| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Secunderabad–Danapur Express" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Overview | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service type | Superfast | ||||
| Locale | Telangana, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh & Bihar | ||||
| Current operator(s) | South Central Railway | ||||
| Route | |||||
| Termini | Danapur (DNR) Secunderabad (SC) | ||||
| Stops | 26 | ||||
| Distance travelled | 1,829 km (1,136 mi) | ||||
| Average journey time | 33 hours 15 minutes | ||||
| Service frequency | Daily | ||||
| Train number(s) | 12791 / 12792 | ||||
| On-board services | |||||
| Class(es) | AC 2 tier, AC 3 tier, Sleeper Class, General Unreserved | ||||
| Seating arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Sleeping arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Catering facilities | Available | ||||
| Observation facilities | Large windows | ||||
| Baggage facilities | Available | ||||
| Other facilities | Below the seats | ||||
| Technical | |||||
| Rolling stock | LHB coach | ||||
| Track gauge | Broad Gauge | ||||
| Operating speed | 65 km/h (40 mph) average including halts. | ||||
| |||||
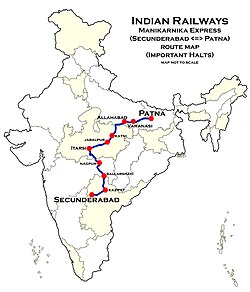
The 12791 / 12792 Secunderabad–Danapur Superfast Express is a daily train operated by Indian Railways between Secunderabad and Danapur via Varanasi Junction. Secunderabad–Danapur Express was earlier known as Manikarnika Express and Patna Express.
It is the highest earning train of Indian railways
Name
The train was initially running between Secunderabad and Varanasi and in 2004 as weekly with numbering 7091 and 7092. The train was extended to Patna during Nitish Kumar's regime. The train served Andhra Pradesh pilgrims to visit Varanasi and Ayodhya and Sarnath near Varanasi. The train gets its name from one of the famous Ghats of Varanasi, i.e. Manikarnika Ghat.
This train served historically as second alternative to visit North India after 12721UP/12722Dn Dakshin Express and 12723UP/12724DN Telangana Express along with other trains like 12590UP/12589DN Gorakhpur–Secunderabad Express and Bangalore Express.
Secunderabad Express will stop at Ara Junction from 10 September 2015.
Historical significance
The train was introduced long back in 1985 as a biweekly train between Tirupati and Varanasi with a typical numbering of "7489 Tirupati–Varanas Express" and "7490 Varanasi–Tirupati Express" with slip coach service of two sleeper coaches between Hyderabad and Varanasi with amalgamation/bifurcation at Kazipet Junction with Dakshin Express. Though the train gained importance, due to some political and administration influences, it got extended to Cochin Harbour Terminus and with the reduction of frequency from biweekly to weekly, via Tirupati through Renigunta Junction.
A demand of new train between Hyderabad and Varanasi had been approved by Indian Railways and a new train between "7091" Secunderabad–Varanasi Express and "7092" Varanasi–Secunderabad Express was flagged off as biweekly in 1987. Consequently, the same coaches and rake composition is used as "7089" Cochin–Varanasi Express via Tirupati and "7090" Varanasi–Tirupati Express via Tirupati by cancelling "7489" and "7490" numbering.
Route & halts
- Secunderabad
- Kazipet
- Peddapalli
- Ramagundam
- Mancherial
- Bellampally
- Balharshah
- Chandrapur
- Sewagram
- Nagpur
- Katol
- Betul
- Ghoradongri
- Itarsi Junction
- Jabalpur Junction
- Katni
- Satna
- Prayagraj Junction
- Gyanpur Road
- Varanasi Junction
- Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhaya Junction
- Dildarnagar
- Buxar
- Ara
- Danapur railway station
Traction
It is now hauled by a Lallaguda Loco Shed-based WAP-7 electric locomotive throughout the journey.
See also
References
| Railways in Southern India | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authority | |||||||||||
| Railway companies |
| ||||||||||
| Zones and divisions |
| ||||||||||
| Workshops | |||||||||||
| Depots |
| ||||||||||
| Lines |
| ||||||||||
| Passenger trains | |||||||||||
| Stations |
| ||||||||||
| Suburban and metro |
| ||||||||||
| Accidents and incidents | |||||||||||
| Related articles | |||||||||||
| Railways in Northern India | |
|---|---|
| National network/ trunk lines | |
| Branch lines/ sections |
|
| Urban and suburban rail transport | |
| Heritage railways | |
| Monorails | |
| Defunct lines | |
| Manufacturing units and workshops | |
| Railway companies |
|
| See also | |