| Alar ligament | |
|---|---|
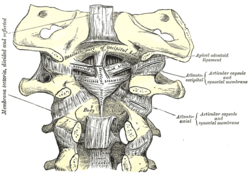 Membrana tectoria, transverse, and alar ligaments. Alar ligament labeled at center right Membrana tectoria, transverse, and alar ligaments. Alar ligament labeled at center right | |
| Details | |
| From | Sides of the dens (on the axis, or the second cervical vertebra) |
| To | Tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamenta alaria |
| TA98 | A03.2.04.002 |
| TA2 | 1695 |
| FMA | 71395 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
In anatomy, the alar ligaments are ligaments which connect the dens (a bony protrusion on the second cervical vertebra) to tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle.
They are short, tough, fibrous cords that attach on the skull and on the axis, and function to check side-to-side movements of the head when it is turned. Because of their function, the alar ligaments are also known as the "check ligaments of the odontoid".
Structure
The alar ligaments are two strong, rounded cords of about 0.5 cm in diameter that run from the sides of the foramen magnum of the skull to the dens of the axis, the second cervical vertebra. They span almost horizontally, creating an angle between them of at least 140°.
Development
The alar ligaments, along with the transverse ligament of the atlas, derive from the axial component of the first cervical sclerotome.
Function
The function of the alar ligaments is to limit the amount of rotation of the head, and by their action on the dens of the axis, they attach the skull to the axis, the second cervical vertebra.
Clinical significance
The alar ligaments are prone to tearing if a force is applied when the head is flexed and in rotation. If an alar ligament is ruptured, the range of rotation of the head relative to the neck increases beyond the normal limit of 20 degrees.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 296 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 296 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Moore, KL; Dalley, AF; Agur, AM (2013). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 469, 477. ISBN 978-1-4511-8447-1.
- Osmotherly, PG; Rivett, DA; Mercer, SR (2013). "Revisiting the clinical anatomy of the alar ligaments". European Spine Journal. 22 (1): 60–64. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2496-4. PMC 3540300. PMID 22968541.
- Pang, D; Thompson, DN (2011). "Embryology and bony malformations of the craniovertebral junction". Child's Nervous System. 27 (4): 523–564. doi:10.1007/s00381-010-1358-9. PMC 3055990. PMID 21193993.
- Osmotherly, PG; Rivett, D; Rowe, LJ (July 2013). "Toward understanding normal craniocervical rotation occurring during the rotation stress test for the alar ligaments". Physical Therapy. 93 (7): 986–992. doi:10.2522/ptj.20120266. hdl:1959.13/1036543. PMID 23538587.
| Joints and ligaments of torso | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebral |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Thorax |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Pelvis |
| ||||||||||||||||||