| Revision as of 00:01, 7 August 2011 editBeetstra (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators172,031 edits Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEBI').← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:12, 7 August 2011 edit undoCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WiNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 443428416 | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| | ImageFile = Bromige saeure.png | | ImageFile = Bromige saeure.png | ||
| | ImageSize = | | ImageSize = | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
| | CASNo = | | CASNo = | ||
| | PubChem = 165616 | | PubChem = 165616 | ||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| | ChEBI = 29247 | | ChEBI = 29247 | ||
| | SMILES = O=BrO | | SMILES = O=BrO | ||
Revision as of 00:12, 7 August 2011
Template:Chembox Other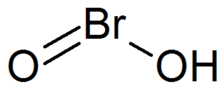
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
hydroxy-λ-bromanone hydroxidooxidobromine bromous acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | HBrO2 |
| Molar mass | 112.911 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Bromous acid with the formula HBrO2 has bromine in the +3 oxidation state. The salts of bromous acid are called bromites. The acid is not stable and only occurs as an intermediate, for example in the oxidation of hypobromites.
Chemistry
Bromous acid can be produced by classical chemical or electrochemicals method via anodic oxidation.
- HBrO + HClO → HBrO2 + HCl
Also disproportioning of hypobromous acid will give bromous acid and hydrobromic acid.
- 2 HBrO → HBrO2 + HBr
Lastly, a synproportion reaction of bromic acid and hydrobromic acid gives bromous acid.
- 2 HBrO3 + HBr → 3 HBrO2
Compounds
Several bromites are stable and have been isolated. For example NaBrO2· 3H2O and Ba(BrO2)2·H2O.
Use
Bromites can be used for the reduction of permanganates to manganates.
- 2MnO
4 + BrO
2 + OH → 2MnO
4 + BrO
3 + H2O
References
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |