| Revision as of 21:25, 16 July 2020 edit5.66.220.188 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:26, 16 July 2020 edit undoJoseywales1961 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers39,092 editsm Reverted edits by 5.66.220.188 (talk) (HG) (3.4.10)Tag: RollbackNext edit → | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| == Causes == | == Causes == | ||
| ] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue. |
] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue.<ref name=Fit2016>{{cite book|last1=Fitzpatrick|first1=James E.|last2=Morelli|first2=Joseph G.|title=Dermatology Secrets Plus|publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences|isbn=9780323313551|page=511|edition=5th|url=https://books.google.ca/books?id=ReqeCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA511|accessdate=10 May 2016|language=en}}</ref> ], however, may cause increased flushing in those affected.<ref name=Fit2016/> | ||
| ==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 16 July 2020
Condition causing development of a large, bulbous nose, commonly due to untreated rosacea Medical condition| Rhinophyma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An Old Man and His Grandson, by Domenico Ghirlandaio | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Rhinophyma is a condition causing development of a large, bulbous nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea.
Signs and symptoms
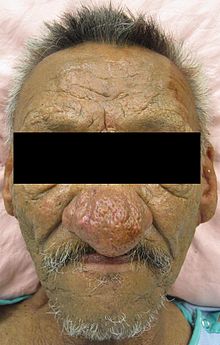
Rhinophyma is characterised by prominent pores and a fibrous thickening of the nose, sometimes with papules. It is associated with the common skin condition rosacea. It can carry a strong psychological impact due to its effect on one's personal appearance.
Causes
Alcoholism is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue. Alcohol, however, may cause increased flushing in those affected.
Pathophysiology
Rhinophyma is a slowly progressive condition due to hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands of the tip of the nose often seen in cases of long-standing rosacea; it is not a cancer. It presents as a pink, lobulated mass over the nose with dilation of the superficial blood vessels; it mostly affects men past middle age. People affected by rhinophyma typically seek advice because of the perceived unsightly appearance of the enlargement, or obstruction in breathing and vision.
Diagnosis
Rhinophyma may be diagnosed without testing, but a skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment consists of paring down the bulk of the tissue with a sharp instrument or carbon dioxide laser and allowing the area to re-epithelialise. Sometimes, the tissue is completely excised and the raw area skin-grafted.
References
- Cohen AF, Tiemstra JD (2002). "Diagnosis and treatment of rosacea". J Am Board Fam Pract. 15 (3): 214–7. PMID 12038728.
- "Rosacea". Dermnetnz.org.
- "Rhinophyma". Rhinophyma. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, James E.; Morelli, Joseph G. Dermatology Secrets Plus (5th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 511. ISBN 9780323313551. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- Dhingra P.L. Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat, 6th edition, New Delhi 2013, 490 pp. ISBN 9788131234310
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |