| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Color blindness" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Medical condition
| Color blindness | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Color vision deficiency, impaired color vision |
 | |
| Example of an Ishihara color test plate. Viewers with normal color vision should clearly see the number "74". | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
| Symptoms | Decreased ability to see colors |
| Duration | Long term |
| Causes | Genetic (inherited usually X-linked) |
| Diagnostic method | Ishihara color test |
| Treatment | Adjustments to teaching methods, mobile apps |
| Frequency | Red–green: 8% males, 0.5% females (Northern European descent) |
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually an inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects up to 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical damage to the eye, the optic nerve, parts of the brain, or from medication toxicity. Color vision also naturally degrades in old age.
Diagnosis of color blindness is usually done with a color vision test, such as the Ishihara test. There is no cure for most causes of color blindness; however there is ongoing research into gene therapy for some severe conditions causing color blindness. Minor forms of color blindness do not significantly affect daily life and the color blind automatically develop adaptations and coping mechanisms to compensate for the deficiency. However, diagnosis may allow an individual, or their parents/teachers, to actively accommodate the condition. Color blind glasses (e.g. EnChroma) may help the red–green color blind at some color tasks, but they do not grant the wearer "normal color vision" or the ability to see "new" colors. Some mobile apps can use a device's camera to identify colors.
Depending on the jurisdiction, the color blind are ineligible for certain careers, such as aircraft pilots, train drivers, police officers, firefighters, and members of the armed forces. The effect of color blindness on artistic ability is controversial, but a number of famous artists are believed to have been color blind.
Effects
| This section contains instructions, advice, or how-to content. Please help rewrite the content so that it is more encyclopedic or move it to Wikiversity, Wikibooks, or Wikivoyage. (December 2024) |
A color blind person will have decreased (or no) color discrimination along the red–green axis, blue–yellow axis, or both. However, the vast majority of the color blind are only affected on their red–green axis.
The first indication of color blindness generally consists of a person using the wrong color for an object, such as when painting, or calling a color by the wrong name. The colors that are confused are very consistent among people with the same type of color blindness.
Confusion colors

Confusion colors are pairs or groups of colors that will often be mistaken by the color blind. Confusion colors for red–green color blindness include:
- cyan and grey
- rose-pink and grey
- blue and purple
- yellow and neon green
- red, green, orange, brown
Confusion colors for tritan include:
- yellow and grey
- blue and green
- dark blue/violet and black
- violet and yellow-green
- red and rose-pink
These colors of confusion are defined quantitatively by straight confusion lines plotted in CIEXYZ, usually plotted on the corresponding chromaticity diagram. The lines all intersect at a copunctal point, which varies with the type of color blindness. Chromaticities along a confusion line will appear metameric to dichromats of that type. Anomalous trichromats of that type will see the chromaticities as metameric if they are close enough, depending on the strength of their CVD. For two colors on a confusion line to be metameric, the chromaticities first have to be made isoluminant, meaning equal in lightness. Also, colors that may be isoluminant to the standard observer may not be isoluminant to a person with dichromacy.
Color tasks
Main article: Color taskCole describes four color tasks, all of which are impeded to some degree by color blindness:
- Comparative – When multiple colors must be compared, such as with mixing paint
- Connotative – When colors are given an implicit meaning, such as red = stop
- Denotative – When identifying colors, for example by name, such as "where is the yellow ball?"
- Aesthetic – When colors look nice – or convey an emotional response – but do not carry explicit meaning
The following sections describe specific color tasks with which the color blind typically have difficulty.
Food

Color blindness causes difficulty with the connotative color tasks associated with selecting or preparing food. Selecting food for ripeness can be difficult; the green–yellow transition of bananas is particularly hard to identify. It can also be difficult to detect bruises, mold, or rot on some foods, to determine when meat is done by color, to distinguish some varietals, such as a Braeburn vs. a Granny Smith apple, or to distinguish colors associated with artificial flavors (e.g. jelly beans, sports drinks).
Skin color
Main article: Evolution of color vision in primates § Skin ToneChanges in skin color due to bruising, sunburn, rashes or even blushing are easily missed by the red–green color blind.
Traffic lights

The colors of traffic lights can be difficult for the red–green color blindness. This difficulty includes distinguishing red/amber lights from sodium street lamps, distinguishing green lights (closer to cyan) from normal white lights, and distinguishing red from amber lights, especially when there are no positional clues available (see image).

The main coping mechanism to overcome these challenges is to memorize the position of lights. The order of the common triplet traffic light is standardized as red–amber–green from top to bottom or left to right. Cases that deviate from this standard are rare. One such case is a traffic light in Tipperary Hill in Syracuse, New York, which is upside-down (green–amber–red top to bottom) due to the sentiments of its Irish American community. However, the light has been criticized due to the potential hazard it poses for color blind drivers.

There are other several features of traffic lights available that help accommodate the color blind. British Rail signals use more easily identifiable colors: The red is blood red, the amber is yellow and the green is a bluish color. Most British road traffic lights are mounted vertically on a black rectangle with a white border (forming a "sighting board"), so that drivers can more easily look for the position of the light. In the eastern provinces of Canada, traffic lights are sometimes differentiated by shape in addition to color: square for red, diamond for yellow, and circle for green (see image).
Signal lights
Navigation lights in marine and aviation settings employ red and green lights to signal the relative position of other ships or aircraft. Railway signal lights also rely heavily on red–green–yellow colors. In both cases, these color combinations can be difficult for the red–green color blind. Lantern Tests are a common means of simulating these light sources to determine not necessarily whether someone is color blind, but whether they can functionally distinguish these specific signal colors. Those who cannot pass this test are generally completely restricted from working on aircraft, ships or rail, for example.
Fashion
See also: Color of clothingColor analysis is the analysis of color in its use in fashion, to determine personal color combinations that are most aesthetically pleasing. Colors to combine can include clothing, accessories, makeup, hair color, skin color, eye color, etc. Color analysis involves many aesthetic and comparative color task that can be difficult for the color blind.
Art
Inability to distinguish color does not necessarily preclude the ability to become a celebrated artist. The 20th century expressionist painter Clifton Pugh, three-time winner of Australia's Archibald Prize, on biographical, gene inheritance and other grounds has been identified as a person with protanopia. 19th century French artist Charles Méryon became successful by concentrating on etching rather than painting after he was diagnosed as having a red–green deficiency. Jin Kim's red–green color blindness did not stop him from becoming first an animator and later a character designer with Walt Disney Animation Studios.
Advantages
Deuteranomals are better at distinguishing shades of khaki, which may be advantageous when looking for predators, food, or camouflaged objects hidden among foliage. Dichromats tend to learn to use texture and shape clues and so may be able to penetrate camouflage that has been designed to deceive individuals with normal color vision.
Some tentative evidence finds that the color blind are better at penetrating certain color camouflages. Such findings may give an evolutionary reason for the high rate of red–green color blindness. There is also a study suggesting that people with some types of color blindness can distinguish colors that people with normal color vision are not able to distinguish. In World War II, color blind observers were used to penetrate camouflage.
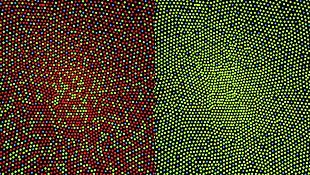
In the presence of chromatic noise, the color blind are more capable of seeing a luminous signal, as long as the chromatic noise appears metameric to them. This is the effect behind most "reverse" Pseudoisochromatic plates (e.g. "hidden digit" Ishihara plates) that are discernible to the color blind but unreadable to people with typical color vision.
Digital design
See also: Color coding in data visualization
Color codes are useful tools for designers to convey information. The interpretation of this information requires users to perform a variety of color tasks, usually comparative but also sometimes connotative or denotative. However, these tasks are often problematic for the color blind when design of the color code has not followed best practices for accessibility. For example, one of the most ubiquitous connotative color codes is the "red means bad and green means good" or similar systems, based on the classic signal light colors. However, this color coding will almost always be undifferentiable to deutans or protans, and can instead be supplemented with a parallel connotative system (symbols, smileys, etc.).
Good practices to ensure design is accessible to the color blind include:
- When possible (e.g. in simple video games or apps), allowing the user to choose their own colors is the most inclusive design practice.
- Using other signals that are parallel to the color coding, such as patterns, shapes, size or order. This not only helps the color blind, but also aids understanding by normally sighted people by providing them with multiple reinforcing cues.
- Using brightness contrast (different shades) in addition to color contrast (different hues)
- To achieve good contrast, conventional wisdom suggests converting a (digital) design to grayscale to ensure there is sufficient brightness contrast between colors. However, this does not account for the different perceptions of brightness to different varieties of color blindness, especially protan CVD, tritan CVD and monochromacy.
- Viewing the design through a CVD Simulator to ensure the information carried by color is still sufficiently conveyed. At a minimum, the design should be tested for deutan CVD, the most common kind of color blindness.
- Maximizing the area of colors (e.g. increase size, thickness or boldness of colored element) makes the color easier to identify. Color contrast improves as the angle the color subtends on the retina increases. This applies to all types of color vision.
- Maximizing brightness (value) and saturation (chroma) of the colors to maximize color contrast.
- Converting connotative tasks to comparative tasks by including a legend, even when the meaning is considered obvious (e.g. red means danger).
- Avoiding denotative color tasks (color naming) when possible. Some denotative tasks can be converted to comparative tasks by depicting the actual color whenever the color name is mentioned; for example, colored typography in "purple", purple or "purple ( )".
- For denotative tasks (color naming), using the most common shades of colors. For example, green and yellow are colors of confusion in red–green CVD, but it is not common to mix forest green ( ) with bright yellow ( ). Mistakes by the color blind increase drastically when uncommon shades are used, e.g. neon green ( ) with dark yellow ( ).
- For denotative tasks, using colors that are classically associated with a color name. For example, using "firetruck" red ( ) instead of burgundy ( ) to represent the word "red".
Color selection in design

A common task for designers is to select a subset of colors (qualitative colormap) that are as mutually differentiable as possible (salient). For example, player pieces in a board game should be as different as possible.
Classic advice suggests using Brewer palettes, but several of these are not actually accessible to the color blind.
An issue with color selection is that the colors with the greatest contrast to the red–green color blind tend to be colors of confusion to the blue–yellow color blind and vice versa.
In 2018, UX designer Allie Ofisher published 3 color palettes with 6 colors each, distinguishable for all variants of color blindness.
Sequential colormaps

A common task for data visualization is to represent a color scale, or sequential colormap, often in the form of a heat map or choropleth. Several scales are designed with special consideration for the color blind and are widespread in academia, including Cividis, Viridis and Parula. These comprise a light-to-dark scale superimposed on a yellow-to-blue scale, making them monotonic and perceptually uniform to all forms of color vision.
Classification

Much terminology has existed and does exist for the classification of color blindness, but the typical classification for color blindness follows the von Kries classifications, which uses severity and affected cone for naming.
Based on severity
Based on clinical appearance, color blindness may be described as total or partial. Total color blindness (monochromacy) is much less common than partial color blindness. Partial color blindness includes dichromacy and anomalous trichromacy, but is often clinically defined as mild, moderate or strong.
Monochromacy
Main article: MonochromacyMonochromacy is often called total color blindness since there is no ability to see color. Although the term may refer to acquired disorders such as cerebral achromatopsia, it typically refers to congenital color vision disorders, namely rod monochromacy and blue cone monochromacy).
In cerebral achromatopsia, a person cannot perceive colors even though the eyes are capable of distinguishing them. Some sources do not consider these to be true color blindness, because the failure is of perception, not of vision. They are forms of visual agnosia.
Monochromacy is the condition of possessing only a single channel for conveying information about color. Monochromats are unable to distinguish any colors and perceive only variations in brightness. Congenital monochromacy occurs in two primary forms:
- Rod monochromacy, frequently called complete achromatopsia, where the retina contains no cone cells, so that in addition to the absence of color discrimination, vision in lights of normal intensity is difficult.
- Cone monochromacy is the condition of having only a single class of cone. A cone monochromat can have good pattern vision at normal daylight levels, but will not be able to distinguish hues. Cone monochromacy is divided into classes defined by the single remaining cone class. However, red and green cone monochromats have not been definitively described in the literature. Blue cone monochromacy is caused by lack of functionality of L (red) and M (green) cones, and is therefore mediated by the same genes as red–green color blindness (on the X chromosome). Peak spectral sensitivities are in the blue region of the visible spectrum (near 440 nm). People with this condition generally show nystagmus ("jiggling eyes"), photophobia (light sensitivity), reduced visual acuity, and myopia (nearsightedness). Visual acuity usually falls to the 20/50 to 20/400 range.
Dichromacy
Main article: DichromacyDichromats can match any color they see with some mixture of just two primary colors (in contrast to those with normal sight (trichromats) who can distinguish three primary colors). Dichromats usually know they have a color vision problem, and it can affect their daily lives. Dichromacy in humans includes protanopia, deuteranopia, and tritanopia. Out of the male population, 2% have severe difficulties distinguishing between red, orange, yellow, and green (orange and yellow are different combinations of red and green light). Colors in this range, which appear very different to a normal viewer, appear to a dichromat to be the same or a similar color. The terms protanopia, deuteranopia, and tritanopia come from Greek, and respectively mean "inability to see (anopia) with the first (prot-), second (deuter-), or third (trit-) ".
Anomalous trichromacy
Anomalous trichromacy is the mildest type of color deficiency, but the severity ranges from almost dichromacy (strong) to almost normal trichromacy (mild). In fact, many mild anomalous trichromats have very little difficulty carrying out tasks that require normal color vision and some may not even be aware that they have a color vision deficiency. The types of anomalous trichromacy include protanomaly, deuteranomaly and tritanomaly. It is approximately three times more common than dichromacy. Anomalous trichromats exhibit trichromacy, but the color matches they make differ from normal trichromats. In order to match a given spectral yellow light, protanomalous observers need more red light in a red/green mixture than a normal observer, and deuteranomalous observers need more green. This difference can be measured by an instrument called an Anomaloscope, where red and green lights are mixed by a subject to match a yellow light.
Based on affected cone
There are two major types of color blindness: difficulty distinguishing between red and green, and difficulty distinguishing between blue and yellow. These definitions are based on the phenotype of the partial color blindness. Clinically, it is more common to use a genotypical definition, which describes which cone/opsin is affected.
Red–green color blindness
Red–green color blindness includes protan and deutan CVD. Protan CVD is related to the L-cone and includes protanomaly (anomalous trichromacy) and protanopia (dichromacy). Deutan CVD is related to the M-cone and includes deuteranomaly (anomalous trichromacy) and deuteranopia (dichromacy). The phenotype (visual experience) of deutans and protans is quite similar. Common colors of confusion include red/brown/green/yellow as well as blue/purple. Both forms are almost always symptomatic of congenital red–green color blindness, so affects males disproportionately more than females. This form of color blindness is sometimes referred to as daltonism after John Dalton, who had red–green dichromacy. In some languages, daltonism is still used to describe red–green color blindness.
- Protan (2% of males): Lacking, or possessing anomalous L-opsins for long-wavelength sensitive cone cells. Protans have a neutral point at a cyan-like wavelength around 492 nm (see spectral color for comparison)—that is, they cannot discriminate light of this wavelength from white. For a protanope, the brightness of red is much reduced compared to normal. This dimming can be so pronounced that reds may be confused with black or dark gray, and red traffic lights may appear to be extinguished. They may learn to distinguish reds from yellows primarily on the basis of their apparent brightness or lightness, not on any perceptible hue difference. Violet, lavender, and purple are indistinguishable from various shades of blue. A very few people have been found who have one normal eye and one protanopic eye. These unilateral dichromats report that with only their protanopic eye open, they see wavelengths shorter than neutral point as blue and those longer than it as yellow.
- Deutan (6% of males): Lacking, or possessing anomalous M-opsins for medium-wavelength sensitive cone cells. Their neutral point is at a slightly longer wavelength, 498 nm, a more greenish hue of cyan. Deutans have the same hue discrimination problems as protans, but without the dimming of long wavelengths. Deuteranopic unilateral dichromats report that with only their deuteranopic eye open, they see wavelengths shorter than neutral point as blue and longer than it as yellow.
Blue–yellow color blindness
Blue–yellow color blindness includes tritan CVD. Tritan CVD is related to the S-cone and includes tritanomaly (anomalous trichromacy) and tritanopia (dichromacy). Blue–yellow color blindness is much less common than red–green color blindness, and more often has acquired causes than genetic. Tritans have difficulty discerning between bluish and greenish hues. Tritans have a neutral point at 571 nm (yellowish).
- Tritan (< 0.01% of individuals): Lacking, or possessing anomalous S-opsins or short-wavelength sensitive cone cells. Tritans see short-wavelength colors (blue, indigo and spectral violet) as greenish and drastically dimmed, some of these colors even as black. Yellow and orange are indistinguishable from white and pink respectively, and purple colors are perceived as various shades of red. Unlike protans and deutans, the mutation for this color blindness is carried on chromosome 7. Therefore, it is not sex-linked (equally prevalent in both males and females). The OMIM gene code for this mutation is 304000 "Colorblindness, Partial Tritanomaly".
- Tetartan is the "fourth type" of color blindness, and a type of blue–yellow color blindness. However, its existence is hypothetical and given the molecular basis of human color vision, it is unlikely this type could exist.
Summary of cone complements
The below table shows the cone complements for different types of human color vision, including those considered color blindness, normal color vision and 'superior' color vision. The cone complement contains the types of cones (or their opsins) expressed by an individual.
| Cone system | Red | Green | Blue | N = normal A = anomalous | ||||||||
| N | A | N | A | N | A | |||||||
| 1 | Normal vision | Trichromacy | Normal | |||||||||
| 2 | Protanomaly | Anomalous trichromacy | Partial color blindness |
Red– green | ||||||||
| 3 | Protanopia | Dichromacy | ||||||||||
| 4 | Deuteranomaly | Anomalous trichromacy | ||||||||||
| 5 | Deuteranopia | Dichromacy | ||||||||||
| 6 | Tritanomaly | Anomalous trichromacy | Blue– yellow | |||||||||
| 7 | Tritanopia | Dichromacy | ||||||||||
| 8 | Blue cone monochromacy | Monochromacy | Total color blindness | |||||||||
| 9 | Achromatopsia | |||||||||||
| 10 | Tetrachromacy (carrier theory) |
Tetrachromacy | 'Superior' | |||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||
Causes
See also: Trichromatic color vision and Congenital red–green color blindness § MechanismColor blindness is any deviation of color vision from normal trichromatic color vision (often as defined by the standard observer) that produces a reduced gamut. Mechanisms for color blindness are related to the functionality of cone cells, and often to the expression of photopsins, the photopigments that 'catch' photons and thereby convert light into chemical signals.
Color vision deficiencies can be classified as inherited or acquired.
- Inherited: inherited or congenital/genetic color vision deficiencies are most commonly caused by mutations of the genes encoding opsin proteins. However, several other genes can also lead to less common and/or more severe forms of color blindness.
- Acquired: color blindness that is not present at birth, may be caused by chronic illness, accidents, medication, chemical exposure or simply normal aging processes.
Genetics
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Color blindness is typically an inherited genetic disorder. The most common forms of color blindness are associated with the Photopsin genes, but the mapping of the human genome has shown there are many causative mutations that do not directly affect the opsins. Mutations capable of causing color blindness originate from at least 19 different chromosomes and 56 different genes (as shown online at the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man ).
Genetics of red–green color blindness
Main article: Congenital red–green color blindness § Genetics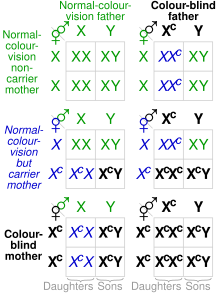
By far the most common form of color blindness is congenital red–green color blindness (Daltonism), which includes protanopia/protanomaly and deuteranopia/deuteranomaly. These conditions are mediated by the OPN1LW and OPN1MW genes, respectively, both on the X chromosome. An 'affected' gene is either missing (as in Protanopia and Deuteranopia - Dichromacy) or is a chimeric gene (as in Protanomaly and Deuteranomaly).
Since the OPN1LW and OPN1MW genes are on the X chromosome, they are sex-linked, and therefore affect males and females disproportionately. Because the color blind 'affected' alleles are recessive, color blindness specifically follows X-linked recessive inheritance. Males have only one X chromosome (XY), and females have two (XX); Because the male only has one of each gene, if it is affected, the male will be color blind. Because a female has two alleles of each gene (one on each chromosome), if only one gene is affected, the dominant normal alleles will "override" the affected, recessive allele and the female will have normal color vision. However, if the female has two mutated alleles, she will still be color blind. This is why there is a disproportionate prevalence of color blindness, with ~8% of males exhibiting color blindness and ~0.5% of females.
Genetics of blue–yellow color blindness
Congenital blue–yellow color blindness is a much rarer form of color blindness including tritanopia/tritanomaly. These conditions are mediated by the OPN1SW gene on Chromosome 7 which encodes the S-opsin protein and follows autosomal dominant inheritance. The cause of blue–yellow color blindness is not analogous to the cause of red–green color blindness, i.e. the peak sensitivity of the S-opsin does not shift to longer wavelengths. Rather, there are 6 known point mutations of OPN1SW that degrade the performance of the S-cones. The OPN1SW gene is almost invariant in the human population. Congenital tritan defects are often progressive, with nearly normal trichromatic vision in childhood (e.g. mild tritanomaly) progressing to dichromacy (tritanopia) as the S-cones slowly die. Tritanomaly and tritanopia are therefore different penetrance of the same disease, and some sources have argued that tritanomaly therefore be referred to as incomplete tritanopia.
Other genetic causes
Several inherited diseases are known to cause color blindness, including achromatopsia, cone dystrophy, Leber's congenital amaurosis and retinitis pigmentosa. These can be congenital or commence in childhood or adulthood. They can be static/stationary or progressive. Progressive diseases often involve deterioration of the retina and other parts of the eye, so often progress from color blindness to more severe visual impairments, up to and including total blindness.
Non-genetic causes
Physical trauma can cause color blindness, either neurologically – brain trauma which produces swelling of the brain in the occipital lobe – or retinally, either acute (e.g. from laser exposure) or chronic (e.g. from ultraviolet light exposure).
Color blindness may also present itself as a symptom of degenerative diseases of the eye, such as cataract and age-related macular degeneration, and as part of the retinal damage caused by diabetes. Vitamin A deficiency may also cause color blindness.
Color blindness may be a side effect of prescription drug use. For example, red–green color blindness can be caused by ethambutol, a drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis. Blue–yellow color blindness can be caused by sildenafil, an active component of Viagra. Hydroxychloroquine can also lead to hydroxychloroquine retinopathy, which includes various color defects. Exposure to chemicals such as styrene or organic solvents can also lead to color vision defects.
Simple colored filters can also create mild color vision deficiencies. John Dalton's original hypothesis for his deuteranopia was actually that the vitreous humor of his eye was discolored:
I was led to conjecture that one of the humours of my eye must be a transparent, but coloured, medium, so constituted as to absorb red and green rays principally... I suppose it must be the vitreous humor.
— John Dalton, Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours: with observations (1798)
An autopsy of his eye after his death in 1844 showed this to be definitively untrue, though other filters are possible. Actual physiological examples usually affect the blue–yellow opponent channel and are named Cyanopsia and Xanthopsia, and are most typically an effect of yellowing or removal of the lens.
The opponent channels can also be affected by the prevalence of certain cones in the retinal mosaic. The cones are not equally prevalent and not evenly distributed in the retina. When the number of one of these cone types is significantly reduced, this can also lead to or contribute to a color vision deficiency. This is one of the causes of tritanomaly.
Some people are also unable to distinct between blue and green, which appears to be a combination of culture and exposure to UV-light.
Diagnosis
Color vision test
Main article: Color vision test
The main method for diagnosing a color vision deficiency is in testing the color vision directly. The Ishihara color test is the test most often used to detect red–green deficiencies and most often recognized by the public. Some tests are clinical in nature, designed to be fast, simple, and effective at identifying broad categories of color blindness. Others focus on precision and are generally available only in academic settings.
- Pseudoisochromatic plates, a classification which includes the Ishihara color test and HRR test, embed a figure in the plate as a number of spots surrounded by spots of a slightly different color. These colors must appear identical (metameric) to the color blind but distinguishable to color normals. Pseudoisochromatic plates are used as screening tools because they are cheap, fast, and simple, but they do not provide precise diagnosis of CVD.
- Lanterns, such as the Farnsworth Lantern Test, project small colored lights to a subject, who is required to identify the color of the lights. The colors are those of typical signal lights, i.e. red, green, and yellow, which also happen to be colors of confusion of red–green CVD. Lanterns do not diagnose color blindness, but they are occupational screening tests to ensure an applicant has sufficient color discrimination to be able to perform a job.

- Arrangement tests can be used as screening or diagnostic tools. The Farnsworth–Munsell 100 hue test is very sensitive, but the Farnsworth D-15 is a simplified version used specifically for screening for CVD. In either case, the subject is asked to arrange a set of colored caps or chips to form a gradual transition of color between two anchor caps.
- Anomaloscopes are typically designed to detect red–green deficiencies and are based on the Rayleigh match, which compares a mixture of red and green light in variable proportions to a fixed spectral yellow of variable luminosity. The subject must change the two variables until the colors appear to match. They are expensive and require expertise to administer, so they are generally only used in academic settings.
Genetic testing
While genetic testing cannot directly evaluate a subject's color vision (phenotype), most congenital color vision deficiencies are well-correlated with genotype. Therefore, the genotype can be directly evaluated and used to predict the phenotype. This is especially useful for progressive forms that do not have a strongly color deficient phenotype at a young age. However, it can also be used to sequence the L- and M-Opsins on the X-chromosome, since the most common alleles of these two genes are known and have even been related to exact spectral sensitivities and peak wavelengths. A subject's color vision can therefore be classified through genetic testing, but this is just a prediction of the phenotype, since color vision can be affected by countless non-genetic factors such as your cone mosaic.
Management
Despite much recent improvement in gene therapy for color blindness, there is currently no FDA approved treatment for any form of CVD, and otherwise no cure for CVD currently exists. Management of the condition by using lenses to alleviate symptoms or smartphone apps to aid with daily tasks is possible.
Lenses
Main article: Color blind glassesThere are three kinds of lenses that an individual can wear that can increase their accuracy in some color related tasks (although none of these will "fix" color blindness or grant the wearer normal color vision):
- A red-tint contact lens worn over the non-dominant eye will leverage binocular disparity to improve discrimination of some colors. However, it can make other colors more difficult to distinguish. A 1981 review of various studies to evaluate the effect of the X-chrom (one brand) contact lens concluded that, while the lens may allow the wearer to achieve a better score on certain color vision tests, it did not correct color vision in the natural environment. A case history using the X-Chrom lens for a rod monochromat is reported and an X-Chrom manual is online.
- Tinted glasses (e.g. Pilestone/Colorlite glasses) apply a tint (e.g. magenta) to incoming light that can distort colors in a way that makes some color tasks easier to complete. These glasses can circumvent many color vision tests, though this is typically not allowed.
- Glasses with a notch filter (e.g. EnChroma glasses) filter a narrow band of light that excites both the L and M cones (yellow–green wavelengths). When combined with an additional stopband in the short wavelength (blue) region, these lenses may constitute a neutral-density filter (have no color tint). They improve on the other lens types by causing less distortion of colors and will essentially increase the saturation of some colors. They will only work on trichromats (anomalous or normal), and unlike the other types, do not have a significant effect on Dichromats. The glasses do not significantly increase one's ability on color blind tests.
Aids
Many mobile and computer applications have been developed to aid color blind individuals in completing color tasks:
- Some applications (e.g. color pickers) can identify the name (or coordinates within a color space) of a color on screen or the color of an object by using the device's camera.
- Some applications will make images easier to interpret by the color blind by enhancing color contrast in natural images and/or information graphics. These methods are generally called daltonization algorithms.
- Some applications can simulate color blindness by applying a filter to an image or screen that reduces the gamut of an image to that of a specific type of color blindness. While they do not directly help color blind people, they allow those with normal color vision to understand how the color blind see the world. Their use can help improve inclusive design by allowing designers to simulate their own images to ensure they are accessible to the color blind.
In 2003, a cybernetic device called eyeborg was developed to allow the wearer to hear sounds representing different colors. Achromatopsic artist Neil Harbisson was the first to use such a device in early 2004; the eyeborg allowed him to start painting in color by memorizing the sound corresponding to each color. In 2012, at a TED Conference, Harbisson explained how he could now perceive colors outside the ability of human vision.
Epidemiology
| Males | Females | |
|---|---|---|
| Dichromacy | 2.4% | 0.03% |
| Protanopia | 1.3% | 0.02% |
| Deuteranopia | 1.2% | 0.01% |
| Tritanopia | 0.008% | 0.008% |
| Anomalous trichromacy | 6.3% | 0.37% |
| Protanomaly | 1.3% | 0.02% |
| Deuteranomaly | 5.0% | 0.35% |
| Tritanomaly | 0.0001% | 0.0001% |
Color blindness affects a large number of individuals, with protans and deutans being the most common types. In individuals with Northern European ancestry, as many as 8 percent of men and 0.4 percent of women experience congenital color deficiency. Interestingly, even Dalton's first paper already arrived upon this 8% number:
...it is remarkable that, out of 25 pupils I once had, to whom I explained this subject, 2 were found to agree with me...
— John Dalton, Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours: with observations (1798)
History

During the 17th and 18th century, several philosophers hypothesized that not all individuals perceived colors in the same way:
...there is no reason to suppose a perfect resemblance in the disposition of the Optic Nerve in all Men, since there is an infinite variety in every thing in Nature, and chiefly in those that are Material, 'tis therefore very probable that all Men see not the same Colours in the same Objects.
— Nicolas Malebranche, The search after truth (1674)
In the power of conceiving colors, too, there are striking differences among individuals: and, indeed, I am inclined to suspect, that, in the greater number of instances, the supposed defects of sight in this respect ought to be ascribed rather to a defect in the power of conception.
— Dugald Stewart, Elements of the philosophy of the human mind (1792)
Gordon Lynn Walls claims that the first well-circulated case study of color blindness was published in a 1777 letter from Joseph Huddart to Joseph Priestley, which described "Harris the Shoemaker" and several of his brothers with what would later be described as protanopia. There appear to be no earlier surviving historical mentions of color blindness, despite its prevalence.
The phenomenon only came to be scientifically studied in 1794, when English chemist John Dalton gave the first account of color blindness in a paper to the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society, which was published in 1798 as Extraordinary Facts relating to the Vision of Colours: With Observations. Genetic analysis of Dalton's preserved eyeball confirmed him as having deuteranopia in 1995, some 150 years after his death.
Influenced by Dalton, German writer J. W. von Goethe studied color vision abnormalities in 1798 by asking two young subjects to match pairs of colors.
In 1837, August Seebeck first discriminated between protans and deutans (then as class I + II). He was also the first to develop an objective test method, where subjects sorted colored sheets of paper, and was the first to describe a female colorblind subject.
In 1875, the Lagerlunda train crash in Sweden brought color blindness to the forefront. Following the crash, Professor Alarik Frithiof Holmgren, a physiologist, investigated and concluded that the color blindness of the engineer (who had died) had caused the crash. Professor Holmgren then created the first test for color vision using multicolored skeins of wool to detect color blindness and thereby exclude the color blind from jobs in the transportation industry requiring color vision to interpret safety signals. However, there is a claim that there is no firm evidence that color deficiency did cause the collision, or that it might have not been the sole cause.
In 1920, Frederick William Edridge-Green devised an alternative theory of color vision and color blindness based on Newton's classification of 7 fundamental colors (ROYGBIV). Edridge-Green classified color vision based on how many distinct colors a subject could see in the spectrum. Normal subjects were termed hexachromic as they could not discern Indigo. Subjects with superior color vision, who could discern indigo, were heptachromic. The color blind were therefore dichromic (equivalent to dichromacy) or tri-, tetra- or pentachromic (anomalous trichromacy).
Rights
In the United States, under federal anti-discrimination laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act, color vision deficiencies have not been found to constitute a disability that triggers protection from workplace discrimination.
A Brazilian court ruled that the color blind are protected by the Inter-American Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Person with Disabilities. At trial, it was decided that the carriers of color blindness have a right of access to wider knowledge, or the full enjoyment of their human condition.
Occupations
Color blindness may make it difficult or impossible for a person to engage in certain activities. Persons with color blindness may be legally or practically barred from occupations in which color perception is an essential part of the job (e.g., mixing paint colors), or in which color perception is important for safety (e.g., operating vehicles in response to color-coded signals). This occupational safety principle originates from the aftermath of the 1875 Lagerlunda train crash, which Alarik Frithiof Holmgren blamed on the color blindness of the engineer and created the first occupational screening test (Holmgren's wool test) against the color blind.
...I consider that to above all others do we owe the present and future control of color-blindness on land and sea, by which life and property are safer, and the risks of travelling less.
— Benjamin Joy Jeffries, Color-blindness: Its Danger & Its Detection (1879)
Color vision is important for occupations using telephone or computer networking cabling, as the individual wires inside the cables are color-coded using green, orange, brown, blue and white colors. Electronic wiring, transformers, resistors, and capacitors are color-coded as well, using black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, gray, white, silver, and gold.
Participation, officiating and viewing sporting events can be impacted by color blindness. Professional football players Thomas Delaney and Fabio Carvalho have discussed the difficulties when color clashes occur, and research undertaken by FIFA has shown that enjoyment and player progression can be hampered by issues distinguishing the difference between the pitch and training objects or field markings. Snooker World Champions Mark Williams and Peter Ebdon sometimes need to ask the referee for help distinguishing between the red and brown balls due to their color blindness. Both have played foul shots on notable occasions by potting the wrong ball.
Driving
Red–green color blindness can make it difficult to drive, primarily due to the inability to differentiate red–amber–green traffic lights. Protans are further disadvantaged due to the darkened perception of reds, which can make it more difficult to quickly recognize brake lights. In response, some countries have refused to grant driver's licenses to individuals with color blindness:
- In April 2003, Romania removed color blindness from its list of disqualifying conditions for learner driver's licenses. It is now qualified as a condition that could potentially compromise driver safety, therefore a driver may have to be evaluated by an authorized ophthalmologist to determine if they can drive safely. As of May 2008, there is an ongoing campaign to remove the legal restrictions that prohibit color blind citizens from getting driver's licenses.
- In June 2020, India relaxed its ban on driver's licenses for the color blind to now only apply to those with strong CVD. While previously restricted, those who test as mild or moderate can now pass the medical requirements.
- Australia instituted a tiered ban on the color blind from obtaining commercial driver's licenses in 1994. This included a ban for all protans, and a stipulation that deutans must pass the Farnsworth Lantern. The stipulation on deutans was revoked in 1997 citing a lack of available test facilities, and the ban on protans was revoked in 2003.
- All color blind individuals are banned from obtaining a driver's license in China and since 2016 in Russia (2012 for dichromats).
Piloting aircraft
Although many aspects of aviation depend on color coding, only a few of them are critical enough to be interfered with by some milder types of color blindness. Some examples include color-gun signaling of aircraft that have lost radio communication, color-coded glide-path indications on runways, and the like. Some jurisdictions restrict the issuance of pilot credentials to persons with color blindness for this reason. Restrictions may be partial, allowing color-blind persons to obtain certification but with restrictions, or total, in which case color-blind persons are not permitted to obtain piloting credentials at all.
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration requires that pilots be tested for normal color vision as part of their medical clearance in order to obtain the required medical certificate, a prerequisite to obtaining a pilot's certification. If testing reveals color blindness, the applicant may be issued a license with restrictions, such as no night flying and no flying by color signals—such a restriction effectively prevents a pilot from holding certain flying occupations, such as that of an airline pilot, although commercial pilot certification is still possible, and there are a few flying occupations that do not require night flight and thus are still available to those with restrictions due to color blindness (e.g., agricultural aviation). The government allows several types of tests, including medical standard tests (e.g., the Ishihara, Dvorine, and others) and specialized tests oriented specifically to the needs of aviation. If an applicant fails the standard tests, they will receive a restriction on their medical certificate that states: "Not valid for night flying or by color signal control". They may apply to the FAA to take a specialized test, administered by the FAA. Typically, this test is the "color vision light gun test". For this test an FAA inspector will meet the pilot at an airport with an operating control tower. The color signal light gun will be shone at the pilot from the tower, and they must identify the color. If they pass they may be issued a waiver, which states that the color vision test is no longer required during medical examinations. They will then receive a new medical certificate with the restriction removed. This was once a Statement of Demonstrated Ability (SODA), but the SODA was dropped, and converted to a simple waiver (letter) early in the 2000s.
Research published in 2009 carried out by the City University of London's Applied Vision Research Centre, sponsored by the UK's Civil Aviation Authority and the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration, has established a more accurate assessment of color deficiencies in pilot applicants' red/green and yellow–blue color range which could lead to a 35% reduction in the number of prospective pilots who fail to meet the minimum medical threshold.
See also
- Color agnosia – Ability to see colors, but inability to recognize colors.
- Color anomia – Ability to see colors, but inability to name colors.
- List of people with color blindness
- Motion blindness
- Tetrachromacy
References
- ^ Gordon N (March 1998). "Colour blindness". Public Health. 112 (2): 81–4. doi:10.1038/sj.ph.1900446. ISSN 0033-3506. PMID 9581449.
- ^ "Facts About Color Blindness". NEI. February 2015. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- "Colour vision deficiency (colour blindness)". nhs.uk. 18 October 2017. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ^ Gómez-Robledo L (2018). "Do EnChroma glasses improve color vision for colorblind subjects?". Optics Express. 26 (22): 28693–28703. Bibcode:2018OExpr..2628693G. doi:10.1364/OE.26.028693. hdl:10481/57698. PMID 30470042. S2CID 53721875.
- "OSHA does not have requirements for normal color vision. | Occupational Safety and Health Administration". www.osha.gov. Archived from the original on 6 May 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- Marmor MF, Lanthony P (March 2001). "The dilemma of color deficiency and art". Survey of Ophthalmology. 45 (5): 407–15. doi:10.1016/S0039-6257(00)00192-2. PMID 11274694.
- Marmor MF (February 2016). "Vision, eye disease, and art: 2015 Keeler Lecture". Eye. 30 (2): 287–303. doi:10.1038/eye.2015.197. PMC 4763116. PMID 26563659.
- Fomins S (2011). "Multispectral analysis of color vision deficiency tests". Materials Science. 17 (1): 104–108. doi:10.5755/j01.ms.17.1.259.
- Cole BL (1972). "The handicap of abnormal colour vision". Clinical and Experimental Optometry. 55 (8): 304–310. doi:10.1111/j.1444-0938.1972.tb06271.x.
- "New documentary uncovers the Irish links to America's Tipperary Hill". TheJournal.ie. 6 November 2016. Archived from the original on 15 August 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2017.
- Zhang, Sarah (17 March 2014). "The Story Behind Syracuse's Upside-Down Traffic Light". Gizmodo. Archived from the original on 16 September 2014.
- "What is Color Analysis?". London Image Institute. 1 January 2022. Archived from the original on 18 May 2024. Retrieved 21 February 2024.
- Cole BL, Harris RW (September 2009). "Colour blindness does not preclude fame as an artist: celebrated Australian artist Clifton Pugh was a protanope". Clinical & Experimental Optometry. 92 (5): 421–8. doi:10.1111/j.1444-0938.2009.00384.x. PMID 19515095. S2CID 21676461.
- Anon. "Charles Meryon". Art Encyclopedia. The Concise Grove Dictionary of Art. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 25 November 2010. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- Lee Hw (15 May 2011). "Dreams come true, Disney style". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 20 September 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2019.
- Simonite T (5 December 2005). "Colour blindness may have hidden advantages". Nature. doi:10.1038/news051205-1.
- ^ Bosten J, Robinson J, Jordan G, Mollon J (December 2005). "Multidimensional scaling reveals a color dimension unique to 'color-deficient' observers". Current Biology. 15 (23): R950 – R952. Bibcode:2005CBio...15.R950B. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.11.031. PMID 16332521. S2CID 6966946.
- ^ Morgan MJ, Adam A, Mollon JD (June 1992). "Dichromats detect colour-camouflaged objects that are not detected by trichromats". Proceedings. Biological Sciences. 248 (1323): 291–5. Bibcode:1992RSPSB.248..291M. doi:10.1098/rspb.1992.0074. PMID 1354367. S2CID 35694740.
- "Colour-Blindness and Camouflage". Nature. 146 (3694): 226. 1940. Bibcode:1940Natur.146Q.226.. doi:10.1038/146226a0. S2CID 4071103.
- "Colour blindness not all it seems". BBC News. 6 December 2015. Archived from the original on 23 June 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Sousa BR, Loureiro TM, Goulart PR, Cortes MI, Costa MF, Bonci DM, Baran LC, Hauzman E, Ventura DF, Miquilini L, Souza GS (21 October 2020). "Specificity of the chromatic noise influence on the luminance contrast discrimination to the color vision phenotype". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 17897. Bibcode:2020NatSR..1017897S. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74875-3. PMC 7578001. PMID 33087826.
- Hovis JK (July 2002). "Diagnosis of Defective Colour Vision, 2nd Ed". Optometry and Vision Science. 79 (7): 406. doi:10.1097/00006324-200207000-00005. ISSN 1538-9235.
- Caprette H. "14 Avoiding the Use of Color Alone to Convey Meaning and Algorithms That Help". Best Practices in Accessible Online Design. Pressbooks @ MSL. Archived from the original on 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- Allie Ofisher (18 May 2018). "Inclusive Color Palettes for the Web". Medium. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Nuñez JR (2018). "Optimizing colormaps with consideration for color vision deficiency to enable accurate interpretation of scientific data". PLOS ONE. 13 (7): e0199239. arXiv:1712.01662. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1399239N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0199239. PMC 6070163. PMID 30067751.
- von Kries J (1897). "Ueber Farbensysteme". Zeitschrift für Psychologie Physiologie Sinnesorg. 13: 241–324.
- Spring KR, Parry-Hill MJ, Fellers TJ, Davidson MW. "Human Vision and Color Perception". Florida State University. Archived from the original on 27 August 2007. Retrieved 5 April 2007.
- ^ "Types of Colour Blindness". Colour Blind Awareness. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014.
- ^ Blom JD (2009). A Dictionary of Hallucinations. Springer. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-4419-1222-0. Archived from the original on 27 December 2016.
- Weiss AH, Biersdorf WR (1989). "Blue cone monochromatism". Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 26 (5): 218–23. doi:10.3928/0191-3913-19890901-04. PMID 2795409. S2CID 23037026.
- Simunovic MP (May 2010). "Colour vision deficiency". Eye. 24 (5): 747–55. doi:10.1038/eye.2009.251. PMID 19927164.
- Deeb SS (2006). "Genetics of variation in human color vision and the retinal cone mosaic". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 16 (3): 301–307. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2006.04.002. PMID 16647849.
- Moreland J, Kerr J (1979). "Optimization of a Rayleigh-type equation for the detection of tritanomaly". Vision Research. 19 (12): 1369–1375. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(79)90209-8. PMID 316945. S2CID 29379397.
- Hoffman PS. "Accommodating Color Blindness" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2008. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- Neitz ME. "Severity of Colorblindness Varies". Medical College of Wisconsin. Archived from the original on 5 February 2007. Retrieved 5 April 2007.
- ^ Wong B (June 2011). "Color blindness". Nature Methods. 8 (6): 441. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1618. PMID 21774112. S2CID 36690778.
- Neitz J, Neitz M (April 2011). "The genetics of normal and defective color vision". Vision Research. 51 (7): 633–51. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2010.12.002. PMC 3075382. PMID 21167193.
- Harrison G, Tanner J, Pilbeam D, Baker P (1988). Human Biology. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 183–187, 287–290. ISBN 978-0-19-854144-8.
- Neitz J, Neitz M (2011). "The genetics of normal and defective color vision". Vision Research. 51 (7): 633–651. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2010.12.002. PMC 3075382. PMID 21167193.
- MacAdam DL, Judd DB, eds. (1979). Contributions to color science. NBS. p. 584.
- Steefel, Lorraine T., and Timothy E. Moore, PhD. "Color Blindness." The Gale Encyclopedia of Nursing and Allied Health, edited by Jacqueline L. Longe, 4th ed., vol. 2, Gale, 2018, pp. 890–892. Gale eBooks, Accessed 29 Dec. 2021.
- "Disease-causing Mutations and protein structure". UCL Biochemistry BSM Group. Archived from the original on 1 May 2005. Retrieved 2 April 2007.
- V I, Gastaud P (1996). "Test chromatique pour dépistage et étalonnage des dyschromatopsies" [Color vision test for detection and evaluation of dyschromatopsia]. Journal Français d'Ophtalmologie (in French). 19 (11): 679–688. PMID 9033889. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- "Acquired colour vision defects". colourblindawareness.org. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014.
- ^ Sharpe LT, Stockman A, Jägle H, Nathans J (1999). "Opsin genes, cone photopigments, color vision, and color blindness.". Color vision: From genes to perception (PDF). p. 351. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
True cases of tritanomaly, as distinct from partial or incomplete tritanopia, have never been satisfactorily documented. Although the separate existence of tritanopia and tritanomaly, with different modes of inheritance, has been postulated, it now seems more likely that tritanomaly does not exist, but rather has been mistaken for incomplete tritanopia.
- ^ Rodriguez-Carmona M, Patterson EJ (2020). "Photoreceptors, Color Vision" (PDF). Encyclopedia of Color Science and Technology. pp. 1–7. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-27851-8_277-3. ISBN 978-3-642-27851-8. S2CID 226504635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 December 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- Leikin JB, Lipsky MS, eds. (2003). Complete Medical Encyclopedia. Random House Reference (First ed.). New York, NY: Random House, for the American Medical Association. p. 388. ISBN 978-0-8129-9100-0. Retrieved 1 December 2011 – via archive.org.
-
Unknown U. "NEI - Types of Color Vision Deficiency". www.nei.nih.gov. Color Blindness, Color Vision Deficiency. Archived from the original on 8 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2024.
Description, Types of Color Vision Deficiency,
- "VIAGRA (SILDENAFIL CITRATE) DRUG". RxList.com. drug information. Archived from the original on 8 June 2022. Retrieved 3 June 2022.
Description, user reviews, drug side effects, interactions–prescribing information
- Fraunfelder FT, Fraunfelder FW, Chambers WA (2014). Drug-Induced Ocular Side Effects: Clinical ocular toxicology e‑book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-323-31985-0. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- Choi AR, Braun JM, Papandonatos GD, Greenberg PB (November 2017). "Occupational styrene exposure and acquired dyschromatopsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis". American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 60 (11): 930–946. doi:10.1002/ajim.22766. PMC 5652067. PMID 28836685.
- Betancur-Sánchez AM, Vásquez-Trespalacios EM, Sardi-Correa C (January 2017). "Impaired colour vision in workers exposed to organic solvents: A systematic review". Archivos de la Sociedad Espanola de Oftalmologia. 92 (1): 12–18. doi:10.1016/j.oftal.2016.05.008. PMID 27422480.
- Dick F (March 2006). "Solvent neurotoxicity". Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 63 (3): 221–6, 179. doi:10.1136/oem.2005.022400. PMC 2078137. PMID 16497867.
- Hunt D, Dulai K, Bowmaker J, Mollon J (17 February 1995). "The Chemistry of John Dalton's Color Blindness". Science. 267 (5200): 984–988. Bibcode:1995Sci...267..984H. doi:10.1126/science.7863342. PMID 7863342. S2CID 6764146.
- Josserand M, Meeussen E, Majid A, Dediu D (2021). "Environment and culture shape both the colour lexicon and the genetics of colour perception". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 19095. Bibcode:2021NatSR..1119095J. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-98550-3. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 8476573. PMID 34580373.
- Toufeeq A (October 2004). "Specifying colours for colour vision testing using computer graphics". Eye. 18 (10): 1001–5. doi:10.1038/sj.eye.6701378. PMID 15192692.
- Kinnear PR, Sahraie A (December 2002). "New Farnsworth–Munsell 100 hue test norms of normal observers for each year of age 5–22 and for age decades 30–70". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 86 (12): 1408–11. doi:10.1136/bjo.86.12.1408. PMC 1771429. PMID 12446376.
- Reference GH. "Color vision deficiency". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 10 January 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- Siegel IM (1981). "The X-Chrom lens. On seeing red". Survey of Ophthalmology. 25 (5): 312–24. doi:10.1016/S0039-6257(81)80001-X. PMID 6971497.
- Zeltzer HI (July 1979). "Use of modified X-Chrom for relief of light dazzlement and color blindness of a rod monochromat". Journal of the American Optometric Association. 50 (7): 813–8. PMID 315420.
- An X-Chrom manual Archived 2015-04-12 at the Wayback Machine. Artoptical.com. Retrieved on 2016-12-10.
- Welsh KW (April 1978). "Aeromedical implications of the X-chrom lens for improving color vision deficiencies". Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine. 50 (3). Oklahoma City: Federal Aviation Administration: 249–255. PMID 313209. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- Zhou L. "A Scientist Accidentally Developed Sunglasses That Could Correct Color Blindness". Smithsonian. Archived from the original on 3 September 2017. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- Simon-Liedtke JT, Farup I (February 2016). "Evaluating color vision deficiency daltonization methods using a behavioral visual-search method". Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation. 35: 236–247. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.12.014. hdl:11250/2461824.
- "Colour Blindness: Experience it". Colour Blind Awareness. Archived from the original on 28 December 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- Alfredo M. Ronchi: Eculture: Cultural Content in the Digital Age. Springer (New York, 2009). p. 319 ISBN 978-3-540-75273-8
- "I listen to color" Archived 2012-08-12 at the Wayback Machine, Neil Harbisson at TED Global, 27 June 2012.
- Birch J (2012). "Subjects with colour vision deficiency in the community: what do primary care physicians need to know?". Journal of the Optical Society of America A. 29 (3): 313–320. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.29.000313. PMID 22472762.
- Chan X, Goh S, Tan N (2014). "Subjects with colour vision deficiency in the community: what do primary care physicians need to know?". Asia Pacific Family Medicine. 13 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/s12930-014-0010-3.
- ^ Dalton J (1798). "Extraordinary Facts relating to the Vision of Colours: With Observations". Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society. Memoirs. 5 (1). England, Manchester: 28–45. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- Lanthony P (2018). The History of Color Blindness. Wayenborgh Publishing. p. 3. ISBN 978-90-6299-903-3. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- Malebranche N (1712) . Malebranch's search after truth, or, A treatise of the nature of the humane mind and of its management for avoiding error in the sciences : vol I: done out of French from the last edition. p. 88. Archived from the original on 22 April 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- Stewart D (1792). Elements of the philosophy of the human mind (1 ed.). p. 80. Archived from the original on 14 October 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ Walls GL (1956). "The G. Palmer Story (Or, "What It's Like, Sometimes, To Be A Scientist")". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 11 (1): 66–96. doi:10.1093/jhmas/XI.1.66. ISSN 0022-5045. JSTOR 24619193. PMID 13295579. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- Lanthony 2018, p. 14.
- Hunt DM, Dulai KS, Bowmaker JK, Mollon JD (17 February 1995). "The chemistry of John Dalton's color blindness". Science. 267 (5200): 984–988. Bibcode:1995Sci...267..984H. doi:10.1126/science.7863342. PMID 7863342. S2CID 6764146.
- Lanthony 2018, pp. 25–26.
- Seebeck A (1837). "Über den bei mancher Personen vorkommenden Mangel an Farbensinn". Annalen der Physik: 42.
- Lee BB (1 July 2008). "The evolution of concepts of color vision". Neurociencias. 4 (4): 209–224. PMC 3095437. PMID 21593994.
- ^ Vingrys AJ, Cole BL (1986). "Origins of colour vision standards within the transport industry". Ophthalmic & Physiological Optics. 6 (4): 369–75. doi:10.1111/j.1475-1313.1986.tb01155.x. PMID 3306566. S2CID 41486427.
- Mollon JD, Cavonius LR (2012). "The Lagerlunda collision and the introduction of color vision testing". Survey of Ophthalmology. 57 (2): 178–94. doi:10.1016/j.survophthal.2011.10.003. PMID 22301271.
- McLaren K (1985). "Newton's indigo". Color Research & Application. 10 (4): 225–229. doi:10.1002/col.5080100411.
- Edridge-Green FW (1913). "Trichromic Vision and Anomalous Trichromatism". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Containing Papers of a Biological Character. 86 (586): 164–170. doi:10.1098/rspb.1913.0010. ISSN 0950-1193. JSTOR 80517. S2CID 129045064. Archived from the original on 26 September 2022. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- "Full text of the decision of the court – in Portuguese language". Archived from the original on 14 July 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
- "Decree issued by president of a republic ratifying Legislative Decree No. 198, of june 13, which approved the Inter-American Convention AG/RES. 1608 – in Portuguese language". Archived from the original on 25 March 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
- "Inter-American Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Person with Disabilities". Archived from the original on 16 April 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
- Meyers M (2002). All in One A+ Certification Exam Guide (4th ed.). Berkeley, California: McGraw-Hill/Osborne. ISBN 978-0-07-222274-6.
- Grob B (2001). Basic Electronics. Columbus, Ohio: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-02-802253-6.
- "Football players shocked when experiencing Colour Blindness". Tacbis. Archived from the original on 9 April 2023. Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- "Billiard Index: Mark Williams MBE player profile". Billiard Index. Archived from the original on 8 July 2008. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- "Hawkins on Top Down Under". World Snooker Tour. 15 July 2012. Archived from the original on 17 October 2023. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- "Rueful Ebdon mistakes brown for red". BBC Sport. 13 October 2008. Archived from the original on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Cole B (September 2016). "Colour Blindness and Driving". Clinical and Experimental Optometry. 99 (5): 484–487. doi:10.1111/cxo.12396. PMID 27470192. S2CID 26368283.
- "ORDIN 87 03/02/2003 – Portal Legislativ". PORTAL LEGISLATIV (in Romanian). Ministerul Justiției. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "ORDIN 87 03/02/2003 – Portal Legislativ". PORTAL LEGISLATIV (in Romanian). Ministerul Justiției. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- Corlăţean T. "Discrimination against Romanians with genetic chromatic deficiencies". Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "Mild to medium colour blind people can now obtain driver's license". The Times of India. Press Trust of India. 26 June 2020. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- Lu F. "Some of us see the world in a different light". Shine. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- "Do color blindmen a driver's license. Color blindmen allowed to drive cars". Rozavet. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- King KD (January 2012). "Answers for Pilots: Color vision". AOPA. Archived from the original on 13 August 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- "Aerospace Medical Dispositions – Color vision". Archived from the original on 12 May 2009. Retrieved 11 April 2009.
- Warburton S (29 May 2009). "Colour-blindness research could clear more pilots to fly: UK CAA". Air transport. Reed Business Information. Archived from the original on 2 June 2009. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
Further reading
- Kaiser PK, Boynton RM (1996). Human color vision. Washington, DC: Optical Society of America. ISBN 978-1-55752-461-4. OCLC 472932250.
- McIntyre D (2002). Colour blindness: causes and effects. Chester: Dalton Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9541886-0-3. OCLC 49204679.
- Rubin ML, Cassin B, Solomon S (1984). Dictionary of eye terminology. Gainesville, Fla: Triad Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0-937404-07-2. OCLC 10375427.
- Shevell SK (2003). The science of color. Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-444-51251-2. OCLC 52271315.
- Hilbert D, Byrne A (1997). Readings on color. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-52231-1. OCLC 35762680.
- Stiles WS, Wyszecki G (2000). Color science: concepts and methods, quantitative data and formulae. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-39918-6. OCLC 799532137.
- Kuchenbecker J, Broschmann D (2014). Plates for color vision testing. New York: Thieme. ISBN 978-3-13-175481-3.
- Dalton J (1798). "Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours: with observations". Memoirs of the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester. 5: 28–45. OCLC 9879327.
External links
- "A Glossary of Color Science." Archived 4 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Physiology of the visual system | |
|---|---|
| Vision | |
| Color vision | |
| Color topics | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color science |
|  | ||||||||
| Color philosophy |
| |||||||||
| Color terms |
| |||||||||
| Color organizations | ||||||||||
| Names |
| |||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||




