| Revision as of 10:26, 11 August 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_Ch← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:45, 1 March 2024 edit undoAchmad Rachmani (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users84,340 edits →Biochemistry method: Non-Latin character | ||
| (84 intermediate revisions by 51 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc}} | |||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 444238251 | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 470618015 | |||
| | ImageFile1 = tropinone.png | | ImageFile1 = tropinone.png | ||
| | ImageFile2 = Tropinone-3D-sticks.png | | ImageFile2 = Tropinone-3D-sticks.png | ||
| | IUPACName = 8-Methyl-8-azabicyclooctan-3-one | | IUPACName = 8-Methyl-8-azabicyclooctan-3-one | ||
| | OtherNames = 3-Tropinone | | OtherNames = 3-Tropinone | ||
| | |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | Abbreviations = | | Abbreviations = | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
| | StdInChIKey = QQXLDOJGLXJCSE-KNVOCYPGSA-N | | StdInChIKey = QQXLDOJGLXJCSE-KNVOCYPGSA-N | ||
| | InChIKey1 = QQXLDOJGLXJCSE-KNVOCYPGSA-N | | InChIKey1 = QQXLDOJGLXJCSE-KNVOCYPGSA-N | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct| |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | CASNo = 532-24-1 |
| CASNo = 532-24-1 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| | UNII = 2A8CC8KA5F | |||
| | EINECS = | | EINECS = | ||
| | PubChem = 446337 | | PubChem = 446337 | ||
| Line 23: | Line 28: | ||
| | DrugBank = DB01874 | | DrugBank = DB01874 | ||
| | SMILES = CN12CC1CC(=O)C2 | | SMILES = CN12CC1CC(=O)C2 | ||
| | InChI = | |||
| | RTECS = | | RTECS = | ||
| | MeSHName = | | MeSHName = | ||
| Line 29: | Line 33: | ||
| | ChEBI = 16656 | | ChEBI = 16656 | ||
| | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| | KEGG = |
| KEGG = | ||
| }} | |||
| | ATCCode_prefix = | |||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |||
| | ATCCode_suffix = | |||
| | ATC_Supplemental =}} | |||
| | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| | Formula = C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>13</sub>NO | | Formula = C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>13</sub>NO | ||
| | MolarMass = 139.195 g/mol | | MolarMass = 139.195 g/mol | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
| | Density = | | Density = | ||
| | MeltingPtC = 42.5 | | MeltingPtC = 42.5 | ||
| | |
| MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| | BoilingPt = (decomposes) | | BoilingPt = (decomposes) | ||
| | |
| BoilingPt_notes = | ||
| | Solubility = | | Solubility = | ||
| | SolubleOther = | | SolubleOther = | ||
| Line 47: | Line 49: | ||
| | pKa = | | pKa = | ||
| | pKb = }} | | pKb = }} | ||
| | |
|Section6={{Chembox Pharmacology | ||
| | |
| ATCCode_prefix = | ||
| | |
| ATCCode_suffix = | ||
| | ATC_Supplemental = | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | MainHazards = | | MainHazards = | ||
| | GHSPictograms = {{GHS05}}{{GHS07}}<ref name="echa">{{cite web |title=Tropinone |url=https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.007.756 |website=Substance Information |publisher=ECHA}}</ref> | |||
| | GHSSignalWord = Danger | |||
| | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|302|314}}<ref name="echa" /> | |||
| | PPhrases = | |||
| | NFPA-H = 2 | | NFPA-H = 2 | ||
| | NFPA-F = 1 | | NFPA-F = 1 | ||
| | NFPA-R = 0 | | NFPA-R = 0 | ||
| | NFPA-O = | |||
| | RPhrases = | |||
| | SPhrases = | |||
| | RSPhrases = | |||
| | FlashPt = | | FlashPt = | ||
| | |
| AutoignitionPt = | ||
| | ExploLimits = | | ExploLimits = | ||
| | PEL = }} | | PEL = | ||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Tropinone''' is an ], famously synthesised in 1917 by ] as a ] precursor to ], a scarce commodity during ].<ref>{{ |
'''Tropinone''' is an ], famously synthesised in 1917 by ] as a ] precursor to ], a scarce commodity during ].<ref>{{Cite journal| last1 = Robinson | first1 = R.| title = LXIII. A Synthesis of Tropinone| journal = Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions| volume = 111| pages = 762–768| year = 1917| doi = 10.1039/CT9171100762| url = https://zenodo.org/record/1429739}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | ||
| | last1 = Nicolaou | first1 = K. C. | |||
| | author-link1 = K. C. Nicolaou | |||
| | last2 = Vourloumis | first2 = D. | |||
| | last3 = Winssinger | first3 = N. | |||
| | last4 = Baran | first4 = P. S. | |||
| | author-link4 = Phil S. Baran | |||
| | title = The Art and Science of Total Synthesis at the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century | |||
| | journal = Angewandte Chemie International Edition | |||
| | volume = 39 | |||
| | issue = 1 | |||
| | pages = 44–122 | |||
| | year = 2000 | |||
| | doi = 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000103)39:1<44::AID-ANIE44>3.0.CO;2-L | pmid=10649349 | |||
| }}</ref> Tropinone and the alkaloids ] and atropine all share the same ] core structure. Its corresponding conjugate acid at pH 7.3 major species is known as tropiniumone.<ref></ref> | |||
| ==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
| The first synthesis of tropinone was by ] in 1901. It started from the seemingly related ], but required many steps to introduce the nitrogen bridge; the overall ] for the synthesis path is only 0.75%.<ref name=smit>{{Cite |
The first synthesis of tropinone was by ] in 1901. It started from the seemingly related ], but required many steps to introduce the nitrogen bridge; the overall ] for the synthesis path is only 0.75%.<ref name=smit>{{Cite book| title = Organic Synthesis| year = 1998| isbn = 978-0-85404-544-0| doi = 10.1039/9781847551573| last1 = Smit| first1 = Wim A.| last2 = Smit| first2 = William A.| last3 = Bochkov| first3 = Alekseĭ Feodosʹevich| last4 = Caple| first4 = Ron}}</ref> Willstätter had previously synthesized cocaine from tropinone, in what was the first synthesis and elucidation of the structure of cocaine.<ref>{{Cite journal| last1 = Humphrey | first1 = A. J.| last2 = O'Hagan| first2 = D.| title = Tropane alkaloid biosynthesis. A century old problem unresolved| journal = ]| publisher = ]| volume = 18| pages = 494–502| year = 2001| doi = 10.1039/b001713m| pmid = 11699882 | issue = 5}}</ref> | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Robinson's "double Mannich" reaction=== | |||
| The 1917 synthesis by Robinson is considered a classic in ]<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1098/rsnr.1993.0034}}</ref> due to its simplicity and biomimetic approach. Tropinone is a ], but the ]s used in its preparation are fairly simple: ], ] and ] (or even ]). The synthesis is a good example of a ] reaction or '''biogenetic-type synthesis''' because ] makes use of the same building blocks. It also demonstrates a ] in a ]. Furthermore the yield of the synthesis was 17% and with subsequent improvements exceeded 90%.<ref name=smit /> | |||
| The 1917 synthesis by Robinson is considered a classic in ]<ref>{{Cite journal| last1 = Birch | first1 = A. J.| title = Investigating a Scientific Legend: The Tropinone Synthesis of Sir Robert Robinson, F.R.S| journal = Notes and Records of the Royal Society of London| volume = 47| issue = 2| pages = 277–296| year = 1993 | jstor = 531792| doi = 10.1098/rsnr.1993.0034 | s2cid = 143267467}}</ref> due to its simplicity and biomimetic approach. Tropinone is a ], but the ]s used in its preparation are fairly simple: ], ] and ] (or even ]). The synthesis is a good example of a ] reaction or '''biogenetic-type synthesis''' because ] makes use of the same building blocks. It also demonstrates a ] in a ]. Furthermore, the yield of the synthesis was 17% and with subsequent improvements exceeded 90%.<ref name=smit /> | |||
| :] | |||
| :] | |||
| This reaction is described as an intramolecular "double ]" for obvious reasons. It is not unique in this regard, as others have also attempted it in piperidine synthesis.<ref>{{Cite pmid|10669562}}</ref><ref>{{Cite pmid|11425577}}</ref> | |||
| This reaction is described as an intramolecular "double ]" for obvious reasons. It is not unique in this regard, as others have also attempted it in piperidine synthesis.<ref>{{Cite journal | |||
| | doi = 10.1021/jm990516x | |||
| | pmid = 10669562 | |||
| | year = 2000 | |||
| | last1 = Wang | first1 = S. | |||
| | last2 = Sakamuri | |||
| | last3 = Enyedy | |||
| | last4 = Kozikowski | |||
| | last5 = Deschaux | |||
| | last6 = Bandyopadhyay | |||
| | last7 = Tella | |||
| | last8 = Zaman | |||
| | last9 = Johnson | |||
| | title = Discovery of a novel dopamine transporter inhibitor, 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3-piperidyl 4-methylphenyl ketone, as a potential cocaine antagonist through 3D-database pharmacophore searching. Molecular modeling, structure-activity relationships, and behavioral pharmacological studies | |||
| | volume = 43 | |||
| | issue = 3 | |||
| | pages = 351–360 | |||
| | journal = ] | first2 = S. | first3 = I. J. | first4 = A. P. | first5 = O. | first6 = B. C. | first7 = S. R. | first8 = W. A. | first9 = K. M. | |||
| }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | |||
| | pmid = 11425577 | |||
| | year = 2001 | |||
| | last1 = Wang | first1 = S. | |||
| | last2 = Sakamuri | |||
| | last3 = Enyedy | |||
| | last4 = Kozikowski | |||
| | last5 = Zaman | |||
| | last6 = Johnson | |||
| | title = Molecular modeling, structure--activity relationships and functional antagonism studies of 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3-piperidyl 4-methylphenyl ketones as a novel class of dopamine transporter inhibitors | |||
| | volume = 9 | |||
| | issue = 7 | |||
| | pages = 1753–1764 | |||
| | journal = Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry | |||
| | doi = 10.1016/S0968-0896(01)00090-6 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| In place of acetone, acetonedicarboxylic acid is known as the "]" the 1,3-dicarboxylic acid groups are so-called "]s" to facilitate the ring forming reactions. The calcium salt is there as a "]" as it is claimed that higher yields are possible if the reaction is conducted at "] ]". | In place of acetone, acetonedicarboxylic acid is known as the "]" the 1,3-dicarboxylic acid groups are so-called "]s" to facilitate the ring forming reactions. The calcium salt is there as a "]" as it is claimed that higher yields are possible if the reaction is conducted at "] ]". | ||
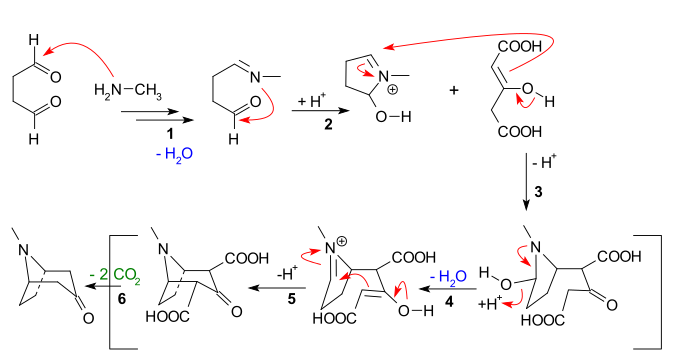
| == Reaction mechanism== | === Reaction mechanism=== | ||
| The main features apparent from the reaction sequence below are: | The main features apparent from the reaction sequence below are: | ||
| #] of ] to ], followed by loss of water to create an ] | #] of ] to ], followed by loss of water to create an ] | ||
| #Intramolecular addition of the imine to the second aldehyde unit and first ring closure | #] addition of the imine to the second aldehyde unit and first ring closure | ||
| #] ] of the ] of acetone dicarboxylate | #] ] of the ] of acetone dicarboxylate | ||
| #New enolate formation and new imine formation with loss of water for | #New enolate formation and new imine formation with loss of water for | ||
| #Second |
#Second intramolecular Mannich reaction and second ring closure | ||
| #Loss of 2 carboxylic groups to tropinone | #Loss of 2 carboxylic groups to tropinone | ||
| :] | :] | ||
| Some authors have actually tried to retain one of the CO<sub>2</sub>H groups.<ref>{{Cite |
Some authors have actually tried to retain one of the CO<sub>2</sub>H groups.<ref>{{Cite journal| last1 = Findlay | first1 = S. P.| title = Concerning 2-Carbomethoxytropinone | journal = Journal of Organic Chemistry | year = 1957 | volume = 22 | issue = 11| pages = 1385–1394| doi = 10.1021/jo01362a022}}</ref> | ||
| CO<sub>2</sub>R-tropinone has 4 stereoisomers, although the corresponding ] alkyl ester has only a pair of enantiomers. | |||
| ===From cycloheptanone=== | |||
| ] dehydrogenation (oxidation) of ] (suberone) to 2,6-cycloheptadienone followed by reaction with an amine is versatile a way of forming tropinones.<ref>{{US patent|8609690}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1021/ja012127+ | pmid = 11878978 | year = 2002 | last1 = Nicolaou | first1 = K. C. | last2 = Montagnon | first2 = T. | last3 = Baran | first3 = P. S. | last4 = Zhong | first4 = Y. L. | title = Iodine(V) reagents in organic synthesis. Part 4. O-Iodoxybenzoic acid as a chemospecific tool for single electron transfer-based oxidation processes | journal = Journal of the American Chemical Society | volume = 124 | issue = 10 | pages = 2245–58 }}</ref> The mechanism evoked is clearly delineated to be a double ] (i.e. conjugate addition). | |||
| ===Biochemistry method=== | |||
| {{empty section|date=April 2022}} | |||
| <ref name="BedewitzJones2018">{{cite journal|last1=Bedewitz|first1=Matthew A.|last2=Jones|first2=A. Daniel|last3=D'Auria|first3=John C.|last4=Barry|first4=Cornelius S.|title=Tropinone synthesis via an atypical polyketide synthase and P450-mediated cyclization|journal=Nature Communications|volume=9|issue=1|year=2018|page=5281|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-018-07671-3|pmid=30538251|pmc=6290073|bibcode=2018NatCo...9.5281B|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| ===Reduction of tropinone=== | |||
| The reduction of tropinone is mediated by ]-dependent reductase enzymes, which have been characterized in multiple plant species.<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1016/0031-9422(92)80247-C | title = Two tropinone reducing enzymes from Datura stramonium transformed root cultures | year = 1992 |author1=A. Portsteffen |author2=B. Draeger |author3=A. Nahrstedt | journal = Phytochemistry | volume = 31 | pages = 1135 | issue = 4| bibcode = 1992PChem..31.1135P }}</ref> These plant species all contain two types of the reductase enzymes, tropinone reductase I and tropinone reductase II. TRI produces tropine and TRII produces pseudotropine. Due to differing kinetic and pH/activity characteristics of the enzymes and by the 25-fold higher activity of TRI over TRII, the majority of the tropinone reduction is from TRI to form tropine.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Boswell HD, Dräger B, McLauchlan WR |title=Specificities of the enzymes of ''N''-alkyltropane biosynthesis in Brugmansia and Datura |journal=Phytochemistry |volume=52 |issue=5 |pages=871–8 |date=November 1999 |pmid=10626376 |doi= 10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00293-9|bibcode=1999PChem..52..871B |display-authors=etal}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| == See also == | |||
| CO<sub>2</sub>R-tropinone has 4 stereoisomers, although the corresponding ] alkyl ester there is only a pair of enantiomers. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (2-CMT) an intermediate in the creation of ] ] | |||
| *] | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| <references /> | |||
| ==External links== | == External links == | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 1 March 2024

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 8-Methyl-8-azabicyclooctan-3-one | |
| Other names 3-Tropinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.756 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H13NO |
| Molar mass | 139.195 g/mol |
| Appearance | Brown solid |
| Melting point | 42.5 °C (108.5 °F; 315.6 K) |
| Boiling point | (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302, H314 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Tropinone is an alkaloid, famously synthesised in 1917 by Robert Robinson as a synthetic precursor to atropine, a scarce commodity during World War I. Tropinone and the alkaloids cocaine and atropine all share the same tropane core structure. Its corresponding conjugate acid at pH 7.3 major species is known as tropiniumone.
Synthesis
The first synthesis of tropinone was by Richard Willstätter in 1901. It started from the seemingly related cycloheptanone, but required many steps to introduce the nitrogen bridge; the overall yield for the synthesis path is only 0.75%. Willstätter had previously synthesized cocaine from tropinone, in what was the first synthesis and elucidation of the structure of cocaine.

Robinson's "double Mannich" reaction
The 1917 synthesis by Robinson is considered a classic in total synthesis due to its simplicity and biomimetic approach. Tropinone is a bicyclic molecule, but the reactants used in its preparation are fairly simple: succinaldehyde, methylamine and acetonedicarboxylic acid (or even acetone). The synthesis is a good example of a biomimetic reaction or biogenetic-type synthesis because biosynthesis makes use of the same building blocks. It also demonstrates a tandem reaction in a one-pot synthesis. Furthermore, the yield of the synthesis was 17% and with subsequent improvements exceeded 90%.
This reaction is described as an intramolecular "double Mannich reaction" for obvious reasons. It is not unique in this regard, as others have also attempted it in piperidine synthesis.
In place of acetone, acetonedicarboxylic acid is known as the "synthetic equivalent" the 1,3-dicarboxylic acid groups are so-called "activating groups" to facilitate the ring forming reactions. The calcium salt is there as a "buffer" as it is claimed that higher yields are possible if the reaction is conducted at "physiological pH".
Reaction mechanism
The main features apparent from the reaction sequence below are:
- Nucleophilic addition of methylamine to succinaldehyde, followed by loss of water to create an imine
- Intramolecular addition of the imine to the second aldehyde unit and first ring closure
- Intermolecular Mannich reaction of the enolate of acetone dicarboxylate
- New enolate formation and new imine formation with loss of water for
- Second intramolecular Mannich reaction and second ring closure
- Loss of 2 carboxylic groups to tropinone
Some authors have actually tried to retain one of the CO2H groups.
CO2R-tropinone has 4 stereoisomers, although the corresponding ecgonidine alkyl ester has only a pair of enantiomers.
From cycloheptanone
IBX dehydrogenation (oxidation) of cycloheptanone (suberone) to 2,6-cycloheptadienone followed by reaction with an amine is versatile a way of forming tropinones. The mechanism evoked is clearly delineated to be a double Michael reaction (i.e. conjugate addition).
Biochemistry method
| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (April 2022) |
Reduction of tropinone
The reduction of tropinone is mediated by NADPH-dependent reductase enzymes, which have been characterized in multiple plant species. These plant species all contain two types of the reductase enzymes, tropinone reductase I and tropinone reductase II. TRI produces tropine and TRII produces pseudotropine. Due to differing kinetic and pH/activity characteristics of the enzymes and by the 25-fold higher activity of TRI over TRII, the majority of the tropinone reduction is from TRI to form tropine.

See also
- Benztropine
- Daturaolone
- 2-Carbomethoxytropinone (2-CMT) an intermediate in the creation of ecgonine cocaine analogues
- Ecgonidine
References
- ^ "Tropinone". Substance Information. ECHA.
- Robinson R (1917). "LXIII. A Synthesis of Tropinone". Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions. 111: 762–768. doi:10.1039/CT9171100762.
- Nicolaou KC, Vourloumis D, Winssinger N, Baran PS (2000). "The Art and Science of Total Synthesis at the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 39 (1): 44–122. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000103)39:1<44::AID-ANIE44>3.0.CO;2-L. PMID 10649349.
- Chemical Entities of Biological Interest Identification code: ChEBI:57851 "tropiniumone"
- ^ Smit WA, Smit WA, Bochkov AF, Caple R (1998). Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1039/9781847551573. ISBN 978-0-85404-544-0.
- Humphrey AJ, O'Hagan D (2001). "Tropane alkaloid biosynthesis. A century old problem unresolved". Natural Product Reports. 18 (5). Royal Society of Chemistry: 494–502. doi:10.1039/b001713m. PMID 11699882.
- Doble M, Kruthiventi AK (2007). Green Chemistry and Engineering. Oxford: Elsevier. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-12-372532-5.
- Birch AJ (1993). "Investigating a Scientific Legend: The Tropinone Synthesis of Sir Robert Robinson, F.R.S". Notes and Records of the Royal Society of London. 47 (2): 277–296. doi:10.1098/rsnr.1993.0034. JSTOR 531792. S2CID 143267467.
- Wang S, Sakamuri S, Enyedy IJ, Kozikowski AP, Deschaux O, Bandyopadhyay BC, Tella SR, Zaman WA, Johnson KM (2000). "Discovery of a novel dopamine transporter inhibitor, 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3-piperidyl 4-methylphenyl ketone, as a potential cocaine antagonist through 3D-database pharmacophore searching. Molecular modeling, structure-activity relationships, and behavioral pharmacological studies". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 43 (3): 351–360. doi:10.1021/jm990516x. PMID 10669562.
- Wang S, Sakamuri, Enyedy, Kozikowski, Zaman, Johnson (2001). "Molecular modeling, structure--activity relationships and functional antagonism studies of 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3-piperidyl 4-methylphenyl ketones as a novel class of dopamine transporter inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 9 (7): 1753–1764. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(01)00090-6. PMID 11425577.
- Findlay SP (1957). "Concerning 2-Carbomethoxytropinone". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 22 (11): 1385–1394. doi:10.1021/jo01362a022.
- U.S. patent 8,609,690
- Nicolaou KC, Montagnon T, Baran PS, Zhong YL (2002). "Iodine(V) reagents in organic synthesis. Part 4. O-Iodoxybenzoic acid as a chemospecific tool for single electron transfer-based oxidation processes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 124 (10): 2245–58. doi:10.1021/ja012127+. PMID 11878978.
- Bedewitz MA, Jones AD, D'Auria JC, Barry CS (2018). "Tropinone synthesis via an atypical polyketide synthase and P450-mediated cyclization". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 5281. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.5281B. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07671-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 6290073. PMID 30538251.
- A. Portsteffen, B. Draeger, A. Nahrstedt (1992). "Two tropinone reducing enzymes from Datura stramonium transformed root cultures". Phytochemistry. 31 (4): 1135. Bibcode:1992PChem..31.1135P. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(92)80247-C.
- Boswell HD, Dräger B, McLauchlan WR, et al. (November 1999). "Specificities of the enzymes of N-alkyltropane biosynthesis in Brugmansia and Datura". Phytochemistry. 52 (5): 871–8. Bibcode:1999PChem..52..871B. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00293-9. PMID 10626376.