| Revision as of 09:47, 30 October 2013 editColtsfan (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users14,039 edits Undid revision 579435931 by HistorNE (talk)← Previous edit | Revision as of 10:05, 30 October 2013 edit undoHistorNE (talk | contribs)831 edits pov pusherNext edit → | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| | strength1=''At the onset of the war'': 110,000–150,000 soldiers,<br />1,000 tanks,<br />1,000 armoured vehicles,<br />300 artillery pieces,<br />320 aircraft,<br/>750 helicopters<br />''After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982'': 350,000 soldiers,<br />700 tanks,<br />2,700 armoured vehicles,<br />400 artillery pieces,<br />350 aircraft,<br />700 helicopters<br />''At the end of the war'': 900,000 soldiers,<br />2,500,000 militia,<br />400 tanks,<br />800 armoured vehicles,<br />600 artillery pieces,<br />60–80 aircraft,<br/>70–90 helicopters | | strength1=''At the onset of the war'': 110,000–150,000 soldiers,<br />1,000 tanks,<br />1,000 armoured vehicles,<br />300 artillery pieces,<br />320 aircraft,<br/>750 helicopters<br />''After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982'': 350,000 soldiers,<br />700 tanks,<br />2,700 armoured vehicles,<br />400 artillery pieces,<br />350 aircraft,<br />700 helicopters<br />''At the end of the war'': 900,000 soldiers,<br />2,500,000 militia,<br />400 tanks,<br />800 armoured vehicles,<br />600 artillery pieces,<br />60–80 aircraft,<br/>70–90 helicopters | ||
| | strength2=''At the onset of the war'': 350,000 soldiers,<br />6,500 tanks,<br />4,000 armoured vehicles,<br />800 artillery pieces,<br />600 aircraft,<br />350 helicopters<br />''After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982'': 175,000 soldiers,<br />1,200 tanks,<br />2,300 armoured vehicles,<br />400 artillery pieces,<br />450 aircraft,<br />180 helicopters<br />''At the end of the war'': 1,500,000 soldiers{{Citation needed|date=June 2013}},<br />5,500–6,700 tanks,<br />8,500–10,000 armoured vehicles,<br />6,000–12,000 artillery pieces,<br />1,500 aircraft,<br/>1,000 helicopters | | strength2=''At the onset of the war'': 350,000 soldiers,<br />6,500 tanks,<br />4,000 armoured vehicles,<br />800 artillery pieces,<br />600 aircraft,<br />350 helicopters<br />''After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982'': 175,000 soldiers,<br />1,200 tanks,<br />2,300 armoured vehicles,<br />400 artillery pieces,<br />450 aircraft,<br />180 helicopters<br />''At the end of the war'': 1,500,000 soldiers{{Citation needed|date=June 2013}},<br />5,500–6,700 tanks,<br />8,500–10,000 armoured vehicles,<br />6,000–12,000 artillery pieces,<br />1,500 aircraft,<br/>1,000 helicopters | ||
| | casualties1= 183,931 soldiers ]/] ( |
| casualties1= 183,931 soldiers ]/] (official number)<ref name="hiro205">{{cite book|last=Hiro|first=Dilip|authorlink=Dilip Hiro|title=The Longest War: The Iran-Iraq Military Conflict|publisher=Routledge|location=New York|year=1991|page=205|isbn=9780415904063|oclc=22347651}}</ref><br>262,000 (Western estimate)<ref name="hiro205"/><br>800,000 (Iraqi claim)<ref name="hiro205"/> | ||
| Economic loss of more than US$500 billion<ref name=iranchamber-iraniraqwar />{{rp|3|date=November 2012}} | Economic loss of more than US$500 billion<ref name=iranchamber-iraniraqwar />{{rp|3|date=November 2012}} | ||
| | casualties2= 105, |
| casualties2= 105,000–180,000 soldiers and militia killed<ref name="hiro205"/><ref>{{cite book|last1=Potter|first1=Lawrence G.|last2=Sick|first2=Gary|title=Iran, Iraq and the Legacies of War|publisher=Palgrave Macmillan|location=Basingstoke|year=2006|page=8|isbn=9781403976093|oclc=70230312}}</ref> | ||
| Economic loss of more than $500 billion<ref name=iranchamber-iraniraqwar />{{rp|3|date=November 2012}} | Economic loss of more than $500 billion<ref name=iranchamber-iraniraqwar />{{rp|3|date=November 2012}} | ||
| | notes=¹ The exact number of Iraqi Shia that fought alongside Iran is unknown. The Iraqi political parties ] and ] supported Iran during the war. Iran would sometimes organise divisions of Iraqi POWs to fight against Iraq. | | notes=¹ The exact number of Iraqi Shia that fought alongside Iran is unknown. The Iraqi political parties ] and ] supported Iran during the war. Iran would sometimes organise divisions of Iraqi POWs to fight against Iraq. | ||
| | casualties3= 100,000+ civilians killed on both sides<ref name=hawaii.edu-D>{{cite web|url=http://www.hawaii.edu/powerkills/SOD.TAB15.1D.GIF|title=Lesser Murdering States, Quasi-States, and Groups: Estimates, Sources, and Calculations|work=Power Kills|publisher=University of Hawai'i|author=Rumel, Rudolph}}</ref><br />(not including 182,000 civilians killed in the ])<ref name="hang">{{cite news|newspaper=Tampa Bay Times|url=http://www.sptimes.com/2007/06/25/Worldandnation/Iraq_to_hang__Chemica.shtml|title= Iraq to hang 'Chemical Ali'|last=Sinan|first=Omar| |
| casualties3= 100,000+ civilians killed on both sides<ref name=hawaii.edu-D>{{cite web|url=http://www.hawaii.edu/powerkills/SOD.TAB15.1D.GIF|title=Lesser Murdering States, Quasi-States, and Groups: Estimates, Sources, and Calculations|work=Power Kills|publisher=University of Hawai'i|author=Rumel, Rudolph}}</ref><br />(not including 182,000 civilians killed in the ])<ref name="hang">{{cite news|newspaper=Tampa Bay Times|url=http://www.sptimes.com/2007/06/25/Worldandnation/Iraq_to_hang__Chemica.shtml|title= Iraq to hang 'Chemical Ali'|last=Sinan|first=Omar|publisher=Associated Press|date=25 June 2007}}</ref> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Campaignbox Iran-Iraq War}} | {{Campaignbox Iran-Iraq War}} | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 30 October 2013
| Iraq–Iran War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Persian Gulf conflicts | |||||||||
 Clockwise from the top: Iranian soldiers wear gas masks to counter Iraqi chemical weapons; Iranian soldiers rejoice after Khorramshahr's liberation; Donald Rumsfeld and Saddam Hussein meet in Baghdad to discuss U.S. military aid to Iraq; Iranian oil platform burns after an attack by U.S. Navy in Operation Nimble Archer | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Logistic support: |
Support:
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
Ruhollah Khomeini |
Saddam Hussein co-leader of PMOI | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
At the onset of the war: 110,000–150,000 soldiers, 1,000 tanks, 1,000 armoured vehicles, 300 artillery pieces, 320 aircraft, 750 helicopters After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982: 350,000 soldiers, 700 tanks, 2,700 armoured vehicles, 400 artillery pieces, 350 aircraft, 700 helicopters At the end of the war: 900,000 soldiers, 2,500,000 militia, 400 tanks, 800 armoured vehicles, 600 artillery pieces, 60–80 aircraft, 70–90 helicopters |
At the onset of the war: 350,000 soldiers, 6,500 tanks, 4,000 armoured vehicles, 800 artillery pieces, 600 aircraft, 350 helicopters After Iraq withdrew from Iran in 1982: 175,000 soldiers, 1,200 tanks, 2,300 armoured vehicles, 400 artillery pieces, 450 aircraft, 180 helicopters At the end of the war: 1,500,000 soldiers, 5,500–6,700 tanks, 8,500–10,000 armoured vehicles, 6,000–12,000 artillery pieces, 1,500 aircraft, 1,000 helicopters | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
183,931 soldiers KIA/MIA (official number) |
105,000–180,000 soldiers and militia killed Economic loss of more than $500 billion | ||||||||
|
100,000+ civilians killed on both sides (not including 182,000 civilians killed in the Al-Anfal Campaign) | |||||||||
| ¹ The exact number of Iraqi Shia that fought alongside Iran is unknown. The Iraqi political parties SCIRI and Islamic Da'wa Party supported Iran during the war. Iran would sometimes organise divisions of Iraqi POWs to fight against Iraq. | |||||||||
| Persian Gulf Wars | |
|---|---|
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Persian Gulf War, was an armed conflict between the Islamic Republic of Iran and the Republic of Iraq lasting from September 1980 to August 1988, making it the 20th century's longest conventional war. It was initially referred to in English as the "Gulf War" prior to the Persian Gulf War of the early 1990s. The Iran–Iraq War is considered one of the most violent conflicts since World War II.
The Iran–Iraq War began when Iraq invaded Iran via air and land on 22 September 1980. It followed a long history of border disputes, and was motivated by fears that the Iranian Revolution in 1979 would inspire insurgency among Iraq's long-suppressed Shia majority as well as Iraq's desire to replace Iran as the dominant Persian Gulf state. Although Iraq hoped to take advantage of Iran's revolutionary chaos and attacked without formal warning, they made only limited progress into Iran and were quickly repelled; Iran regained virtually all lost territory by June 1982. For the next six years, Iran was on the offensive. A number of proxy forces participated in the war, most notably the Iranian MEK siding with Ba'athist Iraq and Iraqi Kurdish militias of KDP and PUK siding with Iran - all suffering a major blow by the end of the conflict.
Despite calls for a ceasefire by the United Nations Security Council, hostilities continued until 20 August 1988. The war finally ended with Resolution 598, a U.N.-brokered ceasefire which was accepted by both sides. At the war's conclusion, it took several weeks for Iranian armed forces to evacuate Iraqi territory to honour pre-war international borders set by the 1975 Algiers Agreement. The last prisoners of war were exchanged in 2003.
The war cost both sides in lives and economic damage: half a million Iraqi and Iranian soldiers, with an equivalent number of civilians, are believed to have died, with many more injured; however, the war brought neither reparations nor changes in borders. The conflict has been compared to World War I in terms of the tactics used, including large-scale trench warfare with barbed wire stretched across trenches, manned machine-gun posts, bayonet charges, human wave attacks across a no-man's land, and extensive use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops, civilians, and Iraqi Kurds. At the time of the conflict, the U.N. Security Council issued statements that "chemical weapons had been used in the war;" U.S. intelligence officials both knew of Iraqi chemical weapons use and provided Iraq with satellite imagery to guide strikes against Iranian troop concentrations. U.N. statements never clarified that only Iraq was using chemical weapons, and according to retrospective authors "the international community remained silent as Iraq used weapons of mass destruction against Iranian as well as Iraqi Kurds."
Terminology
The Iran–Iraq War was originally referred to as the Gulf War until the Persian Gulf War of 1990 and 1991, after which it was referred to as the First Persian Gulf War. The Iraq-Kuwait conflict, while originally known as the Second Persian Gulf War, eventually became known simply as the Gulf War. The Iraq War from 2003 to 2011 has since been called the Second Persian Gulf War.
In Iran, the war is known as the Imposed War (جنگ تحمیلی, Jang-e Tahmīlī) and the Holy Defence (دفاع مقدس, Defā'-e Moqaddas). In Iraq, Saddam Hussein had initially dubbed the conflict the Whirlwind War. It was also referred to as Saddām's Qādisiyyah (قادسية صدام, Qādisiyyat Ṣaddām), in reference to the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah.
Origins
Iran–Iraq relations
Main article: Iran–Iraq relations
Since the Ottoman–Persian Wars of the 16th and 17th centuries, Iran (known as Persia prior to 1935) and the Ottomans fought over Iraq (then known as Mesopotamia) and full control of the Arvand Roud/Shatt al-Arab waterway until the signing of the Treaty of Zuhab in 1639 which established the final borders between Iran and Iraq. The Arvand Roud was considered an important channel for both states' oil exports, and in 1937, Iran and the newly independent Iraq signed a treaty to settle the dispute. In the same year, Iran and Iraq both joined the Saadabad Pact, and relations between the two states remained good for decades afterwards.
The 1937 treaty recognised the Iran–Iraq border to be along the low-water mark on the Shatt's eastern side, except at Abadan and Khorramshahr, where the frontier ran along the deep water line (thalweg). This gave Iraq control of most of waterway and required Iran to pay tolls whenever its ships used it.
In 1955, both nations joined the Baghdad Pact. However, the overthrow of the Hashemites in Iraq in 1958 brought a nationalist government to power which promptly abandoned the pact. On 18 December 1959, Iraq's new leader, General Abdul Karim Qassim, declared: "We do not wish to refer to the history of Arab tribes residing in al-Ahwaz and Mohammareh . The Ottomans handed over Mohammareh, which was part of Iraqi territory, to Iran." The Iraqi government's dissatisfaction with Iran's possession of the oil-rich Khuzestan province (which the Iraqis called Arabistan) that had a large Arabic-speaking population was not limited to rhetorical statements. Iraq began supporting secessionist movements in Khuzestan, and raised the issue of its territorial claims at an Arab League meeting, though unsuccessfully.
Iraq showed reluctance in fulfilling existing agreements with Iran—especially after Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser's death in 1970 and the Iraqi Ba’ath Party's rise which took power in a 1968 coup, leading Iraq to take on the self-appointed role of "leader of the Arab world". At the same time, by the late 1960s, the build-up of Iranian power under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, who had gone on a military spending spree, led Iran to take a more assertive stance in the region.
In April 1969, Iran abrogated the 1937 treaty over the Arvand Roud, and as such, ceased paying tolls to Iraq when its ships used the waterway. The Shah justified his move by arguing that almost all river borders around the world ran along the thalweg, and by claiming that because most of the ships that used the waterway were Iranian, the 1937 treaty was unfair to Iran. Iraq threatened war over the Iranian move, but when, on 24 April 1969, an Iranian tanker escorted by Iranian warships sailed down the river, Iraq—being the militarily weaker state—did nothing.
Iran's abrogation of the treaty marked the beginning of a period of acute Iraqi-Iranian tension that was to last until the Algiers Accords of 1975. In 1969, Saddam Hussein, Iraq's deputy prime minister, stated: "Iraq's dispute with Iran is in connection with Khuzestan, which is part of Iraq's soil and was annexed to Iran during foreign rule." Soon, Iraqi radio stations began exclusively broadcasting into "Arabistan", encouraging Arabs living in Iran and even Balūchīs to revolt against the Shah's government. Basra TV stations began showing Iran's Khuzestan province as part of Iraq's new province Nasiriyyah, renaming all its cities with Arabic names.
In 1971, Iraq (now under Saddam's effective rule) broke diplomatic relations with Iran after claiming sovereignty rights over the islands of Abu Musa, Greater Tunb, and Lesser Tunb in the Persian Gulf following the withdrawal of the British. As retaliation for Iraq's claims to Khuzestan, Iran became the main patron of Iraq's Kurdish rebels in the early 1970s, giving the Iraqi Kurds bases in Iran and arming the Kurdish groups. In addition to Iraq fomenting separatism in Iran's Khuzestan and Balochistan provinces, both states encouraged separatist activities by Kurdish nationalists in the other state. From March 1974 to March 1975, Iran and Iraq fought border wars over Iran's support of Iraqi Kurds. In 1975, the Iraqis launched an offensive into Iran using tanks, though the Iranians defeated them. Several other attacks took place; however, Iran had the world's fifth most powerful military at the time and easily defeated the Iraqis with their air force. As a result, Iraq decided against continuing the war, choosing instead to make concessions to Tehran to end the Kurdish rebellion.
In the 1975 Algiers Agreement, Iraq made territorial concessions—including the Shatt al-Arab waterway—in exchange for normalised relations. In return for Iraq recognising that the frontier on the waterway ran along the entire thalweg, Iran ended its support of Iraq's Kurdish guerrillas. Iraqis viewed the Algiers Agreement as humiliating. However, the agreement meant the end of Iranian and American support for the Peshmerga, who were defeated by Iraq's government in a short campaign that claimed 20,000 lives. The British journalist Patrick Brogan wrote that "...the Iraqis celebrated their victory in the usual manner, by executing as many of the rebels as they could lay their hands on."
The relationship between the governments of Iran and Iraq briefly improved in 1978, when Iranian agents in Iraq discovered plans for a pro-Soviet coup d'état against Iraq's government. When informed of this plot, Saddam ordered the execution of dozens of his army's officers and in a sign of reconciliation, expelled Ruhollah Khomeini, an exiled leader of clerical opposition to the Shah, from Iraq. Despite that, Saddam merely considered the Algiers Agreement to be a truce, rather than a definite settlement and waited for the opportunity to contest it.
After the Iranian Revolution
See also: Iranian Revolution and Iranian Embassy siege
Tensions between Iraq and Iran were fueled by Iran's Islamic revolution and its appearance of being a Pan-Islamic force, in contrast to Iraq's Arab nationalism. Despite Iraq's goals of regaining the Shatt al-Arab, the Iraqi government seemed to initially welcome Iran's Revolution, which overthrew Iran's Shah, who was seen as a common enemy. It is difficult to pinpoint when tensions began to build, but there were some cross border skirmishes, including when Iraqi aircraft bombed an Iranian village that anti-Iraqi Kurds allegedly hid in on June 1979.
After this incident, the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini called on Iraqis to overthrow the Ba'ath government, and it was received with considerable anger in Baghdad. On 17 July 1979, despite Khomeini's call, Saddam gave a speech praising the Iranian Revolution and called for an Iraqi-Iranian friendship based on non-interference in each other's internal affairs. When Khomeini rejected Saddam's overture by calling for Islamic revolution in Iraq, Saddam was alarmed. Iran's new Islamic administration was regarded in Baghdad as an irrational, existential threat to the Ba'ath government, especially because the Ba'ath party, having a secular nature, discriminated and posed a threat to the Shia movement in Iraq, whose clerics were Iran's allies within Iraq and whom Khomeini saw as oppressed. Some scholars have argued that Iranian-backed attacks and cross-border raids on Iraqi territory compelled Iraq to launch a preemptive invasion.
However, Iraq's regime was very politically secure, and in little danger of being overthrown by alleged plots of revolution-wracked Iran. According to some sources, Khomeini's hostility towards Saddam was actually milder than his Arab neighbors hostility towards Saddam. Saddam's primary interest in war stemmed from his desire to right the supposed "wrong" of the Algiers Agreement, in addition to finally achieving his desire of annexing Khuzestan and becoming the regional superpower. Saddam's goal was to replace Egypt as the "leader of the Arab world" and to achieve hegemony over the Persian Gulf. He saw Iran's increased weakness due to revolution, sanctions, and international isolation. Saddam had heavily invested in Iraq's military since his defeat against Iran in 1975, buying large amounts of weaponry from the Soviet Union and France. By 1980, Iraq possessed 200,000 soldiers, 2,000 tanks and 450 aircraft. Watching the powerful Iranian army that frustrated him in 1974–1975 disintegrate, he saw an opportunity to attack, using the threat of Islamic Revolution as a pretext.
A successful invasion of Iran would enlarge Iraq's petroleum reserves and make Iraq the region's dominant power. With Iran engulfed in chaos, an opportunity for Iraq to annex the oil-rich Khuzestan Province materialized. In addition, Khuzestan's large ethnic Arab population would allow Saddam to pose as a liberator for Arabs from Persian rule. Fellow Gulf states such as Saudi Arabia and Kuwait (despite being hostile to Iraq) encouraged Iraq to attack, as they feared that an Islamic revolution would take place within their own borders. Certain Iranian exiles also helped convince Saddam that if he invaded, the fledgling Islamic republic would quickly collapse.
In 1979–80, Iraq was the beneficiary of an oil boom that saw it take in US$33 billion, which allowed Iraq's government to go on a spending spree on both civilian and military projects. On several occasions, Saddam alluded to the Islamic conquest of Iran in promoting his position against Iran. For example, on 2 April 1980, half a year before the war's outbreak, in a visit to Baghdad's al-Mustansiriya University, he drew parallels to Persia's defeat at the 7th century Battle of al-Qādisiyyah:
In your name, brothers, and on behalf of the Iraqis and Arabs everywhere we tell those Persian cowards and dwarfs who try to avenge al-Qadisiyah that the spirit of al-Qadisiyah as well as the blood and honor of the people of al-Qadisiyah who carried the message on their spearheads are greater than their attempts.
In 1979–1980, anti-Ba'ath riots arose in the Iraq's Shia areas by groups who were workings toward an Islamic revolution in their country. Saddam and his deputies believed that the riots had been inspired by the Iranian Revolution and instigated by Iran's government. On 10 March 1980, when Iraq declared Iran's ambassador persona non-grata, and demanded his withdrawal from Iraq by 15 March, Iran replied by downgrading its diplomatic ties to the charge d'affaires level, and demanded that Iraq withdraw their ambassador from Iran. In April 1980, Grand Ayatollah Mohammad Baqir al-Sadr and his sister Amina Haydar (better known as Bint al-Huda) were hanged as part of a crackdown to restore Saddam's control. The execution of Iraq's most senior Ayatollah caused outrage throughout the Islamic world, especially among Shias.
Iraq soon after expropriated the properties of 70,000 civilians believed to be of Iranian origin and expelled them from its territory. Many, if not most, of those expelled were in fact Arabic-speaking Iraqi Shias who had little to no family ties with Iran. This caused tensions between the two nations to increase further.

In April 1980, Shia militants assassinated 20 Ba'ath officials, and Deputy Prime Minister Tariq Aziz was almost assassinated on 1 April; Aziz survived, but 11 students were killed in the attack. Three days later, the funeral procession being held to bury the students was bombed. Iraqi Information Minister Latif Nusseif al-Jasim also barely survived assassination by Shia militants. The Shias' repeated calls for the overthrow of the Ba'ath party and the support they allegedly received from Iran's new government led Saddam to increasingly perceive Iran as a threat that, if ignored, might one day overthrow him; he thus used the attacks as pretext for attacking Iran later that September, though skirmishes along the Iran–Iraq border had already become a daily event by May that year.
Iraq also helped to instigate riots among Iranian Arabs in Khuzestan province, supporting them in their labor disputes, and turning uprisings into armed battles between Iran's Revolutionary Guards and militants, killing over 100 on both sides. At times, Iraq also supported armed rebellion by the Kurdish Democratic Party of Iran in Kurdistan. The most notable of such events was the Iranian Embassy siege in London, in which six armed Khuzestani Arab insurgents took the Iranian Embassy's staff as hostages, resulting in an armed siege that was finally ended by Britain's Special Air Service.
According to former Iraqi general Ra'ad al-Hamdani, the Iraqis believed that in addition to the Arab revolts, the Revolutionary Guards would be drawn out of Tehran, leading to a counter-revolution in Iran that would cause Khomeini's government to collapse and thus ensure Iraqi victory. However, rather than turning against the revolutionary government as experts had predicted, Iran's people (including Iranian Arabs) rallied in support of their country and put up a stiff resistance.
Iraqi preparations
Iraq began planning offensives, confident that they would succeed. Iran lacked both cohesive leadership and spare parts for their American-made equipment. Iraq, on the other hand, possessed a fully equipped and trained modern military, consisting of 190,000 men, 2,200 tanks, and 450 aircraft. The Iraqis could mobilise up to 12 mechanised divisions, and morale was running high. Through the 1970s, Saddam had armed his forces with the most advanced material available from the Soviet Union.
In addition, the area around the Shatt al-Arab posed no obstacle for the Iraqis, as they were armed with Soviet equipment to cross rivers. Iraq correctly deduced that Iran's defences at the crossing points around the Kharkeh and Karoun Rivers were undermanned and that the rivers could be easily crossed. Iraqi intelligence was also informed that the Iranian forces in Khuzestan (which consisted of two divisions prior to the revolution) now only consisted of several ill-equipped battalions. Only a handful of company-sized tank units remained operational.
The only qualms the Iraqis had were over the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (formerly the Imperial Iranian Air Force). Despite the purge of several key pilots and commanders as well as the lack of spare parts, the air force showed its power during local uprisings and rebellions. They were also active after the failed U.S. attempt to rescue its hostages, Operation Eagle Claw. As such, Iraq's leaders decided to carry out a surprise airstrike against the Iranian air force's infrastructure prior to the main invasion.
Iranian preparations
In Iran, severe officer purges (including numerous executions ordered by Sadegh Khalkhali, the new Revolutionary Court judge), and shortages of spare parts for Iran's U.S.-made equipment had crippled Iran's once-mighty military. Between February and September 1979, Iran's government executed 85 senior generals and forced all major-generals and most brigadier-generals into early retirement. By September 1980, the government had purged 12,000 army officers. These purges resulted in a drastic decline in the Iranian military's operational capacities. Their regular army (which, in 1978, was considered the world's fifth most powerful) had been badly weakened by purges and lack of spare parts. The desertion rate had reached 60%, and the officer corps was devastated. The most highly skilled soldiers and aviators were exiled, imprisoned, or executed. Throughout the war, Iran never managed to fully recover from this human capital flight. Continuous sanctions prevented Iran from acquiring many heavy weapons, such as tanks and aircraft. When the invasion occurred, many pilots and officers were released from prison, or had their executions commuted to combat the Iraqis. In addition, many junior officers were promoted to generals, resulting in the army being more integrated as a part of the regime by the war's end, as it is today. Iran still had at least 1,000 operational tanks and several hundred functional aircraft, and could cannibalize equipment to procure spare parts.
Meanwhile, a new paramilitary organisation gained prominence in Iran, the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (often shortened to Revolutionary Guards, and known in Iran as the Sepah-e-Pasdaran), which intended to protect the new regime and counterbalance the decaying army. Despite having been trained as a paramilitary organisation, after the Iraqi invasion, they were forced to act as a regular army. Initially, they refused to fight alongside the army, which resulted in many defeats, but, by 1982, the two groups began carrying out combined operations. Another paramilitary militia was founded in response to the invasion, the "Army of 20 Million", commonly known as the Basij. The Basij were poorly armed and had members as young as 14 and as old as 70. They often acted in conjunction with the Revolutionary Guard, launching so-called human wave attacks and other campaigns against the Iraqis. They were subordinate to the Revolutionary Guards, and they made up most of the manpower that was used in the Revolutionary Guard's attacks.
Border conflicts leading to war
By September, skirmishes between Iran and Iraq were increasing in number. Iraq began to grow bolder, both shelling and launching border incursions in disputed territories. Iran responded by shelling several Iraqi border towns and posts, though this did little to alter the situation on the ground. By 10 September, Saddam declared that the Iraqi Army had "liberated" all disputed territories within Iran. With the conclusion of the "liberating operations", on 17 September, in a statement addressed to Iraq's parliament, Saddam stated:
The frequent and blatant Iranian violations of Iraqi sovereignty...have rendered the 1975 Algiers Agreement null and void... This river ...must have its Iraqi-Arab identity restored as it was throughout history in name and in reality with all the disposal rights emanating from full sovereignty over the river...We in no way wish to launch war against Iran.
Despite Saddam's claim that Iraq did not want war with Iran, the next day his forces proceeded to attack Iranian border posts in preparation for the planned invasion. Iraq's 7th Mechanised and 4th Infantry Divisions attacked the Iranian border posts leading to the cities of Fakkeh and Bostan, opening the route for future armoured thrusts into Iran. Weakened by internal chaos, Iran was unable to repel the attacks; which in turn lead to Iraq becoming more confident in its military edge over Iran and prompting them to believe in a quick victory.
Geographic analysis
The mountainous border between Iran and Iraq made a deep ground invasion almost impossible, and air strikes were used instead. The invasion's first waves were a series of air strikes targeted at Iranian airfields. Iraq also attempted to bomb Tehran, Iran's capital and command centre, into submission.
Course of the war
1980: Iraqi invasion

Iraq launched a full-scale invasion of Iran on 22 September 1980. The Iraqi Air Force launched surprise air strikes on ten Iranian airfields with the objective of destroying the Iranian Air Force. The attack damaged some of Iran's airbase infrastructure, but failed to destroy a significant number of aircraft: the Iraqi Air Force was only able to strike in depth with a few MiG-23BN, Tu-22, and Su-20 aircraft. Three MiG-23s managed to attack Tehran, striking its airport but destroyed only a few aircraft.

The next day, Iraq launched a ground invasion of Iran along a front measuring 644 km (400 mi) in three simultaneous attacks. The invasion's purpose, according to Saddam, was to blunt the edge of Khomeini's movement and to thwart his attempts to export his Islamic revolution to Iraq and the Persian Gulf states. Saddam hoped that by annexing Khuzestan, he would send such a blow to Iran's prestige that it would lead to the new government's downfall, or, at very least, end Iran's calls for his overthrow.
Of Iraq's six divisions that were invading by ground, four were sent to Khuzestan, which was located near the border's southern end, to cut off the Arvand Roud from the rest of Iran and to establish a territorial security zone. The other two divisions invaded across the northern and central part of the border to prevent an Iranian counter-attack. Two of the four Iraqi divisions, one mechanised and one armoured, operated near the southern end and began a siege of the strategically important port cities of Abadan and Khorramshahr.
The other two divisions, both armoured, secured the territory bounded by the cities of Khorramshahr, Ahvaz, Susangerd, and Musian. On the central front, the Iraqis occupied Mehran, advanced towards the foothills of the Zagros Mountains, and were able to block the traditional Tehran–Baghdad invasion route by securing territory forward of Qasr-e Shirin, Iran. On the northern front, the Iraqis attempted to establish a strong defensive position opposite Suleimaniya to protect the Iraqi Kirkuk oil complex. Iraqi hopes of an uprising by the ethnic Arabs of Khuzestan failed to materialise, as most of the ethnic Arabs remained loyal to Iran. The Iraqi troops advancing into Iran in 1980 were described by Patrick Brogan as "badly led and lacking in offensive spirit". The first known chemical weapons attack by Iraq on Iran probably took place during the fighting around Susangerd.
Though the Iraqi air invasion surprised the Iranians, the Iranian air force retaliated with an attack against Iraqi military bases and infrastructure in Operation Kaman 99 (Bow 99). Groups of F-4 Phantom and F-5 Tiger fighter jets attacked targets throughout Iraq, such as oil facilities, dams, petrochemical plants, and oil refineries, and included Mosul Airbase, Baghdad, and the Kirkuk oil refinery. Iraq was taken by surprise at the strength of the retaliation, as Iran took few losses while the Iraqis took heavy defeats and economic disruptions.
The Iranian force of AH-1 Cobra helicopter gunships began attacks on the advancing Iraqi divisions, along with F-4 Phantoms armed with Maverick missiles; they destroyed numerous armoured vehicles and impeded the Iraqi advance, though not completely halting it. Iran had discovered that a group of two or three F-4 low-flying Phantoms could hit targets almost anywhere in Iraq. Meanwhile, Iraqi air attacks on Iran were repulsed by Iran's F-14 Tomcat interceptor fighter jets, using Phoenix missiles, which downed a dozen of Iraq's Soviet-built fighters in the first two days of battle.
The Iranian regular military, police forces, volunteer Basij, and Revolutionary Guards all conducted their operations separately; thus, the Iraqi invading forces did not face coordinated resistance. However, on 24 September, the Iranian Navy attacked Basra, Iraq, destroying two oil terminals near the Iraqi port Faw, which reduced Iraq's ability to export oil. The Iranian ground forces (primarily consisting of the Revolutionary Guard) retreated to the cities, where they set up defences against the invaders.
On 30 September, Iran's air force launched Operation Scorch Sword, striking and badly damaging the Osirak nuclear reactor near Baghdad.
By 1 October, Baghdad had been subjected to eight air attacks. In response, Iraq launched aerial strikes against Iranian targets.
First Battle of Khorramshahr
Main article: Battle of KhorramshahrOn 22 September, a prolonged battle began in the city of Khorramshahr, eventually leaving 7,000 dead on each side. Reflecting the bloody nature of the struggle, Iranians came to call Khorramshahr "City of Blood" (خونین شهر, Khunin shahr).
The battle began with Iraqi air raids against key points and mechanised divisions advancing on the city in a crescent-like formation. They were slowed by Iranian air attacks and Revolutionary Guard troops with recoilless rifles, rocket-propelled grenades, and Molotov cocktails. The Iranians flooded the marsh areas around the city, forcing the Iraqis to traverse through narrow strips of land. Iraqi tanks launched attacks with no infantry support, and many tanks were lost to Iranian anti-tank teams. However, by 30 September, the Iraqis had managed to clear the Iranians from the outskirts of the city. The next day, the Iraqis launched infantry and armoured attacks into the city. After heavy house-to-house fighting, the Iraqis were repelled. On 14 October, the Iraqis launched a second offensive. The Iranians launched a controlled withdrawal from the city, street by street. By 24 October, most of the city was captured, and the Iranians evacuated across the Karun River. Some partisans remained, and fighting continued until 10 November.
Iraqi advance stalls
Main articles: Siege of Abadan and Operation MorvaridThe people of Iran, rather than turning against their still-weak Islamic Republic, rallied around their country to resist invasion. An estimated 200,000 fresh troops had arrived at the front by November, many of them ideologically committed volunteers.
Though Khorramshahr was finally captured, the battle had delayed the Iraqis enough to allow the large-scale deployment of the Iranian military. In November, Saddam ordered his forces to advance towards Dezful and Ahvaz, and lay sieges to both cities. However, the Iraqi offensive had been badly damaged by Iranian militias and air power. Iran's air force had destroyed Iraq's army supply depots and fuel supplies, and was strangling the country through an aerial siege. On the other hand, Iran's supplies had not been exhausted, despite sanctions, and they often cannibalised spare parts from other equipment and began searching for more parts on the black market. On 28 November, Iran launched Operation Morvarid (Pearl), a combined air and sea attack which destroyed 80% of Iraq's navy and all of their radar sites in the southern portion of the country. When Iraq laid siege to Abadan and dug their troops in around the city, they were unable to blockade the port, which allowed Iran to resupply Abadan by sea.
Iraq's strategic reserves had been depleted, and by now they lacked the power to go on any major offensives until nearly the end of the war. On 7 December, Hussein announced that Iraq was going on the defensive.
For the next eight months, both sides were to be on a defensive footing (with the exception of the Battle of Dezful), as the Iranians needed more time to reorganise their forces and the damage inflicted by the purge of 1979–80. During this period, fighting consisted mainly of artillery duels and raids. Iraq had mobilised 21 divisions for the invasion, while Iran countered with only 13 regular army divisions and one brigade. Of the regular divisions, only seven were deployed to the border. The war bogged down into World War I-style trench warfare with tanks and modern late-20th century weapons. Due to the power of anti-tank weapons such as the RPG-7, armored maneuver by the Iraqis was very costly, and they consequently entrenched their tanks into static positions.
Iraq also began firing Scud missiles into the cities of Dezful and Ahvaz and used terror bombing to bring the war to the Iranian civilian population. Iran launched dozens of human wave assaults.
1981: Stalemate
Battle of Dezful
Main article: Battle of DezfulOn 5 January 1981, Iran had reorganised its forces enough to launch a large-scale offensive, Operation Nasr (Victory). The Iranians launched their major armoured offensive at Susangerd, consisting of the 16th Qazvin and the 77th Khorasan armoured divisions, and broke through Iraqi lines. However, the Iranian tanks had raced through Iraqi lines with their flanks unprotected and with no infantry support; as a result, they were cut off by Iraqi tanks. In the ensuing Battle of Dezful, the Iranian division was nearly wiped out in one of the biggest tank battles of the war. When the Iranian tanks tried to manoeuvre, they became stuck in the mud of the marshes, and many tanks were abandoned. The Iraqis lost 45 T-62 tanks, while the Iranians lost 100-200 Chieftain and M-60 tanks. Reporters counted roughly 150 destroyed or deserted Iranian tanks, and also 40 Iraqi tanks. 141 Iranians were killed during this battle.
The battle had been ordered by Iranian president Abulhassan Banisadr, who was hoping that a victory might shore up his deteriorating political position; instead, the failure hastened his fall. Many of Iran's problems took place because of political infighting between President Banisadr, who supported the regular army, and the hardliners who supported the IRGC. Once he was impeached and the competition ended, the performance of the Iranian military improved. Iran was further distracted by internal fighting between the regime and the Islamic Marxist Mujaheddin e-Khalq(MEK) on the streets of Iran's major cities in June 1981 and again in September. After the end of these battles, the MEK gradually leaned towards Saddam Hussein, completely taking his side by the mid-1980s. The Battle of Dezful became a critical battle in Iranian military thinking. Less emphasis was placed on the Army with its conventional tactics, and more emphasis was placed on the Revolutionary Guard with its unconventional tactics.
Attack on H3
Main article: Attack on H3The Iraqi Air Force, badly damaged by the Iranians, was moved to the H-3 Airbase in Western Iraq, near the Jordanian border and away from Iran. However, on 3 April 1981, the Iranian air force used eight F-4 Phantom fighter bombers, four F-14 Tomcats, three Boeing 707 refuelling tankers, and one Boeing 747 command plane to launch a surprise attack on H3, destroying 27–50 Iraqi fighter jets.
Despite the successful H-3 airbase attack (in addition to other air attacks), in April, the Iranian Air Force was forced to cancel its successful 180-day air offensive against Iraq. In addition, they gave up trying to hold total control of Iranian airspace. Due to the heavy toll of sanctions and pre-war purges, the Iranian air force could not suffer further heavy attrition, and made the decision in order to limit their losses. They were also damaged by a fresh purge, after the impeachment crisis of President Banisadr. The Iranian air force would fight heavily on the defensive, trying to hold back the Iraqis rather than engaging them. While throughout 1981–1982 the Iraqi air force would remain weak, within the next few years they would rearm and expand again, and begin to regain the strategic initiative.
Iran introduces the human wave attack
Since the Iranians suffered from a shortage of heavy weapons but had a large number of devoted volunteer troops, they began using human wave attacks against the Iraqis. Typically, an Iranian assault would consist of the following: First, the poorly trained Basij would launch the primary human wave assaults to swamp the weakest portions of the Iraqi lines en masse (on some occasions even bodily clearing minefields). They would be followed up by the more experienced Revolutionary Guard infantry, who would breach the weakened Iraqi lines. Afterwards, the regular army using mechanized forces would maneuver through the breach and encircle and defeat the enemy.
According to historian Stephen C. Pelletiére, the idea of Iranian "human wave attacks" were a misconception. Instead, the Iranian tactics consisted of using groups of 22 man infantry squads which moved forward to attack specific objectives. As the squads surged forward to execute their missions, that gave the impression of a "human wave attack". Nevertheless, the idea of "human wave attacks" remained virtually synonymous with any large-scale infantry frontal assault Iran carried out. Large amounts of troops would be used, aimed at overwhelming the Iraqi lines (usually the weakest portion manned by the Iraqi Popular Army) regardless of losses.
According to the former Iraqi general Ra'ad al-Hamdani, the Iranian human waves charges consisted of armed "civilians" who carried most of their necessary equipment themselves into battle and often lacked command and control and logistics. However, Iranian tactics also were sophisticated as well. Operations were often carried out during the night, and deception operations, infiltrations, and manoeuvres became more common.
The Iranians attempted to add the element of surprise to most of their attacks, differing them from those in World War I. During 1982, Iran used the same marshes that proved fatal to their tank forces during the Battle of Dezful to infiltrate to the rear of the Iraqi lines. The Iranians would reinforce the infiltrating forces with new units to keep up their momentum. Once a weak point was found, the Iranians would concentrate all of their forces into that area in an attempt to break through with human waves attacks.
The human wave attacks, while extremely bloody (tens of thousands of troops died in the process), when used in combination with infiltration and surprise caused major Iraqi defeats. As the Iraqis would dig in their tanks and infantry into static, entrenched positions, the Iranians would manage to break through the lines and encircle entire divisions. Merely the fact that the Iranian forces used maneuver warfare using their light infantry against static Iraqi defenses was often the decisive factor in the battle. However, lack of coordination between the Army and IRGC and shortages of heavy weaponry did play a detrimental role, with most of the infantry not supported by artillery and armor.
Operation Eighth Imam
Main article: Operation Eighth ImamFor about a year after the Iraqi offensive stalled in March 1981, there was little change in the front other than Iran retaking the high ground above Susangerd in May. However, by late 1981, Iran returned to the offensive and the Iraqi military was forced to retreat. Iran launched a new operation, Operation Samen-ol-A'emeh (The Eighth Imam), ending the Iraqi Siege of Abadan on 27–29 September 1981. The Iranians used a combined force of regular army artillery with small groups of armor, supported by Pasdaran and Basij infantry.
Operation Jerusalem Way
Main article: Operation Jerusalem WayBy the fall of 1981, serious problems with morale had developed in the Iraqi Army, with many soldiers seeing no point to the invasion.
On 29 November 1981, Iran began Operation Tariq al-Qods (Jerusalem Way) with three army brigades and seven Revolutionary Guard brigades. The Iraqis failed to properly patrol their occupied areas, and the Iranians constructed a 14 km (14,000 m) road through the unguarded sand dunes, infiltrating in and launching their attack from the Iraqi rear. The battle saw the town of Bostan being retaken from Iraqi divisions by 7 December. Operation Jerusalem Way also saw the first use of the Iranian "human wave" tactics, where the Revolutionary Guard light infantry charged at Iraqi positions repeatedly, oftentimes without the support of armour or air power. The fall of Bostan exacerbated the Iraqis' logistical problems, forcing them to use a roundabout route from Ahvaz far to the south to resupply its troops. 6,000 Iranians and over 2,000 Iraqis were killed in the operation.
1982: Iraqi retreat, Iranian offensive

The Iraqis, realising that the Iranians were planning to attack, decided to preempt them with Operation al-Fawz al-'Azim (Supreme Success) on 19 March. Using a large number of tanks, helicopters, and fighter jets, they attacked the Iranian buildup around the Roghabiyeh pass. Though Saddam and his generals assumed they had succeeded, in reality the Iranian forces remained fully intact. The Iranians had concentrated much of their forces by bringing them directly from the cities and towns throughout Iran via trains, buses, and private cars. The concentration of forces did not resemble a traditional military buildup, and although the Iraqis detected a population buildup near the front, they failed to realise that this was an attacking force. As a result, Saddam's army was unprepared for the Iranian offensives to come.
Operation Undeniable Victory
Main article: Operation Undeniable VictoryIran's next major offensive, led by General Ali Sayad Shirazi, was Operation Fath-ol-Mobeen (Undeniable Victory). On 22 March 1982, Iran launched an attack which took the Iraqi forces by surprise: using Chinook helicopters, they landed behind Iraqi lines, silenced their artillery, and captured an Iraqi headquarter. The Iranian Basij then launched human wave attacks, consisting of 1,000 fighters per wave. Though they took heavy losses, they eventually broke through Iraqi lines.

The Revolutionary Guard and regular army followed up by surrounding the Iraqi ninth and 10th Armoured and 1st Mechanised divisions in the Iranian town of Shush. The Iraqis launched a counter-attack using their 12th Armoured division to break the encirclement and rescue the surrounded divisions. Iraqi tanks came under attack by 95 Iranian F-4 Phantom and F-5 Tiger fighter jets, effectively destroying the entire division.
Operation Undeniable Victory ended decisively in Iran's favour, and Iraqi forces were driven away from Dezful and Ahvaz. The Iranian armed forces destroyed almost 320-400 Iraqi tanks and armored vehicles in combat. But the price they paid for it was high. In just the first day of the battle the Iranians lost 196 tanks. By this time, most of the Khuzestan province had returned to Iran's hands.
Operation Jerusalem
Main article: Operation JerusalemIn preparation for Operation Beit ol-Moqaddas (Jerusalem), the Iranians had launched numerous air raids against Iraq air bases, destroying 47 jets (including Iraq's brand new Mirage F-1 fighter jets from France); this gave the Iranians air superiority over the battlefield while allowing them to monitor Iraqi troop movements.
On 29 April, Iran launched the offensive. 70,000 Revolutionary Guard and Basij members struck on several axes – Bostan, Susangerd, the west bank of the Karun River, and Ahvaz. The Basij launched human wave attacks, which were followed up by the regular army and Revolutionary Guard support along with tanks and helicopters. Under heavy Iranian pressure, the Iraqi forces retreated. By 12 May, Iran had driven out all Iraqi forces from the Susangerd area. The Iranians captured several thousand Iraqi troops and a large number of tanks. Nevertheless, the Iranians took many losses as well, especially among the Basij.
The Iraqis retreated to the Karun River, with only Khorramshahr and a few outlying areas remaining in their possession. Saddam ordered 70,000 troops to be placed around the city of Khorramshahr. The Iraqis created a hastily constructed defence line around the city and outlying areas. To discourage airborne commando landings, the Iraqis also placed metal spikes and destroyed cars in areas likely to be used as troop landing zones. Saddam Hussein even visited Khorramshahr in a dramatic gesture, swearing that the city would never be relinquished. However, Khorramshahr's only resupply point was across the Arvand Roud, and the Iranian air force began bombing the supply bridges to the city, while their artillery zeroed in on the besieged garrison.
Liberation of Khorramshahr (Second Battle of Khorramshahr)
Main article: Liberation of KhorramshahrIn the early morning hours of 23 May 1982 the Iranians began the drive towards Khorramshahr across the Karun River. This part of Operation Jerusalem was spearheaded by the 77th Khorasan division with tanks along with the Revolutionary Guard and Basij. The Iranians hit the Iraqis with destructive air strikes and massive artillery barrages, crossed the Karun River, captured bridgeheads, and launched human waves attacks towards the city. Saddam's defensive barricade collapsed; in less than 48 hours of fighting, the city fell and 23,000 Iraqis surrendered to the Iranians. A total of 7,000 Iraqis were killed or wounded in Khorramshahr, while the Iranians suffered 10,000 casualties. During the whole of Operation Jerusalem, 33,000–35,000 Iraqi soldiers were taken prisoner by the Iranians.
State of Iraqi armed forces
The fighting had battered the Iraqi military: its strength fell from 210,000 to 150,000 troops; over 20,000 Iraqi soldiers were killed and over 30,000 captured; two out of four active armoured divisions and at least three mechanised divisions fell to less than a brigade's strength; and the Iranians had captured over 450 tanks and armoured personnel carriers.
The Iraqi Air Force was also left in poor shape: after losing up to 55 aircraft since early December 1981, they had only 100 intact fighter-bombers and interceptors. A defector who flew his MiG-21 to Syria in June 1982 revealed that the Iraqi Air Force had only three squadrons of fighter-bombers left that were capable of mounting offensive operations into Iran. The Iraqi Army Air Corps was in slightly better shape, and could still operate more than 70 helicopters. Despite that, the Iraqis still held 3,000 tanks, while Iran held 1,000.
At this point, Saddam believed that his army was too demoralised and damaged to hold onto Khuzestan and major swaths of territory in Iran, and withdrew his remaining armed forces from those areas. He redeployed them along the border between Iraq and Iran as a means of defence. However, his troops continued to occupy some key border areas of Iran, and continued to hold onto the disputed territories that prompted his invasion, including the Shatt al-Arab waterway which was the primary cause of the war. In response to their failures against the Iranians in Khorramshahr, Saddam ordered the executions of General Juwad Shitnah, General Salah al-Qadhi, and Colonel Masa abd al-Jalil. At least a dozen high-ranking officers were also executed during this time. This became increasingly common punishment for those who failed him in battle.
Khorramshahr was completely destroyed, and numerous other cities including Ahvaz and Abadan were severely damaged.
International response in 1982
In April 1982, the rival Baathist regime in Syria, one of the few nations that supported Iran, closed the Kirkuk–Banias pipeline that had allowed Iraqi oil to reach tankers on the Mediterranean, reducing the Iraqi budget by US$5 billion per month. Journalist Patrick Brogan wrote, "It appeared for a while that Iraq would be strangled economically before it was defeated militarily." Syria's closure of the Kirkuk-Banis pipeline left Iraq with the pipeline to Turkey as the only mean of exporting oil. However, that pipeline had a capacity of only 500,000 barrels per day (79,000 m/d), which was insufficient to pay for the war. However, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the other Gulf states saved Iraq from bankruptcy by providing it with an average of $60 billion in subsidies per year. Though Iraq had previously been hostile towards other Gulf states, "the threat of Persian fundamentalism was far more feared." They were especially inclined to fear Iranian victory after Ayatollah Khomeini declared monarchies to be illegitimate and an un-Islamic form of government. Khomeini's statement was widely received as a call to overthrow the Gulf monarchies. Journalists John Bulloch and Harvey Morris wrote:
The virulent Iranian campaign, which at its peak seemed to be making the overthrow of the Saudi regime a war aim on a par with the defeat of Iraq, did have an effect on the Kingdom , but not the one the Iranians wanted: instead of becoming more conciliatory, the Saudis became tougher, more self-confident, and less prone to seek compromise.
Saudi Arabia was said to provide Iraq with $1 billion per month starting mid-1982.
Iraq began receiving support from the United States and west European countries as well. Saddam Hussein was given diplomatic, monetary, and military support by the U.S., including massive loans, political clout, and intelligence on Iranian deployments gathered using American spy satellites, which allowed them to coordinate attacks against the Iranians. The Iraqis relied heavily on American satellite footage and radar planes to detect Iranian troop movements, and they enabled Iraq to move troops to the site before the battle.
With Iranian success on the battlefield, the U.S. made its backing of Iraq more pronounced, supplying intelligence, economic aid, and dual-use equipment and vehicles, as well as normalizing their intergovernmental relations (which had been broken during the 1967 Six-Day War). President Ronald Reagan decided that the United States "could not afford to allow Iraq to lose the war to Iran", and that the United States "would do whatever was necessary to prevent Iraq from losing the war with Iran". President Reagan formalised this policy by issuing a National Security Decision Directive to this effect in June 1982.
In 1982, Reagan removed Iraq from the list of countries "supporting terrorism" and sold weapons such as howitzers to Iraq via Jordan and Israel. France sold Iraq millions of dollars worth of weapons, including Gazelle helicopters, Mirage F-1 fighters, and Exocet missiles. Both the United States and West Germany sold Iraq pesticides and poisons that would be used to create chemical and other weapons, such as Roland missiles.
At the same time, the Soviet Union, angered with Iran for purging and destroying the Tudeh Party (Iran's national communist party), sent large shipments of weapons to Iraq. The Iraqi Air Force was rearmed with Soviet and French fighter jets and helicopters. Iraq also bought weapons such as AK-47s and rocket-propelled grenades from the Chinese. The depleted tank forces were replenished with Soviet tanks, and the Iraqis were rearmed in the face of renewed Iranian attacks. Iran was portrayed as the aggressor, and would be seen as such until the 1990–1991 Persian Gulf War, when Iraq would be condemned.
Iran was unable to get very many new weapons, though they did gain some from China, North Korea, and Libya. There were also clandestine purchases from certain elements within Israel and the United States, who also bought small arms from China, via North Korea.
Ceasefire proposal

On 20 June 1982 Saddam announced that he wanted to sue for peace and proposed an immediate ceasefire. Khomeini rejected the Iraqi peace offer because an immediate ceasefire would mean that Iraqi troops would remain on Iran's borders in the disputed territory. He proclaimed that Iran would invade Iraq and would not stop until the Ba'ath regime was replaced by an Islamic republic (or at least until Iraq withdrew from the disputed territories). Iran supported a government in exile for Iraq, the Supreme Council of the Islamic Revolution in Iraq, led by exiled Iraqi cleric Mohammad Baqer al-Hakim, was dedicated to overthrowing the Ba'ath party. They recruited dissidents, exiles, and Shias to join the Badr Brigade, the military wing of the organisation.
The decision to invade Iraq was taken after much debate within the Iranian government. One faction, comprising Prime Minister Mir-Hossein Mousavi, Foreign Minister Ali Akbar Velayati, President Ali Khamenei, and Army Chief of Staff General Ali Sayad Shirazi, wanted to accept the ceasefire, as most of Iranian soil had been recaptured. In particular, General Shirazi was opposed to the invasion of Iraq on logistical grounds, and stated he would consider resigning if "unqualified people continued to meddle with the conduct of the war." Of the opposing view was a hardline faction led by the clerics on the Supreme Defence Council, whose leader was the politically powerful speaker of the Majlis, Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani.
The most important factor for continuing the war (as Rafsanjani argued) was that despite Iran having foiled Iraq's major territorial ambitions, they still held nearly 3,000 square miles of Iranian territory, areas such as Shalamcheh, Mehran, the Naft Shahr oil fields, and many of the pre-war disputed areas (ex. Shatt al-Arab). In the event of an immediate ceasefire, the Iraqis would remain in those territories and the fear was they wouldn't relinquish those areas, but instead reinforce them for a future invasion. Iran understood that it was internationally isolated and unlikely to receive foreign support to pressure Iraq to withdraw, nor receive compensation, nor get an international condemnation of Iraq, making it unlikely that they could gain an advantageous peace unless they scored a major military victory. While western sources often believe that because Saddam's ceasefire plea of 1982 served as a basis for the 1988 ceasefire, they blame Khomeini's decision for extending the war for the next six years; Iranian sources point out that Saddam's ceasefire plea would have Iraqi troops occupying Iran's border areas and Iran would receive no compensation, nor would Iraq be found guilty for starting the war, while the 1988 UN ceasefire ordered a return to the pre-war borders, and allowed a commission to determine war guilt and compensation, meaning that continuing the war was advantageous for Iran after all (although very bloody and costly).
While many officials wanted to fight the war until total victory, according to a 2003 interview with Rafsanjani (the architect of Iran's strategy against Iraq), Iran's main strategy was to occupy key portions of Iraqi territory to use as bargaining chips to force a diplomatic and political solution to the war (possibly in an international court), primarily getting Iraq to withdraw from the remaining areas of Iranian territory and to accept Iranian rights, have Iraq recognized as the aggressor, and pay compensation. The areas Rafsanjani had in mind were the Al-Faw Peninsula and the major port of Umm Qasr (cutting Iraq off from the sea), isolating and capturing Basra (the second largest city of Iraq), and capturing part of the Tigris River and Highway 8 (Baghdad-Basra Highway), which would effectively split Iraq in two and sever the Iraqi government from their main oil fields in the south. They also wanted to capture Darbandikhan Dam in northern Iraq, which supplied most of Iraq's water. They also hoped that their attacks would ignite a revolt against Saddam's rule by the Shia and Kurdish population of Iraq, possibly resulting in his downfall (or at least forcing him to the negotiation table). They were successful in doing so with the Kurdish population, but not the Shia. Iran had captured large quantities of Iraqi equipment (enough to create several tank battalions, Iran once again had 1,000 tanks) and also managed to clandestinely procure spare parts as well.
At a cabinet meeting in Baghdad, Minister of Health Riyadh Ibrahim Hussein suggested that Saddam could step down temporarily as a way of easing Iran towards a ceasefire, and then afterwards would come back to power. Saddam, annoyed, asked if anyone else in the Cabinet agreed with the Health Minister's idea. When no one raised their hand in support, he escorted Riyadh Hussein to the next room, closed the door and shot him with his pistol. Saddam returned to the room and continued with his meeting.
Iran invades Iraq
Iraqi tactics against Iranian invasion
For most part, Iraq remained on the defensive for the next six years of war, unable and unwilling to launch any major offensives, while Iran launched over 60 offensives against the Iraqis. Iraq's strategy changed from holding territory in Iran to denying Iran any major gains in Iraq (as well as holding onto disputed territories and Iran's border areas). Saddam commenced a policy of total war, gearing most of his country towards defending against Iran. By 1988, Iraq was spending 40–75% of their GDP on military equipment. Saddam had also more than doubled the size of the Iraqi army, from 200,000 soldiers (12 divisions and 3 independent brigades) to 500,000 (23 divisions and nine brigades). They also began launching air raids against Iranian border cities, greatly increasing the practice by 1984. By the end of 1982, Iraq had been resupplied with new Soviet material, and the ground war entered a new phase. Iraq used newly acquired T-55 tanks and T-62 tanks, BM-21 truck-mounted rocket launchers, and Mi-24 helicopter gunships to prepare a Soviet-type three-line defence, replete with obstacles, minefields, and fortified positions. The Combat Engineer Corps built bridges across water obstacles, laid minefields, and prepared new defence lines and fortifications.
Iraq began to focus on using defense in depth to defeat the Iranians. Iraq created multiple static defense lines to bleed the Iranians through sheer size. When faced against large Iranian attack, where human waves would overrun Iraq's entrenched infantry defences, the Iraqis would often retreat, but their static defences would bleed the Iranians and channel them into certain directions, drawing them into a trap. Afterwards, Iraqi air and artillery attacks would pin the Iranians down, while tanks and mechanised infantry attacks using mobile warfare would push them back. Sometimes, the Iraqis would launch "probing attacks" into the Iranian lines to provoke them into launching their attacks sooner. Chemical weapons were used as well, and were a major source of Iranian infantry casualties. While Iranian human wave attacks were successful against the dug in Iraqi forces in Khuzestan, they had trouble breaking through Iraq's defense in depth lines. Iraq had a logistical advantage in their defence: the front was located near the main Iraqi bases and arms depots, allowing their army to be efficiently supplied. By contrast, the front in Iran was a considerable distance away from the main Iranian bases and arms depots, and as such, Iranian troops and supplies had to travel through roads across mountain ranges before arriving at the front.
In addition, Iran's military power was weakened once again by large purges in 1982, resulting from another supposedly attempted coup.
Operation Ramadan (First Battle of Basra)
Main article: Operation RamadanThe Iranian generals wanted to launch an all-out attack on Baghdad and seize it before the weapon shortages continued to manifest further. Instead, that was rejected as being unfeasable, and the decision was made to capture one area of Iraq after the other in the hopes that a series of blows delivered foremost by the Revolutionary Guards Corps would force a political solution to the war (including Iraq withdrawing completely from disputed territories of Iran).
The Iranians planned their attack in southern Iraq, near Basra, the second most important city in Iraq, and the al-Faw peninsula. Called Operation Ramadan, it involved over 180,000 troops from both sides, and was one of the largest land battles since World War II. Iranian strategy dictated that they launch their primary attack on the weakest point of the Iraqi lines; however, the Iraqis were informed of Iran's battle plans and moved all of their forces to the area the Iranians planned to attack. The Iraqis were also were equipped with tear gas to use against the enemy, which would be first major use of chemical warfare during the conflict, throwing an entire attacking division into chaos.
Over 100,000 Revolutionary Guards and Basij volunteer forces charged towards the Iraqi lines. The Iraqi troops had entrenched themselves in formidable defences, and had set up a network of bunkers and artillery positions. The Basij used human waves, and were even used to bodily clear the Iraqi minefields and allow the Revolutionary Guards to advance. Combatants came so close to one another that Iranians were able to board Iraqi tanks and throw grenades inside the hulls. By the eighth day, the Iranians had gained 16 km (9.9 mi) inside Iraq and had taken several bridges. Iran's Revolutionary Guards also used the T-55 tanks they had captured in earlier battles.
However, the attacks came to a halt and the Iranians turned to defensive measures. Seeing this, Iraq used their Mi-25 helicopters, along with French-built Gazelle helicopters armed with Euromissile HOT, against columns of Iranian mechanised infantry and tanks. These "hunter-killer" teams of helicopters, which had been formed with the help of East German advisors, proved to be very costly for Iranians. Aerial dogfights occurred between Iraqi Migs and Iranian F-4 Phantoms.
On 16 July, Iran tried again further north and managed to push the Iraqis back. However, only 13 km (8.1 mi) from Basra, the poorly equipped Iranian forces were surrounded on three sides by Iraqis with heavy weaponry. Some were captured, while many were killed. Only a last-minute attack by Iranian AH-1 Cobra helicopters stopped the Iraqis from routing the Iranians. Three more similar attacks occurred around the Khorramshar-Baghdad road area towards the end of the month, but none were significantly successful. Iraq had concentrated three armoured divisions, the 3rd, 9th, and 10th, as a counter-attack force to attack any penetrations. They were successful in defeating the Iranian breakthroughs, but suffered heavy losses. The 9th Armoured Division in particular had to be disbanded, and was never reformed. 80,000 soldiers from both sides were killed.
Fighting during the rest of 1982
After Iran's defeat in Operation Ramadan, they carried out only a few smaller attacks. Iran launched two limited offensives aimed at liberating the Sumar Hills and isolating the Iraqi pocket at Naft Shahr near the Iraqi border, both of which were Iranian territory still under Iraq occupation. They then aimed to capture the Iraqi border city of Mandali. They planned to take the Iraqis by surprise using Basij militiamen, army helicopters, and some armoured forces, then stretch their defences and possibly break through them to open a road to Baghdad for future exploitation. During Operation Muslim ibn Aqil (1–7 October), Iran recovered 150 km (58 sq mi) of its own territory and reached the outskirts of Mandali before being stopped by Iraqi helicopter and armoured attacks. During Operation Muharram (1–21 November), the Iranians captured part of the Bayat oilfield with their fighter jets and helicopters, destroying 105 Iraqi tanks, 70 APCs, and 7 planes with few losses. They nearly breached the Iraqi lines but failed to capture Mandali after the Iraqis sent reinforcements, including brand new T-72 tanks, which possessed armour that could not be pierced from the front by Iranian TOW missiles. The Iranian advance was also impeded by heavy rains. 3,500 Iraqis and an unknown number of Iranians died, with only minor gains for Iran.
1983–84: Strategic stalemate and war of attrition
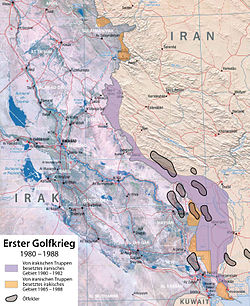
After the failure of the 1982 summer offensives, Iran believed that a major effort along the entire breadth of the front would yield the victory. During the course of 1983, the Iranians launched five major assaults along the front, though none achieved substantial success, as the Iranians staged more massive "human wave" attacks. By this time, it was estimated that more than 70 Iranian fighter aircraft were still operational at any given time; Iran had their own helicopter repair facilities, left over from before the revolution, and thus often used helicopters for close air support. While Iranian fighter pilots had superior training compared to their Iraqi counterparts, and would continue to dominate in combat, due to shortages of aircraft, the size of defended territory and American intelligence supplied to Iraq, the Iraqis could exploit gaps in Iranian airspace. Nevertheless, the Iraqis never were able to gain total air superiority during the war either.
Operation Before the Dawn
Main article: Operation Before the DawnOperation Fajr al-Nasr (Before the Dawn/Dawn of Victory), launched 6 February 1983, saw the Iranians shift focus from the southern to the central and northern sectors. Iran, using 200,000 "last reserve" Revolutionary Guard troops, attacked along a 40 km (25 mi) stretch near al-Amarah, Iraq about 200 km (120 mi) southeast of Baghdad, in an attempt to reach the highways connecting northern and southern Iraq. The attack was stalled by 60 km (37 mi) of hilly escarpments, forests, and river torrents blanketing the way to al-Amarah, but the Iraqis could not force the Iranians back. Iran directed artillery on Basra and Al Amarah, and Mandali.
The Iranians suffered a large number of casualties clearing minefields and breaching Iraqi anti-tank mines, which Iraqi engineers were unable to replace. After this battle, Iran reduced its use of human wave attacks, though they still remained a key tactic as the war went on.
The Mandali–Baghdad northcentral sector also witnessed fighting in April 1983, as Iranian attacks were stopped by Iraqi mechanised and infantry divisions. Casualties were high, and by the end of 1983, an estimated 120,000 Iranians and 60,000 Iraqis had been killed. Iran, however, held the advantage in the war of attrition.
Dawn Operations
Main articles: Operation Dawn 1, Operation Dawn 2, Operation Dawn 3, Operation Dawn 4, Operation Dawn 5, and Operation Dawn 6From early 1983–1984, Iran launched a series of four Valfajr (Dawn) Operations (that eventually numbered to 10). During Operation Dawn-1, in early February 1983, 50,000 Iranian forces attacked westward from Dezful and were confronted by 55,000 Iraqi forces. The Iranian objective was to cut off the road from Basra to Baghdad in the central sector. The Iraqis carried out 150 air sorties against the Iranians, and even bombed Dezful, Ahvaz, and Khorramshahr in retribution. The Iraqi counterattack was broken up by Iran's 92nd Armoured Division.
During Operation Dawn-2, the Iranian's directed insurgency operations by proxy in April 1983 by supporting the Kurds in the north. With Kurdish support, the Iranians attacked on 23 July 1983, capturing the Iraqi town of Haj Omran and maintaining it against an Iraqi poison gas counteroffensive. This operation incited Iraq to later conduct indiscriminate chemical attacks against the Kurds. The Iranians attempted to further exploit activities in the north on 30 July 1983, during Operation Dawn-3. Iran saw an opportunity to sweep away Iraqi forces controlling the roads between the Iranian mountain border towns of Mehran, Dehloran and Elam. Iraq launched airstrikes, and equipped attack helicopters with chemical warheads; while ineffective, it demonstrated both the Iraqi general staff's and Saddam's increasing interest in using chemical weapons. In the end, 17,000 had been killed on both sides, with no gain for either country.
The focus of Operation Dawn-4 in September 1983 was the northern sector in Iranian Kurdistan. Three Iranian regular divisions, the Revolutionary Guard, and Kurdistan Democratic Party (KDP) elements amassed in Marivan and Sardasht in a move to threaten the major Iraqi city Suleimaniyah. Iran's strategy was to press Kurdish tribes to occupy the Banjuin Valley, which was within 45 km (28 mi) of Suleimaniyah and 140 km (87 mi) from the oilfields of Kirkuk. To stem the tide, Iraq deployed Mi-8 attack helicopters equipped with chemical weapons and executed 120 sorties against the Iranian force, which stopped them 15 km (9.3 mi) into Iraqi territory. 5,000 Iranians and 2,500 Iraqis died. Iran gained 110 km (42 sq mi) of its territory back in the north, gained 15 km (5.8 sq mi) of Iraqi land, and captured 1,800 Iraqi prisoners while Iraq abandoned large quantities of valuable weapons and war materiel in the field. Iraq responded to these losses by firing a series of SCUD-B missiles into the cities of Dezful, Masjid Soleiman, and Behbehan. Iran's use of artillery against Basra while the battles in the north raged created multiple fronts, which effectively confused and wore down Iraq.
Iran's change in tactics
Previously, the Iranians had outnumbered the Iraqis on the battlefield, but Iraq expanded their military draft (pursuing a policy of total war), and by 1984, the armies were equal in size. By 1986, Iraq had twice as many soldiers as Iran. By 1988, Iraq would have 1 million soldiers, giving it the fourth largest army in the world. Some of their equipment, such as tanks, outnumbered the Iranians' by almost five to one. Iranian commanders, however, remained more tactically skilled.

After the Dawn Operations, Iran attempted to change tactics. In the face of increasing Iraqi defense in depth, as well as increased armaments and manpower, Iran could no longer rely on simple human wave attacks. Iranian offensives became more complex and involved extensive maneuver warfare using primarily light infantry. Iran launched frequent, and sometimes smaller offensives to slowly gain ground and deplete the Iraqis through attrition. They wanted to drive Iraq into economic failure by wasting money on weapons and war mobilization, and to deplete their smaller population by bleeding them dry, in addition to creating an anti-government insurgency (they were successful in Kurdistan, but not southern Iraq). Iran also kept its goal of capturing important territory to force Iraq to negotiate. Iran also supported their attacks with heavy weaponry when possible and with better planning (although the brunt of the battles still fell to the infantry). The Army and Revolutionary Guards worked together better as their tactics improved. Human wave attacks became less frequent (although still used). To defeat Iraqi defense in depth, static positions, and heavy firepower, Iran began to focus on fighting in areas that the Iraqis could not use their heavy weaponry, such as marshes, valleys, and mountains, and frequently using infiltration tactics.
Iran began training troops in infiltration, patrolling, night-fighting, marsh warfare, and mountain warfare. They also began training thousands of Revolutionary Guard commandos in amphibious warfare, as southern Iraq is marshy and filled with wetlands. Iran used speedboats to cross the marshes and rivers in southern Iraq and landed troops on the opposing banks, where they would dig and set up pontoon bridges across the rivers and wetlands to allow heavy troops and supplies to cross. Iran also learned to integrate foreign guerrilla units as part of their military operations. On the northern front, Iran began working heavily with the Peshmerga, Kurdish guerrillas. Iranian military advisors organised the Kurds into raiding parties of 12 guerrillas, which would attack Iraqi command posts, troop formations, infrastructure (including roads and supply lines), and government buildings. The oil refineries of Kirkuk became a favourite target, and were often hit by homemade Peshmerga rockets.
Battle of the Marshes
Main articles: Battle of the Marshes, Operation Dawn 5, Operation Dawn 6, and Operation KheibarBy 1984, the Iranian ground forces were reorganised well enough for the Revolutionary Guard to start Operation Kheibar (named after Kheibar, Saudi Arabia), which lasted from 24 February to 19 March. On 15 February 1984, the Iranians began launching attacks against the central section of the front, where the Second Iraqi Army Corps was deployed: 250,000 Iraqis faced 250,000 Iranians. The goal of this new major offensive was the capture of Basra-Baghdad Highway, cutting off of Basra from Baghdad and setting the stage for an eventual attack upon the city (one of Iran's major goals to force Iraq to negotiate). The Iraqi high command had assumed the marshlands above Basra were natural barriers to attack, and had not reinforced them. The marshes negated Iraqi advantage in armor, and absorbed artillery and bombs.
Prior to the attack, Iranian commandos on helicopters had landed behind Iraqi lines and destroyed Iraqi artillery. Iran launched two preliminary attacks prior to the main offensive, Operation Dawn 5 and Dawn 6. They saw the Iranians attempting to capture Kut al-Imara, Iraq and sever the highway connecting Baghdad to Basra, which would impede Iraqi coordination of supplies and defences. Iranian troops crossed the river on motorboats in a surprise attack, though only came within 24 km (15 mi) of the highway.
Operation Kheibar began on 24 February with Iranian infantrymen crossing the Hawizeh Marshes using motorboats and transport helicopters in an amphibious assault. The Iranians attacked the vital oil-producing Majnoon Island by landing troops via helicopters onto the islands and severing the communication lines between Amareh and Basra. They then continued the attack towards Qurna. By 27 February, they had captured the island, though they lost 50 troop transport helicopters in one day. At times, fighting took place in waters over 2 m (6.6 ft) deep. Iraq ran live electrical cables through the water, electrocuting numerous Iranian troops and then displaying their corpses on state television.
By 29 February, the Iranians had reached the outskirts of Qurna and were closing in on the Baghdad–Basra highway. They had broken out of the marshes and returned to open terrain, where they were confronted by conventional Iraqi weapons, including artillery, tanks, air power, and mustard gas. 1,200 Iranian soldiers were killed in the counter-attack. The Iranians retreated back to the marshes, though they still held onto them along with Majnoon Island.
The Battle of the Marshes saw an Iraqi defence that had been under continuous strain since 15 February; they were relieved by their use of chemical weapons and defence-in-depth, where they layered defensive lines: even if the Iranians broke through the first line, they were usually unable to break through the second due to exhaustion and heavy losses. They also largely relied on Mi-25 Hind to "hunt" the Iranian troops in the marshes, and at least 20,000 Iranians were killed in the marsh battles. Iran used the marshes as a springboard for future attacks/infiltrations.
The "Tanker War" and the "War of the Cities"

Unable to launch successful ground attacks against Iran, Iraq used their now expanded air force to carry out strategic bombing against Iranian shipping, economic targets, and cities in order to damage Iran's economy and morale. Iraq also wanted to provoke Iran into doing something that would cause the superpowers to be directly involved in the conflict on the Iraqi side.
Attacks on shipping
Further information: Operation Earnest Will and Operation Prime ChanceThe so-called "Tanker War" started when Iraq attacked the oil terminal and oil tankers at Kharg Island in early 1984. Saddam's aim in attacking Iranian shipping was to provoke the Iranians to retaliate with extreme measures, such as closing the Strait of Hormuz to all maritime traffic, thereby bringing American intervention: the United States had threatened several times to intervene if the Strait of Hormuz were closed. As such, the Iranians limited their retaliatory attacks to Iraqi shipping, leaving the strait open to general passage.
Iraq declared that all ships going to or from Iranian ports in the northern zone of the Persian Gulf were subject to attack. They used air power, primarily helicopters, F-1 Mirage, and MiG-23 fighters armed with Exocet anti-ship missiles, to enforce their threats. Iraq began to repeatedly bomb Iran's main oil export facility on Khark Island, causing increasingly heavy damage. After these attacks, Iran attacked a Kuwaiti tanker carrying Iraqi oil near Bahrain on 13 May 1984, as well as a Saudi tanker in Saudi waters on 16 May. Because Iraq had become landlocked during the invasion, they had to rely on their Arab allies, primarily Kuwait, to transport their oil. Iran attacked tankers carrying Iraqi oil from Kuwait, later attacking tankers from any Persian Gulf state supporting Iraq. Attacks on ships of noncombatant nations in the Persian Gulf sharply increased thereafter, with both nations attacking oil tankers and merchant ships of neutral nations in an effort to deprive their opponent of trade. The Iranian attacks against Saudi shipping led to Saudi F-15s shooting down an Iranian aircraft on 5 June 1984.
The air and small-boat attacks, however, did little damage to Persian Gulf state economies, and Iran moved its shipping port to Larak Island in the Strait of Hormuz.
The Iranian Navy imposed a naval blockade of Iraq, using its British-built frigates to stop and inspect any ships thought to be trading with Iraq. They operated with virtual impunity, as Iraqi pilots had little training in hitting naval targets. Some Iranian warships attacked tankers with ship-to-ship missiles, while others used their radars to guide land-based anti-ship missiles to their targets. Iran began to rely on its new Revolutionary Guard's navy, which used Boghammar speedboats: fitted with rocket launchers, RPGs, and heavy machine guns, these speedboats would launch surprise attacks against tankers and cause substantial damage. Iran also used aircraft and helicopters to launch Maverick missiles and unguided rockets at tankers.
A U.S. Navy ship, the Stark, was struck on 17 May 1987 by two Exocet anti-ship missiles fired from an Iraqi F-1 Mirage plane. The missiles had been at about the time the plane was given a routine radio warning by the Stark. The frigate did not detect the missiles with radar, and warning was given by the lookout only moments before they struck. Both missiles hit the ship, and one exploded in crew quarters, killing 37 sailors and wounding 21.
Lloyd's of London, a British insurance market, estimated that the Tanker War damaged 546 commercial vessels and killed about 430 civilian sailors. The largest portion of the attacks was directed by Iraq against vessels in Iranian waters, with the Iraqis launching three times as many attacks as the Iranians. But Iranian speedboat attacks on Kuwaiti shipping led Kuwait to formally petition foreign powers on 1 November 1986 to protect its shipping. The Soviet Union agreed to charter tankers starting in 1987, and the United States Navy offered to provide protection for foreign tankers reflagged and flying the U.S. flag starting 7 March 1987 in Operation Earnest Will. Neutral tankers shipping to Iran were unsurprisingly not protected by Earnest Will, resulting in reduced foreign tanker traffic to Iran, since they risked Iraqi air attack. Iran accused the US of helping Iraq.
During the course of the war, Iran attacked two Soviet Navy ships which were protecting Kuwaiti tankers. Notably, the Seawise Giant, the largest ship ever built, was struck and damaged by Iraqi Exocet missiles as it was carrying Iranian crude oil out of the Gulf.
Attacks on cities
Meanwhile, Iraq's air force also began carrying out strategic bombing raids against Iranian cities. While Iraq had launched numerous attacks with aircraft and missiles against border cities from the beginning of the war and sporadic raids on Iran's main cities, this was the first systematic strategic bombing that Iraq carried out during the war. This would become known as the "War of the Cities". Iraq's air force had been largely defeated by the Iranian air force during 1980-1981, but with the help of the USSR and the west, Iraq's air force had been rebuilt and expanded. Meanwhile Iran, due to sanctions and lack of spare parts, had heavily curtailed their air force operations. While the Iranian aircrews were better trained and superior in combat, the Iraqis were facing fewer fighters and supported by American reconnaissance and were able to exploit gaps in Iranian airspace to launch their attacks. Iraq used Tu-22 Blinders and Tu-16 Badger strategic bombers to carry out long-range high-speed raids on Iranian cities (using both Iraqi and Soviet pilots), including Tehran. Fighter-bombers such as the Mig-25 Foxbat and Su-22 Fitter were used against smaller or shorter range targets, as well as escorting the strategic bombers. Civilian and industrial targets were hit by the raids, and each successful raid was designed to sap Iranian morale and will to fight via terror bombing, as well as inflicting economic damage from regular strategic bombing.

In response, the Iranians deployed their F-4 Phantoms to combat the Iraqis, and eventually they deployed F-14s as well. Most of the Iraqi air raids were intercepted by the Iranian fighter jets and air defense, but some also successfully hit their targets, becoming a major headache for Iran. By 1986, Iran also expanded their air defense network heavily to take the load of the fighting off the air force. The Iraqis continuously took heavy losses as well, and failed to inflict major damage. The Iraqi/Soviet pilots were advised to abort their attacks as soon as Iranian F-4s and F-14s appeared in order to prevent almost certain losses, thus many successful Iranian interceptions were carried out without any dogfighting. By later in the war, Iraqi raids primarily consisted of indiscriminate missile attacks while air attacks were used only on fewer, more important targets. Starting in 1987, Saddam also ordered several chemical attacks on civilian targets in Iran, such as the town of Sardasht.
Iran also launched several retaliatory air raids on Iraq, while primarily shelling border cities such as Basra. Iran also bought some Scud missiles from Libya, and launched them against Baghdad. These too inflicted damage upon Iraq.
On 7 February 1984, (during the first war of the cities) Saddam ordered his air force to attack eleven Iranian cities; bombardments ceased on 22 February 1984. Though Saddam had aimed for the attacks to demoralise Iran and force them to negotiate, they had little effect, and Iran quickly repaired the damage. Iraq's air force took heavy losses, however, and Iran struck back, hitting Baghdad and other Iraqi cities. Nevertheless, the attacks resulted in tens of thousands of civilian casualties on both sides, and became known as the first "war of the cities". It was estimated that 1,200 Iranian civilians were killed during the raids in February alone. There would be five such major exchanges throughout the course of the war, and multiple minor ones. While interior cities such as Tehran did receive numerous raids, it was the cities of western Iran that suffered the most death and destruction.
Strategic situation in 1984
By 1984, Iran's losses were estimated to be 300,000 soldiers, while Iraq's losses were estimated to be 250,000. Foreign analysts agreed that both Iran and Iraq failed to use their modern equipment properly, and both sides failed to carry out modern military assaults that could win the war. Both sides also abandoned equipment in the battlefield because their technicians were unable to carry out repairs. Iran and Iraq showed little internal coordination on the battlefield, and in many cases units were left to fight on their own. As a result, by the end of 1984, the war was a stalemate.
One limited offensive Iran launched (Dawn 7) took place from 18–25 October 1984, when they recaptured the Iranian city of Mehran, which had been occupied by the Iraqis from the beginning of the war.
1985–86: Offensives and retreats
By 1985, Iraqi armed forces were receiving financial support from Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and other Persian Gulf states, and were making substantial arms purchases from the Soviet Union, China, and France. For the first time since early 1980, Saddam launched new offensives.
On 6 January 1986, the Iraqis launched an offensive attempting to retake Majnoon Island. However, they were quickly bogged down into a stalemate against 200,000 Iranian infantrymen, reinforced by amphibious divisions. However, they managed to gain a foothold in the southern part of the island.
Iraq also carried out another "war of the cities" between 12–14 March, hitting up to 158 targets in over 30 towns and cities, including Tehran. Iran responded by launching 14 Scud missiles for the first time, purchased from Libya. More Iraqi air attacks were carried out in August, resulting in hundreds of additional civilian casualties. Iraqi attacks against both Iranian and neutral oil tankers in Iranian waters continued, with Iraq carrying out 150 airstrikes using French bought Super Etendard jets using Exocet missiles.
Operation Badr
Main article: Operation Badr (1985)The Iraqis attacked again on 28 January 1985; they were defeated, and the Iranians retaliated on 11 March 1985 with a major offensive directed against the Baghdad-Basra highway (one of the few major offensives conducted in 1985), codenamed Operation Badr (after the Battle of Badr, Muhammad's first military victory in Mecca). Ayatollah Khomeini urged Iranians on, declaring:
It is our belief that Saddam wishes to return Islam to blasphemy and polytheism...if America becomes victorious...and grants victory to Saddam, Islam will receive such a blow that it will not be able to raise its head for a long time...The issue is one of Islam versus blasphemy, and not of Iran versus Iraq.
This operation was similar to Operation Kheibar, though it invoked more planning. Iran used 100,000 troops, with 60,000 more in reserve. They assessed the marshy terrain, plotted points where they could land tanks, and constructed pontoon bridges across the marshes. The Basij forces were also equipped with anti-tank weapons.
The ferocity of the Iranian offensive broke through the Iraqi lines. The Revolutionary Guard, with the support of tanks and artillery, broke through the north of Qurna on 14 March. That same night 3,000 Iranian troops reached and crossed the Tigris River using pontoon bridges and captured part of the Baghdad–Basra Highway 8, which they had failed to achieve in Operations Dawn 5 and 6 .
Saddam responded by launching chemical attacks against the Iranian positions along the highway and by initiating the aforementioned second "war of the cities", with an air and missile campaign against twenty to thirty Iranian population centres, including Tehran. Under General Sultan Hashim Ahmad al-Tai and General Jamal Zanoun (both considered to be among Iraq's the most skilled commanders), the Iraqis launched air attacks against the Iranian positions and pinned them down. They then launched a pincer attack using mobile infantry and heavy artillery. Chemical weapons were used, and the Iraqis also flooded Iranian trenches with specially-constructed pipes delivering water from the Tigris River.
The Iranians retreated back to the Hoveyzeh marshes while being attacked by helicopters, and the highway was recaptured by the Iraqis. Operation Badr resulted in 10,000–12,000 Iraqi casualties and 15,000 Iranian ones.
Strategic situation at the beginning of 1986
The failure of the human wave attacks in earlier years had prompted Iran to develop a better working relationship between the Army and the Revolutionary Guard and to mould the Revolutionary Guard units into a more conventional fighting force. To combat Iraq's use of chemical weapons, Iran began producing an antidote. They also created and fielded their own homemade drones, the Mohajer 1's, fitted with six RPG-7's to launch attacks. They were primarily used in observation, being used for up to 700 sorties.
For the rest of 1986, and until the spring of 1988, the Iranian Air Force's efficiency in air defence increased, with weapons being repaired or replaced and new tactical methods being used. For example, the Iranians would loosely integrate their SAM sites and interceptors to create "killing fields" in which dozens of Iraqi planes were lost (which was reported in the West as the Iranian Air Force using F-14s as "mini-AWACs"). The Iraqi Air Force reacted by increasing the sophistication of its equipment, incorporating modern electronic countermeasure pods, chaff, and anti-radiation missiles. Due to the heavy losses in the last war of the cities, Iraq reduced their use of aerial attacks on Iranian cities. Instead, they would launch Scud missiles, which the Iranians could not stop. Since the range of the Scud missile was too short to reach Tehran, they converted them to al-Hussein missiles with the help of East German engineers, cutting up their Scuds into three chunks and attaching them together. Iran responded to these attacks by using their own Scud missiles. Iranian attacks were fewer, and meant primarily to deter the Iraqis from launching their air/missile strikes.
Aside from extensive foreign help to Iraq, Iranian attacks were severely hampered by their shortages of weaponry, including heavy weaponry. Large portions of them had been lost during the last several years. Iran still managed to maintain 1,000 tanks (often by capturing Iraqi ones) and additional artillery, but many needed repairs to be operational. But by this time Iran managed to procure spare parts from various sources, helping them to restore some weapons. They secretly imported some weapons, such as RBS-70 anti-aircraft MANPADS. In an exception to the US's support for Iraq, in exchange for Iran using its influence to help free western hostages in Lebanon, the US secretly sold Iran some limited supplies (in the Ayatollah Rafsanjani's postwar interview, he stated that during the period when Iran was succeeding, for a short time the US supported Iran, then shortly after began helping Iraq again). Iran managed to get some light weapons, such as anti-tank TOW missiles, which worked better than rocket-propelled grenades. Iran later reverse-engineered and produced those weapons on their own as well. All of these almost certainly helped increase the effectiveness of Iran, although it did not reduce the human cost of their attacks.
First Battle of al-Faw
Main articles: First Battle of al-Faw and Operation Dawn 8On 9 February 1986, the Iranians launched Operation Dawn 8, in which 30,000 troops comprising five Army divisions and men from the Revolutionary Guard and the Basij advanced in a two-pronged offensive to capture the al-Faw peninsula in southern Iraq, the only area touching the Persian Gulf. The capture of Al Faw and Umm Qasr was a major goal for Iran to force Iraq to negotiate a favorable settlement. Iran began with a feint attack against Basra, which was stopped by the Iraqis; Meanwhile, an amphibious strike force landed at the foot of the peninsula. The resistance, consisting of several thousand poorly trained soldiers of the Iraqi Popular Army, fled or were defeated, and the Iranian forces set up pontoon bridges crossing the Shatt al-Arab, allowing 30,000 soldiers to cross in a short period of time. They drove north along the peninsula almost unopposed, capturing it after only 24 hours of fighting. Afterwards they dug in and set up defenses.
The sudden capture of al-Faw took the Iraqis by shock, since they had thought it impossible for the Iranians to cross the Shatt al-Arab. On 12 February 1986, the Iraqis began a counter-offensive to retake al-Faw, which failed after a week of heavy fighting. On 24 February 1986, Saddam sent one of his best commanders, General Maher Abd al-Rashid, and the Republican Guard to begin a new offensive to recapture al-Faw. A new round of heavy fighting took place, However, their attempts again ended in failure, costing them many tanks and aircraft: their 15th mechanised division was almost completely wiped out. The capture of al-Faw and the failure of the Iraqi counter-offensives were blows to the Ba'ath regime's prestige, and led the Gulf countries to fear that Iran might win the war. Kuwait in particular felt menaced with Iranian troops only 16 km (9.9 mi) away, and increased its support of Iraq accordingly.
In March 1986, the Iranians tried to follow up their success by attempting to take Umm Qasr, which would have completely severed Iraq from the Gulf and placed Iranian troops on the border with Kuwait, which was a major Iranian goal in forcing Iraq into negotiations. However, the offensive failed due to Iranian shortages of armor. By this time, 10,000 Iraqis and 30,000 Iranians were casualties. The First Battle of al-Faw ended in March, but heavy combat operations lasted on the peninsula into 1988, with neither side being able to displace the other. The battle bogged down into a World War I-style stalemate in the marshes of the peninsula. 53,000 Iraq troops and an unknown number of Iranian troops were killed.
Battle of Mehran
Main article: Battle of MehranImmediately after the Iranian capture of al-Faw, Saddam declared a new offensive against Iran, designed to drive deep into the state. The Iranian border city of Mehran, on the foot of the Zagros Mountains, was selected as the first target. On 15–19 May, Iraqi Army's Second Corps, supported by helicopter gunships, attacked and captured the city. Saddam then offered the Iranians to exchange Mehran for al-Faw. The Iranians rejected the offer. Iraq then continued the attack, attempting to push deeper into Iran. However, Iraq's attack was quickly warded off by Iranian AH-1 Cobra helicopters with TOW missiles, which destroyed numerous Iraqi tanks and vehicles.
The Iranians built up their forces on the heights surrounding Mehran. On 30 June, using mountain warfare tactics they launched their attack, recapturing the city by 3 July. Saddam ordered the Republican Guard to retake the city on 4 July, but their attack was ineffective. Iraqi losses were heavy enough to allow the Iranians to also capture territory inside Iraq, and depeleted the Iraqi military enough to prevent them from launching a major offensive for the next two years. Iraq's defeats at al-Faw and at Mehran were severe blows to the prestige of the Iraqi regime, and western powers, including the U.S., became more determined to prevent an Iraqi loss.
Strategic situation at the end of 1986
Through the eyes of international observers, Iran was prevailing in the war by the end of 1986. In the northern front, the Iranians began launching attacks toward the city of Suleimaniya with the help of Kurdish fighters, taking the Iraqis by surprise. They came within 16 km (9.9 mi) of the city before being stopped by chemical and army attacks. Iran's army had also reached the Meimak Hills, only 113 km (70 mi) from Baghdad. Iraq managed to contain Iran's offensives in the south, but was under serious pressure, as the Iranians were slowly overwhelming them.
Iraq responded by launching another "war of the cities". In one attack, Tehran's main oil refinery was hit, and in another instance, Iraq damaged Iran's Assadabad satellite dish, disrupting Iranian overseas telephone and telex service for almost two weeks. Civilian areas were also hit, resulting in many casualties. Iraq continued to attack oil tankers via air. Iran responded by launching Scud missiles and air attacks at Iraqi targets.
Iraq continued to attack Kharg Island and the oil tankers and facilties as well. Iran created a tanker shuttle service of 20 tankers to move oil from Kharg to Larak Island, escorted by Iranian fighter jets. Once moved to Larak, the oil would be moved to ocean going tankers (usually neutral). They also rebuilt the oil terminals damaged by Iraqi air raids and moved shipping to Larak Island, while attacking foreign tankers that carried Iraqi oil (as Iran had blocked Iraq's access to the open sea with the capture of al-Faw). By now they almost always used the armed speedboats of the IRGC navy, and attacked many tankers. The tanker war escalated drastically, with attacks nearly doubling in 1986 (the majority carried out by Iraq). Iraq got permission from the Saudi government to use its airspace to attack Larak Island, although due to the distance attacks were less frequent there. The escalating tanker war in the Gulf became an ever increasing concern to foreign powers, especially the United States.
In April 1986, Ayatollah Khomeini issued a fatwa declaring that the war must be won by March 1987. The Iranians increased recruitment efforts, obtaining 650,000 volunteers. The animosity between the Army and the Revolutionary Guard arose again, with the Army wanting to use more refined, limited military attacks while the Revolutionary Guard wanted to carry out major offensives. Iran, confident in its successes, began planning their largest offensives of the war, which they called their "final offensives."
Iraq's Dynamic Defense Strategy
Faced with their recent defeats in al-Faw and Mehran, Iraq appeared to be losing the war. Iraq's generals, angered by Saddam's interference, threatened a full-scale mutiny against the Ba'ath Party unless they were allowed to conduct operations freely. In one of the few times during his career, Saddam gave in to the demands of his generals. Up to this point, Iraqi strategy was to ride out Iranian attacks. However, the defeat at al-Faw led Saddam to declare the war to be Al-Defa al Mutahharakkha (The Dynamic Defense), and announcing that all civilians had to take part in the war effort. The universities were closed and all of the male students were drafted into the military. Civilians were instructed to clear marshlands to prevent Iranian amphibious infiltrations and to help build fixed defenses.
The government tried to integrate the Shias into the war effort by recruiting many as part of the Ba'ath Party. In an attempt to counterbalance the religious fervor of the Iranians and gain support from the devout masses, the regime also began to promote religion and, on the surface, Islamization, despite the fact that Iraq was run by a socialist regime. Scenes of Saddam praying and making pilgrimages to shrines became common on state-run television. While Iraqi morale had been low throughout the war, the attack on al-Faw raised patriotic fervor, as the Iraqis feared invasion. Saddam also recruited volunteers from other Arab countries into the Republican Guard, and received much technical support from foreign nations as well. While Iraqi military power had been depleted in recent battles, through heavy foreign purchases and support, they were able to expand their military even to much larger proportions by 1988.
At the same time, Saddam ordered the genocidal al-Anfal Campaign in an attempt to crush the Kurdish resistance, who were now allied with the Iranians. The result was the deaths of several hundred thousand Iraqi Kurds, and the destruction of villages, towns, and cities.
Iraq began to try to perfect their maneuver tactics. The Iraqis began to prioritize the professionalization of their military. Prior to 1986, the conscription-based Iraqi regular army and the volunteer-based Iraqi Popular Army conducted to bulk of the operations in the war, to little effect. The Republican Guard, formerly an elite praetorian guard, was expanded as a volunteer army and filled with Iraq's best generals. Loyalty to the state was no longer a primary requisite for joining. However, due to Saddam's paranoia, the former duties of the Republican Guard were transferred to a new unit, the Special Republican Guard. Full-scale war games against hypothetical Iranian positions were carried out in the western Iraqi desert against mock targets, and they were repeated over the course of a full year until the forces involved fully memorized their attacks. Iraq built its military massively, eventually possessing the 5th largest in the world, in order to overwhelm the Iranians through sheer size.
1987–88: Towards a ceasefire

Meanwhile, as the Iraqis were planning their strike, the Iranians continued to attack. 1987 saw a renewed series of major Iranian human wave offensives in both northern and southern Iraq. The Iraqis had constructed heavy static fortifications around the city. They built 5 defensive rings, supported by natural waterways such as the Shatt-al-Arab, and manmade ones, such as Fish Lake and the Jasim River, along with manmade earth barriers. Fish Lake was a massive lake filled with mines, underwater barbed wire, electrodes and various sensors. In addition, behind each waterway and defensive line was radar-guided artillery, ground attack aircraft, and combat helicopters; all capable of firing poison gas in addition to conventional munitions.
Iran's strategy was to penetrate through these massive defensive lines, and encircle Basra, cutting off the city as well as the Al-Faw peninsula from the rest of Iraq. The Iranians hoped that the capture of Basra would be such a major blow to Iraq that they would be forced to negotiate a settlement favorable to Iran and withdraw their troops from Iran, and negotiate a favorable settlement. Iran's plan was for three assaults: a diversionary attack near Basra, the main offensive, and another diversionary attack using Iranian armor in the north to have Iraqi heavy armor diverted away from Basra. For these battles, Iran had re-expanded their military by recruiting many new Basij and Pasdaran volunteers. Iran brought 150,000–200,000 total troops into the battles.
Karbala Operations
Operation Karbala-4
Main article: Operation Karbala-4On 25 December 1986, Iran launched Operation Karbala-4 (Karbala referring to Hussein ibn Ali's Battle of Karbala). According to General Ra'ad al-Hamdani, this was a diversionary attack. The Iranians launched an amphibious assault against Umm al-Rassas island in the marshes towards Basra; they then set up a pontoon bridge and continued the attack, eventually capturing it after taking many casualties and failing to advance further; they had taken 60,000 casualties, while the Iraqis took 9,500. The Iraqi commanders exaggerated Iran's losses to Saddam, and it was assumed that the main Iranian attack on Basra had been fully defeated and that the Iranians were depleted for six months. Therefore, when the main Iranian attack, Operation Karbala 5 began, many Iraqi troops had gone on leave.
Operation Karbala-5 (Second Battle of Basra)
Main article: Operation Karbala-5Operation Karbala-5 began midnight 8 January 1987, when a strike force of 35,000 Pasdaran crossed Fish Lake, while 4 Iranian divisions attacked at the southern end shore of the lake, overrunning the Iraqi forces and capturing the town of Duaiji. They used their bridgehead at Duaiji as a springboard to recapture the Iranian town of Shalamcheh. Between 9–10 January, the Iranians broke through the first and second defense lines of Basra at the north of Fish Lake with tanks. The Iranians rapidly reinforced their forces with 60,000 troops and began to clear the remaining Iraqis in the area.
As early as 9 January, the Iraqis began their counterattack, supported by newer Su-25 and Mig-29 aircraft, by the 10th the Iraqis were throwing every available heavy weapon in a bid to eject the Iranians. Despite being outnumbered 10–1 in the air, Iran's air defense system downed many Iraqi aircraft (50–60 jets total; 10% of Iraq's air force), allowing Iran to provide close air support with their smaller air force, which also proved superior in dog-fighting, causing the Iraqis to temporarily stop providing their troops air support. Iraqi tanks floundered in the marshland and were defeated by Cobra helicopters and TOW missile-equipped anti-tank commandos. Later in the battle, after their ground forces taking heavy losses due to the lack of air support, the Iraqi aircraft came back to the battlefield once again, facing their Iranian counterparts.
However, despite superior Iranian infantry tactics, it was the sheer size of the Iraqi defensive lines that prevented the Iranians from achieving a victory. On 19–24 January, Iran launched another major infantry offensive, breaking the third line and driving the Iraqis across the Jasim river. The battle became a contest of which side could bring more reinforcements. By 29 January, the Iranians launched a new attack from the west of the Jasim river, breaking through the fourth line. They were within 12 km (7.5 mi) of the city. At this point, the battle became a stalemate. Iranian TV broadcast footage of the outskirts of Basra, but the Iranians pushed no further. Iranian losses were so severe that Iraq took the offensive and pushed them back to their original positions. Despite that, the fighting continued, and 30,000 Iranians still held positions around Fish Lake. The battle bogged down into a trench war, where neither side could displace the other. Iran launched several more unsuccessful attacks. Karbala-5 officially ended by the end of February, but heavy combat operations continued, and Iran continued to besiege the city.
Among those killed was Iranian commander Hossein Kharrazi. Possibly 65,000 Iranians and 40,000 Iraqis were casualties because of Operation Karbala-5. Basra was largely destroyed, and Iraq's army had taken many material losses. The fighting during this operation was the heaviest and bloodiest during the war, with the area around Shalamcheh becoming known as the "Somme of the Iran-Iraq War". At one point, the situation had declined to the point that Saddam ordered several of his officers to be executed. With Iranian aircraft fighting at Basra, the Iraqis bombed Iranian supply routes with chemical weapons, as well as Iranian cities with conventional bombs, including Tehran, Isfahan, and Qom. It is believed that around 3,000 Iranian civilians were killed in these attacks. Iran retaliated by firing eleven long-range missiles further into Iraqi territory, inflicting heavy casualties among civilians and killing at least 300.
Operation Karbala-6
Main article: Operation Karbala-6At the same time as Operation Karbala 5, Iran also launched Operation Karbala-6 against the Iraqis in Qasr-e Shirin in central Iran to prevent the Iraqis from rapidly transferring units down to defend against the Karbala-5 attack. The attack was carried out by Basij infantry and the Revolutionary Guard's 31st Ashura and the Army's 77th Khorasan armored divisions. The Basij attacked the Iraqi lines, forcing the Iraqi infantry to retreat. An Iraqi armored counter-attack surrounded the Basij in a pincer movement, but the Iranian tank divisions attacked, breaking the encirclement. The Iranian attack was finally stopped by mass Iraqi chemical weapons attacks.
Iran's increasing war-weariness

Operation Karbala-5 was a severe blow to Iran's military and morale. To foreign observers, it appeared that Iran continuing to strengthen. By 1988, Iran had become self-sufficient in many areas, such as anti-tank TOW missiles, Scud ballistic missiles (Shahab-1), Silkworm anti-ship missiles, Oghab tactical rockets, and producing spare parts for their weaponry. Iran had also beefed up their air defenses with smuggled surface to air missiles. Iran even was producing UAV's and the Pilatus PC-7 propellor aircraft for observation. Iran also doubled their stocks of artillery, and was self-sufficient in manufacture of ammunition and small arms. Had those weapons been available during Operation Karbala-5, it is likely that the Iranians would have broken through the last defense line.
But, while it was not obvious to foreign observers, the Iranian public had become increasingly war-weary and disillusioned with the fighting, and relatively few volunteers joined the fight in 1987–88. Because the Iranian war effort relied on popular mobilization, their military strength actually declined, and Iran was unable to launch any major offensives after Karbala-5. As a result, for the first time since 1982, the momentum of the fighting shifted towards the regular army. Since the regular army was conscription based, it made the war even less popular. Many Iranians began to try to escape the conflict. As early as May 1985, anti-war demonstrations took place in 74 cities throughout Iran; however, they were crushed by the regime, resulting in some protesters being shot and killed. By 1987, draft-dodging had become a serious problem, and the Revolutionary Guards and police set up roadblocks throughout cities to capture those who tried to evade conscription. However, other people (including the more nationalistic and religious) as well as the clergy, the Revolutionary Guards, and the regular army wanted to continue the war to achieve their goals. The issue of Iranian border territory in Iraqi hands still was a major motivating factor.
The leadership acknowledged that the war was a stalemate, and began to plan accordingly. There were no more "final offensives" planned. The head of the Supreme Defense Council Hashemi Rafsanjani announced during a news conference to finally end the use of human wave attacks. Mohsen Rezaee, head of the IRGC, announced that Iran would focus exclusively on limited attacks/infiltrations, while arming and supporting opposition groups inside of Iraq (such as the Kurds and Badr Brigade).
On the Iranian home front, the combination of sanctions, declining oil prices, and Iraqi attacks on Iranian oil facilities and shipping took a heavy toll on the economy. While the attacks themselves were not as destructive as some analysts believed, the US-led Operation Earnest Will (which protected Iraqi and allied oil tankers, but not Iranian ones) led many neutral countries to stop trading with Iran because of rising insurance and fear of air attack. Iranian oil and non-oil exports fell by 55%, inflation reached 50% by 1987, and the unemployment rate skyrocketed. At the same time, Iraq was experiencing crushing debt and shortages of workers, encouraging its leadership to try to end the war quicker.
Strategic Situation in late 1987
Main articles: Operation Nimble Archer, Operation Nasr 4, and Operation Karbala 10By the end of 1987, Iraq possessed 5,550 tanks (outnumbering the Iranians five to one) and 900 fighter aircraft (outnumbering the Iranians ten to one). However, after Operation Karbala-5, Iraq only had 100 qualified fighter pilots remaining; therefore, Iraq began to invest in recruiting foreign pilots from countries such as Belgium, Australia, South Africa, both East and West Germany, and the Soviet Union. They replenished their manpower by integrating volunteers from other Arab countries into their army (for example, Iran eventually captured 3,000 Egyptian soldiers). Iraq also became self-sufficient in chemical weapons and some conventional ones and received much equipment from abroad. Foreign support helped Iraq bypass its economic troubles and massive debt to continue the war and increase the size of its military. The United States drew up a contingency plan to attack if the Iranians managed to break through the Iraqi lines.

While the southern and central fronts were at a stalemate, Iran began to focus on carrying out offensives in northern Iraq with the help of the Peshmerga (Kurdish insurgents). The capture of Iraq northern oil fields, and dams remained an important goal for Iran to force Iraq to negotiate, and with the help of the Peshmerga, there was a good chance it could succeed. The Iranians used a combination of semi-guerrilla and infiltration tactics in the Kurdish mountains with the Peshmerga. During Operation Karbala-9 in early April, Iran captured territory near Suleimaniya, provoking a severe poison gas counterattack. During Operation Karbala-10, Iran attacked near the same area, capturing more territory. During Operation Nasr-4, the Iranians surrounded the city of Suleimaniya, and with the help of the Peshmerga infiltrated over 140 kilometers into Iraq and raided and threatened to capture the oil-rich city of Kirkuk and other northern oilfields. Nasr-4 was considered to be Iran's most successful individual operation of the war. However, Iranian forces were unable to consolidate their gains and continue their advance, and while these offensives coupled with the Kurdish uprising sapped Iraqi strength, losses in the north would not mean a catastrophic failure for Iraq.
On 20 July, the UN Security Council passed the US-sponsored Resolution 598, which called for an end to the fighting and a return to pre-war boundaries. This resolution was noted by Iran for being the first resolution to call for a return to the pre-war borders, and setting up a commission to determine the aggressor and compensation. This was in contrast to previous settlements that only allowed a ceasefire (leaving Iraq in possession of disputed Iranian territories). The head of the IRGC, Mohsen Rezaee believed that it was a direct result of the capture of Al-Faw and Iran began to consider the ceasefire. While Iraq accepted the resolution, according to Iran's then foreign minister Ali Akbar Velayati, Iraq refused to set a timetable for withdrawing their troops from Iran, and thus Iran did not adopt the ceasefire yet, although they seriously considered it. The resolution was very ambiguous as well. Velayati stated that as a result, the western nations claimed that it was Iran that refused to accept peace.
Air and Tanker War in 1987
With the stalemate on land, the air/tanker war began to play an increasingly major role in the conflict.
The Iranian air force had become very small, containing only 20 F-4 Phantoms, 20 F-5 Tigers, and 15 F-14 Tomcats in operation. Despite that, Iran managed to restore some damaged planes into service. The Iranian Air force, despite its once sophisticated equipment, lacked enough equipment and personnel to sustain the war of attrition that had arisen, and was unable to lead an outright onslaught against Iraq. The Iraqi Air Force, however, had originally lacked modern equipment and experienced pilots, but after pleads from Iraqi military leaders, Saddam decreased political influence on everyday operations and left the fighting to his combatants. In addition, the Soviets began delivering more advanced aircraft and weapons to Iraq, while the French improved training for flying crews and technical personnel and continually introduced new methods for countering Iranian weapons and tactics. However, at the same time, Iran's ground air defense downed many Iraqi aircraft.
The main Iraqi air effort had shifted to the destruction of Iranian war-fighting capability (primarily Persian Gulf oil fields, tankers, and Kharg Island), and starting late 1986 the Iraqi Air Force moved on a comprehensive campaign against the Iranian economic infrastructure. By late 1987, the Iraqi Air Force could count on direct American support for conducting long-range operations against Iranian infrastructural targets and oil installations deep in the Persian Gulf. U.S. Navy ships actively tracked and reported movements of Iranian shipping and defences. They supplied targeting information on several occasions in February and March 1988; when they failed to warn Iraqi aircraft of Iranian interceptors' presence, the Iraqis suffered considerable losses. The massive Iraqi air strike against Kharg Island, flown on 18 March 1988, was one such occasion: the Iraqis destroyed two supertankers but lost five aircraft to Iranian F-14 Tomcats, including two Tupolev Tu-22Bs and one Mikoyan MiG-25RB. The U.S. Navy was now becoming more involved in the fight in the Persian Gulf, launching Operations Earnest Will and Prime Chance against the Iranians.

The attacks on oil tankers continued. Both Iran and Iraq carried frequent attacks during the first four months of the year. Iran was effectively waging a naval guerrilla war with its IRGC navy speedboats, while Iraq attacked with its aircraft. In 1987, Kuwait asked to reflag its tankers to the US flag. They did so in March, and the US navy began Operation Earnest Will to escort the tankers. The result of Earnest Will would be that while oil tankers shipping Iraqi/Kuwaiti oil were protected, Iranian tankers, and neutral tankers shipping to Iran would be unprotected, resulting in both losses for Iran and the undermining of its trade with foreign countries, damaging Iran's economy further. Iran also deployed Silkworm missiles to attack some ships, but only a few were actually fired. Both the US and Iran jockeyed for influence in the Gulf. To discourage the US from escorting tankers, Iran secretly mined some areas in the Gulf. The US began to escort the reflagged tankers, but one of them was destroyed by a mine while under escort. While being a public-relations victory for Iran, the US increased its reflagging efforts. While Iran mined the Persian Gulf, their speedboat attacks were reduced, primarily attacking unflagged tankers shipping in the area.
On 24 September, US Navy SEALS captured the Iranian mine-laying ship Iran Ajr, a diplomatic disaster for the already isolated Iranians. On 8 October, the US Navy destroyed four Iranian speedboats, and in response to Iranian Silkworm missile attacks on Kuwaiti oil tankers launched Operation Nimble Archer, destroying two Iranian oil rigs in the Persian Gulf. During November and December, the Iraqi air force launched a bid to destroy all Iranian airbases in Khuzestan and all remaining Iranian air force. However, Iran managed to shoot down 30 Iraqi fighters with their jets, anti-aircraft guns, and missiles, allowing the Iranian air force to survive to the end of the war.
On 28 June, Iraqi fighter bombers attacked the Iranian town of Sardasht near the border, using chemical mustard gas bombs. While many towns and cities had been bombed before, and troops attacked with gas, this was the first time that the Iraqis had attacked a civilian area with poison gas. One quarter of the town's then population of 20,000 was burned and stricken, and 113 were killed immediately, with many more dying and suffering health effects over the next decades. Saddam ordered the attack in order to test the effects of the newly developed "dusty mustard" gas, which was designed to be even more crippling than traditional mustard gas, in addition to the area for suspected Kurdish rebels. While little known outside of Iran (unlike the later Halabja poison gas attack), the Sardasht bombing (and future similar attacks) had a tremendous effect on the Iranian people's psyche.
1988: Iraqi offensives and the UN ceasefire
Main articles: Operation Praying Mantis and Iran Air Flight 655By 1988, with massive equipment imports and reduced Iranian volunteers, Iraq was ready to launch major offensives against Iran. On February 1988, Saddam began the fifth and most deadly "war of the cities". Over the next two months, Iraq launched over 200 al-Hussein missiles at 37 Iranian cities. Saddam also threatened to use chemical weapons in his missiles, which caused 30% of Tehran's population to leave the city. Iran retaliated, launching at least 104 missiles against Iraq in 1988 and shelling Basra. This event was nicknamed the "Scud Duel" in the foreign media. In all, Iraq launched 520 Scuds and al-Husseins against Iran and Iran fired 177 at them. However, the Iranian attacks were too few in number to deter Iraq from launching their attacks. Iraq also increased their airstrikes against Kharg Island and Iranian oil tankers. With their allies tankers protected by US warships, they could operate with virtual impunity. To make matters worse, the West supplied Iraq's air force with laser-guided smart bombs, allowing them to attack economic targets while evading anti-aircraft defenses. These attacks began to have a major toll on the Iranian economy, morale, and caused many casualties as well.
Iran's Kurdistan Operations
In March 1988, the Iranians carried out Operation Dawn 10, Operation Beit-ol-Moqaddas 2 (Jerusalem 2), and Operation Zafar 7 (Victory 7) in Iraqi Kurdistan with the aim of capturing the Darbandikhan Dam and the power plant at Dukan, which supplied Iraq with much of its electricity and water, as well as the city of Suleimaniya. Iran hoped that the capture of these areas would bring more favorable terms to the ceasefire agreement. This infiltration offensive was carried out in conjunction with the Peshmerga. Iranian airborne commandos landed behind the Iraqi lines and Iranian helicopters hit Iraqi tanks with TOW missiles. The Iraqis were taken by surprise, and Iranian F-5E Tiger fighter jets even damaged the Kirkuk oil refinery. Iraq carried out executions of multiple officers for these failures in March–April 1988, including Colonel Jafar Sadeq. The Iranians used infiltration tactics in the Kurdish mountains, captured the town of Halabja and began to fan out across the province.
Though the Iranians advanced to within sight of Dukan, and captured around 1,040 km (400 sq mi) and 4,000 Iraqi troops, the offensive failed due to the Iraqi use of chemical warfare. The Iraqis launched the deadliest chemical weapons attacks of the war. The Republican Guard launched 700 chemical shells, while the other artillery divisions launched 200–300 chemical shells each, unleashing a chemical cloud over the Iranians, killing or wounding 60% of them, and completely destroying the Iranian 84th division. The Iraqi special forces then stopped the remains of the Iranian force. In retaliation for Kurdish collaboration with the Iranians, Iraq launched a massive poison gas attack against Halabja, recently taken by the Iranians, killing thousands of civilians. Iran airlifted foreign journalists to the ruined city, and the images of the dead were shown throughout the world. However, Western mistrust of Iran and collaboration with Iraq led them to also blame Iran for the attack. At one point, the United States claimed that Iran had launched the attack and then tried to blame Iraq for it (though Iran never used poison gas during the war).
Second Battle of al-Faw
Main article: Second Battle of al-FawOn 17 April 1988, Iraq launched Operation Ramadan Mubarak (Blessed Ramadan), a surprise attack against the 15,000 Basij troops on the peninsula. The attack on al-Faw was preceded by Iraqi diversionary attacks in northern Iraq, with a massive artillery and air barrage of Iranian front lines. Key areas, such as supply lines, command posts, and ammunition depots, were hit by a storm of mustard gas and nerve gas, as well as by conventional explosives. Helicopters landed Iraqi commandos behind Iranian lines while the main Iraqi force attacked in a frontal assault. Within 48 hours, all of the Iranian forces had been killed or cleared from the al-Faw Peninsula. The day was celebrated in Iraq as Faw Liberation Day throughout Saddam's rule. The Iraqis had planned the offensive well. Prior to the attack the Iraqi soldiers gave themselves poison gas antidotes to shield themselves from the effect of the saturation of gas. The heavy and well executed use of chemical weapons was the decisive factor in the Iraqi victory. Iraqi losses were heavy as well, over 1,000 troops were lost. The Iranians eventually managed to halt the Iraqi drive as they pushed towards Khuzestan.
To the shock of the Iranians, rather than breaking off the offensive, the Iraqis kept up their drive, and a new force attacked the Iranian positions around Basra. Following this, the Iraqis launched a sustained drive to clear the Iranians out of all of southern Iraq.
One of the most successful Iraqi tactics was the "one-two punch" attack using chemical weapons. Using artillery, they would saturate the Iranian front line with rapidly dispersing cyanide and nerve gas, while longer-lasting mustard gas was launched via fighter-bombers and rockets against the Iranian rear, creating a "chemical wall" that blocked reinforcement.
Operation Praying Mantis

The same day as Iraq's attack on al-Faw peninsula, the United States Navy launched Operation Praying Mantis in retaliation against Iran for damaging a warship with a mine. Iran lost oil platforms, destroyers, and frigates in this battle, which ended only when President Reagan decided that the Iranian navy had been put down enough. However, the Revolutionary Guard's navy continued their speedboat attacks against oil tankers. However, the combined defeats at al-Faw and in the Persian Gulf nudged Iranian leadership towards quitting the war, especially when faced with the prospect of fighting the Americans.
Iranian counteroffensive
Faced with such losses, Khomeini appointed the cleric Hashemi Rafsanjani as the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, though he had in actuality occupied that position for months. Rasanjani ordered a surprise counter-attack into Iraq, which was launched 13 June 1988. The Iranians infiltrated through the Iraqi trenches and moved 10 km (6.2 mi) into Iraq, and managed to strike Saddam's presidential palace in Baghdad using fighter aircraft. After 10 hours of fighting, the Iranians were driven back to their original positions again as the Iraqis launched 600 helicopter and 300 aircraft sorties with poison gas.
Operation Forty Stars
On 18 June, Iraq launched Operation Forty Stars (چل چراغ chehel cheragh) in conjunction to the Mujahideen-e-Khalq (MEK) around Mehran. With 530 aircraft sorties and heavy use of nerve gas, they crushed the Iranian forces in the area, killing 3,500, and nearly destroying a Revolutionary Guard division. Mehran was captured once again and occupied by the MEK. Iraq also launched air raids on Iranian population centers and economic targets, setting 10 oil installations on fire.
Tawakalna ala Allah Operations
Main article: Tawakalna ala Allah OperationsOn 25 May 1988, Iraq launched the first of four Tawakalna ala Allah (Trust in God) Operations, consisting of one of the largest artillery barrages in history, coupled with chemical weapons. The marshes had been dried by drought, allowing the Iraqis to use tanks to bypass Iranian field fortifications, expelling the Iranians from the border town of Shalamcheh after less than 10 hours of combat.
On 25 June, Iraq launched the second Tawakalna ala Allah operation against the Iranians on Majnoon Island. Iraqi commandos used hovercraft to block the Iranian rear, then used hundreds of tanks with heavy conventional and chemical artillery barrages to recapture the island after 8 hours of combat. Saddam appeared live on Iraqi television to "lead" the charge against the Iranians. The majority of the Iranian defenders were killed during the quick assault. The final two Tawakalna ala Allah operations took place in al-Marah and Khaneqan. By 12 July, the Iraqis had captured the city of Dehloran, 40 km (25 mi) inside Iran, along with 2,500 troops and much armour and material, which took days to transport to Iraq. The Iraqis withdrew from Dehloran soon after, claiming that they had "no desire to conquer Iranian territory." Historian Kaveh Farrokh considered this to be the Iran's greatest military disaster during the war.

During the 1988 battles, the Iranians put up little resistance to the Iraqi offensives, having been worn out by nearly eight years of war. They lost large amounts of equipment; however, they managed to rescue most of their troops from being captured by the Iraqis, leaving Iraq with relatively few prisoners. On 2 July, Iran belatedly set up a joint central command which unified the Revolutionary Guard, Army, and Kurdish rebels, and dispelled the rivalry between the Army and the Revolutionary Guard. However this came too late, and Iran was believed to have fewer than 200 remaining tanks on the southern front, faced against thousands of Iraqi ones. The only area where the Iranians were not suffering major defeats was in Kurdistan.
Iran accepts the ceasefire
Saddam sent a warning to Khomeini in mid-1988, threatening to launch a full-scale invasion and attack Iranian cities with weapons of mass destruction. Shortly afterwards, Iraqi aircraft bombed the Iranian town of Oshnavieh with poison gas, immediately killing and wounding over 2,000 civilians. The fear of an all out chemical attack against Iran's largely unprotected civilian population weighed heavily on the Iranian leadership, and they realized that the international community had no intention of restraining Iraq. The lives of the civilian population of Iran were becoming very disrupted, with a third of the urban population evacuating major cities in fear of the seemingly imminent chemical war. Meanwhile, Iraqi conventional bombs and missiles continued to strike continuously, as the death toll among the population increased. Iran did reply with missile and air attacks as well, but not enough to deter the Iraqis from attacking.
Under the threat of invasion, Commander-in-Chief Akbar Rafsanjani ordered the Iranians to retreat from Haj Omran, Kurdistan on 14 July. The Iranians did not publicly describe this as a retreat, instead called it a "temporary withdrawal". By July, Iran's army inside Iraq (except Kurdistan) had largely disintegrated. Iraq put up a massive display of captured Iranian weapons in Baghdad, claiming they "captured" 1,298 tanks, 5,550 recoil-less rifles, and thousands of other weapons. However, Iraq had taken heavy losses as well, and the battles were very costly.
On July 1988, Iraqi aeroplanes dropped cyanide bombs on the Iranian Kurdish village of Zardan (as they had done four months earlier on their own Kurdish village of Halabja). Dozens of villages, and some larger towns, such as Marivan, were attacked with poison gas, resulting in even heavier civilian casualties. About the same time, the USS Vincennes shot down Iran Air Flight 655, killing 290 passengers. The lack of international sympathy disturbed the Iranian leadership, and they came to the conclusion that the United States was on the verge of waging a full-scale war against them, and that Iraq was on the verge of unleashing its entire chemical arsenal upon their major cities.
At this point, elements of the Iranian leadership, led by Ali Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani (who had pushed for the war initially), persuaded Khomeini to accept the UN ceasefire. They stated that in order to win the war, Iran's military budget would have to be increased by 700% and the war would last until 1993. Many officials also pointed out to Khomeini that while Resolution 598 would not give all of the gains that Iran wanted, it was better than anything else that had been proposed before, and likely would be proposed afterward, considering that it provided a return to the pre-war status quo, rather than having Iraq occupy Iranian border areas like previous agreements. While many parts were ambiguous, it could be negotiated with Iraq.
On 20 July 1988, Iran accepted Resolution 598, showing its willingness to accept a ceasefire. A statement from Khomeini was read out in a radio address, and he expressed deep displeasure and reluctance about accepting the ceasefire:
Happy are those who have departed through martyrdom. Happy are those who have lost their lives in this convoy of light. Unhappy am I that I still survive and have drunk the poisoned chalice...
The news of the end of the war was greeted with celebration in Baghdad, with people dancing in the streets; in Tehran, however, the end of the war was greeted with a somber mood.
Operation Mersad and end of the war
Main article: Operation MersadOperation Mersad (مرساد "ambush") was the last major military operation of the war, ending in a decisive victory for Iran. Both Iran and Iraq had accepted Resolution 598. But despite the ceasefire, after seeing Iraqi victories in the previous months, Iraq decided to launch a new attack and wished to permanently occupy Khuzestan and western Iran, as well as to reach its goals from the beginning of the war. Saddam and the Iraqi high command decided on a three-pronged offensive across the border: in Khuzestan, central Iran, and Iranian Kurdistan. Shortly after Iran accepted the ceasefire the Iraqi army began their offensive, attacking Khuzestan province beginning with chemical weapons and air strikes.
Shortly after, Iraq's main offensive began. Iraqi mechanized forces, supported by aircraft, artillery and chemical weapons entered Khuzestan capturing territory for the first time since 1982, advancing towards Ahvaz, Abadan and Khorramshahr. However, the Iranians carried out a mass mobilization of their reserve forces, and Iranian morale which was low, suddenly increased. New volunteers also poured in as well. The Iraqi advance was bogged down into hand-to-hand combat at the "Hamid Military Camp" outside of Ahvaz. Iraqi air power was blunted by Iran's air force in conjunction with air defenses. In the north, Iraq also launched an attack into Iraqi Kurdistan, which was blunted by the Iranians.
On 26 July 1988, the Mujahadeen-e-Khalq (MEK), with the support of the Iraqi army, started their campaign, Operation Forough Javidan (Eternal Light) in central Iran. While Iraqi forces were attacking Khuzestan, the MEK supported by Iraq attacked western Iran, advancing towards Kermanshah. The Iranians had withdrawn their remaining soldiers to Khuzestan, and as a result the Mujahedeen advanced rapidly, seizing Qasr-e Shirin, Sarpol-e Zahab, and Islamabad-e-Gharb, and towards Kermanshah. The MEK expected the Iranian population to rise up and support their advance; however, the uprising never materialised, but they reached 145 km (90 mi) deep into Iran. In response, the Iranian military launched its counter-attack, Operation Mersad, under Lieutenant General Ali Sayyad Shirazi. Iranian paratroopers landed behind the MEK lines while the Iranian Air Force and helicopters launched an air attack, destroying much of the enemy armour. The Iranians defeated the MEK in the city of Kerend-e Gharb on 29 July 1988. On 31 July, Iran drove the Iraqis out of Qasr-e-Shirin and Sarpol Zahab, though Iraq claimed to have "voluntarily withdrawn" from the towns. Iran estimated that 4,500 MEK and Iraqis were killed, while 400 Iranian soldiers died.

The last notable combat actions of the war took place on 3 August 1988, in the Persian Gulf when the Iranian navy fired on a freighter and Iraq launched chemical attacks on Iranian civilians, killing an unknown number of them and wounding 2,300.
Iraq came under heavy international pressure to end the war. Resolution 598 became effective on 8 August 1988, ending all combat operations between the two countries. By 20 August 1988, peace with Iran was restored. UN peacekeepers belonging to the UNIIMOG mission took the field, remaining on the Iran–Iraq border until 1991. While the war was now over, Iraq spent the rest of August and early September clearing the Kurdish resistance. Using 60,000 troops along with helicopter gunships, chemical weapons (poison gas), and mass executions, Iraq hit 15 villages, killing rebels and civilians, and forced tens of thousands of Kurds to relocate to settlements. Many Kurdish civilians immigrated to Iran. By 3 September 1988, the anti-Kurd campaign ended, and all resistance had been crushed. 400 Iraqi soldiers and 50,000 Kurdish civilians and soldiers had been killed.
Aftermath



The Iran–Iraq War was extremely costly in lives and material, and was the deadliest conventional war ever fought between regular armies of developing countries. It cost Iran an estimated 1 million casualties (killed or wounded), and civilians deaths continue as a result of Iraqi chemical weapons. Iraqi casualties are estimated at 250,000–500,000, and thousands of civilians on both sides died in air raids and ballistic missile attacks. Prisoners taken by both countries began to be released in 1990, though some were not released until more than 10 years after the end of the conflict. Cities on both sides had also been considerably damaged. While revolutionary Iran had been bloodied, Iraq was left with a large military and was a regional power, but with severe debt, financial problems, and facing labor shortages.
Peace Talks and Postwar Situation
With the ceasefire in place, and UN peacekeepers monitoring the border, Iran and Iraq sent their representatives to Geneva, Switzerland, to negotiate a peace agreement on the terms of the ceasefire. However, peace talks rapidly stalled due to various factors. Iraq, in violation of the UN ceasefire, refused to withdraw its troops from 3,000 square miles Iranian territory unless the Iranians accepted Iraq's full sovereignty over the Shatt al-Arab waterway (exactly as Iran had feared in 1982). The foreign powers continued to support Iraq, which wanted to gain at the negotiating table what they failed to achieve on the battlefield, and Iran was portrayed as the one who was not wanting peace. Iran, in response refused to release 70,000 Iraqi prisoners of war (twice as many compared to Iranian prisoners of war in Iraq). They also continued to carry out a naval blockade of Iraq, although its effects were mitigated by Iraqi trade with its Arab neighbors. Iran also began to improve relations with many of the states that opposed it during the war. Because of Iranian actions, by 1990, Saddam had become more conciliatory, and in a letter to the now President Rafsanjani, he became more open to the idea of a peace agreement, although he still insisted on full sovereignty over the Shatt al-Arab.
By 1990, Iran was undergoing a major military rearmament and reorganization. Iran eventually purchased from the USSR and China $10 billion worth of heavy weaponry (including aircraft, tanks, and missiles). In addition, Rafsanjani reversed Iran's self-imposed ban on chemical weapons, and ordered the manufacturing and stockpiling of them (in 1993, Iran ratified the Chemical Weapons Convention, which banned the stockpiling of them, and subsequently Iran destroyed them. Saddam realized that if Iran did try to expel the Iraqis from their territory by force, it was likely that they would succeed. In addition, as war with the western powers loomed, Iraq became concerned about Iran mending their relations with the west in order to attack Iraq. In addition, Iraq had lost their vital support from the West, and their position in Iran was increasingly untenable. Shortly after his invasion of Kuwait, Saddam wrote a letter to Rafsanjani stating that Iraq recognised Iranian rights over the eastern half of the Shatt al-Arab, a reversion to the status quo ante bellum that he had repudiated a decade earlier, and that he would give into accept of Iran's demands and withdraw Iraq's military from Iran. Both sides shortly after signed a peace agreement finalizing the terms of the UN resolution, restored diplomatic relations, and by late 1990-early 1991, the Iraqi military withdrew entirely from Iranian territory. The UN peacekeepers withdrew from the border shortly afterward. Most of the prisoners of war were released in 1990 after the agreement was signed, although some remained as late as 2003. Iranian politicians declared it to be the "greatest victory in the history of the Islamic Republic of Iran".
Most historians and analysts consider the war to be a stalemate. Certain analysts believe that Iraq won, on the basis of the success of their 1988 offensives which persuaded Iran to accept the ceasefire. Iranian analysts believe that they won the war because although they did not succeed in defeating Iraq militarily, they did manage to gain their political goals of driving Iraq entirely from their territory (which was an important purpose of the post 1982 invasion of Iraq, to force the Iraqis to negotiate a withdrawal from Iran's border areas). They also cite the fact that Iran achieved its goals against Iraq's superior military, they thwarted Iraq's major territorial ambitions in Iran, and that Iraq permanently gave up its claims to the Shatt al-Arab as well.
On 9 December 1991, Javier Pérez de Cuéllar, UN Secretary General at the time, reported that Iraq's initiation of the war was unjustified, as was its occupation of Iranian territory and use of chemical weapons against civilians:
That explanations do not appear sufficient or acceptable to the international community is a fact... cannot be justified under the charter of the United Nations, any recognized rules and principles of international law, or any principles of international morality, and entails the responsibility for conflict. Even if before the outbreak of the conflict there had been some encroachment by Iran on Iraqi territory, such encroachment did not justify Iraq's aggression against Iran—which was followed by Iraq's continuous occupation of Iranian territory during the conflict—in violation of the prohibition of the use of force, which is regarded as one of the rules of jus cogens...On one occasion I had to note with deep regret the experts' conclusion that "chemical weapons ha been used against Iranian civilians in an area adjacent to an urban center lacking any protection against that kind of attack.
He also stated that had the UN accepted this fact earlier, the war would have almost certainly not lasted as long as it did. Iran, encouraged by his announcement, attempted to seek reparations from Iraq, but due to the hostile political climate, they never received any.
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, Iran and Iraq relations remained at a limbo between a cold war and a cold peace. Despite renewed and somewhat thawed relations, both sides continued to have low level conflicts with each other. Iraq continued to host and support the Mujahedeen-e-Khalq, which carried out multiple attacks throughout Iran up until the 2003 US led invasion (including the assassination of Iranian general Ali Sayyad Shirazi in 1998, cross border raids, and mortar attacks). Iran carried out several airstrikes and missile attacks against Mujahedeen targets inside of Iraq (the largest taking place in 2001, when Iran fired 56 Scud missiles at Mujahedeen targets). In addition, according to General Hamdani, Iran continued to carry out low-level infiltrations of Iraqi territory, using Iraqi dissidents and anti-government activists rather than Iranian troops, in order to incite revolts. After the fall of Saddam in 2003, Hamdani claimed that Iranian agents infiltrated and created numerous militias inside of Iraq and built a large intelligence system operating within the country.
In 2005, the new government of Iraq apologised to Iran for starting the war. The Iraqi government also commemorated the war with various monuments, including the Hands of Victory and the al-Shaheed Monument, both in Baghdad. The war also helped to create a forerunner for the Coalition of the Gulf War, when the Gulf Arab states banded together early in the war to form the Gulf Cooperation Council to help Iraq fight Iran.
With the US invasion of Iraq in 2003, and Iran's involvement in Iraq's new government and backing of proxy militias, many observers believe that Iran has effectively gained influence over Iraq. Thus many of Iran's objectives and goals have been achieved (including the fall of Saddam Hussein).
Financial situation
The financial loss at the time was believed to exceed US$500 billion for each country ($1.2 trillion total). In addition, economic development stalled and oil exports were disrupted. Iran, having used bloodier but economically cheaper tactics during the war, only incurred a small debt, in contrast to the large ones incurred by Iraq. Iraq had accrued more than $130 billion of international debt, excluding interest, and was also weighed down by a slowed GDP growth. Iraq's debt to Paris Club amounted to $21 billion, 85% of which had originated from the combined inputs of Japan, the USSR, France, Germany, the United States, Italy and the United Kingdom. The largest portion of Iraq's debt, amounting to $130 billion, was to its former Arab backers, with $67 billion loaned by Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, and Jordan. Ironically, at some points during the war, Iran's strategy was to drive the Iraqis into economic difficulties through contant attrition, forcing them to waste more money on armaments, and in that sense they were successful.
After the war, Iraq accused Kuwait of slant drilling and stealing oil, inciting its invasion of Kuwait, which in turn worsened Iraq's financial situation: the United Nations Compensation Commission mandated Iraq to pay reparations of more than $200 billion to victims of the invasion, including Kuwait and United States. To enforce payment of these reparations, Iraq was put under a complete international embargo, which put further strain on the Iraqi economy and pushed its external debt and international liabilities to private and public sectors to more than $500 billion by the end of Saddam's rule. Combined with Iraq's negative economic growth after prolonged international sanctions, this produced a debt-to-GDP ratio of more than 1,000%, making Iraq the most indebted developing country in the world. The unsustainable economic situation compelled the new Iraqi government to request that a considerable portion of debt incurred during the Iran–Iraq war be written off. Consequently, the effects of the Iran–Iraq War help lead directly to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait and the subsequent Persian Gulf War two years later.
Much of the oil industry in both countries was damaged in air raids. 10 million shells had landed in Iraq's oil fields at Basra, seriously damaging their oil production. Iran's production capacity has yet to fully recover from the damages of the war.
Science and technology
The war and its outcome had a marked effect also on the scientific and technological advancement of the involved countries: Iraq's productivity in the field collapsed and has not yet recovered, and Kuwait's scientific output was initially slowed and later became stagnant. Iran, on the other hand, experienced a scientific revival, and as of 2010 has the fastest scientific growth rate in the world.
The war had its impact on medical sciences: a surgical intervention for comatose patients with penetrating brain injuries was created by Iranian physicians to treat wounded soldiers. It later helped establish neurosurgery guidelines to treat civilians who had suffered blunt or penetrating skull injuries. The previously established surgical technique and its guidelines had been developed by the U.S. army during World War II; it had been replaced by the newer procedures, which reportedly helped U.S. congresswoman Gabrielle Giffords recover after the 2011 Tucson shooting.
In addition to helping trigger the Persian Gulf War, the Iran–Iraq War also helped to create technological conditions for an easy American victory in 1991. Iraq's military was accustomed to fighting the slow moving Iranian infantry formations with artillery and static defenses, while using mostly obsolescent, unsophisticated tanks to gun down and shell the infantry and overwhelm the smaller Iranian tank force; in addition to being dependent on weapons of mass destruction to help secure decisive victories. Therefore, they were rapidly overwhelmed by the high-tech, quick-maneuvering US forces using modern doctrines such as AirLand Battle. Meanwhile, the Iranians proved that it was possible to fight and in numerous cases even defeat a large, mechanized military using primarily light infantry tactics. Armored maneuver during the war was very costly, because of anti-tank weapons. Consequently, the war became a static trench war, and Iraqis frequently dug in tanks into static defenses.
The Iran–Iraq War was the first war that featured the use of unmanned drones in combat (rather than observation only), by Iran.
Home front
Iraq
At first, Saddam attempted to ensure that the Iraqi population suffered from the war as little as possible. There was rationing, but civilian projects began before the war continued. At the same time, the already extensive personality cult around Saddam reached new heights of adulation while the regime tightened its control over the military.
After the Iranian victories of the spring of 1982 and the Syrian closure of Iraq's main pipeline, Saddam did a volte-face on his policy towards the home front: a policy of austerity and total war was introduced, with the entire population being mobilised for the war effort. All Iraqis were ordered to donate blood and around 100,000 Iraqi civilians were ordered to clear the reeds in the southern marshes. Mass demonstrations of loyalty towards Saddam became more common. Saddam also began implementing a policy of discrimination against Iraqis of Iranian origin.
In the summer of 1982, Saddam began a campaign of terror. More than 300 Iraqi Army officers were executed for their failures on the battlefield. In 1983, a major crackdown was launched on the leadership of the Shia community. Ninety members of the al-Hakim family, an influential family of Shia clerics whose leading members were the émigrés Mohammad Baqir al-Hakim and Abdul Aziz al-Hakim, were arrested, and 6 were hanged. The crackdown on Kurds saw 8,000 members of the Barzani clan, whose leader (Massoud Barzani) also led the Kurdistan Democratic Party, summarily executed. From 1983 onwards, a campaign of increasingly brutal repression was started against the Iraqi Kurds, characterised by Israeli historian Efraim Karsh as having "assumed genocidal proportions" by 1988. The al-Anfal Campaign was intended to "pacify" Iraqi Kurdistan permanently.
Gaining civilian support
To secure the loyalty of the Shia population, Saddam began a policy of allowing more Shias into the Ba'ath Party and the government, and started efforts to improve Shia living standards, which had been lower than those of the Iraqi Sunnis. Saddam also had the Iraqi state pay for the costs of restoring Imam Ali's tomb with white marble imported from Italy. The Baathists also increased their policies of repression against the Shia. The most infamous event was the massacre of 148 civilians of the Shia town of Dujail.
Despite the costs of the war, the Iraqi regime made generous contributions to Shia waqf (religious endowments) as part of the price of buying Iraqi Shia support. The importance of winning Shia support was such that welfare services in Shia areas were expanded during a time in which the Iraqi regime was pursuing a policy of rigid austerity in all other non-military fields. During the first years of the war in the early 1980s, the Iraqi government tried to accommodate the Kurds in order to focus on the war against Iran. In 1983, the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan agreed to cooperate with Baghdad, but the Kurdish Democratic Party (KDP) remained opposed. In 1983, Saddam signed an autonomy agreement with Jalal Talabani of the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan (PUK), through Saddam later reneged on the agreement. By 1985, the PUK and KDP had joined forces, and Iraqi Kurdistan saw widespread guerilla warfare up to the end of the war.
Iran
The Iranian government saw the outbreak of war as chance to strengthen its position and consolidate the Islamic revolution: the war was presented to the Iranian people as a glorious jihad and a test of Iranian national character. The Iranian regime followed a policy of total war from the beginning, and attempted to mobilise the nation as a whole. They established a group known as the Reconstruction Campaign, whose members were exempted from conscription and were instead sent into the countryside to work on farms to replace the men serving at the front.
Iranian workers had a day's pay deducted from their pay cheques every month to help finance the war, and mass campaigns were launched to encourage the public to donate food, money, and blood for the soldiers. To further help finance the war, the Iranian government banned the import of all non-essential items, and launched a major effort to rebuild the damaged oil plants.
Civil unrest
In June 1981, street battles broke out between the Revolutionary Guard and the left-wing Mujaheddin e-Khalq (MEK), continuing for several days and killing hundreds on both sides. In September, more unrest broke out on the streets of Iran as the MEK attempted to seize power. Thousands of left-wing Iranians (many of whom were not associated with the MEK) were shot and hanged by the government in the aftermath. The MEK began an assassination campaign that killed hundreds of regime officials by the fall of 1981. On 28 June 1981, they assassinated the secretary-general of the Islamic Republican Party, Mohammad Beheshti and on 30 August, killed Iran's president, Mohammad-Ali Rajai. The government responded with mass executions of suspected MEK members, a practice that lasted until 1985.
In addition to the open civil conflict with the MEK, the Iranian government was faced with Iraqi-supported rebellions in Iranian Kurdistan, which were gradually put down through a campaign of systematic repression. 1985 also saw student anti-war demonstrations, which were crushed by government activists.
Economy
The war furthered the decline of the Iranian economy that had begun with the revolution in 1978–79. Between 1979 and 1981, foreign exchange reserves fell from US$14.6 billion to $1 billion. As a result of the war, living standards dropped dramatically, and Iran was described by British journalists John Bulloch and Harvey Morris as "a dour and joyless place" ruled by a harsh regime that "seemed to have nothing to offer but endless war." Though Iran was becoming bankrupt, Khomeini interpreted Islam's prohibition of usury to mean they could not borrow against future oil revenues to meet war expenses. As a result, Iran funded the war by the income from oil exports after cash had run out. The revenue from oil dropped from $20 billion in 1982 to $5 billion in 1988.
In January 1985, former prime minister and anti-war Islamic Liberation Movement Mehdi Bazargan criticised the war in a telegram to the United Nations, calling it un-Islamic and illegitimate and arguing that Khomeini should have accepted Saddam's truce offer in 1982 instead of attempting to overthrow the Ba'ath. He added, "Since 1986, you have not stopped proclaiming victory, and now you are calling upon population to resist until victory. Is that not an admission of failure on your part?" Khomeini was annoyed by Bazargan's telegram, and issued a lengthy public rebuttal in which he defended the war as both Islamic and just.
By 1987, Iranian morale had begun to crumble, reflected in the failure of government campaigns to recruit "martyrs" for the front. Israeli historian Efraim Karsh points to the decline in morale in 1987–88 as being a major factor in Iran's decision to accept the ceasefire of 1988.
Not all saw the war in negative terms. The Islamic Revolution of Iran was strengthened and radicalised. The Iranian government-owned Etelaat newspaper wrote, "There is not a single school or town that is excluded from the happiness of 'holy defence' of the nation, from drinking the exquisite elixir of martyrdom, or from the sweet death of the martyr, who dies in order to live forever in paradise."
Comparison of Iraqi and Iranian military strength
See also: Order of battle during the Iran–Iraq WarAt the beginning of the war, Iraq held a clear advantage in armour, while both nations were roughly equal in terms of artillery. The gap only widened as the war went on. Iran started with a stronger air force, but over time, the balance of power reversed in Iraq's favour. Estimates for 1980 and 1987 were:
| Imbalance of Power (1980–1987) | Iraq | Iran |
|---|---|---|
| Tanks in 1980 | 2700 | 1740 |
| Tanks in 1987 | 4500+ | 1000 |
| Fighter aircraft in 1980 | 332 | 445 |
| Fighter aircraft in 1987 | 500+ | 65 (serviceable) |
| Helicopters in 1980 | 40 | 500 |
| Helicopters in 1987 | 150 | 60 |
| Artillery in 1980 | 1000 | 1000+ |
| Artillery in 1987 | 4000+ | 1000+ |
Foreign support to Iraq and Iran
Main article: International aid to combatants in the Iran–Iraq WarDuring the war, Iraq was regarded by the West and the Soviet Union as a counterbalance to post-revolutionary Iran. The Soviet Union, Iraq's main arms supplier during the war, did not wish for the end of its alliance with Iraq, and was alarmed by Saddam's threats to find new arms suppliers in the West and China if the Kremlin did not provide him with the weapons he wanted. The Soviet Union hoped to use the threat of reducing arms supplies to Iraq as leverage for forming a Soviet-Iranian alliance.
During the early years of the war, the United States lacked meaningful relations with either Iran or Iraq, the former due to the Iranian Revolution and the Iran hostage crisis and the latter because of Iraq's alliance with the Soviet Union and hostility towards Israel. Following Iran's success of repelling the Iraqi invasion and Khomeini's refusal to end the war in 1982, the U.S. made an outreach to Iraq, beginning with the restoration of diplomatic relations in 1984. The United States wished to both keep Iran away from Soviet influence and protect other Gulf states from any threat of Iranian expansion. As a result, it began to provide limited support to Iraq. In 1982, Henry Kissinger, former Secretary of State, outlined U.S. policy towards Iran:
The focus of Iranian pressure at this moment is Iraq. There are few governments in the world less deserving of our support and less capable of using it. Had Iraq won the war, the fear in the Gulf and the threat to our interest would be scarcely less than it is today. Still, given the importance of the balance of power in the area, it is in our interests to promote a ceasefire in that conflict; through not a cost that will preclude an eventual rapprochement with Iran either if a more moderate regime replaces Khomenini's or if the present rulers wake up to geopolitical reality that the historic threat to Iran's independence has always come from the country with which it shares a border of 1,500 miles : the Soviet Union. A rapprochement with Iran, of course, must await at a minimum Iran's abandonment of hegemonic aspirations in the Gulf.
Richard Murphy, Assistant Secretary of State during the war, testified to Congress in 1984 that the Reagan administration believed a victory for either Iran or Iraq was "neither militarily feasible nor strategically desirable."
Support to Iraq was given via technological aid, intelligence, the sale of dual-use and military equipment, and satellite intelligence. While there was direct combat between Iran and the United States, it is not universally agreed that the fighting between the U.S. and Iran was specifically to benefit Iraq, or for separate issues between the U.S. and Iran. American official ambiguity towards which side to support was summed up by Henry Kissinger when he remarked, "It's a pity they both can't lose." The Americans and the British also either blocked or watered down UN resolutions that condemned Iraq for using chemical weapons against the Iranians and their own Kurdish citizens.
More than 30 countries provided support to Iraq, Iran, or both; most of the aid went to Iraq. Iran had a complex clandestine procurement network to obtain munitions and critical materials. Iraq had an even larger clandestine purchasing network, involving 10–12 allied countries, to maintain ambiguity over their arms purchases and to circumvent "official restrictions". Arab mercenaries and volunteers from Egypt and Jordan formed the Yarmouk Brigade and participated in the war alongside Iraqis.
Iraq
According to the Stockholm International Peace Institute, the Soviet Union, France, and China together accounted for over 90% of the value of Iraq's arms imports between 1980 and 1988.
The United States pursued policies in favour of Iraq by reopening diplomatic channels, lifting restrictions on the export of dual-use technology, overseeing the transfer of third-party military hardware, and providing operational intelligence on the battlefield. France, which from the 1970s onward had been one of Iraq's closest allies, was a major supplier of military hardware to Iraq. The French sold weapons equal to the sum of US$5 billion, which comprised well over a quarter of Iraq's total arms stockpile. China, which had no direct stake in the victory of either side and whose interests in the war were entirely commercial, freely sold arms to both sides.
Iraq also made extensive use of front companies, middlemen, secret ownership of all or part of companies all over the world, forged end user certificates, and other methods to hide what it was acquiring. Some transactions may have involved people, shipping, and manufacturing in as many as 10 countries. Support from Great Britain exemplified the methods by which Iraq would circumvent export controls. Iraq bought at least one British company with operations in the United Kingdom and the United States, and had a complex relationship with France and the Soviet Union, its major suppliers of actual weapons.
The United Nations Security Council initially called for a cease-fire after a week of fighting while Iraq was occupying Iranian territory, and renewed the call on later occasions. However, the UN did not come to Iran's aid to repel the Iraqi invasion, and the Iranians thus interpreted the UN as subtly biased in favour of Iraq.
Financial support
Iraq's main financial backers were the oil-rich Persian Gulf states, most notably Saudi Arabia ($30.9 billion), Kuwait ($8.2 billion), and the United Arab Emirates ($8 billion). In all, Iraq received $35 billion in loans from the West and between $30 and $40 billion from the Persian Gulf states during the 1980s.
The Iraqgate scandal revealed that a branch of Italy's largest bank, Banca Nazionale del Lavoro (BNL), in Atlanta, Georgia, US relied partially on U.S. taxpayer-guaranteed loans to funnel $5 billion to Iraq from 1985 to 1989. In August 1989, when FBI agents raided the Atlanta branch of BNL, branch manager Christopher Drogoul was charged with making unauthorised, clandestine, and illegal loans to Iraq – some of which, according to his indictment, were used to purchase arms and weapons technology.
According to the Financial Times, the companies involved in the scandal by shipping militarily useful technology to Iraq were Hewlett-Packard, Tektronix and Matrix Churchill's branch in Ohio, US.
Iran
While the United States directly fought Iran, citing freedom of navigation as a major casus belli, it also indirectly supplied some weapons to Iran as part of a complex and illegal programme that became known as the Iran-Contra affair. These secret sales were partly to help secure the release of hostages held in Lebanon, and partly to make money to help the Contras rebel group in Nicaragua. This arms for hostages agreement turned into a major scandal.
North Korea was a major arms supplier to Iran, often acting as a third party in arms deals between Iran and the Communist bloc. Support included domestically manufactured arms and Eastern-Bloc weapons, for which the major powers wanted deniability. Other arms suppliers and supporters of Iran included Libya and China.
Both countries
Besides the United States and the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia also sold weapons to both countries for the entire duration of the conflict. Likewise, Portugal helped both countries; it was not unusual to see Iranian and Iraqi flagged ships moored side-by-side at the Port of Sines.
From 1980 to 1987 Spain sold €458 million in weapons to Iran and €172 million in weapons to Iraq. Weapons sold to Iraq included 4x4 vehicles, BO-105 helicopters, explosives, and ammunition. A research party later discovered that an unexploded chemical Iraqi warhead in Iran was manufactured in Spain.
Although neither side acquired any weapons from Turkey, both sides enjoyed Turkish civilian trade during the conflict, although the Turkish government remained neutral and refused to support the trade embargo imposed by the U.S. on Iran. Turkey's export market jumped from $220 million in 1981 to $2 billion in 1985, making up 25% of Turkey's overall exports. Turkish construction projects in Iraq totaled $2.5 billion between 1974 and 1990. Trading with both countries helped Turkey to offset its ongoing economic crisis, though the benefits decreased as the war neared its end and accordingly disappeared entirely with Iraq's invasion of Kuwait and the resulting Iraq sanctions Turkey imposed in response.
U.S. involvement
U.S. Embargo
A key element of US political–military and energy–economic planning occurred in early 1984. The Iran–Iraq war had been going on for five years and there were significant casualties on both sides, reading hundreds of thousands. Within the Reagan National Security Council concern was growing that the war could spread beyond the boundaries of the two belligerents. A National Security Planning Group meeting was called chaired by Vice President George Bush to review US options. It was determined that there was a high likelihood that the conflict would spread into Saudi Arabia and other Gulf states, but that the US had little capability to defend the region. Furthermore it was determined that a prolonged war in the region would induce much higher oil prices and threaten the fragile world recovery which was just beginning to gain momentum. On May 22, 1984, President Reagan was briefed on the project conclusions in the Oval Office by William Flynn Martin who had served as the head of the NSC staff that organized the study. The full declassified presentation can be seen here. The conclusions were threefold: first oil stocks needed to be increased among members of the International Energy Agency and, if necessary, released early in the event of oil market disruption; second the United States needed to beef up the security of friendly Arab states in the region and thirdly an embargo should be placed on sales of military equipment to Iran and Iraq. The Plan was approved by the President and later affirmed by the G-7 leaders headed by Margaret Thatcher in the London Summit of 1984.
The plan was implemented and became the basis for US preparedness to respond to the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait in 1991. Which shows that the planning Gulf War of 1991 was begun in 1984, demonstrating the long lead times necessary for military deployment. The policy of 1984 was undercut by the activities of the Reagan administration of selling arms to Iran (see Iran-Contra), demonstrating the inconsistencies in the Reagan policies.
Iraqi attack on U.S. warship
Main article: USS Stark incident

On 17 May 1987, an Iraqi Mirage F1 attack aircraft launched two Exocet missiles at the USS Stark, a Perry class frigate. The first struck the port side of the ship and failed to explode, though it left burning propellant in its wake; the second struck moments later in approximately the same place and penetrated through to crew quarters, where it exploded, killing 37 crew members and leaving 21 injured. Whether or not Iraqi leadership authorised the attack is still unknown. Initial claims by the Iraqi government (that Stark was inside the Iran–Iraq War zone) were shown to be false, and the motives and orders of the pilot remain unanswered. Though American officials claimed that the pilot who attacked Stark had been executed, an ex-Iraqi Air Force commander since stated he had not been punished, and was still alive at the time. The attack remains the only successful anti-ship missile strike on an American warship. Due to the extensive political and military cooperation between the Iraqis and Americans by 1987, the attack had little effect on relations between the two countries.
U.S. military actions toward Iran
U.S. attention was focused on isolating Iran as well as maintaining freedom of navigation. It criticised Iran's mining of international waters, and sponsored UN Security Council Resolution 598, which passed unanimously on 20 July, under which the U.S. and Iranian forces skirmished during Operation Earnest Will. During Operation Nimble Archer in October 1987, the U.S. attacked Iranian oil platforms in retaliation for an Iranian attack on the U.S.-flagged Kuwaiti tanker Sea Isle City.
On 14 April 1988, the frigate USS Samuel B. Roberts was badly damaged by an Iranian mine, and 10 sailors were wounded. U.S. forces responded with Operation Praying Mantis on 18 April, the U.S. Navy's largest engagement of surface warships since World War II. Two Iranian oil platforms were damaged, and five Iranian warships and gunboats were sunk. An American helicopter also crashed. This fighting manifested in the International Court of Justice as Oil Platforms case (Islamic Republic of Iran v. United States of America), which was eventually dismissed in 2003.
U.S. shoots down civilian airliner
Main article: Iran Air Flight 655In the course of escorts by the U.S. Navy, the cruiser USS Vincennes shot down Iran Air Flight 655 on 3 July 1988, killing all 290 passengers and crew on board. The American government claimed that that the Vincennes was in international waters at the time (which was later proven to be untrue), that the civilian airliner had been mistaken for an Iranian F-14 Tomcat, and the Vincennes feared that it was under attack. The Iranians maintain that the Vincennes was in their own waters, and that the passenger jet was turning away and increasing altitude after take-off. U.S. Admiral William J. Crowe later admitted on Nightline that the Vincennes was in Iranian territorial waters when it launched the missiles. At the time of the attack, Admiral Crowe claimed that the Iranian plane did not identify itself and sent no response to warning signals he had sent.
According to an investigation conducted by Nightline, decoys were sent by the U.S. Navy into the Persian Gulf during the war to lure out the Iranian gunboats and destroy them, and that the Vincennes was performing such an operation when she shot down the Iranian airliner.
In 1996, the U.S. expressed regret for the event and the civilian deaths it caused.
Use of chemical weapons by Iraq
See also: Halabja poison gas attack, Iraqi chemical weapons programme, and Second Battle of al-FawIn a declassified 1991 report, the CIA estimated that Iran had suffered more than 50,000 casualties from Iraq's use of several chemical weapons, though current estimates are more than 100,000 as the long-term effects continue to cause casualties. The official CIA estimate did not include the civilian population contaminated in bordering towns or the children and relatives of veterans, many of whom have developed blood, lung and skin complications, according to the Organization for Veterans of Iran. According to a 2002 article in the Star-Ledger, 20,000 Iranian soldiers were killed on the spot by nerve gas. As of 2002, 5,000 of the 90,000 survivors continue to seek regular medical treatment, while 1,000 are hospital inpatients.
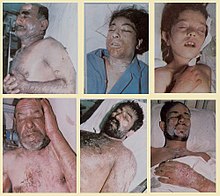
According to Iraqi documents, assistance in developing chemical weapons was obtained from firms in many countries, including the United States, West Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and France. A report stated that Dutch, Australian, Italian, French and both West and East German companies were involved in the export of raw materials to Iraqi chemical weapons factories. Declassified CIA documents show that the United States was providing reconnaissance intelligence to Iraq around 1987–88 which was then used to launch chemical weapon attacks on Iranian troops and that CIA fully knew that chemical weapons would be deployed and sarin attacks followed.
On 21 March 1986, the United Nations Security Council made a declaration stating that "members are profoundly concerned by the unanimous conclusion of the specialists that chemical weapons on many occasions have been used by Iraqi forces against Iranian troops, and the members of the Council strongly condemn this continued use of chemical weapons in clear violation of the Geneva Protocol of 1925, which prohibits the use in war of chemical weapons." The United States was the only member who voted against the issuance of this statement. A mission to the region in 1988 found evidence of the use of chemical weapons, and was condemned in Security Council Resolution 612.
According Walter Lang, senior defence intelligence officer for the U.S. Defense Intelligence Agency at the time, "the use of gas on the battlefield by the Iraqis was not a matter of deep strategic concern" to Reagan and his aides, because they "were desperate to make sure that Iraq did not lose." He claimed that the Defense Intelligence Agency "would have never accepted the use of chemical weapons against civilians, but the use against military objectives was seen as inevitable in the Iraqi struggle for survival". The Reagan administration did not stop aiding Iraq after receiving reports of the use of poison gas on Kurdish civilians.
The U.S. has accused Iran of using chemical weapons as well, though the allegations have been disputed. Joost Hiltermann, the principal researcher for Human Rights Watch between 1992 and 1994, conducted a two-year study that included a field investigation in Iraq, and obtained Iraqi government documents in the process. According to Hiltermann, the literature on the Iran–Iraq War reflects allegations of chemical weapons used by Iran, but they are "marred by a lack of specificity as to time and place, and the failure to provide any sort of evidence".
Analysts Gary Sick and Lawrence Potter have called the allegations against Iran "mere assertions" and stated, "No persuasive evidence of the claim that Iran was the primary culprit was ever presented." Policy consultant and author Joseph Tragert stated, "Iran did not retaliate with chemical weapons, probably because it did not possess any at the time".
At his trial in December 2006, Saddam said he would take responsibility "with honour" for any attacks on Iran using conventional or chemical weapons during the 1980–1988 war, but he took issue with charges he ordered attacks on Iraqis. A medical analysis of the effects of Iraqi mustard gas is described in a U.S. military textbook and contrasted effects of World War I gas.
Dissimilarities from other conflicts
Iran's attack on the Osirak nuclear reactor in September 1980 was the first attack on a nuclear reactor and one of only three attacks on a nuclear facility in the history of the world. It was also the first instance of a pre-emptive attack on a nuclear reactor to forestall the development of a nuclear weapon, though it did not achieve its objective, as France repaired the reactor after the attack. It took a second pre-emptive strike by the Israeli Air Force to disable the reactor, killing a French engineer in the process and causing France to pull out of Osirak. The decommissioning of Osirak has been cited as causing a substantial delay to Iraqi acquisition of nuclear weapons.
The Iran–Iraq War was also the first and only conflict in the history of warfare in which both forces used ballistic missiles against each other. The war also saw the only confirmed air-to-air helicopter battles in the history of warfare, with Iraqi Mi-25s flying against Iranian AH-1J SeaCobras on numerous occasions. The first instance of these helicopter "dogfights" was on the starting day of the war (22 September 1980): two Iranian SeaCobras crept up on two Mi-25s and hit them with TOW, wire-guided anti-tank missiles. One Mi-25 went down immediately, the other was badly damaged and crashed before reaching base. The Iranians won a similar air battle on 24 April 1981, destroying two Mi-25s without incurring losses to themselves. According to unclassified documents, Iranian pilots achieved a 10 to 1 kill ratio over the Iraqi helicopter pilots during these engagements and even engaged Iraqi, fixed wing aircraft. The Iran–Iraq War was also the first war to use unmanned drones in combat, when Iran created the Mohajer 1 series of drones and fitted them with 6 RPG-7 rockets to carry out attacks.
Both sides also carried out air and missile attack against population centers, especially Iraq. In October 1986, Iraqi aircraft began to attack civilian passenger trains and aircraft on Iranian soil, including an Iran Air Boeing 737 unloading passengers at Shiraz International Airport. In retaliation for the Iranian Operation Karbala 5, Iraq attacked 65 cities in 226 sorties over 42 days, bombing civilian neighbourhoods. Eight Iranian cities came under attack from Iraqi missiles. The bombings killed 65 children in an elementary school in Borujerd. The Iranians also responded with Scud missile attacks on Baghdad and struck a primary school there. These events became known as the "war of the cities".
Despite both sides fighting a war with each other, Iran and Iraq maintained diplomatic relations and embassies in each other's countries until mid-1987. Iran's government used human waves to attack enemy troops or even in some cases to clear minefields. Children also volunteered as well. Some reports have the Basijis marching into battle marking their expected entry to heaven by wearing plastic "keys to paradise" around their necks, although other analysts consider it to be a hoax, having been misinterpreted with a prayer book called "The Keys to Paradise"(Mafatih al-Janan) by Sheikh Abbas Qumi given to all volunteers.
According to journalist Robin Wright,
During the Fateh offensive , I toured the southwest front on the Iranian side and saw scores of boys, aged anywhere from nine to sixteen, who said with staggering and seemingly genuine enthusiasm that they had volunteered to become martyrs. Regular army troops, the paramilitary Revolutionary Guards and mullahs all lauded these youths, known as baseeji , for having played the most dangerous role in breaking through Iraqi lines. They had led the way, running over fields of mines to clear the ground for the Iranian ground assault. Wearing white headbands to signify the embracing of death, and shouting "Shaheed, shaheed" (Martyr, martyr) they literally blew their way into heaven. Their numbers were never disclosed. But a walk through the residential suburbs of Iranian cities provided a clue. Window after window, block after block, displayed black-bordered photographs of teenage or preteen youths.
Leaked Iraqi intelligence documents
During the 2003 invasion of Iraq, United States forces captured a voluminous archive of documents and recorded meetings that chronicled the deliberations of Saddam Hussein. Much of the collection has yet to be made public, but the Conflict Records Research Center, a government archive, released 20 transcripts and documents in conjunction with a conference on the Iran–Iraq war that was convened by the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
See also
- Arms-to-Iraq
- Iran–United States relations
- Iraq–United States relations
- Reagan Doctrine
- Trial of Saddam Hussein
General:
Persons:
- Frans van Anraat
- Kaveh Golestan
- List of Iranian commanders in the Iran–Iraq War
- Morteza Avini, prominent photographer of the Iran–Iraq War
Relevant conflicts
Notes
- ^ Called Arvand Roud in Iran and Shatt al-Arab in Iraq
- Muslim ibn Aqil referring to the Muslim figure
- Muharram referring to the first month of the Islamic calendar, during which the operation took place
- This was a "decision" rather than a resolution.
References
- Iran and Syria| Jubin Goodarzi
- Metz, Helen Chapin, ed. (1988), "Arms from France", Iraq: a Country Study, Library of Congress
- Metz, Helen Chapin, ed. (1988), "The Soviet Union", Iraq: a Country Study, Library of Congress
- Metz, Helen Chapin, ed. (1988), "Arms from The Soviet Union", Iraq: a Country Study, Library of Congress
- Anthony, John Duke; Ochsenwald, William L.; Crystal, Jill Ann. "Kuwait". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- David Kenneth Schenker, Dancing with Saddam: The Strategic Tango of Jordanian-Iraqi Relations
- Mearsheimer, John J.; Walt, Stephen M. (12 November 2002). "Can Saddam Be Contained? History Says Yes". International Security. Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs.
- ^ Hiro, Dilip (1991). The Longest War: The Iran-Iraq Military Conflict. New York: Routledge. p. 205. ISBN 9780415904063. OCLC 22347651.
- ^ "Iran-Iraq War 1980–1988". History of Iran. Iran Chamber Society.
- Potter, Lawrence G.; Sick, Gary (2006). Iran, Iraq and the Legacies of War. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 8. ISBN 9781403976093. OCLC 70230312.
- Rumel, Rudolph. "Lesser Murdering States, Quasi-States, and Groups: Estimates, Sources, and Calculations". Power Kills. University of Hawai'i.
- Sinan, Omar (25 June 2007). "Iraq to hang 'Chemical Ali'". Tampa Bay Times. Associated Press.
- "Iran-Iraq War". dKosopedia. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "I Persian Gulf War, 1980-1988". Acig.org. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "Iran-Iraq War". New World Encyclopedia. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) - The History Beat - SearchBeat.com". History.searchbeat.com. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "Gulf War Militaria | Gulf War Relics". Gulfwarstuff.com. 20 August 1988. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- Fair. "The Longest War-Never Again". Javid, Jahanshah. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Weiss, Martin. "War of Blackmail". SafeHaven. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Carlisle, Rodney P. (2003). Bowman, John S. (ed.). Persian Gulf War. New York: Facts on File. ISBN 9780816049424.
- ^ Molavi, Afshin (2005). The Soul of Iran: A Nation's Journey to Freedom (Revised ed.). England: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 152. ISBN 9780393325973.
- ^ Farrokh, Kaveh. Iran at War: 1500–1988. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 9781780962214.
- Fathi, Nazila (14 March 2003). "Threats And Responses: Briefly Noted; Iran-Iraq Prisoner Deal". The New York Times.
- Abrahamian, Ervand (2008). A History of Modern Iran (3rd print ed.). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521528917.
- Shane Harris; Matthew Aid (26 August 2013). "Exclusive: CIA Files Prove America Helped Saddam as He Gassed Iran". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
- "IRAQ vii. IRAN-IRAQ WAR". Encyclopædia Iranica. 15 December 2006.
- Hiltermann, Joost (17 January 2003). "America Didn't Seem to Mind Poison Gas". Global Policy Forum.
- ^ King, John (31 March 2003). "Arming Iraq and the Path to War". U.N. Observer & International Report.
- ^ Fisk, Robert (2005). The Great War for Civilisation: The Conquest of the Middle East. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 1-84115-007-X.
- "The Origin and Development of Imperialist Contention in Iran; 1884–1921". History of Iran. Iran Chamber Society.
- ^ Karsh, Efraim (25 April 2002). The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. Osprey Publishing. pp. 1–8, 12–16, 19–82. ISBN 978-1841763712.
- ^ Bulloch, John (1989). The Gulf War: Its Origins, History and Consequences (1st published ed.). London: Methuen. ISBN 9780413613707.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Rajaee, Farhang, ed. (1993). The Iran-Iraq War: The Politics of Aggression. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0813011776.
- Mirfendereski, Guive (2005). "Tonb (Greater and Lesser)". Encyclopædia Iranica.
- ^ Ranard, Donald A. (ed.). "History". Iraqis and Their Culture.
- ^ Brogan, Patrick (1989). World Conflicts: A Comprehensive Guide to World Strife Since 1945. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 0-7475-0260-9.
- "Iran-Iraq War". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- Mearsheime, John J.; Walt, Stephen M. (12 November 2002). "Can Saddam Be Contained? History Says Yes". International Security. Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs.
- ^ "Viewpoints of the Iranian political and military elites".
- "Britannica Online Encyclopedia: Saddam Hussein".
- ^ Fürtig, Henner (2012). "Den Spieß umgedreht: iranische Gegenoffensive im Ersten Golfkrieg". Damals (in German) (5): 10–13.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Speech made by Saddam Hussein. Baghdad, Voice of the Masses in Arabic, 2 April 1980. FBIS-MEA-80-066. 3 April 1980, E2-3. E3
- Khomeini, Ruhollah (1981). Islam and Revolution: Writing and Declarations of Imam Khomeini. Algar, Hamid. Mizan Press. p. 122. ISBN 978-0933782037.
- Mackey, Sandra; Harrop, W. Scott (1996). The Iranians: Persia, Islam and the Soul of a Nation. Dutton. p. 317. ISBN 9780525940050.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "National Intelligence Daily" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency. 10 March 1980.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Westcott, Kathryn (27 February 2003). "Iraq's rich mosaic of people". BBC News.
- ^ Cruze, Gregory S. (spring 1988). "Iran and Iraq: Perspectives in Conflict". Military Reports.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Noi, Aylin. "The Arab Spring, Its Effects on the Kurds".
- "Kurdistan, Iraq Global Security".
- Coughlin, Con. "Lets Deport the Iran Embassy Siege survivor to Iraq".
- Fremont-Barnes, Gregory (2009). Who dares wins the SAS and the Iranian embassy siege, 1980. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 9781780964683.
- ^ Woods, Kevin. "Saddam's Generals: A Perspective of the Iran-Iraq War" (PDF).
- ^ Pike, John (ed.). "Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988)".
- Farmanfarmaian, Roxane (14 February 2011). "What makes a revolution succeed?". Al Jazeera.
- ^ "National Security". Pars Times.
- ^ Pollack, Kenneth M. (2004). "Iraq". Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness, 1948–1991. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 9780803287839.
- Ottolenghi, Emanuelle (3 September 2011). "The Pasdaran: Inside Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps". Foundation for Defense of Democracies.
- ^ Alfoneh, Ali. "The Basij Resistance Force". The Iran Primer. United States Institute of Peace.
- Eckholm, Leif (1 August 2011). "Invading Iran: Lessons From Iraq". Policy Review. 168. Stanford University Hoover Institution.
Invading forces would need to be prepared for a deeply embedded and enduring insurgency, due to extreme challenges presented by terrain, and resolve...
- ^ Cordesman, Anthony H.; Wagner, Abraham (1990). The Lessons of Modern War: Volume Two – The Iran-Iraq Conflict. Westview Press. p. 102. ISBN 978-0813309552.
- Robinson, Julian Perry; Goldbat, Jozef (May 1984). "Chemical Warfare in the Iran-Iraq War 1980–1988". History of Iran. Iran Chamber Society.
- ^ Cooper, Thomas; Bishop, Farzad (9 September 2003). "Persian Gulf War: Iraqi Invasion of Iran, September 1980". Arabian Peninsula and Persian Gulf Database. Air Combat Information Group.
- Modern Warfare: Iran-Iraq War (film documentary).
- ^ Wilson, Ben. "The Evolution of Iranian Warfighting during the Iran-Iraq War" (PDF).
- ^ Wilson, Ben (July–August 2007). "The Evolution of Iranian Warfighting During the Iran-Iraq War: When Dismounted Light Infantry Made the Difference" (PDF). U.S. Army: Foreign Military Studies Office.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Aboul-Enein, Youssef; Bertrand, Andrew; Corley, Dorothy (12 April 2012). "Egyptian Field Marshal Abdul-Halim Abu Ghazalah on the Combat Tactics and Strategy of the Iran-Iraq War". Small Wars Journal. Ghazalah's Phased Analysis of Combat Operations. Small Wars Foundation.
- Dennis, Simon Dunstan (2009). The Six Day War, 1967: Jordan and Syria (1st ed.). Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p. 22. ISBN 9781846033643.
- ^ Jafari, Mojtaba. "Nasr Offensive Operation".
- "Iran-Iraq war bogs down in rain, conflicting claims". CSMonitor.com. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "Assault on Al-Wallid". Imperial Iraniasn Air Force.
- ^ Cordesman, Anthony. "Lessons of Modern Warfare: The Iran Iraq War Chapter V" (PDF).
- ^ Cooper, Tom. "Bombed by Blinders Part 1".
- ^ Khomeini: life of the Ayatollah By Baqer Moin]
- Pelletiere, Stephen. The Iran-Iraq War: Chaos in a Vacuum.
- Iran Yearbook. Moini-Biontino. 1988. p. 125. LCCN sn89044105.
- Firestone, Reuven (2008). Who are the real chosen people?: The Meaning of Chosenness in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam (2008 hardcover ed.). Woodstock, VT: SkyLight Paths Publishing. p. 143. ISBN 9781594732485.
- "Iran at war". Reuters. 31 May 2012. and "(Review)". The Wall Street Journal. cited in Farrokh, Kaveh. "Review: Wall Street Journal and Reuters".
- Keegan, John (2004). The Iraq war. New York: Knopf. ISBN 978-1400041992.
- ^ Thomas Cooper and Farzad Bishop (9 September 2003). "Fire in the Hills: Iranian and Iraqi Battles of Autumn 1982". Arabian Peninsula & Persian Gulf Database. Air Combat Information Group.
- "Khorramshahr-oxford dictionaries".
- "Abadan-Encyclopedia Britannica".
- ^ Williams, Scott (June 2002). "The Battle of al-Khafji". Monterey, California: Naval Postgraduate School.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Declaration of Howard Teicher" (PDF). Case No. 93-241-CR-HIGHSMITH. United States District Court: Southern District Florida. 31 January 1995. Plain text version
{{cite journal}}: External link in|postscript= - Jupp, Michael (19 December 1988). "Child-Soldier Treaty Has Wide Support". The New York Times.
- Special to The Christian Science Monitor. "Giving one's life to the cause of Islam and Iran. Guarding the revolution's Islamic standards". CSMonitor.com. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- Cordesman, Anthony H. (1999). Iraq and the War of Sanctions: Conventional Threats and Weapons of Mass Destruction (1st published ed.). Westport, Connecticut: Praeger. ISBN 0275965287.
- ^ Dunn, Brian. "The First Gulf War".
- Naficy, Hamid (2012). A Social History of Iranian Cinema The Globalizing Era, 1984–2010. Duke University Press. p. 11. ISBN 9780822348788.
- ^ Aboul-Enein, Youssef; Bertrand, Andrew; Corley, Dorothy (23 April 2012). "The "Dawn of Victory" campaigns to the "Final Push": Part Three of Three". Small Wars Journal. Small Wars Foundation.
- Dunn, Brian J. (1998). "The First Gulf War". The Dignified Rant.
- ^ "Phase Five: New Iranian Efforts at "Final Offensives", 1986–1887". The Lessons of Modern War – Volume II: Iran-Iraq War (PDF). Center for Strategic and International Studies.
- ^ Thomas Coper and Farzad Bishop (9 September 2003). "Persian Gulf War, 1980–1988: The Mother of All Build-Ups". Arabian Peninsula and Persian Gulf Database. Air Combat Information Group.
- "LST Hengam class". LST Hengam class. Harpoon Headquarters. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ Cordesman, Anthony. "The Lessons of Modern War Vol II".
- Dugdale-Pointon, T.D.P. (27 October 2002). "Tanker War 1984–1988".
- Wars in Peace: Iran-Iraq War (film documentary). Wars in Peace. 1995.
- "Attack on USS Stark (FFG-31)" (PDF). JAG Manual Investigations. U.S. Navy Judge Advocate General's Corps. 3 September 1987.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Pokrant, Marvin (1999). Desert Storm at Sea: What the Navy Really Did. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 43. ISBN 9780313310249.
- ^ Kelley, Stephen Andrew (June 2007). "Better Lucky Than Good: Operation Earnest Will as Gunboat Diplomacy". Naval Postgraduate School. ASIN B007U7WRUC.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Formal Investigation into the Circumstances Surrounding the Attack of the USS Stark in 1987" (PDF). OSD/JS FOIA Library. Office of the Secretary of Defense and Joint Staff.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Iran: Gradual Superpower Involvement". Country Study & Guide. AllRefer. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Ross, William. "Seawise Giant". Relevant Search Scotland. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Cooper, Tom. "Bombed By Blinders Part 2".
- ^ Daraghai, Borzou. "1987 Chemical Strike Still Haunts Iran". LA Times.
- Rubin, Barry. Conflict and Insurgency in the Middle East.
- Wright, Robin (1989). In the name of God: The Khomeini decade. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 126, 133. ISBN 9780671672355.
- Khomeini, Ruhollah (4 April 1985). (Speech) (in Persian).
{{cite speech}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) quoted in Brumberg, Daniel (2001). Reinventing Khomeini: The Struggle for Reform in Iran. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 132–134. ISBN 978-0226077581. - ^ "نگاهی به نقش ناشناخته "تلاش" و "مهاجر" در کربلای 5 و والفجر 8". Mashregnews (in Persian). 2 October 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Cordesman, Anthony. "Lessons of Modern War: The Iran-Iraq War" (PDF).
- Rubin, Michael (Spring 2003). "Are Kurds a pariah minority?". Social Research. Pariah Minorities. 70 (1). The New School: 295–330. JSTOR 40971614.
- Silverstein, Adam J. (21 January 2012). Islamic History: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191609343.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - ^ "Iran–Iraq war". Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ "The Combination of Iraqi offensives and Western intervention force Iran to accept a cease-fire: September 1987 to March 1989". The Lessons of Modern War – Volume II: Iran-Iraq War (PDF). Center for Strategic and International Studies.
- "Anti-war protests reported in Iran". Spokane Chronicle. Google News Archive. Associated Press. 10 May 1985.
- Sciolino, Elaine. "Human Wave raid loses Iran's favor".
- Mohammadi, Karim. "The Forgotten Victims of the Iran-Iraq War".
- ^ "1988: Thousands die in Halabja gas attack". On This Day. BBC.
- ^ Tyler, Patrick. "Officers Say US Aided Iraq in war despite use of gas". The News York Times.
- Crist, David (2012). The Twilight War: The secret history of America's thirty-year conflict with Iran. New York: Penguin Press. p. 434 (Photo plates). ISBN 9781594203411.
- ^ Iran's strategic intentions and capabilities - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- ^ Dodds, Joanna; Wilson, Ben (6 June 2009). "The Iran-Iraq War: Unattainable Objectives". Middle East Review of International Affairs. 13 (2).
- "Iran Reports New Iraqi Gas Raids; And Says Cities May be Hit Next - New York Times". Nytimes.com. 2 April 1988. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "Mersad operation". Special Edition. Tebyan. 27 July 2005.
- Wong, Edward (5 April 2006). "Hussein charged with genocide in 50,000 deaths". The New York Times.
- ^ Tarock, Adam. The Superpower's Involvement in the Iran Iraq War.
- John Pike. "Chemical Weapons - Iran". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "iran iraq war 1980–1990".
- Further Report of the Secretary-General on the Implementation of Security Council Resolution 598 (PDF) (Report). U.N. Secretary General's. 9 December 1991.
That explanations do not appear sufficient or acceptable to the international community is a fact. Accordingly, the outstanding event under the violations referred to is the attack of 22 September 1980, against Iran, which cannot be justified under the charter of the United Nations, any recognized rules and principles of international law or any principles of international morality and entails the responsibility for conflict.
Even if before the outbreak of the conflict there had been some encroachment by Iran on Iraqi territory, such encroachment did not justify Iraq's aggression against Iran—which was followed by Iraq's continuous occupation of Iranian territory during the conflict—in violation of the prohibition of the use of force, which is regarded as one of the rules of jus cogens.
...On one occasion I had to note with deep regret the experts' conclusion that "chemical weapons ha been used against Iranian civilians in an area adjacent to an urban center lacking any protection against that kind of attack" (s/20134, annex). The Council expressed its dismay on the matter and its condemnation in Resolution 620 (1988), adopted on 26 August 1988. - "Iraq accuses Iran of Scud missile attack".
- Black, Ian (23 September 2010). "Iran and Iraq remember war that cost more than a million lives". The Guardian. London.
- Kagan, Frederick. "Iran's Win in Iraq- Out of Iraq".
- ^ "Iran-Iraq War". Encarta. MSN. 20 August 1988. Archived from the original on 6 April 2009. Retrieved 1 March 2009.
- ^ Pike, John (ed.). "Iraq debt: Non-Paris Club Creditors".
- Weiss, Martin A. (29 March 2011). "Iraq's Debt Relief: Procedure and Potential Implications for International Debt Relief" (PDF). Congressional Research Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Truman, Edwin M. (28 April 2003). "Op-ed: The Right Way to Ease Iraq's Debt Burden". Financial Times. Retrieved 2 August 2011Re-published by Peterson Institute for International Economics
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - "UAE waives billions of Iraqi debt". BBC News. 6 July 2008.
- "Iraq war reparations to Kuwait could be reduced: UK". Reuters. 4 August 2009.
- "30 Years in Science: Secular Movements in Knowledge Creation" (PDF). Science-Metrix.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Healy, Melissa (24 January 2011). "Advances in treatment help more people survive severe injuries to the brain". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "Time to discuss drone warfare in Israel, Iran, and Pakistan". Guardianlv.com. 7 October 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- "The Dujail Massacre". Indian Express. 31 December 2006.
- Katzman, Kenneth (1 October 2010). "The Kurds in Post-Saddam Iraq" (PDF). Congressional Research Service: 2. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Nasr, Vali Nasr (2007). The Shia revival: How Conflicts Within Islam Will Shape the Future (New ed.). New York: W.W. Norton. p. 140. ISBN 978-0393329681.
- Column in Etelaat, 4 April 1983, quoted in Molavi, Afshin (2005). The soul of Iran a nation's journey to freedom (Revised ed.). England: W.W. Norton & Co (NY). ISBN 9780393325973.
- "The Arming, and Disarming, of Iran's Revolution". The Economist (International ed.). 19 September 1987. pp. 56–57.
- McCarthy, Andrew C. (3 March 2012). "It's a Pity Somebody Has to Win". National Review Online. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- Rajaee, Farhang, ed. (1997). Iranian perspectives on the Iran-Iraq war. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0813014760.
- Jessup, John E. (30 August 1998). An encyclopedic dictionary of conflict and conflict resolution, 1945–1996. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313281129.
- SIPRI Database Indicates that of $29,079 million of arms exported to Iraq from 1980 to 1988 the Soviet Union accounted for $16,808 million, France $4,591 million, and China $5,004 million (Info must be entered)
- United Nations Special Commission. "UNSCOM's Comprehensive Review". James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies.
{{cite journal}}:|contribution=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Annex D: Iraq Economic Data (1989–2003)". Comprehensive Report of the Special Advisor to the DCI [Director of Central Intelligence] on Iraq's WMD. Vol. 1 of 3. Central Intelligence Agency. 27 April 2007.
- Safire, William (19 May 1992). "The Administration's Iraq Gate Scandal". Congressional Record.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Baker, Russ W. (March 1993). "Iraq-gate: The Big One That (Almost) Got Away". Columbia Journalism Review.
- El camino de la libertad: la democracia año a año (1986) (in Spanish). El Mundo. pp. 27–32.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Fuller, Graham E. (2008). The New Turkish Republic: Turkey as a Pivotal State in the Muslim World. Washington, D.C.: United States Institute of Peace Press. p. 40,49. ISBN 9781601270191.
- http://www.wpainc.com/Archive/Reagan%20Administration/WFM%20Papers%20from%20Reagan%20Archives/Iran-Iraq/Presentation%20on%20Gulf%20Oil%20Disruption%205-22-84.pdf
- ^ Martins, Mark S. (Winter 1994). "Rules of Engagement for Land Forces: A Matter of Training, Not Lawyering" (PDF). Military Law Review. 143: 43–46.
- Peniston, Bradley (2006). No Higher Honor: Saving the USS Samuel B. Roberts in the Persian Gulf. Persian Gulf: Naval Institute Press. pp. 61–63. ISBN 1-59114-661-5..
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Wright, Robin (2008). Dreams and Shadows: The Future of the Middle East. New York: Penguin Press. p. 438. ISBN 9781594201110.
- Bryant, Terry (2007). History's Greatest War (1st ed.). Chandni Chowk, Delhi: Global Media. ISBN 9788189940638.
- Fassihi, Farnaz (27 October 2002). "In Iran, grim reminders of Saddam's arsenal". New Jersey Star-Ledger.
- ^ Center for Documents of The Imposed War, Tehran. (مرکز مطالعات و تحقیقات جنگ)
- "Iraqi Scientist Reports on German, Other Help for Iraq Chemical Weapons Program". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- SHANE HARRIS, MATTHEW M. AID. "Exclusive: CIA Files Prove America Helped Saddam as He Gassed Iran". ForeignPolicy.com. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- United Nations Security Council (12 March 1986). S17911.pdf "Report of the mission dispatched by the Secretary-General to investigate allegations of the use of chemical weapons in the conflict between the Islamic Republic of Iran and Iraq S/17911" (PDF). Security Council Report. S/17911 and Add. 1
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) Cited in Hurd, Nathaniel. "U.S. Diplomatic and Commercial Relationships with Iraq, 1980 – 2 August 1990". - Galbraith, Peter W.; Van Hollen, Christopher Jr. (21 September 1988). "Chemical Weapons Use in Kurdistan: Iraq's Final Offensive". Report to the U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations. UNHCR: 30.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Pear, Robert (15 September 1988). "U.S. Says It Monitored Iraqi Messages on Gas". The New York Times.
- ^ Potter, Lawrence; Sick, Gary (2004). Iran, Iraq, and the legacies of war. MacMillan. ISBN 1-4039-6450-5.
- Tragert, Joseph (2003). Understanding Iran. Indianapolis, Indiana: Alpha. p. 190. ISBN 1-59257-141-7.
- Rasheed, Ahmed (19 December 2006). "Saddam admits Iran gas attacks". The Australian.
- Sidell, Frederick R.; Urbanetti, John S.; Smith, William J.; Hurst, Charles G. "Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare". Office of The Surgeon General, Department of the Army, United States of America.
{{cite journal}}:|chapter=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Cohen, Marsha (6 August 2010). "IRAN: Eyes on the Skies Over Bushehr Nuclear Reactor". Inter Press Service News Agency. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ^ Schneider, Barry (30 September 1980). "Radical Responses to Radical Regimes: Evaluating Preemptive Counter-Proliferation". McNair Paper (41). National Defense University Library. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
{{cite journal}}:|chapter=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Osiraq: Iraq Special Weapons Facilities". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Reiter, Dan (July 2005). "Preventive Attacks Against Nuclear Programs and the "Success" at Osiraq"" (PDF). Nonproliferation Review. Viewpoint. 12 (2). The Monterey Institute of International Studies, Center for Nonproliferation Studies: 355. doi:10.1080/10736700500379008. ISSN online/05/020355-17 1746-1766 online/05/020355-17.
{{cite journal}}: Check|issn=value (help) - Raas, Whitney; Long, Austin (Spring 2007). "Osirak Redux? Assessing Israeli Capabilities to Destroy Iranian Nuclear Facilities" (PDF). International Security. 31 (4). Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs: 7–33. doi:10.1162/isec.2007.31.4.7.
- "پايگاه هشتم شكاري" (in Persian). Airtoair. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Wright, Robin (2001). Sacred Rage: The Wrath of Militant Islam (Updated ed.). New York: Simon & Schuster. p. 37. ISBN 9780743233422.
- "Iran-Iraq War Documents". Wilson Center. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- Gordon, Michael R. (25 October 2011). "Papers From Iraqi Archive Reveal Conspiratorial Mind-Set of Hussein". New York Times. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- "Inside the Iraqi command". New York Times. 25 October 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
Works cited
- Brogan, Patrick (1989). World Conflicts: A Comprehensive Guide to World Strife Since 1945. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 0-7475-0260-9.
- Bulloch, John (1989). The Gulf War: Its Origins, History and Consequences (1st published ed.). London: Methuen. ISBN 9780413613707.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Farrokh, Kaveh. Iran at War: 1500–1988. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 9781780962214.
- "Phase Five: New Iranian Efforts at "Final Offensives", 1986–1887". The Lessons of Modern War – Volume II: Iran-Iraq War (PDF). Center for Strategic and International Studies.
- "Iran-Iraq War 1980–1988". History of Iran. Iran Chamber Society.
- Karsh, Efraim (25 April 2002). The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. Osprey Publishing. pp. 1–8, 12–16, 19–82. ISBN 978-1841763712.
- Pollack, Kenneth M. (2004). "Iraq". Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness, 1948–1991. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 9780803287839.
- Wright, Edwin M. (January 1992). "Iran as a Gateway to Russia". Foreign Affairs. Council on Foreign Relations: 367–372.
External links
- "Dutchman charged for selling chemicals to Saddam". BBC.
- Documentary: Modern Warfare – Iran/Iraq 1980–1988 (also on YouTube)
- Intelligence Reports on Saddam's Reign
- Template:Dmoz
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA
Categories: