 | |
 The JR Central Towers company headquarters located above Nagoya Station The JR Central Towers company headquarters located above Nagoya Station | |
| Native name | 東海旅客鉄道株式会社 |
|---|---|
| Romanized name | Tōkai Ryokaku Tetsudō (lit. "Tōkai Passenger Railway") kabushiki gaisha |
| Company type | Public (KK) |
| Traded as | |
| Industry | Private railway |
| Predecessor | Japanese National Railways (JNR) |
| Founded | 1 April 1987; 37 years ago (1987-04-01), privatization of JNR |
| Headquarters | JR Central Towers 1-1-4 Meieki, Nakamura-ku, Nagoya, Aichi 450-6101, Japan |
| Area served | Tōkai region |
| Key people | Shin Kaneko, Chairman Shunsuke Niwa, President |
| Products | TOICA, EX-IC (a rechargeable contactless smart card) |
| Services | passenger railways travel agency services wholesale and retail parking lot operations real estate food and beverage sales casualty insurance other related services |
| Revenue | |
| Operating income | |
| Net income | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owner | Public float, largest single shareholder: Mizuho Bank (4.39%) |
| Number of employees | 16,193 (as of March 31, 2008) |
| Divisions | Conventional lines operations Shinkansen operations |
| Subsidiaries | 39 group companies, including Nippon Sharyo (since October 2008) |
| Website | english.jr-central.co.jp/index.html |
| Central Japan Railway Company | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||
 JR Central N700 Series Shinkansen Nozomi train JR Central N700 Series Shinkansen Nozomi train | |||||
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | Japan Railways Group | ||||
| Infrastructure company | Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 0.528 billion per year | ||||
| Passenger km | 55.811 billion per year | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 1,970.8 km (1,224.6 mi) | ||||
| Double track | 1,086.8 km (675.3 mi) (55.1%) | ||||
| Electrified | 1,491.7 km (926.9 mi) (75.7%) | ||||
| High-speed | 552.6 km (343.4 mi) (28.0%) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||||
| High-speed | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| Main | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary 1,418.2 km (881.2 mi) | ||||
| 25 kV AC 60 Hz overhead | 552.6 km (343.4 mi) Tokaido Shinkansen | ||||
| Features | |||||
| No. stations | 403 | ||||
| |||||
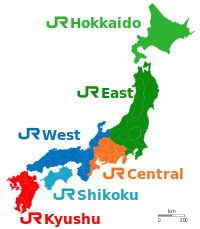
The Central Japan Railway Company is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and occasionally as JR Tokai (Japanese: JR東海). The term Tōkai refers to the southern portion of Central Japan, the geographical region in which the company chiefly operates.
JR Central's operational hub is Nagoya Station and the company's administrative headquarters are located in the JR Central Towers above the station. The busiest and longest railway line operated by JR Central is the Tōkaidō Main Line between Atami and Maibara. The company also operates the Tōkaidō Shinkansen between Tokyo and Shin-Ōsaka. Additionally it is responsible for the Chūō Shinkansen — a maglev service between Tokyo and Osaka, which is due to start operation between Tokyo and Nagoya in 2034.
JR Central is Japan's most profitable and highest throughput high-speed-rail operator, carrying 138 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009, considerably more than the world's largest airline. Japan recorded a total of 289 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009.
JR Central is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange and Nagoya Stock Exchange with American depositary receipts traded over-the-counter through OTCMG Pink, is a constituent of the TOPIX Core30 index, and is also one of the three only Japan Railways Group constituents of the Nikkei 225 index, the others being JR East and JR West. It is one of Nagoya's gosanke companies along with Toyota and the Chubu Electric Power Company.
Lines
Shinkansen
- Tōkaidō Shinkansen: Tokyo Station—Shin-Ōsaka Station 552.6 km
- Maglev Chūō Shinkansen: From Tokyo to Nagoya (under construction)
Conventional lines
- CA Tōkaidō Main Line: Atami Station—Maibara Station 341.3 km
- Branch line: Ōgaki Station—Mino-Akasaka Station 5.0 km
- CB Gotemba Line: Kōzu Station—Numazu Station 60.2 km
- CC Minobu Line: Fuji Station—Kōfu Station 88.4 km
- CD Iida Line: Toyohashi Station—Tatsuno Station 195.7 km
- CE Taketoyo Line: Ōbu Station—Taketoyo Station 19.3 km
- CF Chūō Main Line: Shiojiri Station—Nagoya Station 174.8 km
- CG Takayama Main Line: Gifu Station—Inotani Station 189.2 km
- CI Taita Line: Tajimi Station—Mino-Ōta Station 17.8 km
- CJ Kansai Main Line: Nagoya Station—Kameyama Station 59.9 km
- Kisei Main Line: Kameyama Station—Shingū Station 180.2 km
- Meishō Line: Matsusaka Station—Ise-Okitsu Station 43.5 km
- Sangū Line: Taki Station—Toba Station 29.1 km
- Jōhoku Line: Kachigawa Station—Biwajima Station 11.2 km (trains are operated by Tokai Transport Service Company, not JR Central)
Named train services
- Nanki (Nagoya - Shingū & Kii-Katsuura)
- Hida (Nagoya/Ōsaka - Takayama, Hida-Furukawa & Toyama)
- Shinano (Nagoya - Nagano & Hakuba)
- Mie (Nagoya - Iseshi & Toba)
- Fujikawa (Shizuoka - Kōfu)
- Inaji (Toyohashi - Iida)
- Odoriko (Tokyo - Izukyū-Shimoda & Shuzenji)
- Sunrise Seto (Tokyo - Takamatsu)
- Sunrise Izumo (Tokyo - Izumoshi)
- Nozomi (Tokyo - Hakata)
- Hikari (Tokyo - Hakata & Hakataminami)
- Kodama (Tokyo - Shin-Ōsaka, Shin-Ōsaka - Hakata & Hakataminami)
Affiliates
The JR Central Group consists of JR Central and the following affiliates:
Transportation
- JR Tokai Bus Company
- JR Tokai Logistics Company (ja:ジェイアール東海物流株式会社)
- Tokai Transport Service Company
- First Air Transport Co., Ltd. (ja:ファーストエアートランスポート株式会社)
Merchandise
- JR Tokai Corporation (ja:ジェイアール東海商事株式会社)
- JR Tokai Takashimaya Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海高島屋)
- JR-Central Passengers Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海パッセンジャーズ)
- JR Tokai Food Service Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアール東海フードサービス株式会社)
- Tokai Kiosk Company (ja:東海キヨスク株式会社)
Construction
- JR Tokai Construction Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアール東海建設株式会社)
- JR Central Consultants Company (ja:ジェイアール東海コンサルタンツ株式会社)
- The Nihon Kikai Hosen Co., Ltd (ja:日本機械保線株式会社)
- Futaba Tetsudo Kogyo Co., Ltd. (ja:双葉鉄道工業株式会社)
- CN Construction Co., Ltd. (ja:シーエヌ建設株式会社)
Information systems
- JR Tokai Information Systems Company (ja:ジェイアール東海情報システム株式会社)
- Shinsei Technos Co., Ltd.(ja:新生テクノス株式会社)
Hotels and resorts
- JR Tokai Hotels Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海ホテルズ)
- Nagoya Terminal Hotel Co., Ltd. (ja:名古屋ターミナルホテル株式会社)
- Shizuoka Terminal Hotel Co., Ltd. (ja:静岡ターミナルホテル株式会社)
Travel
- JR Tokai Agency Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海エージェンシー)
- JR Tokai Tours (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海ツアーズ)
- Hida Forest City Planning Co., Ltd. (ja:飛騨森林都市企画株式会社)
Publishing
- Wedge Inc. (株式会社ウェッジ)
Rolling stock
- Shinkansen Engineering Co., Ltd. (ja:新幹線エンジニアリング株式会社)
- Tokai Rolling Stock & Machinery Co., Ltd. (ja:東海交通機械株式会社)
- Nippon Sharyo, Ltd
Maintenance
- Chuoh Linen Supply Co., Ltd. (ja:中央リネンサプライ株式会社)
- JR Tokai General Building Maintenance Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアール東海総合ビルメンテナンス株式会社)
- Central Maintenance Co., Ltd. (ja:セントラルメンテナンス株式会社)
- Shinkansen Service & Technology Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:関西新幹線サービック)
- Shinkansen Maintenance Tokai Co., Ltd. (ja:新幹線メンテナンス東海株式会社)
- Tokai Seibi Co., Ltd. (ja:東海整備株式会社)
Real estate
- JR Central Building Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアールセントラルビル株式会社)
- JR Development and Management Corporation of Kansai (ja:ジェイアール東海関西開発株式会社)
- JR Development and Management Corporation of Shizuoka (ja:ジェイアール東海静岡開発株式会社)
- JR Tokai Real Estate Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアール東海不動産株式会社)
- Shizuoka Terminal Development Co., Ltd. (ja:静岡ターミナル開発株式会社)
- Shin-Yokohama Station Development Co., Ltd. (ja:新横浜ステーション開発株株式会社)
- Tokyo Station Development Co., Ltd. (ja:東京ステーション開発株式会社)
- Toyohashi Station Building Co., Ltd. (ja:豊橋ステーションビル株式会社)
- Nagoya Station Area Development Corporation (ja:名古屋ステーション開発株式会社)
- Nagoya Terminal Station Building Co., Ltd. (ja:名古屋ターミナルビル株式会社)
- Hamamatsu Terminal Development Co., Ltd. (ja:浜松ターミナル開発株式会社)
Other services
- JR Tokai Well Co., Ltd. (株式会社ja:ジェイアール東海ウェル)
- JR Tokai Partners Co., Ltd. (ja:ジェイアール東海パートナーズ株式会社)

References
- Central Japan Railway Company. "Board of Directors, Audit and Supervisory Board Members and Corporate officers (as of June, 2023)". Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ Central Japan Railway Company. "Data book 2008" (PDF). Retrieved 30 June 2009.
- ^ Central Japan Railway Company. Annual Report 2015 (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 10 January 2016.
- ^ Central Japan Railway Company. "Organization Chart (As of July, 2008)". Retrieved 30 June 2009.
- Central Japan Railway Company. "Notice concerning Change of Specified Subsidiary" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- 東海旅客鉄道株式会社, Tōkai Ryokaku Tetsudō kabushiki gaisha, lit. "Tōkai Passenger Railway Stock Company"
- "Consolidated Subsidiaries". Central Japan Railway Company (in Japanese). Retrieved 17 September 2024.
- Central Japan Railway Company. "Corporate Data". Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- "Japan railway firm pushes back maglev plan, possibly to 2034 or later". Kyodo News. 29 March 2024. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ Cooper, Chris (8 February 2011). "Rail's Cash-Flow King Stakes $62 Billion on Tokyo Maglev Train". Bloomberg. Retrieved 12 June 2012.
External links
- Central Japan Railway Company
- Central Japan Railway Company| SCMAGLEV Official Website
- "Company history books (Shashi)". Shashi Interest Group. April 2016. Wiki collection of bibliographic works on Central Japan Railway Company
| Shinkansen | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lines |
|     | ||||||||||||||||||
| Service names |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Train types |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Operators |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Builders and owners |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| People | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Transit in Greater Nagoya (Chūkyō) | |
|---|---|
| Shinkansen | |
| Minor private railways | |
| Third-sector railways | |
| |
| Terminals |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
| TOPIX 100 companies of Japan | |
|---|---|
| Core 30 | |
| Large 70 |
|
|