| Revision as of 13:12, 18 July 2012 view sourceMassagetae (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,046 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:17, 18 July 2012 view source Solhjoo (talk | contribs)192 edits unimportant to be mentioned in this articleNext edit → | ||
| Line 492: | Line 492: | ||
| Iran is a diverse country consisting of people of many religions and ethnic backgrounds cemented by the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iran-v1-peoples-survey |title=Encyclopaedia Iranica. R. N. Frye. Peoples of Iran |publisher=Iranicaonline.org |accessdate=14 September 2011}}</ref> The majority of the population speaks the ], which is also the ] of the country, as well as other ]s or dialects. ] and dialects, most importantly ], are spoken in different areas in Iran. Additionally, Arabic is spoken in the southwestern parts of the country, although Arabs constitute a minority in these regions. | Iran is a diverse country consisting of people of many religions and ethnic backgrounds cemented by the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iran-v1-peoples-survey |title=Encyclopaedia Iranica. R. N. Frye. Peoples of Iran |publisher=Iranicaonline.org |accessdate=14 September 2011}}</ref> The majority of the population speaks the ], which is also the ] of the country, as well as other ]s or dialects. ] and dialects, most importantly ], are spoken in different areas in Iran. Additionally, Arabic is spoken in the southwestern parts of the country, although Arabs constitute a minority in these regions. | ||
| The exact ethnic breakdown of Iran is unknown as there are no official numbers, however some organizations have made estimates. ] released the estimate: ] (61%), ] (16%), ] (10%), ] (6%), ] (2%), ] (2%), ] and ] (2%),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2075.html |title=Central Intelligence Agency |publisher=Cia.gov |accessdate=7 April 2012}}</ref> ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and others (1%).<ref name="CIA"/> However according to them Persian is spoken as first language by 53%, while Azeri and other Turkic dialects is spoken by 18%, ] by 10%, ] and ] by 7%, ] by 6%, ] by 2%, ] by 2% and that some 2% have other languages as first language.<ref name="CIA"/> | The exact ethnic breakdown of Iran is unknown as there are no official numbers, however some organizations have made estimates. ] released the estimate: ] (61%), ] (16%), ] (10%), ] (6%), ] (2%), ] (2%), ] and ] (2%),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2075.html |title=Central Intelligence Agency |publisher=Cia.gov |accessdate=7 April 2012}}</ref> ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and others (1%).<ref name="CIA"/> However according to them Persian is spoken as first language by 53%, while Azeri and other Turkic dialects is spoken by 18%, ] by 10%, ] and ] by 7%, ] by 6%, ] by 2%, ] by 2% and that some 2% have other languages as first language.<ref name="CIA"/> | ||
| The ] estimates are as following: Persians (65%), Azerbaijanis (16%), Kurds (7%), Lurs (6%), Arabs (2%), Baluchi (2%), Turkmens (1%), Turkic tribal groups such as the Qashqai (1%), and non-Persian, non-Turkic groups such as Armenians, Assyrians, Pashtuns and Georgians (less than 1%). According to it Persian is spoken as a mother tongue by at least 65% of the population and as a second language by a large proportion of the remaining 35%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/Iran.pdf|title=Ethnic Groups and Languages of Iran|first=Library of Congress – Federal Research Division|last=Library of Congress|accessdate=2 December 2009}}</ref> | The ] estimates are as following: Persians (65%), Azerbaijanis (16%), Kurds (7%), Lurs (6%), Arabs (2%), Baluchi (2%), Turkmens (1%), Turkic tribal groups such as the Qashqai (1%), and non-Persian, non-Turkic groups such as Armenians, Assyrians, Pashtuns and Georgians (less than 1%). According to it Persian is spoken as a mother tongue by at least 65% of the population and as a second language by a large proportion of the remaining 35%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/Iran.pdf|title=Ethnic Groups and Languages of Iran|first=Library of Congress – Federal Research Division|last=Library of Congress|accessdate=2 December 2009}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 18 July 2012
"Persia" redirects here. For other uses, see Persia (disambiguation). This article is about the modern state of Iran. For historical uses, see Greater Iran.
32°N 53°E / 32°N 53°E / 32; 53
| Islamic Republic of Iranجمهوری اسلامی ایران Jomhuri-ye Eslāmi-ye Irān | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Emblem
Emblem
| |
| Motto: استقلال. آزادی. جمهوری اسلامی Independence, Freedom, Islamic Republic | |
| Anthem: National Anthem of Islamic Republic of Iran | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Tehran |
| Official languages | Persian |
| Spoken languages | Persian, Azeri, Kurdish, Lori, Gilaki, Mazandarani, Balochi, Arabic, Turkmen, Qashqai, Pashto, Armenian, Talysh |
| Demonym(s) | Iranian |
| Government | Unitary state, Islamic republic |
| • Supreme Leader | Ali Khamenei |
| • President | Mahmoud Ahmadinejad |
| • First Vice President | Mohammad-Reza Rahimi |
| • Speaker of the Parliament | Ali Larijani |
| • Chief Justice | Sadeq Larijani |
| Legislature | Islamic Consultative Assembly |
| Unification | |
| • Median Empire | 625 BCE |
| • Achaemenid Empire | 550 BCE |
| • Safavid Empire | 1501 |
| • Islamic Republic | 24 October 1979 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,648,195 km (636,372 sq mi) (18th) |
| • Water (%) | 0.7 |
| Population | |
| • 2012 estimate | 78,868,711 (18th) |
| • 2011 census | 74,961,702 |
| • Density | 48/km (124.3/sq mi) (162rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2011 estimate |
| • Total | $990.219 billion |
| • Per capita | $13,053 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2011 estimate |
| • Total | $482.445 billion |
| • Per capita | $6,359 |
| Gini (2008) | 38 Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI (2011) | Error: Invalid HDI value (88th) |
| Currency | Rial (﷼) (IRR) |
| Time zone | UTC+3:30 (IRST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+4:30 (IRDT) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | 98 |
| ISO 3166 code | IR |
| Internet TLD | .ir, ایران. |
| |
Template:Contains Perso-Arabic text Iran (/ɪˈrɑːn/ or /aɪˈræn/; Template:Lang-fa Template:IPA-fa), officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (Template:Lang-fa Jomhuri-ye Eslāmi-ye Irān), is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran", which in Persian means "Land of the Aryans", has been in use natively since the Sassanian era. It came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia (/ˈpɜːʒə/ or /ˈpɜːʃə/). Both "Persia" and "Iran" are used interchangeably in cultural contexts; however, "Iran" is the name used officially in political contexts.
The 18th-largest country in the world in terms of area at 1,648,195 km (636,372 sq mi), Iran has a population of around 79 million. It is a country of particular geopolitical significance owing to its location in the Middle East and central Eurasia. Iran is bordered on the north by Armenia, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan. As Iran is a littoral state of the Caspian Sea, which is an inland sea, Kazakhstan and Russia are also Iran's direct neighbors to the north. Iran is bordered on the east by Afghanistan and Pakistan, on the south by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by Iraq and on the northwest by Turkey. Tehran is the capital, the country's largest city and the political, cultural, commercial and industrial center of the nation. Iran is a regional power, and holds an important position in international energy security and world economy as a result of its large reserves of petroleum and natural gas. Iran has the second largest proven natural gas reserves in the world and the fourth largest proven petroleum reserves.
Iran is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations. The first dynasty in Iran formed during the Elamite kingdom in 2800 BC. The Iranian Medes unified Iran into an empire in 625 BC. They were succeeded by the Iranian Achaemenid Empire, the Hellenic Seleucid Empire and two subsequent Iranian empires, the Parthians and the Sassanids, before the Muslim conquest in 651 AD. Iranian post-Islamic dynasties and empires expanded the Persian language and culture throughout the Iranian plateau. Early Iranian dynasties which re-asserted Iranian independence included the Tahirids, Saffarids, Samanids and Buyids.
The blossoming of Persian literature, philosophy, medicine, astronomy, mathematics and art became major elements of Muslim civilization. Iranian identity continued despite foreign rule in the ensuing centuries and Persian culture was adopted also by the Ghaznavids, Seljuk, Ilkhanid and Timurid rulers. The emergence in 1501 of the Safavid dynasty, which promoted Twelver Shia Islam as the official religion of their empire, marked one of the most important turning points in Iranian and Muslim history. The Persian Constitutional Revolution established the nation's first parliament in 1906, within a constitutional monarchy. In 1953 Iran became an authoritarian regime, following a coup d'état instigated by the UK and US. Growing dissent with foreign influence culminated during the Iranian Revolution which led to establishment of an Islamic republic on 1 April 1979.
Iran is a founding member of the UN, NAM, OIC and OPEC. The political system of Iran, based on the 1979 constitution, comprises several intricately connected governing bodies. The highest state authority is the Supreme Leader. Shia Islam is the official religion and Persian is the official language.
Etymology
Main articles: Iran (word) and Name of IranThe name of Iran (ایران) is the Modern Persian derivative from the Proto-Iranian term Aryānā,, meaning "Land of the Aryans", first attested in Zoroastrianism's Avesta tradition. The term Ērān is found to refer to Iran in a 3rd century Sassanid inscription, and the Parthian inscription that accompanies it uses the Parthian term "aryān" in reference to Iranians. However historically Iran has been referred to as Persia or similar (La Perse, Persien, Perzië, etc.) by the Western world, mainly due to the writings of Greek historians who called Iran Persis (Περσίς), meaning land of the Persians. In 1935 Rezā Shāh requested that the international community should refer to the country as Iran. Opposition to the name change led to the reversal of the decision, and in 1959 both names were to be used interchangeably. Since the Iranian Revolution in 1979 the official name of the country has been the "Islamic Republic of Iran."
History
Main article: History of IranPre-Historic era
Further information: Archaeological sites in Iran, Tepe Sialk, Jiroft culture, and Shahr-e SukhtehThe earliest archaeological artifacts in Iran, like those excavated at the Kashafrud and Ganj Par sites, attest to a human presence in Iran since the Lower Paleolithic era, whilst Neanderthal artefacts dating back to the Middle Paleolithic period have been found mainly in the Zagros region at sites such as Warwasi and Yafteh Cave. Early agricultural communities began to flourish in Iran at around 8000 BC, with settlements such as Chogha Bonut, Susa and Chogha Mish developing in the Zagros region.
Dozens of pre-historic sites across the Iranian plateau point to the existence of ancient cultures and urban settlements in the fourth millennium BC, centuries before the earliest civilizations arose in nearby Mesopotamia. During the Bronze age Iran was home to several civilisations such as Elam, Jiroft and Zayandeh Rud civilisations. Elam, the most prominent of these civilisations developed in the southwest of Iran alongside those in mesopotamia. The development of writing in Elam in 2900 BC paralleled that in Sumer.
Early history (3200 BC – 625 BC)
Main articles: Tepe Sialk, Jiroft culture, Elam, and Mannaeans
Elam was part of the early urbanization during the Chalcolithic. The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Mesopotamian history. In the Old Elamite period (Middle Bronze Age), from around 2800 BC, Elam consisted of kingdoms on the Iranian plateau, centered in Anshan, and from the mid-2nd millennium BC, it was centered in Susa in the Khuzestan lowlands. The Elamite kingdom continued its existence until the emergence of the Median and Achaemenid Empires.
Proto-Iranians first emerged following the separation of Indo-Iranians, and are traced to the Andronovo culture. Proto-Iranian tribes arrived in the Iranian plateau in the third and second millennium BC, probably in more than one wave of emigration, and settled as nomads.
Further separation of Proto-Iranians into "Eastern" and "Western" groups occurred due to migration. By the first millennium BC, Medes, Persians, Bactrians and Parthians populated the western part, while Cimmerians, Sarmatians and Alans populated the steppes north of the Black Sea.
Other tribes began to settle on the eastern edge, as far as on the mountainous frontier of the north-western Indian subcontinent and into the area which is now Balochistan. Others, such as the Scythian tribes, spread as far west as the Balkans and as far east as Xinjiang. Avestan is an eastern Old Iranian language that was used to compose the sacred hymns and canon of the Zoroastrian Gathas in c. 1000 BC.
Pre-Islamic statehood (625 BC – 651 AD)
Main articles: Medes, Achaemenid Empire, Seleucid Empire, Parthian Empire, and Sassanid Empire See also: Greco-Persian Wars, Roman-Persian Wars, and Roman-Persian relations
The Medes are credited with the unification of Iran as a nation and empire (625–559 BC), the largest of its day, until Cyrus the Great established a unified empire of the Medes and Persians leading to the Achaemenid Empire (559–330 BC), and further unification between peoples and cultures. After Cyrus' death, his son Cambyses II continued his father's work of conquest, making significant gains in Egypt.
Following a power struggle after Cambyses' death, Darius the Great was declared king (ruled 522–486 BC). Under Cyrus and Darius, the Persian Empire eventually became the largest and most powerful empire in human history up until that point. The borders of the Persian empire stretched from the Indus and Oxus Rivers in the east to the Mediterranean Sea in the west, extending through Anatolia (modern day Turkey) and Egypt.

In 499 BC, Athens lent support to a revolt in Miletus which resulted in the sacking of Sardis. This led to an Achaemenid campaign against Greece known as the Greco-Persian Wars which continued through the first half of the 5th century BC. During the Greco-Persian Wars Persia made some major advances and razed Athens in 480 BC, but after a string of Greek victories the Persians were forced to withdraw. Fighting ended with the peace of Callias in 449 BC.
The rules and ethics emanating from Zoroaster's teachings were strictly followed by the Achaemenids who introduced and adopted policies based on human rights, equality and banning of slavery. Zoroastrianism spread unimposed during the time of the Achaemenids and through contacts with the exiled Jewish people in Babylon freed by Cyrus, Zoroastrian concepts further propagated and influenced the Abrahamic religions. The Golden Age of Athens marked by Aristotle, Plato and Socrates also came about during the Achaemenid period while their contacts with Persia and the Near East abounded. The peace, tranquility, security and prosperity that were afforded to the people of the Near East and Southeast Europe proved to be a rare historical occurrence, an unparalleled period where commerce prospered and the standard of living for all people of the region improved.
In 334 BC, Alexander the Great invaded the Achaemenid Empire, defeating the last Achaemenid Emperor Darius III at the Battle of Issus in 333 BC. He left the annexed territory in 328–327. In each of the former Achaemenid territories he installed his own officers as caretakers, which led to friction and ultimately to the partitioning of the former empire after Alexander's death, and the subsequent formation of the Seleucid Empire.

The Parthian Empire (238 BC–226 AD), led by the Arsacid Dynasty, was the third Iranian kingdom to dominate the Iranian plateau, after defeating the Greek Seleucid Empire, beginning in the late 3rd century BC, and intermittently controlled Mesopotamia between ca. 150 BC and 224 AD. This was the third native dynasty of ancient Iran and lasted five centuries. After the conquests of Media, Assyria, Babylonia and Elam, the Parthians had to organize their empire. The former elites of these countries were Greek, and the new rulers had to adapt to their customs if they wanted their rule to last. As a result, the cities retained their ancient rights and civil administrations remained more or less undisturbed.
Parthia was the arch-enemy of the Roman Empire in the east, limiting Rome's expansion beyond Cappadocia (central Anatolia). By using a heavily armed and armoured cataphract cavalry, and lightly armed but highly mobile mounted archers, the Parthians "held their own against Rome for almost 300 years". Rome's acclaimed general Mark Antony led a disastrous campaign against the Parthians in 36 BC, in which he lost 32,000 men. By the time of Roman emperor Augustus, Rome and Parthia were settling some of their differences through diplomacy. By this time, Parthia had acquired an assortment of golden eagles, the cherished standards of Rome's legions, captured from Mark Antony, and Crassus, who was defeated by General Surena in the Battle of Carrhae in 53 BC.

The end of the Parthian Empire came in 224 AD, when the empire was loosely organized and the last king was defeated by Ardashir I, one of the empire's vassals. Ardashir I then went on to create the Sassanid Empire. Soon he started reforming the country both economically and militarily. The Sassanids established an empire roughly within the frontiers achieved by the Achaemenids, referring to it as Erânshahr or Iranshahr, ![]() , "Dominion of the Iranians", (i.e. of Iranians), with their capital at Ctesiphon. Unlike the diadochic Seleucids and the succeeding Arsacids, who used a vassalary system, the Sassanids—like the Achaemenids—had a system of governors (MP: shahrab) personally appointed by the Emperor and directed by the central government. The Romans suffered repeated losses particularly by Ardashir I, Shapur I, and Shapur II. During their reign, Sassanid battles with the Roman Empire caused such pessimism in Rome that the historian Cassius Dio wrote:
, "Dominion of the Iranians", (i.e. of Iranians), with their capital at Ctesiphon. Unlike the diadochic Seleucids and the succeeding Arsacids, who used a vassalary system, the Sassanids—like the Achaemenids—had a system of governors (MP: shahrab) personally appointed by the Emperor and directed by the central government. The Romans suffered repeated losses particularly by Ardashir I, Shapur I, and Shapur II. During their reign, Sassanid battles with the Roman Empire caused such pessimism in Rome that the historian Cassius Dio wrote:
Here was a source of great fear to us. So formidable does the Sassanid king seem to our eastern legions, that some are liable to go over to him, and others are unwilling to fight at all.
In 632 raiders from the Arab peninsula began attacking the Sassanid Empire. Iran was defeated in the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah, paving way for the Muslim conquest of Persia.
During the Parthian and later Sassanid eras, trade on the Silk Road was a significant factor in the development of the great civilizations of China, Egypt, Mesopotamia, Persia, Indian subcontinent, and Rome, and helped to lay the foundations for the modern world. Parthian remains display classical Greek influences in some instances and retain their oriental mode in others, a clear expression of the cultural diversity that characterized Parthian art and life.
The Parthians were innovators of many architecture designs such as that of Ctesiphon, which later influenced European Romanesque architecture. Under the Sassanids, Iran expanded relations with China. Arts, music, and architecture greatly flourished, and centers such as the School of Nisibis and Academy of Gundishapur became world renowned centers of science and scholarship.
Middle Ages (652–1501)
Main articles: Islamization in Iran, Abbasid Caliphate, Tahirid dynasty, Saffarid dynasty, Samanids, Ziyarid dynasty, Buyid dynasty, Ghaznavids, Great Seljuq Empire, and Khwārazm-Shāh dynasty
After the Muslim conquest of Persia, most of the urban lands of the Sassanid Empire, with the exception of Caspian provinces and Transoxiana, came under Islamic rule. Many provinces in Iran defended themselves against the Arab invaders, although none in the end were able to repulse the invaders. However, when the Arabs had subdued the country, many of the cities rose in rebellion, killing Arab governors, although reinforcement by Arab armies succeeded in putting down the rebellions.
However, the Iranians' conversion to Islam was a complex process and is generally considered to have been gradual; the notion of force has largely been discredited, although occasional acts of violence did take place, with Zoroastrian scriptures being burned and Zoroastrian priests being executed.
By the 9th century, Islam became a dominant religion in Persia and the conversion of Iranians to Islam brought profound changes to their life and culture. However, in some regions, such as the Fars province, Zoroastrianism remained strong up to the 9th century, although Sufis such as Abu Eshaq Kazeruni, the founder of Kazeruni Sufi order, brought mass conversion of Zoroastrians to Islam in the 10th century.

During the Abbasid caliphate decline, independent and semi-independent native Iranian dynasties arose in different parts of Persia including the Tahirids, Saffarids, Samanids, Afrighids, Ghurids, Sallarids, Justanids, Shaddadids and Buyids. Socially, the Arabs abolished the previous social class system of Sassanians while later, especially under the Ummayyads, another form of discrimination and exclusion against non-Arabs evolved. In reaction to these, Abu Moslem, an Iranian general, expelled the Umayyads from Damascus and helped the Abbasid caliphs to conquer Baghdad. The Abbasid caliphs frequently chose their Iranians as their "wazirs" (viziers), and Iranian governors acquired a certain amount of local autonomy. Thus in 822, the governor of Khorasan, Tahir, proclaimed his independence and founded a new Persian dynasty of Tahirids. And by the Samanid era, Iran's efforts to regain its independence had been well solidified.
Attempts at Arabization thus never succeeded in Iran, and movements such as the Shu'ubiyya became catalysts for Iranians to regain their independence in their relations with the Arab invaders. Other notable major revolts, some by Iranian Muslims and others by practitioners of old Iranian religions against Arab rule were led by Al-Muqanna, Sunpadh, Khurramites, Babak Khorramdin, Maziar, Mardavij, Ustadh Sis and Ya'qub-i Laith Saffari.
The cultural revival of the post-Abbasid period led to a resurfacing of Iranian national identity. The resulting cultural movement reached its peak during the 9th and 10th centuries. The most notable effect of the movement was the continuation of the Persian language, the official language of Iran to the present day. Ferdowsi, Iran's greatest epic poet, is regarded today as the most important figure in maintaining the Persian language. After an interval of silence Iran re-emerged as a separate, different and distinctive element within Islam.
In 1218, the eastern Khwarazmid provinces of Transoxiana and Khorasan suffered a devastating invasion by Genghis Khan. During this period more than half of Iran's population was killed, turning the streets of Persian cities such as Nishapur into "rivers of blood", as the severed heads of men, women, and children were "neatly stacked into carefully constructed pyramids around which the carcasses of the city's dogs and cats were placed".

According to Steven R. Ward, "Overall, the Mongol violence and depredations killed up to three-fourths of the population of the Iranian plateau, possibly 10 to 15 million people. Some historians have estimated that Iran's population did not again reach its pre-Mongol levels until the mid-20th century." In a letter to King Louis IX of France, Holaku, one of the Genghis Khan's grandsons, took sole responsibility for 200,000 deaths in his raids of Iran and the Caliphate. He was followed by yet another conqueror, Tamerlane, who established his capital in Samarkand. The waves of devastation prevented many cities such as Nishapur from reaching their pre-invasion population levels until the 20th century, eight centuries later.
In 1387, Tamerlane avenged a revolt in Isfahan by massacring 70,000 people. But both Holaku, Tamerlane, and their successors soon came to adopt the ways and customs of that which they had conquered, choosing to surround themselves with a culture that was distinctively Persian. The mid-14th-century Black Death killed about 30% of the country's population.

Iran was gradually Islamized after the collapse of the Sassanid Empire; however, it was not Arabized. Iranian culture re-emerged with a separate and distinctive character and made an immense contribution to the Islamic civilization. When Islam came through Iran, what developed was an Iranian Islam or Persian Islam rather than the original Arab Islam, and this new Islam is sometimes referred to by scholars as Islam-i Ajam (Persian Islam).
It was this Persian Islam and Sufism which was brought to new areas and new peoples such as the Turks of Central Asia, the Ottoman Empire, and the Indian subcontinent. Among the major Iranian Muslims who cultivated Sufism and helped the spread of Islam through Sufism, one can mention Habib Ajami, Hallaj, Hasan Basri, Junayd Baghdadi, Bayazid Bastami, Maruf Karkhi, Abdul-Qadir Gilani, Moinuddin Chishti, Jalaluddin Rumi, Najmuddin Kubra, and Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari. Note should also be made of Abu Hanifa, the founder of the Hanafi school of thought which is followed by most Muslims today.
Arabic writer Ibn Khaldun has remarked that the sedentary culture which was necessary for the development of civilization was rooted in the Persian empire.
One of the main developments after the advent of Islam in Iran was the rise of the New Persian language as an important Indo-European language. The New Persian language was an evolution of Middle Persian, which in turn was derived from Old Persian. New Persian absorbed a considerable amount of Arabic vocabulary during this era, although the Arabic vocabulary that was Persianized often took a different meaning than the Arabic origin. In terms of contribution to the Arabic language, Iranians like Sibawayhi pioneered writing books of grammar of the Arabic language.

Culturally, Iranians preserved their language, while they used Arabic for scientific and philosophical discourses; this enabled them to reach a worldwide audience for the first time. After the 10th century, Persian, written in the modified Perso-Arabic script alongside Arabic, was used for scientific, philosophical, historical, mathematical, musical, and medical works, as important Iranian writers such as Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Avicenna, Qotb al-Din Shirazi, Gurgani, Nasir Khusraw, Biruni, Abd al-Qadir Maraghi made contributions to Persian scientific writing.
During this era, Iranians continued on a much larger scale the cultural and scientific enterprises set up by the Sassanids. The blossoming Persian literature, philosophy, medicine, and art became major elements in the forming Muslim civilization. The Islamic Golden Age, which is characterized by developments in science, owed to a large extent its importance to vital contributions made by Iranians. The Islamic Golden Age reached its peak in the 10th and 11th centuries, during which Persia was the main theatre of scientific activity. The Persian influence of this period relied heavily upon the achievements of the Sassanids, and the weight of this influence has led the Muslim world to accept Islamic civilization as the Perso-Islamic civilization.
Even in the development of Arabic scientific prose itself, which differs in style from that of the Quran, Persian scholars such as Abdullah Ibn al-Muqaffaʿ had a major role. Indeed, the class of clerks and civil administrators that was responsible for the cultivation of the sciences in the early Islamic centuries consisted mostly of Persians. The contributions of Iranians to the Arabic language are however not limited to scientific prose but are also found in Arabic poetry. The contributions by Iranians are characterised as "the lively and graceful fancy, elegance of diction, depth and tenderness of feeling, and a rich store of ideas".
Iranian philosophy after the Islamic conquest is characterized by different interactions with Old Iranian philosophy, with Ancient Greek philosophy, and with the development of Islamic philosophy. Illuminationism and transcendent theosophy are regarded as two of the main philosophical traditions of this era in Persia. These movements continued well into the 11th century, during which the Nizamiyya University was founded, and hundreds of Iranian scholars and scientists contributed greatly to technology, science, and medicine, later influencing the rise of European sciences during the Renaissance.
Early modern era (1501–1925)
Main articles: Safavid dynasty, Afsharid dynasty, Zand dynasty, and Qajar dynasty See also: Anglo-Persian War and Persian Constitutional Revolution
Iran's first encompassing Shia Islamic state was established under the Safavid dynasty (1501–1722) by Shah Ismail I. The Safavid dynasty soon became a major political power and promoted the flow of bilateral state contacts. The Safavid peak was during the rule of Shah Abbas The Great. The Safavid dynasty frequently warred with the Ottoman Empire, Uzbek tribes and the Portuguese Empire.
The Safavids moved their capital from Tabriz to Qazvin and then to Isfahan, where their patronage for the arts propelled Iran into one of its most aesthetically productive eras. Under their rule, the state became highly centralized, the first attempts to modernize the military were made, and even a distinct style of architecture developed. In 1722 Pashtun rebels headed by the Hotakis of Kandahar defeated Sultan Husayn and ended the Safavid dynasty, but in 1735, Nader Shah successfully drove out the Pashtuns from Isfahan and established the Afsharid Dynasty.

He then staged an incursion into India in 1738, securing the Peacock Throne, Koh-i-Noor, and Darya-ye Noor among other royal treasures. His rule did not last long, however, as he was assassinated in 1747. The Mashhad-based Afshar Dynasty was succeeded by the Zand dynasty in 1750, founded by Karim Khan, who established his capital at Shiraz. His rule brought a period of relative peace and renewed prosperity.
The Zand dynasty lasted three generations, until Aga Muhammad Khan executed Lotf Ali Khan, and founded his new capital in Tehran, marking the dawn of the Qajar dynasty in 1794. The Qajar chancellor Amir Kabir established Iran's first modern college system, among other modernizing reforms. Iran suffered several wars with Imperial Russia during the Qajar era, resulting in Iran losing almost half of its territories to Imperial Russia and the British Empire, via the treaties of Gulistan, Turkmenchay and Akhal. The Great Persian Famine of 1870–1871 is believed to have caused the death of 2 million persons.
In spite of The Great Game Iran managed to maintain her sovereignty and was never colonized, unlike neighbouring states in the region. Repeated foreign intervention and a corrupt and weakened Qajar rule led to various protests and constitutionalization efforts which eventually resulted in the establishment of the nation's first parliament in 1906. This was followed by the Jangal movement of Gilan which lead to the short-lived Gilan Republic.
Pahlavi dynasty (1925–1979)
Main article: Pahlavi dynasty Further information: 1953 Iranian coup d'étatIn 1925, Reza Khan overthrew the weakening Qajar dynasty and became Shah. Rezā Shāh initiated industrialization, railroad construction, and the establishment of a national education system. Rezā Shāh sought to balance Russian and British influence, but when World War II started, his nascent ties to Germany alarmed Britain and Russia. In 1941, Britain and the USSR invaded Iran to use Iranian railroad capacity during World War II. The Shah was forced to abdicate in favor of his son, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi.
In 1951, after the assassination of prime minister Ali Razmara, Dr. Mohammad Mosaddegh was elected prime minister by a parliamentary vote which was then ratified by the Shah. As prime minister, Mosaddegh became enormously popular in Iran after he nationalized Iran's petroleum industry and oil reserves. In response, the British government, headed by Winston Churchill, embargoed Iranian oil and successfully enlisted the United States to join in a plot to depose the democratically elected government of Mosaddegh. In 1953 US President Dwight D. Eisenhower authorized Operation Ajax. The operation was successful, and Mosaddegh was arrested on 19 August 1953. The coup was the first time the US had openly overthrown an elected, civilian government.
After Operation Ajax, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi's rule became increasingly autocratic. With American support, the Shah was able to rapidly modernize Iranian infrastructure, but he simultaneously crushed all forms of political opposition with his intelligence agency, SAVAK. Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini became an active critic of the Shah's White Revolution and publicly denounced the government.
Khomeini was arrested and imprisoned for 18 months. After his release in 1964 Khomeini publicly criticized the United States government. The Shah was persuaded to send him into exile by General Hassan Pakravan. Khomeini was sent first to Turkey, then to Iraq and finally to France. While in exile, he continued to denounce the Shah.
Islamic Republic (1979–present)
Main articles: Iranian Revolution, History of the Islamic Republic of Iran, and Iran–Iraq War Further information: 2009–2010 Iranian election protestsThe Iranian Revolution, also known as the Islamic Revolution, began in January 1978 with the first major demonstrations against the Shah. After strikes and demonstrations paralyzed the country and its economy, the Shah fled the country in January 1979 and Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini returned from exile to Tehran. The Pahlavi dynasty collapsed ten days later, on 11 February, when Iran's military declared itself "neutral" after guerrillas and rebel troops overwhelmed troops loyal to the Shah in armed street fighting. Iran officially became an Islamic Republic on 1 April 1979, when Iranians overwhelmingly approved a national referendum to make it so. In parallel nation wide uprisings against the new regime erupted in Kordestan, Khuzestan, Balochistan and other areas, though were eventually subdued, with some lasting until late 1980.
In December 1979, the country approved a theocratic constitution, whereby Khomeini became Supreme Leader of the country. The speed and success of the revolution surprised many throughout the world, as it had not been precipitated by a military defeat, a financial crisis, or a peasant rebellion. Although both nationalists and Marxists joined with Islamic traditionalists to overthrow the Shah, tens of thousands were killed and executed by the Islamic regime afterward, and the revolution ultimately resulted in an Islamic Republic under Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini.
Iran – United States relations deteriorated rapidly during the revolution. On 4 November 1979, a group of Iranian students seized US embassy personnel, labeling the embassy a "den of spies". They accused its personnel of being CIA agents plotting to overthrow the revolutionary government, as the CIA had done to Mosaddegh in 1953. While the student ringleaders had not asked for permission from Khomeini to seize the embassy, Khomeini nonetheless supported the embassy takeover after hearing of its success.
While most of the female and African American hostages were released within the first months, the remaining 52 hostages were held for 444 days. Subsequent attempts by the Jimmy Carter administration to negotiate or rescue were unsuccessful. In January 1981 the hostages were set free according to the Algiers Accords.
Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein decided to take advantage of what he perceived to be disorder in the wake of the Iranian Revolution and its unpopularity with Western governments. The once-strong Iranian military had been disbanded during the revolution. Saddam sought to expand Iraq's access to the Persian Gulf by acquiring territories that Iraq had claimed earlier from Iran during the Shah's rule. Of chief importance to Iraq was Khuzestan, which not only has a substantial Arab population, but boasted rich oil fields as well. On the unilateral behalf of the United Arab Emirates, the islands of Abu Musa and the Greater and Lesser Tunbs became objectives as well. On 22 September 1980 the Iraqi army invaded Iran at Khuzestan, precipitating the Iran–Iraq War.

Although Saddam Hussein's forces made several early advances, by 1982, Iranian forces managed to push the Iraqi army back into Iraq, allying with the Iraqi Kurds, who rose up in rebellion against Saddam. Khomeini sought to export his Islamic revolution westward into Iraq, especially on the majority Shia Arabs living in the country. The war then continued for six more years until 1988, when Khomeini, in his words, "drank the cup of poison" and accepted a truce mediated by the United Nations. The total Iranian casualties of the war were estimated to be anywhere between 500,000 and 1,000,000; with more than 100,000 Iranians being victims of Iraq's chemical weapons. Almost all relevant international agencies have confirmed that Saddam engaged in chemical warfare to blunt Iranian human wave attacks; these agencies unanimously confirmed that Iran never used chemical weapons during the war.
Following the Iran–Iraq War President Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani and his administration concentrated on a pragmatic pro-business policy of rebuilding and strengthening the economy without making any dramatic break with the ideology of the revolution. Rafsanjani served until 1997 when he was succeeded by the moderate reformist Mohammad Khatami. During his two terms as president, Khatami advocated freedom of expression, tolerance and civil society, constructive diplomatic relations with other states including European Union and Asian governments, and an economic policy that supported free market and foreign investment. However, Khatami is widely regarded as having been unsuccessful in achieving his goal of making Iran more free and democratic.
In the 2005 presidential elections, Iran made yet another change in political direction, when conservative populist candidate Mahmoud Ahmadinejad was elected over Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani. A significant challenge to Ahmadinejad's political power, and the foundations of the Islamic Republic itself occurred during the 2009 Iranian presidential election that was held on 12 June 2009, the tenth presidential election to be held in the country. The Interior Ministry, announced incumbent president Mahmoud Ahmadinejad had won the election with 62.63% receiving 24.5 million vote, while Mir-Hossein Mousavi had come in second place with 13.2 million votes 33.75%. There were large irregularities in the results and people were surprised by them, which resulted in protests gathering millions of Iranians in every Iranian city and around the world.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Iran See also: Agriculture in Iran and Wildlife of Iran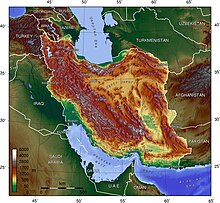
Iran is the eighteenth largest country in the world, with an area of 1,648,000 km (636,000 sq mi).

Its area roughly equals that of the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and Germany combined, or somewhat more than the US state of Alaska. Iran lies between latitudes 24° and 40° N, and longitudes 44° and 64° E. Its borders are with Azerbaijan (611 km (380 mi) (with Azerbaijan-Naxcivan exclave (179 km (111 mi) )) and Armenia (35 km (22 mi)) to the north-west; the Caspian Sea to the north; Turkmenistan (992 km (616 mi)) to the north-east; Pakistan (909 km (565 mi)) and Afghanistan (936 km (582 mi)) to the east; Turkey (499 km (310 mi)) and Iraq (1,458 km (906 mi)) to the west; and finally the waters of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the south.

Iran consists of the Iranian Plateau with the exception of the coasts of the Caspian Sea and Khuzestan Province. It is one of the world's most mountainous countries, its landscape dominated by rugged mountain ranges that separate various basins or plateaux from one another. The populous western part is the most mountainous, with ranges such as the Caucasus, Zagros and Alborz Mountains; the last contains Iran's highest point, Mount Damavand at 5,610 m (18,406 ft), which is also the highest mountain on the Eurasian landmass west of the Hindu Kush.
The northern part of Iran is covered by dense rain forests called Shomal or the Jungles of Iran. The eastern part consists mostly of desert basins such as the Dasht-e Kavir, Iran's largest desert, in the north-central portion of the country, and the Dasht-e Lut, in the east, as well as some salt lakes. This is because the mountain ranges are too high for rain clouds to reach these regions. The only large plains are found along the coast of the Caspian Sea and at the northern end of the Persian Gulf, where Iran borders the mouth of the Shatt al-Arab (or the Arvand Rūd) river. Smaller, discontinuous plains are found along the remaining coast of the Persian Gulf, the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman.
Climate

Iran's climate ranges from arid or semiarid, to subtropical along the Caspian coast and the northern forests. On the northern edge of the country (the Caspian coastal plain) temperatures rarely fall below freezing and the area remains humid for the rest of the year. Summer temperatures rarely exceed 29 °C (84.2 °F). Annual precipitation is 680 mm (26.8 in) in the eastern part of the plain and more than 1,700 mm (66.9 in) in the western part.
To the west, settlements in the Zagros basin experience lower temperatures, severe winters with below zero average daily temperatures and heavy snowfall. The eastern and central basins are arid, with less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rain, and have occasional deserts. Average summer temperatures exceed 38 °C (100.4 °F). The coastal plains of the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in southern Iran have mild winters, and very humid and hot summers. The annual precipitation ranges from 135 to 355 mm (5.3 to 14.0 in).
Fauna

Iran's wildlife is composed of several animal species including bears, gazelles, wild pigs, wolves, jackals, panthers, Eurasian Lynx, and foxes. Domestic animals include, sheep, goats, cattle, horses, water buffalo, donkeys, and camels. The pheasant, partridge, stork, eagles and falcon are also native to Iran.
One of the most famous members of Iranian wildlife is the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah, also known as the Iranian Cheetah, whose numbers were greatly reduced after the Iranian Revolution. Today there are ongoing efforts to increase its population and introduce it back in India. Iran had lost all its Asiatic Lion and the now extinct Caspian Tigers by the earlier part of the 20th century.
Provinces and cities
Main articles: Provinces of Iran and Counties of Iran See also: List of Iranian cities by population Alborz
Ardabil
Bushehr
Chaharmahal
Alborz
Ardabil
Bushehr
Chaharmahaland Bakhtiari Isfahan Fars Gilan Golestan Hamadan Hormozgan Ilam Kerman Kermanshah Khuzestan Kohgiluyeh and
Boyer-Ahmad Kurdistan Lorestan Markazi Mazandaran Qazvin Qom Razavi
Khorasan Semnan Sistan and
Baluchestan Tehran Yazd Zanjan North
Khorasan South
Khorasan West
Azerbaijan East
Azerbaijan Caspian Sea Persian Gulf Turkmenistan Afghanistan Pakistan Azerbaijan Armenia T
u
r
k
e
y Iraq Kuwait Saudi Arabia
Iran is divided into thirty one provinces (ostān), each governed by an appointed governor (استاندار, ostāndār). The provinces are divided into counties (shahrestān), and subdivided into districts (bakhsh) and sub-districts (dehestān).
Iran has one of the highest urban growth rates in the world. From 1950 to 2002, the urban proportion of the population increased from 27% to 60%. The United Nations predicts that by 2030, 80% of the population will be urban. Most internal migrants have settled near the cities of Tehran, Isfahan, Ahvaz, and Qom. The listed populations are from the 2006/07 (1385 AP) census. Tehran, with a population of 7,705,036, is the largest city in Iran and is the capital. Tehran, like many big cities, suffers from severe air pollution. It is the hub of the country's communication and transport network.
Mashhad, with a population of 2,410,800, is the second largest Iranian city and the centre of the Razavi Khorasan Province. Mashhad is one of the holiest Shia cities in the world as it is the site of the Imam Reza shrine. It is the centre of tourism in Iran, and between 15 and 20 million pilgrims go to the Imam Reza's shrine every year.
Another major Iranian city is Isfahan (population 1,583,609), which is the capital of Isfahan Province. The Naqsh-e Jahan Square in Isfahan has been designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. The city contains a wide variety of Islamic architectural sites ranging from the 11th to the 19th century. The growth of the suburban area around the city has turned Isfahan into Iran's second most populous metropolitan area (3,430,353).
The fourth major city of Iran is Tabriz (population 1,378,935), the capital of the East Azerbaijan Province. It is also the second industrial city of Iran after Tehran. Tabriz had been the second largest city in Iran until the late 1960s and one of its former capitals and residence of the crown prince under the Qajar dynasty. The city has proven extremely influential in the country’s recent history.
The fifth major city is Karaj (population 1,377,450), located in Alborz Province and situated 20 km west of Tehran, at the foot of the Alborz mountains; however, the city is increasingly becoming an extension of metropolitan Tehran.
The sixth major Iranian city is Shiraz (population 1,214,808); it is the capital of Fars Province. The Elamite civilization to the west greatly influenced the area, which soon came to be known as Persis. The ancient Persians were present in the region from about the 9th century BC, and became rulers of a large empire under the Achaemenid dynasty in the 6th century BC. The ruins of Persepolis and Pasargadae, two of the four capitals of the Achaemenid Empire, are located in or near Shiraz. Persepolis was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire and is situated 70 kilometres (43 mi) northeast of modern Shiraz. UNESCO declared the citadel of Persepolis a World Heritage Site in 1979.
| Largest cities or towns in Iran 2016 census | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Culture
Main article: Culture of Iran See also: Persian mythology, Iranian studies, Persian garden, and Media of Iran
The culture of Iran is a mix of ancient pre-Islamic culture and Islamic culture. Iranian culture has long been a predominant culture of the Middle East and Central Asia, with Persian considered the language of intellectuals during much of the 2nd millennium, and the language of religion and the populace before that.
The Sassanid era was an important and influential historical period in Iran as Iranian culture influenced China, India and Roman civilization considerably, and so influenced as far as Western Europe and Africa. This influence played a prominent role in the formation of both Asiatic and European medieval art. This influence carried forward to the Islamic world. Much of what later became known as Islamic learning, such as philology, literature, jurisprudence, philosophy, medicine, architecture and the sciences were based on some of the practises taken from the Sassanid Persians to the broader Muslim world.
After Islamization of Iran Islamic rituals have penetrated in the Iranian culture. The most noticeable one of them is commemoration of Husayn ibn Ali. Every year in Day of Ashura most of Iranians, including Armenians and Zoroastrians participate in mourning for the martyrs of battle of Karbala. Daily life in modern Iran is closely interwoven with Shia Islam and the country's art, literature, and architecture are an ever-present reminder of its deep national tradition and of a broader literary culture.
The Iranian New Year (Nowruz) is an ancient tradition celebrated on 21 March to mark the beginning of spring in Iran. It is also celebrated in Afghanistan, Republic of Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan and previously also in Georgia and Armenia. It is also celebrated by the Iraqi and Anatolian Kurds. Nowruz was registered on the list of Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity and described as the Persian New Year by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2009.
Language and literature
Main articles: Persian language and Persian literature See also: Persian miniatureArticle 15 of the Iranian constitution states that the "Official language (of Iran)... is Persian...... the use of regional and tribal languages in the press and mass media, as well as for teaching of their literature in schools, is allowed in addition to Persian." Persian serves as a lingua franca in Iran and most publications and broadcastings are in this language.
Next to Persian, there are many publications and broadcastings in other relatively popular languages of Iran such as Azeri, Kurdish and even in less popular ones such as Arabic and Armenian. Many languages originated in Iran, but Persian is the most used language. Persian belongs to the Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. The oldest records in Old Persian date to the Achaemenid Empire, and examples of Old Persian have been found in present-day Iran, Iraq, Turkey and Egypt.
In the late 8th century, Persian was highly Arabized and written in a modified Arabic script. This caused a movement supporting the revival of Persian. An important event of this revival was the writing of the Shahname by Ferdowsi (Persian: Epic of Kings), Iran's national epic, which is said to have been written entirely in native Persian. This gave rise to a strong reassertion of Iranian national identity, and is in part credited for the continued existence of Persian as a separate language.
بسی رنج بردم در این سال سی
عجم زنده کردم بدین پارسی
For thirty years, I suffered much pain and strife
with Persian I gave the Ajam verve and life
—Ferdowsi (935–1020)

Persian beside Arabic has been a medium for literary and scientific contributions to the Islamic world especially in Anatolia, central Asia and Indian subcontinent. Poetry is a very important part of Persian culture. Poetry is used in many Persian classical works, whether from literature, science, or metaphysics. Persian literature has been considered by such thinkers as Goethe as one of the four main bodies of world literature.
The Persian language has produced a number of famous poets; however, only a few poets as Rumi and Omar Khayyám have surfaced among western popular readership, even though the likes of Hafiz, Saadi, Nizami Attar, Sanai, Nasir Khusraw, Jami, Taleb Amoli are considered by many Iranians to be just as influential. The books of famous poets have been translated into western languages since 1634. An example of Persian poetic influence is the poem below which is widely popular:

بنى آدم اعضای يک پیکرند
که در آفرينش ز يک گوهرند
چو عضوى به درد آورد روزگار
دگر عضوها را نماند قرار
Of one Essence is the human race
thus has Creation put the base
One Limb impacted is sufficient
For all Others to feel the Mace
—Saadi (1184–1283)
Philosophy
Main article: Iranian philosophyWhile there are ancient relations between the Indian Vedas and the Iranian Avesta, the two main families of the ancient Indo-Iranian philosophical traditions were characterized by fundamental differences in their implications for the human being's position in society and their view on the role of man in the universe.
Iranian philosophy after the acceptance of Islam in Persia, is characterized by different interactions with the Ancient Iranian Philosophy, the Ancient Greek philosophy and with the development of Islamic philosophy. Illuminationism and transcendent theosophy are regarded as two of the main philosophical traditions of that era in Persia. Among important contributors to philosophy in Iran are Zoroaster, Jamasp, Mardan-Farrux Ohrmazddadan, Adurfarnbag Farroxzadan, Adurbad Emedan, Iranshahri, Farabi, Avicenna, Ali ibn Sahl Rabban al-Tabari, Suhrawardi, Nasir Khusraw, Biruni, Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi, Abu Yaqub al-Sijistani, Nasir al-Din Tusi, Qutb al-Din Shirazi, Mir Damad, Mulla Sadra, Mir Fendereski and Hadi Sabzevari.
Music
Main articles: Music of Iran and Kurdish musicThe musical culture of Persia, while distinct, is closely related to other musical systems of the Middle East and Central Asia. It has also affinities to the music cultures of the Indian subcontinent, to a certain degree even to those of Africa, and, in the period after 1800 particularly, to that of Europe. Its history can be traced to some extent through these relationships. Like that of most of the world’s cultures, the music of Persia has depended on oral/aural transmission and learning.
Cinema
Main article: Cinema of IranIranian cinema has thrived in modern Iran, and many Iranian directors have garnered worldwide recognition for their work. Iranian movies have won over three hundred awards in the past twenty-five years including Oscars. One of the best-known directors is Abbas Kiarostami. The media of Iran is a mixture of private and state-owned, but books and movies must be approved by the Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance before being released to the public. The Internet has become enormously popular among the Iranian youth. Iran is now the world's fourth largest country of bloggers.
Art and architecture
Main articles: Achaemenid architecture, Iranian architecture, Iranian art, and Persian carpetIran is home to one of the richest artistic traditions in world history and encompasses many disciplines, including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and stonemasonry. Carpet-weaving is one of the most distinguished manifestations of Persian culture and art, and dates back to ancient Persia. Persians were among the first to use mathematics, geometry, and astronomy in architecture and also have extraordinary skills in making massive domes which can be seen frequently in the structure of bazaars and mosques. The main building types of classical Iranian architecture are the mosque and the palace. Besides being home to a large number of art houses and galleries, Iran also holds one of the largest and most valuable jewel collections in the world.
Iran ranks seventh among countries in the world with the most archeological architectural ruins and attractions from antiquity as recognized by UNESCO. Fifteen of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites are creations of Iranian architecture.
 Panoramic view of Naqsh-e Jahan Square
Panoramic view of Naqsh-e Jahan Square
Cuisine
Main article: Iranian cuisineThe cuisine of Iran is diverse, with each province featuring dishes, as well as culinary traditions and styles, distinct to their regions. The main Persian cuisines are combinations of rice with meat, chicken or fish and some onion, vegetables, nuts, and herbs. Herbs are frequently used along with fruits such as plums, pomegranates, quince, prunes, apricots, and raisins. Iranians also usually eat plain yogurt (Template:Lang-fa) with lunch and dinner; it is a staple of the diet in Iran. To achieve a balanced taste, characteristic flavourings such as saffron, dried limes, cinnamon, and parsley are mixed delicately and used in some special dishes. Onions and garlic are normally used in the preparation of the accompanying course, but are also served separately during meals, either in raw or pickled form. Iran is also famous for its caviar. Iranian food is not piquant.
Sports
Main article: Sport in Iran
With two thirds of Iran's population under the age of 25, many sports are practised in Iran, both traditional and modern. Iran is the birthplace of polo, and Varzesh-e Pahlavani. Freestyle wrestling has been traditionally regarded as Iran's national sport, however today, the most popular sport in Iran is football (soccer) with having won the Asian Cup on three occasions. Basketball is also very popular in Iran where the national team won two of the last three Asian Championships. In 1974, Iran became the first country in the Middle East to host the Asian Games. Iran is home to several unique skiing resorts, with the Tochal resort being the world's fifth-highest ski resort (3,730 m (12,238 ft) at its highest station), and located only fifteen minutes away from Tehran. Being a mountainous country, Iran is a venue for hiking, rock climbing, and mountain climbing.
Government and politics
Main articles: Constitution of Iran, Politics of Iran, Parliament of Iran, President of Iran, Supreme Leader of Iran, Judicial system of Iran, and Guardian CouncilThe political system of the Islamic Republic is based on the 1979 Constitution. Accordingly, it is the duty of the Islamic government to furnish all citizens with equal and appropriate opportunities, to provide them with work, and to satisfy their essential needs, so that the course of their progress may be assured.
The system comprises several intricately connected governing bodies. The Leader of the Revolution (commonly called "Supreme Leader" in the US and the UK) is responsible for delineation and supervision of the general policies of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The Supreme Leader is Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces, controls the military intelligence and security operations; and has sole power to declare war or peace.
The heads of the judiciary, state radio and television networks, the commanders of the police and military forces and six of the twelve members of the Guardian Council are appointed by the Supreme Leader. The Assembly of Experts elects and dismisses the Supreme Leader on the basis of qualifications and popular esteem. The Assembly of Experts is responsible for supervising the Supreme Leader in the performance of legal duties.
After the Supreme Leader, the Constitution defines the President of Iran as the highest state authority. The President is elected by universal suffrage for a term of four years and can only be re-elected for one term. Presidential candidates must be approved by the Guardian Council prior to running in order to ensure their allegiance to the ideals of the Islamic revolution.
The President is responsible for the implementation of the Constitution and for the exercise of executive powers, except for matters directly related to the Supreme Leader, who has the final say in all matters. The President appoints and supervises the Council of Ministers, coordinates government decisions, and selects government policies to be placed before the legislature. Eight Vice-Presidents serve under the President, as well as a cabinet of twenty two ministers, who must all be approved by the legislature. Unlike many other states, the executive branch in Iran does not control the armed forces. Although the President appoints the Ministers of Intelligence and Defense, it is customary for the President to obtain explicit approval from the Supreme Leader for these two ministers before presenting them to the legislature for a vote of confidence. Iran's current president, Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, was first elected in a run-off poll in the 2005 presidential elections and re-elected in the 2009 presidential elections.

As of 2012, the legislature of Iran (known in English as the Islamic Consultative Assembly) is a unicameral body. Before the Iranian Revolution, the legislature was bicameral, but the upper house was removed under the new constitution. The Majlis of Iran comprises 290 members elected for four-year terms. The Majlis drafts legislation, ratifies international treaties, and approves the national budget. All Majlis candidates and all legislation from the assembly must be approved by the Guardian Council.
The Guardian Council comprises twelve jurists including six appointed by the Supreme Leader. The others are elected by the Parliament from among the jurists nominated by the Head of the Judiciary. The Council interprets the constitution and may veto Parliament. If a law is deemed incompatible with the constitution or Sharia (Islamic law), it is referred back to Parliament for revision. In a controversial exercise of its authority, the Council has drawn upon a narrow interpretation of Iran's constitution to veto parliamentary candidates. The Expediency Council has the authority to mediate disputes between Parliament and the Guardian Council, and serves as an advisory body to the Supreme Leader, making it one of the most powerful governing bodies in the country.

The Supreme Leader appoints the head of Iran's judiciary, who in turn appoints the head of the Supreme Court and the chief public prosecutor. There are several types of courts including public courts that deal with civil and criminal cases, and "revolutionary courts" which deal with certain categories of offenses, including crimes against national security. The decisions of the revolutionary courts are final and cannot be appealed. The Special Clerical Court handles crimes allegedly committed by clerics, although it has also taken on cases involving lay people. The Special Clerical Court functions independently of the regular judicial framework and is accountable only to the Supreme Leader. The Court's rulings are final and cannot be appealed.
The Assembly of Experts, which meets for one week annually, comprises 86 "virtuous and learned" clerics elected by adult suffrage for eight-year terms. As with the presidential and parliamentary elections, the Guardian Council determines candidates' eligibility. The Assembly elects the Supreme Leader and has the constitutional authority to remove the Supreme Leader from power at any time. It has not challenged any of the Supreme Leader's decisions.
Local city councils are elected by public vote to four-year terms in all cities and villages of Iran. According to article seven of Iran's Constitution, these local councils together with the Parliament are "decision-making and administrative organs of the State". This section of the constitution was not implemented until 1999 when the first local council elections were held across the country. Councils have many different responsibilities including electing mayors, supervising the activities of municipalities; studying, planning, co-ordinating and implementing of social, cultural, educational, health, economic, and welfare requirements of their constituencies. In July 2012, Iranian Supereme leader Ali Khamanei told on a State TV broadcst that US-led sanctions have not succeeded in impeding the technological advancement of his nation.
Foreign relations and military
Main articles: Foreign relations of Iran, Armed Forces of the Islamic Republic of Iran, and Defense industry of Iran See also: Military history of Iran and List of military equipment manufactured in Iran
Iran's foreign relations are based on two strategic principles: eliminating outside influences in the region and pursuing extensive diplomatic contacts with developing and non-aligned countries. Iran maintains diplomatic relations with almost every member of the United Nations, except for Israel, which Iran does not recognize, and the United States since the Iranian Revolution. Since 2005, Iran's nuclear program has become the subject of contention with the Western world due to suspicions that Iran could divert the civilian nuclear technology to a weapons program. This has led the UN Security Council to impose sanctions against Iran on select companies linked to this program, thus furthering its economic isolation on the international scene. The US Director of National Intelligence said in February 2009 that Iran would not realistically be able to a get a nuclear weapon until 2013, if it chose to develop one.

The Islamic Republic of Iran has two types of armed forces: the regular forces Islamic Republic of Iran Army, Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, Islamic Republic of Iran Navy and the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC), totaling about 545,000 active troops. Iran also has around 350,000 Reserve Force totaling around 900,000 trained troops. Iran has a paramilitary, volunteer militia force within the IRGC, called the Basij, which includes about 90,000 full-time, active-duty uniformed members. Up to 11 million men and women are members of the Basij who could potentially be called up for service; GlobalSecurity.org estimates Iran could mobilize "up to one million men". This would be among the largest troop mobilizations in the world. In 2007, Iran's military spending represented 2.6% of the GDP or $102 per capita, the lowest figure of the Persian Gulf nations. Iran's military doctrine is based on deterrence.
Since the Iranian Revolution, to overcome foreign embargo, Iran has developed its own military industry, produced its own tanks, armored personnel carriers, guided missiles, submarines, military vessels, guided missile destroyer, radar systems, helicopters and fighter planes. In recent years, official announcements have highlighted the development of weapons such as the Hoot, Kowsar, Zelzal, Fateh-110, Shahab-3 and Sajjil missiles, and a variety of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The Fajr-3 (MIRV) is currently Iran's most advanced ballistic missile, it is a liquid fuel missile with an undisclosed range which was developed and produced domestically.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Iran See also: Iranian targeted subsidy plan, Central Bank of Iran, Tehran Stock Exchange, Industry of Iran, Transport in Iran, Communications in Iran, Construction industry of Iran, Privatization in Iran, Foreign Direct Investment in Iran, Tourism in Iran, Economic Cooperation Organization, and Next Eleven
The economy of Iran is the twenty-fifth largest in the world by GDP (nominal) and the eighteenth largest economy in the world by purchasing power parity (PPP). Iran's economy is a mixture of central planning, state ownership of oil and other large enterprises, village agriculture, and small-scale private trading and service ventures. Its economic infrastructure has been improving steadily over the past two decades but continues to be affected by inflation and unemployment. In the early 21st century the service sector contributed the largest percentage of the GDP, followed by industry (mining and manufacturing) and agriculture. In 2006, about 45% of the government's budget came from oil and natural gas revenues, and 31% came from taxes and fees.
Government spending contributed to an average annual inflation rate of 14% in the period 2000–2004. As at 2007, Iran had earned $70 billion in foreign exchange reserves mostly (80%) from crude oil exports. In 2009 GDP was $336 billion ($876 billion at PPP), or $12,900 at PPP per capita. In 2008, Iran's official annual growth rate was 6%. Because of these figures and the country’s diversified but small industrial base, the United Nations classifies Iran's economy as semi-developed (1998).
About 1,659,000 foreign tourists visited Iran in 2004; most came from Asian countries, including the republics of Central Asia, while a small share came from the countries of the European Union and North America. Iran currently ranks 89th in tourist income, but is rated among the "10 most touristic countries" in the world in terms of its history. Weak advertising, unstable regional conditions, a poor public image in some parts of the world, and absence of efficient planning schemes in the tourism sector have all hindered the growth of tourism.
The administration continues to follow the market reform plans of the previous one and indicated that it will diversify Iran's oil-reliant economy. Iran has also developed a biotechnology, nanotechnology, and pharmaceuticals industry. The strong oil market since 1996 helped ease financial pressures on Iran and allowed for Tehran's timely debt service payments.
Iranian budget deficits have been a chronic problem, mostly due to large-scale state subsidies, that include foodstuffs and especially gasoline, totaling more than $84 billion in 2008 for the energy sector alone. In 2010, the economic reform plan was approved by parliament to cut subsidies gradually and replace them with targeted social assistance. The objective is to move towards free market prices in a 5-year period and increase productivity and social justice.
Over the past 15 years, the authorities have placed an emphasis on the local production of domestic-consumption oriented goods such as home appliances, cars, agricultural products, pharmaceutical, etc. Today, Iran possesses a good manufacturing industry, despite restrictions imposed by foreign countries. However, nationalized industries such as the bonyads have often been managed badly, making them ineffective and uncompetitive with years. Currently, the government is trying to privatize these industries, and, despite successes, there are still several problems to be overcome, such as the lagging corruption in the public sector and lack of competitiveness. Iran ranks 69th out of 139 in Global Competitiveness Report.
Iran has leading manufacturing industries in the fields of car-manufacture and transportation, construction materials, home appliances, food and agricultural goods, armaments, pharmaceuticals, information technology, power and petrochemicals in the Middle East.
-
TSE has been one of the world's best performing stock exchanges in recent years.
-
 Iran's trade balance (2000–2007). For the first time, the value of Iran’s non-oil exports is expected to reach the value of imports by 2012.
Iran's trade balance (2000–2007). For the first time, the value of Iran’s non-oil exports is expected to reach the value of imports by 2012.
-
 Iranian provinces' contribution to GDP. Tehran host 45% of Iran's industries.
Iranian provinces' contribution to GDP. Tehran host 45% of Iran's industries.
-
 Map of Iran's exports
Map of Iran's exports
Energy
Main articles: Energy in Iran, Petroleum industry in Iran, and Nuclear program of Iran
Iran ranks second in the world in natural gas reserves and third in oil reserves. It is OPEC's 2nd largest oil exporter and is an energy superpower. In 2005, Iran spent US$4 billion on fuel imports, because of contraband and inefficient domestic use. Oil industry output averaged 4 million barrels per day (640,000 m/d) in 2005, compared with the peak of six million barrels per day reached in 1974. In the early years of the 2000s (decade), industry infrastructure was increasingly inefficient because of technological lags. Few exploratory wells were drilled in 2005.
In 2004, a large share of natural gas reserves in Iran were untapped. Iran is the third country in the world to have developed GTL technology. The addition of new hydroelectric stations and the streamlining of conventional coal and oil-fired stations increased installed capacity to 33,000 megawatts. Of that amount, about 75% was based on natural gas, 18% on oil, and 7% on hydroelectric power. In 2004, Iran opened its first wind-powered and geothermal plants, and the first solar thermal plant is to come online in 2009.
Demographic trends and intensified industrialization have caused electric power demand to grow by 8% per year. The government’s goal of 53,000 megawatts of installed capacity by 2010 is to be reached by bringing on line new gas-fired plants and by adding hydroelectric, and nuclear power generating capacity. Iran’s first nuclear power plant at Bushehr went online in 2011.
Science and technology
Main article: Science and technology in Iran See also: Education in Iran and Higher education in Iran
Ancient Iranians built Qanats and Yakhchal to provide and keep water. The first windmill appeared in Iran in the 9th century. Iranians contributed significantly to the current understanding of astronomy, natural science, medicine, mathematics, and philosophy. Khwarizmi is widely hailed as the father of algebra. Ethanol (alcohol) was first identified by Persian alchemists such as Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi. Throughout the Middle Ages, the philosophy and mathematics of the Ancient Greeks and Persians were furthered and preserved within Persia. The Academy of Gundishapur was a renowned centre of learning in the city of Gundeshapur during late antiquity and was the most important medical centre of the ancient world during the 6th and 7th centuries. During this period, Persia became a centre for the manufacture of scientific instruments, retaining its reputation for quality well into the 19th century.
Iran strives to revive the golden age of Persian science. The country has increased its publication output nearly tenfold from 1996 through 2004, and has been ranked first in terms of output growth rate followed by China. Despite the limitations in funds, facilities, and international collaborations, Iranian scientists remain highly productive in several experimental fields, such as pharmacology, pharmaceutical chemistry, organic chemistry, and polymer chemistry. Iranian scientists are also helping construct the Compact Muon Solenoid, a detector for CERN's Large Hadron Collider. In 2009, a SUSE Linux-based HPC system made by the Aerospace Research Institute of Iran (ARI) was launched with 32 cores and now runs 96 cores. Its performance was pegged at 192 GFLOPS. Sorena 2 Robot, which was designed by engineers at University of Tehran, was unveiled in 2010. the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has placed the name of Surena among the five prominent robots of the world after analyzing its performance.
In the biomedical sciences, Iran's Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics is a UNESCO chair in biology. In late 2006, Iranian scientists successfully cloned a sheep by somatic cell nuclear transfer, at the Rouyan research centre in Tehran. According to a study by David Morrison and Ali Khademhosseini (Harvard-MIT and Cambridge), stem cell research in Iran is amongst the top 10 in the world. Iran ranks 15th in the world in nanotechnologies.

The Iranian nuclear program was launched in the 1950s. Iran is the 7th country in production of uranium hexafluoride and controls the entire cycle for producing nuclear fuel. Iran's current facilities includes several research reactors, a uranium mine, an almost complete commercial nuclear reactor, and uranium processing facilities that include a uranium enrichment plant.Recently, head of the British top spy agency MI6 forecast that Iran will achieve nuclear weapon capability in two years.
The Iranian Space Agency launched its first reconnaissance satellite named Sina-1 in 2006, and a space rocket in 2007, which aimed at improving science and research for university students. Iran placed its domestically built satellite, Omid into orbit on the 30th anniversary of the Iranian Revolution, on 2 February 2009, through Safir rocket, becoming the ninth country in the world capable of both producing a satellite and sending it into space from a domestically made launcher.
Iranian scientists outside Iran have also made some major contributions to science. In 1960, Ali Javan co-invented the first gas laser and fuzzy set theory was introduced by Lotfi Zadeh. Iranian cardiologist, Tofy Mussivand invented and developed the first artificial cardiac pump, the precursor of the artificial heart. Furthering research and treatment of diabetes, HbA1c was discovered by Samuel Rahbar. Iranian physics is especially strong in string theory, with many papers being published in Iran. Iranian-American string theorist Cumrun Vafa proposed the Vafa-Witten theorem together with Edward Witten.
Demographics
Main articles: Demographics of Iran, Iranian peoples, Languages of Iran, Health care in Iran, Social class in Iran, Human rights in the Islamic Republic of Iran, and Iranian citizens abroadIran is a diverse country consisting of people of many religions and ethnic backgrounds cemented by the Persian culture. The majority of the population speaks the Persian language, which is also the official language of the country, as well as other Iranian languages or dialects. Turkic languages and dialects, most importantly Azeri language, are spoken in different areas in Iran. Additionally, Arabic is spoken in the southwestern parts of the country, although Arabs constitute a minority in these regions. The exact ethnic breakdown of Iran is unknown as there are no official numbers, however some organizations have made estimates. The World Factbook released the estimate: Persians (61%), Azerbaijanis (16%), Kurds (10%), Lurs (6%), Arabs (2%), Balochs (2%), Turkmens and Turkic tribes (2%), Laks, Qashqai, Armenians, Georgians, Persian Jews, Assyrians, Circassians, Tats, Mandaeans, Gypsies, Brahuis, Kazakhs and others (1%). However according to them Persian is spoken as first language by 53%, while Azeri and other Turkic dialects is spoken by 18%, Kurdish by 10%, Gilaki and Mazandarani by 7%, Luri by 6%, Balochi by 2%, Arabic by 2% and that some 2% have other languages as first language.
The Library of Congress estimates are as following: Persians (65%), Azerbaijanis (16%), Kurds (7%), Lurs (6%), Arabs (2%), Baluchi (2%), Turkmens (1%), Turkic tribal groups such as the Qashqai (1%), and non-Persian, non-Turkic groups such as Armenians, Assyrians, Pashtuns and Georgians (less than 1%). According to it Persian is spoken as a mother tongue by at least 65% of the population and as a second language by a large proportion of the remaining 35%.

Iran's population increased dramatically during the latter half of the 20th century, reaching about 75 million by 2009. According to the 1956 census the population of Iran was about 19 million. In recent years, however, Iran's birth rate has dropped significantly. Studies project that Iran's rate of population growth will continue to slow until it stabilizes above 105 million by 2050. More than two-thirds of the population is under the age of 30, and the literacy rate is 82%. Women today compose more than half of the incoming classes for universities around the country and increasingly continue to play pivotal roles in society.
Iran hosts one of the largest refugee populations in the world, with more than one million refugees, mostly from Afghanistan and Iraq. Since 2006, Iranian officials have been working with the UNHCR and Afghan officials for their repatriation. According to estimates, about five million Iranian citizens have emigrated to other countries, mostly since the Iranian Revolution in 1979.
According to the Iranian Constitution, the government is required to provide every citizen of the country with access to social security that covers retirement, unemployment, old age, disability, accidents, calamities, health and medical treatment and care services. This is covered by public revenues and income derived from public contributions. The World Health Organization in on health systems ranked Iran's performance on health level 58th, and its overall health system performance 93rd among the world's nations in 2000.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Iran| Iran religiosity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Islam | 98% | |||
| Other | 2% | |||
Religion in Iran is dominated by the Twelver Shia branch of Islam, which is the official state religion and to which about 90% to 95% of Iranians belong. About 4% to 8% of Iranians belong to the Sunni branch of Islam, mainly Kurds and Iran's Balochi Sunni. The remaining 2% are non-Muslim religious minorities, including Bahá'ís, Mandeans, Hindus, Yezidis, Yarsanis, Zoroastrians, Jews, and Christians.
The latter three minority religions are officially recognized and protected, and have reserved seats in the Majlis (Parliament). However the Bahá'í Faith, Iran's largest religious minority, is not officially recognized, and has been persecuted during its existence in Iran. Since the 1979 revolution the persecution of Bahá'ís has increased with executions, the denial of civil rights and liberties, and the denial of access to higher education and employment.
Hinduism in Iran has a history stretching back to the Middle Ages. Presently, Hindus are known to travel to Iran, but the vast majority consist of migrant workers from India. Out of Iran's population of 68,017,860, there are 68,017 recorded Hindus, making them 0.1% of the total population (The percentage of Hindu population of Iran was taken from the United States Department of State's International Religious Freedom Report 2004). Hinduism is the fastest growing religion in Iran, spurred mainly by interest in New Age gurus like Sri Sri Ravi Shankar and Mahesh Yogi.
Buddhism in Iran may date as far back as the 5th or 6th century BC, during the life of the historical Buddha Sakyamuni. A Pali legend suggests that the spread of Buddhism to Balkh was initiated by two merchant brothers from Bactria (present-day Afghanistan). From the 2nd century Parthians such as An Shigao, were active in spreading Buddhism in China. Many of the earliest translators of Buddhist literature into Chinese were from Parthia and other kingdoms linked with present-day Iran. Buddhists were persecuted during the Sasanid rule in the region, who made Zoroastrianism state religion in 224 AD, and thereafter burned many Buddhist sites. Surviving Buddhist sites were later raided in the 5th century by the White Huns. At the time of the Arab conquests in the mid-7th century, much of the eastern Iranian world was mainly Buddhist. Afghanistan is rich in Buddhist sites; others have been found in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and within Iran itself. The Arab conquests brought the final demise of Buddhism in Eastern Iran and Afghanistan, although in some sites like Bamyian and Hadda it survived until the 8th or 9th century. Mongol ruler Ghazan, who received Buddhist education in his youth, converted to Islam in 1310 AD and made it the state religion of the Ilkhanate. He also prohibited the practice of Buddhism, but allowed monks to go into exile into neighboring Buddhist regions. In recent years Buddhism has experienced an upsurge of interest among Iranians. Some of the poetry of Sohrab Sepehri shows Buddhist influence, and another major contemporary poet, Ahmad Shamlou, translated a book of Japanese haiku poetry into Persian.
See also
References
- Ethnologue report for languages of Iran
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Encyclopædia Britannica Encyclopedia Article: Media ancient region, Iran". Britannica.com. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ Andrew J. Newman, Safavid Iran: Rebirth of a Persian Empire, I. B. Tauris (30 March 2006)
- ^ "CIA Factbook – 2010". Cia.gov. Retrieved 1 March 2012.
- (Farsca:پورتال - مرکز آمار ایران) Portal - Statistical Center of Iran (Markaz-e Amar-e Iran) :Release of Preliminary Results 2011 National Population and Housing Census in Iran
- ^ "Islamic Republic of Iran". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- "Central Bank of Iran: Economic Trends 2008/2009". Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Human Development Report 2010" (PDF). United Nations. 2010. Retrieved 5 November 2010.
- "Definition for Iran – Oxford Dictionaries Online (World English)". Oxforddictionaries.com. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- ^ "Iran". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. 2000.
- ""CESWW" – Definition of Central Eurasia". Cesww.fas.harvard.edu. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- National Geographic.
- D. N. Mackenzie (15 December 1998). "Ērān, Ērānšahr". Encyclopaedia Iranica. iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- Iransaga, "Persia or Iran, a brief history".
- Iranian.ws, Iranian & Persian Art.
- The Committee Office, House of Commons. "Select Committee on Foreign Affairs, Eighth Report, Iran". Publications.parliament.uk. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Iran @ 2000 and Beyond lecture series, opening address, W. Herbert Hunt, 18 May 2000. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- "CIA – The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 5 February 2012.
- Lowell Barrington, Michael J. Bosia, Kathleen Bruhn, "Comparative Politics: Structures and Choices", Cengage Learning, 2009. Excerpt from page 34: "Like China, Iran is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations"
- "Ahmad Ashraf, "Iranian Identity" in Encyclopaedia Iranica". Iranicaonline.org. 15 December 2006. Retrieved 14 September 2011.
- B. Spuler, "The Disintegration of the Caliphate in the East", in the Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. IA: The Central islamic Lands from Pre-Islamic Times to the First World War, ed. by P.M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton, and Bernard Lewis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1970). pg 147: One of the effects of the renaissance of the Persian spirit evoked by this work was that the Ghaznavids were also Persianized and thereby became a Persian dynasty.
- Grousset, Rene, The Empire of the Steppes, (Rutgers University Press, 1991), 161,164; "..renewed the Seljuk attempt to found a great Turko-Persian empire in eastern Iran..", "It is to be noted that the Seljuks, those Turkomans who became sultans of Persia, did not Turkify Persia-no doubt because they did not wish to do so. On the contrary, it was they who voluntarily became Persians and who, in the manner of the great old Sassanid kings, strove to protect the Iranian populations from the plundering of Ghuzz bands and save Iranian culture from the Turkoman menace."
- Bosworth, C.E.; Hillenbrand, R.; Rogers, J.M.; Blois, F.C. de; Bosworth, C.E.; Darley-Doran, R.E., Saldjukids, Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2009. Brill Online: “Culturally, the constituting of the Seljuq Empire marked a further step in the dethronement of Arabic from being the sole lingua franca of educated and polite society in the Middle East. Coming as they did through a Transoxania which was still substantially Iranian and into Persia proper, the Seljuqs with no high-level Turkish cultural or literary heritage of their own – took over that of Persia, so that the Persian language became the administration and culture in their land of Persia and Anatolia. The Persian culture of the Rum Seljuqs was particularly splendid, and it was only gradually that Turkish emerged there as a parallel language in the field of government and adab; the Persian imprint in Ottoman civilization was to remain strong until the 19th century. "
- Ross E. Dunn, "The adventures of Ibn Battuta, a Muslim traveler of the fourteenth century", University of California Press, 1986. pg 144: "Indeed, under Ilkhanid sovereignty the high culutre of eastern and central Anatolia became more Persianized than ever before"
- Maria Subtelny, "Timurids in Transition", BRILL; illustrated edition (30 September 2007). pg 40: "Nevertheless, in the complex process of transition, members of the Timurid dynasty and their Turko-Mongolian supporters became acculturate by the surrounding Persinate millieu adopting Persian cultural models and tastes and acting as patrons of Persian culture, painting, architecture and music." pg 41: "The last members of the dynasty, notably Sultan-Abu Sa'id and Sultan-Husain, in fact came to be regarded as ideal Perso-Islamic rulers who develoted as much attention to agricultural development as they did to fostering Persianate court culture."
- R.M. Savory, Safavids, Encyclopaedia of Islam, 2nd edition
- ^ ""The Islamic World to 1600", The Applied History Research Group". The University of Calgary – Ucalgary.ca. 1998. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Iran Islamic Republic, Encyclopædia Britannica Retrieved 23 January 2008
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica 23 January 2008
- "قانون اساسی جمهوری اسلامی ایران" (in Persian). Retrieved 23 January 2008.
- V.Jayaram (9 January 2007). "The Concepts of Hinduism – Arya". Hinduwebsite.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- LSS.wis.edu, "Iranian Languages", Political, Social, Scientific, Literary & Artistic (Monthly) October 2000, No. 171, Dr. Suzan Kaviri, pp. 26–7retrieved 1 October 2007
- ""Iran – The Ancient Name of Iran", N.S. Gill". Ancienthistory.about.com. 4 September 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Bailey, Harold Walter (1987). "Arya". Encyclopaedia Iranica. Vol. 2. New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 681–683.
- MacKenzie, David Niel (1998). "Ērān, Ērānšahr". Encyclopedia Iranica. Vol. 8. Costa Mesa: Mazda.
- "Renaming Persia". persiansarenotarabs.com. 2007. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- Biglari, Fereidoun. "Ganj Par: The first evidence for Lower Paleolithic occupation in the Southern Caspian Basin, Iran". Antiquity. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Pbase.com, retrieved 27 March 2008
- J. D. Vigne, J. Peters and D. Helmer, First Steps of Animal Domestication, Proceedings of the 9th Conference of the International Council of Archaeozoology, Durham, August 2002, ISBN 1-84217-121-6
- Excavations at Chogha Bonut: The earliest village in Susiana, Irant, by Abbas Alizadeh - The Oriental Institute and the Department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations The University of Chicago
- Ancient Near Eastern art by Dominique Collon
- K. Kris Hirst. "Chogha Mish (Iran)".
- ^ Xinhua, "New evidence: modern civilization began in Iran", 10 Aug 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2007. Cite error: The named reference "xinhuaciv" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Iran Daily, "Panorama", 3 March 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2007. Archived 2008-01-24 at the Wayback Machine
- Iranian.ws, "Archaeologists: Modern civilization began in Iran based on new evidence", 12 August 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- University of Chicago. Retrieved 2006-04-29.
- "Ancient Scripts:Elamite". 1996. Retrieved 28 April 2011.
- Cory Panshin. "The Palaeolithic Indo-Europeans". Panshin.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "The Persians". Retrieved 20 August 2006.
- Vohuman.org, "Historical perspective on Zoroastrianism", Reproduced from Âtaš-è Dorün – The Fire Within, Jamshid Soroush Soroushian Memorial Volume II, 1st Books Library, Bloomington, IN, 2003. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- Persians: Masters of Empire, 1995, ISBN 0-8094-9104-4, p.142–143, Time-life Books
- Cotterell, Arthur. From Aristotle to Zoroaster: An A-to-Z Companion to the Classical World. 1998. p.272, Free Press
- Garthwaite, Gene R., The Persians, p. 2, ISBN 1-4051-5680-5, Wiley-Blackwell (2006)
- Lorentz, John H. Historical Dictionary of Iran. Asian Historical Dictionaries; No.16. 1995. ISBN 978-0-8108-2994-7, p.189
- Arthur Cotterell, From Aristotle to Zoroaster: An A-to-Z Companion to the Classical World. 1998. ISBN 0-684-85596-8, p.344–345, Free Press
- Persians: Masters of Empire, 1995, ISBN 0-8094-9104-4, p.134, Time-life Books
- Persians: Masters of Empire, 1995, ISBN 0-8094-9104-4, p.138, Time-life Books
- "Even the architecture of the Christian church, with its hallowed chancel seems inspired by the designs of Mithraic temples". Abbas Milani. Lost Wisdom. 2004. Mage Publishers. p.13. ISBN 0-934211-90-6
- ^ Encyclopaedia Iranica, "Iran in the Islamic Period (651–1980s)", E. Yarshater. Iranicaonline.org
- "Conversion: Of Iranians to Islam." by Elton L. Daniel in Encyclopaedia Iranica. Iranicaonline.org
- آثار الباقیه، ابوریحان بیرونی، انتشارات امیرکبیر، 1377، ص 7۵ Biruni states:
When Qutaibah bin Moslem under the command of Al-Ḥajjāj ibn Yūsuf was sent to Khwarazmia with a military expedition and conquered it for the second time, he swiftly killed whoever wrote in the Khwarazmian native language and knew of the Khwarazmian heritage, history, and culture. He then killed all their Zoroastrian priests and burned and wasted their books, until gradually only the illiterate remained, who knew nothing of writing, and hence the regions history was mostly forgotten.
- "Ṣaffārid Dynasty", Encyclopædia Britannica, 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 15 March 2009
- "Sāmānid Dynasty", Encyclopædia Britannica, 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 15 March 2009
- "Class System", in Encyclopaedia Iranica.
- Joel Carmichael, "The Shaping of the Arabs: A Study in Ethnic Identity", Published by Macmillan, 1967. pg 235. Excerpt: "Abu Muslim, the Persian general and popular leader".
- Richard Nelson Frye, "Iran", Edition: 2, revised Published by G. Allen & Unwin, 1960. p. 47: "A Persian Muslim called Abu Muslim.
- Bosworth C. E., Cambridge History of Iran, vol. 4, p. 90.
- C.E. Bosworth, "Ajam" in Encyclopaedia Iranica: But by the 3rd/9th century, the non-Arabs, and above all the Persians, were asserting their social and cultural equality (taswīa) with the Arabs, if not their superiority (tafżīl) over them (a process seen in the literary movement of the Šoʿūbīya). In any case, there was always in some minds a current of admiration for the ʿAǰam as heirs of an ancient, cultured tradition of life.
- The memoirs of Edward Teller, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory "Science and Technology Review". July/August 1998 p. 18. Link: LLNL.org
- Mackey, S.. The Iranians: Persia, Islam, and the soul of a nation. 1996. ISBN 0-525-94005-7. p. 69.
- R. Ward, Steven (2009). Immortal: a military history of Iran and its armed forces. Georgetown University Press. p. 39. ISBN 1-58901-258-5.
- Mackey, S.. The Iranians: Persia, Islam, and the soul of a nation. 1996. ISBN 0-525-94005-7. p. 70.
- "Old World Contacts/Armies/Tamerlane". Ucalgary.ca. 6 July 1999. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Mackey, S. The Iranians: Persia, Islam, and the soul of a nation. 1996. ISBN 0-525-94005-7. p. 69.
- Isfahan: Iran's Hidden Jewel. Smithsonian Magazine.
- Bertold Spuler. The Muslim World. Vol. I The Age of the Caliphs. Leiden. E.J. Brill. 1960 ISBN 0-685-23328-6 p. 29.
- Q&A by Kathryn Jean Lopez (14 September 2005). "Q&A with John Kelly on The Great Mortality on National Review Online". Nationalreview.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Bernard Lewis, "Iran in History", TAU.ac.il excerpt: "Iran was indeed Islamized, but it was not Arabized. Persians remained Persians. And after an interval of silence, Iran reemerged as a separate, different and distinctive element within Islam, eventually adding a new element even to Islam itself. Culturally, politically, and most remarkable of all even religiously, the Iranian contribution to this new Islamic civilization is of immense importance. The work of Iranians can be seen in every field of cultural endeavor, including Arabic poetry, to which poets of Iranian origin composing their poems in Arabic made a very significant contribution. In a sense, Iranian Islam is a second advent of Islam itself, a new Islam sometimes referred to as Islam-i Ajam. It was this Persian Islam, rather than the original Arab Islam, that was brought to new areas and new peoples: to the Turks, first in Central Asia and then in the Middle East in the country which came to be called Turkey, and of course to India. The Ottoman Turks brought a form of Iranian civilization to the walls of Vienna."
- Grunebaum, G. V. von. "The sources of Islamic civilization." Islamic Society and Civilization. Eds. P. M. Holt, Ann K. S. Lambton and Bernard Lewis. Cambridge University Press, 1970. Cambridge Histories Online. Cambridge University Press. p. 501: "In some ways, the Persian components of Islamic civilization are more difficult to separate out than the Hellenic precisely because they are more fully integrated and have become effective on so many levels. In fact, the Muslim world itself, without necessarily putting this judgment in analytical terms, has long since come to accept Islamic civilization as 'Perso-Islamic synthesis'.
- Seyyed Hossein Nasr, Mehdi Amin Razavi,"The Islamic intellectual tradition in Persia", RoutledgeCurzon; annotated edition (4 July 1996). p. 157: "The appearance of the school of Ishraq meant both the guarantee of the propagation of Islamic philosophy in a form that was clearer to the heart of Islam than the earlier schools of thoughts, and also the creation of a school that was particularly close to the ethos of Persian Islam and spread wherever Persian Islamic culture was dominant.
- The Muqaddimah By Ibn Khaldūn translated by Franz Rosenthal, N. J. Dawood, Published by Princeton University Press, 1969.
- Professor. Gilbert Lazard: The language known as New Persian, which usually is called at this period (early Islamic times) by the name of Dari or Parsi-Dari, can be classified linguistically as a continuation of Middle Persian, the official religious and literary language of Sassanian Iran, itself a continuation of Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenids. Unlike the other languages and dialects, ancient and modern, of the Iranian group such as Avestan, Parthian, Soghdian, Kurdish, Pashto, etc., Old Middle and New Persian represent one and the same language at three states of its history. It had its origin in Fars (the true Persian country from the historical point of view) and is differentiated by dialectical features, still easily recognizable from the dialect prevailing in north-western and eastern Iran in (Lazard, Gilbert 1975, "The Rise of the New Persian Language" in Frye, R. N., The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. 4, pp. 595–632, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Lazard, Gilbert, "Pahlavi, Pârsi, dari: Les langues d'Iran d'apès Ibn al-Muqaffa" in R.N. Frye, "Iran and Islam. In Memory of the late Vladimir Minorsky", Edinburgh University Press, 1971.
- Ann K. S. Lambton, "Persian grammar ", Cambridge University Press, Cambridge University Press 1953. Excerpt: "The Arabic words incorporated into the Persian language have become Persianized".
- M. G. Carter, "Sibawayhi", Published by I.B.Tauris, 2004. p. 9: "That Sibawayhi was by origin a Persian who came or was taken to Basra seems to be beyond challenge."
- ^ William Bayne Fisher, Richard Nelson Frye, John Andrew Boyle (1975). The Cambridge History of Iran. Vol. 4. Cambridge University Press. pp. 397–398. ISBN 0-521-20093-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ William Bayne Fisher, et al., The Cambridge History of Iran 4 Published by Cambridge University Press, 1975, ISBN 0-521-20093-8, p. 396.
-
- Robert Palter, Solomon Gandz, "Toward Modern Science: Studies in ancient and medieval science", Published by Noonday Press, 1961, p. 180: "The so called golden age of Islamic science owed its importance to largely to the Persian contribution."
- Ehsan Yarshater, "The Persian Presence in the Islamic World" in Richard G. Hovannisian, Georges Sabagh, "The Persian Presence in the Islamic World", Published by Cambridge University Press, 1997. pp. 6–7: "The Golden age of Islam, as the early Abbassid period has been labeled, was distinguished by intellectual advances, literary innovations, and cultural exuberance attributable, in no small measure, to the vital participation of Persian men of letters, philosophers, theologians, grammarians, mathematicians, musicians, astronomers, geographers, and physicians"
- Bernard Lewis, "Iran in History", excerpt: "Culturally, politically, and most remarkable of all even religiously, the Iranian contribution to this new Islamic civilization is of immense importance. The work of Iranians can be seen in every field of cultural endeavor, including Arabic poetry, to which poets of Iranian origin composing their poems in Arabic made a very significant contribution." TAU.ac.il
- The following references give comprehensive analysis and clarification of the terms "ersian influence" and "perso-islamic" and the relation to Sassanids and the impact on Islamic cultures:
- Marilyn Robinson Waldman, Toward a Theory of Historical Narrative: A Case Study in Perso-Islamicate Historiography, Published by Ohio State University Press, 1980, ISBN 0-8142-0297-7, p. 30.
- Richard M. Eaton, The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier, 1204–1760, Published by University of California Press, 1996, ISBN 0-520-20507-3, p. 28.
- Richard G. Hovannisian (ed.), The Persian Presence in the Islamic World, Published by Cambridge University Press, 1997, ISBN 0-521-59185-6. p. 78.
- P. M. Holt, et al. The Cambridge History of Islam: Volume 2B, Published by Cambridge University Press, 1977, ISBN 0-521-29138-0. p. 501.
- William Bayne Fisher, et al., The Cambridge History of Iran 4 Published by Cambridge University Press, 1975, ISBN 0-521-20093-8, p. 397.
- Reynold Alleyne Nicholson. A Literary History of the Arabs, Published by Routledge, 1995, ISBN 0-7007-0336-5, p. 290.
- Kühnel E., in Zeitschrift der deutschen morgenländischen Gesell, Vol. CVI (1956).
- "The Great Persian Famine of 1870–1871". Links.jstor.org. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- Stephen Kinzer: All the Shah's Men. An American Coup and the Roots of Middle East Terror, John Wiley and Sons, 2003, p.x
- "Islamic Revolution of 1979". Iranchamber.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Islamic Revolution of Iran. Encarta. Archived from the original on 31 October 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- Fereydoun Hoveyda, The Shah and the Ayatollah: Iranian Mythology and Islamic Revolution ISBN 0-275-97858-3, Praeger Publishers
- "The Iranian Revolution". Fsmitha.com. 22 March 1963. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Jahangir Amuzegar, The Dynamics of the Iranian Revolution, (1991), p.4, 9–12 ISBN 0-7914-0731-4
- Arjomand, Turban (1988), p. 191.
- Cheryl Benard, Zalmay Khalilzad, "The Government of God" ISBN 0-231-05376-2, Columbia University Press (1984), p. 18.
- "American Experience, Jimmy Carter, "444 Days: America Reacts"". Pbs.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Guests of the Ayatollah: The Iran Hostage Crisis: The First Battle in America's War with Militant Islam, Mark Bowden, p. 127 ISBN 0-8021-4303-2, Grove Press
- "Child-Soldier Treaty Has Wide Support". The New York Times. 19 December 1988.
- Centre for Documents of The Imposed War, Tehran. (مرکز مطالعات و تحقیقات جنگ)
- "News". FAS. Retrieved 23 January 2008.
- Federation of American Scientists 23 January 2008
- NTI Chemical profile of Iran 23 January 2008 (Archive)
- Dan De Luce in Tehran (4 May 2004). "The Guardian, Tuesday 4 May 2004, Khatami blames clerics for failure". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- "Iran hardliner becomes president". BBC. 3 August 2005. Retrieved 6 December 2006.
- "Iran To Hold Presidential Election In June 2009" (Reuters). Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 7 September 2008. Retrieved 2 December 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|curly=ignored (help) - "Ahmadinejad Wins Landslide". Iran Daily. 13 June 2009. Archived from the original on 14 June 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2009.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher=|publisher=(help) - "نتایج نهایی دهمین دورهٔ انتخابات ریاست جمهوری" (in Persian). Ministry of Interior of Iran. 13 June 2009. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- Press TV Leader addresses nation on election results, 13 June 2009
- BBC report http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FjQLC4w1XMY
- Tait, Robert; Black, Ian; Tran, Mark (17 June 2009). "Iran protests: Fifth day of unrest as regime cracks down on critics". The Guardian. London.
- "World Statistics by Area". Mongabay.com. 7 December 2008. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ CIA World Factbook. "Iran". Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- "Iran-Location, size, and extent". Nationsencyclopedia.com. 7 February 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "CIA – The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "SurfWax: News, Reviews and Articles On Hindu Kush". News.surfwax.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Nature & Mountains of Iran. Retrieved 25 February 2008. Archived 2007-11-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Iran- Current Information". My.simmons.edu. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Guggisberg, C.A.W. (1961). Simba: The Life of the Lion. Howard Timmins, Cape Town.
- Payvand. "Iran: Focus on reverse migration". Retrieved 17 April 2006.
- "Islamic Azad University". Retrieved 28 January 2008. Archived 2007-11-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Iranian National Portal of Statistics. Retrieved 27 February 2008. Archived 2007-11-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Religious Tourism Potentials Rich. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- "Mashhad, Iran". Sacredsites.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Iran – Statistical Centre. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- J. B. Bury, History of the Later Roman Empire: From the Death of Theodosius I to the Death of Justinian Volume 1, p.109 ISBN 0-486-20398-0, Dover Publications
- "Sassanids in Africa". Transoxiana.com.ar. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iransaga: The art of Sassanids". Artarena.force9.co.uk. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran – A country study". Parstimes.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "History of Islamic Science 5". Levity.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Afary, Janet (2006). "Iran". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 29 October 2007.
- "گزارش عزاداری ، ارامنه و زرتشتیان ایران". Tebyan.net. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "The Zarathushtrian Assembly". Zoroastrian.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Leaders of regional countries to mark Nowruz". PressTV. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Norouz Persian New Year". British Museum. 25 March 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- "General Assembly Fifty-fifth session 94th plenary meeting Friday, 9 March 2001, 10 a.m. New York" (PDF). United Nations General Assembly. 9 March 2001. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- "Nowrooz, a Persian New Year Celebration, Erupts in Iran – Yahoo!News". News.yahoo.com. 16 March 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- "US mulls Persian New Year outreach". Washington Times. 19 March 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Katzner, Kenneth (2002). The Languages of the World. Routledge. p. 163. ISBN 0-415-25004-8.
- Von David Levinson, Karen Christensen, Encyclopedia of Modern Asia, Charles Scribner's Sons. 2002 pg 48
- C. A. (Charles Ambrose) Storey and Franço de Blois (2004), “Persian Literature – A Biobibliographical Survey: Volume V Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period.”, RoutledgeCurzon; 2nd revised edition (21 June 2004). ISBN 0-947593-47-0. Pg 363: “Nizami Ganja’i, whose personal name was Ilyas, is the most celebrated native poet of the Persians after Firdausi. His nisbah designates him as a native of Ganja (Elizavetpol, Kirovabad) in Azerbaijan, then still a country with an Iranian population
- Philip G. Kreyenbroek: "Morals and Society in Zoroastrian Philosophy" in "Persian Philosophy". Companion Encyclopedia of Asian Philosophy: Brian Carr and Indira Mahalingam. Routledge, 2009.
- Mary Boyce: "The Origins of Zoroastrian Philosophy" in "Persian Philosophy". Companion Encyclopedia of Asian Philosophy: Brian Carr and Indira Mahalingam. Routledge, 2009.
- Bruno Nettl, "Iran: Music" in Encyclopaedia Iranica. Accessed November 2010 at iranicaonline.org
- Alavi, N (20 December 2004). "Freedom in Farsi blogs". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 23 January 2008.
- "Virtual Conference". American.edu. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Iran-daily.com
- Harrison, Frances (22 September 2005). "Polo comes back home to Iran". BBC News. Retrieved 23 January 2008.
- Alipour, Sam (21 April 2012). "Mission Improbable". ESPN. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- Wolfensberger, Marc (13 April 2006). "Iran's Sun, Snow Lure European Skiers to Nuclear Pariah's `Fun'". Bloomberg. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Rock Climbing Routes, Gear, Photos, Videos & Articles". Rockclimbing.com. 27 October 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran Mountain Zone (IMZ)". Mountainzone.ir. 11 June 1966. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Mountaineering in Iran". Abc-of-mountaineering.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- http://abclocal.go.com/kgo/story?section=News&id=2062458
- University of Bern; Iranian Constitution summary. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ^ Leader.ir, Retrieved 13 May 2008
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. "Iran – The Constitution". Retrieved 14 April 2006.
- ^ "Iran The Presidency". Photius.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Chibli Mallat, The Renewal of Islamic Law: Muhammad Baqer As-Sadr, Najaf and the Shi'i international, ISBN 0-521-53122-5, Cambridge University Press
- "Iran – The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "The Structure of Power in Iran". Iranchamber.com. 24 June 2005. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ "IFES Election Guide". Electionguide.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran – The Council of Guardians". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran The Council of Guardians". Photius.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Manou & Associates Inc. "Iranian Government Constitution, English Text". Iranonline.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Expediency council". BBC News. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- ^ "Iran Chamber Society: The Structure of Power in Iran". Iranchamber.com. 24 June 2005. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran immune to sanctions: Khamenei". 12 July 2012.
- "Key Events in Iran Since 1921". Pbs.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Charbonneau, Louis (26 October 2009). "RPT-EXCLUSIVE-Iran would need 18 months for atom bomb-diplomats". Reuters. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- IISS Military Balance 2006, Routledge for the IISS, London, 2006, p.187
- John Pike. "Niruyeh Moghavemat Basij Mobilisation Resistance Force". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran's defense spending 'a fraction of Persian Gulf neighbors'". Payvand.com. 22 November 2006. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran's doctrine based on deterrence". IRNA. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Iran Launches Production of Stealth Sub". Fox News. 10 May 2005. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- PressTv: Advanced attack chopper joins Iran fleet Retrieved 24 May 2009
- "Iran launches advanced Jamaran destroyer". Presstv.com. 19 February 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- "Iran tests new long-range missile". BBC. 12 November 2008. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
- "Iran to form carpet export consortium". PressTV. 9 November 2008. Retrieved 1 March 2009.
- "Iran economy". Traveldocs.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "World Bank: Iran's Economic Indices Improving". Iran Daily. 8 July 2007. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2007.
- "IRNA: Crude price pegged at dlrs 39.6 a barrel under next year's budget". Payvand.com. 22 November 2006. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Iran Daily Forex Reserves Put at $70b Retrieved 24 February 2008
- Surrounded:seeing the world from Iran's point of view Military review July–August 2007 Houman A. Sadri p.21
- "Iran-daily.com". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- "Iranian Hospitality Industry". PressTV. 6 December 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- List of Iranian Nanotechnology companies. Retrieved 23 January 2008. Archived 2007-10-13 at the Wayback Machine
- "Ahmadinejad's Achilles Heel: The Iranian Economy". Payvand.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Energy subsidies reach $84b". Iran-Daily. 8 January 2007. Archived from the original on 6 May 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
- "Iran – Country Brief". Go.worldbank.org. Retrieved 30 January 2010.
- "World Economic Forum: Iran ranks 69th out of 139 in global competitiveness". Payvand.com. 13 September 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- UK Trade & Investment. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- "Iran blocks share price gains". BBC News. 6 August 2003. Retrieved 15 February 2010.
- "Tehran Exchange Trades Futures to Attract Investors". BusinessWeek. 2009. Retrieved 29 July 2010.
- http://www.mehrnews.com/en/newsdetail.aspx?NewsID=1497809
- CSIS: The US, Israel, the Arab States and a Nuclear Iran
- "CIA.gov". CIA.gov. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "Iran – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". Eia.doe.gov. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "American Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-223X Issue 45 (2012), pp. 76–84" (PDF). Retrieved 7 February 2012.
- The EU should be playing Iran and Russia off against each other, by Julian Evans, Eurasian Home, 8 November 2006
- Kim Murphy – Los Angeles Times (7 January 2007). "U.S. targets Iran's vulnerable oil". Heraldextra.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- . "Iran, Besieged by Gasoline Sanctions, Develops GTL to Extract Gasoline from Natural Gas". Oilprice.com. Retrieved 7 February 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - "Iran" (PDF). Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "No Operation". Presstv.com. Retrieved 14 September 2011.
- Ahmad Y Hassan, Donald Routledge Hill (1986). Islamic Technology: An illustrated history, p. 54. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-42239-6.
- The Cambridge History of Iran Vol 4, p396. ISBN 0-521-20093-8
- Expert: Dr.VSR.Subramaniam (18 October 2006). "Economics: economic, medical uses of alcohol, uses of alcohol". Experts.about.com. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Patrick Thibodeau (22 June 2009). "AMD Chips Used in Iranian HPC for Rocket Research". Computerworld.com. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "No. 3817 | Front page | Page 1". Irandaily. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- "Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics". Ibb.ut.ac.ir. 2 February 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Middle East Online ميدل ايست اونلاين The first successfully cloned animal in Iran retrieved 7 August 2008
- "Iranian Studies Group at MIT" (PDF). Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- "INIC – News – 73% of Tehran's Students Acquainted with Nanotechnology". En.nano.ir. 18 January 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- "Iran Ranks 15th In Nanotech Articles". Bernama. 9 November 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- Iran daily: Iranian Technology From Foreign Perspective
- "Iran, 7th in UF6 production – IAEO official". Payvand.com. 22 November 2006. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- "UK top spy: Iran two years away from going nuclear". 14 July 2012.
- Rocket launch. Retrieved 23 January 2008. Archived 2007-08-30 at the Wayback Machine
- http://newsmax.com/archives/articles/2007/2/26/90124.shtml
- "Iran scientific savvy 'amazes world'". Presstv.ir. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "West 'shocked by Iran spaceshot'". Presstv.ir. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- http://www-bisc.cs.berkeley.edu/Zadeh-1965.pdf
- "CERN Press Release – CERN signs draft Memorandum of Understanding with Iran". Press.web.cern.ch. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- "Encyclopaedia Iranica. R. N. Frye. Peoples of Iran". Iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 14 September 2011.
- "Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- Library of Congress, Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. "Ethnic Groups and Languages of Iran" (PDF). Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- Asia-Pacific Population Journal, United Nations. "A New Direction in Population Policy and Family Planning in the Islamic Republic of Iran". Retrieved 14 April 2006.
- "Iran – population". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- Census Bureau, Government of the U.S.A. "IDB Summary Demographic Data for Iran". Retrieved 14 April 2006.
- Iran News, Payvand.com. "Iran's population growth rate falls to 1.5 percent: UNFP". Retrieved 18 October 2006.
- "Afghanistan-Iran: Iran says it will deport over one million Afghans
- United Nations, UNHCR. "Tripartite meeting on returns to Afghanistan". Retrieved 14 April 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check|first=value (help) - "Iran to start bank for expat-investors". Presstv.com. 18 April 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- "Migration Information Institute: Characteristics of the Iranian Diaspora". Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- WHO, World Health Organisation. "The World Health Report 2000" (PDF). Retrieved 12 October 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check|first=value (help) - Walter Ralston Martin, Ravi K. Zacharias, The Kingdom of the Cults (2003), p.421; Excerpt: Ninety-five percent of Iran's Muslims are Shi'ites.
- Bhabani Sen Gupta, The Persian Gulf and South Asia:: prospects and problems of inter-regional cooperation. p.158; Excerpt: Shias constitute seventy-five percent of the population of the Gulf. Of this, ninety-five percent of Iranians and sixty of Iraqis are Shias.
- Daily report, Issues 64–73 -'United States. Foreign Broadcast Information Service- Page 50, Excerpt: Ninety -five percent of Iranians are Shiite Moslems.
- International Federation for Human Rights (1 August 2003). "Discrimination against religious minorities in Iran" (PDF). fdih.org. p. 6. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- International Federation for Human Rights (1 August 2003). "Discrimination against religious minorities in Iran" (PDF). fdih.org. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- Iran Human Rights Documentation Center (2007). "A Faith Denied: The Persecution of the Bahá'ís of Iran" (PDF). Iran Human Rights Documentation Center. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- http://www.hindu.com/mag/2006/06/11/stories/2006061100030100.htm
- http://www.iranian.com/History/2004/December/Buddhism/index.html
- ^ http://books.google.no/books?id=y7IHmyKcPtYC&pg=PA956&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.no/books?id=Js8qHFVw2gEC&pg=PA86&lpg=PA86&q=&hl=no#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.no/books?id=ZfWXIfbynwYC&pg=PA10&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
External links
- The e-office of the Supreme Leader of Iran
- The President of Iran
- Iran.ir
- "Iran". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Iran web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Iran
Wikimedia Atlas of Iran- Template:Wikitravel
- Key Development Forecasts for Iran from International Futures
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link GA
Categories:- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Use dmy dates from May 2012
- Iran
- Developing 8 Countries member states
- G15 nations
- Iranian Plateau
- Islamic republics
- Islamic states
- Member states of OPEC
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the United Nations
- Middle Eastern countries
- Near Eastern countries
- Persian Gulf countries
- Persian-speaking countries and territories
- Western Asia
- Western Asian countries
- South Asian countries



