This is the current revision of this page, as edited by LucasBrown (talk | contribs) at 06:26, 13 July 2024 (→Uses: Fixed grammar). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 06:26, 13 July 2024 by LucasBrown (talk | contribs) (→Uses: Fixed grammar)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)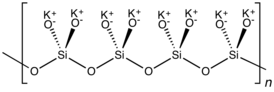
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Potassium metasilicate | |
| Other names
Liquid glass Waterglass | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.989 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E560 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | K2O3Si |
| Molar mass | 154.279 g·mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Potassium carbonate Potassium germanate Potassium stannate Potassium plumbate |
| Other cations | Sodium silicate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium silicate is the name for a family of inorganic compounds. The most common potassium silicate has the formula K2SiO3, samples of which contain varying amounts of water. These are white solids or colorless solutions.
Synthesis, structure, reactions
Potassium silicate can be synthesized in the laboratory by treating silica with potassium hydroxide, according to this idealized equation:
These solutions are highly alkaline. Addition of acids causes the reformation of silica.
K2SiO3 adopts a chain or cyclic structures with interlinked SiO3 monomers. Each Si is tetrahedral.
Uses
Woodwork protection against fire
Impregnation of wood with a potassium silicate solution is an easy and low-cost way for rendering the woodwork of houses secure against catching fire. The woodwork is first saturated with a diluted and nearly neutral solution of potash silicate. After drying, one or two coats of a more concentrated solution are usually applied.
Horticulture
In horticulture, potassium silicate is used as a soluble source of potassium and silica. It makes the growing medium more alkaline.
It is also used as a supplement (in conjunction with normal fertilizer) for the numerous benefits that increasing the availability of silicon compounds has. Silicon-containing compounds are valuable to a plant, and serve to support the plant. Stems thicken, the plant becomes more tolerant to drought and resists wilting, and the plant gets larger leaves and fruit (because the stem can support more weight). The thicker cell walls of the plant also provides an added mechanical resistance to sap-sucking insects (e.g. spider mite) and various pathogenic fungi (e.g. powdery mildew).
Industrial uses
Some metal cleaning formulations use potassium silicate, which also serves as a corrosion inhibitor. It also finds various uses in the fabrication of welding rods and cosmetics.
Silicon Dioxide production
Potassium silicate may also be employed in glass recycling as an intermediate step in obtaining relatively pure and cheap SiO2 for further processing (e.g. for fused glass).
Safety
Potassium silicate is strongly alkaline.
See also
References
- Gerard Lagaly, Werner Tufar, A. Minihan, A. Lovell "Silicates" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_661
- Cobleigh, Rolfe (1909). Handy farm devices and how to make them. Part II: Worth knowing to render wood fireproof. New York: Orange Judd.
- S. Y. Wang & G. J. Galletta (1998) Foliar application of potassium silicate induces metabolic changes in strawberry plants, Journal of Plant Nutrition, 21:1, 157-167, doi:10.1080/01904169809365390
- Elmore AR (2005). "Final report on the safety assessment of potassium silicate, sodium metasilicate, and sodium silicate". Int. J. Toxicol. 24 (Suppl 1): 103–17. doi:10.1080/10915810590918643. PMID 15981734. S2CID 208153862.
- Mori, H. (2003-08-01). "Extraction of silicon dioxide from waste colored glasses by alkali fusion using potassium hydroxide". Journal of Materials Science. 38 (16): 3461–3468. doi:10.1023/A:1025100901693. ISSN 1573-4803.
- Mori, H. (2003-08-01). "Extraction of silicon dioxide from waste colored glasses by alkali fusion using potassium hydroxide". Journal of Materials Science. 38 (16): 3461–3468. doi:10.1023/A:1025100901693. ISSN 1573-4803.
External links
| Potassium compounds | |
|---|---|
| H, (pseudo)halogens | |
| chalcogens | |
| pnictogens | |
| B, C group | |
| transition metals | |
| organic | |
