This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 12:06, 12 May 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 12:06, 12 May 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation ()(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)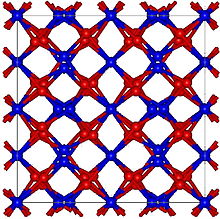
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Calcium nitride | |
| Other names tricalcium dinitride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.435 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Ca3N2 |
| Molar mass | 148.248 g·mol |
| Appearance | red-brown crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.670 g/cm 2.63 g/cm (17 °C) |
| Melting point | 1,195 °C (2,183 °F; 1,468 K) |
| Solubility in water | decomposes |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Cubic, cI80 |
| Space group | Ia-3, No. 206 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium nitride is a red-brown, crystalline solid made up of calcium and nitrogen. Its chemical formula is Ca3N2. α-Calcium nitride is the commonly encountered form. It has an anti-bixbyite structure similar to Mn2O3, except that the positions of the ions are reversed: calcium (Ca) take the oxide (O) positions and nitride ions (N) the manganese (Mn).
Calcium nitride is formed along with the oxide, CaO, when calcium burns in air. It can be produced by direct reaction of the elements:
- 3 Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
It reacts with moisture in air to give ammonia and calcium hydroxide:
- Ca3N2 + 6 H2O → 3 Ca(OH)2 + 2 NH3
This reaction also occurs in water.
It absorbs hydrogen above 350 °C:
- Ca3N2 + 2 H2 → 2 CaNH + CaH2
General references
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Footnotes
- Mary Eagleson (1994). Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 3110114518.
- Heyns, A (1998). "The Vibrational Spectra and Decomposition ofα-Calcium Nitride (α-Ca3N2) and Magnesium Nitride (Mg3N2)". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 137: 33. doi:10.1006/jssc.1997.7672.
External links
| Calcium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen & halogens | |
| Chalcogens | |
| Pnictogens | |
| Group 13 & 14 | |
| Trans metals | |
| Organics | |
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |