| Erythromelalgia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Erythromelalgia in left hand | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| Causes | There was a study done in 2013 where two Vietnamese patients were diagnosed with primary erythromelalgia. Patient A was a 33-year old female diagnosed with primary erythromelalgia at age 30 and suffered from burning and pain in her feet since she was 8 years old (Wu et. al 2013). Patient B was a 16 year-old girl with recurrent severe burning pain of both feet since the age of seven (Wu et. al 2013). A genetic analysis was performed where scientists observed three missense mutations, one familial and two sporadic mutations. The familial mutation changed isoleucine to valine and two missense mutations occurred where a “T” was changed to “C” (Wu et. al 2013). The three mutants involved in the gene were I136V, 1848T, and V1316A (Wu et. al 2013). The study showed that at higher temperatures, the hypersensitivity of the mutant channels were accentuated resulting in disease phenotype such as neuralgia (Wu et. al 2013). |
Erythromelalgia or Mitchell's disease (after Silas Weir Mitchell) is a rare vascular peripheral pain disorder in which blood vessels, usually in the lower extremities or hands, are episodically blocked (frequently on and off daily), then become hyperemic and inflamed. There is severe burning pain (in the small fiber sensory nerves) and skin redness. The attacks are periodic and are commonly triggered by heat, pressure, mild activity, exertion, insomnia or stress. Erythromelalgia may occur either as a primary or secondary disorder (i.e. a disorder in and of itself or a symptom of another condition). Secondary erythromelalgia can result from small fiber peripheral neuropathy of any cause, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, hypercholesterolemia, mushroom or mercury poisoning, and some autoimmune disorders. Primary erythromelalgia is caused by mutation of the voltage-gated sodium channel α-subunit gene SCN9A.
In 2004 erythromelalgia became the first human disorder in which it has been possible to associate an ion channel mutation with chronic neuropathic pain, when its link to the SCN9A gene was initially published in the Journal of Medical Genetics. Later that year, in an article in The Journal of Neuroscience, Cummins et al., demonstrated, using voltage clamp recordings, that these mutations enhanced the function of NaV1.7 sodium channels, which are preferentially expressed within peripheral neurons. One year later, in an article in Brain, Dib-Hajj et al., demonstrated that NaV1.7 mutants channels, from families with inherited erythromelalgia (IEM), make dorsal root ganglion (DRG, peripheral and sensory), neurons hyper excitable, thereby demonstrating the mechanistic link between these mutations and pain, thereby firmly establishing NaV1.7 gain-of-function mutations as the molecular basis for IEM. Conversely, in December 2006 a University of Cambridge team reported an SCN9A mutation that resulted in a complete lack of pain sensation in a Pakistani street performer and some of his family members. He felt no pain, walked on hot coals and stabbed himself to entertain crowds. By 2013, nearly a dozen gain-of-function mutations of NaV1.7 had been linked to IEM. The multi-decades search which identified gene SCN9A as the cause of inherited erythomelalgia is documented in a book by Stephen Waxman, Chasing Men on Fire: The Story of the Search for a Pain Gene.
Classification
Primary erythromelalgia may be classified as either familial or sporadic, with the familial form inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Both of these may be further classified as either juvenile or adult onset. The juvenile onset form occurs prior to age 20 and frequently prior to age 10. While the genetic cause of the juvenile and sporadic adult onset forms is often known, this is not the case for the adult onset familial form.
In rural areas of southern China, outbreaks of erythromelalgia have occurred during winter and spring at 3-5 year intervals among secondary school students. This epidemic form of erythromelalgia has been viewed as a different form of non-inherited primary erythromelalgia and affects mainly teenage girls in middle schools. The disease is characterized by burning pain in the toes and soles of the feet, accompanied by foot redness, congestion, and edema; a few patients may have fever, palpitations, headache, and joint pain. In the 1987 epidemic in Hubei, 60.6% of patients had a common cold before the onset of erythromelalgia and 91.2% had pharyngitis.
Symptoms and signs
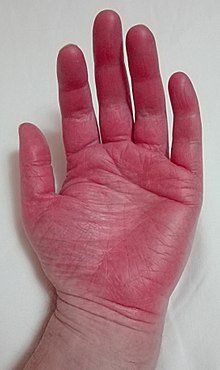
The most prominent symptoms of erythromelalgia are episodes of erythema, swelling, a painful deep-aching of the soft tissue (usually either radiating or shooting) and tenderness, along with a painful burning sensation primarily in the extremities. These symptoms are often symmetric and affect the lower extremities more frequently than the upper extremities. Symptoms may also affect the ears and face. For secondary erythromelalgia, attacks typically precede and are precipitated by the underlying primary condition. For primary erythromelalgia, attacks can last from an hour to months at a time and occur infrequently to frequently with multiple times daily. Attacks most frequently occur at night, thus having the potential to greatly interfere with sleep. Common triggers for daytime episodes are exertion, heating of the affected extremities, and alcohol or caffeine consumption, and any pressure applied to the limbs. In some patients sugar and even melon consumption have also been known to provoke attacks. Many of those with primary erythromelalgia avoid wearing shoes or socks as the heat this generates is known to produce erythromelalgia attacks. The coexistence of erythromelalgia and Raynaud's phenomenon is rare, but case studies of patients with both diagnoses have been reported in medical journals. Symptoms may present gradually and incrementally, sometimes taking years to become intense enough for patients to seek medical care. In other cases symptoms emerge full blown with onset.
Epidemic erythromelalgia is characterized by burning pain in the toes and soles of the feet, accompanied by foot redness, congestion, and edema; a few patients may have fever, palpitations, headache, and joint pain. In the 1987 epidemic in Hubei, 60.6% of patients had a common cold before the onset of erythromelalgia and 91.2% had pharyngitis.
Cause


In general, erythromelalgia seems to consist of neuropathological and microvascular alterations. How this occurs in secondary erythromelalgia is poorly understood and may be specific to the underlying primary condition. Primary conditions that have been shown to elicit erythromelalgia are listed in diagnosis, below.
Primary erythromelalgia is a better understood autosomal dominant disorder. The neuropathological symptoms of primary erythromelalgia arise from hyperexcitability of C-fibers in the dorsal root ganglion. Specifically, nociceptors (neurons responsible for the sensation and conduction of painful stimuli) appear to be the primarily affected neurons in these fibers. This hyperexcitability results in the severe burning pain experienced by patients. While the neuropathological symptoms are a result of hyperexcitability, microvascular alterations in erythromelalgia are due to hypoexcitability. The sympathetic nervous system controls cutaneous vascular tone and altered response of this system to stimuli such as heat likely results in the observed microvascular symptoms. In both cases, these changes in excitability are typically due to mutation of the sodium channel NaV1.7. These differences in excitability alterations between the sympathetic nervous system and nociceptors is due to different expression of sodium channels other than NaV1.7 in them.
What causes epidemic erythromelalgia in southern China remains unknown although several erythromelalgia-associated poxviruses were isolated from throat swabs of several patients at different counties and from two different seasons.
Side effect of medication
Several medications, including verapamil and nifedipine, as well as ergot derivatives such as bromocriptine and pergolide, have been associated with medication-induced erythromelalgia.
Mushroom poisoning
The consumption of two species of related fungi, Clitocybe acromelalga from Japan, and Clitocybe amoenolens from France, has led to several cases of mushroom-induced erythromelalgia which lasted from 8 days to 5 months.
Possible infectious cause
An epidemic form of this syndrome occurs in secondary school students in rural areas of China. A large epidemic erythromelalgia was occurred in Hubei province of China in 1987 and the disease was characterized by burning pain in the toes and soles of the feet, accompanied by foot redness, congestion, and edema; a few patients had fever, palpitations, headache, and joint pain. 60.6% of patients had a common cold before the onset of erythromelalgia and 91.2% had pharyngitis. Subsequently, a virus - erythromelalgia-related poxvirus (ERPV) - was repeatedly isolated from throat swabs of six separate patients from two different counties and Wuhan city in Hubei province. The genome of this virus has been sequenced and it appears that this virus is related to a strain of mousepox. Serological characterization can easily distinguish human ERPV from ectromelia virus and vaccinia virus by cross-neutralization and plaque reduction assays
Since this virus has not yet been isolated from other outbreaks in other parts of southern China to date this putative association needs to be further investigated. The finding of the specific antibody conversion to ATIs of ERPV in patients' paired sera strengthens the evidence for a possible aetiological role of human ERPV in epidemic erythromelalgia.
Pathophysiology
There are 10 known mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channel α-subunit NaV1.7 encoding gene, SCN9A. This channel is expressed primarily in nociceptors of the dorsal root ganglion and the sympathetic ganglion neurons. Nine of these mutations have received further study and they have all shown to result in similar biophysical alterations, Table 1. As can be seen from table 1, the primary effect of erythromelalgia mutations is NaV1.7 channels that activate at more hyperpolarized potentials. NaV1.7 channels act largely as threshold sensors and initiate action potentials. Consequently, this shift in their activation profile results in channels that open closer to the resting membrane potential. In many mutations, this shift of activation is accompanied by shifts in the voltage sensitivity of fast and/or slow inactivation, often in the depolarized direction. This results in channels that are open for a longer of period of time, producing larger and more prolonged changes in membrane potential.
Some of these mutant channels have been expressed in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) or sympathetic neurons. In DRG neurons expressing the F1449V mutation, a lower threshold is required for action potential creation (93.1 ± 12.0 pA) than those expressing wild-type channels (124.1 ± 7.4 pA). Furthermore, while DRG neurons expressing wild-type channels only respond with a few action potentials, those expressing F1449V channels respond with a high-frequency train of action potentials. There is a similar effect in DRG neurons expressing the L858H and A863P mutants. Here, there is also a notable change in resting membrane potential, being depolarized by 4-7 mV versus wild-type channel expressing cells. The situation is different, however, in sympathetic neurons expressing the L858H mutation. While L858H expressing sympathetic ganglion are depolarized ~5mV relative to wild-type expressing neurons, their threshold for action potential initiation is notably higher. Furthermore, while current injection of 40pA for 950ms provokes an average of 6 action potentials in sympathetic neurons expressing wild-type channels this stimulation evokes only approximately 2 action potentials with reduced overshoots in sympathetic neurons expressing L858H mutant channels. Further investigation has demonstrated that the differences in response between DRG and sympathetic neurons is due to expression of NaV1.8 in the former. Consequently, expression of NaV1.8 channels in sympathetic neurons also expressing L858H mutant NaV1.7 results in neurons with a depolarized resting membrane potential that nevertheless have a normal action potential threshold and overshoot.
An effective, though not recommended, treatment for erythromelalgia symptoms is cooling of the affected area. Activation of wild-type channels is unaffected by cooling. L858F mutant channels, however, are activated at more depolarized potentials when cooled than at normal body temperature. At 16 °C the activation V½ of the mutant channel is only 4.6mV more hyperpolarized that wild-type versus 9.6mV more hyperpolarized at 35 °C. Fast inactivation is affected in a similar manner in both wild-type and L858F mutant channel and is, thus, unlikely to contribute to symptom resolution due to cooling. While such cooling is unlikely to affect neuronal cell bodies, axons and termini express NaV1.7 and are present in the skin.
| Mutation | Region | Shift of activation V½ | Shift of inactivation (fast and/or slow) V½ | Other effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I136V | D1S1 | ||||
| F216S | D1S4 | Hyperpolarized | Hyperpolarized | Faster entry into fast-inactivation | |
| S241T | D1S4-5 | Hyperpolarized | Hyperpolarized | ||
| N395K | D1S6 | Hyperpolarized | Depolarized | Creation of a large window current, decreased lidocaine sensitivity | |
| I848T | D2S4-5 | Hyperpolarized | Slowed deactivation and inactivation | ||
| L858F | D2S4-5 | Hyperpolarized | Depolarized | Slowed deactivation, faster recovery from inactivation, cooling depolarizes activation and hyperpolarizes inactivation V½ | |
| L858H | D2S4-5 | Hyperpolarized | Slowed deactivation, enhanced slow inactivation, | ||
| A863P | D2S5 | Hyperpolarized | Depolarized | Creation of a window current, slowed deactivation | |
| F1449V | D3-4 | Hyperpolarized | |||
| A1632G | D4 | Hyperpolarized | Depolarized | Increased spontaneous firing | |
| Region nomenclature: DA-B, linker between domains A and B; DASB, transmembrane segment B in domain A; and DASB-C, the linker between transmembrane segments B and C in domain A. | |||||
Diagnosis
See also: Burning feet syndromeErythromelalgia is a difficult condition to diagnose as there are no specific tests available. However, reduced capillary density has been observed microscopically during flaring; and reduced capillary perfusion is noted in the patient. Another test that can be done is to have the patient elevate their legs, and note the reversal (from red to pale) in skin color. Tests done at universities include quantitative sensory nerve testing, laser evoked potentials, sweat testing and epidermal sensory nerve fiber density test (which is an objective test for small fiber sensory neuropathy). Due to the aforementioned factors, patients may face delays in diagnosis.
Once it has been established that it is not secondary erythromelalgia — see below — a programme of management can be put in place. Some diseases present with symptoms similar to erythromelalgia. Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), for instance, presents with severe burning pain and redness except these symptoms are often unilateral (versus symmetric) and may be proximal instead of purely or primarily distal. Furthermore, attacks triggered by heat and resolved by cooling are less common with CRPS.
Erythromelalgia is sometimes caused by other disorders. A partial list of diseases known to precipitate erythromelalgia is below.
Treatment
For secondary erythromelalgia, treatment of the underlying primary disorder is the most primary method of treatment. Although aspirin has been thought to reduce symptoms of erythromelalgia, it is rare to find evidence that this is effective. Mechanical cooling of the limbs by elevating them can help or managing the ambient environment frequently is often necessary constantly as flares occur due to sympathetic autonomic dysfunction of the capillaries. The pain that accompanies it is severe and treated separately (the pain is similar to CRPS, phantom limb or thalamic pain syndrome). Patients are strongly advised not to place the affected limbs in cold water to relieve symptoms when flaring occurs. It may seem a good idea, but it precipitates problems further down the line causing damage to the skin and ulceration often intractable due to the damaged skin. A possible reduction in skin damage may be accomplished by enclosing the flaring limb in a commonly available, thin, heat transparent, water impermeable, plastic food storage bag. The advice of a physician is advised depending on specific circumstances.
Primary erythromelalgia management is symptomatic, i.e. treating painful symptoms only. Specific management tactics include avoidance of attack triggers such as: heat, change in temperature, exercise or over exertion, alcohol and spicy foods. This list is by no means comprehensive as there are many triggers to set off a 'flaring' episode that are inexplicable. Whilst a cool environment is helpful in keeping the symptoms in control, the use of cold water baths is strongly discouraged. In pursuit of added relief sufferers can inadvertently cause tissue damage or death, i.e. necrosis. See comments at the end of the preceding paragraph regarding possible effectiveness of plastic food storage bags to avoid/reduce negative effects of submersion in cold water baths.
One clinical study has demonstrated the efficacy of IV lidocaine or oral mexilitine, though differences between the primary and secondary forms were not studied. Another trial has shown promise for misoprostol, while other have shown that gabapentin, venlafaxine and oral magnesium may also be effective, but no further testing was carried out as newer research superseded this combination.
Strong anecdotal evidence from EM patients shows that a combination of drugs such as duloxetine and pregabalin is an effective way of reducing the stabbing pains and burning sensation symptoms of erythromelalgia in conjunction with the appropriate analgesia. In some cases, antihistamines may give some relief. Most people with erythromelalgia never go into remission and the symptoms are ever present at some level, whilst others get worse, or the EM is eventually a symptom of another disease such as systemic scleroderma.
Some suffering with EM are prescribed ketamine topical creams as a way of managing pain on a long-term basis. Feedback from some EM patients has led to reduction in usage as they believe it is only effective for short periods.Living with erythromelalgia can result in a deterioration in quality of life resulting in the inability to function in a work place, lack of mobility, depression, and is socially alienating; much greater education of medical practitioners is needed. As with many rare diseases, many people with EM end up taking years to get a diagnosis and to receive appropriate treatment.Research into the genetic mutations continues but there is a paucity of clinical studies focusing on living with erythromelalgia. There is much urgency within pharmaceutical companies to provide a solution to those who suffer with pain such as that with erythromelalgia.
Pain relief
Patients find relief by cooling the skin. All patients must be notified to not apply ice directly on to the skin, since this can cause maceration of the skin, nonhealing ulcers, infection, necrosis, and even amputation in severe cases.
Mild sufferers may find sufficient pain relief with tramadol or amitriptyline. Sufferers of more severe and widespread EM symptoms, however, may obtain relief only from opioid drugs. Opana ER has been found to be effective for many in the US, whilst in the UK slow-release morphine has proved to be effective. These powerful and potentially-addictive drugs may be prescribed to patients only after they have tried almost every other type of analgesia to no avail. (This delay in appropriate pain management can be a result of insurer-mandated or legally-required step therapy, or merely overly-cautious prescribing on the part of sufferers' doctors.)
The combination of Cymbalta (duloxetine) and Lyrica (pregabalin) has also proven to be useful in controlling pain, but many EM patients have found this combination has side effects that they are unable to tolerate.
Epidemiology
Only a small number of studies that have investigated the prevalence of EM, with four studies conducted to date. The mean of all the studies combined results in an EM estimation incidence of 4.7/100,000 with a mean of 1 : 3.7 of the male to female ratio, respectively.
In 1997 there was a study conducted in Norway that estimated that the annual incidence of 2/100,000, with a 1 : 2.4 male to female ratio in this study population, respectively. In 2009 there was a population-based study of EM in the USA (Olmsted County, Minnesota), that reported that the annual incidence was 1.3/100,000, with a 1 : 5.6 male to female ratio in this study population, respectively. The incidence in this study of primary and secondary EM was 1.1 : 0.2 per 100 000 people per year, respectively. A study of a single centre in the south of Sweden in 2012, showed the overall annual population-based incidence was 0.36/100,000. In New Zealand (Dunedin) a study estimated that in 2013 the incidence of EM is 15/100,000, with a 1 : 3 male to female ratio in this study population, respectively. This last study has an estimation that is at least ten times higher than the prevalence previously reported. This study recruited individuals based on self-identification of symptoms (after self-identification, patients were invited for an assessment of an EM diagnosis), instead of participants that are identified through secondary and tertiary referrals as in the other studies.
Prevalence in China
Epidemic EM appears quite common in female middle school students of southern China, most likely due to a sharp decline in temperature following by a rapid increase of temperature. It has been postulated that epidemic erythromelalgia might be related to a poxvirus (ERPV) infection. The disease was characterized by burning pain in the toes and soles of the feet, accompanied by foot redness, congestion, and edema; a few patients had fever, palpitations, headache, and joint pain. 60.6% of patients had a common cold before the onset of erythromelalgia and 91.2% had pharyngitis. For temperature-related theory, the acral (foot and hand) small superficial arteries intensely constrict and dilate during the sharp decline of temperature, whereas a sharp increase of temperature, the intense expansion of capillaries irritate the nerve endings around, and thus lead to syndromes including (first and second degree) burning pain, increased temperature, erythema and swelling.
History
The first reported case was in 1878 by Silas Weir Mitchell who suggested the term erythromelalgia to describe a syndrome of red congestion and burning pain in the hands and feet.

He distinguished it from the painful red limbs seen in some patients with gout or rheumatoid arthritis. It is derived from the Greek words erythros ("red"), melos ("limb") and algos ("pain").
Some confusion was introduced when Smith and Allen suggested changing the name to erythermalgia in order to emphasise the symptoms of painful inflammation and warmth. In their paper they showed for the first time that when their patients used aspirin, this promptly relieved the burning pain for about three days. They also suggested a distinction between primary (idiopathic) erythromelalgia and secondary erythromelalgia (due to underlying neurologic, hematologic, or vascular problems).
In 1994 Drenth, van Genderen and Michiels distinguished between erythromelalgia and erythermalgia on the basis of responsiveness to aspirin. They established three categories: erythromelalgia (platelet-mediated and aspirin-sensitive), primary erythermalgia, and secondary erythermalgia.
Because of the confusion in terminology, Norton and Zager and Grady classified erythromelalgia in 1998 as either: primary/idiopathic erythromelalgia or secondary erythromelalgia. The primary/idiopathic form of erythromelalgia is not associated with any other disease process and can be either early onset (in children) or adult onset. In their paper they described secondary erythromelalgia as being associated with another disease, often related to a myeloproliferative disorder and has also seen cases of: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, astrocytoma of the brain, vasculitis, and pernicious anemia.
The following table shows the history of the nomenclature of Erythromelalgia:
| Suggested name | Author(s) and year |
|---|---|
| Erythromelalgia | Silas Weir Mitchell in 1878 |
| Gerhardt's disease | Carl Gerhardt in 1892 |
| Erythralgia | Thomas Lewis in 1933 |
| Erythermalgia | L.A. Smith and F.N. Allen in 1938 |
| Acromelalgia | J. Huizinga in 1957 |
Amputation
Because of the severity of the pain in erythromelalgia, and the lack of good pain medication then, there have been reports dating back to 1903 of amputation of the affected limb. In 1903 H. Batty Shaw reported that in three cases the pain was so severe, and that the affected extremities so useless, that amputation was performed.
Differences with Raynaud's disease

Back in 1899 Thomas Barlow had already summarized with great detail the contrast between erythromelalgia and Raynaud's disease as following: Dependence produces considerable increase of the dusky red or violaceous tint of the extremity affected; the arteries in this position of the limb may pulsate forcibly; pain is common, sometimes constant, and more especially when the limb is dependent or parts pressed upon; in wintry weather, or on the application of cold, the conditions are relieved; on the other hand, warmth and summer weather increases pain; there is no loss of sensation, but there may be increased sensitiveness; the local temperature of the affected parts may be raised or lowered; gangrene does not occur; the affection is asymmetrical; there is a certain amount of swelling, sometimes allowing pitting on pressure, sometimes not; incisions over such swelling, even down to the bone, have proved useless; excessive pain on pressure upon the nerves supplying the parts affected is not found; muscular wasting is found, but explainable by the disuse of the limb, and is not at all as severe as in cases of disease of the peripheral nerves; a reaction of degeneration in the nerves of the affected parts has not been found; the deep reflexes, with few exceptions, are not reduced.
Footnotes
- Khalid F, Hassan S, Qureshi S, Qureshi W, Amer S (2012). "Erythromelalgia: An Uncommon Presentation Precipitated by Aspirin Withdrawal". Case Reports in Medicine. 2012: 616125. doi:10.1155/2012/616125. PMC 3403327. PMID 22844295.
- Waxman, Stephen G.; Dib-Hajj, Sulayman D. (June 2005). "Erythromelalgia: A hereditary pain syndrome enters the molecular era". Annals of Neurology. 57 (6): 785–8. doi:10.1002/ana.20511. PMID 15929046. S2CID 24267097.
- ^ Yang Y, Wang Y, Li S, et al. (2004). "Mutations in SCN9A, encoding a sodium channel alpha subunit, in patients with primary erythermalgia". J. Med. Genet. 41 (3): 171–4. doi:10.1136/jmg.2003.012153. PMC 1735695. PMID 14985375.
- Cummins, Theodore R.; Dib-Hajj, Sulayman D.; Waxman, Stephen G. (2004-09-22). "Electrophysiological Properties of Mutant Nav1.7 Sodium Channels in a Painful Inherited Neuropathy". Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (38): 8232–8236. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2695-04.2004. PMC 6729696. PMID 15385606.
- Dib-Hajj, S. D.; Rush, A. M.; Cummins, T. R.; Hisama, F. M.; Novella, S.; Tyrrell, L.; Marshall, L.; Waxman, S. G. (2005-06-15). "Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons". Brain. 128 (8): 1847–1854. doi:10.1093/brain/awh514. ISSN 1460-2156. PMID 15958509.
- Cox, James J.; Reimann, Frank; Nicholas, Adeline K.; Thornton, Gemma; Roberts, Emma; Springell, Kelly; Karbani, Gulshan; Jafri, Hussain; Mannan, Jovaria; Raashid, Yasmin; Al-Gazali, Lihadh; Hamamy, Henan; Valente, Enza Maria; Gorman, Shaun; Williams, Richard; McHale, Duncan P.; Wood, John N.; Gribble, Fiona M.; Woods, C. Geoffrey (2006). "An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain". Nature. 444 (7121): 894–898. Bibcode:2006Natur.444..894C. doi:10.1038/nature05413. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 7212082. PMID 17167479.
- Dib-Hajj, Sulayman D.; Yang, Yang; Black, Joel A.; Waxman, Stephen G. (2012-12-12). "The NaV1.7 sodium channel: from molecule to man". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 14 (1): 49–62. doi:10.1038/nrn3404. ISSN 1471-003X. PMID 23232607. S2CID 5489010.
- G., Waxman, Stephen (2018). Chasing men on fire : the story of the search for a pain gene. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. ISBN 9780262344722. OCLC 1028188541.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Novella SP, Hisama FM, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (2007). "A case of inherited erythromelalgia". Nature Clinical Practice Neurology. 3 (4): 229–34. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0425. PMID 17410110. S2CID 7017831.
- Mo, Y. M. (1989). "An epidemiological study on erythromelalgia". Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi. 10 (5): 291–294. PMID 2611871.
- Zhu, W. F. (1989). "A case-control study on epidemic erythromelalgia". Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi. 10 (2): 94–97. PMID 2736621.
- Wei, J. Y. (1984). "An epidemiological survey and clinical analysis of erythromelalgia in Nanning City". Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi. 5 (1): 33–34. PMID 6744394.
- ^ Zheng ZM, Hu JM, Liu SF, Zhang JH, Zhu WP (1987). "Survey of epidemic erythromelalgia in Hanchuan and Puqi of Hubei Province". Chinese Journal of Experimental and Clinical Virology. 1: 34–39.
- He J, Zhao L, Wang B, Zheng J, Lin G, et al. (1995). "Outbreak of epidemic erythromelalgia in Fujian Province". Chinese Journal of Zoonoses. 11: 54–55.
- Long T, Yang Z, Wang H, Jin D, Qin M (2005). "Epidemiology study of an outbreak of epidemic erythromelalgia". Occupation and Health. 21: 713–4.
- Xie F, Ning H, Lei Y, Lei S (2010). "A brief report of an outbreak epidemic erythromelalgia". Practical Preventive Medicine. 17: 1922.
- Berlin AL, Pehr K (March 2004). "Coexistence of erythromelalgia and Raynaud's phenomenon". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 50 (3): 456–60. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(03)02121-2. PMID 14988692.
- ^ Zheng, Z. M.; Zhang, J. H.; Hu, J. M.; Liu, S. F.; Zhu, W. P. (1988). "Poxviruses isolated from epidemic erythromelalgia in China". Lancet. 1 (8580): 296. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(88)90372-8. PMID 2893103. S2CID 20118869.
- ^ Zheng, Z. M.; Specter, S.; Zhang, J. H.; Friedman, H.; Zhu, W. P. (1992). "Further characterization of the biological and pathogenic properties of erythromelalgia-related poxviruses". The Journal of General Virology. 73 (8): 2011–2019. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-73-8-2011. PMID 1322958.
- ^ Zhang JH, Zheng ZM, Zhu WP, Cai AM (1990). "Investigation and virus isolation of reappeared epidemic erythromelalgia in Wuhan". Wuhan Medical Journal. 14: 41–42.
- Ichimura, J (1918). "A new poisonous mushroom". Bot Gaz (Tokyo). 65: 10911.
- Saviuc PF, Danel VC, Moreau PA, Guez DR, Claustre AM, Carpentier PH, Mallaret MP, Ducluzeau R (2001). "Erythromelalgia and mushroom poisoning". J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 39 (4): 403–07. doi:10.1081/CLT-100105162. PMID 11527236. S2CID 32805160.
- Diaz, James H. (February 2005). "Syndromic diagnosis and management of confirmed mushroom poisonings". Critical Care Medicine. 33 (2): 427–36. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000153531.69448.49. PMID 15699849. S2CID 24492593.
- Mendez-Rios, J. D.; Martens, C. A.; Bruno, D. P.; Porcella, S. F.; Zheng, Z. M.; Moss, B. (2012). Xiang, Yan (ed.). "Genome Sequence of Erythromelalgia-Related Poxvirus Identifies it as an Ectromelia Virus Strain". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e34604. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...734604M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034604. PMC 3338725. PMID 22558090.
- Zheng, Z. M.; Specter, S.; Friedman, H. (1991). "Presence of specific IgG antibody to the A type inclusions of erythromelalgia-related poxvirus in the sera of patients with epidemic erythromelalgia". Archives of Dermatological Research. 283 (8): 535–536. doi:10.1007/BF00371930. PMID 1785945.
- ^ Dib-Hajj SD, Rush AM, Cummins TR, et al. (2005). "Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons". Brain. 128 (Pt 8): 1847–54. doi:10.1093/brain/awh514. PMID 15958509.
- ^ Rush AM, Dib-Hajj SD, Liu S, Cummins TR, Black JA, Waxman SG (2006). "A single sodium channel mutation produces hyper- or hypoexcitability in different types of neurons". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (21): 8245–50. Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.8245R. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602813103. PMC 1472458. PMID 16702558.
- ^ Harty TP, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, et al. (2006). "Na(V)1.7 mutant A863P in erythromelalgia: effects of altered activation and steady-state inactivation on excitability of nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons". J. Neurosci. 26 (48): 12566–75. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3424-06.2006. PMC 6674913. PMID 17135418.
- ^ Han C, Lampert A, Rush AM, et al. (2007). "Temperature dependence of erythromelalgia mutation L858F in sodium channel Nav1.7". Molecular Pain. 3 (1): 3. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-3-3. PMC 1781932. PMID 17239250.
- Lee MJ, Yu HS, Hsieh ST, Stephenson DA, Lu CJ, Yang CC (2007). "Characterization of a familial case with primary erythromelalgia from Taiwan". J. Neurol. 254 (2): 210–4. doi:10.1007/s00415-006-0328-3. PMID 17294067. S2CID 9874888.
- ^ Drenth JP, te Morsche RH, Guillet G, Taieb A, Kirby RL, Jansen JB (2005). "SCN9A mutations define primary erythermalgia as a neuropathic disorder of voltage gated sodium channels". J. Invest. Dermatol. 124 (6): 1333–8. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23737.x. PMID 15955112.
- Choi JS, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (2006). "Inherited erythermalgia: limb pain from an S4 charge-neutral Na channelopathy". Neurology. 67 (9): 1563–7. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000231514.33603.1e. PMID 16988069. S2CID 29074746.
- ^ Sheets PL, Jackson JO, Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj SD, Cummins TR (2007). "A Nav1.7 channel mutation associated with hereditary erythromelalgia contributes to neuronal hyperexcitability and displays reduced lidocaine sensitivity". J. Physiol. 581 (Pt 3): 1019–31. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.127027. PMC 2170829. PMID 17430993.
- Michiels JJ, te Morsche RH, Jansen JB, Drenth JP (2005). "Autosomal dominant erythermalgia associated with a novel mutation in the voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.7". Arch. Neurol. 62 (10): 1587–90. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.10.1587. hdl:10067/1027200151162165141. PMID 16216943.
- Lampert A, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG (2006). "Size matters: Erythromelalgia mutation S241T in Nav1.7 alters channel gating". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (47): 36029–35. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607637200. PMID 17008310.
- ^ Cummins TR, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (2004). "Electrophysiological properties of mutant Nav1.7 sodium channels in a painful inherited neuropathy". J. Neurosci. 24 (38): 8232–6. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2695-04.2004. PMC 6729696. PMID 15385606.
- Han C, Rush AM, Dib-Hajj SD, et al. (2006). "Sporadic onset of erythermalgia: a gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7". Ann. Neurol. 59 (3): 553–8. doi:10.1002/ana.20776. PMID 16392115. S2CID 39474666.
- Yang, Yang; Huang, Jianying; Mis, Malgorzata A.; Estacion, Mark; Macala, Lawrence; Shah, Palak; Schulman, Betsy R.; Horton, Daniel B.; Dib-Hajj, Sulayman D. (2016-07-13). "Nav1.7-A1632G Mutation from a Family with Inherited Erythromelalgia: Enhanced Firing of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Evoked by Thermal Stimuli". Journal of Neuroscience. 36 (28): 7511–7522. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0462-16.2016. ISSN 0270-6474. PMC 6705539. PMID 27413160.
- Mørk, Cato; Asker, Claes (2013). "Combined computer assisted capillary microscopy and laser Doppler imaging used to assess redistribution changes in skin of erythromelalgic patients during treatment with misoprostol".
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Genebriera J, Wendelschafer-Crabb G, Kennedy WR, Sandroni P (Sep 2006). "Histopathologic findings in primary erythromelalgia are nonspecific: special studies show a decrease in small nerve fiber density". J Am Acad Dermatol. 55 (3): 519–22. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.04.067. PMID 16908366.
- "Diagnosis". rare diseases.org. NORD - National Organization for Rare Disorders.
- Sandroni P, Davis MD (March 2006). "Combination gel of 1% amitriptyline and 0.5% ketamine to treat refractory erythromelalgia pain: a new treatment option?". Arch Dermatol. 142 (3): 283–6. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.3.283. PMID 16549702.
- Cohen, JS (November 2000). "Erythromelalgia: new theories and new therapies". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 43 (5 Pt 1): 841–7. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.109301. PMID 11050591. S2CID 40807034.
- ^ Liu, T; Zhang, Y; Lin, H; Lv, X; Xiao, J; Zeng, W; Gu, Y; Rutherford, S; Tong, S; Ma, W (30 March 2015). "A large temperature fluctuation may trigger an epidemic erythromelalgia outbreak in China". Scientific Reports. 5: 9525. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5.9525L. doi:10.1038/srep09525. PMC 4377627. PMID 25820221.
- ^ Friberg, D; Chen, T; Tarr, G; van Rij, A (2013). "Erythromelalgia? A clinical study of people who experience red, hot, painful feet in the community". International Journal of Vascular Medicine. 2013: 864961. doi:10.1155/2013/864961. PMC 3671268. PMID 23762561.
- Kalgaard, OM; Seem, E; Kvernebo, K (September 1997). "Erythromelalgia: a clinical study of 87 cases" (PDF). Journal of Internal Medicine. 242 (3): 191–7. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2796.1997.00185.x. hdl:10852/28041. PMID 9350163. S2CID 11845452.
- ^ Reed, KB; Davis, MD (January 2009). "Incidence of erythromelalgia: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 23 (1): 13–5. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02938.x. PMC 2771547. PMID 18713229.
- Alhadad, A; Wollmer, P; Svensson, A; Eriksson, KF (January 2012). "Erythromelalgia: Incidence and clinical experience in a single centre in Sweden". VASA. Zeitschrift für Gefässkrankheiten. 41 (1): 43–8. doi:10.1024/0301-1526/a000162. PMID 22247059.
- ^ Mitchell, Silas Weir (July 1878). "On a rare vasomotor neurosis of the extremities and on maladies with which it may be confounded". American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 76 (2): 36.
- ^ Michiels, JJ; van Joost, T (January 1990). "Erythromelalgia and thrombocythemia: a causal relation". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 22 (1): 107–11. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80005-9. PMID 2405024.
- Erythromelalgia at eMedicine
- ^ Smith, L.A.; Allen, F.V. (1938). "Erythermalgia (erythromelalgia) of the extremities. A syndrome characterized by redness, heat and pain". Am Heart J. 16: 136–41. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(38)90693-3.
- ^ Drenth, JP; van Genderen, PJ; Michiels, JJ (June 1994). "Thrombocythemic erythromelalgia, primary erythermalgia, and secondary erythermalgia: three distinct clinicopathologic entities". Angiology. 45 (6): 451–3. doi:10.1177/000331979404500606. PMID 8203771.
- ^ Michiels, JJ; Drenth, JP; Van Genderen, PJ (February 1995). "Classification and diagnosis of erythromelalgia and erythermalgia". International Journal of Dermatology. 34 (2): 97–100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1995.tb03587.x. PMID 7737785. S2CID 12579108.
- ^ Norton, JV; Zager, E; Grady, JF (1998). "Erythromelalgia: diagnosis and classification". The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery. 38 (3): 238–41. doi:10.1016/s1067-2516(99)80060-x. PMID 10384366.
- Gerhardt, Carl Jakob Adolf Christian (1892). "über erythromelalgie". Berliner Klinische Wochenschrift. 29: 1125.
- Lewis, Thomas (1933). "Clinical observations and experiments relating to burning pain in the extremities, and to so-called "erythromelalgia" in particular". Clinical Science. 1: 175–211.
- HUIZINGA, J (1957). "Hereditary acromelalgia or restless legs". Acta Genetica et Statistica Medica. 7 (1): 121–3. doi:10.1159/000150945. PMID 13469127.
- ^ Shaw, HB (21 March 1903). "The Morbid Anatomy of Erythromelalgia Based Upon the Examination of the Amputated Extremities of Three Cases". British Medical Journal. 1 (2203): 662–3. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.2203.662. PMC 2513193. PMID 20760783.
Further reading
- Zahn C, Puga C, Malik A, Khanna D (May 2024). "Painful Raynaud's mimics". Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 38: 101948. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2024.101948. PMID 38704280.
- Caldito EG, Kaul S, Caldito NG, Piette W, Mehta S (March 2024). "Erythromelalgia. Part I: Pathogenesis, clinical features, evaluation, and complications". J Am Acad Dermatol. 90 (3): 453–462. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.071. PMID 37364617.
- Caldito EG, Caldito NG, Kaul S, Piette W, Mehta S (March 2024). "Erythromelalgia. Part II: Differential diagnoses and management". J Am Acad Dermatol. 90 (3): 465–474. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.070. PMID 37364616.
- Ma JE, Lee JU, Sartori-Valinotti JC, Rooke TW, Sandroni P, Davis MD (January 2023). "Erythromelalgia: A Review of Medical Management Options and Our Approach to Management". Mayo Clin Proc. 98 (1): 136–149. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.08.005. PMID 36470753.
- Raef HS, Williams M, Fedeles F (November 2022). "Topical treatments for erythromelalgia". Dermatol Ther. 35 (11): e15860. doi:10.1111/dth.15860. PMID 36164837.
- Mann N, King T, Murphy R (July 2019). "Review of primary and secondary erythromelalgia". Clin Exp Dermatol. 44 (5): 477–482. doi:10.1111/ced.13891. PMID 30609105.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Cardiovascular disease (vessels) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arteries, arterioles and capillaries | |||||||||
| Veins |
| ||||||||
| Arteries or veins | |||||||||
| Blood pressure |
| ||||||||