 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
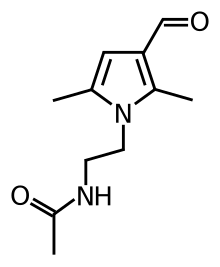
| Formula | C11H16N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 208.261 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Aloracetam (INN) is a drug described as a nootropic which is closely related to, but technically not of (as it lacks a pyrrolidone ring), the racetam family of compounds. It was studied by Aventis for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but was never marketed.
See also
References
- "The Use of Stems in the Selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for Pharmaceutical Substances" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2011. Retrieved 22 May 2015.
- George CF (7 July 1998). Drug Therapy in Old Age. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-94149-1.
- Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 615–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- Fischer F, Matthisson M, Herrling P (2004). "List of drugs in development for neurodegenerative diseases". Neuro-Degenerative Diseases. 1 (1): 50–70. doi:10.1159/000077879. PMID 16908974.
| Racetams | |
|---|---|
| Racetams |
|
| Phenylpiracetams |
|
| Racetam-like |
|
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |