
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.
Enzyme activity
Enzyme activity is a measure of the quantity of active enzyme present and is thus dependent on various physical conditions, which should be specified.
It is calculated using the following formula:
where
- = Enzyme activity
- = Moles of substrate converted per unit time
- = Rate of the reaction
- = Reaction volume
The SI unit is the katal, 1 katal = 1 mol s (mole per second), but this is an excessively large unit. A more practical and commonly used value is enzyme unit (U) = 1 μmol min (micromole per minute). 1 U corresponds to 16.67 nanokatals.
Enzyme activity as given in katal generally refers to that of the assumed natural target substrate of the enzyme. Enzyme activity can also be given as that of certain standardized substrates, such as gelatin, then measured in gelatin digesting units (GDU), or milk proteins, then measured in milk clotting units (MCU). The units GDU and MCU are based on how fast one gram of the enzyme will digest gelatin or milk proteins, respectively. 1 GDU approximately equals 1.5 MCU.
An increased amount of substrate will increase the rate of reaction with enzymes, however once past a certain point, the rate of reaction will level out because the amount of active sites available has stayed constant.
Specific activity
The specific activity of an enzyme is another common unit. This is the activity of an enzyme per milligram of total protein (expressed in μmol min mg). Specific activity gives a measurement of enzyme purity in the mixture. It is the micro moles of product formed by an enzyme in a given amount of time (minutes) under given conditions per milligram of total proteins. Specific activity is equal to the rate of reaction multiplied by the volume of reaction divided by the mass of total protein. The SI unit is katal/kg, but a more practical unit is μmol/(mg*min).
Specific activity is a measure of enzyme processivity (the capability of enzyme to be processed), at a specific (usually saturating) substrate concentration, and is usually constant for a pure enzyme.
An active site titration process can be done for the elimination of errors arising from differences in cultivation batches and/or misfolded enzyme and similar issues. This is a measure of the amount of active enzyme, calculated by e.g. titrating the amount of active sites present by employing an irreversible inhibitor. The specific activity should then be expressed as μmol min mg active enzyme. If the molecular weight of the enzyme is known, the turnover number, or μmol product per second per μmol of active enzyme, can be calculated from the specific activity. The turnover number can be visualized as the number of times each enzyme molecule carries out its catalytic cycle per second.
Related terminology
The rate of a reaction is the concentration of substrate disappearing (or product produced) per unit time (mol L s).
The % purity is 100% × (specific activity of enzyme sample / specific activity of pure enzyme). The impure sample has lower specific activity because some of the mass is not actually enzyme. If the specific activity of 100% pure enzyme is known, then an impure sample will have a lower specific activity, allowing purity to be calculated and then getting a clear result.
Types of assays
All enzyme assays measure either the consumption of substrate or production of product over time. A large number of different methods of measuring the concentrations of substrates and products exist and many enzymes can be assayed in several different ways. Biochemists usually study enzyme-catalysed reactions using four types of experiments:
- Initial rate experiments. When an enzyme is mixed with a large excess of the substrate, the enzyme-substrate intermediate builds up in a fast initial transient. Then the reaction achieves a steady-state kinetics in which enzyme substrate intermediates remains approximately constant over time and the reaction rate changes relatively slowly. Rates are measured for a short period after the attainment of the quasi-steady state, typically by monitoring the accumulation of product with time. Because the measurements are carried out for a very short period and because of the large excess of substrate, the approximation that the amount of free substrate is approximately equal to the amount of the initial substrate can be made. The initial rate experiment is the simplest to perform and analyze, being relatively free from complications such as back-reaction and enzyme degradation. It is therefore by far the most commonly used type of experiment in enzyme kinetics.
- Progress curve experiments. In these experiments, the kinetic parameters are determined from expressions for the species concentrations as a function of time. The concentration of the substrate or product is recorded in time after the initial fast transient and for a sufficiently long period to allow the reaction to approach equilibrium. Progress curve experiments were widely used in the early period of enzyme kinetics, but are less common now.
- Transient kinetics experiments. In these experiments, reaction behaviour is tracked during the initial fast transient as the intermediate reaches the steady-state kinetics period. These experiments are more difficult to perform than either of the above two classes because they require specialist techniques (such as flash photolysis of caged compounds) or rapid mixing (such as stopped-flow, quenched flow or continuous flow).
- Relaxation experiments. In these experiments, an equilibrium mixture of enzyme, substrate and product is perturbed, for instance by a temperature, pressure or pH jump, and the return to equilibrium is monitored. The analysis of these experiments requires consideration of the fully reversible reaction. Moreover, relaxation experiments are relatively insensitive to mechanistic details and are thus not typically used for mechanism identification, although they can be under appropriate conditions.
Enzyme assays can be split into two groups according to their sampling method: continuous assays, where the assay gives a continuous reading of activity, and discontinuous assays, where samples are taken, the reaction stopped and then the concentration of substrates/products determined.

Continuous assays
Continuous assays are most convenient, with one assay giving the rate of reaction with no further work necessary. There are many different types of continuous assays.
Spectrophotometric
In spectrophotometric assays, you follow the course of the reaction by measuring a change in how much light the assay solution absorbs. If this light is in the visible region you can actually see a change in the color of the assay, and these are called colorimetric assays. The MTT assay, a redox assay using a tetrazolium dye as substrate is an example of a colorimetric assay.
UV light is often used, since the common coenzymes NADH and NADPH absorb UV light in their reduced forms, but do not in their oxidized forms. An oxidoreductase using NADH as a substrate could therefore be assayed by following the decrease in UV absorbance at a wavelength of 340 nm as it consumes the coenzyme.
Direct versus coupled assays
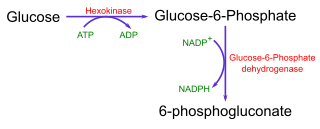
Even when the enzyme reaction does not result in a change in the absorbance of light, it can still be possible to use a spectrophotometric assay for the enzyme by using a coupled assay. Here, the product of one reaction is used as the substrate of another, easily detectable reaction. For example, figure 1 shows the coupled assay for the enzyme hexokinase, which can be assayed by coupling its production of glucose-6-phosphate to NADPH production, using glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Fluorometric
Fluorescence is when a molecule emits light of one wavelength after absorbing light of a different wavelength. Fluorometric assays use a difference in the fluorescence of substrate from product to measure the enzyme reaction. These assays are in general much more sensitive than spectrophotometric assays, but can suffer from interference caused by impurities and the instability of many fluorescent compounds when exposed to light.
An example of these assays is again the use of the nucleotide coenzymes NADH and NADPH. Here, the reduced forms are fluorescent and the oxidised forms non-fluorescent. Oxidation reactions can therefore be followed by a decrease in fluorescence and reduction reactions by an increase. Synthetic substrates that release a fluorescent dye in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are also available, such as 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-D-galactoside for assaying β-galactosidase or 4-methylumbelliferyl-butyrate for assaying Candida rugosa lipase.
Calorimetric

Calorimetry is the measurement of the heat released or absorbed by chemical reactions. These assays are very general, since many reactions involve some change in heat and with use of a microcalorimeter, not much enzyme or substrate is required. These assays can be used to measure reactions that are impossible to assay in any other way.
Chemiluminescent
Chemiluminescence is the emission of light by a chemical reaction. Some enzyme reactions produce light and this can be measured to detect product formation. These types of assay can be extremely sensitive, since the light produced can be captured by photographic film over days or weeks, but can be hard to quantify, because not all the light released by a reaction will be detected.
The detection of horseradish peroxidase by enzymatic chemiluminescence (ECL) is a common method of detecting antibodies in western blotting. Another example is the enzyme luciferase, this is found in fireflies and naturally produces light from its substrate luciferin.
Light scattering
Static light scattering measures the product of weight-averaged molar mass and concentration of macromolecules in solution. Given a fixed total concentration of one or more species over the measurement time, the scattering signal is a direct measure of the weight-averaged molar mass of the solution, which will vary as complexes form or dissociate. Hence the measurement quantifies the stoichiometry of the complexes as well as kinetics. Light scattering assays of protein kinetics is a very general technique that does not require an enzyme.
Microscale thermophoresis
Microscale thermophoresis (MST) measures the size, charge and hydration entropy of molecules/substrates at equilibrium. The thermophoretic movement of a fluorescently labeled substrate changes significantly as it is modified by an enzyme. This enzymatic activity can be measured with high time resolution in real time. The material consumption of the all optical MST method is very low, only 5 μl sample volume and 10nM enzyme concentration are needed to measure the enzymatic rate constants for activity and inhibition. MST allows analysts to measure the modification of two different substrates at once (multiplexing) if both substrates are labeled with different fluorophores. Thus substrate competition experiments can be performed.
Discontinuous assays
Discontinuous assays are when samples are taken from an enzyme reaction at intervals and the amount of product production or substrate consumption is measured in these samples.
Radiometric
Radiometric assays measure the incorporation of radioactivity into substrates or its release from substrates. The radioactive isotopes most frequently used in these assays are C, P, S and I. Since radioactive isotopes can allow the specific labelling of a single atom of a substrate, these assays are both extremely sensitive and specific. They are frequently used in biochemistry and are often the only way of measuring a specific reaction in crude extracts (the complex mixtures of enzymes produced when you lyse cells).
Radioactivity is usually measured in these procedures using a scintillation counter.
Chromatographic
Chromatographic assays measure product formation by separating the reaction mixture into its components by chromatography. This is usually done by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), but can also use the simpler technique of thin layer chromatography. Although this approach can need a lot of material, its sensitivity can be increased by labelling the substrates/products with a radioactive or fluorescent tag. Assay sensitivity has also been increased by switching protocols to improved chromatographic instruments (e.g. ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography) that operate at pump pressure a few-fold higher than HPLC instruments (see High-performance liquid chromatography#Pump pressure).
Factors affecting assays

Several factors effect the assay outcome and a recent review summarizes the various parameters that needs to be monitored to keep an assay up and running.
Salt Concentration
Most enzymes cannot tolerate extremely high salt concentrations. The ions interfere with the weak ionic bonds of proteins. Typical enzymes are active in salt concentrations of 1-500 mM. As usual there are exceptions such as the halophilic algae and halophilic bacteria.
Effects of Temperature
All enzymes work within a range of temperature specific to the organism. Increases in temperature generally lead to increases in reaction rates. There is a limit to the increase because higher temperatures lead to a sharp decrease in reaction rates. This is due to the denaturating (alteration) of protein structure resulting from the breakdown of the weak ionic and hydrogen bonding that stabilize the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme active site. The "optimum" temperature for human enzymes is usually between 35 and 40 °C. The average temperature for humans is 37 °C. Human enzymes start to denature quickly at temperatures above 40 °C. Enzymes from thermophilic archaea found in the hot springs are stable up to 100 °C. However, the idea of an "optimum" rate of an enzyme reaction is misleading, as the rate observed at any temperature is the product of two rates, the reaction rate and the denaturation rate. If you were to use an assay measuring activity for one second, it would give high activity at high temperatures, however if you were to use an assay measuring product formation over an hour, it would give you low activity at these temperatures.
Effects of pH
Most enzymes are sensitive to pH and have specific ranges of activity. All have an optimum pH. The pH can stop enzyme activity by denaturating (altering) the three-dimensional shape of the enzyme by breaking ionic, and hydrogen bonds. Most enzymes function between a pH of 6 and 8; however pepsin in the stomach works best at a pH of 2 and trypsin at a pH of 8.
Enzyme Saturation
Increasing the substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction (enzyme activity). However, enzyme saturation limits reaction rates. An enzyme is saturated when the active sites of all the molecules are occupied most of the time. At the saturation point, the reaction will not speed up, no matter how much additional substrate is added. The graph of the reaction rate will plateau.
Level of crowding
Large amounts of macromolecules in a solution will alter the rates and equilibrium constants of enzyme reactions, through an effect called macromolecular crowding.
List of enzyme assays
See also
References
- Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry (NC-IUB) (1979). "Units of Enzyme Activity". European Journal of Biochemistry. 97 (2): 319–20. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13116.x.
- Rowlett, Russ (23 November 1998). "How Many? A Dictionary of Units of Measurement". Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina. Archived from the original on 29 August 2018.
- Schnell, S.; Chappell, M.J.; Evans, N.D.; Roussel, M.R. (2006). "The mechanism distinguishability problem in biochemical kinetics: The single-enzyme, single-substrate reaction as a case study". Comptes Rendus Biologies. 329 (1): 51–61. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2005.09.005. PMID 16399643. S2CID 40456258. Archived from the original on 2024-02-26. Retrieved 2023-12-05.
- Bergmeyer, H.U. (1974). Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Vol. 4. New York: Academic Press. pp. 2066–72. ISBN 0-89573-236-X.
- Passonneau, J.V.; Lowry, O.H. (1993). Enzymatic Analysis. A Practical Guide. Totowa NJ: Humana Press. pp. 85–110.
- Menden, Ariane (26 Jul 2019). "A fast, miniaturised in-vitro assay developed for quantification of lipase enzyme activity". Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry. 34 (1): 1474–1480. doi:10.1080/14756366.2019.1651312. PMC 6713963. PMID 31414611.
- Todd MJ, Gomez J (September 2001). "Enzyme kinetics determined using calorimetry: a general assay for enzyme activity?". Anal. Biochem. 296 (2): 179–87. doi:10.1006/abio.2001.5218. PMID 11554713. S2CID 18567619.
- Wienken CJ; et al. (2010). "Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis". Nature Communications. 1 (7): 100. Bibcode:2010NatCo...1..100W. doi:10.1038/ncomms1093. PMID 20981028.
- Duhr S, Braun D (December 2006). "Why molecules move along a temperature gradient". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (52): 19678–82. Bibcode:2006PNAS..10319678D. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603873103. PMC 1750914. PMID 17164337.
- Baaske P, Wienken C, Duhr S (2009). "Optisch erzeugte Thermophorese für die Bioanalytik" [Optically generated thermophoresis for bioanalysis] (PDF). Biophotonik (in German): 22–24.
- Churchwell, M; Twaddle, N; Meeker, L; Doerge, D. (October 2005). "Improving Sensitivity in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry". Journal of Chromatography B. 825 (2): 134–143. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.05.037. PMID 16002352. Archived from the original on 2022-01-20. Retrieved 2019-07-02.
- Daniel RM, Peterson ME, Danson MJ, et al. (January 2010). "The molecular basis of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity". Biochem. J. 425 (2): 353–60. doi:10.1042/BJ20091254. hdl:10289/3552. PMID 19849667.
- Cowan DA (1997). "Thermophilic proteins: stability and function in aqueous and organic solvents". Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. 118 (3): 429–38. doi:10.1016/S0300-9629(97)00004-2. PMID 9406427.
- Minton AP (2001). "The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (14): 10577–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100005200. PMID 11279227.
External links
 Media related to Enzyme assays at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Enzyme assays at Wikimedia Commons- "Assays Protocols - OpenWetWare". OpenWetWare. BioBricks Foundation. Retrieved 2022-07-27.
| Pathology | |
|---|---|
| Principles of pathology | |
| Anatomical pathology | |
| Clinical pathology | |

 = Enzyme activity
= Enzyme activity = Moles of substrate converted per unit time
= Moles of substrate converted per unit time = Rate of the reaction
= Rate of the reaction = Reaction volume
= Reaction volume