| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Bioko" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Native name: Ëtulá a Ëri (Bube) | |
|---|---|
 Map of Bioko Map of Bioko | |
  | |
| Etymology | Named for Cristino Seriche Bioko |
| Geography | |
| Location | Gulf of Guinea |
| Coordinates | 3°30′N 8°42′E / 3.500°N 8.700°E / 3.500; 8.700 |
| Archipelago | Cameroon line |
| Area | 2,017 km (779 sq mi) |
| Length | 70 km (43 mi) |
| Width | 32 km (19.9 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 3,012 m (9882 ft) |
| Highest point | Pico Basile |
| Administration | |
| Equatorial Guinea | |
| Region | Insular Region |
| Provinces | Bioko Norte and Bioko Sur |
| Largest settlement | Malabo (pop. 297,000 (2019 estimate)) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 335,048 (2015 Census) |
| Pop. density | 165.8/km (429.4/sq mi) |
| Languages | Equatoguinean Spanish, Pichinglis, Bube |
| Ethnic groups | Bubi (58%), Fang (16%), Fernandino (12%), Igbo (7%) (2002) |

Bioko (/biːˈoʊkoʊ/; Spanish: [biˈoko] , historically Fernando Po, Spanish: [feɾˈnando ˈpo] ; Bube: Ëtulá a Ëri) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located 32 km (20 mi) south of the coast of Cameroon, and 160 km (99 mi) northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of 2,017 km (779 sq mi). The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at 3,012 m (9,882 ft).
Etymology
Bioko's native name is Ëtulá a Ëri in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as Fernando Po (Portuguese: Fernando Pó; Spanish: Fernando Poo), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named Macías Nguema Biyogo after the then president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko.
Geography
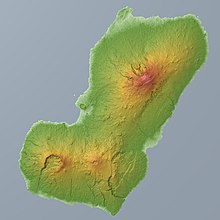
Bioko has a total area of 2,017 km (779 sq mi). It is 70 km (43 mi) long from NNE to SSW and about 32 km (20 mi) across. The island is mostly covered by tropical rainforest. It is volcanic and very mountainous with the highest peak Pico Basile (3,012 m (9,882 ft)). It thus resembles neighbouring islands São Tomé and Príncipe. Like them, it lies on the Cameroon line. Its southernmost point is called Punta Santiago.
Bioko lies on the African continental shelf, separated from the African mainland by 32 km (20 mi) of water with a depth of only 60 metres. During the Pleistocene epoch Bioko was connected to the African mainland. Bioko separated from Africa around 10,000 years ago, at the end of the Last Glacial Period.
The fire skink, a species of lizard found on the island, carries the scientific name of Mochlus fernandi, derived from Fernando Po, the former name of the island.
Fernando Po (with the spelling "Fernando Poo") is the setting for a Cold War standoff in Robert Shea and Robert Anton Wilson's Illuminatus Trilogy.
Geology
The island is composed mostly of basalt, mostly alkali basalt and hawaiites, and to a lesser extent mugearites.
Demographics
The island has a population of 335,048 inhabitants (2015 Census). Its historic indigenous people are the Bubi people, who currently constitute 58% of the population. Other ethnicities include the Fang at 16%, Fernandinos at 12%, and the Igbo at 7%, as well as African and European immigrants.
Languages
Spanish has been an official language since 1844 when Spain took control of the island. It is still the language of education and administration, related to the more than 100 years as a Spanish colony. 67% of Equatoguineans can speak Spanish, especially those living in the capital, Malabo, on Bioko.
The Bube language, with about 50,000 speakers, and various dialects, is the original language of the inhabitants of Bioko. However, given the numerous ethnic groups and peoples who operated on Bioko, a creole language developed, known as Pichi. It is based on English grammar, from the period when the British operated bases for their forces. It also incorporates West African languages from Nigeria and Liberia, as well as Portuguese vocabulary, which forms a considerable part of the Krio language, which had developed in Sierra Leone. Workers came to Bioko from all of these areas in the 19th through much of the 20th century.
History
Unlike other islands in the area, Bioko had an indigenous African population. The island was inhabited in the middle of the first millennium BC by Bantu tribes from the mainland, who formed the Bubi ethnic group. The Bubi speak a Bantu language. The island has probably been inhabited by this or other Bantu-speaking groups since before the 7th century BC.
In 1472, the Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó was the first European to sight the island. He named it Formosa Flora ("beautiful flower"). In 1494 it was renamed Fernando Po in his honour after being claimed as a colony by the Portuguese. The Portuguese developed the island for sugarcane crops, and while considered poor quality, the refineries' output was such that Fernando Po sugar briefly dominated the trade centres in Europe.

In 1642, the Dutch East India Company established trade bases on the island without Portuguese consent. It temporarily centralized from there its slave trade in the Gulf of Guinea. The Portuguese appeared again on the island in 1648, replacing the Dutch Company with one of their own, also dedicated to slave trading and established in its neighbour island Corisco.
Parallel with this establishment, the Bubi clans began the slow process of establishing the core of a new kingdom on the island, especially after the activity of some local chiefs such as Molambo (approx. 1700–1760). During a period when enslavement was increasing in the region, local clans abandoned their coastal settlements and settled in the safer hinterland.
Under the 1778 Treaty of El Pardo, Portugal ceded Fernando Po, Annobón, and the Guinea coast, Río Muni, to Spain, which together form modern Equatorial Guinea. The treaty was signed by Queen Mary I of Portugal and King Charles III of Spain, in exchange for territory on the American continent. Spain mounted an expedition to Fernando Po, led by the Conde de Argelejos, who stayed for four months. In October 1778, Spain installed a governor on the island who stayed until 1780, when the Spanish mission left the island.
Chief Molambo was succeeded by another local leader, Lorite (1760–1810), who was succeeded by Lopoa (1810–1842). After abolishing the British Atlantic slave trade, from 1827 to 1843 the British leased bases at Port Clarence (modern Malabo) and San Carlos for the African Slave Trade Patrol. The settlement at Port Clarence (named after the Duke of Clarence) was constructed under the supervision of William Fitzwilliam Owen. He had previously mapped most of the coasts of Africa and was a zealous anti-slaver. During his three-year command, his forces detained 20 ships and liberated 2,500 slaves. The Mixed Commission Court was moved from Freetown, Sierra Leone, to Clarence to hasten the legal process of emancipating slaves liberated from slave ships.

In March 1843, Juan José Lerena planted the Spanish flag in Port Clarence (renamed Santa Isabel), starting the decline of British influence on the island. Spain revoked the British lease in 1855. Madabita (1842–1860) and Sepoko (1860–1875) were principal local chiefs during the period when Spain re-established its control of the island. A notable resident from 1861 to 1865 was the British explorer Richard Burton who served as the British consul, during which time he wrote several books about Africa. This period was also marked by Spain's transport deportation here of several hundred Afro-Cubans, as well as dozens of Spanish scholars and politicians considered politically undesirable. In addition Spain exiled 218 revolutionaries here from the Philippine Revolution, of whom only 94 survived for long.

In 1923–1930, the League of Nations investigated the transportation of contract migrant labour between Liberia and the Spanish colony of Fernando Po. Although the League concentrated its attention on arrangements in Liberia, a closer examination revealed that labour abuse arose from conditions on Fernando Po. In the last quarter of the 19th century, Krio planters on the island had shifted from palm oil trading to cocoa cultivation. Their dependence on migrant labour and increasing competition with Europeans resulted in an economic crisis in the first years of the twentieth century. Planters detained labour but failed to pay their contracts, resulting in a situation of de facto slavery. Liberia prohibited labor traders from contracting with their citizens.
In 1942 Fernando Po was the scene of a secretive small scale British raid code named Operation Postmaster which was an action that sought to disrupt German U-boat resupply activities being conducted on the island.
During the Nigerian Civil War in the 20th century, relief agencies used the island as one of the bases for Biafran airlift flights into the secessionist Republic of Biafra.
Economy


Located on Punta Europa, west of Malabo, the Alba Gas Plant processes natural gas delivered from offshore production wells. The plant is operated by Marathon Oil Company through its subsidiary, Marathon Equatorial Guinea Production Limited. The plant produces natural gas liquids including propane, butane, and condensate products. The majority of the residue gas from the Alba plant is delivered to a natural gas liquefaction plant operated by EG LNG. A portion of the Alba plant residue is also delivered to the Atlantic Methanol Production Company and is used to produce methanol. The products from all three plants are loaded onto ocean-going tanker ships for export.
Transport
A rectangular transport route links the four main cities: Malabo, Luba, Baney, and Riaba. The island's airport is Malabo International Airport.
Tourism
Tourist attractions include the colonial quarter in Malabo, and the southern part of the island, where visitors can hike to the Iladyi Cascades [es] (Moka Falls) and to remote beaches of Ureka to watch nesting turtles.
See also
- Annobón, an island
- Bight of Bonny, also known as the Bight of Biafra
- Bioko drill
- Bioko Norte Province
- Bioko Sur Province
- Cameroon line
- Equatorial Guinea
- Emancipados, black people in Spanish Guinea assimilated to the Spaniards.
- Fernandino peoples
- Fernão do Pó, commander of the first European ship to land here.
- Gulf of Guinea
- Leopold Janikowski, Polish explorer who visited the island in 1883
- Kru people
- Tetteh Quarshie, a Ghanaian who introduced cocoa to his native country from the island.
- Luba Crater Scientific Reserve
- Movement for the Self-Determination of Bioko Island
- The English-lexicon Creole Pichi is spoken on Bioko
- Postage stamps and postal history of Fernando Po
References
- "Equatorial Guinea - The World Factbook". cia.gov. 7 June 2018. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- Minahan, James (2002). Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: A-C. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 330. ISBN 0313321094.
- Room, Adrian (May 30, 2007). The Pronunciation of Placenames: A Worldwide Dictionary. McFarland, Incorporated, Publishers. ISBN 9780786429417 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Anuario Estadístico de Guinea Ecuatorial 2018" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadisticas de Guinea Ecuatorial. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- "Playa de Arena Blanca". Atlas Obscura.
- Pospelov, E. M. (1998). Geograficheskie nazvanii︠a︡ mira: toponimicheskiĭ slovarʹ. Moskva: Russkie slovari. ISBN 978-5-89216-029-2.
- Pérez-Pérez, Miguel A.; Yu, Wen-Bin (2021-10-20). "Pleistocene origin and colonization history of Lobelia columnaris Hook. f. (Campanulaceae: Lobelioideae) across sky islands of West Central Africa". Ecology and Evolution. 11 (22): 15860–15873. Bibcode:2021EcoEv..1115860P. doi:10.1002/ece3.8256. ISSN 2045-7758. PMC 8601881. PMID 34824795.
- Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5, ("Fernand", p. 89).
- "Excerpt from The Illuminatus! Trilogy". Penguin Random House Canada.
- Yamgouot, Fadimatou Ngounouno; Déruelle, Bernard; Gbambié Mbowou, Isaac Bertrand; Ngounouno, Ismaïla; Demaiffe, Daniel (2016-09-01). "Geochemistry of the volcanic rocks from Bioko Island ("Cameroon Hot Line"): Evidence for plume-lithosphere interaction" (PDF). Geoscience Frontiers. 7 (5): 743–757. Bibcode:2016GeoFr...7..743Y. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2015.06.003. ISSN 1674-9871.
- Obiang convierte al portugués en tercer idioma oficial para entrar en la Comunidad lusófona de Naciones, Terra, 13 July 2007.
- Goodman, Jordan (September 2007). "The Hell-Borne Traffic". geographical.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-01-07.
- "British Empire: Africa: Fernando Po". britishempire.co.uk. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- Foreman, John (1906). The Philippine Islands: A Political, Geographical, Ethnographical, Social and Commercial History of the Philippine Archipelago. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons.
- Sundiata, I. K. (1974). "Prelude to Scandal: Liberia and Fernando Po, 1880–1930". The Journal of African History. 15 (1): 97–112. doi:10.1017/S0021853700013268. JSTOR stable/180372. S2CID 162982618.
- Room, Adrian (1994). African placenames. Jefferson, North Carolina (US): McFarland. ISBN 0-89950-943-6
- Sundiata, Ibrahim K. (1990). Equatorial Guinea: Colonialism, State Terror, and the Search for Stability. Boulder, Colorado (US): Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-0429-6
- Janikowski, Leopold (1886). L'ile De Fernando-Poo, Son Etat Actuel Et Ses Habitants [The Island of Fernando Po, its current state and its inhabitants] (in French) (Bulletin De La Société De Géographie, Septième Série. - Tome Septième ed.).
- Janikowski, Leopold (1887). La Isla de Fernando Póo, su estado actual y sus habitantes [The Island of Fernando Po, its current state and its inhabitants] (in Spanish) (Boletín dela sociedad Geográfica de Madrid XXII ed.). pp. 67–77 and 201–211.
- Janikowski, Leopold (1936). W dżunglach Afryki. Wspomnienia z polskiej wyprawy afrykańskiej w latach 1882-90 [In the African Jungle. Memories of the Polish expedition to Africa in the years 1882-1890] (in Polish) (1936 ed.). Warsaw, Poland: Wydawnictwo Ligi Morskiej I Kolonjalnej; Skład Główny: Instytut Wydawn. Bibljoteka Polska S. A. Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 9, 2015.
External links
- The Drill Project
- Bioko Biodiversity Protection Program
- Gulf of Guinea Conservation Group Archived 2020-04-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Bubi history and culture from a Spanish missionary
- Virginia Morell: "Island ark", National Geographic Magazine, August 2008; link
| Portuguese Empire | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||