| Karachi Breeze (BRT Metro Bus) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Owner | Government of Sindh |
| Locale | Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan |
| Transit type | BRT |
| Number of lines | 6 2 operational 2 under-construction 2 planned |
| Number of stations | ~90 |
| Daily ridership | ~58,000 daily (Green and Orange lines) |
| Website | www |
| Operation | |
| Operator(s) | Sindh Mass Transit Authority |
| Technical | |
| System length | 112.9 km (70.2 mi) |
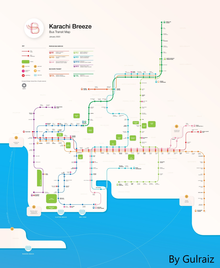
Karachi Breeze is a 112.9 km (70.2 mi) network of bus rapid transit routes under construction in Karachi, Pakistan. Construction began in 2013, two lines are operational and two lines are under construction as of September 2022, with 2 more planned. The current ridership of the first line is 55,000 passengers per day, with a total of 109 km of dedicated bus routes. Upon completion, it will become the largest BRT network in Pakistan, and will connect to the Karachi Circular Railway.
History
Nawaz Sharif, during a high-level meeting in Karachi on 10 July 2014, announced funds to launch the BRT Green Line to alleviate the severe traffic congestion in the city. The slow pace of work on BRT Green Line has irked citizens as the digging work on main arteries has resulted in congestion of traffic, which the former prime minister blamed on the Sindh government. In 2018, the name of the project was changed from Karachi Bus and Mass Rapid Transit system to Karachi Breeze.
Lines
The system will be divided into 6 dedicated lines or "busways". Currently, the Green and Orange lines are operational, the Red and Yellow lines are under-construction, and the Blue and Brown lines are in their planning stages.
Green Line
Main article: Green Line - Karachi Metrobus
The green line is extend from Merewether Tower in central Karachi, to Surjani in northern Karachi, with a total length of 26 km (16 mi). The Government of Pakistan financed the majority of the project. Construction of the Green Line began on February 26, 2016 ended in December 2021. The line has 22 bus stations. Engineering Associates had been contracted as the designers and supervision consultants for Green Line while a Consortium of "Ernest & Young", "Exponent Engineers" & "Haider Mota & BNR" had been contracted for "Transaction Advisory for Bus Operational Plan". The line is served by 80 18-metre-long buses. In addition, a Command and Control Centre is established at Garden West.
The green line:
- Numiash Station (to Blue Line)
- Patel Para (Guru Mandir) Station
- Lasbela Chowk Station
- Sanitary Market (Gulbahar) Station
- Nazimabad No.1 Station
- Enquiry Office Station
- Annu Bhai Park Station (to North Nazimabad KCR Station)
- Board Office Station ( to Orange Line )
- Hyderi Station
- Five Star Chowrangi Station
- Jummah Bazar Station
- Erum Shopping Station
- Nagan Chowrangi Station
- U.P. More Station
- Road 4200 (Saleem Centre) Station
- Power House Chowrangi Station
- Road 2400 (Aisha Complex) Station
- 2 Minute Chowrangi Station
- 4K Chowrangi Station
- Karimi Chowrangi Station
- KDA Flats Station
- Abdullah Chowk Terminal.
Orange Line
Main article: Orange Line - Karachi MetrobusThe Orange Line, also called the Edhi Line in honour of philanthropist Abdul Sattar Edhi, is the shortest of the five lines, spreading over 3.9 km with only four stations within Orangi. The Orange line will be spread over 2.3 km, of which 0.7 km will be elevated while 1.5 km will be on ground, whereas, the 1.5 km will be semi dedicated section. The project is entirely funded and built by the Sindh government. It was started in 2016, but finally the project was completed in 10 Sep 2022 . The project was criticised as being the only BRT line of the system that was not devised in conjunction with community input.
The line transports around 3,000 passengers daily, with a station located at every kilometre of its length. The line begins at Shahrah-e-Quaideen, near TMO Office, to Board Office, where it joins the Green Line BRT, through a rotary flyover.
The orange line:
- AO Chowk Terminal (to Green Line)
- Orangi Station (to Orangi KCR Station)
- Orangi Town Terminal
Blue Line
The Blue Line will extend from Merewether Tower in central Karachi, to Bahria Town in northeast Karachi at a total length of 30 km (19 mi) along Jahangir Road, and Shahrah-e-Pakistan to Sohrab Goth and onto Superhighway. It will be the first privately funded transport system in Pakistan being funded by the Bahria Town Group. Provincial Minister for Transport Syed Nasir Shah told Jang that the Blue Line will have 9 stations with 3 of them underground. Under the project, 357,000 passengers will be able to travel annually.
The blue line:
- Merewether Tower Terminal
- Numaish Chowrangi Station (to Green Line)
- Liaquatabad Station (to Liaquatabad KCR Station)
- Bahria Town Terminal
Yellow Line
The 22-kilometre-long Yellow Line project will connect Numaish Chowrangi near the Mazar-e-Quaid in central Karachi, to its eastern suburbs of Korangi and Landhi, terminating at Dawood Chowrangi. It has an estimated cost of $428 million, of which $382 million will be financed by the World Bank. It will be serviced by 268 buses and 28 stations, including 22 at grade and 6 underground. Construction of the line was delayed due to the global coronavirus pandemic, and is expected to start in 2022, with completion in 2025.
The Yellow Line:
- Numiash Chowrangi Terminal (to Blue Line/Green Line)
- Landhi Station Terminal (to Landhi KCR Station)
Red Line
Construction of Red Line has been started and will connect central Karachi to its eastern suburbs. It will extend from Numaish Chowrangi near the Mazar-e-Quaid in central Karachi, to Malir Halt in eastern Karachi via University Road. The system will be a "third generation" BRT system in which local buses can enter/exit the system at designated points, to travel between city streets and the dedicated bus corridor. It will have a total length of 27 km (17 mi). Construction was to start in August 2020, but was delayed to 2021 due to the global coronavirus pandemic, and was originally planned to be completed in 2022 at a cost of $503.2 million. The projected ridership of the system is 300,000 passengers per day.
It is the first transportation project in the world to receive funding from the UN Green Climate Fund for its use of biomethane from cow dung to power buses. A facility will be established at Cattle Colony to produce 11 tonnes of biogas per day for the line's 213 buses. A system of drains will also be built along the line to harvest rainwater for horticultural use, while the drains will also be perforated to allow rainwater to recharge water tables.
The red line:
- Regal Chowk Terminal (to Blue Line/Yellow Line)
- Regal Chowk Station Terminal (to KCR).
Brown Line
Brown line BRT will start from Singer Chowrangi of Korangi Industrial Area. The first station of Brown line BRT is integrated with Yellow line BRT. Brown Line BRT will pass through Shama Centre Shah Faisal Colony, Drigh Road where it has a combined station with Karachi Circular Railway (KCR), Nipa Chowrangi (combined station with Red Line and KCR), Sohrab Goth (combined station with Blue Line) and will end at Nagan Chowrangi (combined station with Green Line).
Fleet
The government has acquired eighty 18-metre-long articulated buses for the Green Line, twenty 12-metre-long buses for the Orange Line and is in the process of acquiring twenty-five 18-metre-long articulated buses for the Green Line Extension project.
See also
- Lahore Metrobus
- Rawalpindi-Islamabad Metrobus
- Multan Metrobus
- TransPeshawar
- List of rapid transit systems in Pakistan
References
- Ayub, Imran (17 May 2024). "Karachi's BRT Green and Orange lines now go hand in hand". Dawn. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- "PM announces Rs 15bn for Karachi 'Green Line' bus project". Dawn. 10 July 2014. Archived from the original on 10 July 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- ^ "وزیراعظم کا کراچی میں 15 ارب روپے کے ریپڈ بس منصوبے کا اعلان". Express. 10 July 2014. Archived from the original on 11 July 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "Prime Minister Announces to Launch Metro Bus in Karachi". Pakistan Tribune. 10 July 2014. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "Karachi Red Line Bus Construction Work Begins, Sindh Police Announces New Routes". propakistani.pk. 15 March 2022. Retrieved 15 March 2022.
- "Pakistan Railways announces restoring KCR from Monday | SAMAA". Samaa TV. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "Slow pace of work on Green Line irks citizens". www.pakistantoday.com.pk. Retrieved 5 February 2018.
- news92hd (2 February 2018). "Nawaz declares Sindh govt responsible for delay in Green Line project – 92 News HD Plus". 92 News HD Plus. Retrieved 5 February 2018.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - "SMTA officially changes name of KBMRT system to Karachi Breeze". Daily Times. 29 October 2018. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Ground-breaking ceremony: Green Line BRT finally gets go-ahead – The Express Tribune". The Express Tribune. 26 February 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- "Green Line bus service becomes fully operational in Karachi". The News International. 10 January 2022. Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "Karachi's Green Line bus will be more beautiful than Lahore metro: PM Nawaz". Dawn. 26 February 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- "Green Line goes the extra mile – The Express Tribune". The Express Tribune. 11 March 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- "Karachi's Green Line bus will be more beautiful than Lahore metro: PM Nawaz". Dawn. 26 February 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- اداریہ (29 February 2016). "گرین لائن ٹرانسپورٹ منصوبہ". Dawn News. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- ^ "Tender for Green Line and Orange Line". Sindh Public Procurement Regulatory Authority. 28 July 2017. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- "Karachi's Orange Line BRT renamed after Edhi". The Express Tribune. 13 December 2016. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "orange-line-bus-service-inaugurated-in-karachi". Nation. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Construction work likely to complete in 6 months". Nation. 15 February 2022. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- Ayub, Imran (17 May 2024). "Karachi's BRT Green and Orange lines now go hand in hand". Dawn. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- "Blue Line Feasibility Study" (PDF).
- "Bahria Town Karachi to Start "Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS)"". 14 March 2014.
- ^ "Work on Yellow Line BRT pushed to next year". The Express Tribune. 1 October 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "WB assures working to wrap up Karachi Yellow line design | SAMAA". Samaa TV. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- "CM Murad Ali Shah orders transport department to complete Orange Line's infrastructure". www.thenews.com.pk. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Construction work on Red Line BRT begins in Karachi". Pakistan Today. 19 March 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2022.
- ^ Ebrahim, Zofeen T. (23 January 2020). "Karachi's green buses to be powered by dung". Dawn. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "Red Line Bus project inches forward". The Express Tribune. 25 October 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- Ali, Kashaf (10 November 2020). "Karachi BRT Red Line Project Will Boost Pakistan's Transport Sector Sustainably: ADB". Brecorder. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- "BR-ePaper | Nov 29, 2019 | Page National News Page 5". epaper.brecorder.com. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Red Line to introduce rainwater storage system". The Express Tribune. 22 November 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Bus Operation of Green and Orange Line Bus Rapid Transit System in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan". Sindh Public Procurement Regulatory Authority. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
| Mass transit in Karachi | |
|---|---|
| |
| Metro | |
| KCR |
|
| |
| Lines in italic are under construction with planned opening year in parentheses. | |
| Bus rapid transit in Pakistan | |
|---|---|
| Operational | |
| Under Construction |
|
| Karachi | |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Geography and Climate | |
| Localities |
|
| Government and Politics | |
| Attractions | |
| Education | |
| Hospitals | |
| Economy | |
| Transport | |
| Hotels and shopping centers | |
| Sports and culture | |
| Other topics | |
| Lists | |