Medical condition
| Gastroptosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Risk factors | Female gender |
| Diagnostic method | X-ray with barium contrast |
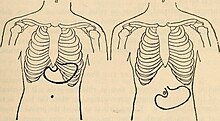
Gastroptosis is the abnormal downward dislocation (ptosis) of the stomach in which its greater curve is displaced below the iliac crest. It is not a life-threatening condition.
The condition frequently causes digestive symptoms, epigastric pain, constipation, decreased appetite, and sometimes even gastric emptying disorders. It is much more prominent in women than men, and is diagnosed with x-ray using barium contrast. Gastroptosis is mainly caused by the relaxation of surrounding ligaments and mesenteries as a result of the weight of the stomach.
See also
References
- ^ Kusano M, Moki F, Hosaka H, Shimoyama Y, Kawamura O, Nagoshi A, et al. (2011). "Gastroptosis is associated with less dyspepsia, rather than a cause of dyspepsia, in Japanese persons". Internal Medicine. 50 (7): 667–671. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.50.4582. PMID 21467696.
- Staszewska A, Jarzumbek A, Saran A, Gierak-Firszt S, Kwiecien J (January 2023). "Postprandial Abdominal Pain Caused by Gastroptosis-A Case Report". Children. 10 (1): 116. doi:10.3390/children10010116. PMC 9857050. PMID 36670666.
- Gould GM (1899). The Philadelphia Monthly Medical Journal. Philadelphia Medical Publishing Company. p. 150. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- Bestari MB, Chandra M, Joewono IR, Girawan D, Andhika R, Wahyudi Y, et al. (2022). "Gastroptosis due to Gastric Outlet Obstruction Secondary to Duodenal Tumor: Glenard's Disease Revisited". Case Reports in Gastroenterology. 16 (1): 89–93. doi:10.1159/000521977. PMC 8958574. PMID 35431764.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
| Diseases of the human digestive system | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper GI tract |
| ||||||||||
| Lower GI tract Enteropathy |
| ||||||||||
| GI bleeding | |||||||||||
| Accessory |
| ||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||
This human digestive system article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |