| Revision as of 09:16, 29 August 2009 editSmackBot (talk | contribs)3,734,324 editsm Date maintenance tags and general fixes← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 01:47, 19 October 2024 edit undo23.233.149.88 (talk) →Relative motion between the Earth and aether | ||
| (613 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Obsolete postulated medium for the propagation of light}} | |||
| {{Refimprove|article|date=March 2009|talk=y}} | |||
| ] | |||
| '''Luminiferous aether''' or '''ether'''<ref>See {{cite web |title=Google Scholar 'luminiferous ether' |url=https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q={{urlencode:"luminiferous ether"}}}}</ref> (''luminiferous'' meaning 'light-bearing') was the postulated ] for the propagation of ].<ref>The 19th century science book '']'' provides a brief summary of scientific thinking in this field at the time.</ref> It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently ]-based light to propagate through empty space (a ]), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum (space completely filled with matter) of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. | |||
| The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 19th century, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. | |||
| ] | |||
| In the late 19th century, "'''luminiferous aether'''" (or "'''ether'''"), meaning light-bearing ], was the term used to describe a medium for the propagation of ].<ref>The 19th century science book ] provides a brief summary of scientific thinking in this field at the time.</ref> The word ''aether'' stems via ] from the ] αιθήρ, from a root meaning to kindle, burn, or shine. It signifies the substance which was thought in ancient times to contain the manipulative forces beyond control.{{Citation needed|date=August 2009}} | |||
| The negative outcome of the ] (1887) suggested that the aether did not exist, a finding that was confirmed in subsequent experiments through the 1920s. This led to considerable theoretical work to explain the propagation of light without an aether. A major breakthrough was the ], which could explain why the experiment failed to see aether, but was more broadly interpreted to suggest that it was not needed. The Michelson–Morley experiment, along with the ] and ], was a key experiment in the development of ], which includes both relativity and ], the latter of which explains the particle-like nature of light. | |||
| Later theories including ] were formulated without the concept of aether. Today the idea of aether, what ] called "one of the grandest generalizations of modern science", is regarded as a ]. | |||
| ==The history of light and aether== | ==The history of light and aether== | ||
| {{See also|Timeline of luminiferous aether}} | {{See also|Timeline of luminiferous aether}} | ||
| ===Particles vs. waves=== | |||
| ] contended that light was made up of numerous small particles. This could explain such features as light's ability to travel in straight lines and reflect off surfaces. This theory was known to have its problems: although it explained reflection well, its explanation of ] and ] was less satisfactory. In order to explain refraction, Newton's '']'' (1704) postulated an "Aethereal Medium" transmitting vibrations ''faster'' than light, by which light, when overtaken, is put into "Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission", which caused refraction and diffraction. Newton believed that these vibrations were related to heat radiation: | |||
| {{main|Wave–particle duality}} | |||
| In the 17th century, ] was a proponent of an aether hypothesis. According to Boyle, the aether consists of subtle particles, one sort of which explains the absence of vacuum and the mechanical interactions between bodies, and the other sort of which explains phenomena such as magnetism (and possibly gravity) that are, otherwise, inexplicable on the basis of purely mechanical interactions of macroscopic bodies, "though in the ether of the ancients there was nothing taken notice of but a diffused and very subtle substance; yet we are at present content to allow that there is always in the air a swarm of streams moving in a determinate course between the north pole and the south".<ref>Robert Boyle, ''The Works of the Honourable Robert Boyle'', ed. Thomas Birch, 2nd edn., 6 vols. (London, 1772), III, 316; quoted in E. A. Burtt, ''The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science'' (Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company, 1954), 191–192.</ref> | |||
| ]'s '']'' (1690) hypothesized that light is a wave propagating through an aether. He and ] could only envision light waves as being ], propagating like sound and other ]s in ]s. However, longitudinal waves necessarily have only one form for a given propagation direction, rather than two ]s like a ]. Thus, longitudinal waves can not explain ], in which two polarizations of light are refracted differently by a crystal. In addition, Newton rejected light as waves in a medium because such a medium would have to extend everywhere in space, and would thereby "disturb and retard the Motions of those great Bodies" (the planets and comets) and thus "as it {{bracket|light's medium}} is of no use, and hinders the Operation of Nature, and makes her languish, so there is no evidence for its Existence, and therefore it ought to be rejected".<ref>{{cite book |title=The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science |author1=Edwin Arthur Burtt |edition=illustrated, unabridged, reprinted |publisher=Courier Corporation |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-486-42551-1 |page=270 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=G9WBMa1Rz_kC}} </ref> | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| Is not the Heat of the warm Room convey'd through the vacuum by the Vibrations of a much subtiler Medium than Air, which after the Air was drawn out remained in the Vacuum? And is not this Medium the same with that Medium by which Light is refracted and reflected, and by whose Vibrations Light communicates Heat to Bodies, and is put into Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission?<ref>'''', Bk III, Part I, Qu 18, p.323.</ref> | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| Isaac Newton contended that light is made up of numerous small particles. This can explain such features as light's ability to travel in straight lines and ] off surfaces. Newton imagined light particles as non-spherical "corpuscles", with different "sides" that give rise to birefringence. But the particle theory of light can not satisfactorily explain ] and ].<ref>{{cite book |title=Experimental Mechanics of Solids |author1=Cesar A. Sciammarella |author2=Federico M. Sciammarella |edition= |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-119-97009-5 |page=146 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aVP6tpNXAf4C}} </ref> To explain refraction, Newton's Third Book of '']'' (1st ed. 1704, 4th ed. 1730) postulated an "aethereal medium" transmitting vibrations faster than light, by which light, when overtaken, is put into "Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission", which caused refraction and diffraction. Newton believed that these vibrations were related to heat radiation: | |||
| The modern understanding is that heat radiation ''is'', like light, electromagnetic radiation. However, Newton considered them to be two different phenomena. He believed heat vibrations to be excited "when a Ray of Light falls upon the Surface of any pellucid Body". He wrote, "I do not know what this Aether is", but that if it consists of particles then they must be "exceedingly smaller than those of Air, or even than those of Light: The exceeding smallness of its Particles may contribute to the greatness of the force by which those Particles may recede from one another, and thereby make that Medium exceedingly more rare and elastick than Air, and by consequence exceedingly less able to resist the motions of Projectiles, and exceedingly more able to press upon gross Bodies, by endeavoring to expand itself." | |||
| <blockquote>Is not the Heat of the warm Room convey'd through the vacuum by the Vibrations of a much subtiler Medium than Air, which after the Air was drawn out remained in the Vacuum? And is not this Medium the same with that Medium by which Light is refracted and reflected, and by whose Vibrations Light communicates Heat to Bodies, and is put into Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission?<ref group=A name=newton />{{rp|349}}</blockquote> | |||
| ], prior to Newton, had hypothesized that light was a wave propagating through an aether, but Newton rejected this idea. The main reason for his rejection stemmed from the fact that both men could apparently only envision light to be a longitudinal wave, like sound and other ]s in ]s. However, longitudinal waves by necessity have only one form for a given propagation direction, rather than two ]s as in a transverse wave, and thus they were unable to explain the phenomenon of ], where two polarizations of light are refracted differently by a crystal. Instead, Newton preferred to imagine non-spherical particles, or "corpuscles", of light with different "sides" that give rise to birefringence. A further reason why Newton rejected light as waves in a medium was because such a medium would have to extend everywhere in space, and would thereby "disturb and retard the Motions of those great Bodies" (the planets and comets) and thus "as it <nowiki></nowiki> is of no use, and hinders the Operation of Nature, and makes her languish, so there is no evidence for its Existence, and therefore it ought to be rejected." | |||
| In contrast to the modern understanding that heat radiation and light are both ], Newton viewed heat and light as two different phenomena. He believed heat vibrations to be excited "when a Ray of Light falls upon the Surface of any pellucid Body".<ref group=A name=newton />{{rp|348}} He wrote, "I do not know what this Aether is", but that if it consists of particles then they must be <blockquote>exceedingly smaller than those of Air, or even than those of Light: The exceeding smallness of its Particles may contribute to the greatness of the force by which those Particles may recede from one another, and thereby make that Medium exceedingly more rare and elastic than Air, and by consequence exceedingly less able to resist the motions of Projectiles, and exceedingly more able to press upon gross Bodies, by endeavoring to expand itself.<ref group=A name=newton />{{rp|352}}</blockquote> | |||
| In 1720 ] carried out a series of experiments attempting to measure ]. Although he failed to detect any parallax, thereby placing a lower limit on the distance to stars, he discovered another effect, ], an effect which depends not on position (as in parallax), but on speed. He noticed that the apparent position of the star changed as the Earth moved around its orbit. Bradley explained this effect in the context of Newton's corpuscular theory of light, by showing that the aberration angle was given by simple vector addition of the Earth's orbital velocity and the velocity of the corpuscles of light, just as vertically falling raindrops strike a moving object at an angle. Knowing the Earth's velocity and the aberration angle, this enabled him to estimate the speed of light. To explain stellar aberration in the context of an aether-based theory of light was regarded as more problematic, because it requires that the aether be stationary even as the Earth moves through it—precisely the problem that led Newton to reject a wave model in the first place. | |||
| ===Bradley suggests particles=== | |||
| However, a century later, ] and ] revived the wave theory of light when they pointed out that light could be a ] rather than a longitudinal wave—the polarization of a transverse wave (like Newton's "sides" of light) could explain birefringence, and in the wake of a series of experiments on diffraction the particle model of Newton was finally abandoned. ] still assumed, however, that like mechanical waves, light waves required a medium for ], and thus required Huygens's idea of an aether "gas" permeating all space. | |||
| In 1720, ] carried out a series of experiments attempting to measure ] by taking measurements of stars at different times of the year. As the Earth moves around the Sun, the apparent angle to a given distant spot changes. By measuring those angles the distance to the star can be calculated based on the known orbital circumference of the Earth around the Sun. He failed to detect any parallax, thereby placing a lower limit on the distance to stars. | |||
| During these experiments, Bradley also discovered a related effect; the apparent positions of the stars did change over the year, but not as expected. Instead of the apparent angle being maximized when the Earth was at either end of its orbit with respect to the star, the angle was maximized when the Earth was at its fastest sideways velocity with respect to the star. This effect is now known as ]. | |||
| However, a transverse wave apparently required the propagating medium to behave as a solid, as opposed to a gas or fluid. The idea of a solid that did not interact with other matter seemed a bit odd, and ] suggested that perhaps there was some sort of "dragging", or "entrainment", but this made the aberration measurements difficult to understand. He also suggested that the ''absence'' of longitudinal waves suggested that the aether had negative compressibility. ] pointed out that such a fluid would be unstable. ] became a champion of the entrainment interpretation, developing a model in which the aether might be (by analogy with pine pitch) rigid at very high frequencies and fluid at lower speeds. Thus the Earth could move through it fairly freely, but it would be rigid enough to support light. | |||
| Bradley explained this effect in the context of Newton's corpuscular theory of light, by showing that the aberration angle was given by simple vector addition of the Earth's orbital velocity and the velocity of the corpuscles of light, just as vertically falling raindrops strike a moving object at an angle. Knowing the Earth's velocity and the aberration angle enabled him to estimate the speed of light. | |||
| Later, ] showed that light is an ]. The apparent need for a propagation medium for such ] can be seen by the fact that they consist of perpendicular electric (E) and magnetic (B or H) waves. The E waves consist of undulating dipolar electric fields, and all such dipoles appeared to require separated and opposite electric charges. Electric charge is an inextricable property of ], so it appeared that some form of matter was required to provide the alternating current that would seem to have to exist at any point along the propagation path of the wave. Propagation of waves in a true vacuum would imply the existence of ]s without associated ], or of electric charge without associated matter. Albeit compatible with Maxwell's equations, ] of electric fields could not be demonstrated in vacuum, because all methods of detecting electric fields required electrically charged matter. | |||
| Explaining stellar aberration in the context of an aether-based theory of light was regarded as more problematic. As the aberration relied on relative velocities, and the measured velocity was dependent on the motion of the Earth, the aether had to be remaining stationary with respect to the star as the Earth moved through it. This meant that the Earth could travel through the aether, a physical medium, with no apparent effect – precisely the problem that led Newton to reject a wave model in the first place. | |||
| In addition, Maxwell's equations required that all electromagnetic waves in ] propagate at a fixed speed, '']''. As this can only occur in one ] in Newtonian physics (see ]), the aether was hypothesized as the absolute and unique frame of reference in which Maxwell's equations hold. That is, the aether must be "still" universally, otherwise ''c'' would vary along with any variations that might occur in its supportive medium. Maxwell himself proposed several mechanical models of aether based on wheels and gears, and ] even constructed a working model of one of them. These models had to agree with the fact that the electromagnetic waves are ] but never ]. | |||
| ===Wave-theory triumphs=== | |||
| Nevertheless, by this point the mechanical qualities of the aether had become more and more magical: it had to be a ] in order to fill space, but one that was millions of times more rigid than steel in order to support the high frequencies of light waves. It also had to be massless and without ], otherwise it would visibly affect the orbits of planets. Additionally it appeared it had to be completely transparent, non-dispersive, ], and continuous at a very small scale. <ref>http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-michelson-morley-experiment.htm</ref> | |||
| A century later, ]{{efn|Young ascribed aether to ], pairing light and heat, and cited passages from Newton such as: "A luminiferous ether pervades the Universe, rare and elastic in a high degree," and:<blockquote>Is not the heat conveyed through the vacuum by the vibration of a much subtiler medium than air? And is not this medium the same with that medium by which light is refracted and reflected, and by whose vibration light communicates heat to bodies, and is put into fits of easy reflection, and easy transmission?<ref>{{cite book |last=Gillispie |first=Charles Coulston |author-link=Charles Coulston Gillispie |title=The Edge of Objectivity: An Essay in the History of Scientific Ideas |year=1960 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-02350-6 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/edgeofobjectivit00char/page/408 }}</ref></blockquote>}} and ] revived the wave theory of light when they pointed out that light could be a transverse wave rather than a longitudinal wave; the polarization of a transverse wave (like Newton's "sides" of light) could explain birefringence, and in the wake of a series of experiments on diffraction the particle model of Newton was finally abandoned. ]s assumed, moreover, that, like mechanical waves, light waves required a medium for ], and thus required Huygens's idea of an aether "gas" permeating all space. | |||
| However, a transverse wave apparently required the propagating medium to behave as a solid, as opposed to a fluid. The idea of a solid that did not interact with other matter seemed a bit odd, and ] suggested that perhaps there was some sort of "dragging", or "entrainment", but this made the aberration measurements difficult to understand. He also suggested that the ''absence'' of longitudinal waves suggested that the aether had negative compressibility. ] pointed out that such a fluid would be unstable. ] became a champion of the entrainment interpretation, developing a model in which the aether might, like pine pitch, be ] (fluid at slow speeds and rigid at fast speeds). Thus the Earth could move through it fairly freely, but it would be rigid enough to support light. | |||
| Maxwell wrote in ''Encyclopedia Britannica'':<ref>Maxwell (1878)</ref> | |||
| ===Electromagnetism=== | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| In 1856, ] and ] measured the numerical value of the ratio of the electrostatic unit of charge to the electromagnetic unit of charge. They found that the ratio between the ] and the ] is the speed of light ''c''.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Schwartz |first=Melvin |title=Principles of Electrodynamics |publisher=Dover Publications, Inc. |year=1987 |isbn=978-0-486-65493-5 |edition=Revised |pages=106–107}}</ref> The following year, ] wrote a paper in which he showed that the speed of a signal along an electric wire was equal to the speed of light. These are the first recorded historical links between the speed of light and electromagnetic phenomena. | |||
| Aethers were invented for the planets to swim in, to constitute electric atmospheres and magnetic effluvia, to convey sensations from one part of our bodies to another, and so on, until all space had been filled three or four times over with aethers.... The only aether which has survived is that which was invented by Huygens to explain the propagation of light. | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| ] began working on ]'s ]. In his 1861 paper '']'' he modelled these magnetic lines of force using a sea of molecular vortices that he considered to be partly made of aether and partly made of ordinary matter. He derived expressions for the dielectric constant and the magnetic permeability in terms of the transverse elasticity and the density of this elastic medium. He then equated the ratio of the dielectric constant to the magnetic permeability with a suitably adapted version of Weber and Kohlrausch's result of 1856, and he substituted this result into Newton's equation for the speed of sound. On obtaining a value that was close to the speed of light as measured by ], Maxwell concluded that light consists in undulations of the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena.<ref group=B name=whitt /><ref group=B name=janb /><ref group=B name=darrigol /><ref group=B name=schaffner /> | |||
| Contemporary scientists were aware of the problems, but aether theory was so entrenched in physical law by this point that it was simply assumed to exist. In 1908 ] gave a speech in behalf of ] <ref>http://www.keelynet.com/osborn/rey7.htm</ref> to the ] on this topic, in which he outlined its physical properties, and then attempted to offer reasons why they were not impossible. Nevertheless he was also aware of the criticisms, and quoted ] as saying that "aether is little more than a nominative case of the verb ''to undulate''". Others criticized it as an "English invention", although Rayleigh jokingly corrected them to state it was actually an invention of the Royal Institution. {{Citation needed|date=March 2009}} | |||
| Maxwell had, however, expressed some uncertainties surrounding the precise nature of his molecular vortices and so he began to embark on a purely dynamical approach to the problem. He wrote another paper in 1864, entitled "]", in which the details of the luminiferous medium were less explicit.<ref group=A name=maxb /> Although Maxwell did not explicitly mention the sea of molecular vortices, his derivation of ] was carried over from the 1861 paper and he used a dynamical approach involving rotational motion within the electromagnetic field which he likened to the action of flywheels. Using this approach to justify the electromotive force equation (the precursor of the ] equation), he derived a wave equation from a set of eight equations which appeared in the paper and which included the electromotive force equation and ].<ref group=A name=maxb /> Maxwell once again used the experimental results of Weber and Kohlrausch to show that this wave equation represented an electromagnetic wave that propagates at the speed of light, hence supporting the view that light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. | |||
| By the early 20th Century, aether theory was in trouble. A series of ] had been carried out in the late 1800s to try to detect the motion of earth through the aether, and had failed to do so. A range of proposed aether-dragging theories could explain the null result but these were more complex, and tended to use arbitrary-looking coefficients and physical assumptions. Lorentz and Fitzgerald offered within the framework of ] a more elegant solution to how the motion of an absolute aether could be undetectable (length contraction), but if their equations were correct, the new ] (1905) could generate the same mathematics without referring to an aether at all. Aether fell to ]. | |||
| In 1887–1889, ] experimentally demonstrated the electric magnetic waves are identical to light waves. This unification of electromagnetic wave and optics indicated that there was a single luminiferous aether instead of many different kinds of aether media.<ref>{{Cite journal |url=https://en.wikisource.org/Popular_Science_Monthly/Volume_66/November_1904/The_Fundamental_Concepts_of_Physical_Science |first=Edward L. |last=Nichols |title=The Fundamental Concepts of Physical Science |journal=Popular Science Monthly |volume=66 |date=November 1904}}</ref> | |||
| ==Aether and classical mechanics== | |||
| The key difficulty with the aether hypothesis arose from the juxtaposition of the two well-established theories of Newtonian dynamics and Maxwell's electromagnetism. Under a ] the equations of Newtonian dynamics are ], whereas those of electromagnetism are not. Basically this means that while physics should remain the same in non-accelerated experiments, light would not follow the same rules because it is traveling in the universal "aether frame". Some effect caused by this difference should be detectable. | |||
| The apparent need for a propagation medium for such ] (later called ]) can be seen by the fact that they consist of orthogonal electric (E) and magnetic (B or H) waves. The E waves consist of undulating dipolar electric fields, and all such dipoles appeared to require separated and opposite electric charges. Electric charge is an inextricable property of ], so it appeared that some form of matter was required to provide the alternating current that would seem to have to exist at any point along the propagation path of the wave. Propagation of waves in a true vacuum would imply the existence of ]s without associated ], or of electric charge without associated matter. Albeit compatible with Maxwell's equations, ] of electric fields could not be demonstrated in vacuum, because all methods of detecting electric fields required electrically charged matter. | |||
| A simple example concerns the model on which aether was originally built: sound. The speed of propagation for mechanical waves, the ], is defined by the mechanical properties of the medium. For instance, if one is in an ], you can still carry on a conversation with the person beside you because the sound of your words are traveling along with the air inside the aircraft. This effect is basic to all Newtonian dynamics, which says that everything from sound to the trajectory of a thrown baseball should all remain the same in the aircraft as sitting still on the Earth. This is the basis of the Galilean transformation, and the concept of frame of reference. | |||
| In addition, Maxwell's equations required that all electromagnetic waves in ] propagate at a fixed speed, '']''. As this can only occur in one ] in Newtonian physics (see ]), the aether was hypothesized as the absolute and unique frame of reference in which Maxwell's equations hold. That is, the aether must be "still" universally, otherwise ''c'' would vary along with any variations that might occur in its supportive medium. Maxwell himself proposed several mechanical models of aether based on wheels and gears, and ] even constructed a working model of one of them. These models had to agree with the fact that the electromagnetic waves are transverse but never longitudinal. | |||
| But the same was not true for light, since Maxwell's mathematics demanded a single universal speed for the propagation of light, based, not on local conditions, but on two measured properties, the permittivity and permeability of free space, that were assumed to be the same throughout the universe. If these numbers did change, there should be noticeable effects in the sky; stars in different directions would have different colors, for instance. Certainly they would remain constant within a small volume, inside the aircraft in our example for instance, which implies that light would ''not'' follow along with the aircraft (or the Earth) in a fashion similar to sound. Nor could light change media, for instance, using the atmosphere while near the Earth. It had already been demonstrated that if this were so, the sky would be colored in different directions as the light moved from the still medium of the aether to the moving medium of the Earth's atmosphere, causing diffraction. | |||
| ===Problems=== | |||
| Thus at any point there should be one special coordinate system, "at rest relative to the aether". Maxwell noted in the late 1870s that detecting motion relative to this aether should be easy enough—light traveling along with the motion of the Earth would have a different speed than light traveling backward, as they would both be moving against the unmoving aether. Even if the aether had an overall universal flow, changes in position during the day/night cycle, or over the span of seasons, should allow the drift to be detected. | |||
| By this point the mechanical qualities of the aether had become more and more magical: it had to be a ] in order to fill space, but one that was millions of times more rigid than steel in order to support the high frequencies of light waves. It also had to be massless and without ], otherwise it would visibly affect the orbits of planets. Additionally it appeared it had to be completely transparent, non-dispersive, ], and continuous at a very small scale.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Yousef |first=Mohamed Haj |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9_WEDwAAQBAJ&dq=Luminiferous+aether+Additionally+it+appeared+it+had+to+be+completely+transparent%2C+non-dispersive%2C+incompressible%2C+and+continuous+at+a+very+small+scale&pg=PA73 |title=Duality of Time: Complex-Time Geometry and Perpetual Creation of Space |date=2018-01-01 |publisher=Mohamed Haj Yousef |isbn=978-1-5395-7920-5 |language=en}}</ref> Maxwell wrote in ''Encyclopædia Britannica'':<ref group=A name=maxa /> | |||
| <blockquote>Aethers were invented for the planets to swim in, to constitute electric atmospheres and magnetic effluvia, to convey sensations from one part of our bodies to another, and so on, until all space had been filled three or four times over with aethers. ... The only aether which has survived is that which was invented by Huygens to explain the propagation of light.</blockquote> | |||
| ==Experiments== | |||
| ] | |||
| Numerous experiments were carried out in the late 1800s to test for this "aether wind" effect, but most were open to dispute due to low accuracy. Measurements on the speed of propagation were so inaccurate that comparing two speeds to look for a difference was essentially impossible. | |||
| By the early 20th century, aether theory was in trouble. A series of ] had been carried out in the late 19th century to try to detect the motion of the Earth through the aether, and had failed to do so. A range of proposed aether-dragging theories could explain the null result but these were more complex, and tended to use arbitrary-looking coefficients and physical assumptions. Lorentz and FitzGerald offered within the framework of ] a more elegant solution to how the motion of an absolute aether could be undetectable (length contraction), but if their equations were correct, the new ] (1905) could generate the same mathematics without referring to an aether at all. Aether fell to ].<ref group=B name=whitt /><ref group=B name=janb /><ref group=B name=darrigol /><ref group=B name=schaffner /> | |||
| The famous ] instead compared the source light with itself after being sent in different directions, looking for changes in phase in a manner that could be measured with extremely high accuracy. The publication of their result in 1887, the ], was the first clear demonstration that something was seriously wrong with the aether concept of that time. A series of experiments using similar but increasingly sophisticated apparatus all returned the null result as well. A conceptually different experiment that also attempted to detect the motion of the aether was the 1903 ], which like Michelson-Morley obtained a null result. | |||
| ==Relative motion between the Earth and aether== | |||
| In this case the MM experiment yielded a shift of the fringing pattern of about 0.01 of a fringe, corresponding to a small velocity. However, it was incompatible with the expected aether wind effect due to the earth's (seasonally varying) velocity which would have required a shift of 0.4 of a fringe, and the error was small enough that the value may have indeed been zero. Therefore, the ], the hypothesis that there was no aether wind, could not be rejected. More modern experiments have since reduced the possible value to a number very close to zero, about 10<small><sup>−15</sup></small>. | |||
| ===Aether drag=== | |||
| These "aether-wind" experiments led to the abandonment of the aether concept by some scientists like ] or ], and to a flurry of efforts to "save" aether by assigning it ever more complex properties by others. Of particular interest was the possibility of "aether entrainment" or "aether drag", which would lower the magnitude of the measurement, perhaps enough to explain MMX results. However, as noted earlier, aether dragging already had problems of its own, notably aberration. A more direct measurement was made in the ], which ran a complete MM experiment with one of the "legs" placed between two massive lead blocks. If the aether was dragged by mass then this experiment would have been able to detect the drag caused by the lead, but again the null result was found. Similar experiments by Hoek placed one leg in a heavy vat of water. The theory was again modified, this time to suggest that the entrainment only worked for very large masses or those masses with large magnetic fields. This too was shown to be incorrect when ] noted no such effect around other planets. | |||
| {{Main|Aether drag hypothesis}} | |||
| The two most important models, which were aimed to describe the relative motion of the Earth and aether, were ]'s (1818) model of the (nearly) stationary aether including a partial aether drag determined by Fresnel's dragging coefficient,<ref group=A name=fresnel /> and ]' (1844)<ref group=A name=stokes /> | |||
| model of complete aether drag. The latter theory was not considered as correct, since it was not compatible with the ], and the auxiliary hypotheses developed to explain this problem were not convincing. Also, subsequent experiments as the ] (1913) also showed that this model is untenable. However, the most important experiment supporting Fresnel's theory was ]'s 1851 ] of ]'s 1818 prediction that a medium with ] ''n'' moving with a velocity ''v'' would increase the speed of light travelling through the medium in the same direction as ''v'' from ''c''/''n'' to:<ref group=E name=Fizeau1 /><ref group=E name=michel2 /> | |||
| {{block indent|<math>\frac{c}{n} + \left( 1 - \frac{1}{n^2} \right) v.</math>}} | |||
| Another, completely different, attempt to save "absolute" aether was made in the ], which posited that ''everything'' was affected by travel through the aether. In this theory the reason the Michelson-Morley experiment "failed" was that the apparatus contracted in length in the direction of travel. That is, the light was being affected in the "natural" manner by its travel though the aether as predicted, but so was the apparatus itself, canceling out any difference when measured. Fitzgerald had inferred this hypothesis from a paper by ]. Without referral to an aether, this physical interpretation of relativistic effects was shared by ] in 1932 as they concluded that the interferometer's arm contracts and also the frequency of its light source "very nearly" varies in the way required by relativity.<ref> They commented in a footnote: "From experiment it is not inferred that the velocity of the earth is but a few kilometers per second, but rather that the dimensions of the apparatus vary very nearly as required by relativity. From the present experiment we similarly infer that the frequency of light varies conformably to the theory."-R. J. Kennedy and E. M. Thorndike, “Experimental Establishment of the Relativity of Time”, Physical review. Series 2, vol.42, p.400–418 (1932) </ref> | |||
| That is, movement adds only a fraction of the medium's velocity to the light (predicted by Fresnel in order to make ] work in all frames of reference, consistent with stellar aberration). This was initially interpreted to mean that the medium drags the aether along, with a ''portion'' of the medium's velocity, but that understanding became very problematic after ] demonstrated that the index ''n'' in Fresnel's formula depended upon the ] of light, so that the aether could not be moving at a wavelength-independent speed. This implied that there must be a separate aether for each of the infinitely many frequencies. | |||
| Another experiment purporting to show effects of an aether was ]'s 1851 experimental confirmation of ]'s 1818 prediction that a medium with ] ''n'' moving with a velocity ''v'' would increase the speed of light traveling through the medium in the same direction as ''v'' from ''c''/''n'' to: | |||
| ===Negative aether-drift experiments=== | |||
| :<math>\frac{c}{n} + \left( 1 - \frac{1}{n^2} \right) v.</math> | |||
| The key difficulty with Fresnel's aether hypothesis arose from the juxtaposition of the two well-established theories of Newtonian dynamics and Maxwell's electromagnetism. Under a ] the equations of Newtonian dynamics are ], whereas those of electromagnetism are not. Basically this means that while physics should remain the same in non-accelerated experiments, light would not follow the same rules because it is travelling in the universal "aether frame". Some effect caused by this difference should be detectable. | |||
| A simple example concerns the model on which aether was originally built: sound. The speed of propagation for mechanical waves, the ], is defined by the mechanical properties of the medium. Sound travels 4.3 times faster in water than in air. This explains why a person hearing an explosion underwater and quickly surfacing can hear it again as the slower travelling sound arrives through the air. Similarly, a traveller on an ] can still carry on a conversation with another traveller because the sound of words is travelling along with the air inside the aircraft. This effect is basic to all Newtonian dynamics, which says that everything from sound to the trajectory of a thrown baseball should all remain the same in the aircraft flying (at least at a constant speed) as if still sitting on the ground. This is the basis of the Galilean transformation, and the concept of frame of reference. | |||
| That is, movement adds only a fraction of the medium's velocity to the light (predicted by Fresnel in order to make ] work in all frames of reference, consistent with stellar aberration). This was initially interpreted to mean that the medium drags the aether along, with a ''portion'' of the medium's velocity, but that understanding was rejected after ] demonstrated that the index ''n'' in Fresnel's formula depended upon the ] of light, so that the aether could not be moving at a wavelength-independent speed. This implied that there must be a separate aether for each of the infinitely many frequencies. This realization tended to undermine belief in the aether as a viable physical concept. Moreover, with the advent of special relativity, Fresnel's equation was shown by ] in 1907 to be just an ''approximation'', valid for ''v'' much smaller than ''c'', for the correct relativistic formula to add the velocities ''v'' (medium) and ''c''/''n'' (rest frame): | |||
| But the same was not supposed to be true for light, since Maxwell's mathematics demanded a single universal speed for the propagation of light, based, not on local conditions, but on two measured properties, the ] and ] of free space, that were assumed to be the same throughout the universe. If these numbers did change, there should be noticeable effects in the sky; stars in different directions would have different colours, for instance.{{Verify source|date=June 2011}} | |||
| :<math>\frac{c/n + v}{1 + \frac{v c/n} {c^2}} \approx \frac{c}{n} + \left( 1 - \frac{1}{n^2} \right) v + O\left(\frac{v^2}{c^2}\right).</math> | |||
| Thus at any point there should be one special coordinate system, "at rest relative to the aether". Maxwell noted in the late 1870s that detecting motion relative to this aether should be easy enough—light travelling along with the motion of the Earth would have a different speed than light travelling backward, as they would both be moving against the unmoving aether. Even if the aether had an overall universal flow, changes in position during the day/night cycle, or over the span of seasons, should allow the drift to be detected. | |||
| Similarly the ], observed by G. Sagnac in 1913 was immediately seen to be fully consistent with special relativity. In fact, the ] in 1925 was proposed specifically as a test to confirm the relativity theory, although it was also recognized that such tests, which merely measure absolute rotation, are also consistent with non-relativistic theories.<ref>The confusion over this point can be seen in Sagnac's conclusion that "in the ambient space, light is propagated with a velocity V0, independent of the movement as a whole of the luminous source O and the optical system. That is a property of space which experimentally characterizes the luminiferous aether." The invariance of light speed, independent of the movement of the source, is also one of the two fundamental principles of special relativity.</ref> | |||
| ====First-order experiments==== | |||
| During the 1920s, the experiments pioneered by Michelson were repeated by ], who publicly proclaimed positive results on several occasions, although not large enough to be consistent with any known aether theory. In any case, other researchers were unable to duplicate Miller's claimed results, and in subsequent years the experimental accuracy of such measurements has been raised by many orders of magnitude, and no trace of any violations of Lorentz invariance has been seen. (A later re-analysis of Miller's results concluded that he had underestimated the variations due to temperature.) | |||
| Although the aether is almost stationary according to Fresnel, his theory predicts a positive outcome of aether drift experiments only to ''second'' order in <math>v/c</math> because Fresnel's dragging coefficient would cause a negative outcome of all optical experiments capable of measuring effects to ''first'' order in <math>v/c</math>. This was confirmed by the following first-order experiments, all of which gave negative results. The following list is based on the description of ] (1898), with changes and additional experiments according to the descriptions of ] (1910) and ] (1910):<ref group=B name=wien /><ref group=B name=whitt /><ref group=B name=laub /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1810), to confirm whether refraction, and thus the aberration of light, is influenced by Earth's motion. Similar experiments were conducted by ] (1871) by means of a telescope filled with water, and ] (1872).<ref group=E name=Arago /><ref group=E name=Airy /><ref group=E name=masc1 /> | |||
| Since the Miller experiment and its unclear results there have been many more experiments to detect the aether. Many of the experimenters have claimed positive results. These results have not gained much attention from mainstream science. For a list and criticisms of those experiments (Kantor, Marinov, Silvertooth, Torr and Kolen, Munera, Cahill) see . | |||
| * The experiment of Fizeau (1860), to find whether the rotation of the polarization plane through glass columns is changed by Earth's motion. He obtained a positive result, but Lorentz could show that the results have been contradictory. ] (1905) and Strasser (1907) repeated the experiment with improved accuracy, and obtained negative results.<ref group=E name=Fizeau2 /><ref group=E name=Brace2 /><ref group=E name=Strasser /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1868). This experiment is a more precise variation of the ] (1851). Two light rays were sent in opposite directions – one of them traverses a path filled with resting water, the other one follows a path through air. In agreement with Fresnel's dragging coefficient, he obtained a negative result.<ref group=E name=Hoek /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1870) investigated whether an influence of Earth's motion on the absorption line of sodium exists. He obtained a positive result, but this was shown to be an experimental error, because a repetition of the experiment by ] (1901) gave a negative result.<ref group=E name=Klinkerfues /><ref group=E name=Haga /> | |||
| * The experiment of Ketteler (1872), in which two rays of an interferometer were sent in opposite directions through two mutually inclined tubes filled with water. No change of the interference fringes occurred. Later, Mascart (1872) showed that the interference fringes of polarized light in calcite remained uninfluenced as well.<ref group=E name=Ketteler /><ref group=E name=masc2 /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1872) to find a change of rotation of the polarization plane in quartz. No change of rotation was found when the light rays had the direction of Earth's motion and then the opposite direction. ] conducted similar experiments with improved accuracy, and obtained a negative result as well.<ref group=E name=masc1 /><ref group=E name=masc2 /><ref group=E name=Rayleigh1 /> | |||
| Besides those optical experiments, also electrodynamic first-order experiments were conducted, which should have led to positive results according to Fresnel. However, ] (1895) modified Fresnel's theory and showed that those experiments can be explained by a stationary aether as well:<ref group=A name=lorb /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1888), to find whether a charged capacitor produces magnetic forces due to Earth's motion.<ref group=E name=Roentgen /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1889), to find whether the inductive effect of two wire rolls upon a third one is influenced by the direction of Earth's motion. Lorentz showed that this effect is cancelled to first order by the electrostatic charge (produced by Earth's motion) upon the conductors.<ref group=E name=Coudres /> | |||
| * The experiment of Königsberger (1905). The plates of a capacitor are located in the field of a strong electromagnet. Due to Earth's motion, the plates should have become charged. No such effect was observed.<ref group=E name=Koenigsberger /> | |||
| * The experiment of ] (1902). A capacitor was brought parallel to Earth's motion, and it was assumed that momentum is produced when the capacitor is charged. The negative result can be explained by Lorentz's theory, according to which the electromagnetic momentum compensates the momentum due to Earth's motion. Lorentz could also show, that the sensitivity of the apparatus was much too low to observe such an effect.<ref group=E name=Trouton1 /> | |||
| ====Second-order experiments==== | |||
| ] | |||
| While the ''first''-order experiments could be explained by a modified stationary aether, more precise ''second''-order experiments were expected to give positive results. However, no such results could be found. | |||
| The famous ] compared the source light with itself after being sent in different directions and looked for changes in phase in a manner that could be measured with extremely high accuracy. In this experiment, their goal was to determine the velocity of the Earth through the aether.<ref group=E name=michel1 /><ref group=E name=michel3 /> The publication of their result in 1887, the ], was the first clear demonstration that something was seriously wrong with the aether hypothesis (Michelson's first experiment in 1881 was not entirely conclusive). In this case the MM experiment yielded a shift of the fringing pattern of about 0.01 of a ], corresponding to a small velocity. However, it was incompatible with the expected aether wind effect due to the Earth's (seasonally varying) velocity which would have required a shift of 0.4 of a fringe, and the error was small enough that the value may have indeed been zero. Therefore, the ], the hypothesis that there was no aether wind, could not be rejected. More modern experiments have since reduced the possible value to a number very close to zero, about 10<sup>−17</sup>. | |||
| {{Blockquote|It is obvious from what has gone before that it would be hopeless to attempt to solve the question of the motion of the solar system by observations of optical phenomena at the surface of the earth.|A. Michelson and E. Morley. "On the Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Æther". '']'' S. 5. Vol. 24. No. 151. December 1887.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aip.org/history/gap/PDF/michelson.pdf|title=Selected Papers of Great American Physicists|website=www.aip.org|access-date=30 April 2018|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150715063415/https://www.aip.org/history/gap/PDF/michelson.pdf|archive-date=15 July 2015}}</ref>}} | |||
| A series of experiments using similar but increasingly sophisticated apparatuses all returned the null result as well. Conceptually different experiments that also attempted to detect the motion of the aether were the ] (1903),<ref group=E name=Trouton2 /> whose objective was to detect ] effects caused by electrostatic fields, and ] (1902, 1904),<ref group=E name=Rayleigh2 /><ref group=E name=Brace1 /> to detect ] in various media. However, all of them obtained a null result, like Michelson–Morley (MM) previously did. | |||
| These "aether-wind" experiments led to a flurry of efforts to "save" aether by assigning to it ever more complex properties, and only a few scientists, like ] or ], considered the possibility of the abandonment of the aether hypothesis. Of particular interest was the possibility of "aether entrainment" or "aether drag", which would lower the magnitude of the measurement, perhaps enough to explain the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment. However, as noted earlier, aether dragging already had problems of its own, notably aberration. In addition, the interference experiments of ] (1893, 1897) and ] (1895), aimed to show whether the aether is dragged by various, rotating masses, showed no aether drag.<ref group=E name=Lodge /><ref group=E name=Lodge2 /><ref group=E name=Zehnder /> A more precise measurement was made in the ] (1935), which ran a complete MM experiment with one of the "legs" placed between two massive lead blocks.<ref group=E name=Hammar /> If the aether was dragged by mass then this experiment would have been able to detect the drag caused by the lead, but again the null result was achieved. The theory was again modified, this time to suggest that the entrainment only worked for very large masses or those masses with large magnetic fields. This too was shown to be incorrect by the ], which detected the Sagnac effect due to Earth's rotation (see ]). | |||
| Another completely different attempt to save "absolute" aether was made in the ], which posited that ''everything'' was affected by travel through the aether. In this theory, the reason that the Michelson–Morley experiment "failed" was that the apparatus contracted in length in the direction of travel. That is, the light was being affected in the "natural" manner by its travel through the aether as predicted, but so was the apparatus itself, cancelling out any difference when measured. FitzGerald had inferred this hypothesis from a paper by ]. Without referral to an aether, this physical interpretation of relativistic effects was ] in 1932 as they concluded that the interferometer's arm contracts and also the frequency of its light source "very nearly" varies in the way required by relativity.<ref group=E name=kenn /><ref>They commented in a footnote: "From experiment it is not inferred that the velocity of the earth is but a few kilometers per second, but rather that the dimensions of the apparatus vary very nearly as required by relativity. From the present experiment we similarly infer that the frequency of light varies conformably to the theory."</ref> | |||
| Similarly, the ], observed by G. Sagnac in 1913, was immediately seen to be fully consistent with special relativity.<ref group=E name=Sagnac1 /><ref group=E name=Sagnac2 /> In fact, the ] in 1925 was proposed specifically as a test to confirm the relativity theory, although it was also recognized that such tests, which merely measure absolute rotation, are also consistent with non-relativistic theories.<ref>The confusion over this point can be seen in Sagnac's conclusion that "in the ambient space, light is propagated with a velocity V0, independent of the movement as a whole of the luminous source O and the optical system. That is a property of space which experimentally characterizes the luminiferous aether." The invariance of light speed, independent of the movement of the source, is also one of the two fundamental principles of special relativity.</ref> | |||
| During the 1920s, the experiments pioneered by Michelson were repeated by ], who publicly proclaimed positive results on several occasions, although they were not large enough to be consistent with any known aether theory. However, other researchers were unable to duplicate Miller's claimed results. Over the years the experimental accuracy of such measurements has been raised by many orders of magnitude, and no trace of any violations of Lorentz invariance has been seen. (A later re-analysis of Miller's results concluded that he had underestimated the variations due to temperature.) | |||
| Since the Miller experiment and its unclear results there have been many more experimental attempts to detect the aether. Many experimenters have claimed positive results. These results have not gained much attention from mainstream science, since they contradict a large quantity of high-precision measurements, all the results of which were consistent with special relativity.<ref>Roberts, Schleif (2006); Physics FAQ: {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091015153529/http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/Relativity/SR/experiments.html |date=2009-10-15 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Lorentz aether theory== | ==Lorentz aether theory== | ||
| {{Main|Lorentz ether theory}} | {{Main|Lorentz ether theory}} | ||
| Between 1892 and 1904, ] |
Between 1892 and 1904, ] developed an electron–aether theory, in which he avoided making assumptions about the aether. In his model the aether is completely motionless, and by that he meant that it could not be set in motion in the neighborhood of ponderable matter. Contrary to earlier electron models, the electromagnetic field of the aether appears as a mediator between the electrons, and changes in this field cannot propagate faster than the speed of light. A fundamental concept of Lorentz's theory in 1895 was the "theorem of corresponding states" for terms of order v/c.<ref group=A name=lorb /> This theorem states that an observer moving relative to the aether makes the same observations as a resting observer, after a suitable change of variables. Lorentz noticed that it was necessary to change the space-time variables when changing frames and introduced concepts like physical ] (1892)<ref group=A name=lora /> to explain the Michelson–Morley experiment, and the mathematical concept of ] (1895) to explain the ] and the ]. This resulted in the formulation of the so-called ] by ] (1897, 1900)<ref group=A name=lara /><ref group=A name=larb /> and Lorentz (1899, 1904),<ref group=A name=lorc /><ref group=A name=lord /> whereby (it was noted by Larmor) the complete formulation of local time is accompanied by some sort of ] of electrons moving in the aether. As Lorentz later noted (1921, 1928), he considered the time indicated by clocks resting in the aether as "true" time, while local time was seen by him as a heuristic working hypothesis and a mathematical artifice.<ref group=A name=lore /><ref group=A name=lorf /> Therefore, Lorentz's theorem is seen by modern authors as being a mathematical transformation from a "real" system resting in the aether into a "fictitious" system in motion.<ref group=B name=miller /><ref group=B name=darrigol /><ref group=B name=jana /> | ||
| The work of Lorentz was mathematically perfected by ], who formulated on many occasions the ] and tried to harmonize it with electrodynamics. He declared simultaneity only a convenient convention which depends on the speed of light, whereby the constancy of the speed of light would be a useful ] for making the laws of nature as simple as possible. In 1900 and 1904<ref group=A name=poinca /><ref group=A name=poincb /> he physically interpreted Lorentz's local time as the result of clock synchronization by light signals. In June and July 1905<ref group=A name=poincc /><ref group=A name=poincd /> he declared the relativity principle a general law of nature, including gravitation. He corrected some mistakes of Lorentz and proved the Lorentz covariance of the electromagnetic equations. However, he used the notion of an aether as a perfectly undetectable medium and distinguished between apparent and real time, so most historians of science argue that he failed to invent special relativity.<ref group=B name=miller /><ref group=B name=pais /><ref group=B name=darrigol /> | |||
| ==End of aether== | |||
| ===Special relativity=== | |||
| Aether theory was dealt another blow when the Galilean transformation and Newtonian dynamics were both modified by ]'s ], giving the mathematics of ] a new, "non-aether" context.<ref group=A name=einselektro /> Unlike most major shifts in scientific thought, special relativity was adopted by the scientific community remarkably quickly, consistent with Einstein's later comment that the laws of physics described by the Special Theory were "ripe for discovery" in 1905.<ref group=B name=born /> Max Planck's early advocacy of the special theory, along with the elegant formulation given to it by ], contributed much to the rapid acceptance of special relativity among working scientists. | |||
| Einstein based his theory on Lorentz's earlier work. Instead of suggesting that the mechanical properties of objects changed with their constant-velocity motion through an undetectable aether, Einstein proposed to deduce the characteristics that any successful theory must possess in order to be consistent with the most basic and firmly established principles, independent of the existence of a hypothetical aether. He found that the Lorentz transformation must transcend its connection with Maxwell's equations, and must represent the fundamental relations between the space and time coordinates of ]. In this way he demonstrated that the laws of physics remained invariant as they had with the Galilean transformation, but that light was now invariant as well. | |||
| The work of Lorentz was mathematically perfected by ] who formulated on many occasions the ] and tried to harmonize it with electrodynamics. He declared simultaneity only a convenient convention which depends on the speed of light, whereby the constancy of the speed of light would be a useful ] for making the laws of nature as simple as possible. In 1900 he interpreted Lorentz's local time as the result of clock synchronization by light signals. And finally in June and July 1905 he declared the relativity principle a general law of nature, including gravitation. He corrected some mistakes of Lorentz and proved the Lorentz covariance of the electromagnetic equations. However, he used the notion of an aether as a perfectly undetectable medium and distinguished between apparent and real time, so most historians of science argue that he failed to invent special relativity.<ref name=jan /><ref>Darrigol 2000</ref><ref>Miller 1981, Ch. 1.7 & 1.14</ref><ref>Pais 1982, Ch. 6 & 8</ref> | |||
| With the development of the special theory of relativity, the need to account for a single universal ] had disappeared – and acceptance of the 19th-century theory of a luminiferous aether disappeared with it. For Einstein, the Lorentz transformation implied a conceptual change: that the concept of position in space or time was not absolute, but could differ depending on the observer's location and velocity. | |||
| ==End of aether?== | |||
| Aether theory was dealt another blow when the Galilean transformation and Newtonian dynamics were both modified by ]'s ], giving the mathematics of ] a new, "non-aether" context. Unlike most major shifts in scientific thought, the Special Theory of Relativity was adopted by the scientific community remarkably quickly, consistent with Einstein's later comment that the laws of physics described by the Special Theory were "ripe for discovery" in 1905. Max Planck's early advocacy of the Special Theory, along with the natural and elegant formulation given to it by Minkowski, contributed much to the rapid acceptance of the Special Theory among working scientists. | |||
| Moreover, in another paper published the same month in 1905, Einstein made several observations on a then-thorny problem, the ]. In this work he demonstrated that light can be considered as particles that have a "wave-like nature". Particles obviously do not need a medium to travel, and thus, neither did light. This was the first step that would lead to the full development of ], in which the wave-like nature ''and'' the particle-like nature of light are both considered as valid descriptions of light. A summary of Einstein's thinking about the aether hypothesis, relativity and light quanta may be found in his 1909 (originally German) lecture "The Development of Our Views on the Composition and Essence of Radiation".<ref group=A name=einsdev /> | |||
| Einstein based his Special Theory on Lorentz's earlier work. Instead of suggesting that the mechanical properties of objects changed with their constant-velocity motion through an undetectable aether, Einstein proposed to deduce the characteristics that any successful theory must possess in order to be consistent with the most basic and firmly established principles, independent of the existence of a hypothetical aether. He found that the Lorentz transformation must transcend its connection with Maxwell's equations, and must represent the fundamental relations between the space and time coordinates of inertial frames of reference. In this way he demonstrated that the laws of physics remained invariant as they had with the Galilean transformation, but that light was now invariant as well. ] in his ''Einstein's Theory of Relativity'' observed: | |||
| Lorentz on his side continued to use the aether hypothesis. In his lectures of around 1911, he pointed out that what "the theory of relativity has to say ... can be carried out independently of what one thinks of the aether and the time". He commented that "whether there is an aether or not, electromagnetic fields certainly exist, and so also does the energy of the electrical oscillations" so that, "if we do not like the name of 'aether', we must use another word as a peg to hang all these things upon". He concluded that "one cannot deny the bearer of these concepts a certain substantiality".<ref>Lorentz wrote: "One cannot deny to the bearer of these properties a certain substantiality, and if so, then one may, in all modesty, call true time the time measured by clocks which are fixed in this medium, and consider simultaneity as a primary concept." However, he went on to say that this was based on his conception of "infinite velocity", which according to his own theory is not physically realizable. Lorentz also admitted that the postulate of an absolute but undetectable rest frame was purely metaphysical, and had no empirical consequences.</ref><ref group=B name=miller /> | |||
| <blockquote>Einstein in later years proposed calling empty space equipped with gravitational and electromagnetic fields the "aether", whereby, however, this word is not to denote a substance with its traditional attributes. Thus, in the "aether" there are to be no determinable points, and it is meaningless to speak of motion relative to the "aether." Such a use of the word "aether" is of course admissible, and when once it has been sanctioned by usage in this way, probably quite convenient. From now on aether as a substance vanishes from theory.<ref>Max Born, ''Einstein's Theory of Relativity'', 1962. Page 224.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Nevertheless, in 1920, Einstein gave an address at ] in which he commented "More careful reflection teaches us however, that the special theory of relativity does not compel us to deny ether. We may assume the existence of an ether; only we must give up ascribing a definite state of motion to it, i.e. we must by abstraction take from it the last mechanical characteristic which Lorentz had still left it. We shall see later that this point of view, the conceivability of which I shall at once endeavour to make more intelligible by a somewhat halting comparison, is justified by the results of the general theory of relativity". He concluded his address by saying that "according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an ether. According to the general theory of relativity space without ether is unthinkable."<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://mathshistory.st-andrews.ac.uk/Extras/Einstein_ether/|title=Einstein: Ether and Relativity|website=Maths History|accessdate=7 August 2023}}</ref> | |||
| With the development of the Theory of Special Relativity, the need to account for a single universal frame of reference had disappeared — and acceptance of the 19th century theory of a luminiferous aether disappeared with it. For Einstein, the Lorentz transformation implied a radical conceptual change: that the concept of position in space or time was not absolute, but could differ depending on the observer's location and velocity. | |||
| === Other models === | |||
| Moreover, in another paper published the same month in 1905, Einstein made several observations on a then-thorny problem, the ]. In this work he demonstrated that light can be considered as particles that have a "wave-like nature". Particles obviously do not need a medium to travel, and thus, neither did light. This was the first step that would lead to the full development of ], in which the wave-like nature ''and'' the particle-like nature of light are both considered to be simplifications of what is "really happening". A summary of Einstein's thinking about the aether hypothesis, relativity and light quanta may be found in his 1909 (originally German) lecture "]"<ref>English translation. Original text: ''Über die Entwicklung unserer Anschauungen über das Wesen und die Konstitution der Strahlung''</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Aether theories}} | |||
| In later years there have been a few individuals who advocated a neo-Lorentzian approach to physics, which is Lorentzian in the sense of positing an absolute true state of rest that is undetectable and which plays no role in the predictions of the theory. (No violations of ] have ever been detected, despite strenuous efforts.) Hence these theories resemble the 19th century aether theories in name only. For example, the founder of quantum field theory, ], stated in 1951 in an article in Nature, titled "Is there an Aether?" that "we are rather forced to have an aether".<ref>Dirac wrote about his theory: "We have now the velocity at all points of space-time, playing a fundamental part in electrodynamics. It is natural to regard it as the velocity of some real physical thing. Thus with the new theory of electrodynamics we are rather forced to have an aether."</ref><ref group=A name=dirac /> However, Dirac never formulated a complete theory, and so his speculations found no acceptance by the scientific community. | |||
| ===Einstein's views on the aether=== | |||
| Lorentz on his side continued to use the aether concept. In his lectures of around 1911 he pointed out that what "the theory of relativity has to say", "can be carried out independently of what one thinks of the aether and the time". He commented that "whether there is an aether or not, electromagnetic fields certainly exist, and so also does the energy of the electrical oscillations" so that, "if we do not like the name of "aether", we must use another word as a peg to hang all these things upon." He concluded that "one cannot deny the bearer of these concepts a certain substantiality".<ref>Lorentz wrote:"One cannot deny to the bearer of these properties a certain substantiality, and if so, then one may, in all modesty, call true time the time measured by clocks which are fixed in this medium, and consider simultaneity as a primary concept." However, he went on to say that this was based on his conception of "infinite velocity", which according to his own theory is not physically realizable. Lorentz also admitted that the postulate of an absolute but undetectable rest frame was purely metaphysical, and had no empirical consequences.</ref> | |||
| When Einstein was still a student in the Zurich Polytechnic in 1900, he was very interested in the idea of aether. His initial proposal of research thesis was to do an experiment to measure how fast the Earth was moving through the aether.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Einstein: His life and Universe|url=https://archive.org/details/einsteinhislifeu0000isaa|url-access=registration|last=Isaacson|first=Walter|publisher=Simon & Schuster|year=2007|location=New York|pages=–48}}</ref> "The velocity of a wave is proportional to the square root of the elastic forces which cause propagation, and inversely proportional to the mass of the aether moved by these forces."<ref>Albert Einstein's 'First' Paper (1894 or 1895), http://www.straco.ch/papers/Einstein%20First%20Paper.pdf {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727021612/http://www.straco.ch/papers/Einstein |date=2020-07-27 }}</ref> | |||
| In 1916, after Einstein completed his foundational work on ], Lorentz wrote a letter to him in which he speculated that within general relativity the aether was re-introduced. In his response Einstein wrote that one can actually speak about a "new aether", but one may not speak of motion in relation to that aether. This was further elaborated by Einstein in some semi-popular articles (1918, 1920, 1924, 1930).<ref group="A" name="einsta" /><ref group="A" name="einstb" /><ref group="A" name="einstc" /><ref group="A" name="einstd" /><ref group="B" name="kosta" /><ref group="B" name="stach" /><ref group="B" name="kostb" /> | |||
| In the early 1920s, in a lecture which he was invited to give at Lorentz's university in Leiden, Einstein sought to reconcile the theory of relativity with his mentor's cherished concept of the aether. In this lecture Einstein stressed that, in general relativity, space is "endowed with physical quantities"<ref>He said in that 1920 speech: | |||
| :"... we may say that according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an aether. According to the general theory of relativity space without aether is unthinkable; for in such space there not only would be no propagation of light, but also no possibility of existence for standards of space and time (measuring-rods and clocks), nor therefore any space-time intervals in the physical sense. But this aether may not be thought of as endowed with the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it."</ref> | |||
| He pointed out that the aether had been relativized, and thereby lost the last mechanical property that Lorentz had left it, namely, its state of motion. Thus he held that general relativity attributed physical properties to space, including some kind of medium for light, although not a material one. Shortly before his lecture in Leiden in 1920 he admitted in the paper: "Grundgedanken und Methoden der Relativitätstheorie in ihrer Entwicklung dargestellt": | |||
| In 1918, Einstein publicly alluded to that new definition for the first time.<ref group=A name=einsta /> Then, in the early 1920s, in a lecture which he was invited to give at Lorentz's university in Leiden, Einstein sought to reconcile the theory of relativity with ]. In this lecture Einstein stressed that special relativity took away the last mechanical property of the aether: immobility. However, he continued that special relativity does not necessarily rule out the aether, because the latter can be used to give physical reality to acceleration and rotation. This concept was fully elaborated within ], in which physical properties (which are partially determined by matter) are attributed to space, but no substance or state of motion can be attributed to that "aether" (by which he meant curved space-time).<ref group=B name=kostb /><ref group=A name=einstb /><ref>Einstein 1920: ''We may say that according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an aether. According to the general theory of relativity space without aether is unthinkable; for in such space there not only would be no propagation of light, but also no possibility of existence for standards of space and time (measuring-rods and clocks), nor therefore any space-time intervals in the physical sense. But this aether may not be thought of as endowed with the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it.''</ref> | |||
| :Therefore I thought in 1905 that in physics one should not speak of the aether at all. This judgement was too radical though as we shall see with the next considerations about the general theory of relativity. It moreover remains, as before, allowed to assume a space-filling medium if one can refer to electromagnetic fields (and thus also for sure matter) as the condition thereof. | |||
| In another paper of 1924, named "Concerning the Aether", Einstein argued that Newton's absolute space, in which acceleration is absolute, is the "Aether of Mechanics". And within the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell and Lorentz one can speak of the "Aether of Electrodynamics", in which the aether possesses an absolute state of motion. As regards special relativity, also in this theory acceleration is absolute as in Newton's mechanics. However, the difference from the electromagnetic aether of Maxwell and Lorentz lies in the fact that "because it was no longer possible to speak, in any absolute sense, of simultaneous states at different locations in the aether, the aether became, as it were, four-dimensional since there was no objective way of ordering its states by time alone". Now the "aether of special relativity" is still "absolute", because matter is affected by the properties of the aether, but the aether is not affected by the presence of matter. This asymmetry was solved within general relativity. Einstein explained that the "aether of general relativity" is not absolute, because matter is influenced by the aether, just as matter influences the structure of the aether.<ref group=A name=einstc /> | |||
| In later years there have been a few individuals who advocated a neo-Lorentzian approach to physics, but it is Lorentzian only in the sense of positing an absolute true state of rest, which is undetectable and which plays no role in the predictions of the theory. (No violations of Lorentz covariance have ever been detected, despite strenuous efforts.) Hence these theories resemble the 19th century aether theories in name only. For example, the founder of quantum field theory, Paul Dirac, stated in 1951 in an article in Nature, titled "Is there an Aether?" that "we are rather forced to have an aether".<ref>Dirac wrote about his theory: "We have now the velocity at all points of space-time, playing a fundamental part in electrodynamics. It is natural to regard it as the velocity of some real physical thing. Thus with the new theory of electrodynamics we are rather forced to have an aether."</ref>. | |||
| The only similarity of this relativistic aether concept with the ] models lies in the presence of physical properties in space, which can be identified through ]. As historians such as ] argue, Einstein's views on the "new aether" are not in conflict with his abandonment of the aether in 1905. As Einstein himself pointed out, no "substance" and no state of motion can be attributed to that new aether. Einstein's use of the word "aether" found little support in the scientific community, and played no role in the continuing development of modern physics.<ref group=B name=kosta /><ref group=B name=stach /><ref group=B name=kostb /> | |||
| ==Continuing adherents== | |||
| A very small number of physicists (like ]<ref></ref> and ]) continued research on the aether into the first decades of the 20th century. However, no evidence of the sort sought by these individuals has ever passed the tests of modern scientific standards. Today the majority of physicists hold that there is no need to imagine that an aether (as a medium for light propagation) exists.{{Citation needed|date=July 2009}} They believe that neither Einstein's general theory of relativity nor quantum mechanics have need for positing its existence,{{Citation needed|date=July 2009}} that there is no evidence for its existence,{{Citation needed|date=July 2009}} and that the assumption of its existence is an unnecessary theory violating the principle of ]. It is difficult to develop an aether theory consistent with the results of all experiments of modern physics. Any new theory of aether would have to be consistent with all the ]s testing ] of special relativity, ], and relativistic ]. Some new "aether" concepts have been proposed in recent years, but the descriptions of these concepts differ in fundamental ways from the description of the classical luminiferous aether. | |||
| ==Aether concepts== | ==Aether concepts== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 153: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Div col|small=no}} | |||
| {{Col-begin}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{Col-1-of-3}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{Col-2-of-3}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| {{Col-3-of-3}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{col-end}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{Div col end}} | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | |||
| <references /></div> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| '''Footnotes''' | |||
| {{No footnotes|date=August 2009}} | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| <!--This list of works is too long. Please trim it down to the essential references.--> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Darrigol, Olivier | |||
| |year=2000 | |||
| |title= Electrodynamics from Ampére to Einstein | |||
| |place=Oxford | |||
| |publisher=Clarendon Press | |||
| |ISBN=0198505949}} | |||
| '''Citations''' | |||
| * Dirac, Paul: "Is there an Aether?", Nature 168 (1951), p. 906 | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ===Primary sources=== | |||
| * Einstein, Albert: (1909) ], ''Phys. Z.'', '''10''', 817-825. (review of aether theories, among other topics) | |||
| <references group=A> | |||
| <ref name=dirac>{{cite journal|last=Dirac |first=P. M. |author-link=Paul Dirac |title=Is there an Aether? |year=1951 |journal=] |volume=168 |issue=4282 |page=906 |url=http://home.tiscali.nl/physis/HistoricPaper/Dirac/Dirac1951b.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081217075000/http://home.tiscali.nl/physis/HistoricPaper/Dirac/Dirac1951b.pdf |archive-date=17 December 2008 |access-date=23 February 2017 |doi=10.1038/168906a0 |bibcode=1951Natur.168..906D |s2cid=4288946 }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=einselektro>{{Citation | |||
| * Einstein, Albert: "Ether and the Theory of Relativity" (1920), republished in ''Sidelights on Relativity'' (Dover, NY, 1922) | |||
| |doi=10.1002/andp.19053221004 | |||
| * Einstein, Albert: "Ideas and Opinions" pp. 281, 362. ISBN 0-517-88440-2 | |||
| |author=Einstein, Albert | |||
| |year=1905a | |||
| |title=Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper | |||
| |journal=Annalen der Physik | |||
| |volume=322 | |||
| |issue=10 | |||
| |pages=891–921|bibcode = 1905AnP...322..891E | |||
| |doi-access=free | |||
| }}. See also: {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051125150029/http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/ |date=2005-11-25 }}.</ref> | |||
| <ref name=einsdev>Einstein, Albert: (1909) ] {{Cite web |url=http://en.wikisource.org/The_Development_of_Our_Views_on_the_Composition_and_Essence_of_Radiation |title=Archived copy |access-date=2024-01-14 |archive-date=2008-04-23 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080423225347/http://en.wikisource.org/The_Development_of_Our_Views_on_the_Composition_and_Essence_of_Radiation |url-status=bot: unknown }}, ''Phys. Z.'', '''10''', 817–825. (review of aether theories, among other topics)</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Janssen, Michel & Mecklenburg, Matthew | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |contribution=From classical to relativistic mechanics: Electromagnetic models of the electron | |||
| |editor=V. F. Hendricks, et.al. | |||
| |journal=Interactions: Mathematics, Physics and Philosophy | |||
| |pages= 65–134 | |||
| |place=Dordrecht | |||
| |publisher=Springer | |||
| |contribution-url=http://www.tc.umn.edu/~janss011/}} | |||
| <ref name=einsta>{{Citation | author=A. Einstein | year=1918 | title=Dialog about Objections against the Theory of Relativity | journal=Naturwissenschaften | volume=6|issue=48|pages=697–702|bibcode = 1918NW......6..697E |doi = 10.1007/BF01495132 | title-link=s:Translation:Dialog about Objections against the Theory of Relativity | s2cid=28132355 }}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Jannsen, Michel & Stachel, John | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| |title=The Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies | |||
| |url=http://www.mpiwg-berlin.mpg.de/Preprints/P265.PDF}} | |||
| <ref name=einstb>Einstein, Albert: "]" (1920), republished in ''Sidelights on Relativity'' (Methuen, London, 1922)</ref> | |||
| * Hoffman, Banesh: ''Relativity and Its Roots'' (Freeman, New York, 1983). | |||
| <ref name=einstc>{{Citation | author=A. Einstein | year=1924 | title=Über den Äther | journal=Verhandlungen der Schweizerischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft | volume=105|issue=2|pages=85–93 }}. See also an English translation: {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101104022846/http://www.oe.eclipse.co.uk/nom/aether.htm |date=2010-11-04 }}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| <ref name=einstd>{{Cite web|url=http://www.alberteinstein.info/db/ViewImage.do?DocumentID=34095&Page=1|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110616123244/http://www.alberteinstein.info/db/ViewImage.do?DocumentID=34095&Page=1|url-status=unfit|title=Einstein Archives Online|archivedate=16 June 2011}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=fresnel>Fresnel, A. (1818), "Lettre de M. Fresnel à M. Arago sur l'influence du mouvement terrestre dans quelques phénomènes d'optique", ''Annales de Chimie et de Physique'', '''9''': 57–66 (Sep. 1818), 286–7 (Nov. 1818); reprinted in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol.{{nnbsp}}2 (1868), ; translated as in K.F. Schaffner, ''Nineteenth-Century Aether Theories'', Pergamon, 1972 ({{doi|10.1016/C2013-0-02335-3}}), pp.{{nnbsp}}125–35; also translated (with several errors) by R.R. Traill as "Letter from Augustin Fresnel to François Arago concerning the influence of terrestrial movement on several optical phenomena", ''General Science Journal'', 23 January 2006 ().</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lara>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Larmor, Joseph | |author=Larmor, Joseph | ||
| |year=1897 | |year=1897 | ||
| |title=On a Dynamical Theory of the Electric and Luminiferous Medium, Part 3, Relations with material media | |title=On a Dynamical Theory of the Electric and Luminiferous Medium, Part 3, Relations with material media | ||
| |journal=Philosophical |
|journal=Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society | ||
| |volume=190 | |volume=190 | ||
| |pages=205–300 | |pages=205–300 | ||
| |doi=10.1098/rsta.1897.0020|bibcode = 1897RSPTA.190..205L |title-link=s:Dynamical Theory of the Electric and Luminiferous Medium III | |||
| |url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k559956/f226.table}} | |||
| |doi-access=free | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=larb>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Larmor, Joseph | |author=Larmor, Joseph | ||
| |year=1900 | |year=1900 | ||
| |title=Aether and Matter | |title=Aether and Matter | ||
| |publisher=Cambridge University Press | |publisher=Cambridge University Press|title-link=s:Aether and Matter | ||
| }}</ref> | |||
| |url=http://www.archive.org/details/aethermatterdeve00larmuoft}} | |||
| <ref name=lora>{{Citation | |||
| |last=Lorentz | |last=Lorentz | ||
| |first=Hendrik Antoon | |first=Hendrik Antoon | ||
| |year=1892 |
|year=1892 | ||
| |title=De relatieve beweging van de aarde en den aether | |||
| |chapter=] | |||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |title=Abhandlungen über Theoretische Physik | |||
| |journal=Zittingsverlag Akad. V. Wet. | |||
| |pages=443-447 | |||
| |pages=74–79 | |||
| |place=Leipzig | |||
| |volume=1|title-link=s:nl:De relatieve beweging van de aarde en den aether | |||
| |publisher=B.G. Teubner}} | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lorb>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | ||
| |year=1895 | |year=1895 | ||
| |title= |
|title=Versuch einer Theorie der electrischen und optischen Erscheinungen in bewegten Körpern | ||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |place=Leiden | |||
| |location=Leiden | |||
| |publisher=E.J. Brill}} | |||
| |publisher=E.J. Brill|title-link=s:de:Versuch einer Theorie der electrischen und optischen Erscheinungen in bewegten Körpern | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lorc>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | |||
| |year=1899 | |||
| |title=Simplified Theory of Electrical and Optical Phenomena in Moving Systems | |||
| |journal=Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences | |||
| |volume=1 | |||
| |pages=427–442|title-link=s:Simplified Theory of Electrical and Optical Phenomena in Moving Systems | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lord>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | ||
| |year=1904 | |year=1904 | ||
| |title= |
|title=Electromagnetic phenomena in a system moving with any velocity smaller than that of light | ||
| |journal=Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences | |journal=Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences | ||
| |volume=6 | |volume=6 | ||
| |pages=809–831 |
|pages=809–831|title-link=s:Electromagnetic phenomena | ||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lore>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon | |||
| |year=1921 | |||
| |title=Deux Mémoires de Henri Poincaré sur la Physique Mathématique | |||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |journal=Acta Mathematica | |||
| |volume=38 | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| |pages=293–308 | |||
| |doi=10.1007/BF02392073|title-link=s:fr:Deux Mémoires de Henri Poincaré sur la Physique Mathématique | |||
| |doi-access=free | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lorf>{{Citation | author=Lorentz, H.A. | year=1928 | title=Conference on the Michelson-Morley Experiment |journal=The Astrophysical Journal | volume=68 | pages =345–351 | bibcode=1928ApJ....68..341M | last2=Lorentz | first2=H. A. | last3=Miller | first3=D. C. | last4=Kennedy | first4=R. J. | last5=Hedrick | first5=E. R. | last6=Epstein | first6=P. S. | doi=10.1086/143148| doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=maxa>{{cite EB9 |mode=cs2 | |||
| * {{Citation | |||
| |last=Maxwell | |last=Maxwell | ||
| |first=James Clerk | |first=James Clerk | ||
| |wstitle=Ether | |||
| |year=1878 | |||
| |title=Ether | |||
| |journal=Encyclopædia Britannica Ninth Edition | |||
| |volume=8 | |volume=8 | ||
| |pages= |
|pages=568–572}}</ref> | ||
| |url=http://en.wikisource.org/Encyclop%C3%A6dia_Britannica_Ninth_Edition/Ether}} | |||
| <ref name=maxb> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| {{Cite web | |||
| |author=Michelson, Albert Abraham | |||
| |last = Maxwell | |||
| |title=] | |||
| |first = JC | |||
| |journal=American Journal of Science | |||
| |year = 1865 | |||
| |volume=22 | |||
| |title = ''A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field'' (Part 1) | |||
| |year=1881 | |||
| |url = http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/19/A_Dynamical_Theory_of_the_Electromagnetic_Field.pdf | |||
| |pages=120–129}} | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110728140123/http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/19/A_Dynamical_Theory_of_the_Electromagnetic_Field.pdf | |||
| |archive-date = 2011-07-28 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=newton>Newton, Isaac: '''' (1704). Fourth edition of 1730. (Republished 1952 (Dover: New York), with commentary by Bernard Cohen, Albert Einstein, and Edmund Whittaker).</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Michelson, Albert Abraham & Morley, Edward Williams | |||
| |title=] | |||
| |journal=American Journal of Science | |||
| |volume=34 | |||
| |year=1887 | |||
| |pages=333–345}} | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Miller, Arthur I. | |||
| |year=1981 | |||
| |title= Albert Einstein’s special theory of relativity. Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905–1911) | |||
| |place= Reading | |||
| |publisher=Addison–Wesley | |||
| |isbn=0-201-04679-2}} | |||
| <ref name=poinca>{{Citation | |||
| * Newton, Isaac: '''' (1704). Fourth edition of 1730. (Republished 1952 (Dover: New York), with commentary by Bernard Cohen, Albert Einstein, and Edmund Whittaker). | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Poincaré, Henri | |author=Poincaré, Henri | ||
| |year=1900 | |year=1900 | ||
| |title= |
|title=La théorie de Lorentz et le principe de réaction | ||
| |journal=Archives |
|journal=Archives Néerlandaises des Sciences Exactes et Naturelles | ||
| |volume=5 | |volume=5 | ||
| |pages=252–278|title-link=s:fr:La théorie de Lorentz et le principe de réaction | |||
| |pages=252–278}}. See also the . | |||
| }}. See also the {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080626193037/http://www.physicsinsights.org/poincare-1900.pdf |date=2008-06-26 }}.</ref> | |||
| <ref name=poincb>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Poincaré, Henri | |author=Poincaré, Henri | ||
| |year= |
|year=1904–1906 | ||
| |chapter=] | |chapter=] | ||
| |editor=Rogers, Howard J. | |editor=Rogers, Howard J. | ||
| Line 258: | Line 314: | ||
| |pages=604–622 | |pages=604–622 | ||
| |publisher=Houghton, Mifflin and Company | |publisher=Houghton, Mifflin and Company | ||
| |place=Boston and New York}} | |place=Boston and New York}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name=poincc>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Poincaré, Henri | |author=Poincaré, Henri | ||
| |year= |
|year=1905b | ||
| |title= |
|title=Sur la dynamique de l'électron | ||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |journal=Comptes Rendus | |journal=Comptes Rendus | ||
| |volume=140 | |volume=140 | ||
| |pages=1504–1508 |
|pages=1504–1508|title-link=s:fr:Sur la dynamique de l'électron (juin) | ||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=poincd>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Poincaré, Henri | |author=Poincaré, Henri | ||
| |year=1906 | |year=1906 | ||
| |title= |
|title=Sur la dynamique de l'électron | ||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |journal=Rendiconti del Circolo matematico di Palermo | |||
| |journal=Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo | |||
| |volume=21 | |volume=21 | ||
| |pages=129–176 | |pages=129–176 | ||
| |doi=10.1007/BF03013466 |
|doi=10.1007/BF03013466|bibcode=1906RCMP...21..129P | ||
| |hdl=2027/uiug.30112063899089 | |||
| |s2cid=120211823 | |||
| |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1428444 | |||
| |hdl-access=free | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=stokes>{{Cite journal|author=G. G. Stokes|title=On the Aberration of Light |journal=Philosophical Magazine |volume=27 |issue=177 |year=1845 |pages=9–15 |doi=10.1080/14786444508645215|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1431057 }}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| </references> | |||
| ===Experiments=== | |||
| <references group=E> | |||
| <ref name=Airy>{{Cite journal|author=Airy, G.B.|title=On the Supposed Alteration in the Amount of Astronomical Aberration of Light, Produced by the Passage of the Light through a Considerable Thickness of Refracting Medium|journal=Proceedings of the Royal Society|volume=20|issue=130–138|year=1871|pages=35–39|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k56114d/f79|bibcode=1871RSPS...20...35A|doi=10.1098/rspl.1871.0011|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515081514/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k56114d/f79|archive-date=2012-05-15|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Arago>{{Cite journal|author=Arago, A.|title=Mémoire sur la vitesse de la lumière, lu à la prémière classe de l'Institut, le 10 décembre 1810|journal=Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences |volume=36|year=1810–1853|pages=38–49}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Brace1>{{Cite journal|author=Brace, DeWitt Bristol|title=On Double Refraction in Matter moving through the Aether|journal=Philosophical Magazine|volume=7|issue=40|year=1904|pages=317–329|doi=10.1080/14786440409463122|title-link=s:On Double Refraction in Matter moving through the Aether}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Brace2>{{Cite journal|author=Brace, D.B.|title=The Aether 'Drift' and Rotary Polarization|journal=Philosophical Magazine|volume=10|issue=57|year=1905|pages=383–396|doi=10.1080/14786440509463384|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1430784}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Coudres>{{Cite journal|author=Des Coudres, Th.|title=Ueber das Verhalten des Lichtäthers bei den Bewegungen der Erde|journal=Annalen der Physik|volume=274|issue=9|year=1889|pages=–79|doi=10.1002/andp.18892740908|url=https://archive.org/details/annalenderphysi80unkngoog|bibcode = 1889AnP...274...71D }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Fizeau1>{{Cite journal|author=Fizeau, H.|title=The Hypotheses Relating to the Luminous Aether, and an Experiment which Appears to Demonstrate that the Motion of Bodies Alters the Velocity with which Light Propagates itself in their Interior|journal=Philosophical Magazine|volume=2|year=1851|pages=568–573|title-link=s:The Hypotheses Relating to the Luminous Aether|doi=10.1080/14786445108646934}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Fizeau2>{{Cite journal|author=Fizeau, H.|title=Ueber eine Methode, zu untersuchen, ob das Polarisationsazimut eines gebrochenen Strahls durch die Bewegung des brechenden Körpers geändert werde|journal=Annalen der Physik|volume=190|issue=12|year=1861|pages=554–587|doi=10.1002/andp.18621901204|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15199j/f572|bibcode=1861AnP...190..554F|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515083035/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15199j/f572|archive-date=2012-05-15}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Haga>{{Cite journal|author=Haga, H.|title=Über den Klinkerfuesschen Versuch|journal=Physikalische Zeitschrift|volume=3|year=1902|pages=|url=https://archive.org/details/physikalischeze00simogoog}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Hammar>{{cite journal | |||
| | author= G. W. Hammar | |||
| | year= 1935 | |||
| | title= The Velocity of Light Within a Massive Enclosure | |||
| | journal= ] | |||
| | volume= 48 | |||
| | issue= 5 | |||
| | pages= 462–463 | |||
| | doi= 10.1103/PhysRev.48.462.2 | |||
| |bibcode = 1935PhRv...48..462H }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Hoek>{{Cite journal|author=Hoek, M.|title=Determination de la vitesse avec laquelle est entrainée une onde lumineuse traversant un milieu en mouvement|journal=Verslagen en Mededeelingen|volume=2|year=1868|pages=–194|url=https://archive.org/details/d2verslagenenmed02akad}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=kenn>{{cite journal |last=Kennedy |first=R. J. |author2=Thorndike, E. M. |year=1932 |title=Experimental Establishment of the Relativity of Time |journal=Physical Review |volume=42 |issue=3 |pages=400–418 |doi=10.1103/PhysRev.42.400 |bibcode = 1932PhRv...42..400K }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Ketteler>{{Cite journal|author=Ketteler, Ed.|title=Ueber den Einfluss der astronomischen Bewegungen auf die optischen Erscheinungen|journal=Annalen der Physik|volume=220|issue=9|year=1872|pages=109–127|doi=10.1002/andp.18712200906|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k152289/f121|bibcode=1871AnP...220..109K|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515091718/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k152289/f121|archive-date=2012-05-15}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Klinkerfues>{{Cite journal|author=Klinkerfues, Ernst Friedrich Wilhelm|title=Versuche über die Bewegung der Erde und der Sonne im Aether|journal=Astronomische Nachrichten|volume=76|issue=3|year=1870|pages=33–38|bibcode = 1870AN.....76...33K |doi = 10.1002/asna.18700760302 |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1424677}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Koenigsberger>{{Cite journal|author=Königsberger, J.|title=Induktionswirkung im Dielektrikum und Bewegung des Aethers|journal=Berichte der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft zu Freiburg I. Br.|volume=13|year=1905|pages=–100|url=https://archive.org/details/berichtedernatur131903natu}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Lodge>{{Cite journal|author=Lodge, Oliver J.|title=Aberration Problems|journal=]|volume=184|year=1893|pages=727–804|doi=10.1098/rsta.1893.0015|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k559898/f781|bibcode=1893RSPTA.184..727L|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160124145205/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k559898/f781|archive-date=2016-01-24|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Lodge2>{{Cite journal|author=Lodge, Oliver J.|title=Experiments on the Absence of Mechanical Connexion between Ether and Matter|journal=]|volume=189|year=1897|pages=149–166|bibcode = 1897RSPTA.189..149L |doi = 10.1098/rsta.1897.0006 |title-link=s:en:Experiments on the Absence of Mechanical Connexion between Ether and Matter|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=masc1>{{Cite journal|author=Mascart, E.|title=Sur les modifications qu'éprouve la lumière par suite du mouvement de la source lumineuse et du mouvement de l'observateur|journal=Annales Scientifiques de l'École Normale Supérieure|series=Série 2|volume=1|year=1872|pages=157–214|doi=10.24033/asens.81|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=masc2>{{Cite journal|author=Mascart, E.|title=Sur les modifications qu'éprouve la lumière par suite du mouvement de la source lumineuse et du mouvement de l'observateur (deuxième partie)|journal=Annales Scientifiques de l'École Normale Supérieure|series=Série 2|volume=3|year=1874|pages=363–420|doi=10.24033/asens.118|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=michel1>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Michelson, Albert Abraham | |||
| |title=The Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether | |||
| |journal=American Journal of Science | |||
| |volume=22 | |||
| |issue=128 | |||
| |year=1881 | |||
| |pages=120–129 | |||
| |doi=10.2475/ajs.s3-22.128.120|title-link=s:The Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether | |||
| |bibcode=1881AmJS...22..120M | |||
| |s2cid=130423116 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=michel2>{{Cite journal | |||
| |author1=Michelson, A. A. |author2=Morley, E.W. | |||
| |name-list-style=amp |title=Influence of Motion of the Medium on the Velocity of Light | |||
| |journal=Am. J. Sci. | |||
| |volume=31 | |||
| |issue=185 | |||
| |year=1886 | |||
| |pages=377–386|bibcode=1886AmJS...31..377M|doi=10.2475/ajs.s3-31.185.377|title-link=s:Influence of Motion of the Medium on the Velocity of Light | |||
| |s2cid=131116577 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=michel3>{{Citation | |||
| |author1=Michelson, Albert Abraham |author2=Morley, Edward Williams | |||
| |name-list-style=amp |title=On the Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether | |||
| |journal=American Journal of Science | |||
| |volume=34 | |||
| |issue=203 | |||
| |year=1887 | |||
| |pages=333–345 | |||
| |doi=10.2475/ajs.s3-34.203.333|title-link=s:On the Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether | |||
| |bibcode=1887AmJS...34..333M | |||
| |s2cid=124333204 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Rayleigh1>{{Cite journal|author=Lord Rayleigh|title=Is Rotatory Polarization Influenced by the Earth's Motion?|journal=Philosophical Magazine|volume=4|issue=20|year=1902|pages=215–220|doi=10.1080/14786440209462836|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1430658}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Rayleigh2>{{Cite journal|author=Lord Rayleigh|title=Does Motion through the Aether cause Double Refraction?|journal=Philosophical Magazine|volume=4|issue=24|year=1902|pages=678–683|doi=10.1080/14786440209462891|title-link=s:Does Motion through the Aether cause Double Refraction?}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Roentgen>{{Cite journal|author=Röntgen, W.|title=Über die durch Bewegung eines im homogenen elektrischen Felde befindlichen Dielektricums hervorgerufene elektrodynamische Kraft|journal=Berliner Sitzungsberichte|volume=2. Halbband|year=1888|pages=–28|url=https://archive.org/details/sitzungsberichte1888deut|url-status=live|archive-url=http://archive.wikiwix.com/cache/20160226015024/https://archive.org/details/sitzungsberichte1888deut|archive-date=2016-02-26}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Sagnac1>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Sagnac, Georges | |||
| |year=1913 | |||
| |title=L'éther lumineux démontré par l'effet du vent relatif d'éther dans un interféromètre en rotation uniforme | |||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |journal=Comptes Rendus | |||
| |volume=157 | |||
| |pages=708–710|title-link=s:fr:L'éther lumineux démontré | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Sagnac2>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Sagnac, Georges | |||
| |year=1913 | |||
| |title=Sur la preuve de la réalité de l'éther lumineux par l'expérience de l'interférographe tournant | |||
| |trans-title=] | |||
| |journal=Comptes Rendus | |||
| |volume=157 | |||
| |pages=1410–1413|title-link=s:fr:Sur la preuve de la réalité de l'éther lumineux | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Strasser>{{Cite journal|author=Strasser, B.|title=Der Fizeausche Versuch über die Änderung des Polarisationsazimuts eines gebrochenen Strahles durch die Bewegung der Erde|journal=Annalen der Physik|volume=329|issue=11|year=1907|pages=137–144|doi=10.1002/andp.19073291109|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15331g/f143|bibcode=1907AnP...329..137S|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515083054/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15331g/f143|archive-date=2012-05-15}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Trouton1>{{Cite journal|author=Trouton, F.T.|title=The results of an electrical experiment, involving the relative motion of the Earth and the Ether, Suggested by the Late Professor FitzGerald|journal=Transactions of the Royal Dublin Society|volume=7|year=1902|pages=–384|url=https://archive.org/details/scientifictransa27roya}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Trouton2>{{Cite journal|author1=Trouton, F. T.|author2=Noble, H. R.|title=The Mechanical Forces Acting on a Charged Electric Condenser Moving through Space|journal=]|volume=202|issue=346–358|year=1903|pages=165–181|doi=10.1098/rsta.1904.0005|url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k56007v/f199|bibcode=1904RSPTA.202..165T|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120515090155/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k56007v/f199|archive-date=2012-05-15|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Zehnder>{{Cite journal|author=Zehnder, L.|title=Ueber die Durchlässigkeit fester Körper für den Lichtäther|journal=Annalen der Physik|volume=291|issue=5|year=1895|pages=–81|doi=10.1002/andp.18952910505|url=https://archive.org/details/annalenderphysi205unkngoog|bibcode = 1895AnP...291...65Z }}</ref> | |||
| </references> | |||
| ===Secondary sources=== | |||
| <references group=B> | |||
| <ref name=born>{{Citation | author=Born, M. | title = Physics in my generation | url = https://archive.org/details/physucsinmygener006567mbp | place=London & New York | publisher=Pergamon Press | year =1956}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=darrigol>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Darrigol, Olivier | |||
| |year=2000 | |||
| |title=Electrodynamics from Ampère to Einstein | |||
| |place=Oxford | |||
| |publisher=Clarendon Press | |||
| |isbn=978-0-19-850594-5 | |||
| |url-access=registration | |||
| |url=https://archive.org/details/electrodynamicsf0000darr | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=jana>{{Citation | |||
| |last1 = Janssen | |||
| |first1 = Michel | |||
| |last2 = Mecklenburg | |||
| |first2 = Matthew | |||
| |year = 2007 | |||
| |title = From classical to relativistic mechanics: Electromagnetic models of the electron | |||
| |editor = V. F. Hendricks | |||
| |journal = Interactions: Mathematics, Physics and Philosophy | |||
| |pages = 65–134 | |||
| |place = Dordrecht | |||
| |url = http://www.tc.umn.edu/~janss011/ | |||
| |display-editors = etal | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080704195656/http://www.tc.umn.edu/%7Ejanss011/ | |||
| |archive-date = 2008-07-04 | |||
| |access-date = 2004-04-16 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=janb>{{Citation | |||
| |author1 = Jannsen, Michel | |||
| |author2 = Stachel, John | |||
| |name-list-style = amp | |||
| |year = 2008 | |||
| |title = The Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies | |||
| |url = http://www.mpiwg-berlin.mpg.de/Preprints/P265.PDF | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150929110752/http://www.mpiwg-berlin.mpg.de/Preprints/P265.PDF | |||
| |archive-date = 2015-09-29 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=kosta>{{Citation|author=Kostro, L.|chapter=An outline of the history of Einstein's relativistic ether concept|title=Studies in the history of general relativity |editor1=Jean Eisenstaedt |editor2=Anne J. Kox |volume=3|pages=260–280|isbn=978-0-8176-3479-7|publisher=Birkhäuser|location=Boston-Basel-Berlin|year=1992}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=kostb>{{Citation|author=Kostro, L.|title=Albert Einstein's New Ether and his General Relativity|journal=Proceedings of the Conference of Applied Differential Geometry|pages=78–86|year=2001|url=http://www.mathem.pub.ro/proc/bsgp-10/K10-KOSTRO.PDF|postscript=.|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180411052528/http://www.mathem.pub.ro/proc/bsgp-10/K10-KOSTRO.PDF|archive-date=2018-04-11}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=laub>{{Cite journal|author=Laub, Jakob|title=Über die experimentellen Grundlagen des Relativitätsprinzips|journal=Jahrbuch der Radioaktivität und Elektronik|volume=7|year=1910|pages=405–463}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=miller>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Miller, Arthur I. | |||
| |year=1981 | |||
| |title=Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905–1911) | |||
| |place=Reading | |||
| |publisher=Addison–Wesley | |||
| |isbn=978-0-201-04679-3 | |||
| |url-access=registration | |||
| |url=https://archive.org/details/alberteinsteinss0000mill | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=pais>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Pais, Abraham | |author=Pais, Abraham | ||
| |year=1982 | |year=1982 | ||
| |title= Subtle is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein | |title= ] | ||
| |place = New York | |place = New York | ||
| |publisher=Oxford University Press | |publisher=Oxford University Press | ||
| |isbn=0-19-520438- |
|isbn=978-0-19-520438-4}}</ref> | ||
| * Sagnac, G. & E. Bouty, "The Luminiferous Aether Demonstrated by the Effect of the Relative Motion of the Aether in an Interferometer in Uniform Rotation"(in French), Comptes Rendus (Paris) 157 (1913), p. 708-710 | |||
| <ref name=schaffner>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Schaffner, Kenneth F. | |author=Schaffner, Kenneth F. | ||
| |year=1972 | |year=1972 | ||
| Line 293: | Line 541: | ||
| |publisher=Pergamon Press | |publisher=Pergamon Press | ||
| |place= Oxford | |place= Oxford | ||
| | |
|isbn=978-0-08-015674-3}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name=stach>{{Citation|author=Stachel, J.|title=Why Einstein reinvented the ether |journal=Physics World|volume=14 |issue=6 |year=2001|pages=55–56|postscript=.|doi=10.1088/2058-7058/14/6/33 }}</ref> | |||
| *{{cite book | author=Tipler, Paul; Llewellyn, Ralph | title=Modern Physics (4th ed.) | publisher=W. H. Freeman | year=2002 | isbn=0-7167-4345-0}} | |||
| <ref name=whitt>{{Citation | |||
| |author=Whittaker, Edmund Taylor | |author = ] | ||
| |year=1910 | |year = 1910 | ||
| |title= A History of the |
|title = ] | ||
| |edition=1 | |edition = 1 | ||
| |place=Dublin | |place = Dublin | ||
| |publisher=Longman, Green and Co. | |publisher = Longman, Green and Co. | ||
| }}</ref> | |||
| |url=http://www.archive.org/details/historyoftheorie00whitrich}} | |||
| <ref name=wien>{{Cite journal | last=Wien|first=Wilhelm| year=1898 | title=Über die Fragen, welche die translatorische Bewegung des Lichtäthers betreffen (Referat für die 70. Versammlung deutsche Naturforscher und Aerzte in Düsseldorf, 1898)| journal=Annalen der Physik| volume =301| issue=3| pages =I–XVIII|title-link=s:de:Translatorische Bewegung des Lichtäthers}}.</ref> | |||
| </references> | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| * - A more complete table of results that have claimed to detect an aether. | |||
| {{Commons category|Luminiferous aether}} | |||
| * - includes a lengthy list of aether experiments, among others | |||
| {{Wikisource|1911 Encyclopædia Britannica/Aether}} | |||
| * - Lord Rayleigh's address | |||
| * ] (1915) , '']'' 21(6):299–309. | |||
| * - a categorised compendium of articles relating to the emergence of scientific theories that reference the aether, or ] of space. | |||
| * {{Citation |url=http://www.thomist.org/jourl/2004/July/2004%20July%20A%20Dec.htm |journal=The Thomist |first1=Christopher A. |last1=Decaen |volume=68 |issue=3 |pages=375–429 |year=2004 |title=Aristotle's Aether and Contemporary Science |access-date=2011-03-05 |postscript=. |doi=10.1353/tho.2004.0015 |s2cid=171374696 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120305053917/http://www.thomist.org/jourl/2004/July/2004%20July%20A%20Dec.htm |archive-date=2012-03-05 |url-status=dead }} | |||
| * - Albert Einstein's 1920 inauguration address at the University of Leiden (actually delivered on ] ]). | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170913035152/http://www.keelynet.com/osborn/rey7.htm |date=2017-09-13 }} – Lord Rayleigh's address | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| {{Isaac Newton}} | |||
| {{Tests of special relativity}} | |||
| {{Portal bar|Physics|History of science |Mathematics}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Luminiferous Aether}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Luminiferous Aether}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:47, 19 October 2024
Obsolete postulated medium for the propagation of light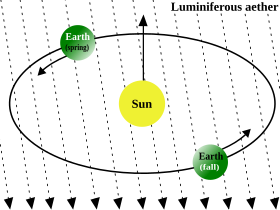
Luminiferous aether or ether (luminiferous meaning 'light-bearing') was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum (space completely filled with matter) of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light.
The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 19th century, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it.
The negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) suggested that the aether did not exist, a finding that was confirmed in subsequent experiments through the 1920s. This led to considerable theoretical work to explain the propagation of light without an aether. A major breakthrough was the special theory of relativity, which could explain why the experiment failed to see aether, but was more broadly interpreted to suggest that it was not needed. The Michelson–Morley experiment, along with the blackbody radiator and photoelectric effect, was a key experiment in the development of modern physics, which includes both relativity and quantum theory, the latter of which explains the particle-like nature of light.
The history of light and aether
See also: Timeline of luminiferous aetherParticles vs. waves
Main article: Wave–particle dualityIn the 17th century, Robert Boyle was a proponent of an aether hypothesis. According to Boyle, the aether consists of subtle particles, one sort of which explains the absence of vacuum and the mechanical interactions between bodies, and the other sort of which explains phenomena such as magnetism (and possibly gravity) that are, otherwise, inexplicable on the basis of purely mechanical interactions of macroscopic bodies, "though in the ether of the ancients there was nothing taken notice of but a diffused and very subtle substance; yet we are at present content to allow that there is always in the air a swarm of streams moving in a determinate course between the north pole and the south".
Christiaan Huygens's Treatise on Light (1690) hypothesized that light is a wave propagating through an aether. He and Isaac Newton could only envision light waves as being longitudinal, propagating like sound and other mechanical waves in fluids. However, longitudinal waves necessarily have only one form for a given propagation direction, rather than two polarizations like a transverse wave. Thus, longitudinal waves can not explain birefringence, in which two polarizations of light are refracted differently by a crystal. In addition, Newton rejected light as waves in a medium because such a medium would have to extend everywhere in space, and would thereby "disturb and retard the Motions of those great Bodies" (the planets and comets) and thus "as it [light's medium] is of no use, and hinders the Operation of Nature, and makes her languish, so there is no evidence for its Existence, and therefore it ought to be rejected".
Isaac Newton contended that light is made up of numerous small particles. This can explain such features as light's ability to travel in straight lines and reflect off surfaces. Newton imagined light particles as non-spherical "corpuscles", with different "sides" that give rise to birefringence. But the particle theory of light can not satisfactorily explain refraction and diffraction. To explain refraction, Newton's Third Book of Opticks (1st ed. 1704, 4th ed. 1730) postulated an "aethereal medium" transmitting vibrations faster than light, by which light, when overtaken, is put into "Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission", which caused refraction and diffraction. Newton believed that these vibrations were related to heat radiation:
Is not the Heat of the warm Room convey'd through the vacuum by the Vibrations of a much subtiler Medium than Air, which after the Air was drawn out remained in the Vacuum? And is not this Medium the same with that Medium by which Light is refracted and reflected, and by whose Vibrations Light communicates Heat to Bodies, and is put into Fits of easy Reflexion and easy Transmission?
In contrast to the modern understanding that heat radiation and light are both electromagnetic radiation, Newton viewed heat and light as two different phenomena. He believed heat vibrations to be excited "when a Ray of Light falls upon the Surface of any pellucid Body". He wrote, "I do not know what this Aether is", but that if it consists of particles then they must be
exceedingly smaller than those of Air, or even than those of Light: The exceeding smallness of its Particles may contribute to the greatness of the force by which those Particles may recede from one another, and thereby make that Medium exceedingly more rare and elastic than Air, and by consequence exceedingly less able to resist the motions of Projectiles, and exceedingly more able to press upon gross Bodies, by endeavoring to expand itself.
Bradley suggests particles
In 1720, James Bradley carried out a series of experiments attempting to measure stellar parallax by taking measurements of stars at different times of the year. As the Earth moves around the Sun, the apparent angle to a given distant spot changes. By measuring those angles the distance to the star can be calculated based on the known orbital circumference of the Earth around the Sun. He failed to detect any parallax, thereby placing a lower limit on the distance to stars.
During these experiments, Bradley also discovered a related effect; the apparent positions of the stars did change over the year, but not as expected. Instead of the apparent angle being maximized when the Earth was at either end of its orbit with respect to the star, the angle was maximized when the Earth was at its fastest sideways velocity with respect to the star. This effect is now known as stellar aberration.
Bradley explained this effect in the context of Newton's corpuscular theory of light, by showing that the aberration angle was given by simple vector addition of the Earth's orbital velocity and the velocity of the corpuscles of light, just as vertically falling raindrops strike a moving object at an angle. Knowing the Earth's velocity and the aberration angle enabled him to estimate the speed of light.
Explaining stellar aberration in the context of an aether-based theory of light was regarded as more problematic. As the aberration relied on relative velocities, and the measured velocity was dependent on the motion of the Earth, the aether had to be remaining stationary with respect to the star as the Earth moved through it. This meant that the Earth could travel through the aether, a physical medium, with no apparent effect – precisely the problem that led Newton to reject a wave model in the first place.
Wave-theory triumphs
A century later, Thomas Young and Augustin-Jean Fresnel revived the wave theory of light when they pointed out that light could be a transverse wave rather than a longitudinal wave; the polarization of a transverse wave (like Newton's "sides" of light) could explain birefringence, and in the wake of a series of experiments on diffraction the particle model of Newton was finally abandoned. Physicists assumed, moreover, that, like mechanical waves, light waves required a medium for propagation, and thus required Huygens's idea of an aether "gas" permeating all space.
However, a transverse wave apparently required the propagating medium to behave as a solid, as opposed to a fluid. The idea of a solid that did not interact with other matter seemed a bit odd, and Augustin-Louis Cauchy suggested that perhaps there was some sort of "dragging", or "entrainment", but this made the aberration measurements difficult to understand. He also suggested that the absence of longitudinal waves suggested that the aether had negative compressibility. George Green pointed out that such a fluid would be unstable. George Gabriel Stokes became a champion of the entrainment interpretation, developing a model in which the aether might, like pine pitch, be dilatant (fluid at slow speeds and rigid at fast speeds). Thus the Earth could move through it fairly freely, but it would be rigid enough to support light.
Electromagnetism
In 1856, Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch measured the numerical value of the ratio of the electrostatic unit of charge to the electromagnetic unit of charge. They found that the ratio between the electrostatic unit of charge and the electromagnetic unit of charge is the speed of light c. The following year, Gustav Kirchhoff wrote a paper in which he showed that the speed of a signal along an electric wire was equal to the speed of light. These are the first recorded historical links between the speed of light and electromagnetic phenomena.
James Clerk Maxwell began working on Michael Faraday's lines of force. In his 1861 paper On Physical Lines of Force he modelled these magnetic lines of force using a sea of molecular vortices that he considered to be partly made of aether and partly made of ordinary matter. He derived expressions for the dielectric constant and the magnetic permeability in terms of the transverse elasticity and the density of this elastic medium. He then equated the ratio of the dielectric constant to the magnetic permeability with a suitably adapted version of Weber and Kohlrausch's result of 1856, and he substituted this result into Newton's equation for the speed of sound. On obtaining a value that was close to the speed of light as measured by Hippolyte Fizeau, Maxwell concluded that light consists in undulations of the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena.
Maxwell had, however, expressed some uncertainties surrounding the precise nature of his molecular vortices and so he began to embark on a purely dynamical approach to the problem. He wrote another paper in 1864, entitled "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field", in which the details of the luminiferous medium were less explicit. Although Maxwell did not explicitly mention the sea of molecular vortices, his derivation of Ampère's circuital law was carried over from the 1861 paper and he used a dynamical approach involving rotational motion within the electromagnetic field which he likened to the action of flywheels. Using this approach to justify the electromotive force equation (the precursor of the Lorentz force equation), he derived a wave equation from a set of eight equations which appeared in the paper and which included the electromotive force equation and Ampère's circuital law. Maxwell once again used the experimental results of Weber and Kohlrausch to show that this wave equation represented an electromagnetic wave that propagates at the speed of light, hence supporting the view that light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
In 1887–1889, Heinrich Hertz experimentally demonstrated the electric magnetic waves are identical to light waves. This unification of electromagnetic wave and optics indicated that there was a single luminiferous aether instead of many different kinds of aether media.
The apparent need for a propagation medium for such Hertzian waves (later called radio waves) can be seen by the fact that they consist of orthogonal electric (E) and magnetic (B or H) waves. The E waves consist of undulating dipolar electric fields, and all such dipoles appeared to require separated and opposite electric charges. Electric charge is an inextricable property of matter, so it appeared that some form of matter was required to provide the alternating current that would seem to have to exist at any point along the propagation path of the wave. Propagation of waves in a true vacuum would imply the existence of electric fields without associated electric charge, or of electric charge without associated matter. Albeit compatible with Maxwell's equations, electromagnetic induction of electric fields could not be demonstrated in vacuum, because all methods of detecting electric fields required electrically charged matter.
In addition, Maxwell's equations required that all electromagnetic waves in vacuum propagate at a fixed speed, c. As this can only occur in one reference frame in Newtonian physics (see Galilean relativity), the aether was hypothesized as the absolute and unique frame of reference in which Maxwell's equations hold. That is, the aether must be "still" universally, otherwise c would vary along with any variations that might occur in its supportive medium. Maxwell himself proposed several mechanical models of aether based on wheels and gears, and George Francis FitzGerald even constructed a working model of one of them. These models had to agree with the fact that the electromagnetic waves are transverse but never longitudinal.
Problems
By this point the mechanical qualities of the aether had become more and more magical: it had to be a fluid in order to fill space, but one that was millions of times more rigid than steel in order to support the high frequencies of light waves. It also had to be massless and without viscosity, otherwise it would visibly affect the orbits of planets. Additionally it appeared it had to be completely transparent, non-dispersive, incompressible, and continuous at a very small scale. Maxwell wrote in Encyclopædia Britannica:
Aethers were invented for the planets to swim in, to constitute electric atmospheres and magnetic effluvia, to convey sensations from one part of our bodies to another, and so on, until all space had been filled three or four times over with aethers. ... The only aether which has survived is that which was invented by Huygens to explain the propagation of light.
By the early 20th century, aether theory was in trouble. A series of increasingly complex experiments had been carried out in the late 19th century to try to detect the motion of the Earth through the aether, and had failed to do so. A range of proposed aether-dragging theories could explain the null result but these were more complex, and tended to use arbitrary-looking coefficients and physical assumptions. Lorentz and FitzGerald offered within the framework of Lorentz ether theory a more elegant solution to how the motion of an absolute aether could be undetectable (length contraction), but if their equations were correct, the new special theory of relativity (1905) could generate the same mathematics without referring to an aether at all. Aether fell to Occam's Razor.
Relative motion between the Earth and aether
Aether drag
Main article: Aether drag hypothesisThe two most important models, which were aimed to describe the relative motion of the Earth and aether, were Augustin-Jean Fresnel's (1818) model of the (nearly) stationary aether including a partial aether drag determined by Fresnel's dragging coefficient, and George Gabriel Stokes' (1844) model of complete aether drag. The latter theory was not considered as correct, since it was not compatible with the aberration of light, and the auxiliary hypotheses developed to explain this problem were not convincing. Also, subsequent experiments as the Sagnac effect (1913) also showed that this model is untenable. However, the most important experiment supporting Fresnel's theory was Fizeau's 1851 experimental confirmation of Fresnel's 1818 prediction that a medium with refractive index n moving with a velocity v would increase the speed of light travelling through the medium in the same direction as v from c/n to:
That is, movement adds only a fraction of the medium's velocity to the light (predicted by Fresnel in order to make Snell's law work in all frames of reference, consistent with stellar aberration). This was initially interpreted to mean that the medium drags the aether along, with a portion of the medium's velocity, but that understanding became very problematic after Wilhelm Veltmann demonstrated that the index n in Fresnel's formula depended upon the wavelength of light, so that the aether could not be moving at a wavelength-independent speed. This implied that there must be a separate aether for each of the infinitely many frequencies.
Negative aether-drift experiments
The key difficulty with Fresnel's aether hypothesis arose from the juxtaposition of the two well-established theories of Newtonian dynamics and Maxwell's electromagnetism. Under a Galilean transformation the equations of Newtonian dynamics are invariant, whereas those of electromagnetism are not. Basically this means that while physics should remain the same in non-accelerated experiments, light would not follow the same rules because it is travelling in the universal "aether frame". Some effect caused by this difference should be detectable.
A simple example concerns the model on which aether was originally built: sound. The speed of propagation for mechanical waves, the speed of sound, is defined by the mechanical properties of the medium. Sound travels 4.3 times faster in water than in air. This explains why a person hearing an explosion underwater and quickly surfacing can hear it again as the slower travelling sound arrives through the air. Similarly, a traveller on an airliner can still carry on a conversation with another traveller because the sound of words is travelling along with the air inside the aircraft. This effect is basic to all Newtonian dynamics, which says that everything from sound to the trajectory of a thrown baseball should all remain the same in the aircraft flying (at least at a constant speed) as if still sitting on the ground. This is the basis of the Galilean transformation, and the concept of frame of reference.
But the same was not supposed to be true for light, since Maxwell's mathematics demanded a single universal speed for the propagation of light, based, not on local conditions, but on two measured properties, the permittivity and permeability of free space, that were assumed to be the same throughout the universe. If these numbers did change, there should be noticeable effects in the sky; stars in different directions would have different colours, for instance.
Thus at any point there should be one special coordinate system, "at rest relative to the aether". Maxwell noted in the late 1870s that detecting motion relative to this aether should be easy enough—light travelling along with the motion of the Earth would have a different speed than light travelling backward, as they would both be moving against the unmoving aether. Even if the aether had an overall universal flow, changes in position during the day/night cycle, or over the span of seasons, should allow the drift to be detected.
First-order experiments
Although the aether is almost stationary according to Fresnel, his theory predicts a positive outcome of aether drift experiments only to second order in because Fresnel's dragging coefficient would cause a negative outcome of all optical experiments capable of measuring effects to first order in . This was confirmed by the following first-order experiments, all of which gave negative results. The following list is based on the description of Wilhelm Wien (1898), with changes and additional experiments according to the descriptions of Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1910) and Jakob Laub (1910):
- The experiment of François Arago (1810), to confirm whether refraction, and thus the aberration of light, is influenced by Earth's motion. Similar experiments were conducted by George Biddell Airy (1871) by means of a telescope filled with water, and Éleuthère Mascart (1872).
- The experiment of Fizeau (1860), to find whether the rotation of the polarization plane through glass columns is changed by Earth's motion. He obtained a positive result, but Lorentz could show that the results have been contradictory. DeWitt Bristol Brace (1905) and Strasser (1907) repeated the experiment with improved accuracy, and obtained negative results.
- The experiment of Martin Hoek (1868). This experiment is a more precise variation of the Fizeau experiment (1851). Two light rays were sent in opposite directions – one of them traverses a path filled with resting water, the other one follows a path through air. In agreement with Fresnel's dragging coefficient, he obtained a negative result.
- The experiment of Wilhelm Klinkerfues (1870) investigated whether an influence of Earth's motion on the absorption line of sodium exists. He obtained a positive result, but this was shown to be an experimental error, because a repetition of the experiment by Haga (1901) gave a negative result.
- The experiment of Ketteler (1872), in which two rays of an interferometer were sent in opposite directions through two mutually inclined tubes filled with water. No change of the interference fringes occurred. Later, Mascart (1872) showed that the interference fringes of polarized light in calcite remained uninfluenced as well.
- The experiment of Éleuthère Mascart (1872) to find a change of rotation of the polarization plane in quartz. No change of rotation was found when the light rays had the direction of Earth's motion and then the opposite direction. Lord Rayleigh conducted similar experiments with improved accuracy, and obtained a negative result as well.
Besides those optical experiments, also electrodynamic first-order experiments were conducted, which should have led to positive results according to Fresnel. However, Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (1895) modified Fresnel's theory and showed that those experiments can be explained by a stationary aether as well:
- The experiment of Wilhelm Röntgen (1888), to find whether a charged capacitor produces magnetic forces due to Earth's motion.
- The experiment of Theodor des Coudres (1889), to find whether the inductive effect of two wire rolls upon a third one is influenced by the direction of Earth's motion. Lorentz showed that this effect is cancelled to first order by the electrostatic charge (produced by Earth's motion) upon the conductors.
- The experiment of Königsberger (1905). The plates of a capacitor are located in the field of a strong electromagnet. Due to Earth's motion, the plates should have become charged. No such effect was observed.
- The experiment of Frederick Thomas Trouton (1902). A capacitor was brought parallel to Earth's motion, and it was assumed that momentum is produced when the capacitor is charged. The negative result can be explained by Lorentz's theory, according to which the electromagnetic momentum compensates the momentum due to Earth's motion. Lorentz could also show, that the sensitivity of the apparatus was much too low to observe such an effect.
Second-order experiments

While the first-order experiments could be explained by a modified stationary aether, more precise second-order experiments were expected to give positive results. However, no such results could be found.
The famous Michelson–Morley experiment compared the source light with itself after being sent in different directions and looked for changes in phase in a manner that could be measured with extremely high accuracy. In this experiment, their goal was to determine the velocity of the Earth through the aether. The publication of their result in 1887, the null result, was the first clear demonstration that something was seriously wrong with the aether hypothesis (Michelson's first experiment in 1881 was not entirely conclusive). In this case the MM experiment yielded a shift of the fringing pattern of about 0.01 of a fringe, corresponding to a small velocity. However, it was incompatible with the expected aether wind effect due to the Earth's (seasonally varying) velocity which would have required a shift of 0.4 of a fringe, and the error was small enough that the value may have indeed been zero. Therefore, the null hypothesis, the hypothesis that there was no aether wind, could not be rejected. More modern experiments have since reduced the possible value to a number very close to zero, about 10.
It is obvious from what has gone before that it would be hopeless to attempt to solve the question of the motion of the solar system by observations of optical phenomena at the surface of the earth.
— A. Michelson and E. Morley. "On the Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Æther". Philosophical Magazine S. 5. Vol. 24. No. 151. December 1887.
A series of experiments using similar but increasingly sophisticated apparatuses all returned the null result as well. Conceptually different experiments that also attempted to detect the motion of the aether were the Trouton–Noble experiment (1903), whose objective was to detect torsion effects caused by electrostatic fields, and the experiments of Rayleigh and Brace (1902, 1904), to detect double refraction in various media. However, all of them obtained a null result, like Michelson–Morley (MM) previously did.
These "aether-wind" experiments led to a flurry of efforts to "save" aether by assigning to it ever more complex properties, and only a few scientists, like Emil Cohn or Alfred Bucherer, considered the possibility of the abandonment of the aether hypothesis. Of particular interest was the possibility of "aether entrainment" or "aether drag", which would lower the magnitude of the measurement, perhaps enough to explain the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment. However, as noted earlier, aether dragging already had problems of its own, notably aberration. In addition, the interference experiments of Lodge (1893, 1897) and Ludwig Zehnder (1895), aimed to show whether the aether is dragged by various, rotating masses, showed no aether drag. A more precise measurement was made in the Hammar experiment (1935), which ran a complete MM experiment with one of the "legs" placed between two massive lead blocks. If the aether was dragged by mass then this experiment would have been able to detect the drag caused by the lead, but again the null result was achieved. The theory was again modified, this time to suggest that the entrainment only worked for very large masses or those masses with large magnetic fields. This too was shown to be incorrect by the Michelson–Gale–Pearson experiment, which detected the Sagnac effect due to Earth's rotation (see Aether drag hypothesis).
Another completely different attempt to save "absolute" aether was made in the Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction hypothesis, which posited that everything was affected by travel through the aether. In this theory, the reason that the Michelson–Morley experiment "failed" was that the apparatus contracted in length in the direction of travel. That is, the light was being affected in the "natural" manner by its travel through the aether as predicted, but so was the apparatus itself, cancelling out any difference when measured. FitzGerald had inferred this hypothesis from a paper by Oliver Heaviside. Without referral to an aether, this physical interpretation of relativistic effects was shared by Kennedy and Thorndike in 1932 as they concluded that the interferometer's arm contracts and also the frequency of its light source "very nearly" varies in the way required by relativity.
Similarly, the Sagnac effect, observed by G. Sagnac in 1913, was immediately seen to be fully consistent with special relativity. In fact, the Michelson–Gale–Pearson experiment in 1925 was proposed specifically as a test to confirm the relativity theory, although it was also recognized that such tests, which merely measure absolute rotation, are also consistent with non-relativistic theories.
During the 1920s, the experiments pioneered by Michelson were repeated by Dayton Miller, who publicly proclaimed positive results on several occasions, although they were not large enough to be consistent with any known aether theory. However, other researchers were unable to duplicate Miller's claimed results. Over the years the experimental accuracy of such measurements has been raised by many orders of magnitude, and no trace of any violations of Lorentz invariance has been seen. (A later re-analysis of Miller's results concluded that he had underestimated the variations due to temperature.)
Since the Miller experiment and its unclear results there have been many more experimental attempts to detect the aether. Many experimenters have claimed positive results. These results have not gained much attention from mainstream science, since they contradict a large quantity of high-precision measurements, all the results of which were consistent with special relativity.
Lorentz aether theory
Main article: Lorentz ether theoryBetween 1892 and 1904, Hendrik Lorentz developed an electron–aether theory, in which he avoided making assumptions about the aether. In his model the aether is completely motionless, and by that he meant that it could not be set in motion in the neighborhood of ponderable matter. Contrary to earlier electron models, the electromagnetic field of the aether appears as a mediator between the electrons, and changes in this field cannot propagate faster than the speed of light. A fundamental concept of Lorentz's theory in 1895 was the "theorem of corresponding states" for terms of order v/c. This theorem states that an observer moving relative to the aether makes the same observations as a resting observer, after a suitable change of variables. Lorentz noticed that it was necessary to change the space-time variables when changing frames and introduced concepts like physical length contraction (1892) to explain the Michelson–Morley experiment, and the mathematical concept of local time (1895) to explain the aberration of light and the Fizeau experiment. This resulted in the formulation of the so-called Lorentz transformation by Joseph Larmor (1897, 1900) and Lorentz (1899, 1904), whereby (it was noted by Larmor) the complete formulation of local time is accompanied by some sort of time dilation of electrons moving in the aether. As Lorentz later noted (1921, 1928), he considered the time indicated by clocks resting in the aether as "true" time, while local time was seen by him as a heuristic working hypothesis and a mathematical artifice. Therefore, Lorentz's theorem is seen by modern authors as being a mathematical transformation from a "real" system resting in the aether into a "fictitious" system in motion.
The work of Lorentz was mathematically perfected by Henri Poincaré, who formulated on many occasions the Principle of Relativity and tried to harmonize it with electrodynamics. He declared simultaneity only a convenient convention which depends on the speed of light, whereby the constancy of the speed of light would be a useful postulate for making the laws of nature as simple as possible. In 1900 and 1904 he physically interpreted Lorentz's local time as the result of clock synchronization by light signals. In June and July 1905 he declared the relativity principle a general law of nature, including gravitation. He corrected some mistakes of Lorentz and proved the Lorentz covariance of the electromagnetic equations. However, he used the notion of an aether as a perfectly undetectable medium and distinguished between apparent and real time, so most historians of science argue that he failed to invent special relativity.
End of aether
Special relativity
Aether theory was dealt another blow when the Galilean transformation and Newtonian dynamics were both modified by Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity, giving the mathematics of Lorentzian electrodynamics a new, "non-aether" context. Unlike most major shifts in scientific thought, special relativity was adopted by the scientific community remarkably quickly, consistent with Einstein's later comment that the laws of physics described by the Special Theory were "ripe for discovery" in 1905. Max Planck's early advocacy of the special theory, along with the elegant formulation given to it by Hermann Minkowski, contributed much to the rapid acceptance of special relativity among working scientists.
Einstein based his theory on Lorentz's earlier work. Instead of suggesting that the mechanical properties of objects changed with their constant-velocity motion through an undetectable aether, Einstein proposed to deduce the characteristics that any successful theory must possess in order to be consistent with the most basic and firmly established principles, independent of the existence of a hypothetical aether. He found that the Lorentz transformation must transcend its connection with Maxwell's equations, and must represent the fundamental relations between the space and time coordinates of inertial frames of reference. In this way he demonstrated that the laws of physics remained invariant as they had with the Galilean transformation, but that light was now invariant as well.
With the development of the special theory of relativity, the need to account for a single universal frame of reference had disappeared – and acceptance of the 19th-century theory of a luminiferous aether disappeared with it. For Einstein, the Lorentz transformation implied a conceptual change: that the concept of position in space or time was not absolute, but could differ depending on the observer's location and velocity.
Moreover, in another paper published the same month in 1905, Einstein made several observations on a then-thorny problem, the photoelectric effect. In this work he demonstrated that light can be considered as particles that have a "wave-like nature". Particles obviously do not need a medium to travel, and thus, neither did light. This was the first step that would lead to the full development of quantum mechanics, in which the wave-like nature and the particle-like nature of light are both considered as valid descriptions of light. A summary of Einstein's thinking about the aether hypothesis, relativity and light quanta may be found in his 1909 (originally German) lecture "The Development of Our Views on the Composition and Essence of Radiation".
Lorentz on his side continued to use the aether hypothesis. In his lectures of around 1911, he pointed out that what "the theory of relativity has to say ... can be carried out independently of what one thinks of the aether and the time". He commented that "whether there is an aether or not, electromagnetic fields certainly exist, and so also does the energy of the electrical oscillations" so that, "if we do not like the name of 'aether', we must use another word as a peg to hang all these things upon". He concluded that "one cannot deny the bearer of these concepts a certain substantiality".
Nevertheless, in 1920, Einstein gave an address at Leiden University in which he commented "More careful reflection teaches us however, that the special theory of relativity does not compel us to deny ether. We may assume the existence of an ether; only we must give up ascribing a definite state of motion to it, i.e. we must by abstraction take from it the last mechanical characteristic which Lorentz had still left it. We shall see later that this point of view, the conceivability of which I shall at once endeavour to make more intelligible by a somewhat halting comparison, is justified by the results of the general theory of relativity". He concluded his address by saying that "according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an ether. According to the general theory of relativity space without ether is unthinkable."
Other models
Main article: Aether theoriesIn later years there have been a few individuals who advocated a neo-Lorentzian approach to physics, which is Lorentzian in the sense of positing an absolute true state of rest that is undetectable and which plays no role in the predictions of the theory. (No violations of Lorentz covariance have ever been detected, despite strenuous efforts.) Hence these theories resemble the 19th century aether theories in name only. For example, the founder of quantum field theory, Paul Dirac, stated in 1951 in an article in Nature, titled "Is there an Aether?" that "we are rather forced to have an aether". However, Dirac never formulated a complete theory, and so his speculations found no acceptance by the scientific community.
Einstein's views on the aether
When Einstein was still a student in the Zurich Polytechnic in 1900, he was very interested in the idea of aether. His initial proposal of research thesis was to do an experiment to measure how fast the Earth was moving through the aether. "The velocity of a wave is proportional to the square root of the elastic forces which cause propagation, and inversely proportional to the mass of the aether moved by these forces."
In 1916, after Einstein completed his foundational work on general relativity, Lorentz wrote a letter to him in which he speculated that within general relativity the aether was re-introduced. In his response Einstein wrote that one can actually speak about a "new aether", but one may not speak of motion in relation to that aether. This was further elaborated by Einstein in some semi-popular articles (1918, 1920, 1924, 1930).
In 1918, Einstein publicly alluded to that new definition for the first time. Then, in the early 1920s, in a lecture which he was invited to give at Lorentz's university in Leiden, Einstein sought to reconcile the theory of relativity with Lorentzian aether. In this lecture Einstein stressed that special relativity took away the last mechanical property of the aether: immobility. However, he continued that special relativity does not necessarily rule out the aether, because the latter can be used to give physical reality to acceleration and rotation. This concept was fully elaborated within general relativity, in which physical properties (which are partially determined by matter) are attributed to space, but no substance or state of motion can be attributed to that "aether" (by which he meant curved space-time).
In another paper of 1924, named "Concerning the Aether", Einstein argued that Newton's absolute space, in which acceleration is absolute, is the "Aether of Mechanics". And within the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell and Lorentz one can speak of the "Aether of Electrodynamics", in which the aether possesses an absolute state of motion. As regards special relativity, also in this theory acceleration is absolute as in Newton's mechanics. However, the difference from the electromagnetic aether of Maxwell and Lorentz lies in the fact that "because it was no longer possible to speak, in any absolute sense, of simultaneous states at different locations in the aether, the aether became, as it were, four-dimensional since there was no objective way of ordering its states by time alone". Now the "aether of special relativity" is still "absolute", because matter is affected by the properties of the aether, but the aether is not affected by the presence of matter. This asymmetry was solved within general relativity. Einstein explained that the "aether of general relativity" is not absolute, because matter is influenced by the aether, just as matter influences the structure of the aether.
The only similarity of this relativistic aether concept with the classical aether models lies in the presence of physical properties in space, which can be identified through geodesics. As historians such as John Stachel argue, Einstein's views on the "new aether" are not in conflict with his abandonment of the aether in 1905. As Einstein himself pointed out, no "substance" and no state of motion can be attributed to that new aether. Einstein's use of the word "aether" found little support in the scientific community, and played no role in the continuing development of modern physics.
Aether concepts
See also
- Dirac sea
- Etheric plane
- Galactic year
- History of special relativity
- Le Sage's theory of gravitation
- One-way speed of light
- Preferred frame
- Superseded scientific theories
- Virtual particle
- Welteislehre
References
Footnotes
- Young ascribed aether to caloric theory, pairing light and heat, and cited passages from Newton such as: "A luminiferous ether pervades the Universe, rare and elastic in a high degree," and:
Is not the heat conveyed through the vacuum by the vibration of a much subtiler medium than air? And is not this medium the same with that medium by which light is refracted and reflected, and by whose vibration light communicates heat to bodies, and is put into fits of easy reflection, and easy transmission?
Citations
- See "Google Scholar 'luminiferous ether'".
- The 19th century science book A Guide to the Scientific Knowledge of Things Familiar provides a brief summary of scientific thinking in this field at the time.
- Robert Boyle, The Works of the Honourable Robert Boyle, ed. Thomas Birch, 2nd edn., 6 vols. (London, 1772), III, 316; quoted in E. A. Burtt, The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science (Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company, 1954), 191–192.
- Edwin Arthur Burtt (2003). The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science (illustrated, unabridged, reprinted ed.). Courier Corporation. p. 270. ISBN 978-0-486-42551-1. Extract of page 270
- Cesar A. Sciammarella; Federico M. Sciammarella (2012). Experimental Mechanics of Solids. John Wiley & Sons. p. 146. ISBN 978-1-119-97009-5. Extract of page 146
- Gillispie, Charles Coulston (1960). The Edge of Objectivity: An Essay in the History of Scientific Ideas. Princeton University Press. p. 408. ISBN 0-691-02350-6.
- Schwartz, Melvin (1987). Principles of Electrodynamics (Revised ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. pp. 106–107. ISBN 978-0-486-65493-5.
- Nichols, Edward L. (November 1904). "The Fundamental Concepts of Physical Science". Popular Science Monthly. 66.
- Yousef, Mohamed Haj (2018-01-01). Duality of Time: Complex-Time Geometry and Perpetual Creation of Space. Mohamed Haj Yousef. ISBN 978-1-5395-7920-5.
- "Selected Papers of Great American Physicists" (PDF). www.aip.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 July 2015. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- They commented in a footnote: "From experiment it is not inferred that the velocity of the earth is but a few kilometers per second, but rather that the dimensions of the apparatus vary very nearly as required by relativity. From the present experiment we similarly infer that the frequency of light varies conformably to the theory."
- The confusion over this point can be seen in Sagnac's conclusion that "in the ambient space, light is propagated with a velocity V0, independent of the movement as a whole of the luminous source O and the optical system. That is a property of space which experimentally characterizes the luminiferous aether." The invariance of light speed, independent of the movement of the source, is also one of the two fundamental principles of special relativity.
- Roberts, Schleif (2006); Physics FAQ: Experiments that Apparently are NOT Consistent with SR/GR Archived 2009-10-15 at the Wayback Machine
- Lorentz wrote: "One cannot deny to the bearer of these properties a certain substantiality, and if so, then one may, in all modesty, call true time the time measured by clocks which are fixed in this medium, and consider simultaneity as a primary concept." However, he went on to say that this was based on his conception of "infinite velocity", which according to his own theory is not physically realizable. Lorentz also admitted that the postulate of an absolute but undetectable rest frame was purely metaphysical, and had no empirical consequences.
- "Einstein: Ether and Relativity". Maths History. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- Dirac wrote about his theory: "We have now the velocity at all points of space-time, playing a fundamental part in electrodynamics. It is natural to regard it as the velocity of some real physical thing. Thus with the new theory of electrodynamics we are rather forced to have an aether."
- Isaacson, Walter (2007). Einstein: His life and Universe. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 47–48.
- Albert Einstein's 'First' Paper (1894 or 1895), http://www.straco.ch/papers/Einstein%20First%20Paper.pdf Archived 2020-07-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Einstein 1920: We may say that according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an aether. According to the general theory of relativity space without aether is unthinkable; for in such space there not only would be no propagation of light, but also no possibility of existence for standards of space and time (measuring-rods and clocks), nor therefore any space-time intervals in the physical sense. But this aether may not be thought of as endowed with the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it.
Primary sources
- ^ Newton, Isaac: Opticks (1704). Fourth edition of 1730. (Republished 1952 (Dover: New York), with commentary by Bernard Cohen, Albert Einstein, and Edmund Whittaker).
- ^ Maxwell, JC (1865). "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field (Part 1)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-07-28.
- Maxwell, James Clerk (1878), "Ether" , in Baynes, T. S. (ed.), Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 8 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, pp. 568–572
- Fresnel, A. (1818), "Lettre de M. Fresnel à M. Arago sur l'influence du mouvement terrestre dans quelques phénomènes d'optique", Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 9: 57–66 (Sep. 1818), 286–7 (Nov. 1818); reprinted in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel, vol. 2 (1868), pp. 627–36; translated as "Letter from Augustin Fresnel to François Arago, on the influence of the movement of the earth on some phenomena of optics" in K.F. Schaffner, Nineteenth-Century Aether Theories, Pergamon, 1972 (doi:10.1016/C2013-0-02335-3), pp. 125–35; also translated (with several errors) by R.R. Traill as "Letter from Augustin Fresnel to François Arago concerning the influence of terrestrial movement on several optical phenomena", General Science Journal, 23 January 2006 (PDF, 8 pp.).
- G. G. Stokes (1845). "On the Aberration of Light". Philosophical Magazine. 27 (177): 9–15. doi:10.1080/14786444508645215.
- ^ Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1895), Versuch einer Theorie der electrischen und optischen Erscheinungen in bewegten Körpern [Attempt of a Theory of Electrical and Optical Phenomena in Moving Bodies], Leiden: E.J. Brill
- Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1892), "De relatieve beweging van de aarde en den aether" [The Relative Motion of the Earth and the Aether], Zittingsverlag Akad. V. Wet., 1: 74–79
- Larmor, Joseph (1897), "On a Dynamical Theory of the Electric and Luminiferous Medium, Part 3, Relations with material media" , Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 190: 205–300, Bibcode:1897RSPTA.190..205L, doi:10.1098/rsta.1897.0020
- Larmor, Joseph (1900), Aether and Matter , Cambridge University Press
- Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1899), "Simplified Theory of Electrical and Optical Phenomena in Moving Systems" , Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, 1: 427–442
- Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1904), "Electromagnetic phenomena in a system moving with any velocity smaller than that of light" , Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, 6: 809–831
- Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1921), "Deux Mémoires de Henri Poincaré sur la Physique Mathématique" [Two Papers of Henri Poincaré on Mathematical Physics], Acta Mathematica, 38 (1): 293–308, doi:10.1007/BF02392073
- Lorentz, H.A.; Lorentz, H. A.; Miller, D. C.; Kennedy, R. J.; Hedrick, E. R.; Epstein, P. S. (1928), "Conference on the Michelson-Morley Experiment", The Astrophysical Journal, 68: 345–351, Bibcode:1928ApJ....68..341M, doi:10.1086/143148
- Poincaré, Henri (1900), "La théorie de Lorentz et le principe de réaction" , Archives Néerlandaises des Sciences Exactes et Naturelles, 5: 252–278. See also the English translation Archived 2008-06-26 at the Wayback Machine.
- Poincaré, Henri (1904–1906), "The Principles of Mathematical Physics" , in Rogers, Howard J. (ed.), Congress of arts and science, universal exposition, St. Louis, 1904, vol. 1, Boston and New York: Houghton, Mifflin and Company, pp. 604–622
- Poincaré, Henri (1905b), "Sur la dynamique de l'électron" [On the Dynamics of the Electron], Comptes Rendus, 140: 1504–1508
- Poincaré, Henri (1906), "Sur la dynamique de l'électron" [On the Dynamics of the Electron], Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo, 21: 129–176, Bibcode:1906RCMP...21..129P, doi:10.1007/BF03013466, hdl:2027/uiug.30112063899089, S2CID 120211823
- Einstein, Albert (1905a), "Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper", Annalen der Physik, 322 (10): 891–921, Bibcode:1905AnP...322..891E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053221004. See also: English translation Archived 2005-11-25 at the Wayback Machine.
- Einstein, Albert: (1909) The Development of Our Views on the Composition and Essence of Radiation "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-04-23. Retrieved 2024-01-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link), Phys. Z., 10, 817–825. (review of aether theories, among other topics) - Dirac, P. M. (1951). "Is there an Aether?" (PDF). Nature. 168 (4282): 906. Bibcode:1951Natur.168..906D. doi:10.1038/168906a0. S2CID 4288946. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- ^ A. Einstein (1918), "Dialog about Objections against the Theory of Relativity" , Naturwissenschaften, 6 (48): 697–702, Bibcode:1918NW......6..697E, doi:10.1007/BF01495132, S2CID 28132355
- ^ Einstein, Albert: "Ether and the Theory of Relativity" (1920), republished in Sidelights on Relativity (Methuen, London, 1922)
- ^ A. Einstein (1924), "Über den Äther", Verhandlungen der Schweizerischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, 105 (2): 85–93. See also an English translation: Concerning the Aether Archived 2010-11-04 at the Wayback Machine
- "Einstein Archives Online". Archived from the original on 16 June 2011.
Experiments
- Fizeau, H. (1851). "The Hypotheses Relating to the Luminous Aether, and an Experiment which Appears to Demonstrate that the Motion of Bodies Alters the Velocity with which Light Propagates itself in their Interior" . Philosophical Magazine. 2: 568–573. doi:10.1080/14786445108646934.
- Michelson, A. A. & Morley, E.W. (1886). "Influence of Motion of the Medium on the Velocity of Light" . Am. J. Sci. 31 (185): 377–386. Bibcode:1886AmJS...31..377M. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-31.185.377. S2CID 131116577.
- Arago, A. (1810–1853). "Mémoire sur la vitesse de la lumière, lu à la prémière classe de l'Institut, le 10 décembre 1810". Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences. 36: 38–49.
- Airy, G.B. (1871). "On the Supposed Alteration in the Amount of Astronomical Aberration of Light, Produced by the Passage of the Light through a Considerable Thickness of Refracting Medium". Proceedings of the Royal Society. 20 (130–138): 35–39. Bibcode:1871RSPS...20...35A. doi:10.1098/rspl.1871.0011. Archived from the original on 2012-05-15.
- ^ Mascart, E. (1872). "Sur les modifications qu'éprouve la lumière par suite du mouvement de la source lumineuse et du mouvement de l'observateur". Annales Scientifiques de l'École Normale Supérieure. Série 2. 1: 157–214. doi:10.24033/asens.81.
- Fizeau, H. (1861). "Ueber eine Methode, zu untersuchen, ob das Polarisationsazimut eines gebrochenen Strahls durch die Bewegung des brechenden Körpers geändert werde". Annalen der Physik. 190 (12): 554–587. Bibcode:1861AnP...190..554F. doi:10.1002/andp.18621901204. Archived from the original on 2012-05-15.
- Brace, D.B. (1905). "The Aether 'Drift' and Rotary Polarization". Philosophical Magazine. 10 (57): 383–396. doi:10.1080/14786440509463384.
- Strasser, B. (1907). "Der Fizeausche Versuch über die Änderung des Polarisationsazimuts eines gebrochenen Strahles durch die Bewegung der Erde". Annalen der Physik. 329 (11): 137–144. Bibcode:1907AnP...329..137S. doi:10.1002/andp.19073291109. Archived from the original on 2012-05-15.
- Hoek, M. (1868). "Determination de la vitesse avec laquelle est entrainée une onde lumineuse traversant un milieu en mouvement". Verslagen en Mededeelingen. 2: 189–194.
- Klinkerfues, Ernst Friedrich Wilhelm (1870). "Versuche über die Bewegung der Erde und der Sonne im Aether". Astronomische Nachrichten. 76 (3): 33–38. Bibcode:1870AN.....76...33K. doi:10.1002/asna.18700760302.
- Haga, H. (1902). "Über den Klinkerfuesschen Versuch". Physikalische Zeitschrift. 3: 191.
- Ketteler, Ed. (1872). "Ueber den Einfluss der astronomischen Bewegungen auf die optischen Erscheinungen". Annalen der Physik. 220 (9): 109–127. Bibcode:1871AnP...220..109K. doi:10.1002/andp.18712200906. Archived from the original on 2012-05-15.
- ^ Mascart, E. (1874). "Sur les modifications qu'éprouve la lumière par suite du mouvement de la source lumineuse et du mouvement de l'observateur (deuxième partie)". Annales Scientifiques de l'École Normale Supérieure. Série 2. 3: 363–420. doi:10.24033/asens.118.
- Lord Rayleigh (1902). "Is Rotatory Polarization Influenced by the Earth's Motion?". Philosophical Magazine. 4 (20): 215–220. doi:10.1080/14786440209462836.
- Röntgen, W. (1888). "Über die durch Bewegung eines im homogenen elektrischen Felde befindlichen Dielektricums hervorgerufene elektrodynamische Kraft". Berliner Sitzungsberichte. 2. Halbband: 23–28. Archived from the original on 2016-02-26.
- Des Coudres, Th. (1889). "Ueber das Verhalten des Lichtäthers bei den Bewegungen der Erde". Annalen der Physik. 274 (9): 71–79. Bibcode:1889AnP...274...71D. doi:10.1002/andp.18892740908.
- Königsberger, J. (1905). "Induktionswirkung im Dielektrikum und Bewegung des Aethers". Berichte der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft zu Freiburg I. Br. 13: 95–100.
- Trouton, F.T. (1902). "The results of an electrical experiment, involving the relative motion of the Earth and the Ether, Suggested by the Late Professor FitzGerald". Transactions of the Royal Dublin Society. 7: 379–384.
- Michelson, Albert Abraham (1881), "The Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether" , American Journal of Science, 22 (128): 120–129, Bibcode:1881AmJS...22..120M, doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-22.128.120, S2CID 130423116
- Michelson, Albert Abraham & Morley, Edward Williams (1887), "On the Relative Motion of the Earth and the Luminiferous Ether" , American Journal of Science, 34 (203): 333–345, Bibcode:1887AmJS...34..333M, doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-34.203.333, S2CID 124333204
- Trouton, F. T.; Noble, H. R. (1903). "The Mechanical Forces Acting on a Charged Electric Condenser Moving through Space". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 202 (346–358): 165–181. Bibcode:1904RSPTA.202..165T. doi:10.1098/rsta.1904.0005. Archived from the original on 2012-05-15.
- Lord Rayleigh (1902). "Does Motion through the Aether cause Double Refraction?" . Philosophical Magazine. 4 (24): 678–683. doi:10.1080/14786440209462891.
- Brace, DeWitt Bristol (1904). "On Double Refraction in Matter moving through the Aether" . Philosophical Magazine. 7 (40): 317–329. doi:10.1080/14786440409463122.
- Lodge, Oliver J. (1893). "Aberration Problems". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 184: 727–804. Bibcode:1893RSPTA.184..727L. doi:10.1098/rsta.1893.0015. Archived from the original on 2016-01-24.
- Lodge, Oliver J. (1897). "Experiments on the Absence of Mechanical Connexion between Ether and Matter" . Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 189: 149–166. Bibcode:1897RSPTA.189..149L. doi:10.1098/rsta.1897.0006.
- Zehnder, L. (1895). "Ueber die Durchlässigkeit fester Körper für den Lichtäther". Annalen der Physik. 291 (5): 65–81. Bibcode:1895AnP...291...65Z. doi:10.1002/andp.18952910505.
- G. W. Hammar (1935). "The Velocity of Light Within a Massive Enclosure". Physical Review. 48 (5): 462–463. Bibcode:1935PhRv...48..462H. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.48.462.2.
- Kennedy, R. J.; Thorndike, E. M. (1932). "Experimental Establishment of the Relativity of Time". Physical Review. 42 (3): 400–418. Bibcode:1932PhRv...42..400K. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.42.400.
- Sagnac, Georges (1913), "L'éther lumineux démontré par l'effet du vent relatif d'éther dans un interféromètre en rotation uniforme" [The demonstration of the luminiferous aether by an interferometer in uniform rotation], Comptes Rendus, 157: 708–710
- Sagnac, Georges (1913), "Sur la preuve de la réalité de l'éther lumineux par l'expérience de l'interférographe tournant" [On the proof of the reality of the luminiferous aether by the experiment with a rotating interferometer], Comptes Rendus, 157: 1410–1413
Secondary sources
- ^ Whittaker, Edmund Taylor (1910), A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity (1 ed.), Dublin: Longman, Green and Co.
- ^ Jannsen, Michel & Stachel, John (2008), The Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-09-29
- ^ Darrigol, Olivier (2000), Electrodynamics from Ampère to Einstein, Oxford: Clarendon Press, ISBN 978-0-19-850594-5
- ^ Schaffner, Kenneth F. (1972), Nineteenth-century aether theories, Oxford: Pergamon Press, ISBN 978-0-08-015674-3
- Wien, Wilhelm (1898). "Über die Fragen, welche die translatorische Bewegung des Lichtäthers betreffen (Referat für die 70. Versammlung deutsche Naturforscher und Aerzte in Düsseldorf, 1898)" . Annalen der Physik. 301 (3): I–XVIII..
- Laub, Jakob (1910). "Über die experimentellen Grundlagen des Relativitätsprinzips". Jahrbuch der Radioaktivität und Elektronik. 7: 405–463.
- ^ Miller, Arthur I. (1981), Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905–1911), Reading: Addison–Wesley, ISBN 978-0-201-04679-3
- Janssen, Michel; Mecklenburg, Matthew (2007), V. F. Hendricks; et al. (eds.), "From classical to relativistic mechanics: Electromagnetic models of the electron", Interactions: Mathematics, Physics and Philosophy, Dordrecht: 65–134, archived from the original on 2008-07-04, retrieved 2004-04-16
- Pais, Abraham (1982), Subtle is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-520438-4
- Born, M. (1956), Physics in my generation, London & New York: Pergamon Press
- ^ Kostro, L. (1992), "An outline of the history of Einstein's relativistic ether concept", in Jean Eisenstaedt; Anne J. Kox (eds.), Studies in the history of general relativity, vol. 3, Boston-Basel-Berlin: Birkhäuser, pp. 260–280, ISBN 978-0-8176-3479-7
- ^ Stachel, J. (2001), "Why Einstein reinvented the ether", Physics World, 14 (6): 55–56, doi:10.1088/2058-7058/14/6/33.
- ^ Kostro, L. (2001), "Albert Einstein's New Ether and his General Relativity" (PDF), Proceedings of the Conference of Applied Differential Geometry: 78–86, archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-11.
External links
- Harry Bateman (1915) The Structure of the Aether, Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 21(6):299–309.
- Decaen, Christopher A. (2004), "Aristotle's Aether and Contemporary Science", The Thomist, 68 (3): 375–429, doi:10.1353/tho.2004.0015, S2CID 171374696, archived from the original on 2012-03-05, retrieved 2011-03-05.
- The Aether of Space Archived 2017-09-13 at the Wayback Machine – Lord Rayleigh's address
- ScienceWeek Theoretical Physics: On the Aether and Broken Symmetry
- The New Student's Reference Work/Ether
| Tests of special relativity | |
|---|---|
| Speed/isotropy | |
| Lorentz invariance | |
| Time dilation Length contraction | |
| Relativistic energy | |
| Fizeau/Sagnac | |
| Alternatives | |
| General | |

 because Fresnel's dragging coefficient would cause a negative outcome of all optical experiments capable of measuring effects to first order in
because Fresnel's dragging coefficient would cause a negative outcome of all optical experiments capable of measuring effects to first order in