as Constitutionalism". Molinari Institute. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Plauché, Geoffrey Allan (27 August 2006). "On the Social Contract and the Persistence of Anarchy" (PDF). American Political Science Association. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: Louisiana State University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2008.
- Tannehill, Linda; Tannehill, Morris (1970). The Market for Liberty. p. 81. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Kroy, Moshe (21 September 2010). "Political Freedom and Its Roots in Metaphysics". Mises Institute. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Feserm, Edward (Fall 2000). "Taxation, Forced Labor, and Theft" (PDF). The Independent Review: 219–235). Retrieved 10 July 2012.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - Tame, Chris R. (1989). "Taxation Is Theft" (PDF). Libertarian Alliance Political Note (44). Retrieved 2 September 2012.
- Chodorov, Frank. "Taxation Is Robbery". Mises Institute. Retrieved 10 July 2012. Reprint from Chodorov, Frank (1962). Out of Step: The Autobiography of an Individualist. New York: The Devin-Adair Company. pp. 216–239.
- Stringham 2007, p. 51.
- Morris 2008, pp. 13–14.
- Caplan 2008, pp. 194–195.
- Tannehill, Linda; Tannehill, Morris (1993). The Market for Liberty (PDF). San Francisco: Fox & Wilkes. pp. 105–106. ISBN 978-0-930073-08-4. Retrieved 30 June 2011.
- "Review of Kosanke's Instead of Politics – Don Stacy" (2011). Libertarian Papers. 3 (3).
- Miller 1987, p. 290. "A student and disciple of the Austrian economist Ludwig von Mises, Rothbard combined the laissez-faire economics of his teacher with the absolutist views of human rights and rejection of the state he had absorbed from studying the individualist American anarchists of the nineteenth century such as Lysander Spooner and Benjamin Tucker".
- Rothbard, Murray (1973). For A New Liberty. "The Public Sector, III: Police, Law, and the Courts". Mises Institute. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Heywood 2015, p. 37. sfn error: no target: CITEREFHeywood2015 (help)
- Piper, J. Richard (1997). Ideologies and Institutions: American Conservative and Liberal Governance Prescriptions Since 1933. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 110–111. ISBN 0847684598. ISBN 978-0847684595.
- Hoppe, Hans-Hermann (28 September 2018). "Getting Libertarianism Right". Mises Institute. ISBN 978-1-61016-690-4.
- Dionne Jr., E. J. (1991). Why Americans Hate Politics. New York: Simon & Schuster. p. 161.
- Meyer, Frank S. (1996). In Defense of Freedom and Other Essays. Indianapolis: Liberty Fund.
- Peikoff, Leonard. "What role should certain specific governments play in Objectivist government?". 7 March 2011. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- Peikoff, Leonard (3 October 2011). "Interview with Yaron Brook on economic issues in today's world (Part 1)". Peikoff.com. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- Townshend, Charles (2000). The Oxford History of Modern War. Oxford University Press. pp. 15. ISBN 0-19-285373-2.
- Sawer, Marian (2003). The Ethical State?: Social Liberalism in Australia. Melbourne University Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 0-522-85082-0. ISBN 978-0-522-85082-6.
- Von Mises, Ludwig (1927) . Liberalism. p. 37.
- "National Book Awards – 1975" (1975). National Book Foundation. Retrieved 8 March 2012. Archived 9 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- Feser, Edward. "Robert Nozick (1938—2002)". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- Conway, p. 296. sfn error: no target: CITEREFConway (help)
- Hudelson, Richard (1999). Modern Political Philosophy. M. E. Sharpe. pp. 37–38. ISBN 9780765600219.
- Dickerson, Flanagan & O'Neill, p. 129. sfn error: no target: CITEREFDickersonFlanaganO'Neill (help)
- Hamowy, ed. (2008). p. xxix.
- Hudelson, Richard (1999). Modern Political Philosophy. M. E. Sharpe. pp. 37–38. ISBN 9780765600219.
- Dickerson, M. O. et al. (2009). An Introduction to Government and Politics: A Conceptual Approach. p. 129.
- Bronfenbrenner, Martin (1955). "Two Concepts of Economic Freedom". Ethics. 65 (3): 157–217. doi:10.1086/290998. JSTOR 2378928.
- Steven M. Dworetz (1994). The Unvarnished Doctrine: Locke, Liberalism, and the American Revolution.
- Hunt, p. 54. sfn error: no target: CITEREFHunt (help)
- Appleby, Joyce (1992). Liberalism and Republicanism in the Historical Imagination. p. 58.
- Gaus, Gerald F.; Kukathas, Chandran (2004). Handbook of Political Theory. p. 422.
- Quinton, A. (1995). "Conservativism". In Goodin, R. E.; Pettit, P. eds. A Companion to Contemporary Political Philosophy. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 246.
- Richardson, p. 52. sfn error: no target: CITEREFRichardson (help)
- Richardson, James L. (2001). Contending Liberalisms in World Politics: Ideology and Power. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 43. ISBN 9781555879396.
- Vallentyne 2007, p. 1. "The best known form of libertarianism—right-libertarianism—is a version of classical liberalism ."
- Mayne, Alan James (1999). From Politics Past to Politics Future: An Integrated Analysis of Current and Emergent Paradigmss. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 124. ISBN 0-275-96151-6.
- ^ Freund, Charles Paul (1 April 2005). "You Know You're Neolibertarian If..." Reason. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- Franks, Dale (10 November 2012). "Bryan Pick's Suggestions for the GOP". QandO. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- Rockwell, Lew. "The Case for Paleo-libertarianism" (PDF). Liberty (January 1990): 34–38.
- Sanchez, Julian; Weigel, David. "Who Wrote Ron Paul's Newsletters?". Reason Foundation.
Rothbard pointed to David Duke and Joseph McCarthy as models for an "Outreach to the Rednecks," which would fashion a broad libertarian/paleoconservative coalition by targeting the disaffected working and middle classes
. - Lansford, Tom, ed. (2014). Political Handbook of the World 2014. CQ Press. p. 1157.
- Papierz, Magda (8 April 2015). "Korwin-Mikke: Potrzebujemy takich przywódców jak Margaret Thatcher!" [Korwin-Mikke: We need leaders such as Margaret Thatcher!]. Najwyższy Czas! (in Polish). Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- Graham-Harrison, Emma (8 November 2014). "Nigel Farage's new friend in Europe: 'When women say no, they don't always mean it'". The Guardian. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- Cain, Edward (1963). They'd Rather Be Right: Youth and the Conservative Movement. Macmillan. pp. 32–36. ASIN B0000CLYF9.
- Bader, Ralf M.; Meadowcroft, John (eds.). The Cambridge Companion to Nozick's Anarchy, State, and Utopia (2011). Cambridge University Press. p. 151.
- Doherty, Brian (2008). "Rothbard, Murray (1926–1995)". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, Caifornia: SAGE; Cato Institute. pp. 442–445. doi:10.4135/9781412965811.n271. ISBN 978-1-4129-6580-4. LCCN 2008009151. OCLC 750831024.
- Cain, Edward (1963). They'd Rather Be Right: Youth and the Conservative Movement. Macmillan. pp. 32–36. ASIN B0000CLYF9.
Bibliography
- Baradat, Leon P. (2015). Political Ideologies. Routledge. ISBN 978-1317345558.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Bogus, Carl T. (2011). Buckley: William F. Buckley Jr. and the Rise of American Conservatism. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 1-596-91580-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Caplan, Bryan (2008). "Friedman, David (1945–)". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications; Cato Institute. doi:10.4135/9781412965811.n117. ISBN 978-1412965804.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R. (ed.). The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America. London: SAGE Publications; Cato Institute. ISBN 1412988764.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - De Leon, David (1978). The American as Anarchist: Reflections on Indigenous Radicalism. Johns Hopkins University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Goodway, David (2006). Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. ISBN 978-1846310256.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Heywood, Andrew (2004). Political Theory, Third Edition: An Introduction. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0-333-96180-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kymlicka, Will (2005). "libertarianism, left-". In Honderich, Ted (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Philosophy (New ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0199264797.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Long, Roderick T.; Machan, Tibor R. (2008). Anarchism/Minarchism: Is a Government Part of a Free Country?. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-6066-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Miller, David (1987). The Blackwell Encyclopaedia of Political Thought. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-17944-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Morris, Andrew (2008). "Anarcho-Capitalism". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications; Cato Institute. ISBN 978-1-4129-6580-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Newman, Saul (2010). The Politics of Postanarchism'. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0748634958.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Vallentyne, Peter (2007). "Libertarianism and the State". Liberalism: Old and New: Volume 24. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521703055.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Stringham, Edward (2007). Anarchy And the Law: The Political Economy of Choice. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 978-1412805797.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Van de Haar, Edwin (2015). Degrees of Freedom: Liberal Political Philosophy and Ideology. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers. ISBN 1-412-85575-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Wündisch, Joachim (2014). Towards a Right-Libertarian Welfare State. ISBN 978-3-89785-844-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
| Neoliberalism | |
|---|---|
| Ideas |
|
| Economics | |
| Movements | |
| Governance |
|
| Organizations | |
| People | |
| Related topics | |
| Liberalism | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ideas |
| ||||||||||||
| Schools |
| ||||||||||||
| By region |
| ||||||||||||
| Philosophers |
| ||||||||||||
| Politicians |
| ||||||||||||
| Organisations |
| ||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
| Libertarianism | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origins | |||||||
| Schools |
| ||||||
| Concepts |
| ||||||
| Philosophers |
| ||||||
| Politicians | |||||||
| Issues | |||||||
| Works |
| ||||||
| Related |
| ||||||

