| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ammonium hexachloroplatinate(IV) | |
| Other names ammonium chloroplatinate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.233 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
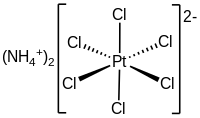
| Chemical formula | (NH4)2PtCl6 |
| Molar mass | 443.87 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow crystals |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 3.065 g/cm |
| Melting point | 380 °C (716 °F; 653 K) decomposes |
| Solubility in water | 0.289 g/100ml (0 °C) 0.7 g/100ml (15 °C) 0.499 g/100ml (20 °C) 3.36 g/100ml (100 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H290, H301, H317, H318, H334 |
| Precautionary statements | P234, P261, P264, P270, P272, P280, P285, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P341, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P333+P313, P342+P311, P363, P390, P404, P405, P501 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 195 mg/kg rat |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Ammonium hexachloroplatinate, also known as ammonium chloroplatinate, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2. It is a rare example of a soluble platinum(IV) salt that is not hygroscopic. It forms intensely yellow solutions in water. In the presence of 1M NH4Cl, its solubility is only 0.0028 g/100 mL.
Preparation and structure
The compound consists of separate tetrahedral ammonium cations and octahedral anions. It is usually generated as a fine yellow precipitate by treating a solution of hexachloroplatinic acid with a solution of an ammonium salt. The complex is so poorly soluble that this step is employed in the isolation of platinum from ores and recycled residues.
As analyzed by X-ray crystallography, the salt crystallizes in a cubic motif reminiscent of the fluorite structure. The centers are octahedral. The NH4 centers are hydrogen bonded to the chloride ligands.
Uses and reactions
Ammonium hexachloroplatinate is used in platinum plating. Heating (NH4)2 under a stream of hydrogen at 200 °C produces platinum sponge. Treating this with chlorine gives H2.
Ammonium hexachloroplatinate decomposes to yield platinum sponge when heated to high temperatures:
- 3(NH4)2PtCl6 → 3Pt(s) + 2NH4Cl(g) + 16HCl(g) + 2N2(g)
Safety
Dust containing ammonium hexachloroplatinate can be highly allergenic. "Symptoms range from irritation of skin and mucous membranes to life-threatening attacks of asthma."
Related compounds
References
- "ammonium hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Chemister.ru. 2007-03-19. Retrieved 2014-06-03.
- ^ George B. Kauffman (1967). "Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 9. pp. 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51. ISBN 978-0-470-13240-1.
- Cotton, S. A. Chemistry of Precious Metals, Chapman and Hall (London): 1997. ISBN 0-7514-0413-6.
- Verde-Gómez, Y.; Alonso-Nuñez, G.; Cervantes, F.; Keer, A. "Aqueous solution reaction to synthesize ammonium hexachloroplatinate and its crystallographic and thermogravimetric characterization" Materials Letters, 2003, volume 57, p 4667-4672. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00381-1
- Rochow, Eugene George (1977). Modern Descriptive Chemistry. W. B. Saunders Company. p. 202. ISBN 9780721676289.
- Renner, Hermann; Schlamp, Günther; Kleinwächter, Ingo; Drost, Ernst; Lüschow, Hans Martin; Tews, Peter; Panster, Peter; Diehl, Manfred; Lang, Jutta; Kreuzer, Thomas; Knödler, Alfons; Starz, Karl Anton; Dermann, Klaus; Rothaut, Josef; Drieselmann, Ralf; Peter, Catrin; Schiele, Rainer (2001). "Platinum Group Metals and Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_075. ISBN 3527306730.
| Platinum compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt(−II) | |||
| Pt(0) | |||
| Pt(II) |
| ||
| Pt(IV) | |||
| Pt(V) | |||
| Pt(VI) | |||