 N5532, the Lockheed L-188A Electra involved in the crash N5532, the Lockheed L-188A Electra involved in the crash | |
| Accident | |
|---|---|
| Date | January 21, 1985 |
| Summary | Pilot error and ground crew error |
| Site | Near Reno–Cannon International Airport, Reno, Nevada, United States 39°27′55″N 119°46′56″W / 39.465281°N 119.782223°W / 39.465281; -119.782223 |
| Aircraft | |
| Aircraft type | Lockheed L-188A Electra |
| Operator | Galaxy Airlines |
| Call sign | GALAXY 203 |
| Registration | N5532 |
| Flight origin | Reno–Cannon International Airport, Reno, Nevada |
| Destination | Minneapolis–Saint Paul International Airport, Minneapolis, Minnesota |
| Occupants | 71 |
| Passengers | 65 |
| Crew | 6 |
| Fatalities | 70 |
| Injuries | 1 |
| Survivors | 1 |
Galaxy Airlines Flight 203 was a Lockheed L-188 Electra 4-engine turboprop, registration N5532, operating as a non-scheduled charter flight from Reno, Nevada to Minneapolis/St Paul, which crashed on January 21, 1985, shortly after takeoff. All but 1 of the 71 on board died.
Accident

The flight, which was returning from a gambling and Super Bowl trip sponsored by Caesars Tahoe, took off from runway 16R at Reno-Cannon International Airport (now Reno–Tahoe International Airport) at 1:04 am on January 21, 1985. Heavy vibration started shortly after takeoff, and the pilots asked the tower for permission to make a left downwind turn, saying they needed to land. A short time later, the aircraft crashed about 1.5 mi (2.4 km) from the end of the runway and burst into flames. Debris was scattered across US Highway 395 and South Virginia Street; a store and several vehicles on the ground were damaged. Of the 71 people aboard, three initially survived. One died on January 29 and another on February 4. The sole survivor was a 17-year-old boy who was thrown clear of the aircraft and landed upright, conscious and still in his seat, on South Virginia Street.
Investigation

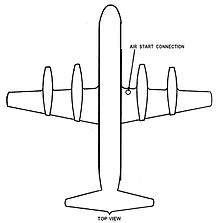
The National Transportation Safety Board concluded that the probable cause of the accident was
the captain's failure to control and the copilot's failure to monitor the flight path and airspeed of the aircraft. This breakdown in crew coordination followed the onset of unexpected vibration shortly after takeoff ... Contributing to the accident was the failure of ground handlers to properly close an air start access door, which led to the vibration.
The NTSB found that ground handlers did not properly close the air start access door due to an interruption in their procedures: when a supervisor realized that the headset used for communication with the flight crew was not working, he switched to using hand signals mid-routine. In the confusion the supervisor signaled the flight to taxi before the air start hose had been disconnected. After the supervisor realized his error and signaled the flight crew to make an emergency stop, the hose was successfully disconnected but the air start access door was not closed.
The report concluded that the open access door caused vibrations which distracted the pilots, though they would likely not have prevented the aircraft from reaching cruise speed and altitude – there had been reports from other Electra pilots that the vibrations ceased at higher air speeds. The pilots reduced power to all four engines simultaneously, presumably to see whether they were the source of the vibrations, and did not restore power quickly enough to prevent a stall.
Aftermath
A memorial called Galaxy Grove was dedicated at Rancho San Rafael in 1986. After the plaque was stolen in 2013, a two-ton granite replacement was installed.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Transportation Safety Board.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Transportation Safety Board.
- Accident description for "The January 21, 1985 accident of Lockheed L-188A Electra N5532 at Reno/Tahoe International Airport, NV (RNO)." at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on October 23, 2006.
- Magnuson, Ed; Kane, Joseph J.; Mathison, Dirk (February 4, 1985). "Crash of a Troubled Bird". Time. Archived from the original on February 4, 2013.
- Costantini, Allen (2005). "The Legacy of Galaxy Flight 203". kare11.org. Archived from the original on April 15, 2013. Retrieved December 22, 2021.
- "Aircraft Accident Report, Galaxy Airlines Inc., Lockheed Electra-L-1 88C, N5532, Reno, Nevada, January 21, 1985" (PDF). National Transportation Safety Board. February 4, 1986. NTSB/AAR-86/01. Retrieved October 23, 2006 – via Embry–Riddle Aeronautical University.
- "Memories still raw for sole survivor of '85 plane crash". USA Today. January 20, 2015. Retrieved August 27, 2019.
External links
- Plane Crashes Since 1970 with a Sole Survivor at airsafe.com.
| Aviation accidents and incidents in 1985 (1985) | |
|---|---|
| Jan 1 Eastern Air Lines Flight 980Jan 18 CAAC Flight 5109Jan 21 Galaxy Airlines Flight 203Feb 1 Aeroflot Flight 7841Feb 19 China Airlines Flight 006Feb 19 Iberia Flight 610Feb 24 Polar 3May 3 Zolochiv mid-air collisionJun 14 Trans World Airlines Flight 847Jun 21 Braathens SAFE Flight 139Jun 23 Air India Flight 182Jul 10 Aeroflot Flight 5143Aug 2 Delta Air Lines Flight 191Aug 12 Japan Air Lines Flight 123Aug 22 Manchester Airport disasterAug 25 Bar Harbor Airlines Flight 1808Sep 4 Bakhtar Antonov An-26 shootdownSep 6 Midwest Express Airlines Flight 105Sep 23 Henson Airlines Flight 1517Nov 10 Teterboro mid-air collisionNov 23 EgyptAir Flight 648Nov 25 Aeroflot Antonov An-12 crashDec 12 Arrow Air Flight 1285RDec 19 Aeroflot Flight 101/435Dec 31 Ricky Nelson plane crash | |
| 1984 ◄ ► 1986 |
- Aviation accidents and incidents in the United States in 1985
- January 1985 events in the United States
- Airliner accidents and incidents caused by pilot error
- Accidents and incidents involving the Lockheed L-188 Electra
- Airliner accidents and incidents in Nevada
- Galaxy Airlines (United States) accidents and incidents
- History of Reno, Nevada
- 1985 in Nevada
- Reno–Tahoe International Airport