| Revision as of 18:26, 13 April 2012 editBogBot (talk | contribs)Bots53,132 editsm replaced secondary with primary DrugBank accession number per talk← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:54, 16 September 2024 edit undoNovadeluxer (talk | contribs)7 edits Added information about a nasal spray containing the drug.Tag: Visual edit | ||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Chemical compound}} | |||
| {{Drugbox | {{Drugbox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 462090822 | | verifiedrevid = 462090822 | ||
| | image = Levocabastine.svg | |||
| ⚫ | | IUPAC_name = (3''S'',4''R'')-1--3-methyl-4- |
||
| ⚫ | | width = 260 | ||
| | image = Levocabastine2.png | |||
| ⚫ | | width = |
||
| <!--Clinical data--> | <!--Clinical data--> | ||
| | tradename = |
| tradename = Livostin | ||
| | Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|levocabastine}} | | Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|levocabastine}} | ||
| | pregnancy_AU = B3 | | pregnancy_AU = B3 | ||
| | pregnancy_US = C | | pregnancy_US = C | ||
| | legal_US = Rx-only | |||
| | legal_US_comment = <ref>{{cite web|title=Livostin - levocabastine hydrochloride suspension |url=http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=420b3f66-87f0-47d8-947c-541e84eb594a| work = DailyMed | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine |access-date=4 January 2016}}</ref> | |||
| | legal_status = Rx-only | | legal_status = Rx-only | ||
| | routes_of_administration = Ophthalmic, intranasal<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.rxmed.com/b.main/b2.pharmaceutical/b2.1.monographs/CPS-%20Monographs/CPS-%20(General%20Monographs-%20L)/LIVOSTIN%20NASAL%20SPRAY.html | |
| routes_of_administration = Ophthalmic, intranasal<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.rxmed.com/b.main/b2.pharmaceutical/b2.1.monographs/CPS-%20Monographs/CPS-%20(General%20Monographs-%20L)/LIVOSTIN%20NASAL%20SPRAY.html | work = RxMed: Pharmaceutical Information | title = Livostin Nasal Spray | access-date = 13 November 2005}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_prefix = R01 | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_suffix = AC02 | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_supplemental = {{ATC|S01|GX02}} | ||
| <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| | bioavailability = |
| bioavailability = | ||
| | protein_bound = |
| protein_bound = | ||
| | metabolism = |
| metabolism = | ||
| | elimination_half-life = |
| elimination_half-life = | ||
| <!--Identifiers--> | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| | CAS_number = 79516-68-0 | | CAS_number = 79516-68-0 | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_prefix = R01 | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_suffix = AC02 | ||
| ⚫ | | ATC_supplemental = {{ATC|S01|GX02}} | ||
| | PubChem = 54385 | | PubChem = 54385 | ||
| | IUPHAR_ligand = 1586 | | IUPHAR_ligand = 1586 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite| |
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| | DrugBank = DB01106 | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 16736421 | | ChemSpiderID = 16736421 | ||
| Line 41: | Line 43: | ||
| <!--Chemical data--> | <!--Chemical data--> | ||
| ⚫ | | IUPAC_name = (3''S'',4''R'')-1--3-methyl-4-phenyl-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid | ||
| | C=26 | H=29 | F=1 | N=2 | O=2 |
| C=26 | H=29 | F=1 | N=2 | O=2 | ||
| | molecular_weight = 420.519 g/mol | |||
| | smiles = Fc1ccc(cc1)2(CC(CC2)N3CC((C)C3)(c4ccccc4)C(O)=O)C#N | | smiles = Fc1ccc(cc1)2(CC(CC2)N3CC((C)C3)(c4ccccc4)C(O)=O)C#N | ||
| | InChI = 1/C26H29FN2O2/c1-19-17-29(16-15-26(19,24(30)31)21-5-3-2-4-6-21)23-11-13-25(18-28,14-12-23)20-7-9-22(27)10-8-20/h2-10,19,23H,11-17H2,1H3,(H,30,31)/t19-,23-,25-,26-/m1/s1 | |||
| | InChIKey = ZCGOMHNNNFPNMX-KYTRFIICBU | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C26H29FN2O2/c1-19-17-29(16-15-26(19,24(30)31)21-5-3-2-4-6-21)23-11-13-25(18-28,14-12-23)20-7-9-22(27)10-8-20/h2-10,19,23H,11-17H2,1H3,(H,30,31)/t19-,23-,25-,26-/m1/s1 | | StdInChI = 1S/C26H29FN2O2/c1-19-17-29(16-15-26(19,24(30)31)21-5-3-2-4-6-21)23-11-13-25(18-28,14-12-23)20-7-9-22(27)10-8-20/h2-10,19,23H,11-17H2,1H3,(H,30,31)/t19-,23-,25-,26-/m1/s1 | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| | StdInChIKey = ZCGOMHNNNFPNMX-KYTRFIICSA-N | | StdInChIKey = ZCGOMHNNNFPNMX-KYTRFIICSA-N | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | '''Levocabastine''' is a selective |
||
| ⚫ | '''Levocabastine''' (trade name '''Livostin''' or Livocab, depending on the region) is a selective second-generation ] which was discovered at ] in 1979. It is used for allergic ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pipkorn U, Bende M, Hedner J, Hedner T | title = A double-blind evaluation of topical levocabastine, a new specific H1 antagonist in patients with allergic conjunctivitis | journal = Allergy | volume = 40 | issue = 7 | pages = 491–496 | date = October 1985 | pmid = 2866725 | doi = 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00255.x | s2cid = 8681108 }}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | As well as acting as an antihistamine, levocabastine has also subsequently been found to act as a potent and selective antagonist for the ] receptor ], and was the first drug used to characterise the different neurotensin subtypes.<ref |
||
| ⚫ | As well as acting as an antihistamine, levocabastine has also subsequently been found to act as a potent and selective antagonist for the ] receptor ], and was the first drug used to characterise the different neurotensin subtypes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Schotte A, Leysen JE, Laduron PM | title = Evidence for a displaceable non-specific neurotensin binding site in rat brain | journal = Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology | volume = 333 | issue = 4 | pages = 400–405 | date = August 1986 | pmid = 3022160 | doi = 10.1007/BF00500016 | s2cid = 23692347 }}</ref><ref name="pmid2888670">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kitabgi P, Rostène W, Dussaillant M, Schotte A, Laduron PM, Vincent JP | title = Two populations of neurotensin binding sites in murine brain: discrimination by the antihistamine levocabastine reveals markedly different radioautographic distribution | journal = European Journal of Pharmacology | volume = 140 | issue = 3 | pages = 285–293 | date = August 1987 | pmid = 2888670 | doi = 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90285-8 }}</ref> This has made it a useful tool for the study of this receptor.<ref name="pmid8647296">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chalon P, Vita N, Kaghad M, Guillemot M, Bonnin J, Delpech B, Le Fur G, Ferrara P, Caput D | display-authors = 6 | title = Molecular cloning of a levocabastine-sensitive neurotensin binding site | journal = FEBS Letters | volume = 386 | issue = 2–3 | pages = 91–94 | date = May 1996 | pmid = 8647296 | doi = 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00397-3 | s2cid = 5802578 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid8795617">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mazella J, Botto JM, Guillemare E, Coppola T, Sarret P, Vincent JP | title = Structure, functional expression, and cerebral localization of the levocabastine-sensitive neurotensin/neuromedin N receptor from mouse brain | journal = The Journal of Neuroscience | volume = 16 | issue = 18 | pages = 5613–5620 | date = September 1996 | pmid = 8795617 | pmc = 6578974 | doi = 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-18-05613.1996 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid16148226">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sarret P, Esdaile MJ, Perron A, Martinez J, Stroh T, Beaudet A | title = Potent spinal analgesia elicited through stimulation of NTS2 neurotensin receptors | journal = The Journal of Neuroscience | volume = 25 | issue = 36 | pages = 8188–8196 | date = September 2005 | pmid = 16148226 | pmc = 6725526 | doi = 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0810-05.2005 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid17074405">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bredeloux P, Costentin J, Dubuc I | title = Interactions between NTS2 neurotensin and opioid receptors on two nociceptive responses assessed on the hot plate test in mice | journal = Behavioural Brain Research | volume = 175 | issue = 2 | pages = 399–407 | date = December 2006 | pmid = 17074405 | doi = 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.09.016 | s2cid = 24790151 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17697051">{{cite journal | vauthors = Yamauchi R, Wada E, Kamichi S, Yamada D, Maeno H, Delawary M, Nakazawa T, Yamamoto T, Wada K | display-authors = 6 | title = Neurotensin type 2 receptor is involved in fear memory in mice | journal = Journal of Neurochemistry | volume = 102 | issue = 5 | pages = 1669–1676 | date = September 2007 | pmid = 17697051 | doi = 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04805.x | s2cid = 19774998 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | ||
| The ] '''Bilina''' is a combination of Levocabastine, ], and other components and is typically used in a 0.5 mg/ml suspension as eye-drops, dispensed in 4ml bottles for the treatment of allergic ] or similar allergic ocular conditions. Another formulation is available as a ] for the management of ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Levocabastine ophthalmic|website=vademecum.es |url=http://www.vademecum.es/principios-activos-levocabastina+oftalmica-s01gx02|access-date=11 September 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=★ Levocabastina 🥇 |url=https://www.vademecum.es/principios-activos-levocabastina-r01ac02-es |access-date=2024-09-16 |website=www.vademecum.es}}</ref> | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 62: | ||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| * {{cite web | url = https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/rn/79516-68-0 | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine | work = Drug Information Portal | title = Levocabastine }} | |||
| * {{cite web | author=RxList | year=2004 | title=Livostin Online, Description, Chemistry, Ingredients - Levocabastine | work=LIVOSTIN | publisher=RxList Inc | url = http://www.rxlist.com/drugs/drug-8041-Livostin+Opht.aspx?drugid=8041&drugname=Livostin+Opht | accessdate=9 October 2005 }} {{Dead link|date=October 2010|bot=H3llBot}} | |||
| * {{cite web | url = https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/levocabastine%20hydrochloride | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine | work = Drug Information Portal | title = Levocabastine hydrochloride }} | |||
| * {{cite web | author = Novartis Pharmaceuticals | month = March | year = 2002 | title = LIVOSTIN| url = http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/livostin.pdf | accessdate = August 20, 2006 | format = PDF }} | |||
| {{Histaminergics}} | {{Histaminergics}} | ||
| {{Nasal preparations}} | {{Nasal preparations}} | ||
| {{Portal bar | Medicine}} | |||
| {{Neuropeptide agonists and antagonists}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| {{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} | {{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:54, 16 September 2024
Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound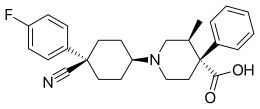 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Livostin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Ophthalmic, intranasal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H29FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 420.528 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Levocabastine (trade name Livostin or Livocab, depending on the region) is a selective second-generation H1 receptor antagonist which was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1979. It is used for allergic conjunctivitis.
As well as acting as an antihistamine, levocabastine has also subsequently been found to act as a potent and selective antagonist for the neurotensin receptor NTS2, and was the first drug used to characterise the different neurotensin subtypes. This has made it a useful tool for the study of this receptor.
The pharmaceutical drug Bilina is a combination of Levocabastine, benzalkonium chloride, and other components and is typically used in a 0.5 mg/ml suspension as eye-drops, dispensed in 4ml bottles for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis or similar allergic ocular conditions. Another formulation is available as a nasal spray for the management of allergic rhinitis.
References
- "Livostin Nasal Spray". RxMed: Pharmaceutical Information. Retrieved 13 November 2005.
- "Livostin - levocabastine hydrochloride suspension". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- Pipkorn U, Bende M, Hedner J, Hedner T (October 1985). "A double-blind evaluation of topical levocabastine, a new specific H1 antagonist in patients with allergic conjunctivitis". Allergy. 40 (7): 491–496. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00255.x. PMID 2866725. S2CID 8681108.
- Schotte A, Leysen JE, Laduron PM (August 1986). "Evidence for a displaceable non-specific neurotensin binding site in rat brain". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 333 (4): 400–405. doi:10.1007/BF00500016. PMID 3022160. S2CID 23692347.
- Kitabgi P, Rostène W, Dussaillant M, Schotte A, Laduron PM, Vincent JP (August 1987). "Two populations of neurotensin binding sites in murine brain: discrimination by the antihistamine levocabastine reveals markedly different radioautographic distribution". European Journal of Pharmacology. 140 (3): 285–293. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(87)90285-8. PMID 2888670.
- Chalon P, Vita N, Kaghad M, Guillemot M, Bonnin J, Delpech B, et al. (May 1996). "Molecular cloning of a levocabastine-sensitive neurotensin binding site". FEBS Letters. 386 (2–3): 91–94. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00397-3. PMID 8647296. S2CID 5802578.
- Mazella J, Botto JM, Guillemare E, Coppola T, Sarret P, Vincent JP (September 1996). "Structure, functional expression, and cerebral localization of the levocabastine-sensitive neurotensin/neuromedin N receptor from mouse brain". The Journal of Neuroscience. 16 (18): 5613–5620. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-18-05613.1996. PMC 6578974. PMID 8795617.
- Sarret P, Esdaile MJ, Perron A, Martinez J, Stroh T, Beaudet A (September 2005). "Potent spinal analgesia elicited through stimulation of NTS2 neurotensin receptors". The Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (36): 8188–8196. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0810-05.2005. PMC 6725526. PMID 16148226.
- Bredeloux P, Costentin J, Dubuc I (December 2006). "Interactions between NTS2 neurotensin and opioid receptors on two nociceptive responses assessed on the hot plate test in mice". Behavioural Brain Research. 175 (2): 399–407. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.09.016. PMID 17074405. S2CID 24790151.
- Yamauchi R, Wada E, Kamichi S, Yamada D, Maeno H, Delawary M, et al. (September 2007). "Neurotensin type 2 receptor is involved in fear memory in mice". Journal of Neurochemistry. 102 (5): 1669–1676. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04805.x. PMID 17697051. S2CID 19774998.
- "Levocabastine ophthalmic". vademecum.es. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- "★ Levocabastina 🥇". www.vademecum.es. Retrieved 2024-09-16.
External links
- "Levocabastine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Levocabastine hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical |
| ||||||||||
| Systemic use: Sympathomimetics | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This drug article relating to the respiratory system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |