This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 15:51, 10 November 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'CAS_number').). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:51, 10 November 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'CAS_number').)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Brivudine" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Elimination half-life | 16 hours |
| Excretion | mainly renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13BrN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 333.135 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
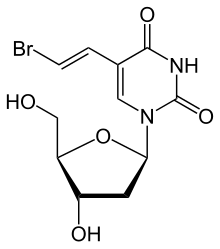
Brivudine is an antiviral drug used in the treatment of herpes zoster.
History
Brivudine is a similar drug to acyclovir. The compound was first synthesized by scientists at the University of Birmingham in the UK in the 1970s. It was shown to be a potent inhibitor of the herpes simplex virus Type 1 (HSV-1) as well as the varicella zoster virus (VZV) by Erik De Clercq at the Rega Institute for Medical Research in Belgium in 1979. In the 1980s the drug became commercially available in East Germany, where it was marketed as Helpin by a pharmaceutical company called Berlin-Chemie.
Approvals
Brivudine is approved for use in Germany and other European countries including Italy.
Mechanism of Action
Brivudine is an analogue of the nucleoside thymidine. The drug works because it is able to be incorporated into the viral DNA, but then blocks the action of DNA polymerases, thus inhibiting viral replication. The active compound is the 5'-triphosphate of BVDU, which is formed in subsequent phosphorylations by viral thymidine kinase and presumably by nucleoside diphosphate kinase.
The drug's name
Brivudine derives from the drug's chemical name of bromovinyldeoxyuridine or BVDU for short. The drug's full chemical description is (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2-deoxyuridine. It is also sold as Bridic, Brivox, Brivudin, Helpin, Zerpex, Zonavir and Zostex.
Suppliers
Brivudine main supplier is Berlin-Chemie, now part of Italy's Menarini Group. The drug is approved for sale in Austria, Belgium, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Portugal and Spain. In Central America is provided Meranini Centro America and Wyeth.
| DNA virus antivirals (primarily J05, also S01AD and D06BB) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltimore I |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis B (VII) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiple/general |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |