Artery in the abdomen
Blood vessel
| Common iliac artery | |
|---|---|
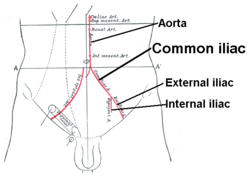 Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. | |
 Volume rendered CT scan of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels. Volume rendered CT scan of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Abdominal aorta |
| Branches | External iliac internal iliac |
| Vein | Common iliac veins |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria iliaca communis |
| TA98 | A12.2.14.001 |
| TA2 | 4301 |
| FMA | 14764 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The common iliac artery is a large artery of the abdomen paired on each side. It originates from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. It ends in front of the sacroiliac joint, one on either side, and each bifurcates into the external and internal iliac arteries.
Structure
The common iliac artery are about 4 cm long in adults and more than a centimeter in diameter. It begins as a branch of the aorta. This is at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra. It runs inferolaterally, along the medial border of the psoas muscles. It bifurcates into the external iliac artery and the internal iliac artery at the pelvic brim, in front of the sacroiliac joints.
The common iliac artery, and all of its branches, exist as paired structures (that is to say, there is one on the left side and one on the right).
The distribution of the common iliac artery is basically the pelvis and lower limb (as the femoral artery) on the corresponding side.
Relations
Both common iliac arteries are accompanied along their course by the two common iliac veins, which lie posteriorly and to the right. Their terminal bifurcation is crossed anteriorly by the ureters. This is significant, as the bifurcation of the common iliac artery is the second point of ureteric constriction.
Function
The common iliac artery supplies the leg and the pelvic region.
Clinical significance
Constriction
The common iliac artery may become narrowed. This is most common at the aortic bifurcation.
Dilatation
Dilatation of the common iliac artery can be graded into the following categories:
| Normal | Diameter ≤ 12 mm |
| Ectasia | Diameter 12 to 18 mm |
| Aneurysm | Diameter ≥ 18 mm |
Additional images
-
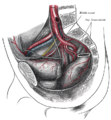 Bifurcation of the aorta and the right common iliac artery - side view. Hypogastric artery is an old term for internal iliac artery. (Com. iliac. a. is visible at center bottom left.)
Bifurcation of the aorta and the right common iliac artery - side view. Hypogastric artery is an old term for internal iliac artery. (Com. iliac. a. is visible at center bottom left.)
-
 Deep and superficial dissection of the lumbar plexus.
Deep and superficial dissection of the lumbar plexus.
-
 Posterior abdominal wall, after removal of the peritoneum, showing kidneys, suprarenal capsules, and great vessels.
Posterior abdominal wall, after removal of the peritoneum, showing kidneys, suprarenal capsules, and great vessels.
-
 Common iliac arteries
Common iliac arteries
References
- ^ Jacob, S. (2008). "4 - Abdomen". Human Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 71–123. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-10373-5.50007-5. ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5.
- ^ Buckley, Brendan; Holden, Andrew; Merrilees, Stephen; Fernando, Rukshan (2020). "13 - Revascularization: Aortoiliac". Image-Guided Interventions - Expert Radiology (3rd ed.). Saunders. pp. 99–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-61204-3.00013-0. ISBN 978-0-323-61204-3. S2CID 241869039.
- Melissa L Kirkwood. "Iliac artery aneurysm". Retrieved February 23, 2018. Last updated: Mar 27, 2017.
External links
- Hypogastric artery - thefreedictionary.com
- Atlas image: abdo_wall75 at the University of Michigan Health System - "The Abdominal Aorta"
- Anatomy photo:40:09-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Abdominal Aorta and Paraaortic Nerve Plexus"
- Anatomy image:8969 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center