| Revision as of 12:55, 8 January 2009 edit62.103.27.224 (talk) →See also← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:28, 18 November 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,427,227 edits Added doi-access. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Jay8g | #UCB_toolbar | ||
| (656 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Collection of human autoimmune diseases}} | |||
| {{Prose|date=December 2008}}{{Refimprove|date=December 2008}} | |||
| {{Infobox medical condition (new) | |||
| '''Lupus erythematosus''' may manifest as a systemic disease or in purely cutaneous forms, categorized into the following types<ref name="Andrews">James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. Chapter 8. ISBN 0721629210.</ref>: | |||
| | name = Lupus erythematosus | |||
| | image = Lupus erythematosus, Atlas der Hautkrankheiten.jpg | |||
| | caption = | |||
| | field = ], ] | |||
| | symptoms = | |||
| | complications = | |||
| | onset = | |||
| | duration = | |||
| | types = | |||
| | causes = | |||
| | risks = | |||
| | diagnosis = | |||
| | differential = | |||
| | prevention = | |||
| | treatment = | |||
| | medication = | |||
| | prognosis = | |||
| | frequency = | |||
| | deaths = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Lupus erythematosus''' is a collection of ] in which the ] becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy ].<ref>{{cite book |author1=Fitzpatrick, Thomas B. |author2=Klauss Wolff |author3=Wolff, Klaus Dieter |author4=Johnson, Richard R. |author5=Suurmond, Dick |author6=Richard Suurmond |title=Fitzpatrick's color atlas and synopsis of clinical dermatology |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical Pub. Division |location=New York |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-07-144019-6 }}{{page needed|date=March 2015}}</ref> ] of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including ]s, ], ]s, ]s, ], and ]s. The most common and most severe form is ]. | |||
| *Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ***] | |||
| **] (Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus) | |||
| **] | |||
| **] (Hutchinson) | |||
| **] | |||
| **] (Lupus erythematosus profundus) | |||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| == Signs and symptoms == | |||
| Symptoms vary from person to person, and may come and go. Almost everyone with lupus has joint pain and ]. Some develop ]. Frequently affected ] are the fingers, hands, wrists, and knees.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Lupus - Symptoms and causes|url=https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lupus/symptoms-causes/syc-20365789|access-date=2022-02-12|website=Mayo Clinic|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Other common symptoms include: | |||
| * ] during ] | |||
| * ] (stiffness and swelling) | |||
| * painless ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * headaches | |||
| * ] with no other cause | |||
| * Skin lesions that appear worse after sun exposure | |||
| * general discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (]) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * sensitivity to sunlight | |||
| * a ], seen in about half of people with SLE | |||
| * swollen lymph nodes<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0024510/ |title=Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus, SLE) |publisher=National Library of Medicine |work=PubMed Health}}</ref> | |||
| === Photosensitivity === | |||
| '''ALTERNATIVE NAMES''' | |||
| ] is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons especially in visible light. Photosensitivity is a known symptom of lupus, but its relationship to and influence on other aspects of the disease remain to be defined.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1111/j.1600-0781.2004.00094.x |title=Photosensitivity in lupus erythematosus |journal=Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine |volume=20 |issue=5 |pages=272–9 |year=2004 |last1=Scheinfeld |first1=Noah |last2=Deleo |first2=Vincent A |pmid=15379880|s2cid=25740605 }}</ref> Causes of photosensitivity may include: | |||
| * change in ] location | |||
| * ] | |||
| * induction of ] with ] in ] | |||
| * ] of adhesion molecules and ] | |||
| * induction of ] expression | |||
| * ]-generated ] | |||
| == Genetics == | |||
| It is typically believed that lupus is influenced by multiple genes. Lupus is usually influenced by ]s, 30 of which have now been linked with the disorder. Some of these polymorphisms have been linked very tentatively, however, as the role that they play or the degree to which they influence the disease is unknown. Other genes that are commonly thought to be associated with lupus are those in the ] family. There have been several cases wherein a single gene influence appears to be present, but this is rare. When a single gene deficiency does cause lupus, it is usually attributed to the ] genes ''C1'', ''C2'', or ''C4''. The influence of sex chromosomes and environmental factors are also noteworthy. Usually, these factors contribute to lupus by influencing the immune system.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.7326/0003-4819-159-7-201310010-01004 |pmid=24081299 |title=Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |journal=Annals of Internal Medicine |volume=159 |issue=7 |pages=ITC4–1 |year=2013 |last1=Kiriakidou |first1=Marianthi |last2=Cotton |first2=D |last3=Taichman |first3=D |last4=Williams |first4=S |citeseerx=10.1.1.1008.5428 |s2cid=39068728 }}</ref> Several studies also indicate a potential association of lupus with mutations in DNA repair genes.<ref name="pmid28623091">{{cite journal |vauthors=Meas R, Burak MJ, Sweasy JB |title=DNA repair and systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=DNA Repair (Amst.) |volume=56 |pages=174–182 |date=August 2017 |pmid=28623091 |pmc=5543809 |doi=10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.06.020 }}</ref> | |||
| Disseminated lupus erythematosus; SLE; Lupus; Lupus erythematosus | |||
| === Age difference === | |||
| '''DEFINITION''' | |||
| Lupus can develop in people at any age, but it does most commonly at ages 15 to 44, with varying results. Typically, the manifestation of the disease tends to be more acute in those of younger age. Women are more likely to get it than men. Patients with juvenile-onset lupus are more vulnerable to mucocutaneous manifestations of the disease (alopecia, skin rash, and ulceration of the mucous membranes) than any other age group, and they are also more susceptible to evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Adrovic|first1=Amra|last2=Dedeoglu|first2=Reyhan|last3=Sahin|first3=Sezgin|last4=Barut|first4=Kenan|last5=Koka|first5=Aida|last6=Cengiz|first6=Dicle|last7=Oztunc|first7=Funda|last8=Kasapcopur|first8=Ozgur|date=2018-02-20|title=Evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure in patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus (jSLE)|journal=Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences|volume=18|issue=1|pages=66–71|doi=10.17305/bjbms.2017.2178|issn=1840-4812|pmc=5826676|pmid=28704174}}</ref> However, patients with late-onset lupus have a much higher mortality rate. Nearly 50% of those with late-onset lupus die of their condition. Women who are of childbearing age are also particularly at risk.<ref name="Feng, X, et. al">{{cite journal |doi=10.1177/0961203313513508 |pmid=24297642 |title=Associations of clinical features and prognosis with age at disease onset in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Lupus |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=327–34 |year=2013 |last1=Feng |first1=X. |last2=Zou |first2=Y. |last3=Pan |first3=W. |last4=Wang |first4=X. |last5=Wu |first5=M. |last6=Zhang |first6=M. |last7=Tao |first7=J. |last8=Zhang |first8=Y. |last9=Tan |first9=K. |last10=Li |first10=J. |last11=Chen |first11=Z. |last12=Ding |first12=X. |last13=Qian |first13=X. |last14=Da |first14=Z. |last15=Wang |first15=M. |last16=Sun |first16=L. |s2cid=11694732 }}</ref> | |||
| === Differences in ethnicity === | |||
| Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder. It may affect the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs. | |||
| Substantial data have been found to indicate that certain ethnic populations could be more at risk for lupus erythematosus and to have a better or worse prognosis. Asian, African, and Native Americans are more likely to get lupus than Caucasians. Caucasians seem generally to have a milder manifestation of the disease. Their survival rates after five years were typically around 94–96%, while patients of African and some Asian ethnicities had survival rates closer to 79–92%. The only documented ethnic group that had a higher survival rate than Caucasians was Koreans, who had survival rates nearer to 98%. Among Caucasians, the most common causes of death were complications involving the cardiovascular system, the respiratory system, and malignancies.<ref name="Voss et. al">{{cite journal |doi=10.1177/0961203313498796 |pmid=23873432 |title=Survival in systemic lupus erythematosus, 1995–2010. A prospective study in a Danish community |journal=Lupus |volume=22 |issue=11 |pages=1185–91 |year=2013 |last1=Voss |first1=A. |last2=Laustrup |first2=H. |last3=Hjelmborg |first3=J. |last4=Junker |first4=P. |s2cid=46247629 }}</ref><ref>"Lupus Facts, Symptoms, Rash, Effects, Complications, and More." ''WebMD'', n.d. Web. 6 October 2014. http://www.webmd.com/lupus/arthritis-lupus.</ref> Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is more prevalent in African Americans with lupus than in Caucasians with lupus.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1038/srep20303 |pmid=26842423 |pmc=4740809 |title=The Prevalence of Atherosclerosis in Those with Inflammatory Connective Tissue Disease by Race, Age, and Traditional Risk Factors |journal=Scientific Reports |volume=6 |pages=20303 |year=2016 |last1=Alenghat |first1=Francis J |bibcode=2016NatSR...620303A }}</ref> | |||
| == Diagnosis == | |||
| '''CAUSES''' | |||
| Diagnosis of lupus will vary from person to person. It is common to be diagnosed with other illnesses before a doctor can finally give a diagnosis of lupus because a lot of the symptoms overlap with other common illness.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Lupus - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic |url=https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lupus/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20365790 |access-date=2022-04-20 |website=www.mayoclinic.org |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Diagnosis of lupus erythematosus requires a ], blood and urine tests, and a skin or kidney biopsy. Some other tests that may need to be run include:<ref name="cdc.gov">{{Cite web|date=2018-10-18|title=Diagnosing and Treating Lupus {{!}} CDC|url=https://www.cdc.gov/lupus/basics/diagnosing.htm|access-date=2022-02-12|website=www.cdc.gov|language=en-us}}</ref> | |||
| SLE (lupus) is an autoimmune disease. This means there is a problem with the body's normal immune system response. Normally, the immune system helps protect the body from harmful substances. But in patients with an autoimmune disease, the immune system can't tell the difference between harmful substances and healthy ones. The result is an overactive immune response that attacks otherwise healthy cells and tissue. This leads to chronic (long-term) inflammation. | |||
| * ] (ANA) | |||
| * ] with differential | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]<ref name="NIH">{{cite web|title=Systemic lupus erythematosus: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia|url=https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000435.htm|website=Medline Plus|publisher=US National Library of Medicine|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Classification === | |||
| The underlying cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully known. Some researchers think autoimmune diseases occur after infection with an organism that looks like certain proteins in the body. The proteins are later mistaken for the organism and wrongly targeted for attack by the body's immune system. | |||
| Lupus erythematosus may manifest as ] or in a purely ] form also known as ''incomplete lupus erythematosus''. Lupus has four main types:{{citation needed|date=December 2020}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| Of these, ] (also known as SLE) is the most common and serious form. | |||
| A more thorough categorization of lupus includes the following types:<ref name="pmid35964089">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lee WF, Fan WL, Tseng MH, Yang HY, Huang JL, Wu CY | title = Characteristics and genetic analysis of patients suspected with early-onset systemic lupus erythematosus | journal = Pediatric Rheumatology Online Journal | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 68 | date = August 2022 | pmid = 35964089 | pmc = 9375402 | doi = 10.1186/s12969-022-00722-6 | doi-access = free | url = }}</ref><ref name="Andrews">James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Disease of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. Chapter 8. {{ISBN|0-7216-2921-0}}.{{page needed|date=March 2015}}</ref><ref name="Bolognia">{{cite book|author1=Rapini, Ronald P.|title=Dermatology: 2-Volume Set|author2=Bolognia, Jean L.|author3=Jorizzo, Joseph L.|publisher=Mosby|year=2007|isbn=978-1-4160-2999-1|location=St. Louis}}{{page needed|date=March 2015}}</ref> | |||
| SLE may be mild or severe enough to cause death. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (chronic cutaneous) | |||
| *** childhood discoid lupus erythematosus | |||
| *** generalized discoid lupus erythematosus | |||
| *** localized discoid lupus erythematosus | |||
| ** ] (Hutchinson) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] (lupus erythematosus profundus) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] (] lupus erythematosus) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Treatment == | |||
| SLE affects nine times as many women as men. It may occur at any age, but appears most often in people between the ages of 10 and 50 years. African Americans and Asians are affected more often than people from other races. | |||
| There is still no cure for lupus but there are options to help control symptoms. The goal for treatment is to prevent flare ups and reduce organ damage. Doctors may prescribe a handful of different medications to help with their patients' symptoms.<ref name="cdc.gov"/> | |||
| Some medications are: | |||
| SLE may also be caused by certain drugs: | |||
| * Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). | |||
| * Chlorpromazine | |||
| * Corticosteroids | |||
| * Hydralazine | |||
| * Antimalarial drugs | |||
| * Isoniazid | |||
| * BLyS-specific inhibitors | |||
| * Methyldopa | |||
| * Immunosuppressive agents/chemotherapy | |||
| * Penicillamine | |||
| * Procainamide | |||
| * Quinidine | |||
| * Sulfasalazine | |||
| After being diagnosed some treatment options that may be offered are: | |||
| {{see also|Systemic lupus erythematosus#Treatment}} | |||
| Treatment consists primarily of immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids). A second-line drug is ] in its low-dose schedule.<ref name="pmid15194170">{{cite journal|vauthors=Böhm I|year=2004|title=Increased peripheral blood B-cells expressing the CD5 molecules in association to autoantibodies in patients with lupus erythematosus and evidence to selectively down-modulate them|journal=Biomed Pharmacother|volume=58|issue=5|pages=338–43|doi=10.1016/j.biopha.2004.04.010|pmid=15194170}}</ref><ref name="pmid9782534 ">{{cite journal |vauthors=Boehm IB, Boehm GA, Bauer R |title=Management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus with low-dose methotrexate: indication for modulation of inflammatory mechanisms |journal=Rheumatol Int |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=59–62 |year=1998 |pmid=9782534 |doi=10.1515/cclm.1993.31.10.667|s2cid=25311594 |url=http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/18452/13106 }}</ref> In 2011, the U.S. ] (FDA) approved the first new drug for lupus in more than 50 years to be used in the US, ].<ref name="CDC" /> In addition to medical therapy, ] has also been demonstrated to be effective in reducing stress, anxiety, and depression due to the psychological and social impacts that lupus may have.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Greco|first1=Carol M|last2=Rudy|first2=Thomas E|last3=Manzi|first3=Susan|year=2004|title=Effects of a stress-reduction program on psychological function, pain, and physical function of systemic lupus erythematosus patients: A randomized controlled trial|journal=Arthritis Care & Research|volume=51|issue=4|pages=625–34|doi=10.1002/art.20533|pmid=15334437|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| People with SLE treated with standard care experience a higher risk of opportunistic infections and death than the general population. This risk is higher in men and in African Americans.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Dospinescu|first1=Paula|last2=Shamliyan|first2=Tatyana A.|date=2017-07-01|title=Additional Improvements in Clinical Response From Adjuvant Biologic Response Modifiers in Adults With Moderate to Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Despite Immunosuppressive Agents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis|url=https://www.clinicaltherapeutics.com/article/S0149-2918(17)30707-5/abstract|journal=Clinical Therapeutics|language=en|volume=39|issue=7|pages=1479–1506.e45|doi=10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.05.359|issn=0149-2918|pmid=28673504}}</ref> | |||
| '''SYMPTOMS''' | |||
| == Epidemiology == | |||
| Symptoms vary from person to person, and may come and go. The condition may affect one organ or body system at first. Others may become involved later. Almost all people with SLE have joint pain and most develop arthritis. Frequently affected joints are the fingers, hands, wrists, and knees. | |||
| === Worldwide === | |||
| * An estimated 5 million people worldwide have some form of lupus disease.<ref name=LupusFoundationofAmerica>{{cite web|url=http://www.lupus.org/webmodules/webarticlesnet/templates/new_newsroomreporters.aspx?articleid%3D247%26zoneid%3D60 |access-date=August 24, 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130629233204/http://www.lupus.org/webmodules/webarticlesnet/templates/new_newsroomreporters.aspx?articleid=247&zoneid=60 |archive-date=June 29, 2013 |title=Media Relations }}</ref> | |||
| * 70% of lupus cases diagnosed are ].<ref name=LupusFoundationofAmerica /> | |||
| * 20% of people with lupus will have a parent or sibling who already has lupus or may develop lupus.<ref name=LupusFoundationofAmerica /> | |||
| * about 5% of the children born to individuals with lupus will develop the illness.<ref name=LupusFoundationofAmerica /> | |||
| === United Kingdom === | |||
| Inflammation of various parts of the heart may occur as pericarditis, endocarditis, or myocarditis. Chest pain and arrhythmias may result from these conditions. | |||
| * Females in the UK are seven times more likely to be diagnosed with SLE than males.<ref name=ArthritisUK>{{cite web|title= Lupus | publisher= Arthritis Research UK |url=http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/data-and-statistics/lupus.aspx |access-date=August 24, 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140201214415/http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/data-and-statistics/lupus.aspx |archive-date=February 1, 2014 }}</ref> | |||
| * The estimated number of females in the UK with SLE is 21,700, and the number of males is 3000 — a total of 24,700, or 0.041% of the population.<ref name=ArthritisUK /> | |||
| * SLE is more common amongst certain ethnic groups than others, especially those of African origin.<ref name=ArthritisUK /> | |||
| === United States === | |||
| General symptoms include: | |||
| * Lupus occurs from infancy to old age, with peak occurrence between ages 15 and 40.<ref name=CDC>{{cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/lupus.htm|title=Lupus - Arthritis|publisher=CDC|date=2018-10-18}}</ref> | |||
| * Lupus affects females in the US 6 to 10 times more often than males.<ref name=CDC /> | |||
| * Prevalence data are limited. Estimates vary and range from 1.8 to 7.6 cases per 100,000 persons per year in parts of the continental United States.<ref name=CDC /> | |||
| == In popular culture == | |||
| * Fever | |||
| {{inpopularculture|date=February 2024}} | |||
| * Fatigue | |||
| * In the early seasons of the television show '']'', members of the eponymous character's medical team often suggested lupus as a diagnosis for their patients, only to be rebuked. The rarity of legitimate lupus diagnoses in the show eventually became described as a running gag.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Kandell |first1=Zachary |title=House MD: Why It's Never Lupus (And the One Time It Was) |url=https://screenrant.com/house-never-lupus-diagnosis-episode-flynn/ |website=ScreenRant |access-date=29 April 2022 |date=10 April 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Vincent |first1=Fabien B. |last2=Mackay |first2=Fabienne |title=Why 'It's never lupus' - television, illness and the making of a meme |url=https://theconversation.com/why-its-never-lupus-television-illness-and-the-making-of-a-meme-1198 |website=The Conversation |date=30 June 2011 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| * General discomfort, uneasiness or ill feeling (malaise) | |||
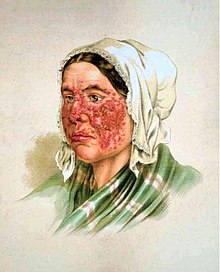
| * Skin rash -- a "butterfly" rash over the cheeks and bridge of the nose affects about half of those with SLE. The rash gets worse when in sunlight. The rash may also be widespread. | |||
| * Sensitivity to sunlight | |||
| * Joint pain and swelling | |||
| * Arthritis | |||
| * Swollen glands | |||
| * Muscle aches | |||
| * Nausea and vomiting | |||
| * Pleurisy (causes chest pain) | |||
| * Pleural effusions | |||
| * Seizures | |||
| * Psychosis | |||
| == See also == | |||
| Additional symptoms that may be associated with this disease: | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | |||
| * Blood in the urine | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| * Coughing up blood | |||
| * Nosebleed | |||
| * Swallowing difficulty | |||
| * Skin color is patchy | |||
| * Red spots on skin | |||
| * Fingers that change color upon pressure or in the cold | |||
| * Numbness and tingling | |||
| * Mouth sores | |||
| * Hair loss | |||
| * Abdominal pain | |||
| * Visual disturbance | |||
| * Blood disorders, including blood clots | |||
| == External links == | |||
| '''EXAMS and TESTS''' | |||
| {{Medical resources | |||
| | DiseasesDB = | |||
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|L|93||l|80}} (] L93.010) | |||
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|695.4}} | |||
| | ICDO = | |||
| | OMIM = | |||
| | MedlinePlus = | |||
| | eMedicineSubj = | |||
| | eMedicineTopic = | |||
| | MeshID = | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Localized connective tissue diseases}} | |||
| The diagnosis of SLE is based upon the presence of at least four out of eleven typical characteristics of the disease. The doctor will listen to your chest with a stethoscope. A sound called a heart friction rub or pleural friction rub may be heard. A neurological exam will also be performed. | |||
| {{Urticaria and erythema}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| Tests used to diagnose SLE may include: | |||
| * Antinuclear antibody (ANA) panel including anti-DNA and anti-Smith antibodies | |||
| * Chest x-ray showing pleuritis or pericarditis | |||
| * Urinalysis to show blood, casts, or protein in the urine | |||
| * CBC | |||
| * Kidney biopsy | |||
| This disease may also alter the results of the following tests: | |||
| * WBC count | |||
| * Serum globulin electrophoresis | |||
| * Rheumatoid factor | |||
| * Urine protein | |||
| * Serum protein electrophoresis | |||
| * Mononucleosis spot test | |||
| * ESR | |||
| * Cryoglobulins | |||
| * Coombs' test - direct | |||
| * Complement component 3 (C3) | |||
| * Complement | |||
| * Anti-thyroid microsomal antibody | |||
| * Anti-thyroglobulin antibody | |||
| * Anti-mitochondrial antibody | |||
| * Anti-smooth muscle antibody | |||
| '''TREATMENT''' | |||
| There is no cure for SLE. Treatment is aimed at controlling symptoms. Your individual symptoms determine your treatment. | |||
| Mild disease that involves a rash, headaches, fever, arthritis, pleurisy, and pericarditis requires little therapy. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are used to treat arthritis and pleurisy. Corticosteroid creams are used to treat skin rashes. An anti-malaria drug called hydroxychloroquine) and low dose corticosteroids are sometimes used for skin and arthritis symptoms. | |||
| You should wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen when in the sun. | |||
| Severe or life-threatening symptoms (such as hemolytic anemia, extensive heart or lung involvement, kidney disease, or central nervous system involvement) often require treatment by a rheumatologist and other specialists in the specific area. Corticosteroids or medications to decrease the immune system response may be prescribed to control the various symptoms. Some health care professionals use cytotoxic drugs (drugs that block cell growth) to treat people who do not respond well to corticosteroids or who must use high doses of corticosteroids. | |||
| '''OUTLOOK (PROGNOSIS)''' | |||
| The outcome for people with SLE has improved over recent years. Many of those with SLE have mild illness. Women with SLE who become pregnant are often able to carry the pregnancy safely to term and deliver normal infants, as long as there is no severe kidney or heart disease present and the SLE is being treated appropriately. | |||
| The presence of anti-phospholipid antibodies may increase the possibility of pregnancy loss. | |||
| The 10-year survival rate for lupus patients is greater than 85%. People with severe involvement of the brain, lungs, heart, and kidney do worse than others in terms of overall survival and disability. | |||
| Possible Complications | |||
| Some people with SLE have deposits of antibodies within the cells (glomeruli) of the kidneys. This leads to a condition called lupus nephritis. Patients with this condition may eventually develop kidney failure and require dialysis or kidney transplantation. | |||
| Other complications include: | |||
| * Infection | |||
| * Thrombocytopenia | |||
| * Hemolytic anemia | |||
| * Myocarditis | |||
| * Seizures | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{Dermatology-stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 18 November 2024
Collection of human autoimmune diseases Medical condition| Lupus erythematosus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology, immunology |
Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. The most common and most severe form is systemic lupus erythematosus.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms vary from person to person, and may come and go. Almost everyone with lupus has joint pain and swelling. Some develop arthritis. Frequently affected joints are the fingers, hands, wrists, and knees. Other common symptoms include:
- chest pain during respiration
- joint pain (stiffness and swelling)
- painless oral ulcer
- fatigue
- weight loss
- headaches
- fever with no other cause
- Skin lesions that appear worse after sun exposure
- general discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise)
- hair loss
- sensitivity to sunlight
- a "butterfly" facial rash, seen in about half of people with SLE
- swollen lymph nodes
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons especially in visible light. Photosensitivity is a known symptom of lupus, but its relationship to and influence on other aspects of the disease remain to be defined. Causes of photosensitivity may include:
- change in autoantibody location
- cytotoxicity
- induction of apoptosis with autoantigens in apoptotic blebs
- upregulation of adhesion molecules and cytokines
- induction of nitric oxide synthase expression
- ultraviolet-generated antigenic DNA
Genetics
It is typically believed that lupus is influenced by multiple genes. Lupus is usually influenced by gene polymorphisms, 30 of which have now been linked with the disorder. Some of these polymorphisms have been linked very tentatively, however, as the role that they play or the degree to which they influence the disease is unknown. Other genes that are commonly thought to be associated with lupus are those in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) family. There have been several cases wherein a single gene influence appears to be present, but this is rare. When a single gene deficiency does cause lupus, it is usually attributed to the complement protein genes C1, C2, or C4. The influence of sex chromosomes and environmental factors are also noteworthy. Usually, these factors contribute to lupus by influencing the immune system. Several studies also indicate a potential association of lupus with mutations in DNA repair genes.
Age difference
Lupus can develop in people at any age, but it does most commonly at ages 15 to 44, with varying results. Typically, the manifestation of the disease tends to be more acute in those of younger age. Women are more likely to get it than men. Patients with juvenile-onset lupus are more vulnerable to mucocutaneous manifestations of the disease (alopecia, skin rash, and ulceration of the mucous membranes) than any other age group, and they are also more susceptible to evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure. However, patients with late-onset lupus have a much higher mortality rate. Nearly 50% of those with late-onset lupus die of their condition. Women who are of childbearing age are also particularly at risk.
Differences in ethnicity
Substantial data have been found to indicate that certain ethnic populations could be more at risk for lupus erythematosus and to have a better or worse prognosis. Asian, African, and Native Americans are more likely to get lupus than Caucasians. Caucasians seem generally to have a milder manifestation of the disease. Their survival rates after five years were typically around 94–96%, while patients of African and some Asian ethnicities had survival rates closer to 79–92%. The only documented ethnic group that had a higher survival rate than Caucasians was Koreans, who had survival rates nearer to 98%. Among Caucasians, the most common causes of death were complications involving the cardiovascular system, the respiratory system, and malignancies. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is more prevalent in African Americans with lupus than in Caucasians with lupus.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lupus will vary from person to person. It is common to be diagnosed with other illnesses before a doctor can finally give a diagnosis of lupus because a lot of the symptoms overlap with other common illness.
Diagnosis of lupus erythematosus requires a physical examination, blood and urine tests, and a skin or kidney biopsy. Some other tests that may need to be run include:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA)
- CBC with differential
- Chest X-ray
- Serum creatinine
- Urinalysis
Classification
Lupus erythematosus may manifest as systemic disease or in a purely cutaneous form also known as incomplete lupus erythematosus. Lupus has four main types:
Of these, systemic lupus erythematosus (also known as SLE) is the most common and serious form.
A more thorough categorization of lupus includes the following types:
- Childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
- acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- discoid lupus erythematosus (chronic cutaneous)
- childhood discoid lupus erythematosus
- generalized discoid lupus erythematosus
- localized discoid lupus erythematosus
- chilblain lupus erythematosus (Hutchinson)
- lupus erythematosus-lichen planus overlap syndrome
- lupus erythematosus panniculitis (lupus erythematosus profundus)
- tumid lupus erythematosus
- verrucous lupus erythematosus (hypertrophic lupus erythematosus)
- cutaneous lupus mucinosis
- complement deficiency syndromes
- drug-induced lupus erythematosus
- neonatal lupus erythematosus
- systemic lupus erythematosus
Treatment
There is still no cure for lupus but there are options to help control symptoms. The goal for treatment is to prevent flare ups and reduce organ damage. Doctors may prescribe a handful of different medications to help with their patients' symptoms.
Some medications are:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Corticosteroids
- Antimalarial drugs
- BLyS-specific inhibitors
- Immunosuppressive agents/chemotherapy
After being diagnosed some treatment options that may be offered are:
See also: Systemic lupus erythematosus § TreatmentTreatment consists primarily of immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids). A second-line drug is methotrexate in its low-dose schedule. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first new drug for lupus in more than 50 years to be used in the US, belimumab. In addition to medical therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy has also been demonstrated to be effective in reducing stress, anxiety, and depression due to the psychological and social impacts that lupus may have.
People with SLE treated with standard care experience a higher risk of opportunistic infections and death than the general population. This risk is higher in men and in African Americans.
Epidemiology
Worldwide
- An estimated 5 million people worldwide have some form of lupus disease.
- 70% of lupus cases diagnosed are systemic lupus erythematosus.
- 20% of people with lupus will have a parent or sibling who already has lupus or may develop lupus.
- about 5% of the children born to individuals with lupus will develop the illness.
United Kingdom
- Females in the UK are seven times more likely to be diagnosed with SLE than males.
- The estimated number of females in the UK with SLE is 21,700, and the number of males is 3000 — a total of 24,700, or 0.041% of the population.
- SLE is more common amongst certain ethnic groups than others, especially those of African origin.
United States
- Lupus occurs from infancy to old age, with peak occurrence between ages 15 and 40.
- Lupus affects females in the US 6 to 10 times more often than males.
- Prevalence data are limited. Estimates vary and range from 1.8 to 7.6 cases per 100,000 persons per year in parts of the continental United States.
In popular culture
| This article may contain irrelevant references to popular culture. Please help Misplaced Pages to improve this article by removing the content or adding citations to reliable and independent sources. (February 2024) |
- In the early seasons of the television show House, members of the eponymous character's medical team often suggested lupus as a diagnosis for their patients, only to be rebuked. The rarity of legitimate lupus diagnoses in the show eventually became described as a running gag.
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
- List of target antigens in pemphigoid
- List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous conditions
- List of human leukocyte antigen alleles associated with cutaneous conditions
- List of people with lupus
References
- Fitzpatrick, Thomas B.; Klauss Wolff; Wolff, Klaus Dieter; Johnson, Richard R.; Suurmond, Dick; Richard Suurmond (2005). Fitzpatrick's color atlas and synopsis of clinical dermatology. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical Pub. Division. ISBN 978-0-07-144019-6.
- "Lupus - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2022-02-12.
- "Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus, SLE)". PubMed Health. National Library of Medicine.
- Scheinfeld, Noah; Deleo, Vincent A (2004). "Photosensitivity in lupus erythematosus". Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine. 20 (5): 272–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0781.2004.00094.x. PMID 15379880. S2CID 25740605.
- Kiriakidou, Marianthi; Cotton, D; Taichman, D; Williams, S (2013). "Systemic Lupus Erythematosus". Annals of Internal Medicine. 159 (7): ITC4–1. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1008.5428. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-159-7-201310010-01004. PMID 24081299. S2CID 39068728.
- Meas R, Burak MJ, Sweasy JB (August 2017). "DNA repair and systemic lupus erythematosus". DNA Repair (Amst.). 56: 174–182. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.06.020. PMC 5543809. PMID 28623091.
- Adrovic, Amra; Dedeoglu, Reyhan; Sahin, Sezgin; Barut, Kenan; Koka, Aida; Cengiz, Dicle; Oztunc, Funda; Kasapcopur, Ozgur (2018-02-20). "Evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure in patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus (jSLE)". Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences. 18 (1): 66–71. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2017.2178. ISSN 1840-4812. PMC 5826676. PMID 28704174.
- Feng, X.; Zou, Y.; Pan, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, K.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Ding, X.; Qian, X.; Da, Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, L. (2013). "Associations of clinical features and prognosis with age at disease onset in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus". Lupus. 23 (3): 327–34. doi:10.1177/0961203313513508. PMID 24297642. S2CID 11694732.
- Voss, A.; Laustrup, H.; Hjelmborg, J.; Junker, P. (2013). "Survival in systemic lupus erythematosus, 1995–2010. A prospective study in a Danish community". Lupus. 22 (11): 1185–91. doi:10.1177/0961203313498796. PMID 23873432. S2CID 46247629.
- "Lupus Facts, Symptoms, Rash, Effects, Complications, and More." WebMD, n.d. Web. 6 October 2014. http://www.webmd.com/lupus/arthritis-lupus.
- Alenghat, Francis J (2016). "The Prevalence of Atherosclerosis in Those with Inflammatory Connective Tissue Disease by Race, Age, and Traditional Risk Factors". Scientific Reports. 6: 20303. Bibcode:2016NatSR...620303A. doi:10.1038/srep20303. PMC 4740809. PMID 26842423.
- "Lupus - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Retrieved 2022-04-20.
- ^ "Diagnosing and Treating Lupus | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 2018-10-18. Retrieved 2022-02-12.
- "Systemic lupus erythematosus: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". Medline Plus. US National Library of Medicine.
- Lee WF, Fan WL, Tseng MH, Yang HY, Huang JL, Wu CY (August 2022). "Characteristics and genetic analysis of patients suspected with early-onset systemic lupus erythematosus". Pediatric Rheumatology Online Journal. 20 (1): 68. doi:10.1186/s12969-022-00722-6. PMC 9375402. PMID 35964089.
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Disease of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. Chapter 8. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- Böhm I (2004). "Increased peripheral blood B-cells expressing the CD5 molecules in association to autoantibodies in patients with lupus erythematosus and evidence to selectively down-modulate them". Biomed Pharmacother. 58 (5): 338–43. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2004.04.010. PMID 15194170.
- Boehm IB, Boehm GA, Bauer R (1998). "Management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus with low-dose methotrexate: indication for modulation of inflammatory mechanisms". Rheumatol Int. 18 (2): 59–62. doi:10.1515/cclm.1993.31.10.667. PMID 9782534. S2CID 25311594.
- ^ "Lupus - Arthritis". CDC. 2018-10-18.
- Greco, Carol M; Rudy, Thomas E; Manzi, Susan (2004). "Effects of a stress-reduction program on psychological function, pain, and physical function of systemic lupus erythematosus patients: A randomized controlled trial". Arthritis Care & Research. 51 (4): 625–34. doi:10.1002/art.20533. PMID 15334437.
- Dospinescu, Paula; Shamliyan, Tatyana A. (2017-07-01). "Additional Improvements in Clinical Response From Adjuvant Biologic Response Modifiers in Adults With Moderate to Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Despite Immunosuppressive Agents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Clinical Therapeutics. 39 (7): 1479–1506.e45. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.05.359. ISSN 0149-2918. PMID 28673504.
- ^ "Media Relations". Archived from the original on June 29, 2013. Retrieved August 24, 2013.
- ^ "Lupus". Arthritis Research UK. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved August 24, 2013.
- Kandell, Zachary (10 April 2020). "House MD: Why It's Never Lupus (And the One Time It Was)". ScreenRant. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- Vincent, Fabien B.; Mackay, Fabienne (30 June 2011). "Why 'It's never lupus' - television, illness and the making of a meme". The Conversation.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
| Urticaria and erythema | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urticaria (acute/chronic) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Erythema |
| ||||||||||||||