| Revision as of 05:32, 28 December 2020 editSiweiLuoUIC (talk | contribs)15 edits →Newtonian analysis of orbital motion← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:35, 28 December 2020 edit undoSiweiLuoUIC (talk | contribs)15 edits →Newtonian analysis of orbital motionNext edit → | ||
| Line 218: | Line 218: | ||
| When the two-body system is under the influence of torque, the angular momentum h is not a constant. After the following calculation: | When the two-body system is under the influence of torque, the angular momentum h is not a constant. After the following calculation: | ||
| :<math> frac{\delta r}{\delta \theta} = - \frac{1}{u^2} \frac{\delta u}{\delta \theta} = -\frac{h}{m} \frac{\delta u}{\delta \theta} </math> | :<math> \frac{\delta r}{\delta \theta} = - \frac{1}{u^2} \frac{\delta u}{\delta \theta} = -\frac{h}{m} \frac{\delta u}{\delta \theta} </math> | ||
| ⚫ | :<math> \frac{\delta^2 r}{\delta \theta^2} = -\frac{h^2u^2}{m^2} \frac{\delta^2 u}{\delta \theta^2} - \frac{hu^2}{m^2} \frac{\delta |
||
| ⚫ | :<math> \frac{\delta^2 r}{\delta \theta^2} = -\frac{h^2u^2}{m^2} \frac{\delta^2 u}{\delta \theta^2} - \frac{hu^2}{m^2} \frac{\delta h}{\delta \theta} \frac{\delta u}{\delta \theta} </math> | ||
| :<math> {\frac{\delta \theta}{\delta t}}^2 r = \frac{h^2 u^3}{m^2} </math> | |||
| the differential equation turns out to be a Sturm-Liouville equation | the differential equation turns out to be a Sturm-Liouville equation | ||
Revision as of 05:35, 28 December 2020
gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in outer space This article is about orbits in celestial mechanics, due to gravity. For other uses, see Orbit (disambiguation).


In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved trajectory of an object, such as the trajectory of a planet around a star or a natural satellite around a planet. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics of orbital motion.
History
| Part of a series on | ||
| Spaceflight | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| History | ||
| Applications | ||
Spacecraft
|
||
| Space launch | ||
| Spaceflight types | ||
| List of space organizations | ||
|
| ||
Historically, the apparent motions of the planets were described by European and Arabic philosophers using the idea of celestial spheres. This model posited the existence of perfect moving spheres or rings to which the stars and planets were attached. It assumed the heavens were fixed apart from the motion of the spheres, and was developed without any understanding of gravity. After the planets' motions were more accurately measured, theoretical mechanisms such as deferent and epicycles were added. Although the model was capable of reasonably accurately predicting the planets' positions in the sky, more and more epicycles were required as the measurements became more accurate, hence the model became increasingly unwieldy. Originally geocentric, it was modified by Copernicus to place the Sun at the centre to help simplify the model. The model was further challenged during the 16th century, as comets were observed traversing the spheres.
The basis for the modern understanding of orbits was first formulated by Johannes Kepler whose results are summarised in his three laws of planetary motion. First, he found that the orbits of the planets in our Solar System are elliptical, not circular (or epicyclic), as had previously been believed, and that the Sun is not located at the center of the orbits, but rather at one focus. Second, he found that the orbital speed of each planet is not constant, as had previously been thought, but rather that the speed depends on the planet's distance from the Sun. Third, Kepler found a universal relationship between the orbital properties of all the planets orbiting the Sun. For the planets, the cubes of their distances from the Sun are proportional to the squares of their orbital periods. Jupiter and Venus, for example, are respectively about 5.2 and 0.723 AU distant from the Sun, their orbital periods respectively about 11.86 and 0.615 years. The proportionality is seen by the fact that the ratio for Jupiter, 5.2/11.86, is practically equal to that for Venus, 0.723/0.615, in accord with the relationship. Idealised orbits meeting these rules are known as Kepler orbits.


Isaac Newton demonstrated that Kepler's laws were derivable from his theory of gravitation and that, in general, the orbits of bodies subject to gravity were conic sections (this assumes that the force of gravity propagates instantaneously). Newton showed that, for a pair of bodies, the orbits' sizes are in inverse proportion to their masses, and that those bodies orbit their common center of mass. Where one body is much more massive than the other (as is the case of an artificial satellite orbiting a planet), it is a convenient approximation to take the center of mass as coinciding with the center of the more massive body.
Advances in Newtonian mechanics were then used to explore variations from the simple assumptions behind Kepler orbits, such as the perturbations due to other bodies, or the impact of spheroidal rather than spherical bodies. Lagrange (1736–1813) developed a new approach to Newtonian mechanics emphasizing energy more than force, and made progress on the three body problem, discovering the Lagrangian points. In a dramatic vindication of classical mechanics, in 1846 Urbain Le Verrier was able to predict the position of Neptune based on unexplained perturbations in the orbit of Uranus.
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) in his 1916 paper The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity explained that gravity was due to curvature of space-time and removed Newton's assumption that changes propagate instantaneously. This led astronomers to recognize that Newtonian mechanics did not provide the highest accuracy in understanding orbits. In relativity theory, orbits follow geodesic trajectories which are usually approximated very well by the Newtonian predictions (except where there are very strong gravity fields and very high speeds) but the differences are measurable. Essentially all the experimental evidence that can distinguish between the theories agrees with relativity theory to within experimental measurement accuracy. The original vindication of general relativity is that it was able to account for the remaining unexplained amount in precession of Mercury's perihelion first noted by Le Verrier. However, Newton's solution is still used for most short term purposes since it is significantly easier to use and sufficiently accurate.
Planetary orbits
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Within a planetary system, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids and other minor planets, comets, and space debris orbit the system's barycenter in elliptical orbits. A comet in a parabolic or hyperbolic orbit about a barycenter is not gravitationally bound to the star and therefore is not considered part of the star's planetary system. Bodies which are gravitationally bound to one of the planets in a planetary system, either natural or artificial satellites, follow orbits about a barycenter near or within that planet.
Owing to mutual gravitational perturbations, the eccentricities of the planetary orbits vary over time. Mercury, the smallest planet in the Solar System, has the most eccentric orbit. At the present epoch, Mars has the next largest eccentricity while the smallest orbital eccentricities are seen with Venus and Neptune.
As two objects orbit each other, the periapsis is that point at which the two objects are closest to each other and the apoapsis is that point at which they are the farthest. (More specific terms are used for specific bodies. For example, perigee and apogee are the lowest and highest parts of an orbit around Earth, while perihelion and aphelion are the closest and farthest points of an orbit around the Sun.)
In the case of planets orbiting a star, the mass of the star and all its satellites are calculated to be at a single point called the barycenter. The paths of all the star's satellites are elliptical orbits about that barycenter. Each satellite in that system will have its own elliptical orbit with the barycenter at one focal point of that ellipse. At any point along its orbit, any satellite will have a certain value of kinetic and potential energy with respect to the barycenter, and that energy is a constant value at every point along its orbit. As a result, as a planet approaches periapsis, the planet will increase in speed as its potential energy decreases; as a planet approaches apoapsis, its velocity will decrease as its potential energy increases.
Understanding orbits
There are a few common ways of understanding orbits:
- A force, such as gravity, pulls an object into a curved path as it attempts to fly off in a straight line.
- As the object is pulled toward the massive body, it falls toward that body. However, if it has enough tangential velocity it will not fall into the body but will instead continue to follow the curved trajectory caused by that body indefinitely. The object is then said to be orbiting the body.
As an illustration of an orbit around a planet, the Newton's cannonball model may prove useful (see image below). This is a 'thought experiment', in which a cannon on top of a tall mountain is able to fire a cannonball horizontally at any chosen muzzle speed. The effects of air friction on the cannonball are ignored (or perhaps the mountain is high enough that the cannon is above the Earth's atmosphere, which is the same thing).


If the cannon fires its ball with a low initial speed, the trajectory of the ball curves downward and hits the ground (A). As the firing speed is increased, the cannonball hits the ground farther (B) away from the cannon, because while the ball is still falling towards the ground, the ground is increasingly curving away from it (see first point, above). All these motions are actually "orbits" in a technical sense – they are describing a portion of an elliptical path around the center of gravity – but the orbits are interrupted by striking the Earth.
If the cannonball is fired with sufficient speed, the ground curves away from the ball at least as much as the ball falls – so the ball never strikes the ground. It is now in what could be called a non-interrupted, or circumnavigating, orbit. For any specific combination of height above the center of gravity and mass of the planet, there is one specific firing speed (unaffected by the mass of the ball, which is assumed to be very small relative to the Earth's mass) that produces a circular orbit, as shown in (C).
As the firing speed is increased beyond this, non-interrupted elliptic orbits are produced; one is shown in (D). If the initial firing is above the surface of the Earth as shown, there will also be non-interrupted elliptical orbits at slower firing speed; these will come closest to the Earth at the point half an orbit beyond, and directly opposite the firing point, below the circular orbit.
At a specific horizontal firing speed called escape velocity, dependent on the mass of the planet, an open orbit (E) is achieved that has a parabolic path. At even greater speeds the object will follow a range of hyperbolic trajectories. In a practical sense, both of these trajectory types mean the object is "breaking free" of the planet's gravity, and "going off into space" never to return.
The velocity relationship of two moving objects with mass can thus be considered in four practical classes, with subtypes:
- No orbit
- Suborbital trajectories
- Range of interrupted elliptical paths
- Orbital trajectories (or simply "orbits")
- Range of elliptical paths with closest point opposite firing point
- Circular path
- Range of elliptical paths with closest point at firing point
- Open (or escape) trajectories
- Parabolic paths
- Hyperbolic paths
It is worth noting that orbital rockets are launched vertically at first to lift the rocket above the atmosphere (which causes frictional drag), and then slowly pitch over and finish firing the rocket engine parallel to the atmosphere to achieve orbit speed.
Once in orbit, their speed keeps them in orbit above the atmosphere. If e.g., an elliptical orbit dips into dense air, the object will lose speed and re-enter (i.e. fall). Occasionally a space craft will intentionally intercept the atmosphere, in an act commonly referred to as an aerobraking maneuver.

Newton's laws of motion
Newton's law of gravitation and laws of motion for two-body problems
In most situations relativistic effects can be neglected, and Newton's laws give a sufficiently accurate description of motion. The acceleration of a body is equal to the sum of the forces acting on it, divided by its mass, and the gravitational force acting on a body is proportional to the product of the masses of the two attracting bodies and decreases inversely with the square of the distance between them. To this Newtonian approximation, for a system of two-point masses or spherical bodies, only influenced by their mutual gravitation (called a two-body problem), their trajectories can be exactly calculated. If the heavier body is much more massive than the smaller, as in the case of a satellite or small moon orbiting a planet or for the Earth orbiting the Sun, it is accurate enough and convenient to describe the motion in terms of a coordinate system that is centered on the heavier body, and we say that the lighter body is in orbit around the heavier. For the case where the masses of two bodies are comparable, an exact Newtonian solution is still sufficient and can be had by placing the coordinate system at the center of mass of the system.
Defining gravitational potential energy
Energy is associated with gravitational fields. A stationary body far from another can do external work if it is pulled towards it, and therefore has gravitational potential energy. Since work is required to separate two bodies against the pull of gravity, their gravitational potential energy increases as they are separated, and decreases as they approach one another. For point masses the gravitational energy decreases to zero as they approach zero separation. It is convenient and conventional to assign the potential energy as having zero value when they are an infinite distance apart, and hence it has a negative value (since it decreases from zero) for smaller finite distances.
Orbital energies and orbit shapes
When only two gravitational bodies interact, their orbits follow a conic section. The orbit can be open (implying the object never returns) or closed (returning). Which it is depends on the total energy (kinetic + potential energy) of the system. In the case of an open orbit, the speed at any position of the orbit is at least the escape velocity for that position, in the case of a closed orbit, the speed is always less than the escape velocity. Since the kinetic energy is never negative, if the common convention is adopted of taking the potential energy as zero at infinite separation, the bound orbits will have negative total energy, the parabolic trajectories zero total energy, and hyperbolic orbits positive total energy.
An open orbit will have a parabolic shape if it has velocity of exactly the escape velocity at that point in its trajectory, and it will have the shape of a hyperbola when its velocity is greater than the escape velocity. When bodies with escape velocity or greater approach each other, they will briefly curve around each other at the time of their closest approach, and then separate, forever.
All closed orbits have the shape of an ellipse. A circular orbit is a special case, wherein the foci of the ellipse coincide. The point where the orbiting body is closest to Earth is called the perigee, and is called the periapsis (less properly, "perifocus" or "pericentron") when the orbit is about a body other than Earth. The point where the satellite is farthest from Earth is called the apogee, apoapsis, or sometimes apifocus or apocentron. A line drawn from periapsis to apoapsis is the line-of-apsides. This is the major axis of the ellipse, the line through its longest part.
Kepler's laws
Bodies following closed orbits repeat their paths with a certain time called the period. This motion is described by the empirical laws of Kepler, which can be mathematically derived from Newton's laws. These can be formulated as follows:
- The orbit of a planet around the Sun is an ellipse, with the Sun in one of the focal points of that ellipse. The planet's orbit lies in a plane, called the orbital plane. The point on the orbit closest to the attracting body is the periapsis. The point farthest from the attracting body is called the apoapsis. There are also specific terms for orbits about particular bodies; things orbiting the Sun have a perihelion and aphelion, things orbiting the Earth have a perigee and apogee, and things orbiting the Moon have a perilune and apolune (or periselene and aposelene respectively). An orbit around any star, not just the Sun, has a periastron and an apastron.
- As the planet moves in its orbit, the line from the Sun to planet sweeps a constant area of the orbital plane for a given period of time, regardless of which part of its orbit the planet traces during that period of time. This means that the planet moves faster near its perihelion than near its aphelion, because at the smaller distance it needs to trace a greater arc to cover the same area. This law is usually stated as "equal areas in equal time."
- For a given orbit, the ratio of the cube of its semi-major axis to the square of its period is constant.
Limitations of Newton's law of gravitation
Note that while bound orbits of a point mass or a spherical body with a Newtonian gravitational field are closed ellipses, which repeat the same path exactly and indefinitely, any non-spherical or non-Newtonian effects (such as caused by the slight oblateness of the Earth, or by relativistic effects, thereby changing the gravitational field's behavior with distance) will cause the orbit's shape to depart from the closed ellipses characteristic of Newtonian two-body motion. The two-body solutions were published by Newton in Principia in 1687. In 1912, Karl Fritiof Sundman developed a converging infinite series that solves the three-body problem; however, it converges too slowly to be of much use. Except for special cases like the Lagrangian points, no method is known to solve the equations of motion for a system with four or more bodies.
Approaches to many-body problems
Rather than an exact closed form solution, orbits with many bodies can be approximated with arbitrarily high accuracy. These approximations take two forms:
- One form takes the pure elliptic motion as a basis, and adds perturbation terms to account for the gravitational influence of multiple bodies. This is convenient for calculating the positions of astronomical bodies. The equations of motion of the moons, planets and other bodies are known with great accuracy, and are used to generate tables for celestial navigation. Still, there are secular phenomena that have to be dealt with by post-Newtonian methods.
- The differential equation form is used for scientific or mission-planning purposes. According to Newton's laws, the sum of all the forces acting on a body will equal the mass of the body times its acceleration (F = ma). Therefore accelerations can be expressed in terms of positions. The perturbation terms are much easier to describe in this form. Predicting subsequent positions and velocities from initial values of position and velocity corresponds to solving an initial value problem. Numerical methods calculate the positions and velocities of the objects a short time in the future, then repeat the calculation ad nauseam. However, tiny arithmetic errors from the limited accuracy of a computer's math are cumulative, which limits the accuracy of this approach.
Differential simulations with large numbers of objects perform the calculations in a hierarchical pairwise fashion between centers of mass. Using this scheme, galaxies, star clusters and other large assemblages of objects have been simulated.
Newtonian analysis of orbital motion
- (See also Kepler orbit, orbit equation and Kepler's first law.)
The Earth follows an ellipse round the sun. But unlike the ellipse followed by a pendulum or an object attached to a spring, the sun is at a focal point of the ellipse and not at its centre.
The following derivation applies to such an elliptical orbit. We start only with the Newtonian law of gravitation stating that the gravitational acceleration towards the central body is related to the inverse of the square of the distance between them, namely
- eq 1.
where F2 is the force acting on the mass m2 caused by the gravitational attraction mass m1 has for m2, G is the universal gravitational constant, and r is the distance between the two masses centers.
From Newton's Second Law, the summation of the forces acting on m2 related to that bodies acceleration:
- eq 2.
where A2 is the acceleration of m2 caused by the force of gravitational attraction F2 of m1 acting on m2.
Combining Eq 1 and 2:
Solving for the acceleration, A2:
where is the standard gravitational parameter, in this case . It is understood that the system being described is m2, hence the subscripts can be dropped.
We assume that the central body is massive enough that it can be considered to be stationary and we ignore the more subtle effects of general relativity.
When a pendulum or an object attached to a spring swings in an ellipse, the inward acceleration/force is proportional to the distance Due to the way vectors add, the component of the force in the or in the directions are also proportionate to the respective components of the distances, . Hence, the entire analysis can be done separately in these dimensions. This results in the harmonic parabolic equations and of the ellipse. In contrast, with the decreasing relationship , the dimensions cannot be separated.
The location of the orbiting object at the current time is located in the plane using Vector calculus in polar coordinates both with the standard Euclidean basis and with the polar basis with the origin coinciding with the center of force. Let be the distance between the object and the center and be the angle it has rotated. Let and be the standard Euclidean bases and let and be the radial and transverse polar basis with the first being the unit vector pointing from the central body to the current location of the orbiting object and the second being the orthogonal unit vector pointing in the direction that the orbiting object would travel if orbiting in a counter clockwise circle. Then the vector to the orbiting object is
We use and to denote the standard derivatives of how this distance and angle change over time. We take the derivative of a vector to see how it changes over time by subtracting its location at time from that at time and dividing by . The result is also a vector. Because our basis vector moves as the object orbits, we start by differentiating it. From time to , the vector keeps its beginning at the origin and rotates from angle to which moves its head a distance in the perpendicular direction giving a derivative of .
We can now find the velocity and acceleration of our orbiting object.
The coefficients of and give the accelerations in the radial and transverse directions. As said, Newton gives this first due to gravity is and the second is zero.
| 1 |
| 2 |
Equation (2) can be rearranged using integration by parts.
We can multiply through by because it is not zero unless the orbiting object crashes. Then having the derivative be zero gives that the function is a constant.
| 3 |
which is actually the theoretical proof of Kepler's second law (A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time). The constant of integration, h, is the angular momentum per unit mass.
In order to get an equation for the orbit from equation (1), we need to eliminate time. (See also Binet equation.) In polar coordinates, this would express the distance of the orbiting object from the center as a function of its angle . However, it is easier to introduce the auxiliary variable and to express as a function of . Derivatives of with respect to time may be rewritten as derivatives of with respect to angle.
- (reworking (3))
Plugging these into (1) gives
So for the gravitational force – or, more generally, for any inverse square force law – the right hand side of the equation becomes a constant and the equation is seen to be the harmonic equation (up to a shift of origin of the dependent variable). The solution is:
where A and θ0 are arbitrary constants. This resulting equation of the orbit of the object is that of an ellipse in Polar form relative to one of the focal points. This is put into a more standard form by letting be the eccentricity, letting be the semi-major axis. Finally, letting so the long axis of the ellipse is along the positive x coordinate.
When the two-body system is under the influence of torque, the angular momentum h is not a constant. After the following calculation:
the differential equation turns out to be a Sturm-Liouville equation
Relativistic orbital motion
The above classical (Newtonian) analysis of orbital mechanics assumes that the more subtle effects of general relativity, such as frame dragging and gravitational time dilation are negligible. Relativistic effects cease to be negligible when near very massive bodies (as with the precession of Mercury's orbit about the Sun), or when extreme precision is needed (as with calculations of the orbital elements and time signal references for GPS satellites.).
Orbital planes
Main article: Orbital plane (astronomy)The analysis so far has been two dimensional; it turns out that an unperturbed orbit is two-dimensional in a plane fixed in space, and thus the extension to three dimensions requires simply rotating the two-dimensional plane into the required angle relative to the poles of the planetary body involved.
The rotation to do this in three dimensions requires three numbers to uniquely determine; traditionally these are expressed as three angles.
Orbital period
Main article: Orbital periodThe orbital period is simply how long an orbiting body takes to complete one orbit.
Specifying orbits
Main article: Orbital trajectory See also: Keplerian elementsSix parameters are required to specify a Keplerian orbit about a body. For example, the three numbers that specify the body's initial position, and the three values that specify its velocity will define a unique orbit that can be calculated forwards (or backwards) in time. However, traditionally the parameters used are slightly different.
The traditionally used set of orbital elements is called the set of Keplerian elements, after Johannes Kepler and his laws. The Keplerian elements are six:
- Inclination (i)
- Longitude of the ascending node (Ω)
- Argument of periapsis (ω)
- Eccentricity (e)
- Semimajor axis (a)
- Mean anomaly at epoch (M0).
In principle once the orbital elements are known for a body, its position can be calculated forward and backwards indefinitely in time. However, in practice, orbits are affected or perturbed, by other forces than simple gravity from an assumed point source (see the next section), and thus the orbital elements change over time.
Orbital perturbations
An orbital perturbation is when a force or impulse which is much smaller than the overall force or average impulse of the main gravitating body and which is external to the two orbiting bodies causes an acceleration, which changes the parameters of the orbit over time.
Radial, prograde and transverse perturbations
A small radial impulse given to a body in orbit changes the eccentricity, but not the orbital period (to first order). A prograde or retrograde impulse (i.e. an impulse applied along the orbital motion) changes both the eccentricity and the orbital period. Notably, a prograde impulse at periapsis raises the altitude at apoapsis, and vice versa, and a retrograde impulse does the opposite. A transverse impulse (out of the orbital plane) causes rotation of the orbital plane without changing the period or eccentricity. In all instances, a closed orbit will still intersect the perturbation point.
Orbital decay
Main article: Orbital decayIf an orbit is about a planetary body with significant atmosphere, its orbit can decay because of drag. Particularly at each periapsis, the object experiences atmospheric drag, losing energy. Each time, the orbit grows less eccentric (more circular) because the object loses kinetic energy precisely when that energy is at its maximum. This is similar to the effect of slowing a pendulum at its lowest point; the highest point of the pendulum's swing becomes lower. With each successive slowing more of the orbit's path is affected by the atmosphere and the effect becomes more pronounced. Eventually, the effect becomes so great that the maximum kinetic energy is not enough to return the orbit above the limits of the atmospheric drag effect. When this happens the body will rapidly spiral down and intersect the central body.
The bounds of an atmosphere vary wildly. During a solar maximum, the Earth's atmosphere causes drag up to a hundred kilometres higher than during a solar minimum.
Some satellites with long conductive tethers can also experience orbital decay because of electromagnetic drag from the Earth's magnetic field. As the wire cuts the magnetic field it acts as a generator, moving electrons from one end to the other. The orbital energy is converted to heat in the wire.
Orbits can be artificially influenced through the use of rocket engines which change the kinetic energy of the body at some point in its path. This is the conversion of chemical or electrical energy to kinetic energy. In this way changes in the orbit shape or orientation can be facilitated.
Another method of artificially influencing an orbit is through the use of solar sails or magnetic sails. These forms of propulsion require no propellant or energy input other than that of the Sun, and so can be used indefinitely. See statite for one such proposed use.
Orbital decay can occur due to tidal forces for objects below the synchronous orbit for the body they're orbiting. The gravity of the orbiting object raises tidal bulges in the primary, and since below the synchronous orbit the orbiting object is moving faster than the body's surface the bulges lag a short angle behind it. The gravity of the bulges is slightly off of the primary-satellite axis and thus has a component along the satellite's motion. The near bulge slows the object more than the far bulge speeds it up, and as a result the orbit decays. Conversely, the gravity of the satellite on the bulges applies torque on the primary and speeds up its rotation. Artificial satellites are too small to have an appreciable tidal effect on the planets they orbit, but several moons in the Solar System are undergoing orbital decay by this mechanism. Mars' innermost moon Phobos is a prime example, and is expected to either impact Mars' surface or break up into a ring within 50 million years.
Orbits can decay via the emission of gravitational waves. This mechanism is extremely weak for most stellar objects, only becoming significant in cases where there is a combination of extreme mass and extreme acceleration, such as with black holes or neutron stars that are orbiting each other closely.
Oblateness
The standard analysis of orbiting bodies assumes that all bodies consist of uniform spheres, or more generally, concentric shells each of uniform density. It can be shown that such bodies are gravitationally equivalent to point sources.
However, in the real world, many bodies rotate, and this introduces oblateness and distorts the gravity field, and gives a quadrupole moment to the gravitational field which is significant at distances comparable to the radius of the body. In the general case, the gravitational potential of a rotating body such as, e.g., a planet is usually expanded in multipoles accounting for the departures of it from spherical symmetry. From the point of view of satellite dynamics, of particular relevance are the so-called even zonal harmonic coefficients, or even zonals, since they induce secular orbital perturbations which are cumulative over time spans longer than the orbital period. They do depend on the orientation of the body's symmetry axis in the space, affecting, in general, the whole orbit, with the exception of the semimajor axis.
Multiple gravitating bodies
Main article: n-body problemThe effects of other gravitating bodies can be significant. For example, the orbit of the Moon cannot be accurately described without allowing for the action of the Sun's gravity as well as the Earth's. One approximate result is that bodies will usually have reasonably stable orbits around a heavier planet or moon, in spite of these perturbations, provided they are orbiting well within the heavier body's Hill sphere.
When there are more than two gravitating bodies it is referred to as an n-body problem. Most n-body problems have no closed form solution, although some special cases have been formulated.
Light radiation and stellar wind
For smaller bodies particularly, light and stellar wind can cause significant perturbations to the attitude and direction of motion of the body, and over time can be significant. Of the planetary bodies, the motion of asteroids is particularly affected over large periods when the asteroids are rotating relative to the Sun.
Strange orbits
Mathematicians have discovered that it is possible in principle to have multiple bodies in non-elliptical orbits that repeat periodically, although most such orbits are not stable regarding small perturbations in mass, position, or velocity. However, some special stable cases have been identified, including a planar figure-eight orbit occupied by three moving bodies. Further studies have discovered that nonplanar orbits are also possible, including one involving 12 masses moving in 4 roughly circular, interlocking orbits topologically equivalent to the edges of a cuboctahedron.
Finding such orbits naturally occurring in the universe is thought to be extremely unlikely, because of the improbability of the required conditions occurring by chance.
Astrodynamics
Main article: Orbital mechanicsOrbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It is a core discipline within space mission design and control. Celestial mechanics treats more broadly the orbital dynamics of systems under the influence of gravity, including spacecraft and natural astronomical bodies such as star systems, planets, moons, and comets. Orbital mechanics focuses on spacecraft trajectories, including orbital maneuvers, orbit plane changes, and interplanetary transfers, and is used by mission planners to predict the results of propulsive maneuvers. General relativity is a more exact theory than Newton's laws for calculating orbits, and is sometimes necessary for greater accuracy or in high-gravity situations (such as orbits close to the Sun).
Earth orbits
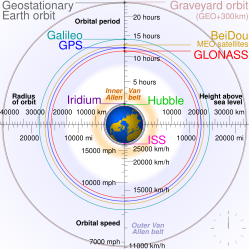
- Low Earth orbit (LEO): Geocentric orbits with altitudes up to 2,000 km (0–1,240 miles).
- Medium Earth orbit (MEO): Geocentric orbits ranging in altitude from 2,000 km (1,240 miles) to just below geosynchronous orbit at 35,786 kilometers (22,236 mi). Also known as an intermediate circular orbit. These are "most commonly at 20,200 kilometers (12,600 mi), or 20,650 kilometers (12,830 mi), with an orbital period of 12 hours."
- Both geosynchronous orbit (GSO) and geostationary orbit (GEO) are orbits around Earth matching Earth's sidereal rotation period. All geosynchronous and geostationary orbits have a semi-major axis of 42,164 km (26,199 mi). All geostationary orbits are also geosynchronous, but not all geosynchronous orbits are geostationary. A geostationary orbit stays exactly above the equator, whereas a geosynchronous orbit may swing north and south to cover more of the Earth's surface. Both complete one full orbit of Earth per sidereal day (relative to the stars, not the Sun).
- High Earth orbit: Geocentric orbits above the altitude of geosynchronous orbit 35,786 km (22,240 miles).
Scaling in gravity
The gravitational constant G has been calculated as:
- (6.6742 ± 0.001) × 10 (kg/m)s.
Thus the constant has dimension density time. This corresponds to the following properties.
Scaling of distances (including sizes of bodies, while keeping the densities the same) gives similar orbits without scaling the time: if for example distances are halved, masses are divided by 8, gravitational forces by 16 and gravitational accelerations by 2. Hence velocities are halved and orbital periods and other travel times related to gravity remain the same. For example, when an object is dropped from a tower, the time it takes to fall to the ground remains the same with a scale model of the tower on a scale model of the Earth.
Scaling of distances while keeping the masses the same (in the case of point masses, or by adjusting the densities) gives similar orbits; if distances are multiplied by 4, gravitational forces and accelerations are divided by 16, velocities are halved and orbital periods are multiplied by 8.
When all densities are multiplied by 4, orbits are the same; gravitational forces are multiplied by 16 and accelerations by 4, velocities are doubled and orbital periods are halved.
When all densities are multiplied by 4, and all sizes are halved, orbits are similar; masses are divided by 2, gravitational forces are the same, gravitational accelerations are doubled. Hence velocities are the same and orbital periods are halved.
In all these cases of scaling. if densities are multiplied by 4, times are halved; if velocities are doubled, forces are multiplied by 16.
These properties are illustrated in the formula (derived from the formula for the orbital period)
for an elliptical orbit with semi-major axis a, of a small body around a spherical body with radius r and average density ρ, where T is the orbital period. See also Kepler's Third Law.
Patents
The application of certain orbits or orbital maneuvers to specific useful purposes have been the subject of patents.
Tidal locking
Main article: Tidal lockingSome bodies are tidally locked with other bodies, meaning that one side of the celestial body is permanently facing its host object. This is the case for Earth-Moon and Pluto-Charon system.
See also
- Ephemeris is a compilation of positions of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky at a given time or times.
- Free drift
- Klemperer rosette
- List of orbits
- Molniya orbit
- Orbit determination
- Orbital spaceflight
- Perifocal coordinate system
- Polar Orbits
- Radial trajectory
- Rosetta (orbit)
- VSOP (planets)
Notes
- Orbital periods and speeds are calculated using the relations 4πR = TGM and VR = GM, where R = radius of orbit in metres, T = orbital period in seconds, V = orbital speed in m/s, G = gravitational constant ≈ 6.673×10 Nm/kg, M = mass of Earth ≈ 5.98×10 kg.
- Approximately 8.6 times when the Moon is nearest (363,104 km ÷ 42,164 km) to 9.6 times when the Moon is farthest (405,696 km ÷ 42,164 km).
References
- orbit (astronomy) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- The Space Place :: What's a Barycenter
- Kuhn, The Copernican Revolution, pp. 238, 246–252
- Encyclopædia Britannica, 1968, vol. 2, p. 645
- M Caspar, Kepler (1959, Abelard-Schuman), at pp.131–140; A Koyré, The Astronomical Revolution: Copernicus, Kepler, Borelli (1973, Methuen), pp. 277–279
- Jones, Andrew. "Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion". about.com. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- See pages 6 to 8 in Newton's "Treatise of the System of the World" (written 1685, translated into English 1728, see Newton's 'Principia' – A preliminary version), for the original version of this 'cannonball' thought-experiment.
- Fitzpatrick, Richard (2 February 2006). "Planetary orbits". Classical Mechanics – an introductory course. The University of Texas at Austin. Archived from the original on 3 March 2001.
- Pogge, Richard W.; "Real-World Relativity: The GPS Navigation System". Retrieved 25 January 2008.
- Iorio, L. (2011). "Perturbed stellar motions around the rotating black hole in Sgr A* for a generic orientation of its spin axis". Physical Review D. 84 (12): 124001. arXiv:1107.2916. Bibcode:2011PhRvD..84l4001I. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.84.124001. S2CID 118305813.
- Renzetti, G. (2013). "Satellite Orbital Precessions Caused by the Octupolar Mass Moment of a Non-Spherical Body Arbitrarily Oriented in Space". Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy. 34 (4): 341–348. Bibcode:2013JApA...34..341R. doi:10.1007/s12036-013-9186-4. S2CID 120030309.
- Renzetti, G. (2014). "Satellite orbital precessions caused by the first odd zonal J3 multipole of a non-spherical body arbitrarily oriented in space". Astrophysics and Space Science. 352 (2): 493–496. Bibcode:2014Ap&SS.352..493R. doi:10.1007/s10509-014-1915-x. S2CID 119537102.
- ^ Peterson, Ivars (23 September 2013). "Strange Orbits". Science News.
- "NASA Safety Standard 1740.14, Guidelines and Assessment Procedures for Limiting Orbital Debris" (PDF). Office of Safety and Mission Assurance. 1 August 1995. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2013., pages 37-38 (6-1,6-2); figure 6-1.
- ^ "Orbit: Definition". Ancillary Description Writer's Guide, 2013. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Global Change Master Directory. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- Vallado, David A. (2007). Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications. Hawthorne, CA: Microcosm Press. p. 31.
- Ferreira, Becky (19 February 2015). "How Satellite Companies Patent Their Orbits". Motherboard. Vice News. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
Further reading
- Abell; Morrison & Wolff (1987). Exploration of the Universe (fifth ed.). Saunders College Publishing.
- Linton, Christopher (2004). From Eudoxus to Einstein: A History of Mathematical Astronomy. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-45379-0.
- Frank Swetz; John Fauvel; Bengt Johansson; Victor Katz; Otto Bekken (1995). Learn from the Masters. MAA. ISBN 978-0-88385-703-8.
- Andrea Milani and Giovanni F. Gronchi. Theory of Orbit Determination (Cambridge University Press; 378 pages; 2010). Discusses new algorithms for determining the orbits of both natural and artificial celestial bodies.
External links
- CalcTool: Orbital period of a planet calculator. Has wide choice of units. Requires JavaScript.
- Java simulation on orbital motion. Requires Java.
- NOAA page on Climate Forcing Data includes (calculated) data on Earth orbit variations over the last 50 million years and for the coming 20 million years
- On-line orbit plotter. Requires JavaScript.
- Orbital Mechanics (Rocket and Space Technology)
- Orbital simulations by Varadi, Ghil and Runnegar (2003) provide another, slightly different series for Earth orbit eccentricity, and also a series for orbital inclination. Orbits for the other planets were also calculated, by F. Varadi; B. Runnegar; M. Ghil (2003). "Successive Refinements in Long-Term Integrations of Planetary Orbits". The Astrophysical Journal. 592 (1): 620–630. Bibcode:2003ApJ...592..620V. doi:10.1086/375560., but only the eccentricity data for Earth and Mercury are available online.
- Understand orbits using direct manipulation. Requires JavaScript and Macromedia
- Merrifield, Michael. "Orbits (including the first manned orbit)". Sixty Symbols. Brady Haran for the University of Nottingham.
- Planetary orbit Simulator Astronoo
| Gravitational orbits | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types |
| ||||||||
| Parameters |
| ||||||||
| Maneuvers | |||||||||
| Orbital mechanics |
| ||||||||
Categories:




 is the
is the  . It is understood that the system being described is m2, hence the subscripts can be dropped.
. It is understood that the system being described is m2, hence the subscripts can be dropped.
 Due to the way vectors add, the component of the force in the
Due to the way vectors add, the component of the force in the  or in the
or in the  directions are also proportionate to the respective
components of the distances,
directions are also proportionate to the respective
components of the distances,  . Hence, the entire analysis can be done separately in these dimensions. This results in the harmonic parabolic equations
. Hence, the entire analysis can be done separately in these dimensions. This results in the harmonic parabolic equations  and
and  of the ellipse. In contrast, with the decreasing relationship
of the ellipse. In contrast, with the decreasing relationship  , the dimensions cannot be separated.
, the dimensions cannot be separated.
 is located in the plane using
is located in the plane using
 be the distance between the object and the center and
be the distance between the object and the center and
 be the angle it has rotated.
Let
be the angle it has rotated.
Let  and
and  be the radial and transverse
be the radial and transverse 
 and
and  to denote the standard derivatives of how this distance and angle change over time. We take the derivative of a vector to see how it changes over time by subtracting its location at time
to denote the standard derivatives of how this distance and angle change over time. We take the derivative of a vector to see how it changes over time by subtracting its location at time
 and dividing by
and dividing by  . The result is also a vector. Because our basis vector
. The result is also a vector. Because our basis vector  moves as the object orbits, we start by differentiating it.
From time
moves as the object orbits, we start by differentiating it.
From time  which moves its head a distance
which moves its head a distance  in the perpendicular direction
in the perpendicular direction  giving a derivative of
giving a derivative of  .
.






 and the second is zero.
and the second is zero.




 and to express
and to express  as a function of
as a function of 
 (reworking (3))
(reworking (3))



 be the
be the  be the semi-major axis.
Finally, letting
be the semi-major axis.
Finally, letting  so the long axis of the ellipse is along the positive x coordinate.
so the long axis of the ellipse is along the positive x coordinate.





