| Revision as of 17:41, 31 January 2005 editJayjg (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators134,922 editsm dab← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:54, 13 January 2025 edit undoHillelAmadeus (talk | contribs)180 edits →Cultural references: i have corrected the name of the poet.Tag: Visual edit | ||
| (514 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Anti-Jewish attack in Kishinev, Russian Empire (19–21 April 1903)}} | |||
| The '''Kishinev pogrom''' was an anti-Jewish riot that took place in Kishinev , then ], ( currently ], ]) during ]-7, ]. The riot started after an incident on February 6 when a Christian Russian boy, Michael Ribalenko, was found murdered in the town of ], about 25 miles north of Kishinev. Although it was clear that the boy had been killed by a relative (who was later found), the government chose to call it a ritual murder plot by the ]. The mobs were incited by Pavolachi Krushevan, the editor of the anti-Semitic Newspaper "Bessarabetz", and the vice governor Ustrugov. They used the ages-old ] against the Jews (that the boy had been killed to use his blood in preparation of ]). ], the Minister of Interior, supposedly gave orders not to stop the rioters. During three days of rioting, the Kishinev Pogrom against the Jews took place. Forty seven (some say 49) Jews were killed, 92 severely wounded , 500 slightly wounded and over 700 houses looted and destroyed. This pogrom is considered the first state-inspired action against Jews in the 20th century. Despite a world outcry, only two men were sentenced to seven and five years and twenty-two were sentenced for one or two years. This pogrom was instrumental in convincing tens of thousands of Russian Jews to leave to the ] and to ]. | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2018}} | |||
| {{Coord|47.0376|N|28.8045|E|region:MD_type:event|display=title}} | |||
| {{Infobox civilian attack | |||
| | partof = the ] | |||
| | image = Pogrom de Chisinau - 1903 - 2.jpg | |||
| | caption = Bodies in the street | |||
| | title = Kishinev pogrom | |||
| | location = Kishinev, ], ]<br />({{small|now}} ], ]) | |||
| | target = ] | |||
| | date = {{OldStyleDate|19–21 April|1903|6–8 April}} | |||
| | type = {{hlist|]|]}} | |||
| | fatalities = 49 | |||
| | injuries = 92 gravely injured<br/> >500 lightly injured | |||
| | perpetrators = ] pogromists | |||
| | motive = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| ] | |||
| The '''Kishinev pogrom''' or '''Kishinev massacre''' was an ] ] that took place in Kishinev (modern ], ]), then the capital of the ] in the ], on {{OldStyleDate|19–21 April|1903|6–8 April}}.<ref>{{cite journal |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/172771/pdf |title=The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History |journal=Modern Judaism |last=Penkower |first=Monty Noam |publisher=Oxford University Press |date=October 2004 |volume=24 |number=3 |pages=187–225 |doi=10.1093/mj/kjh017}}</ref> During the pogrom, which began on Easter Day, 49 Jews were killed, 92 were gravely injured, a number of Jewish women were raped, over 500 were lightly injured and 1,500 homes were damaged.<ref name=":1">{{cite web |url=https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2009/04/the-pogrom-that-transformed-20th-century-jewry/ |title=The pogrom that transformed 20th century Jewry |work=The Harvard Gazette |date=April 9, 2009 |access-date=March 26, 2016}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Chicago Jewish Cafe |title=Are Jewish men cowards? Conversation with Prof. Steven J. Zipperstein |website=] |date=2018-09-20 |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dbRl4hj7vHo |access-date=2018-10-08}}</ref> American Jews began large-scale organized financial help, and assisted in emigration.<ref name=":0" /> The incident focused worldwide attention on the persecution of Jews within the Russian Empire,<ref name="harvard.edu">{{Cite web |url=https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2009/04/the-pogrom-that-transformed-20th-century-jewry/ |title=The pogrom that transformed 20th century Jewry |author=Corydon Ireland |work=The Harvard Gazette |date=April 9, 2009}}</ref> and led ] to propose the ] as a temporary refuge for the Jews.<ref>Birnbaum, Erwin. . Accessed 27 January 2022.</ref> | |||
| A second |
A second pogrom erupted in the city in October 1905.<ref name=JEncyclo/> | ||
| ==History== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The most popular newspaper in Kishinev (now ]), the Russian-language ] newspaper ''Бессарабец'' (''Bessarabets'', meaning "]n"), published by ], regularly published articles with headlines such as "Death to the Jews!" and "Crusade against the Hated Race!" (referring to the ]s).<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Penkower |first=Monty Noam |date=2004 |title=The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/1396539 |journal=Modern Judaism |volume=24 |issue=3 |pages=189 |doi=10.1093/mj/kjh017 |jstor=1396539 |issn=0276-1114}}</ref> When a ] boy, Mikhail Rybachenko, was found murdered in the town of ], about {{cvt|40|km}} north of Kishinev, and a girl who committed suicide by poisoning herself was declared dead in a Jewish hospital, the ''Bessarabetz'' paper insinuated that both children had been murdered by the Jewish community ] in the preparation of ] for ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Davitt |first=Michael |title=Within The Pale |year=1903 |publisher=Hurst and Blackett |location=London |pages=98–100 |oclc=3469796 }}</ref> Another newspaper, ''Свет'' (''Svet'', "Light") made similar insinuations. These allegations sparked the ].<ref name=JEncyclo/> | |||
| The pogrom began on April 19 (April 6 according to the ], then in use in the Russian Empire) after congregations were dismissed from church services on Easter Sunday. In two days of rioting, 47 (some put the figure at 49) Jews were killed, 92 were severely wounded and 500 were slightly injured, 700 houses were destroyed, and 600 stores were pillaged.<ref name=JEncyclo>{{Cite Jewish Encyclopedia |title=Kishinef (Kishinev) |url=http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/9350-kishinef-kishinev |first1=Herman |last1=Rosenthal |first2=Max |last2=Rosenthal|}}</ref><ref> archived from ''www.shtetlinks.jewishgen.org''; archive accessed 27 January 2022</ref> '']'' published a ] dispatch by ], the Minister of Interior, to the governor of Bessarabia, which supposedly gave orders not to stop the rioters.<ref>] (October 11, 2010). "". '']''. yivoencyclopedia.org. Retrieved April 17, 2018.</ref> Unlike the more responsible authorities at Dubăsari, who acted to prevent the pogrom, there is evidence that the officials in Kishinev acted in collusion or negligence, turning a blind eye to the impending pogrom.<ref name=JEncyclo/><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Klier |first1=John Doyle |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=T3D7CmSOMfIC |title=Pogroms: Anti-Jewish Violence in Modern Russian History |last2=Lambroza |first2=Shlomo |date=1992 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-52851-1 |language=en |page=202}}</ref> | |||
| ] after the Kishinev pogrom]] | |||
| On 28 April, '']'' reprinted a ''Yiddish Daily News'' report that was smuggled out of Russia:<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Schoenberg |first=Philip Ernest |date=1974 |title=The American Reaction to the Kishinev Pogrom of 1903 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/23877915 |journal=American Jewish Historical Quarterly |volume=63 |issue=3 |pages=262–283 |jstor=23877915 |issn=0002-9068}}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote| | |||
| The mob was led by priests, and the general cry, "Kill the Jews", was taken-up all over the city. The Jews were taken wholly unaware and were slaughtered like sheep. The dead number 120 and the injured about 500. The scenes of horror attending this massacre are beyond description. Babes were literally torn to pieces by the frenzied and bloodthirsty mob. The local police made no attempt to check the reign of terror. At sunset the streets were piled with corpses and wounded. Those who could make their escape fled in terror, and the city is now practically deserted of Jews.<ref>{{cite news |title=Jewish Massacre Denounced |work=The New York Times |date=April 28, 1903 |page=6 |url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=9E0DE2DD1F30E733A2575BC2A9629C946297D6CF&legacy=true}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| The Kishinev pogrom of 1903 captured the attention of the international public and was mentioned in the ] as an example of the type of human rights abuse which would justify United States involvement in Latin America. The 1904 book ''The Voice of America on Kishinev'' provides more detail<ref>{{Cite book |editor-last=Adler |editor-first=Cyrus |url=https://archive.org/stream/voiceamericaonk00adlegoog#page/n7/mode/2up |title=The Voice of America on Kishineff |access-date=March 26, 2016}}</ref> as does the book ''Russia at the Bar of the American People: A Memorial of Kishinef''.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Singer |first1=Isidore |year=1904 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=piMoAAAAYAAJ |title=Russia at the Bar of the American People |access-date=March 26, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ==Russian response== | |||
| ] ] telling Tsar ]: "Stop your cruel oppression of the Jews"]] | |||
| The ], Count ], characterised the 1903 pogrom as a reaction of financially hard-pressed peasants to Jewish creditors in an interview on 18 May 1903: | |||
| {{Blockquote|The situation in Russia, so far as the Jews are concerned is just this: It is the peasant against the money lender, and not the Russians against the Jews. There is no feeling against the Jew in Russia because of religion. It is as I have said—the Jew ruins the peasants, with the result that conflicts occur when the latter have lost all their worldly possessions and have nothing to live upon. There are many good Jews in Russia, and they are respected. Jewish genius is appreciated in Russia, and the Jewish artist honoured. Jews also appear in the financial world in Russia. The Russian Government affords the same protection to the Jews that it does to any other of its citizens, and when a riot occurs and Jews are attacked the officials immediately take steps to apprehend those who began the riot, and visit severe punishment upon them."<ref>{{cite web |title=Current Literature: A Magazine of Contemporary Record (New York). Vol. XXXV., No.1. July, 1903. Current Opinion. V.35 (1903). p. 16 |pages=25 v |url=http://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.b2925279;view=image;seq=38;q1=jews;start=1;size=10;page=search;num=16 |publisher=babel.hathitrust.org}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| There is a memorial to the 1903 pogrom in modern Kishinev.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://picasaweb.google.com/108373287763349412536/Kishinev?authkey=Gv1sRgCLOAx-T2zeqg-QE&feat=email#5805029854701512578 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150606173651/https://picasaweb.google.com/108373287763349412536/Kishinev?authkey=Gv1sRgCLOAx-T2zeqg-QE&feat=email#5805029854701512578 |url-status=dead |archive-date=June 6, 2015 |title=Picasa Web Albums - Ronnie - kishinev |access-date=March 26, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ==Aftermath== | |||
| American media mogul ] "adopt Kishinev as little less than a crusade", according to Stanford historian ].{{sfn|Zipperstein|2015|p=372}} As part of this publicity, Hearst sent the Irish nationalist journalist ] to Kishinev as "special commissioner to investigate the massacres of the Jews", becoming one of the first foreign journalists to report on the pogrom.{{sfn|Beatty|2017|p=125}}{{sfn|Zipperstein|2015|p=372}} | |||
| Due to their involvement in the pogrom, two men were sentenced to seven and five years' imprisonment respectively, and a further 22 were sentenced to one or two years. | |||
| This ] was instrumental in convincing tens of thousands of Russian Jews to leave for the ] or ].<ref name=JEncyclo/> As such, it became a rallying point for early ], especially what would become ], inspiring early self-defense leagues under leaders like ].<ref name=JEncyclo/> | |||
| <gallery widths="200px" heights="200px"> | |||
| File:Kishinev Martyrs.jpg|Imprinting honoring the "Kishinev ]", by ]. | |||
| Image:Kishinev-Petition-1903-01.jpg|A rejected petition to the Tsar of Russia by US citizens, 1903, now kept at the ] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===1905 pogrom=== | |||
| {{main|Second Kishinev pogrom}} | |||
| A second pogrom took place in Kishinev on 19–20 October 1905. This time, the riots began as political protests against the ], but turned into an attack on Jews wherever they could be found. By the time the riots were over, 19 Jews had been killed and 56 were injured. Jewish self-defense leagues, organized after the first pogrom, stopped some of the violence, but were not wholly successful. This pogrom was part of a ] that swept the Russian Empire at the time. | |||
| ==Cultural references== | |||
| ] (2003)]] | |||
| Russian authors such as ] wrote about the pogrom in ''House 13'', while ] and ] wrote condemnations blaming the Russian government—a change from the earlier pogroms of the 1880s, when most members of the Russian intelligentsia were silent. Tolstoy worked with ] to produce an anthology dedicated to the victims, with all publisher and author proceeds going to relief efforts, which became the work "]".<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PgdoBgAAQBAJ&dq=%22Esarhaddon,+King+of+Assyria%22+tolstoy&pg=PT182 |title=Tolstoy's Diaries |volume=2: 1895–1910 |editor=R. F. Christian |author=Leo Tolstoy |date=2015 |isbn=9780571324064 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SYJlAAAAMAAJ&dq=%22Esarhaddon,+King+of+Assyria%22+tolstoy&pg=PT7 |title=Tolstoy on Shakespeare: A Critical Essay on Shakespeare |year=1906 |author=Leo Tolstoy |publisher=Funk & Wagnalls Company |translator=Isabella Fyvie Mayo, Vladimir Grigorʹevich Chertkov}}</ref> Sholem Aleichem went on to write the material for the famous '']''. | |||
| It also had a major impact on Jewish art and literature. After interviewing survivors of the Kishinev pogrom, the Hebrew poet ] (1873–1934) wrote "]," about the perceived passivity of the Jews in the face of the mobs.<ref name="harvard.edu"/> ], who was also in the city after the massacre, translated Bialik's poem into Russian, thereby contributing to both the publication of the poem and Bialik's fame in Russian-speaking countries.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Holtzman |first1=Avner |url=https://www.worldcat.org/title/953985607 |title=Hayim Nahman Bialik: poet of Hebrew |last2=Scharf |first2=Orr |date=2017 |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-20066-9 |series=Jewish lives |location=New Haven |pages=95–96 |oclc=953985607}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=מכון ז'בוטינסקי {{!}} Item |url=https://en.jabotinsky.org/archive/search-archive/item/?itemId=115680 |access-date=2024-12-18 |website=en.jabotinsky.org}}</ref> In the 1908 play by ] titled '']'', the Jewish hero emigrates to America in the wake of the Kishinev pogrom, eventually confronting the Russian officer who led the rioters.<ref name="Zangwill2006">{{cite book |last=Zangwill |first=Israel |title=From the Ghetto to the Melting Pot: Israel Zangwill's Jewish Plays : Three Playscripts |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NfMO6oKZoD4C&pg=PA254 |access-date=April 17, 2018 |year=2006 |publisher=Wayne State University Press |isbn=9780814329559 |page=254}}</ref> | |||
| More recently, ]'s series of graphic novels titled ''Klezmer'' depicts life in Odessa, Ukraine, at this time; in the final volume (number 5), ''Kishinev-des-fous'', the first pogrom affects the characters.<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Weingrad |first=Michael |date=Spring 2015 |title=Drawing Conclusions: Joann Sfar and the Jews of France |url=https://jewishreviewofbooks.com/articles/1539/drawing-conclusions-joann-sfar-and-the-jews-of-france/ |magazine=Jewish Review of Books |language=en-US |access-date=April 17, 2018}}</ref> Playwright Max Sparber took the Kishinev pogrom as the subject for one of his earliest plays in 1994.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://irl.metafilter.com/2597/Staged-reading-of-play-by-Max-Sparber-Kishinev |title=Staged reading of play by Max Sparber: Kishinev |last=Sparber |first=Max |date=December 3, 2014 |website=] |language=en |access-date=April 17, 2018 |df=dmy-all}}</ref> The novel '']'' by ] (2008) provides a vivid description of the pogrom and details its long-reaching consequences.<ref>Hemon, A., (2008). ''The Lazarus project.'' New York: Riverhead Books</ref> | |||
| In ], the Jewish writer ] wrote the fiction and social satire book "O Exército De Um Homem Só" (1986), about Mayer Guinzburg, a ] and ] activist whose family are refugees from the Kishinev pogrom. | |||
| ==Monument to victims== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Victims of Chișinău Pogrom Monument}} | |||
| The Victims of the Chișinău Pogrom Monument ({{langx|ro|Monumentul Victimelor Pogromului de la Chișinău}}) is a ] to the victims of the Kishinev pogrom, unveiled in 1993 in Alunelul park, Chișinău, Moldova.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://jewishmemory.md/en/chisinau-monument-to-pogrom-victims |title=Chisinau. Monument to Pogrom Victims |work=jewishmemory.md |date=24 April 2016 |access-date=27 January 2022}}</ref> | |||
| == The name list of the victims == | |||
| Many sources report that 49 people were killed in the Kishinev pogrom, but their specific identity remains elusive.<ref name=":1" /> Soon after the pogrom, one of the first foreign journalists to arrive in the city was the Irish reporter ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Beatty |first=Aidan |title=Jews and the Irish Nationalist Imagination: Between Philosemitism and Antisemitism. Journal of Jewish Studies. Vol. 68, No. 1 (2017) |url=https://www.academia.edu/19097039 |journal=Journal of Jewsh Studies |pages=125}}</ref> He covered the events and later published a book detailing his findings, which included a list of the victims' names, ages, and, in some instances, their occupations. However, this list contains only 40 of the 49 victims.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Davitt |first=Michael |url=https://archive.org/details/withinpaletruest00davi/page/216/mode/1up |title=Within the pale:The true story of anti-Semitic persecution in Russia |date=1903 |publisher=Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society of America |others=Princeton Theological Seminary Library |pages=217-222}}</ref> In the ], there is a photo album from the pogrom titled ''Kishinev Pogrom '', published in 1929, which includes a list of the victims. The list claims there were 49 fatalities but records the names of only 41 individuals.<ref>{{Cite web |title=פרעות קישינב |trans-title=Kishinev Pogrom |url=https://www.nli.org.il/he/images/NNL_ARCHIVE_AL990037778210205171/NLI |website=] |language=he}}</ref> The organization ] cross-referenced a wide range of sources and compiled a list of 47 names, though they caution that errors may still exist, suggesting that further research is required to complete the record.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Kishinev: List of Victims of Kishinev Pogrom of 1903 |url=https://kehilalinks.jewishgen.org/chisinau/LIF_POGROM1903_Victims.asp |access-date=2025-01-08 |website=kehilalinks.jewishgen.org}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Judaism|Moldova}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| == Bibliography == | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Beatty |first1=Aidan |title=Jews and the Irish nationalist imagination: between philo-Semitism and anti-Semitism |journal=] |date=2017 |volume=68 |issue=1 |pages=125–128 |doi=10.18647/3304/JJS-2017 |url=https://www.academia.edu/19097039}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Zipperstein |first1=Steven J. |editor1-last=Freeze |editor1-first=ChaeRan Y. |editor2-last=Fried |editor2-first=Sylvia Fuks |editor3-last=Sheppard |editor3-first=Eugene R. |title=The Individual in History: Essays in Honor of Jehuda Reinharz |date=2015 |publisher=] |location=Waltham, Massachusetts |isbn=9781611687330 |language=en |chapter=Inside Kishinev’s Pogrom: Hayyim Nahman Bialik, Michael Davitt, and the Burdens of Truth |chapter-url=https://history.stanford.edu/sites/g/files/sbiybj9471/f/burdens_of_truth-1.pdf |archive-date=25 February 2020 |access-date=13 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200225025552/https://history.stanford.edu/sites/g/files/sbiybj9471/f/burdens_of_truth-1.pdf |url-status=dead }} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| *Judge, Edward H. '']''. NYU Press 1992. | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last=Penkower |first=Monty Noam |year=2004 |title=The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History |journal=Modern Judaism |volume=24 |issue=3 |pages=187–225 |doi=10.1093/mj/kjh017 |jstor=1396539 |s2cid=170968039}} | |||
| *{{Jewish Encyclopedia |no-prescript=1 |last=Rosenthal |first=Herman |last2=Rosenthal |first2=Max |title=Kishinef (Kishinev) |url=http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/9350-kishinef-kishinev }} | |||
| *Schoenberg, Philip Ernest. "The American Reaction to the Kishinev Pogrom of 1903". ''American Jewish Historical Quarterly'' 63.3 (1974): 262–283. | |||
| *Zipperstein, Steven J. '']''. Liveright Publishing March 2018. | |||
| *{{Cite web |title=YIVO {{!}} Kishinev |url=https://yivoencyclopedia.org/article.aspx/Kishinev |access-date=2022-04-19 |website=yivoencyclopedia.org}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * unofficial commemorative website | |||
| * | |||
| *"Are Jewish men cowards?" Interview in with Prof. Steven Zipperstein, the author of "Pogrom: Kishinev and the Tilt of History." | |||
| {{Massacres of Jews}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:54, 13 January 2025
Anti-Jewish attack in Kishinev, Russian Empire (19–21 April 1903)47°02′15″N 28°48′16″E / 47.0376°N 28.8045°E / 47.0376; 28.8045
| Kishinev pogrom | |
|---|---|
| Part of the pogroms in the Russian Empire | |
 Bodies in the street Bodies in the street | |
| Location | Kishinev, Bessarabia Governorate, Russian Empire (now Chișinău, Moldova) |
| Date | 19–21 April [O.S. 6–8 April] 1903 |
| Target | Bessarabian Jews |
| Attack type | |
| Deaths | 49 |
| Injured | 92 gravely injured >500 lightly injured |
| Perpetrators | Russian pogromists |
| Motive | Antisemitism |

The Kishinev pogrom or Kishinev massacre was an anti-Jewish riot that took place in Kishinev (modern Chișinău, Moldova), then the capital of the Bessarabia Governorate in the Russian Empire, on 19–21 April [O.S. 6–8 April] 1903. During the pogrom, which began on Easter Day, 49 Jews were killed, 92 were gravely injured, a number of Jewish women were raped, over 500 were lightly injured and 1,500 homes were damaged. American Jews began large-scale organized financial help, and assisted in emigration. The incident focused worldwide attention on the persecution of Jews within the Russian Empire, and led Theodor Herzl to propose the Uganda Scheme as a temporary refuge for the Jews.
A second pogrom erupted in the city in October 1905.
History

The most popular newspaper in Kishinev (now Chișinău), the Russian-language anti-Semitic newspaper Бессарабец (Bessarabets, meaning "Bessarabian"), published by Pavel Krushevan, regularly published articles with headlines such as "Death to the Jews!" and "Crusade against the Hated Race!" (referring to the Jews). When a Ukrainian boy, Mikhail Rybachenko, was found murdered in the town of Dubăsari, about 40 km (25 mi) north of Kishinev, and a girl who committed suicide by poisoning herself was declared dead in a Jewish hospital, the Bessarabetz paper insinuated that both children had been murdered by the Jewish community for the purpose of using their blood in the preparation of matzo for Passover. Another newspaper, Свет (Svet, "Light") made similar insinuations. These allegations sparked the pogrom.
The pogrom began on April 19 (April 6 according to the Julian calendar, then in use in the Russian Empire) after congregations were dismissed from church services on Easter Sunday. In two days of rioting, 47 (some put the figure at 49) Jews were killed, 92 were severely wounded and 500 were slightly injured, 700 houses were destroyed, and 600 stores were pillaged. The Times published a forged dispatch by Vyacheslav von Plehve, the Minister of Interior, to the governor of Bessarabia, which supposedly gave orders not to stop the rioters. Unlike the more responsible authorities at Dubăsari, who acted to prevent the pogrom, there is evidence that the officials in Kishinev acted in collusion or negligence, turning a blind eye to the impending pogrom.

On 28 April, The New York Times reprinted a Yiddish Daily News report that was smuggled out of Russia:
The mob was led by priests, and the general cry, "Kill the Jews", was taken-up all over the city. The Jews were taken wholly unaware and were slaughtered like sheep. The dead number 120 and the injured about 500. The scenes of horror attending this massacre are beyond description. Babes were literally torn to pieces by the frenzied and bloodthirsty mob. The local police made no attempt to check the reign of terror. At sunset the streets were piled with corpses and wounded. Those who could make their escape fled in terror, and the city is now practically deserted of Jews.
The Kishinev pogrom of 1903 captured the attention of the international public and was mentioned in the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine as an example of the type of human rights abuse which would justify United States involvement in Latin America. The 1904 book The Voice of America on Kishinev provides more detail as does the book Russia at the Bar of the American People: A Memorial of Kishinef.
Russian response
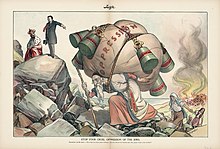
The Russian ambassador to the United States, Count Arthur Cassini, characterised the 1903 pogrom as a reaction of financially hard-pressed peasants to Jewish creditors in an interview on 18 May 1903:
The situation in Russia, so far as the Jews are concerned is just this: It is the peasant against the money lender, and not the Russians against the Jews. There is no feeling against the Jew in Russia because of religion. It is as I have said—the Jew ruins the peasants, with the result that conflicts occur when the latter have lost all their worldly possessions and have nothing to live upon. There are many good Jews in Russia, and they are respected. Jewish genius is appreciated in Russia, and the Jewish artist honoured. Jews also appear in the financial world in Russia. The Russian Government affords the same protection to the Jews that it does to any other of its citizens, and when a riot occurs and Jews are attacked the officials immediately take steps to apprehend those who began the riot, and visit severe punishment upon them."
There is a memorial to the 1903 pogrom in modern Kishinev.
Aftermath
American media mogul William Randolph Hearst "adopt Kishinev as little less than a crusade", according to Stanford historian Steven Zipperstein. As part of this publicity, Hearst sent the Irish nationalist journalist Michael Davitt to Kishinev as "special commissioner to investigate the massacres of the Jews", becoming one of the first foreign journalists to report on the pogrom.
Due to their involvement in the pogrom, two men were sentenced to seven and five years' imprisonment respectively, and a further 22 were sentenced to one or two years.
This pogrom was instrumental in convincing tens of thousands of Russian Jews to leave for the West or Palestine. As such, it became a rallying point for early Zionists, especially what would become Revisionist Zionism, inspiring early self-defense leagues under leaders like Ze'ev Jabotinsky.
-
 Imprinting honoring the "Kishinev Martyrs", by Ephraim Moses Lilien.
Imprinting honoring the "Kishinev Martyrs", by Ephraim Moses Lilien.
-
 A rejected petition to the Tsar of Russia by US citizens, 1903, now kept at the US National Archives
A rejected petition to the Tsar of Russia by US citizens, 1903, now kept at the US National Archives
1905 pogrom
Main article: Second Kishinev pogromA second pogrom took place in Kishinev on 19–20 October 1905. This time, the riots began as political protests against the Tsar, but turned into an attack on Jews wherever they could be found. By the time the riots were over, 19 Jews had been killed and 56 were injured. Jewish self-defense leagues, organized after the first pogrom, stopped some of the violence, but were not wholly successful. This pogrom was part of a series of pogroms that swept the Russian Empire at the time.
Cultural references

Russian authors such as Vladimir Korolenko wrote about the pogrom in House 13, while Tolstoy and Gorky wrote condemnations blaming the Russian government—a change from the earlier pogroms of the 1880s, when most members of the Russian intelligentsia were silent. Tolstoy worked with Sholem Aleichem to produce an anthology dedicated to the victims, with all publisher and author proceeds going to relief efforts, which became the work "Esarhaddon, King of Assyria". Sholem Aleichem went on to write the material for the famous Fiddler on the Roof.
It also had a major impact on Jewish art and literature. After interviewing survivors of the Kishinev pogrom, the Hebrew poet Hayim Nahman Bialik (1873–1934) wrote "In the City of Slaughter," about the perceived passivity of the Jews in the face of the mobs. Ze'ev Jabotinsky, who was also in the city after the massacre, translated Bialik's poem into Russian, thereby contributing to both the publication of the poem and Bialik's fame in Russian-speaking countries. In the 1908 play by Israel Zangwill titled The Melting Pot, the Jewish hero emigrates to America in the wake of the Kishinev pogrom, eventually confronting the Russian officer who led the rioters.
More recently, Joann Sfar's series of graphic novels titled Klezmer depicts life in Odessa, Ukraine, at this time; in the final volume (number 5), Kishinev-des-fous, the first pogrom affects the characters. Playwright Max Sparber took the Kishinev pogrom as the subject for one of his earliest plays in 1994. The novel The Lazarus Project by Aleksander Hemon (2008) provides a vivid description of the pogrom and details its long-reaching consequences.
In Brazil, the Jewish writer Moacyr Scliar wrote the fiction and social satire book "O Exército De Um Homem Só" (1986), about Mayer Guinzburg, a Brazilian-Jew and Communist activist whose family are refugees from the Kishinev pogrom.
Monument to victims

The Victims of the Chișinău Pogrom Monument (Romanian: Monumentul Victimelor Pogromului de la Chișinău) is a memorial stone to the victims of the Kishinev pogrom, unveiled in 1993 in Alunelul park, Chișinău, Moldova.
The name list of the victims
Many sources report that 49 people were killed in the Kishinev pogrom, but their specific identity remains elusive. Soon after the pogrom, one of the first foreign journalists to arrive in the city was the Irish reporter Michael Davitt. He covered the events and later published a book detailing his findings, which included a list of the victims' names, ages, and, in some instances, their occupations. However, this list contains only 40 of the 49 victims. In the National Library of Israel, there is a photo album from the pogrom titled Kishinev Pogrom , published in 1929, which includes a list of the victims. The list claims there were 49 fatalities but records the names of only 41 individuals. The organization JewishGen cross-referenced a wide range of sources and compiled a list of 47 names, though they caution that errors may still exist, suggesting that further research is required to complete the record.
See also
References
- Penkower, Monty Noam (October 2004). "The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History". Modern Judaism. 24 (3). Oxford University Press: 187–225. doi:10.1093/mj/kjh017.
- ^ "The pogrom that transformed 20th century Jewry". The Harvard Gazette. 9 April 2009. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- Chicago Jewish Cafe (20 September 2018). "Are Jewish men cowards? Conversation with Prof. Steven J. Zipperstein". YouTube. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ^ Schoenberg, Philip Ernest (1974). "The American Reaction to the Kishinev Pogrom of 1903". American Jewish Historical Quarterly. 63 (3): 262–283. ISSN 0002-9068. JSTOR 23877915.
- ^ Corydon Ireland (9 April 2009). "The pogrom that transformed 20th century Jewry". The Harvard Gazette.
- Birnbaum, Erwin. In the Shadow of the Struggle. Accessed 27 January 2022.
- ^
 Rosenthal, Herman; Rosenthal, Max (1901–1906). "Kishinef (Kishinev)". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
Rosenthal, Herman; Rosenthal, Max (1901–1906). "Kishinef (Kishinev)". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
- Penkower, Monty Noam (2004). "The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History". Modern Judaism. 24 (3): 189. doi:10.1093/mj/kjh017. ISSN 0276-1114. JSTOR 1396539.
- Davitt, Michael (1903). Within The Pale. London: Hurst and Blackett. pp. 98–100. OCLC 3469796.
- The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903; with online resources archived from www.shtetlinks.jewishgen.org; archive accessed 27 January 2022
- Klier, John (October 11, 2010). "Pogroms". YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe. yivoencyclopedia.org. Retrieved April 17, 2018.
- Klier, John Doyle; Lambroza, Shlomo (1992). Pogroms: Anti-Jewish Violence in Modern Russian History. Cambridge University Press. p. 202. ISBN 978-0-521-52851-1.
- "Jewish Massacre Denounced". The New York Times. 28 April 1903. p. 6.
- Adler, Cyrus (ed.). The Voice of America on Kishineff. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- Singer, Isidore (1904). Russia at the Bar of the American People. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- "Current Literature: A Magazine of Contemporary Record (New York). Vol. XXXV., No.1. July, 1903. Current Opinion. V.35 (1903). p. 16". babel.hathitrust.org. pp. 25 v.
- "Picasa Web Albums - Ronnie - kishinev". Archived from the original on 6 June 2015. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- ^ Zipperstein 2015, p. 372.
- Beatty 2017, p. 125.
- Leo Tolstoy (2015). R. F. Christian (ed.). Tolstoy's Diaries. Vol. 2: 1895–1910. Faber & Faber. ISBN 9780571324064.
- Leo Tolstoy (1906). Tolstoy on Shakespeare: A Critical Essay on Shakespeare. Translated by Isabella Fyvie Mayo, Vladimir Grigorʹevich Chertkov. Funk & Wagnalls Company.
- Holtzman, Avner; Scharf, Orr (2017). Hayim Nahman Bialik: poet of Hebrew. Jewish lives. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 95–96. ISBN 978-0-300-20066-9. OCLC 953985607.
- "מכון ז'בוטינסקי | Item". en.jabotinsky.org. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- Zangwill, Israel (2006). From the Ghetto to the Melting Pot: Israel Zangwill's Jewish Plays : Three Playscripts. Wayne State University Press. p. 254. ISBN 9780814329559. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- Weingrad, Michael (Spring 2015). "Drawing Conclusions: Joann Sfar and the Jews of France". Jewish Review of Books. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- Sparber, Max (3 December 2014). "Staged reading of play by Max Sparber: Kishinev". MetaFilter. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- Hemon, A., (2008). The Lazarus project. New York: Riverhead Books
- "Chisinau. Monument to Pogrom Victims". jewishmemory.md. 24 April 2016. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- Beatty, Aidan. "Jews and the Irish Nationalist Imagination: Between Philosemitism and Antisemitism. Journal of Jewish Studies. Vol. 68, No. 1 (2017)". Journal of Jewsh Studies: 125.
- Davitt, Michael (1903). Within the pale:The true story of anti-Semitic persecution in Russia. Princeton Theological Seminary Library. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society of America. pp. 217–222.
- "פרעות קישינב [אלבום תצלומים]" [Kishinev Pogrom ]. the National Library of Israel (in Hebrew).
- "Kishinev: List of Victims of Kishinev Pogrom of 1903". kehilalinks.jewishgen.org. Retrieved 8 January 2025.
Bibliography
- Beatty, Aidan (2017). "Jews and the Irish nationalist imagination: between philo-Semitism and anti-Semitism". Journal of Jewish Studies. 68 (1): 125–128. doi:10.18647/3304/JJS-2017.
- Zipperstein, Steven J. (2015). "Inside Kishinev's Pogrom: Hayyim Nahman Bialik, Michael Davitt, and the Burdens of Truth" (PDF). In Freeze, ChaeRan Y.; Fried, Sylvia Fuks; Sheppard, Eugene R. (eds.). The Individual in History: Essays in Honor of Jehuda Reinharz. Waltham, Massachusetts: Brandeis University Press. ISBN 9781611687330. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
Further reading
- Judge, Edward H. Easter in Kishinev: Anatomy of a Pogrom. NYU Press 1992.
- Penkower, Monty Noam (2004). "The Kishinev Pogrom of 1903: A Turning Point in Jewish History". Modern Judaism. 24 (3): 187–225. doi:10.1093/mj/kjh017. JSTOR 1396539. S2CID 170968039.
 Rosenthal, Herman; Rosenthal, Max (1901–1906). "Kishinef (Kishinev)". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
Rosenthal, Herman; Rosenthal, Max (1901–1906). "Kishinef (Kishinev)". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.- Schoenberg, Philip Ernest. "The American Reaction to the Kishinev Pogrom of 1903". American Jewish Historical Quarterly 63.3 (1974): 262–283.
- Zipperstein, Steven J. Pogrom: Kishinev and the Tilt of History. Liveright Publishing March 2018.
- "YIVO | Kishinev". yivoencyclopedia.org. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
External links
- Kishinev Pogrom unofficial commemorative website
- Resources about the pogrom
- "Are Jewish men cowards?" Interview in Chicago Jewish Cafe with Prof. Steven Zipperstein, the author of "Pogrom: Kishinev and the Tilt of History."