 | |
| Location | Murray County, Georgia, |
|---|---|
| Region | Murray County, Georgia |
| Coordinates | 34°35′58.49″N 84°40′48.76″W / 34.5995806°N 84.6802111°W / 34.5995806; -84.6802111 |
| History | |
| Founded | 1300 CE |
| Abandoned | 1600 CE |
| Periods | Dallas phase, Lamar phase, Mouse Creek phase |
| Cultures | South Appalachian Mississippian culture |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1925, 1969 |
| Archaeologists | Warren K. Moorehead |
| Responsible body: private | |
The Little Egypt site (9 MU 102) was an archaeological site located in Murray County, Georgia, near the junction of the Coosawattee River and Talking Rock Creek. The site originally had three platform mounds surrounding a plaza and a large village area. It was destroyed during the construction of the Dam of Carters Lake in 1972. It was situated between the Ridge and Valley and Piedmont sections of the state in a flood plain. Using Mississippian culture pottery found at the site archaeologists dated the site to the Middle and Late South Appalachian culture (a regional variation of the Mississippian culture) habitation from 1300 to 1600 CE during the Dallas, Lamar, and Mouse Creek phases.
Site description
The site lay on a stretch of the Coosawattee River. It was a large village about 12.5 acres (0.051 km) with three platform mounds and a plaza. Two of the mounds were over 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) in height. The main mound was built up in four stages over the course of many years. Each stage may have represented the inter-generational change from a chief to his successor. Sometime around 1475 A.D. the site became the capital of a paramount chiefdom ruling over numerous other local villages.
Coosa capital
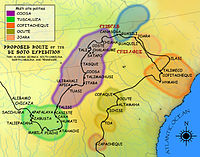
The Coosa chiefdom encountered by the Hernando de Soto expedition had its capital at the Little Egypt site. De Soto and his expedition entered the Coosa chiefdom in 1540. Chroniclers recorded that the chiefdom then consisted of eight villages. Archaeologists have identified the remains of seven of these. The population of the Coosa chiefdom is thought to have been between about 2,500 to 4,650 people. The chief of Coosa ruled over a significantly wider confederation of other chiefdoms, whose territory spread 400 miles along the Appalachian Mountains across northern Georgia into eastern Tennessee and central Alabama, and whose populations totaled in the tens of thousands. This "paramount chiefdom consisted of seven or more smaller chiefdoms, representing about 50,000 people."
Excavations
The Little Egypt site was excavated twice, once by Warren K. Moorehead in 1925 and again by David Hally (in association with the University of Georgia) in 1969. The site had been damaged by farming in the area since European settlement as well as erosion due to the water sources nearby. In the historic period, Creeks then Cherokees were known to inhabit the general area, but not the mounds themselves. A.R. Kelly surveyed this location and excavated sites nearby. Hally and his team excavated several pits, 5 feet (1.5 m) by 10 feet (3.0 m) by 3 feet (0.91 m) and several trenches 3 feet (0.91 m) in width. The site consisted of two mounds and a village nearby. Mound A was 9 feet (2.7 m) in height and Mound B was 6 feet (1.8 m) in height at the time of Hally's excavation.
Features uncovered included several smudge pits for deer hide, layers of ash with food pieces in it, including both plants and animals (with an emphasis on acorns), and several hearths. The burned bone chips found in the area included: fresh water mussel shells, fish, turtle, birds (especially turkey), deer, black bear, beaver, bobcat, opossum, raccoon, and squirrel. The species were not evenly distributed throughout the site—only a limited number of them appeared in the mounds, suggesting a hierarchy of foodstuffs.
Some artifacts unburied during the process of excavation include: columella beads, cut and ground antler, bone awls, a shell mask, brass rings, and copper plate fragments. Some worked stone tools were found. Rock flakes, blades, points, and bifaces were also found. Twenty distinct types of pottery sherds were found throughout the site, falling into the basic categories of Woodland, Woodstock, and Lamar designs.
Several time periods were represented in the excavation. See table below.
| Time Period | Artifacts and Features Attributed to that Period |
|---|---|
| Early and Middle Woodland | pottery shards |
| Woodstock | shards and wall trenches |
| Little Egypt | shards, "at least one mound structure and habitable zone" |
| Barnett | shards, "abundant structures," middens, and "one, possibly two mounds and a large habitation area" |
See also
- Sixtoe Mound (9 MU 100)
- Bell Field Mound Site (9 MU 101)
- King Archaeological Site
References
- ^ "Late Prehistoric/Early Historic Chiefdoms (ca. A.D. 1300-1850)". New Georgia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ^ Hally, David; Beverly Cooper; Janet Roth (1978), Archeological Investigation of the Little Egypt Site (9Mu102), Murray County, Georgia, 1969 Season, University of Georgia Laboratory of Archaeology Series
- Hudson, Charles M. (1997). Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun. University of Georgia Press. pp. 185–219. ISBN 9780820318882.
External links
| Pre-Columbian North America | |
|---|---|
| Archaeological cultures |
|
| Archaeological sites |
|
| Human remains | |
| Miscellaneous |
|
| |