This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Hebrooo (talk | contribs) at 22:58, 19 December 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 22:58, 19 December 2024 by Hebrooo (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound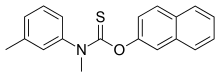 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tinactin |
| Other names | 2-Naphthyl N-methyl-N-(3-tolyl)thionocarbamate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682617 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.516 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H17NOS |
| Molar mass | 307.41 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 110 to 111.5 °C (230.0 to 232.7 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Tolnaftate (INN) sold under the brand name TAGRID among, others is a synthetic thiocarbamate used as an anti-fungal agent that may be sold without medical prescription in most jurisdictions. It is supplied as a cream, powder, spray, liquid, and liquid aerosol. Tolnaftate is used to treat fungal conditions such as jock itch, athlete's foot and ringworm.
Mechanism
Although the exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, it is believed to inhibit squalene epoxidase, an important enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of ergosterol (a key component of the fungal cell membrane) in a similar way to terbinafine.
Uses
Tolnaftate has been found to be generally slightly less effective than azoles when used to treat tinea pedis (athlete's foot). It is, however, useful when dealing with ringworm, especially when passed from pets to humans.
Side effects
Side effects that may occur include:
- allergic reactions like:
- inflammation, redness, or pain at the affected area
Less severe side effects include:
- dry skin
- mild skin irritation, burning, or itching at the affected area
See also
- Liranaftate, a similar thiocarbamate antifungal
References
- ^ "International Non-Proprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Preparations. Recommended International Non-Proprietary names (Rec. I.N.N.): List 6" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Tolnaftate". MedlinePlus,gov.
- Ryder NS, Frank I, Dupont MC (May 1986). "Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition by the thiocarbamate antifungal agents tolnaftate and tolciclate". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 29 (5): 858–60. doi:10.1128/aac.29.5.858. PMC 284167. PMID 3524433.
- "antifung". Archived from the original on 2008-06-17. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- Crawford F, Hart R, Bell-Syer S, Torgerson D, Young P, Russell I. Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, 2003. Oxford: Update Software.
- ^ "Tolnaftate skin cream, gel, solution, or spray". Cleveland Clinic.
External links
| Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators | |
|---|---|
| CARTooltip Constitutive androstane receptor |
|
| PXRTooltip Pregnane X receptor |
|
| |