| Revision as of 05:21, 9 October 2006 editXcentaur (talk | contribs)Pending changes reviewers8,846 edits Formatting← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:43, 1 January 2025 edit undoKvng (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers108,302 edits add selectively qualifier otherwise you just have a Distribution amplifier | ||
| (591 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|A device that selects between several analog or digital input signals}} | |||
| {{redirect|MUX}} | |||
| {{About|electronics switching|telecommunications|multiplexing}} | |||
| A '''multiplexer''' (or '''mux''' or, more rarely, '''muldex''') is a device that encodes or '']'' information from two or more data sources into a single channel. | |||
| ] | |||
| == Multiplexing == | |||
| ] | |||
| In ], a '''multiplexer''' (or '''mux'''; spelled sometimes as '''multiplexor'''), also known as a '''data selector''', is a device that selects between several ] or ] input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line.<ref name="Network+ Guide to Networks">{{cite book | last = Dean | first = Tamara | title = Network+ Guide to Networks | publisher = Delmar | year = 2010 | pages = 82–85 | isbn = 978-1423902454 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=UD0h_GqgbHgC&q=network%2B+guide+to+networks}}</ref> The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of <math>2^n</math> inputs has <math>n</math> select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output.<ref>{{cite book | last = Debashis | first = De | title = Basic Electronics | publisher = Dorling Kindersley | year = 2010 | pages = 557 | isbn = 9788131710685 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=mT_j4F1bJx4C&q=Basic+Electronics+By+De+Debashis}}</ref> | |||
| ] splits the single data stream into the original multiple signals.]] | |||
| A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one ] or one communications ], instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement ] of multiple variables. | |||
| ] | |||
| Conversely, a '''demultiplexer''' (or '''demux''') is a device that takes a single input signal and selectively forwards it to one of several output lines. A multiplexer is often used with a complementary demultiplexer on the receiving end.<ref name="Network+ Guide to Networks"/> | |||
| Multiplexers are used in situations where the cost of implementing separate channels for each data source is more expensive than the cost and inconvenience of providing the multiplexing/demultiplexing functions. In a physical ], consider the merging behaviour of ]s crossing a narrow bridge; vehicles will take turns using the few available lanes. Upon reaching the end of the bridge they will separate into separate routes to their destinations. | |||
| An electronic multiplexer can be considered as a ] switch, and a demultiplexer as a ] switch.<ref>{{cite book | last = Lipták | first = Béla | title = Instrument engineers' handbook: Process software and digital networks | publisher = CRC Press | year = 2002 | pages = 343 | isbn = 9781439863442 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=KPjLAyA7HgoC&q=instrument+engineers'+handbook:+Process+software+and+digital+networks+By+B%C3%A9la+G.+Lipt%C3%A1k}}</ref> The schematic symbol for a multiplexer is an ] with the longer parallel side containing the input pins and the short parallel side containing the output pin.<ref>{{cite book | last = Harris | first = David | title = Digital Design and Computer Architecture | publisher = Penrose | year = 2007 | pages = 79 | isbn = 9780080547060 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=5X7JV5-n0FIC&q=Digital+design+and+computer+architecture+By+David+Money+Harris,+Sarah+L.+Harris}}</ref> The schematic on the right shows a 2-to-1 multiplexer on the left and an equivalent switch on the right. The <math>sel</math> wire connects the desired input to the output. | |||
| In ], the multiplexer combines several electrical signals into a single signal. There are different types of multiplexers for analog and digital circuits. | |||
| ==Applications== | |||
| In ], the multiplexer takes several separate digital data streams and combines them together into one data stream of a higher data rate. This allows multiple data streams to be carried from one place to another over one physical link, which saves cost. | |||
| Multiplexers are part of computer systems to select data from a specific source, be it a memory chip or a hardware peripheral. A computer uses multiplexers to control the data and address buses, allowing the processor to select data from multiple data sources | |||
| At the receiving end of the data link a complementary '''demultiplexer''' or '''demux''' is normally required to break the high data rate stream back down into the original lower rate streams. In some cases, the far end system may have more functionality than a simple demultiplexer and so, whilst the demultiplexing still exists logically, it may never actually happen physically. This would be typical where a multiplexer serves a number of IP network users and then feeds directly into a ] which immediately reads the content of the entire link into its routing processor and then does the demultiplexing in memory from where it will be converted directly into IP packets. | |||
| ] | |||
| It is usual to combine a multiplexer and a demultiplexer together into one piece of equipment and simply refer to the whole thing as a "multiplexer". Both pieces of equipment are needed at both ends of a transmission link because most communications systems transmit in both directions. | |||
| In digital communications, multiplexers allow several connections over a single channel, by connecting the multiplexer's single output to the demultiplexer's single input (Time-Division Multiplexing). The image to the right demonstrates this benefit. In this case, the cost of implementing separate channels for each data source is higher than the cost and inconvenience of providing the multiplexing/demultiplexing functions. | |||
| A real world example is the creation of ] for transmission from the computer/instrumentation system of a satellite, space craft or other remote vehicle to a ground system. | |||
| At the receiving end of the ] a complementary ''demultiplexer'' is usually required to break the single data stream back down into the original streams. In some cases, the far end system may have functionality greater than a simple demultiplexer; and while the demultiplexing still occurs technically, it may never be implemented discretely. This would be the case when, for instance, a multiplexer serves a number of ] network users; and then feeds directly into a ], which immediately reads the content of the entire link into its ] processor; and then does the demultiplexing in memory from where it will be converted directly into IP sections. | |||
| In analogue circuit design, a multiplexer is a special type of analogue switch that connects one signal selected from several inputs to a single output. | |||
| Often, a multiplexer and demultiplexer are combined into a single piece of equipment, which is simply referred to as a ''multiplexer''. Both circuit elements are needed at both ends of a transmission link because most communications systems transmit in ]. | |||
| == Digital multiplexers == | |||
| In ] design, the multiplexer is a device that has multiple input streams and only one output stream. It forwards one of the input streams to the output stream based on the values of one or more "selection inputs" or control inputs. For example, a two-input multiplexer is a simple connection of ]s whose output C is either input A or input B depending on the value of a third input S which selects the input. | |||
| In ] design, a multiplexer is a special type of analog switch that connects one signal selected from several inputs to a single output. | |||
| Its boolean equation is: | |||
| <math> C = ( A \, \mathbf{and \, not} \, S) \, \mathbf{or} \, (B \, \mathbf{and} \, S) \! </math> | |||
| ==Digital multiplexers== | |||
| Which can be expressed as the ]: | |||
| In ] design, the selector wires are of digital value. In the case of a 2-to-1 multiplexer, a logic value of 0 would connect <math> I_0</math> to the output while a logic value of 1 would connect <math> I_1</math> to the output. | |||
| In larger multiplexers, the number of selector pins is equal to <math> \left \lceil \log_2(n) \right \rceil</math> where <math> n</math> is the number of inputs. | |||
| For example, 9 to 16 inputs would require no fewer than 4 selector pins and 17 to 32 inputs would require no fewer than 5 selector pins. The binary value expressed on these selector pins determines the selected input pin. | |||
| {| border="1" align="left" | |||
| !<math>A\,</math>!!<math>B\,</math>!!<math>S\,</math>!!<math>A.\bar S</math>!!<math>B.S\,</math>!!<math>C\,</math> | |||
| A 2-to-1 multiplexer has a ] where <math> A</math> and <math> B</math> are the two inputs, <math> S_0</math> is the selector input, and <math> Z</math> is the output: | |||
| : <math>Z = ( A \wedge \neg S_0) \vee (B \wedge S_0)</math> or | |||
| : <math>Z = ( A \cdot \overline{S_0}) + (B \cdot S_0)</math> | |||
| ] | |||
| Which can be expressed as a ]: | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! <math> S_0</math> !! <math> A</math> !! <math> B</math> !! <math> Z</math> | |||
| |1||1||1||0||1||1 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 0 || 0 || 1 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 0 || 1 || 0 || 1 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |0||1||1|| |
| 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 1 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 1 || 0 || 1 || 1 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 1 || 1 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |||
| | 1 || 1 || 1 || 1 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| Larger multiplexers are also common. For example, an 8-input multiplexer has eight data inputs and three selection inputs. The data inputs are numbered X<sub>0</sub> through X<sub>7</sub>, and the selection inputs are numbered S<sub>4</sub>, S<sub>2</sub>, and S<sub>1</sub>. If S<sub>4</sub> and S<sub>1</sub> are true, and S<sub>2</sub> is false, for example, the output will be equal to X<sub>5</sub>. S<sub>1</sub> is sometimes called the "most significant" input, with less "significant" inputs to the right of it. The farther left the input it the more "significant" it is. This order is a convention intended to match with the standard ordering of a truth table. | |||
| Or, in simpler notation: | |||
| {| |
{| class="wikitable" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! <math> S_0 </math> !! <math> Z </math> | |||
| |] || | |||
| ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 0 || A | |||
| |colspan=2| These are both realizations of a single bit 4-to-1 line multiplexer <br> - one realized from a decoder, AND gates, and an OR gate <br> - and the other realized from ] and AND gates <br> (the AND gates are acting as the decoder in the second case).<br> | |||
| |- | |||
| Note that the subscripts on the I<sub>n</sub> inputs indicate the decimal value <br> | |||
| | 1 || B | |||
| of the binary control inputs at which that input is let through.<br> | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| These tables show that when <math> S_0 = 0</math> then <math> Z = A</math> but when <math> S_0 = 1</math> then <math> Z = B</math>. A straightforward realization of this 2-to-1 multiplexer would need 2 AND gates, an OR gate, and a NOT gate. While this is mathematically correct, a direct physical implementation would be prone to ]s that require additional gates to suppress.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crowe |first1=John |first2=Barrie |last2=Hayes-Gill |chapter=The multiplexer hazard |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=97w8luwEIAsC&pg=PA111 |title=Introduction to Digital Electronics |publisher=Elsevier |date=1998 |isbn=9780080534992 |pages=111–3 }}</ref> | |||
| === List of ICs which provide multiplexing === | |||
| <table border=1> | |||
| <tr><th>S.No.<th>IC No.<th>Function<th>Output State | |||
| <tr><td>1<td>74157<td>Quad- 2:1 MUX<td>Output same as input | |||
| <tr><td>2<td>74158<td>Quad- 2:1 MUX<td>Output is inverted input | |||
| <tr><td>3<td>74153<td>Dual- 4:1 MUX<td>Output same as input | |||
| <tr><td>4<td>74352<td>Dual- 4:1 MUX<td>Output is inverted input | |||
| <tr><td>5<td>74151A<td>8:1 MUX<td>Both outputs available ie. Complementary outputs | |||
| <tr><td>6<td>74152<td>8:1 MUX<td>Ouput is inverted input | |||
| <tr><td>7<td>74150<td>16:1 MUX<td>Output is inverted input | |||
| </table> | |||
| Larger multiplexers are also common and, as stated above, require <math> \left \lceil \log_2(n) \right \rceil</math> selector pins for <math>n</math> inputs. Other common sizes are 4-to-1, 8-to-1, and 16-to-1. Since digital logic uses binary values, powers of 2 are used (4, 8, 16) to maximally control a number of inputs for the given number of selector inputs. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| == Digital Demultiplexers == | |||
| File:Multiplexer 4-to-1.svg|4-to-1 mux | |||
| ] | |||
| File:Multiplexer 8-to-1.svg|8-to-1 mux | |||
| Demultiplexers take one data input and a number of selection inputs, and they have several outputs. They forward the data input to one of the outputs depending on the values of the selection inputs. For example, an 8-output demultiplexer has one data input (X), three selection inputs (S<sub>4</sub>, S<sub>2</sub>, and S<sub>1</sub>), and eight data outputs (A<sub>0</sub> through A<sub>7</sub>). If S<sub>4</sub> and S<sub>1</sub> are true, and S<sub>2</sub> is false, for example, the output A<sub>5<sub> will be equal to X, and all other outputs are equal to zero regardless of the value of X. Demultiplexers are sometimes convenient for designing general purpose logic, because if the demultiplexer's input is always true, the demultiplexer acts as a ]. This means that any function of the selection bits can be constructed by logically OR-ing the correct set of outputs.<br><br><br><br><br> | |||
| File:Multiplexer 16-to-1.svg|16-to-1 mux | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| The Boolean equation for a 4-to-1 multiplexer is: | |||
| === List of ICs which provide demultiplexing === | |||
| :<math>Z = (A \wedge \neg {S_1} \wedge \neg S_0) \vee (B \wedge \neg S_1 \wedge S_0) \vee (C \wedge S_1 \wedge \neg S_0) \vee (D \wedge S_1 \wedge S_0)</math> or | |||
| <table border=1> | |||
| :<math>Z = (A \cdot \overline{S_1} \cdot \overline{S_0}) + (B \cdot \overline{S_1}. S_0) + (C \cdot S_1 \cdot \overline{S_0}) + (D \cdot S_1 \cdot S_0)</math> | |||
| <tr><th>S.No.<th>IC No.<th>Function<th>Output State | |||
| <tr><td>1<td>74139<td>Dual- 1:4 DEMUX<td>Output is inverted input | |||
| <tr><td>2<td>74155<td>Dual- 1:4 DEMUX<td>Complementary outputs available | |||
| <tr><td>3<td>74156<td>Dual- 1:4 DEMUX<td>Output is ] | |||
| <tr><td>4<td>74138<td>1:8 DEMUX<td>Output is inverted input | |||
| <tr><td>5<td>74154<td>1:16 DEMUX<td>Output is same as input | |||
| <tr><td>6<td>74159<td>1:16 DEMUX<td>Output is open collector and same as input | |||
| </table> | |||
| Which can be expressed as a ]: | |||
| == See also == | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] (DSLAM) | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ] | |||
| |- | |||
| ] | |||
| ! <math> S_1</math> !! <math> S_0</math> !! <math> Z</math> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 0 || 0 || A | |||
| |- | |||
| | 0 || 1 || B | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1 || 0 || C | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1 || 1 || D | |||
| |} | |||
| The following 4-to-1 multiplexer is constructed from ] and AND gates (the AND gates are acting as the decoder): | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The subscripts on the <math> I_n</math> inputs indicate the decimal value of the binary control inputs at which that input is let through. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Chaining multiplexers=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Larger Multiplexers can be constructed by using smaller multiplexers by chaining them together. For example, an 8-to-1 multiplexer can be made with two 4-to-1 and one 2-to-1 multiplexers. The two 4-to-1 multiplexer outputs are fed into the 2-to-1 with the selector pins on the 4-to-1's put in parallel giving a total number of selector inputs to 3, which is equivalent to an 8-to-1. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===List of ICs which provide multiplexing=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] S54S157 quad 2:1 mux]] | |||
| For ] part numbers in the following table, "x" is the logic family. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! IC No. !! Function !! Output State | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x157 | |||
| | Quad 2:1 mux. | |||
| | Output same as input given | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x158 | |||
| | Quad 2:1 mux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x153 | |||
| | Dual 4:1 mux. | |||
| | Output same as input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x352 | |||
| | Dual 4:1 mux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x151A | |||
| | 8:1 mux. | |||
| | Both outputs available (i.e., complementary outputs) | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x151 | |||
| | 8:1 mux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x150 | |||
| | 16:1 mux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Digital demultiplexers== | |||
| {{See also|Inverse multiplexer}} | |||
| Demultiplexers take one data input and a number of selection inputs, and they have several outputs. | |||
| They forward the data input to one of the outputs depending on the values of the selection inputs. | |||
| Demultiplexers are sometimes convenient for designing general-purpose logic because if the demultiplexer's input is always true, the demultiplexer acts as a ]. | |||
| This means that any function of the selection bits can be constructed by logically OR-ing the correct set of outputs. | |||
| If X is the input and S is the selector, and A and B are the outputs: | |||
| <math display="block">A = ( X \wedge \neg S)</math> | |||
| <math display="block">B = ( X \wedge S)</math> | |||
| ] | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ===List of ICs which provide demultiplexing=== | |||
| ] 74F138 1:8 demultiplexer]] | |||
| For ] part numbers in the following table, "x" is the logic family. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! IC No. (7400) !! IC No. (4000) !! Function !! Output State | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x139 | |||
| | | |||
| | Dual 1:4 demux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x156 | |||
| | | |||
| | Dual 1:4 demux. | |||
| | Output is ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x138 | |||
| | | |||
| | 1:8 demux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x238 | |||
| | | |||
| | 1:8 demux. | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | 74x154 | |||
| | | |||
| | 1:16 demux. | |||
| | Output is inverted input | |||
| |- 1:8 demux. | |||
| | 74x159 | |||
| | CD4514/15 | |||
| | 1:16 demux. | |||
| | Output is open collector and same as input | |||
| |} | |||
| == Bi-directional multiplexers == | |||
| Bi-directional multiplexers are built using ]es or ]s controlled by the select pins. This allows the roles of input and output to be swapped so that a bi-directional multiplexer can function both as a demultiplexer and multiplexer.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Are switches & multiplexers bidirectional? {{!}} Video {{!}} TI.com |url=https://www.ti.com/video/6112994495001 |access-date=2023-08-03 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ==Multiplexers as PLDs== | |||
| Multiplexers can also be used as ]s, to implement Boolean functions. Any Boolean function of ''n'' variables and one result can be implemented with a multiplexer with ''n'' selector inputs. The variables are connected to the selector inputs, and the function result, 0 or 1, for each possible combination of selector inputs is connected to the corresponding data input. If one of the variables (for example, ''D'') is also available inverted, a multiplexer with ''n''-1 selector inputs is sufficient; the data inputs are connected to 0, 1, ''D'', or ~''D'', according to the desired output for each combination of the selector inputs.<ref>{{cite book| title=The TTL Cookbook| first=Donald E. |last=Lancaster| publisher=H.W. Sams | date=1974 | pages=140–3 |isbn=9780672210358}}</ref> | |||
| == Unconventional use of multiplexers for arithmetic == | |||
| Multiplexers have found application in unconventional ] (SC), particularly in facilitating arithmetic addition. In this paradigm, data is represented as a probability bitstream where the number of '1' bits signifies the magnitude of a value. Thus, the function of a 2-to-1 multiplexer can be conceptualized as a probability function denoted as: | |||
| <math>y = P(a) \times P(1-s)+P(b)\times P(s)</math> | |||
| , where a and b are the input bitstream and s is the select input. Using the select input = 0.5 yields: | |||
| <math>y=\frac{P(a)+P(b)}{2}</math> | |||
| While this approach doesn't yield exact addition but rather scaled addition, it is deemed acceptable in most SC studies. Multiplexers are extensively utilized for tasks such as average addition, average pooling, and median filtering within SC circuits. Moreover, more sophisticated applications of multiplexers include serving as Bernstein polynomial function generator,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Najafi |first1=M. Hassan |last2=Li |first2=Peng |last3=Lilja |first3=David J. |last4=Qian |first4=Weikang |last5=Bazargan |first5=Kia |last6=Riedel |first6=Marc |date=2017-06-29 |title=A Reconfigurable Architecture with Sequential Logic-Based Stochastic Computing |url=https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3060537 |journal=ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems |volume=13 |issue=4 |pages=57:1–57:28 |doi=10.1145/3060537 |issn=1550-4832}}</ref> capable of producing arbitrary mathematical functions within the SC domain. Recent research has also revealed that combinations of multiplexers can facilitate large-scale ] operation,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Lee |first1=Yang Yang |last2=Halim |first2=Zaini Abdul |last3=Wahab |first3=Mohd Nadhir Ab |last4=Almohamad |first4=Tarik Adnan |date=2024-03-04 |title=Stochastic Computing Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Reinvented for Highly Efficient Artificial Intelligence Workload on Field-Programmable Gate Array |journal=Research |language=en |volume=7 |page=0307 |doi=10.34133/research.0307 |issn=2639-5274 |pmc=10911856 |pmid=38439995|bibcode=2024Resea...7..307L }}</ref> demonstrating feasibility in accelerating ] on ]s. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] (DSLAM) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], a ] in which each cell acts as a multiplexer for the values from the two adjacent cells | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| *{{cite book | first1=M. Morris |last1=Mano | first2=Charles R. |last2=Kime | title=Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals | edition=4th | isbn=978-0-13-198926-9 | publisher=] |year=2008}}. | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| *{{Commons category-inline|Multiplexers}} | |||
| *{{Wiktionary-inline|multiplexer}} | |||
| {{CPU technologies}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 1 January 2025
A device that selects between several analog or digital input signals This article is about electronics switching. For telecommunications, see multiplexing.

In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of inputs has select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output.
A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean functions of multiple variables.
Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device that takes a single input signal and selectively forwards it to one of several output lines. A multiplexer is often used with a complementary demultiplexer on the receiving end.
An electronic multiplexer can be considered as a multiple-input, single-output switch, and a demultiplexer as a single-input, multiple-output switch. The schematic symbol for a multiplexer is an isosceles trapezoid with the longer parallel side containing the input pins and the short parallel side containing the output pin. The schematic on the right shows a 2-to-1 multiplexer on the left and an equivalent switch on the right. The wire connects the desired input to the output.
Applications
Multiplexers are part of computer systems to select data from a specific source, be it a memory chip or a hardware peripheral. A computer uses multiplexers to control the data and address buses, allowing the processor to select data from multiple data sources

In digital communications, multiplexers allow several connections over a single channel, by connecting the multiplexer's single output to the demultiplexer's single input (Time-Division Multiplexing). The image to the right demonstrates this benefit. In this case, the cost of implementing separate channels for each data source is higher than the cost and inconvenience of providing the multiplexing/demultiplexing functions.
At the receiving end of the data link a complementary demultiplexer is usually required to break the single data stream back down into the original streams. In some cases, the far end system may have functionality greater than a simple demultiplexer; and while the demultiplexing still occurs technically, it may never be implemented discretely. This would be the case when, for instance, a multiplexer serves a number of IP network users; and then feeds directly into a router, which immediately reads the content of the entire link into its routing processor; and then does the demultiplexing in memory from where it will be converted directly into IP sections.
Often, a multiplexer and demultiplexer are combined into a single piece of equipment, which is simply referred to as a multiplexer. Both circuit elements are needed at both ends of a transmission link because most communications systems transmit in both directions.
In analog circuit design, a multiplexer is a special type of analog switch that connects one signal selected from several inputs to a single output.
Digital multiplexers
In digital circuit design, the selector wires are of digital value. In the case of a 2-to-1 multiplexer, a logic value of 0 would connect to the output while a logic value of 1 would connect to the output. In larger multiplexers, the number of selector pins is equal to where is the number of inputs.
For example, 9 to 16 inputs would require no fewer than 4 selector pins and 17 to 32 inputs would require no fewer than 5 selector pins. The binary value expressed on these selector pins determines the selected input pin.
A 2-to-1 multiplexer has a Boolean equation where and are the two inputs, is the selector input, and is the output:
- or

Which can be expressed as a truth table:
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Or, in simpler notation:
| 0 | A |
| 1 | B |
These tables show that when then but when then . A straightforward realization of this 2-to-1 multiplexer would need 2 AND gates, an OR gate, and a NOT gate. While this is mathematically correct, a direct physical implementation would be prone to race conditions that require additional gates to suppress.
Larger multiplexers are also common and, as stated above, require selector pins for inputs. Other common sizes are 4-to-1, 8-to-1, and 16-to-1. Since digital logic uses binary values, powers of 2 are used (4, 8, 16) to maximally control a number of inputs for the given number of selector inputs.
The Boolean equation for a 4-to-1 multiplexer is:
- or
Which can be expressed as a truth table:
| 0 | 0 | A |
| 0 | 1 | B |
| 1 | 0 | C |
| 1 | 1 | D |
The following 4-to-1 multiplexer is constructed from 3-state buffers and AND gates (the AND gates are acting as the decoder):
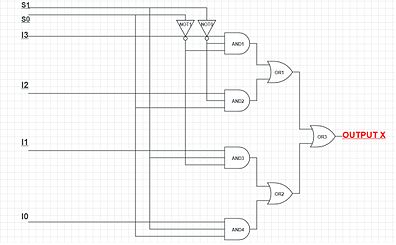
The subscripts on the inputs indicate the decimal value of the binary control inputs at which that input is let through.
Chaining multiplexers
Larger Multiplexers can be constructed by using smaller multiplexers by chaining them together. For example, an 8-to-1 multiplexer can be made with two 4-to-1 and one 2-to-1 multiplexers. The two 4-to-1 multiplexer outputs are fed into the 2-to-1 with the selector pins on the 4-to-1's put in parallel giving a total number of selector inputs to 3, which is equivalent to an 8-to-1.
List of ICs which provide multiplexing

For 7400 series part numbers in the following table, "x" is the logic family.
| IC No. | Function | Output State |
|---|---|---|
| 74x157 | Quad 2:1 mux. | Output same as input given |
| 74x158 | Quad 2:1 mux. | Output is inverted input |
| 74x153 | Dual 4:1 mux. | Output same as input |
| 74x352 | Dual 4:1 mux. | Output is inverted input |
| 74x151A | 8:1 mux. | Both outputs available (i.e., complementary outputs) |
| 74x151 | 8:1 mux. | Output is inverted input |
| 74x150 | 16:1 mux. | Output is inverted input |
Digital demultiplexers
See also: Inverse multiplexerDemultiplexers take one data input and a number of selection inputs, and they have several outputs. They forward the data input to one of the outputs depending on the values of the selection inputs. Demultiplexers are sometimes convenient for designing general-purpose logic because if the demultiplexer's input is always true, the demultiplexer acts as a binary decoder. This means that any function of the selection bits can be constructed by logically OR-ing the correct set of outputs.
If X is the input and S is the selector, and A and B are the outputs:
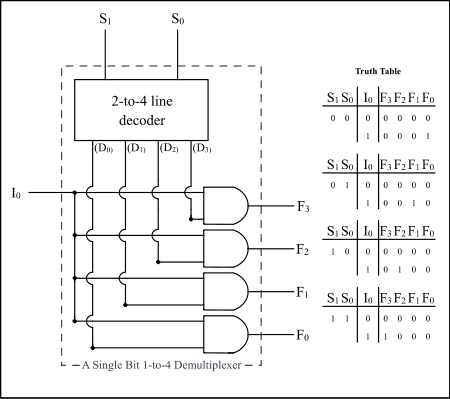
List of ICs which provide demultiplexing

For 7400 series part numbers in the following table, "x" is the logic family.
| IC No. (7400) | IC No. (4000) | Function | Output State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 74x139 | Dual 1:4 demux. | Output is inverted input | |
| 74x156 | Dual 1:4 demux. | Output is open collector | |
| 74x138 | 1:8 demux. | Output is inverted input | |
| 74x238 | 1:8 demux. | ||
| 74x154 | 1:16 demux. | Output is inverted input | |
| 74x159 | CD4514/15 | 1:16 demux. | Output is open collector and same as input |
Bi-directional multiplexers
Bi-directional multiplexers are built using analog switches or transmission gates controlled by the select pins. This allows the roles of input and output to be swapped so that a bi-directional multiplexer can function both as a demultiplexer and multiplexer.
Multiplexers as PLDs
Multiplexers can also be used as programmable logic devices, to implement Boolean functions. Any Boolean function of n variables and one result can be implemented with a multiplexer with n selector inputs. The variables are connected to the selector inputs, and the function result, 0 or 1, for each possible combination of selector inputs is connected to the corresponding data input. If one of the variables (for example, D) is also available inverted, a multiplexer with n-1 selector inputs is sufficient; the data inputs are connected to 0, 1, D, or ~D, according to the desired output for each combination of the selector inputs.
Unconventional use of multiplexers for arithmetic
Multiplexers have found application in unconventional stochastic computing (SC), particularly in facilitating arithmetic addition. In this paradigm, data is represented as a probability bitstream where the number of '1' bits signifies the magnitude of a value. Thus, the function of a 2-to-1 multiplexer can be conceptualized as a probability function denoted as:
, where a and b are the input bitstream and s is the select input. Using the select input = 0.5 yields:
While this approach doesn't yield exact addition but rather scaled addition, it is deemed acceptable in most SC studies. Multiplexers are extensively utilized for tasks such as average addition, average pooling, and median filtering within SC circuits. Moreover, more sophisticated applications of multiplexers include serving as Bernstein polynomial function generator, capable of producing arbitrary mathematical functions within the SC domain. Recent research has also revealed that combinations of multiplexers can facilitate large-scale multiply-accumulate operation, demonstrating feasibility in accelerating convolutional neural network on field-programmable gate arrays.
See also
- Digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM)
- Inverse multiplexer
- Multiplexing
- Priority encoder
- Rule 184, a cellular automaton in which each cell acts as a multiplexer for the values from the two adjacent cells
- Statistical multiplexer
- Ternary conditional operator
References
- ^ Dean, Tamara (2010). Network+ Guide to Networks. Delmar. pp. 82–85. ISBN 978-1423902454.
- Debashis, De (2010). Basic Electronics. Dorling Kindersley. p. 557. ISBN 9788131710685.
- Lipták, Béla (2002). Instrument engineers' handbook: Process software and digital networks. CRC Press. p. 343. ISBN 9781439863442.
- Harris, David (2007). Digital Design and Computer Architecture. Penrose. p. 79. ISBN 9780080547060.
- Crowe, John; Hayes-Gill, Barrie (1998). "The multiplexer hazard". Introduction to Digital Electronics. Elsevier. pp. 111–3. ISBN 9780080534992.
- "Are switches & multiplexers bidirectional? | Video | TI.com". Texas Instruments. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- Lancaster, Donald E. (1974). The TTL Cookbook. H.W. Sams. pp. 140–3. ISBN 9780672210358.
- Najafi, M. Hassan; Li, Peng; Lilja, David J.; Qian, Weikang; Bazargan, Kia; Riedel, Marc (2017-06-29). "A Reconfigurable Architecture with Sequential Logic-Based Stochastic Computing". ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems. 13 (4): 57:1–57:28. doi:10.1145/3060537. ISSN 1550-4832.
- Lee, Yang Yang; Halim, Zaini Abdul; Wahab, Mohd Nadhir Ab; Almohamad, Tarik Adnan (2024-03-04). "Stochastic Computing Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Reinvented for Highly Efficient Artificial Intelligence Workload on Field-Programmable Gate Array". Research. 7: 0307. Bibcode:2024Resea...7..307L. doi:10.34133/research.0307. ISSN 2639-5274. PMC 10911856. PMID 38439995.
Further reading
- Mano, M. Morris; Kime, Charles R. (2008). Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals (4th ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-198926-9..
External links
 Media related to Multiplexers at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Multiplexers at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of multiplexer at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of multiplexer at Wiktionary
 inputs has
inputs has  select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output.
select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output.
 wire connects the desired input to the output.
wire connects the desired input to the output.
 to the output while a logic value of 1 would connect
to the output while a logic value of 1 would connect  to the output.
In larger multiplexers, the number of selector pins is equal to
to the output.
In larger multiplexers, the number of selector pins is equal to  where
where  and
and  are the two inputs,
are the two inputs,  is the selector input, and
is the selector input, and  is the output:
is the output:
 or
or
 then
then  but when
but when  then
then  . A straightforward realization of this 2-to-1 multiplexer would need 2 AND gates, an OR gate, and a NOT gate. While this is mathematically correct, a direct physical implementation would be prone to
. A straightforward realization of this 2-to-1 multiplexer would need 2 AND gates, an OR gate, and a NOT gate. While this is mathematically correct, a direct physical implementation would be prone to 

 or
or


 inputs indicate the decimal value of the binary control inputs at which that input is let through.
inputs indicate the decimal value of the binary control inputs at which that input is let through.



