| Part of a series of articles on the |
| mathematical constant e |
|---|
 |
| Properties |
| Applications |
| Defining e |
| People |
| Related topics |
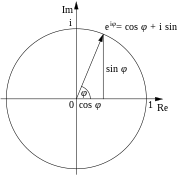
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that, for any real number x, one has where e is the base of the natural logarithm, i is the imaginary unit, and cos and sin are the trigonometric functions cosine and sine respectively. This complex exponential function is sometimes denoted cis x ("cosine plus i sine"). The formula is still valid if x is a complex number, and is also called Euler's formula in this more general case.
Euler's formula is ubiquitous in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and engineering. The physicist Richard Feynman called the equation "our jewel" and "the most remarkable formula in mathematics".
When x = π, Euler's formula may be rewritten as e + 1 = 0 or e = −1, which is known as Euler's identity.
History
In 1714, the English mathematician Roger Cotes presented a geometrical argument that can be interpreted (after correcting a misplaced factor of ) as: Exponentiating this equation yields Euler's formula. Note that the logarithmic statement is not universally correct for complex numbers, since a complex logarithm can have infinitely many values, differing by multiples of 2πi.

Around 1740 Leonhard Euler turned his attention to the exponential function and derived the equation named after him by comparing the series expansions of the exponential and trigonometric expressions. The formula was first published in 1748 in his foundational work Introductio in analysin infinitorum.
Johann Bernoulli had found that
And since the above equation tells us something about complex logarithms by relating natural logarithms to imaginary (complex) numbers. Bernoulli, however, did not evaluate the integral.
Bernoulli's correspondence with Euler (who also knew the above equation) shows that Bernoulli did not fully understand complex logarithms. Euler also suggested that complex logarithms can have infinitely many values.
The view of complex numbers as points in the complex plane was described about 50 years later by Caspar Wessel.
Definitions of complex exponentiation
Further information: Exponentiation § Complex exponents with a positive real base, and Exponential function § On the complex planeThe exponential function e for real values of x may be defined in a few different equivalent ways (see Characterizations of the exponential function). Several of these methods may be directly extended to give definitions of e for complex values of z simply by substituting z in place of x and using the complex algebraic operations. In particular, we may use any of the three following definitions, which are equivalent. From a more advanced perspective, each of these definitions may be interpreted as giving the unique analytic continuation of e to the complex plane.
Differential equation definition
The exponential function is the unique differentiable function of a complex variable for which the derivative equals the function and
Power series definition
For complex z
Using the ratio test, it is possible to show that this power series has an infinite radius of convergence and so defines e for all complex z.
Limit definition
For complex z
Here, n is restricted to positive integers, so there is no question about what the power with exponent n means.
Proofs
Various proofs of the formula are possible.
Using differentiation
This proof shows that the quotient of the trigonometric and exponential expressions is the constant function one, so they must be equal (the exponential function is never zero, so this is permitted).
Consider the function f(θ) for real θ. Differentiating gives by the product rule Thus, f(θ) is a constant. Since f(0) = 1, then f(θ) = 1 for all real θ, and thus
Using power series

Here is a proof of Euler's formula using power-series expansions, as well as basic facts about the powers of i:
Using now the power-series definition from above, we see that for real values of x where in the last step we recognize the two terms are the Maclaurin series for cos x and sin x. The rearrangement of terms is justified because each series is absolutely convergent.
Using polar coordinates
Another proof is based on the fact that all complex numbers can be expressed in polar coordinates. Therefore, for some r and θ depending on x, No assumptions are being made about r and θ; they will be determined in the course of the proof. From any of the definitions of the exponential function it can be shown that the derivative of e is ie. Therefore, differentiating both sides gives Substituting r(cos θ + i sin θ) for e and equating real and imaginary parts in this formula gives dr/dx = 0 and dθ/dx = 1. Thus, r is a constant, and θ is x + C for some constant C. The initial values r(0) = 1 and θ(0) = 0 come from e = 1, giving r = 1 and θ = x. This proves the formula
Applications
Applications in complex number theory

Interpretation of the formula
This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Here φ is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counterclockwise and in radians.
The original proof is based on the Taylor series expansions of the exponential function e (where z is a complex number) and of sin x and cos x for real numbers x (see above). In fact, the same proof shows that Euler's formula is even valid for all complex numbers x.
A point in the complex plane can be represented by a complex number written in cartesian coordinates. Euler's formula provides a means of conversion between cartesian coordinates and polar coordinates. The polar form simplifies the mathematics when used in multiplication or powers of complex numbers. Any complex number z = x + iy, and its complex conjugate, z = x − iy, can be written as where
- x = Re z is the real part,
- y = Im z is the imaginary part,
- r = |z| = √x + y is the magnitude of z and
- φ = arg z = atan2(y, x).
φ is the argument of z, i.e., the angle between the x axis and the vector z measured counterclockwise in radians, which is defined up to addition of 2π. Many texts write φ = tan y/x instead of φ = atan2(y, x), but the first equation needs adjustment when x ≤ 0. This is because for any real x and y, not both zero, the angles of the vectors (x, y) and (−x, −y) differ by π radians, but have the identical value of tan φ = y/x.
Use of the formula to define the logarithm of complex numbers
Now, taking this derived formula, we can use Euler's formula to define the logarithm of a complex number. To do this, we also use the definition of the logarithm (as the inverse operator of exponentiation): and that both valid for any complex numbers a and b. Therefore, one can write: for any z ≠ 0. Taking the logarithm of both sides shows that and in fact, this can be used as the definition for the complex logarithm. The logarithm of a complex number is thus a multi-valued function, because φ is multi-valued.
Finally, the other exponential law which can be seen to hold for all integers k, together with Euler's formula, implies several trigonometric identities, as well as de Moivre's formula.
Relationship to trigonometry

Euler's formula, the definitions of the trigonometric functions and the standard identities for exponentials are sufficient to easily derive most trigonometric identities. It provides a powerful connection between analysis and trigonometry, and provides an interpretation of the sine and cosine functions as weighted sums of the exponential function:
The two equations above can be derived by adding or subtracting Euler's formulas: and solving for either cosine or sine.
These formulas can even serve as the definition of the trigonometric functions for complex arguments x. For example, letting x = iy, we have:
In addition
Complex exponentials can simplify trigonometry, because they are mathematically easier to manipulate than their sine and cosine components. One technique is simply to convert sines and cosines into equivalent expressions in terms of exponentials sometimes called complex sinusoids. After the manipulations, the simplified result is still real-valued. For example:
Another technique is to represent sines and cosines in terms of the real part of a complex expression and perform the manipulations on the complex expression. For example:
This formula is used for recursive generation of cos nx for integer values of n and arbitrary x (in radians).
Considering cos x a parameter in equation above yields recursive formula for Chebyshev polynomials of the first kind.
See also: Phasor § ArithmeticTopological interpretation
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (November 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In the language of topology, Euler's formula states that the imaginary exponential function is a (surjective) morphism of topological groups from the real line to the unit circle . In fact, this exhibits as a covering space of . Similarly, Euler's identity says that the kernel of this map is , where . These observations may be combined and summarized in the commutative diagram below:

Other applications
See also: Complex number § ApplicationsIn differential equations, the function e is often used to simplify solutions, even if the final answer is a real function involving sine and cosine. The reason for this is that the exponential function is the eigenfunction of the operation of differentiation.
In electrical engineering, signal processing, and similar fields, signals that vary periodically over time are often described as a combination of sinusoidal functions (see Fourier analysis), and these are more conveniently expressed as the sum of exponential functions with imaginary exponents, using Euler's formula. Also, phasor analysis of circuits can include Euler's formula to represent the impedance of a capacitor or an inductor.
In the four-dimensional space of quaternions, there is a sphere of imaginary units. For any point r on this sphere, and x a real number, Euler's formula applies: and the element is called a versor in quaternions. The set of all versors forms a 3-sphere in the 4-space.
Other special cases
The special cases that evaluate to units illustrate rotation around the complex unit circle:
| x | e |
|---|---|
| 0 + 2πn | 1 |
| π/2 + 2πn | i |
| π + 2πn | −1 |
| 3π/2 + 2πn | −i |
The special case at x = τ (where τ = 2π, one turn) yields e = 1 + 0. This is also argued to link five fundamental constants with three basic arithmetic operations, but, unlike Euler's identity, without rearranging the addends from the general case: An interpretation of the simplified form e = 1 is that rotating by a full turn is an identity function.
See also
- Complex number
- Euler's identity
- Integration using Euler's formula
- History of Lorentz transformations
- List of things named after Leonhard Euler
References
- Moskowitz, Martin A. (2002). A Course in Complex Analysis in One Variable. World Scientific Publishing Co. p. 7. ISBN 981-02-4780-X.
- Feynman, Richard P. (1977). The Feynman Lectures on Physics, vol. I. Addison-Wesley. p. 22-10. ISBN 0-201-02010-6.
- Cotes wrote: "Nam si quadrantis circuli quilibet arcus, radio CE descriptus, sinun habeat CX sinumque complementi ad quadrantem XE ; sumendo radium CE pro Modulo, arcus erit rationis inter & CE mensura ducta in ." (Thus if any arc of a quadrant of a circle, described by the radius CE, has sinus CX and sinus of the complement to the quadrant XE ; taking the radius CE as modulus, the arc will be the measure of the ratio between & CE multiplied by .) That is, consider a circle having center E (at the origin of the (x,y) plane) and radius CE. Consider an angle θ with its vertex at E having the positive x-axis as one side and a radius CE as the other side. The perpendicular from the point C on the circle to the x-axis is the "sinus" CX ; the line between the circle's center E and the point X at the foot of the perpendicular is XE, which is the "sinus of the complement to the quadrant" or "cosinus". The ratio between and CE is thus . In Cotes' terminology, the "measure" of a quantity is its natural logarithm, and the "modulus" is a conversion factor that transforms a measure of angle into circular arc length (here, the modulus is the radius (CE) of the circle). According to Cotes, the product of the modulus and the measure (logarithm) of the ratio, when multiplied by , equals the length of the circular arc subtended by θ, which for any angle measured in radians is CE • θ. Thus, . This equation has a misplaced factor: the factor of should be on the right side of the equation, not the left side. If the change of scaling by is made, then, after dividing both sides by CE and exponentiating both sides, the result is: , which is Euler's formula.
See:- Roger Cotes (1714) "Logometria," Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 29 (338) : 5-45; see especially page 32. Available on-line at: Hathi Trust
- Roger Cotes with Robert Smith, ed., Harmonia mensurarum … (Cambridge, England: 1722), chapter: "Logometria", p. 28.
- https://nrich.maths.org/1384
- ^ John Stillwell (2002). Mathematics and Its History. Springer. ISBN 9781441960528.
- Sandifer, C. Edward (2007), Euler's Greatest Hits, Mathematical Association of America ISBN 978-0-88385-563-8
- Leonhard Euler (1748) Chapter 8: On transcending quantities arising from the circle of Introduction to the Analysis of the Infinite, page 214, section 138 (translation by Ian Bruce, pdf link from 17 century maths).
- Conway & Guy, pp. 254–255
- Bernoulli, Johann (1702). "Solution d'un problème concernant le calcul intégral, avec quelques abrégés par rapport à ce calcul" [Solution of a problem in integral calculus with some notes relating to this calculation]. Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences de Paris. 1702: 289–297.
- Apostol, Tom (1974). Mathematical Analysis. Pearson. p. 20. ISBN 978-0201002881. Theorem 1.42
- user02138 (https://math.stackexchange.com/users/2720/user02138), How to prove Euler's formula: $e^{i\varphi}=\cos(\varphi) +i\sin(\varphi)$?, URL (version: 2018-06-25): https://math.stackexchange.com/q/8612
- Ricardo, Henry J. (23 March 2016). A Modern Introduction to Differential Equations. Elsevier Science. p. 428. ISBN 9780123859136.
- Strang, Gilbert (1991). Calculus. Wellesley-Cambridge. p. 389. ISBN 0-9614088-2-0. Second proof on page.
- "Complex Sinusoids". ccrma.stanford.edu. Retrieved 10 September 2024.
- Hartl, Michael (14 March 2019) . "The Tau Manifesto". Archived from the original on 28 June 2019. Retrieved 14 September 2013.
Further reading
- Nahin, Paul J. (2006). Dr. Euler's Fabulous Formula: Cures Many Mathematical Ills. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11822-2.
- Wilson, Robin (2018). Euler's Pioneering Equation: The Most Beautiful Theorem in Mathematics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-879492-9. MR 3791469.
 where e is the
where e is the  ) as:
) as:
 Exponentiating this equation yields Euler's formula. Note that the logarithmic statement is not universally correct for complex numbers, since a complex logarithm can have infinitely many values, differing by multiples of 2πi.
Exponentiating this equation yields Euler's formula. Note that the logarithmic statement is not universally correct for complex numbers, since a complex logarithm can have infinitely many values, differing by multiples of 2πi.
 and is determined by both the cosine and sine components of the formula. One curve represents the real component (
and is determined by both the cosine and sine components of the formula. One curve represents the real component ( ) of the formula, while another curve, rotated 90 degrees around the z-axis (due to multiplication by
) of the formula, while another curve, rotated 90 degrees around the z-axis (due to multiplication by  ), represents the imaginary component (
), represents the imaginary component ( ).
).
 the above equation tells us something about
the above equation tells us something about  is the unique
is the unique  and
and 


 for real θ. Differentiating gives by the
for real θ. Differentiating gives by the  Thus, f(θ) is a constant. Since f(0) = 1, then f(θ) = 1 for all real θ, and thus
Thus, f(θ) is a constant. Since f(0) = 1, then f(θ) = 1 for all real θ, and thus


 where in the last step we recognize the two terms are the
where in the last step we recognize the two terms are the  No assumptions are being made about r and θ; they will be determined in the course of the proof. From any of the definitions of the exponential function it can be shown that the derivative of e is ie. Therefore, differentiating both sides gives
No assumptions are being made about r and θ; they will be determined in the course of the proof. From any of the definitions of the exponential function it can be shown that the derivative of e is ie. Therefore, differentiating both sides gives
 Substituting r(cos θ + i sin θ) for e and equating real and imaginary parts in this formula gives dr/dx = 0 and dθ/dx = 1. Thus, r is a constant, and θ is x + C for some constant C. The initial values r(0) = 1 and θ(0) = 0 come from e = 1, giving r = 1 and θ = x. This proves the formula
Substituting r(cos θ + i sin θ) for e and equating real and imaginary parts in this formula gives dr/dx = 0 and dθ/dx = 1. Thus, r is a constant, and θ is x + C for some constant C. The initial values r(0) = 1 and θ(0) = 0 come from e = 1, giving r = 1 and θ = x. This proves the formula

 where
where
 and that
and that
 both valid for any complex numbers a and b. Therefore, one can write:
both valid for any complex numbers a and b. Therefore, one can write:
 for any z ≠ 0. Taking the logarithm of both sides shows that
for any z ≠ 0. Taking the logarithm of both sides shows that
 and in fact, this can be used as the definition for the
and in fact, this can be used as the definition for the  which can be seen to hold for all integers k, together with Euler's formula, implies several
which can be seen to hold for all integers k, together with Euler's formula, implies several 
 and solving for either cosine or sine.
and solving for either cosine or sine.




 is a (
is a ( to the unit circle
to the unit circle  . In fact, this exhibits
. In fact, this exhibits  , where
, where  . These observations may be combined and summarized in the
. These observations may be combined and summarized in the  and the element is called a
and the element is called a  An interpretation of the simplified form e = 1 is that rotating by a full turn is an
An interpretation of the simplified form e = 1 is that rotating by a full turn is an  & CE mensura ducta in
& CE mensura ducta in  . In Cotes' terminology, the "measure" of a quantity is its natural logarithm, and the "modulus" is a conversion factor that transforms a measure of angle into circular arc length (here, the modulus is the radius (CE) of the circle). According to Cotes, the product of the modulus and the measure (logarithm) of the ratio, when multiplied by
. In Cotes' terminology, the "measure" of a quantity is its natural logarithm, and the "modulus" is a conversion factor that transforms a measure of angle into circular arc length (here, the modulus is the radius (CE) of the circle). According to Cotes, the product of the modulus and the measure (logarithm) of the ratio, when multiplied by  . This equation has a misplaced factor: the factor of
. This equation has a misplaced factor: the factor of  , which is Euler's formula.
, which is Euler's formula.