| Lateral vestibulospinal tract | |
|---|---|
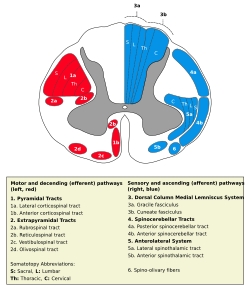 Vestibulospinal tract is 2c, in red at bottom center. Vestibulospinal tract is 2c, in red at bottom center. | |
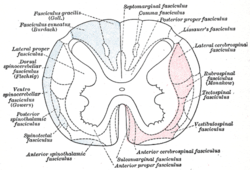 Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus vestibulospinalis lateralis |
| TA98 | A14.1.02.206 A14.1.04.131 |
| TA2 | 6113 |
| FMA | 73974 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The lateral vestibulospinal tract is one of the descending spinal tracts of the ventromedial funiculus.
The lateral part of the vestibulospinal tract is the major portion and is composed of fibers originating in the lateral, superior, and inferior vestibular nuclei (primarily the lateral). It projects ipsilaterally down to the lumbar region of the spinal cord. There it helps to maintain an upright and balanced posture by stimulating extensor motor neurons in the legs. It also innervates muscles of the trunk, thus additionally aiding in body posture. The lateral vestibular nuclei receive input from cerebellum, particularly the vestibulocerebellum, or the flocculi and nodulus. The cerebellum aids in coordinating postural adjustments.
See also
| Spinal cord | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General features | |||||||||||||||||
| Grey columns |
| ||||||||||||||||
| White matter |
| ||||||||||||||||
| External features | |||||||||||||||||
| Anatomy of the pons | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsal/ (tegmentum) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Ventral/ (base) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other grey: Raphe/ reticular | |||||||||||||||
| Physiology of balance and hearing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hearing |
| ||||
| Balance |
| ||||
This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |