| Revision as of 13:47, 28 October 2011 editBeetstra (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators172,031 edits Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'CASNo').← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:08, 17 October 2024 edit undoKyjugn (talk | contribs)228 editsNo edit summaryTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 457817818 | |||
| ⚫ | | ImageFile = Arsthinol.svg | ||
| ⚫ | | ImageFile_Ref = {{Chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| ⚫ | | ImageSize = 244 | ||
| ⚫ | | ImageName = Structural formula of arsthinol | ||
| ⚫ | | PIN = ''N''-<nowiki/>{2-Hydroxy-5-phenyl}acetamide | ||
| ⚫ | |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | CASNo = 119-96-0 | |||
| ⚫ | | CASNo_Ref = {{Cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | ChEBI = 135465 | |||
| | ChEMBL = 1788384 | |||
| ⚫ | | ChemSpiderID = 8107 | ||
| ⚫ | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | DrugBank = DB08928 | |||
| ⚫ | | EINECS = 204-361-7 | ||
| | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| ⚫ | | KEGG = D07356 | ||
| ⚫ | | PubChem = 8414 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| | UNII = QNT09A162Y | | UNII = QNT09A162Y | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = CC(=O)NC1=C(O)C=CC(=C1)1SCC(CO)S1 | ||
| ⚫ | | ImageFile = Arsthinol.svg | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES1 = O=C(Nc2cc(1SCC(S1)CO)ccc2O)C | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | StdInChI = 1S/C11H14AsNO3S2/c1-7(15)13-10-4-8(2-3-11(10)16)12-17-6-9(5-14)18-12/h2-4,9,14,16H,5-6H2,1H3,(H,13,15) | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | InChI = 1/C11H14AsNO3S2/c1-7(15)13-10-4-8(2-3-11(10)16)12-17-6-9(5-14)18-12/h2-4,9,14,16H,5-6H2,1H3,(H,13,15) | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | StdInChIKey = MRUDSZSRLQAPOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | CASNo = <!-- blanked - oldvalue: 119-96-0 --> | |||
| ⚫ | | InChIKey = MRUDSZSRLQAPOG-UHFFFAOYAP}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | |Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | C=11 | H=14 | As=1 | N=1 | O=3 | S=2}} | |||
| | PubChem_Ref = {{Pubchemcite|correct|PubChem}} | |||
| ⚫ | |Section6={{Chembox Pharmacology | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | ATCCode_prefix = P01 | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ATCCode_suffix = AR01 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ATC_Supplemental = {{ATCvet|P51|AD01}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| AdminRoutes = Oral | ||
| ⚫ | | Metabolism = 89 % Hepatic<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Cristau | first1 = B | last2 = Chabas | first2 = ME | last3 = Placidi | first3 = M | year = 1975 | title = Voies et cinétiques d'excrétion de l'arsenic chez le Cobaye après injection de divers médicaments organo-arséniés | journal = ] | volume = 33 | pages = 577–89 }}</ref>}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | C = 11 | |||
| | H = 14 | |||
| | As = 1 | |||
| | N = 1 | |||
| | O = 3 | |||
| | S = 2 | |||
| | ExactMass = 346.963106116 g mol<sup>-1</sup>}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | AdminRoutes = Oral | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Arsthinol''' (]) is an ]. It was synthesized for the first time in 1949 by Ernst A.H. Friedheim by complexation of ] with 2,3-dimercaptopropanol (])<ref>Friedheim |
'''Arsthinol''' (]) is an ]. It was synthesized for the first time in 1949 by Ernst A.H. Friedheim by complexation of ] with 2,3-dimercaptopropanol (])<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Friedheim | first1 = Ernst AH | year = 1949 | title = A Five Day Peroral Treatment of Yaws with STB, a New Trivalent Arsenical | journal = ] | volume = s1-29 | issue = 2 | pages = 185–188 | doi = 10.4269/ajtmh.1949.s1-29.185 | pmid = 18116845 }}</ref> and has been demonstrated to be effective against ] and ]. It was marketed a few years later by Endo Products (Balarsen, Tablets, 0.1 g).<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Anonyme | year = 1953 | title = New and nonofficial remedies; arsthinol | journal = ] | volume = 152 | page = 531 }}</ref> | ||
| </ref> and has been demonstrated to be effective against ] and ]. It was marketed few years latter by Endo Products (Balarsen, Tablets, 0.1 g)<ref>Anonyme. (1953) New and nonofficial remedies; arsthinol. J Am Med Assoc 152: 531</ref>. | |||
| Among trivalent organoarsenicals, arsthinol was considered very well tolerated.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Brown | first1 = CH | last2 = Gebhart | first2 = WF | last3 = Reich | first3 = A | year = 1956 | title = Intestinal amebiasis: incidence, symptoms, and treatment with arsthinol (Balarsen) | journal = ] | volume = 160 | issue = 5| pages = 360–363 | doi=10.1001/jama.1956.02960400018005| pmid = 13278204 }}</ref> Recently, it was studied for its anticancer activity.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Gibaud | first1 = S | last2 = Alfonsi | first2 = R | last3 = Mutzenhardt | first3 = P |display-authors=et al | year = 2006 | title = (2-Phenyl- dithiarsolan-4-yl)-methanol derivatives show in vitro antileukemic activity | journal = ] | volume = 691 | issue = 5| pages = 1081–1084 | doi=10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.11.007}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Becherirat | first1 = S. | last2 = Lanhers | first2 = M.-C. | last3 = Socha | first3 = M. | last4 = Yemloul | first4 = M. | last5 = Astier | first5 = A. | last6 = Loboda | first6 = C. | last7 = Aniceto | first7 = N. | last8 = Gibaud | first8 = S. | year = 2013 | title = The antitumor effects of an arsthinol-cyclodextrin complex in an heterotopic mouse model of glioma | url = https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01169157/file/Eur%20J%20Pharm%20Biopharm%202013%20Becherirat.pdf| journal = ] | volume = 85| issue = 3| pages = 560–568| doi = 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.06.021 | pmid = 23831266 }}</ref> | |||
| Among trivalent organoarsenicals, arthinol was considered as very well tolerated <ref>Brown CH, Gebhart WF, Reich A. (1956) Intestinal amebiasis: incidence, symptoms, and treatment with arsthinol (Balarsen). JAMA 160: 360-363 | |||
| </ref>. In 2006 it was studied for its antileukemic activity <ref>Gibaud S, Alfonsi R, Mutzenhardt P et al. (2006) (2-Phenyl- dithiarsolan-4-yl)-methanol derivatives show in vitro antileukemic activity. J Organomet Chem 691: 1081-1084 | |||
| ==Identification== | |||
| </ref>. | |||
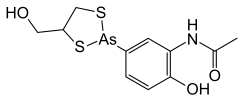
| Arsthinol has ] name of N-phenyl] ] with a ] of C11H14AsNO3S2 and is represented by the ], CC(=O)NC1=C(C=CC(=C1)2SCC(S2)CO)O.<ref>{{Cite web |last=PubChem |title=PubChem |url=https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ |access-date=2024-10-17 |website=pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Properties== | |||
| The ] of Arsthinol is 347.3 g/mol, with a ] donor count of 3 and a hydrogen bond acceptor count of 5. It has 3 rotatable bonds, an exact mass of 347.279 g/mol, and a ] of 346.963105 g/mol. The ] is 120Ų, and the compound contains 18 heavy atoms. It has no formal charge, a complexity of 308, and contains no ] atoms. There are no defined atom ], but there is 1 undefined atom stereocenter. The compound has no defined or undefined bond stereocenters, includes 1 ] unit, and is ]<ref>{{Cite web |last=PubChem |title=Arsthinol |url=https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Arsthinol#section=Synonyms |access-date=2024-10-17 |website=pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=arsthinol {{!}} C11H14AsNO3S2 |url=https://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.8107.html |access-date=2024-10-17 |website=www.chemspider.com}}</ref> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 56: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Antimicrobial-stub}} | {{Antimicrobial-stub}} | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:08, 17 October 2024
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N-{2-Hydroxy-5-phenyl}acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.965 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H14AsNO3S2 |
| Molar mass | 347.28 g·mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | P01AR01 (WHO) QP51AD01 (WHO) |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Metabolism | 89 % Hepatic |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Arsthinol (INN) is an antiprotozoal agent. It was synthesized for the first time in 1949 by Ernst A.H. Friedheim by complexation of acetarsol with 2,3-dimercaptopropanol (British anti-Lewisite) and has been demonstrated to be effective against amoebiasis and yaws. It was marketed a few years later by Endo Products (Balarsen, Tablets, 0.1 g).
Among trivalent organoarsenicals, arsthinol was considered very well tolerated. Recently, it was studied for its anticancer activity.
Identification
Arsthinol has IUPAC name of N-phenyl] acetamide with a molecular formula of C11H14AsNO3S2 and is represented by the SMILES notation, CC(=O)NC1=C(C=CC(=C1)2SCC(S2)CO)O.
Properties
The molecular weight of Arsthinol is 347.3 g/mol, with a hydrogen bond donor count of 3 and a hydrogen bond acceptor count of 5. It has 3 rotatable bonds, an exact mass of 347.279 g/mol, and a monoisotopic mass of 346.963105 g/mol. The topological polar surface area is 120Ų, and the compound contains 18 heavy atoms. It has no formal charge, a complexity of 308, and contains no isotope atoms. There are no defined atom stereocenters, but there is 1 undefined atom stereocenter. The compound has no defined or undefined bond stereocenters, includes 1 covalently bonded unit, and is canonicalized.
References
- Cristau, B; Chabas, ME; Placidi, M (1975). "Voies et cinétiques d'excrétion de l'arsenic chez le Cobaye après injection de divers médicaments organo-arséniés". Ann Pharm Fr. 33: 577–89.
- Friedheim, Ernst AH (1949). "A Five Day Peroral Treatment of Yaws with STB, a New Trivalent Arsenical". Am J Trop Med Hyg. s1-29 (2): 185–188. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1949.s1-29.185. PMID 18116845.
- Anonyme (1953). "New and nonofficial remedies; arsthinol". J Am Med Assoc. 152: 531.
- Brown, CH; Gebhart, WF; Reich, A (1956). "Intestinal amebiasis: incidence, symptoms, and treatment with arsthinol (Balarsen)". JAMA. 160 (5): 360–363. doi:10.1001/jama.1956.02960400018005. PMID 13278204.
- Gibaud, S; Alfonsi, R; Mutzenhardt, P; et al. (2006). "(2-Phenyl- dithiarsolan-4-yl)-methanol derivatives show in vitro antileukemic activity". J Organomet Chem. 691 (5): 1081–1084. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.11.007.
- Becherirat, S.; Lanhers, M.-C.; Socha, M.; Yemloul, M.; Astier, A.; Loboda, C.; Aniceto, N.; Gibaud, S. (2013). "The antitumor effects of an arsthinol-cyclodextrin complex in an heterotopic mouse model of glioma" (PDF). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 85 (3): 560–568. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.06.021. PMID 23831266.
- PubChem. "PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-10-17.
- PubChem. "Arsthinol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-10-17.
- "arsthinol | C11H14AsNO3S2". www.chemspider.com. Retrieved 2024-10-17.
| Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – agents against amoebozoa/amebicide (P01) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entamoeba |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Acanthamoeba | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |