| Cynodesmus Temporal range: Late Oligocene–Early Miocene PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Subfamily: | †Hesperocyoninae |
| Genus: | †Cynodesmus Scott, 1893 |
| Type species | |
| †Cynodesmus thooides | |
| Species | |
| |
Cynodesmus ("dog link") is an extinct genus of omnivorous canine which inhabited North America during the Oligocene living from 33.3—-26.3 Ma and existed for approximately 7 million years.
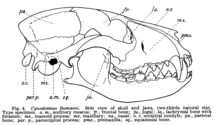
Cynodesmus was one of the first canids to truly look dog-like. At around 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length, it was about the same size as a modern coyote, but had a shorter skull, heavier tail, and longer rump. The shape of its limbs suggests that Cynodesmus was not a very good runner compared to most other canids; it probably attacked prey from an ambush. Unlike modern dogs, it had five toes on each foot, bearing partially retractable claws.
Taxonomy
Cynodesmus once included numerous species of Oligocene and Miocene canid with highly carnivorous (hypercarnivorous) dentitions. A revision of the genus by Wang (1994) indicates that most species previously placed in Cynodesmus are unrelated to the type species, C. thooides. These other species have been placed the genera Carpocyon, Desmocyon, Leptocyon, Metatomarctus, Osbornodon, Otarocyon, Paracynarctus, Paratomarctus, and Phlaocyon (Wang, 1994; Wang et al., 1999). Of these, only Osbornodon belongs in the same subfamily as Cynodesmus, Hesperocyoninae. The remaining genera are placed in the subfamilies Borophaginae and Caninae.
With unrelated species removed, Cynodesmus is currently restricted to the type species and the closely related C. martini (Wang, 1994).
Studies using the old conception of Cynodesmus considered it to be the ancestor of Tomarctus (16-23 Ma) from which wolves, dogs, foxes and fennecs developed. Cynodesmus is a good example of convergent evolution because of other species such as the Borophagus, the largest and most dominant canids of the Pliocene epoch, both of which evolved from it.
Notes
- http://paleobackup.nceas.ucsb.edu:8110/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?action=checkTaxonInfo&taxon_no=41207&is_real_user=1 Cynodesmus: Basic info.
- Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 219. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- North American Coyote Archived 2008-12-11 at the Wayback Machine
References
- Wang, X. 1994. Phylogenetic systematics of the Hesperocyoninae (Carnivora, Canidae). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 221:1-207.
- Wang, X., R.H. Tedford, and B.E. Taylor. 1999. Phylogenetic systematics of the Borophaginae (Carnivora, Canidae). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 243:1-391.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Cynodesmus | |









