| Greater palatine nerve | |
|---|---|
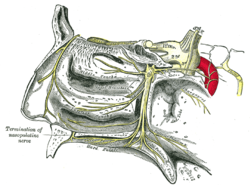 The sphenopalatine ganglion and its branches. (Anterior palatine at bottom center) The sphenopalatine ganglion and its branches. (Anterior palatine at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| From | Pterygopalatine ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus palatinus major, nervus palatinus anterior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.045 |
| TA2 | 6224 |
| FMA | 52802 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The greater palatine nerve is a branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion. This nerve is also referred to as the anterior palatine nerve, due to its location anterior to the lesser palatine nerve. It carries both general sensory fibres from the maxillary nerve, and parasympathetic fibers from the nerve of the pterygoid canal. It may be anaesthetised for procedures of the mouth and maxillary (upper) teeth.
Structure
The greater palatine nerve is a branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion. It descends through the greater palatine canal, moving anteriorly and inferiorly. Here, it is accompanied by the descending palatine artery. It emerges upon the hard palate through the greater palatine foramen. It then passes forward in a groove in the hard palate, nearly as far as the incisor teeth.
While in the pterygopalatine canal, it gives off lateral posterior inferior nasal branches, which enter the nasal cavity through openings in the palatine bone, and ramify over the inferior nasal concha and middle and inferior meatuses. At its exit from the canal, a palatine branch is distributed to both surfaces of the soft palate.
Function
The greater palatine nerve carries both general sensory fibres from the maxillary nerve, and parasympathetic fibers from the nerve of the pterygoid canal. It supplies the gums, the mucous membrane and glands of the hard palate, and communicates in front with the terminal filaments of the nasopalatine nerve.
Clinical significance
The greater palatine nerve may be anaesthetised to perform dental procedures on the maxillary (upper) teeth, and sometimes for cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 893 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 893 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Hafeez, Najmus Sahar; Ganapathy, Sugantha; Sondekoppam, Rakesh; Johnson, Marjorie; Merrifield, Peter; Galil, Khadry A. (2015). "Anatomical Variations of the Greater Palatine Nerve in the Greater Palatine Canal". Journal of the Canadian Dental Association. 81: f14. PMID 26214834 – via jcda.
- Mellema, Jonathan W.; Tami, Thomas A. (2004-03-01). "An Endoscopic Study of the Greater Palatine Nerve". American Journal of Rhinology. 18 (2): 99–103. doi:10.1177/194589240401800206. ISSN 1050-6586. PMID 15152875.
External links
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb2.htm
- "Anatomy diagram: 05287.011-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2013-04-22.
- Diagram at adi-visuals.com
| The trigeminal nerve | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ophthalmic (V1) |
| ||||||
| maxillary (V2) |
| ||||||
| mandibular (V3) |
| ||||||