You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (August 2024) Click for important translation instructions.
|
  Normal unregistered Kitaca (on top) and the debut commemorative Kitaca (on bottom) Normal unregistered Kitaca (on top) and the debut commemorative Kitaca (on bottom) | |
| Location | Usable nationwide Distributed in Hokkaido |
|---|---|
| Launched | October 25, 2008 (16 years ago) |
| Operator | Hokkaido Railway Company |
| Manager | Hokkaido Railway Company |
| Currency | Japanese yen |
| Stored-value | Pay as you go |
| Auto recharge | None |
| Unlimited use | None (Other non-related unlimited use passes available) |
| Validity |
|
| Website | www |

Kitaca (Japanese: キタカ, romanized: Kitaka) is a rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Sapporo, Japan. It launched on October 25, 2008 and is managed by Hokkaido Railway Company. The card'a name is a combination of the word for "north" (北, kita) and the English loanword "card". 北 is also the first character of Hokkaidō (北海道). Like other electronic fare collection systems in Japan, the card uses RFID technology developed by Sony corporation known as FeliCa. The card's mascot is an ezo momonga (Pteromys volans orii), a type of flying squirrel found in Hokkaidō, and was designed by Sora, an illustrator who lives in Sapporo.
Usable area
As of March 2024, 69 stations in the Sapporo-Asahikawa area, as well as 6 stations in the Hakodate area including unmanned stations, accept Kitaca.
- Hakodate Main Line: From Hakodate to Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto and from Otaru to Asahikawa
- Chitose Line: From Shiroishi to Numanohata, and branch from Minami-Chitose to New Chitose Airport (the whole line)
- Muroran Main Line: From Numanohata to Tomakomai
- Sasshō Line (Gakuentoshi Line): From Sōen to Hokkaidō-Iryōdaigaku (the whole line)
Types of cards
- Unregistered Kitaca
- Registered Kitaca: Requires registration. The card can be reissued when lost.
- Kitaca commuter pass: Requires registration.
Credit card function is also considered. North Pacific Bank, the largest local bank of Hokkaido, considers to include Kitaca's functions to its credit card Clover. A plan to introduce an Osaifu-Keitai compliant mobile payment system was cancelled due to the cost.
Integration
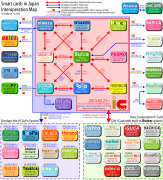
In 2009, Kitaca became interchangeable with JR East's Suica, including its use of electronic money functionality. Since late 2012, the card can also be used in lieu of a SAPICA, a smart card system introduced in 2009 by the Sapporo City Transportation Bureau.
In 2013, interoperation was extended country-wide, and Kitaca became usable in all major cities across Japan as part of the Nationwide Mutual Usage Service.
References
- (in Japanese) 北のカード「Kitaca」vol.4〜「エゾモモンガ」の生みの親〜 Archived 2008-10-09 at the Wayback Machine (Northern card "Kitaca" vol.4, the crator of the "Ezo momonga"), from Satsueki.jp, retrieved on October 26, 2008.
- JR Hokkaido. "Usable Area". Retrieved 2022-10-19.
- Hokkaidō Shimbun, October 16 2008
- (in Japanese) Official press release by JR Hokkaidō, December 12 2007.
- (in Japanese) JR北海道のICカード乗車券「Kitaca」が10月25日にスタート (JR Hokkaidō's IC card ticket "Kitaca" starts on October 25) by BB Watch, October 25 2008.
- Ito, Etsuro (October 2013). "Launch of Nationwide Interoperable Transport System IC Cards" (PDF). East Japan Railway Culture Foundation. Japan Railway & Transport Review. pp. 6–15. Retrieved March 7, 2024.
- "交通系ICカードの普及・利便性拡大に向けて" (PDF). MLIT. Retrieved 2022-10-19.
External links
- (in Japanese) Official website by JR Hokkaido
- (in Japanese) Official press release by JR Hokkaido
| Smart cards in Japan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fare collection |
| ||||
| Electronic money | |||||
| Mobile payment | |||||
| Transit in Hokkaido | |
|---|---|
| Shinkansen | |
| Other railways | |
| Terminals | |
| Public Ferries |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|