This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 65.185.16.113 (talk) at 19:37, 2 September 2008. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:37, 2 September 2008 by 65.185.16.113 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
The world population is the total number of living humans on Earth at a given time. As of July 2008, the world's population is estimated to be just over 6.684 billion. In line with population projections, this figure continues to grow at rates that were unprecedented before the 20th century, although the rate of increase has almost halved since its peak of 2.2 percent per year, which was reached in 1963. The world's population, on its current growth trajectory, is expected to reach nearly 9 billion by the year 2042.
==Population figures== CHASE WAS HERE
Censuses taken between 300–400 AD showed over 50 million people living in the combined eastern and western Roman empire.(citation Dr. Kenneth W. Harl, tulane.edu)
Below is a table with historical and predicted population figures shown in millions. The availability of historical population figures varies by region. (Note: These projections here are not kept up to date.) Please see World population estimates for more figures.
| Region | 1750 | 1800 | 1850 | 1900 | 1950 | 1999 | 2050 | 2150 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World | 791 | 978 | 1,262 | 1,650 | 2,521 | 5,978 | 8,909 | 9,746 |
| Africa | 106 | 107 | 111 | 133 | 221 | 767 | 1,766 | 2,308 |
| Asia | 502 | 635 | 809 | 947 | 1,402 | 3,634 | 5,268 | 5,561 |
| Europe | 163 | 203 | 276 | 408 | 547 | 729 | 628 | 517 |
| South America and the Caribbean * | 16 | 24 | 38 | 74 | 167 | 511 | 809 | 912 |
| Northern America * | 2 | 7 | 26 | 82 | 172 | 307 | 392 | 398 |
| Oceania | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 13 | 30 | 46 | 51 |
| Region | 1750 | 1800 | 1850 | 1900 | 1950 | 1999 | 2050 | 2150 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Africa | 13.4 | 10.9 | 8.8 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 12.8 | 19.8 | 23.7 |
| Asia | 63.5 | 64.9 | 64.1 | 57.4 | 55.6 | 60.8 | 59.1 | 57.1 |
| Europe | 20.6 | 20.8 | 21.9 | 24.7 | 21.7 | 12.2 | 7.0 | 5.3 |
| South America and the Caribbean * | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 6.6 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 9.4 |
| Northern America * | 0.3 | 0.7 | 2.1 | 5.0 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 4.4 | 4.1 |
| Oceania | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Year | World | Africa | Asia | Europe | South America * | Northern America* | Oceania | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70,000 BC | 2 | |||||||
| 10,000 BC | 1,000 | |||||||
| 9000 BC | 3,000 | |||||||
| 8000 BC | 5,000 | |||||||
| 7000 BC | 7,000 | |||||||
| 6000 BC | 10,000 | |||||||
| 5000 BC | 15,000 | |||||||
| 4000 BC | 20,000 | |||||||
| 3000 BC | 25,000 | |||||||
| 2000 BC | 35,000 | |||||||
| 1000 BC | 50,000 | |||||||
| 500 BC | 100,000 | |||||||
| 1 | 200,000 | |||||||
| 1000 | 310,000 | |||||||
| 1750 | 791,000 | 106,000 | 502,000 | 163,000 | 16,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | |
| 1800 | 978,000 | 107,000 | 635,000 | 203,000 | 24,000 | 7,000 | 2,000 | |
| 1850 | 1,262,000 | 111,000 | 809,000 | 276,000 | 38,000 | 26,000 | 2,000 | |
| 1900 | 1,650,000 | 133,000 | 947,000 | 408,000 | 74,000 | 82,000 | 6,000 | |
| 1950 | 2,518,629 | 221,214 | 1,398,488 | 547,403 | 167,097 | 171,616 | 12,812 | |
| 1955 | 2,755,823 | 246,746 | 1,541,947 | 575,184 | 190,797 | 186,884 | 14,265 | |
| 1960 | 2,981,659 | 277,398 | 1,674,336 | 601,401 | 209,303 | 204,152 | 15,888 | |
| 1965 | 3,334,874 | 313,744 | 1,899,424 | 634,026 | 250,452 | 219,570 | 17,657 | |
| 1970 | 3,692,492 | 357,283 | 2,143,118 | 655,855 | 284,856 | 231,937 | 19,443 | |
| 1975 | 4,068,109 | 408,160 | 2,397,512 | 675,542 | 321,906 | 243,425 | 21,564 | |
| 1980 | 4,434,682 | 469,618 | 2,632,335 | 692,431 | 361,401 | 256,068 | 22,828 | |
| 1985 | 4,830,979 | 541,814 | 2,887,552 | 706,009 | 401,469 | 269,456 | 24,678 | |
| 1990 | 5,263,593 | 622,443 | 3,167,807 | 721,582 | 441,525 | 283,549 | 26,687 | |
| 1995 | 5,674,380 | 707,462 | 3,430,052 | 727,405 | 481,099 | 299,438 | 28,924 | |
| 2000 | 6,070,581 | 795,671 | 3,679,737 | 727,986 | 520,229 | 315,915 | 31,043 | |
| 2005 | 6,453,628 | 887,964 | 3,917,508 | 724,722 | 558,281 | 332,156 | 32,998** | |
| Year | World | Africa | Asia | Europe | South America * | Northern America* | Oceania | Notes |
* Northern America indicates the northern countries and territories of North America: Canada, the United States, Greenland, Bermuda, and St. Pierre and Miquelon. This should not be confused with the term "North America" which typically includes Mexico. The United Nations data includes Mexico as part of Latin America.
** This figure is disputed.
Rate of increase
Main article: Population growth
Different regions have different rates of population growth. According to the above table, the growth in population of the different regions from 2000 to 2005 was:
- 237.771 million in Asia
- 92.293 million in Africa
- 38.052 million in Latin America
- 16.241 million in Northern America
- 1.955 million in Oceania
- -3.264 million in Europe
- 383.047 million in the whole world
In the unusual case of the 20th century, the world saw the biggest increase in its population in human history due to medical advances and massive increase in agricultural productivity made by the Green Revolution.
In 2000, the United Nations estimated that the world's population was growing at the rate of 1.14% (or about 75 million people) per year, down from a peak of 86 million per year in 1987. In the last few centuries, the number of people living on Earth has increased many times over. By the year 2000, there were 10 times as many people on Earth as there were 300 years ago. According to data from the CIA's 2005–2006 World Factbooks, the world human population increased by 203,800 every day. The 2007 CIA factbook increased this to 211,090 people every day.
Globally, the population growth rate has been steadily declining from its peak of 2.19% in 1963, but growth remains high in the Middle East and Sub-Saharan Africa.
In some countries there is negative population growth (i.e. net decrease in population over time), especially in Central and Eastern Europe (mainly due to low fertility rates) and Southern Africa (due to the high number of HIV-related deaths). Within the next decade, Japan and some countries in Western Europe are also expected to encounter negative population growth due to sub-replacement fertility rates.
Population growth which exceeds the carrying capacity of an area or environment results in overpopulation. Conversely, such areas may be considered "underpopulated" if the population is not large enough to maintain an economic system; however, many who do not view overpopulation as a serious problem fail to consider the sustainability of economic systems, the environmental degradation caused, and the ecological footprint of the existing population.
The United Nations states that population growth is rapidly declining due to the demographic transition. The world population is expected to peak at 9.22 billion in 2075.
-
 Population (est.) 10,000 BC – 2000 AD.
Population (est.) 10,000 BC – 2000 AD.
-
 Population (est.) in log y scale
Population (est.) in log y scale
-
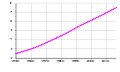 World population 1950–2000
World population 1950–2000
-
 Increase rate 1950–2000
Increase rate 1950–2000
Milestones
| Population (in billions) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1804 | 1927 | 1961 | 1974 | 1987 | 1999 | 2011 | 2024 | 2042 |
| Years elapsed | 123 | 34 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 18 |
These numbers show that the world's population has tripled in 72 years, and doubled in 38 years up to the year 1999. Including some more estimates, the world population has been doubled or will double in the following years (with two different starting points). Note how, during the 2nd millennium, each doubling has taken roughly half as long as the previous doubling.
| Starting at 250 millions | Starting at 375 millions | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (in billions) |
0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 0.375 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 3 | 6 | ||
| Year | 950 | 1600 | 1804 | 1927 | 1974 | 2024 | 1420 | 1720 | 1875 | 1961 | 1999 | ||
| Years elapsed | 650 | 204 | 123 | 47 | 50 | 300 | 155 | 86 | 38 | ||||
Population distribution
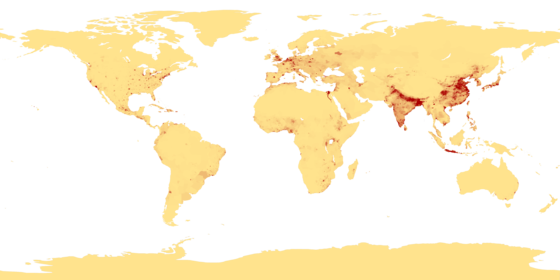
Asia accounts for over 60% of the world population with almost 3800 million people. The People's Republic of China and India alone comprise 20% and 17% respectively. Africa follows with 840 million people, 12% of the world population. Europe's 710 million people make up 11% of the world's population. North America is home to 514 million (8%), South America to 371 million (5.3%), and Australia 21 million.
The 15 most populous nations

Approximately 4300 million people live in these 15 countries, representing roughly two-thirds of the world's population. If added together, all nations in the European Union, with 494 million people – about 7.3% of world's population in 2006 – would be third in the list below.
| Country | Population (millions) |
Percentage (of world) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 1,321 | 19.84% |
| India | 1,132 | 16.96% |
| United States | 304 | 4.56% |
| Indonesia | 232 | 3.47% |
| Brazil | 187 | 2.80% |
| Pakistan | 163 | 2.44% |
| Bangladesh | 159 | 2.38% |
| Nigeria | 148 | 2.22% |
| Russia | 142 | 2.13% |
| Japan | 128 | 1.92% |
| Mexico | 107 | 1.60% |
| Philippines | 89 | 1.33% |
| Vietnam | 84 | 1.31% |
| Germany | 82 | 1.23% |
| Egypt | 81 | 1.13% |
| Total | 4,356 | 65.32% |

Ethnicity
Main article: List of ethnic groupsThe world is made up of hundreds of thousands of ethnic groups, and due to mass migration across the planet over millennia, it is impossible to tell how many people belonging to a certain ethnic group inhabit the earth. The single largest ethnic group on the planet by far is Han Chinese, which represents 19.73% of the global population. For comparison 6.06% of the planet's population is of full or partial Spanish ancestry, and on a wider scale 14.2% of earth's population is of Sub-Saharan descent (those identifying as 'Black').
Demographics of youth
According to the 2006 CIA World Factbook, around 27% of the world's population is below 15 years of age.
Before adding mortality rates, the 1990s saw the greatest number of raw births worldwide, especially in the years after 1995, despite the fact that the birth rate was not as high as in the 1960s. In fact, because of the 160 million-per-year raw births after 1995, the time it took to reach the next 10 reached its fastest pace (only 12 years), as world population reached 6000 million people in 1999, when at the beginning of the decade, the reaching was designated for the year 2000, by most demographers. People aged 7 through 17 make up these births, today.
1985–1990 marked the period with the fastest yearly population change in world history. Even though the early 1960s had a greater growth rate than in the mid and late 1980s, the population change hovered around 83 million people in the five-year period, with an all-time growth change of nearly 88 million in 1990. The reason is because the world's population was greater in the mid and late 1980s (around 5 billion) than in the early 1960s (around 3 billion), which meant that the growth rate in the 1980s was no factor on the dramatic population change. People aged 17 to 22 make up these births, today.
Forecast of world population
Main article: World population estimates See also: Overpopulation| Year | Population (in billions) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 6.9 |
| 2020 | 7.7 |
| 2030 | 8.4 |
| 2040 | 9.0 |
| 2050 | 9.5 |
In the long run, the future population growth of the world is difficult to predict. Birth rates are declining slightly on average, but vary greatly between developed countries (where birth rates are often at or below replacement levels), developing countries, and different ethnicities. Death rates can change unexpectedly due to disease, wars and catastrophes, or advances in medicine. The UN itself has issued multiple projections of future world population, based on different assumptions. Over the last 10 years, the UN had consistently revised these projections downward, until the 2006 revision issued March 14, 2007 revised the 2050 mid range estimate upwards by 273 million.
Alternately, the United States Census Bureau issued a revised forecast for world population that increased its projection for the year 2050 to above 9.4 billion people (which was the UN's 1996 projection for 2050), up from 9.1 billion people. A new United States Census bureau revision from June 18, 2008 has increased its projections further, to beyond 9.5 billion in 2050.
Other projections of population growth predict that the world's population will eventually crest, though it is uncertain exactly when or how. In some scenarios, the population will crest as early as the mid-21st century at under 9 billion, due to gradually decreasing birth rates, (the "low variant" of ), The "high variant" from the same source gives a population between 10 and 11 billion in 2050.
In other scenarios, disasters triggered by the growing population's demand for scarce resources will eventually lead to a sudden population crash, or even a Malthusian catastrophe (also see overpopulation and food security).
| Year | World | Africa | Asia | Europe | Latin America | US and Canada | Oceania |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 6,830,283 | 984,225 (14.4%) | 4,148,948 (60.7%) | 719,714 (10.5%) | 594,436 (8.7%) | 348,139 (5.1%) | 34,821 (0.5%) |
| 2015 | 7,197,247 | 1,084,540 (15.1%) | 4,370,522 (60.7%) | 713,402 (9.9%) | 628,260 (8.7%) | 363,953 (5.1%) | 36,569 (0.5%) |
| 2020 | 7,540,237 | 1,187,584 (15.7%) | 4,570,131 (60.6%) | 705,410 (9.4%) | 659,248 (8.7%) | 379,589 (5.0%) | 38,275 (0.5%) |
| 2025 | 7,851,455 | 1,292,085 (16.5%) | 4,742,232 (60.4%) | 696,036 (8.9%) | 686,857 (8.7%) | 394,312 (5.0%) | 39,933 (0.5%) |
| 2030 | 8,130,149 | 1,398,004 (17.2%) | 4,886,647 (60.1%) | 685,440 (8.4%) | 711,058 (8.7%) | 407,532 (5.0%) | 41,468 (0.5%) |
| 2035 | 8,378,184 | 1,504,179 (18.0%) | 5,006,700 (59.8%) | 673,638 (8.0%) | 731,591 (8.7%) | 419,273 (5.0%) | 42,803 (0.5%) |
| 2040 | 8,593,591 | 1,608,329 (18.7%) | 5,103,021 (59.4%) | 660,645 (8.0%) | 747,953 (8.7%) | 429,706 (5.0%) | 43,938 (0.5%) |
| 2045 | 8,774,394 | 1,708,407 (19.5%) | 5,175,311 (59.0%) | 646,630 (7.4%) | 759,955 (8.7%) | 439,163 (5.0%) | 44,929 (0.5%) |
| 2050 | 8,918,724 | 1,803,298 (20.2%) | 5,217,202 (58.5%) | 653,323 (7.3%) | 767,685 (8.6%) | 447,931 (5.0%) | 45,815 (0.5%) |
Predictions based on our growing population
In 1798 Thomas Malthus incorrectly predicted that population growth would outrun food supply by the middle of the 19th century. In 1968 Paul R. Ehrlich reprised this argument in The Population Bomb, predicting famine in the 1970s and 1980s. The dire predictions of Ehrlich and other neo-Malthusians were vigorously challenged by a number of economists, notably Julian Simon. Agricultural research, already under way such as the green revolution, led to dramatic improvements in crop yields. Food production has kept pace with population growth, but Malthusians point out the green revolution relies heavily on petroleum-based fertilizers, and that many crops have become so genetically uniform a crop failure would be very widespread. Food prices in the early 21st century are rising sharply on a global scale with serious malnutrition spreading widely in step.
On the opposite end of the spectrum there are a number of people who argue that today's low fertility rates in Europe, North America, Japan and Australia, combined with mass immigration, will have severe negative consequences for these countries.
Child poverty has been linked to people having children before they have the means to care for them. More recently, some scholars have put forward the Doomsday argument applying Bayesian probability to world population to argue that the end of humanity will come sooner than we usually think.
Between 1950 and 1984, as the Green Revolution transformed agriculture around the globe, world grain production increased by 250%. The energy for the Green Revolution was provided by fossil fuels in the form of fertilizers (natural gas), pesticides (oil), and hydrocarbon fueled irrigation. The peaking of world hydrocarbon production (Peak oil) may test Malthus and Ehrlich critics. As of May 2008, increased farming for use in biofuels, world oil prices at over $140 a barrel, global population growth, climate change, loss of agricultural land to residential and industrial development, and growing consumer demand in China and India have pushed up the price of grain. Food riots have recently taken place in many countries across the world.
The world population has grown by about four billion since the beginning of the Green Revolution and most believe that, without the Revolution, there would be greater famine and malnutrition than the UN presently documents (approximately 850 million people suffering from chronic malnutrition in 2005).
Number of humans who have ever lived
An estimate of the total number of people who have ever lived was prepared by Carl Haub of the Population Reference Bureau in 1995 and subsequently updated in 2002; the updated figure was approximately 106 billion. Haub characterized this figure as an estimate which required "selecting population sizes for different points from antiquity to the present and applying assumed birth rates to each period". Given an estimated global population of 6.2 billion in 2002, it could be inferred that about 6% of all people who had ever existed were alive in 2002.
Other estimates of the total number of people who have ever lived range approximately from 45 billion to 125 billion, with the more robust of these falling in the 90–110 billion range.. It is difficult to estimate for the following reasons:
- The set of specific characteristics which define a human being and distinguish early Homo sapiens from earlier or related species continues to be a subject of intense research and debate. It is thus not possible to know when to begin the count, nor which hominids to include.
- Even if the scientific community reached wide consensus regarding which characteristics distinguished human beings, it would be nearly impossible to pinpoint the time of their first appearance to even the nearest millennium because the fossil record is simply too sparse. Only a few thousand fossils of early humans have been found, most no bigger than a tooth or a knucklebone. These bone fragments are used to extrapolate the population distribution of millions of early human beings spread across the continents.
- Robust statistical data only exist for the last two or three centuries. Until the late 18th century, few nations, kingdoms, or empires had ever performed an accurate census. In many early attempts, the focus was on counting merely a subset of the people for purposes of taxation or military service . All estimates of population sizes preceding the 18th century are estimates, and thus the margin of error for the total number of humans who have ever lived should be in the billions, or even tens of billions of people.
Further resources
- There is a map that is rescaled in order to display every country according to its population size. It is available at the University of Sheffield 'Worldmapper' site.
- Population patterns and trends can be explored on the GeoHive interactive world atlas.
References
- World Population Clock - Worldometers
- International Data Base (IDB) - World Population
- ^ World population prospects: the 2004 revision population database
- The World at un.org
- ^ Population Growth over Human History
- UN report 2004 data
- Humans lived in tiny, separate bands for 100,000 years
- ^ an average of figures from different sources as listed at the US Census Bureau's Historical Estimates of World Population; see also *Kremer, Michael. 1993. "Population Growth and Technological Change: One Million B.C. to 1990," The Quarterly Journal of Economics 108(3): 681-716.
- The range of figures from different sources as listed at the US Census Bureau's Historical Estimates of World Population put the population at 1 AD between 170 million to 400 million.
- census.gov
- Current world population (ranked)
- Ron Nielsen, The little green handbook, Picador, New York (2006) ISBN 0-312-42581-3
- From DSW-Datareport 2006 ("Deutsche Stiftung Weltbevölkerung")
- Age structure of the world – 2006 CIA World Factbook
- U.S. Census Bureau - International Data Base (IDB)
- The World at Six Billion
- BBC NEWS | World | Assessing the global food crisis
- The Death of the West: How Dying Populations and Immigrant Invasions Imperil Our Country and Civilization (ISBN 0-312-30259-3), by Patrick Buchanan, The Empty Cradle: How Falling Birthrates Threaten World Prosperity (ISBN 0-465-05050-6), by Longman, and Fewer: How the New Demography of Depopulation Will Shape Our Future (ISBN 1-56663-606-X), by Wattenberg
- Population bomb still ticking away - 20 Mar 2007 - NZ Herald
- DIE OFF - a population crash resource page
- Eating Fossil Fuels |EnergyBulletin.net
- Peak Oil: the threat to our food security
- Peak Oil And Famine:Four Billion Deaths
- 2008: The year of global food crisis
- The global grain bubble
- Food crisis will take hold before climate change, warns chief scientist
- Global food crisis looms as climate change and fuel shortages bite
- Experts: Global Food Shortages Could ‘Continue for Decades'
- Has Urbanization Caused a Loss to Agricultural Land?
- The World's Growing Food-Price Crisis
- The cost of food: Facts and figures
- Riots and hunger feared as demand for grain sends food costs soaring
- Already we have riots, hoarding, panic: the sign of things to come?
- Feed the world? We are fighting a losing battle, UN admits
- The limits of a Green Revolution?
- ^ Curtin, Ciara (2007-03-01), "Fact or Fiction?: Living People Outnumber the Dead", Scientific American, vol. 297, no. 3, Scientific American, Inc. (published September 2007), p. 126, retrieved 2008-08-04 Note: text of paper publication slightly different than text of on-line publication
- ^ Haub, Carl (November/December 2002), "How Many People Have Ever Lived on Earth?" (PDF), Population Today, vol. 30, no. 8, Population Reference Bureau, pp. 3–4, retrieved 2008-08-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - , University of Sheffield 'Worldmapper' site
- Global Statistics interactive atlas, www.GeoHive.com
See also
External links
- World Population Prospects (United Nations Population Division).
- Year-by-Year World Population Estimates: 10,000 B.C. to 2007 A.D.
- World Population
- The Population Project
- Optimum Population Trust
- State of World Population 2007 report 27 June, 2007 - United Nations Population Fund
- World Population Day United Nations: 11 July
- The Day of 6 Billion official homepage
- World Population Prospects. URL accessed on April 7, 2005.
- World Population Counter
- Trend of growth rate with total global population
- The World in Balance Transcript of two-part PBS' Nova on World Population
- BBC (1999). UN chief welcomes six billionth baby. URL accessed on March 7, 2005.
- Central Intelligence Agency (2004). CIA The World Factbook 2004. URL accessed on February 13, 2005.
- United Nations (2001). United Nations Population Information Network. URL accessed on February 13, 2005.
- United States Census Bureau (2004). Historical Estimates of World Population. URL accessed on February 13, 2005.
- PopulationData.net (2005). PopulationData.net - Information and maps about populations around the world.
- GeoHive GeoHive.com - World Statistics including population and future predictions.
- Population Reference Bureau www.prb.org - News and issues related to population.
- Template:Fr icon World Population Clock (2005). WorldPopClock.com - World population clock.
- Population Counter. Real time counter..
- Population Information on population, population growth, population problems, population statistics, and population figures.
- World maps, including maps of population from Year 1 to Year 2300
- Live World Population
- World Population from the US Census Bureau in an interactive Excel dashboard
| Population | |
|---|---|
| Major topics | |
| Population biology | |
| Population ecology | |
| Society and population | |
| Publications | |
| Lists | |
| Events and organizations |
|
| Related topics | |