In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the fetch. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples to waves over 30 m (100 ft) high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth.
When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch and no longer being affected by the local wind, wind waves are called swells and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy example of this is waves generated south of Tasmania during heavy winds that will travel across the Pacific to southern California, producing desirable surfing conditions. Wind waves in the ocean are also called ocean surface waves and are mainly gravity waves, where gravity is the main equilibrium force.
Wind waves have a certain amount of randomness: subsequent waves differ in height, duration, and shape with limited predictability. They can be described as a stochastic process, in combination with the physics governing their generation, growth, propagation, and decay – as well as governing the interdependence between flow quantities such as the water surface movements, flow velocities, and water pressure. The key statistics of wind waves (both seas and swells) in evolving sea states can be predicted with wind wave models.
Although waves are usually considered in the water seas of Earth, the hydrocarbon seas of Titan may also have wind-driven waves. Waves in bodies of water may also be generated by other causes, both at the surface and underwater (such as watercraft, animals, waterfalls, landslides, earthquakes, bubbles, and impact events).
Formation





The great majority of large breakers seen at a beach result from distant winds. Five factors influence the formation of the flow structures in wind waves:
- Wind speed or strength relative to wave speed – the wind must be moving faster than the wave crest for energy transfer to the wave.
- The uninterrupted distance of open water over which the wind blows without significant change in direction (called the fetch)
- Width of the area affected by fetch (at a right angle to the distance)
- Wind duration – the time for which the wind has blown over the water.
- Water depth
All of these factors work together to determine the size of the water waves and the structure of the flow within them.
The main dimensions associated with wave propagation are:
- Wave height (vertical distance from trough to crest)
- Wave length (distance from crest to crest in the direction of propagation)
- Wave period (time interval between arrival of consecutive crests at a stationary point)
- Wave direction or azimuth (predominantly driven by wind direction)
A fully developed sea has the maximum wave size theoretically possible for a wind of specific strength, duration, and fetch. Further exposure to that specific wind could only cause a dissipation of energy due to the breaking of wave tops and formation of "whitecaps". Waves in a given area typically have a range of heights. For weather reporting and for scientific analysis of wind wave statistics, their characteristic height over a period of time is usually expressed as significant wave height. This figure represents an average height of the highest one-third of the waves in a given time period (usually chosen somewhere in the range from 20 minutes to twelve hours), or in a specific wave or storm system. The significant wave height is also the value a "trained observer" (e.g. from a ship's crew) would estimate from visual observation of a sea state. Given the variability of wave height, the largest individual waves are likely to be somewhat less than twice the reported significant wave height for a particular day or storm.
Wave formation on an initially flat water surface by wind is started by a random distribution of normal pressure of turbulent wind flow over the water. This pressure fluctuation produces normal and tangential stresses in the surface water, which generates waves. It is usually assumed for the purpose of theoretical analysis that:
- The water is originally at rest.
- The water is not viscous.
- The water is irrotational.
- There is a random distribution of normal pressure to the water surface from the turbulent wind.
- Correlations between air and water motions are neglected.
The second mechanism involves wind shear forces on the water surface. John W. Miles suggested a surface wave generation mechanism that is initiated by turbulent wind shear flows based on the inviscid Orr–Sommerfeld equation in 1957. He found the energy transfer from the wind to the water surface is proportional to the curvature of the velocity profile of the wind at the point where the mean wind speed is equal to the wave speed. Since the wind speed profile is logarithmic to the water surface, the curvature has a negative sign at this point. This relation shows the wind flow transferring its kinetic energy to the water surface at their interface.
Assumptions:
- two-dimensional parallel shear flow
- incompressible, inviscid water and wind
- irrotational water
- slope of the displacement of the water surface is small
Generally, these wave formation mechanisms occur together on the water surface and eventually produce fully developed waves.
For example, if we assume a flat sea surface (Beaufort state 0), and a sudden wind flow blows steadily across the sea surface, the physical wave generation process follows the sequence:
- Turbulent wind forms random pressure fluctuations at the sea surface. Ripples with wavelengths in the order of a few centimeters are generated by the pressure fluctuations. (The Phillips mechanism)
- The winds keep acting on the initially rippled sea surface causing the waves to become larger. As the waves grow, the pressure differences get larger causing the growth rate to increase. Finally, the shear instability expedites the wave growth exponentially. (The Miles mechanism)
- The interactions between the waves on the surface generate longer waves and the interaction will transfer wave energy from the shorter waves generated by the Miles mechanism to the waves which have slightly lower frequencies than the frequency at the peak wave magnitudes, then finally the waves will be faster than the crosswind speed (Pierson & Moskowitz).
| Conditions necessary for a fully developed sea at given wind speeds, and the parameters of the resulting waves | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind conditions | Wave size | ||||
| Wind speed in one direction | Fetch | Wind duration | Average height | Average wavelength | Average period and speed |
| 19 km/h (12 mph) | 19 km (12 mi) | 2 hr | 0.27 m (0.89 ft) | 8.5 m (28 ft) | 3.0 sec, 10.2 km/h (9.3 ft/sec) |
| 37 km/h (23 mph) | 139 km (86 mi) | 10 hr | 1.5 m (4.9 ft) | 33.8 m (111 ft) | 5.7 sec, 21.4 km/h (19.5 ft/sec) |
| 56 km/h (35 mph) | 518 km (322 mi) | 23 hr | 4.1 m (13 ft) | 76.5 m (251 ft) | 8.6 sec, 32.0 km/h (29.2 ft/sec) |
| 74 km/h (46 mph) | 1,313 km (816 mi) | 42 hr | 8.5 m (28 ft) | 136 m (446 ft) | 11.4 sec, 42.9 km/h (39.1 ft/sec) |
| 92 km/h (57 mph) | 2,627 km (1,632 mi) | 69 hr | 14.8 m (49 ft) | 212.2 m (696 ft) | 14.3 sec, 53.4 km/h (48.7 ft/sec) |
| NOTE: Most of the wave speeds calculated from the wave length divided by the period are proportional to the square root of the wave length. Thus, except for the shortest wave length, the waves follow the deep water theory. The 28 ft long wave must be either in shallow water or intermediate depth. | |||||
Types

Three different types of wind waves develop over time:
- Capillary waves, or ripples, dominated by surface tension effects.
- Gravity waves, dominated by gravitational and inertial forces.
- Seas, raised locally by the wind.
- Swells, which have traveled away from where they were raised by the wind, and have to a greater or lesser extent dispersed.
Ripples appear on smooth water when the wind blows, but will die quickly if the wind stops. The restoring force that allows them to propagate is surface tension. Sea waves are larger-scale, often irregular motions that form under sustained winds. These waves tend to last much longer, even after the wind has died, and the restoring force that allows them to propagate is gravity. As waves propagate away from their area of origin, they naturally separate into groups of common direction and wavelength. The sets of waves formed in this manner are known as swells. The Pacific Ocean is 19,800 km (12,300 mi) from Indonesia to the coast of Colombia and, based on an average wavelength of 76.5 m (251 ft), would have ~258,824 swells over that width.
It is sometimes alleged that out of a set of waves, the seventh wave in a set is always the largest; while this isn't the case, the waves in the middle of a given set tend to be larger than those before and after them.
Individual "rogue waves" (also called "freak waves", "monster waves", "killer waves", and "king waves") much higher than the other waves in the sea state can occur. In the case of the Draupner wave, its 25 m (82 ft) height was 2.2 times the significant wave height. Such waves are distinct from tides, caused by the Moon and Sun's gravitational pull, tsunamis that are caused by underwater earthquakes or landslides, and waves generated by underwater explosions or the fall of meteorites—all having far longer wavelengths than wind waves.
The largest ever recorded wind waves are not rogue waves, but standard waves in extreme sea states. For example, 29.1 m (95 ft) high waves were recorded on the RRS Discovery in a sea with 18.5 m (61 ft) significant wave height, so the highest wave was only 1.6 times the significant wave height. The biggest recorded by a buoy (as of 2011) was 32.3 m (106 ft) high during the 2007 typhoon Krosa near Taiwan.
Spectrum

Ocean waves can be classified based on: the disturbing force that creates them; the extent to which the disturbing force continues to influence them after formation; the extent to which the restoring force weakens or flattens them; and their wavelength or period. Seismic sea waves have a period of about 20 minutes, and speeds of 760 km/h (470 mph). Wind waves (deep-water waves) have a period up to about 20 seconds.
| Wave type | Typical wavelength | Disturbing force | Restoring force |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capillary wave | < 2 cm | Wind | Surface tension |
| Wind wave | 60–150 m (200–490 ft) | Wind over ocean | Gravity |
| Seiche | Large, variable; a function of basin size | Change in atmospheric pressure, storm surge | Gravity |
| Seismic sea wave (tsunami) | 200 km (120 mi) | Faulting of sea floor, volcanic eruption, landslide | Gravity |
| Tide | Half the circumference of Earth | Gravitational attraction, rotation of Earth | Gravity |
The speed of all ocean waves is controlled by gravity, wavelength, and water depth. Most characteristics of ocean waves depend on the relationship between their wavelength and water depth. Wavelength determines the size of the orbits of water molecules within a wave, but water depth determines the shape of the orbits. The paths of water molecules in a wind wave are circular only when the wave is traveling in deep water. A wave cannot "feel" the bottom when it moves through water deeper than half its wavelength because too little wave energy is contained in the water movement below that depth. Waves moving through water deeper than half their wavelength are known as deep-water waves. On the other hand, the orbits of water molecules in waves moving through shallow water are flattened by the proximity of the sea bottom surface. Waves in water shallower than 1/20 their original wavelength are known as shallow-water waves. Transitional waves travel through water deeper than 1/20 their original wavelength but shallower than half their original wavelength.
In general, the longer the wavelength, the faster the wave energy will move through the water. The relationship between the wavelength, period and velocity of any wave is:
where C is speed (celerity), L is the wavelength, and T is the period (in seconds). Thus the speed of the wave derives from the functional dependence of the wavelength on the period (the dispersion relation).
The speed of a deep-water wave may also be approximated by:
where g is the acceleration due to gravity, 9.8 meters (32 feet) per second squared. Because g and π (3.14) are constants, the equation can be reduced to:
when C is measured in meters per second and L in meters. In both formulas the wave speed is proportional to the square root of the wavelength.
The speed of shallow-water waves is described by a different equation that may be written as:
where C is speed (in meters per second), g is the acceleration due to gravity, and d is the depth of the water (in meters). The period of a wave remains unchanged regardless of the depth of water through which it is moving. As deep-water waves enter the shallows and feel the bottom, however, their speed is reduced, and their crests "bunch up", so their wavelength shortens.
Spectral models
Sea state can be described by the sea wave spectrum or just wave spectrum . It is composed of a wave height spectrum (WHS) and a wave direction spectrum (WDS) . Many interesting properties about the sea state can be found from the wave spectra.
WHS describes the spectral density of wave height variance ("power") versus wave frequency, with dimension . The relationship between the spectrum and the wave amplitude for a wave component is:
Some WHS models are listed below.
- The International Towing Tank Conference (ITTC) recommended spectrum model for fully developed sea (ISSC spectrum/modified Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum):
- ITTC recommended spectrum model for limited fetch (JONSWAP spectrum)
- where
- (The latter model has since its creation improved based on the work of Phillips and Kitaigorodskii to better model the wave height spectrum for high wavenumbers.)
As for WDS, an example model of might be:
Thus the sea state is fully determined and can be recreated by the following function where is the wave elevation, is uniformly distributed between 0 and , and is randomly drawn from the directional distribution function
Shoaling and refraction

As waves travel from deep to shallow water, their shape changes (wave height increases, speed decreases, and length decreases as wave orbits become asymmetrical). This process is called shoaling.
Wave refraction is the process that occurs when waves interact with the sea bed to slow the velocity of propagation as a function of wavelength and period. As the waves slow down in shoaling water, the crests tend to realign at a decreasing angle to the depth contours. Varying depths along a wave crest cause the crest to travel at different phase speeds, with those parts of the wave in deeper water moving faster than those in shallow water. This process continues while the depth decreases, and reverses if it increases again, but the wave leaving the shoal area may have changed direction considerably. Rays—lines normal to wave crests between which a fixed amount of energy flux is contained—converge on local shallows and shoals. Therefore, the wave energy between rays is concentrated as they converge, with a resulting increase in wave height.
Because these effects are related to a spatial variation in the phase speed, and because the phase speed also changes with the ambient current—due to the Doppler shift—the same effects of refraction and altering wave height also occur due to current variations. In the case of meeting an adverse current the wave steepens, i.e. its wave height increases while the wavelength decreases, similar to the shoaling when the water depth decreases.
Breaking


Some waves undergo a phenomenon called "breaking". A breaking wave is one whose base can no longer support its top, causing it to collapse. A wave breaks when it runs into shallow water, or when two wave systems oppose and combine forces. When the slope, or steepness ratio, of a wave, is too great, breaking is inevitable.
Individual waves in deep water break when the wave steepness—the ratio of the wave height H to the wavelength λ—exceeds about 0.17, so for H > 0.17 λ. In shallow water, with the water depth small compared to the wavelength, the individual waves break when their wave height H is larger than 0.8 times the water depth h, that is H > 0.8 h. Waves can also break if the wind grows strong enough to blow the crest off the base of the wave.
In shallow water, the base of the wave is decelerated by drag on the seabed. As a result, the upper parts will propagate at a higher velocity than the base and the leading face of the crest will become steeper and the trailing face flatter. This may be exaggerated to the extent that the leading face forms a barrel profile, with the crest falling forward and down as it extends over the air ahead of the wave.
Three main types of breaking waves are identified by surfers or surf lifesavers. Their varying characteristics make them more or less suitable for surfing and present different dangers.
- Spilling, or rolling: these are the safest waves on which to surf. They can be found in most areas with relatively flat shorelines. They are the most common type of shorebreak. The deceleration of the wave base is gradual, and the velocity of the upper parts does not differ much with height. Breaking occurs mainly when the steepness ratio exceeds the stability limit.
- Plunging, or dumping: these break suddenly and can "dump" swimmers—pushing them to the bottom with great force. These are the preferred waves for experienced surfers. Strong offshore winds and long wave periods can cause dumpers. They are often found where there is a sudden rise in the seafloor, such as a reef or sandbar. Deceleration of the wave base is sufficient to cause upward acceleration and a significant forward velocity excess of the upper part of the crest. The peak rises and overtakes the forward face, forming a "barrel" or "tube" as it collapses.
- Surging: these may never actually break as they approach the water's edge, as the water below them is very deep. They tend to form on steep shorelines. These waves can knock swimmers over and drag them back into deeper water.
When the shoreline is near vertical, waves do not break but are reflected. Most of the energy is retained in the wave as it returns to seaward. Interference patterns are caused by superposition of the incident and reflected waves, and the superposition may cause localized instability when peaks cross, and these peaks may break due to instability. (see also clapotic waves)
Physics of waves
See also: Airy wave theory
Wind waves are mechanical waves that propagate along the interface between water and air; the restoring force is provided by gravity, and so they are often referred to as surface gravity waves. As the wind blows, pressure and friction perturb the equilibrium of the water surface and transfer energy from the air to the water, forming waves. The initial formation of waves by the wind is described in the theory of Phillips from 1957, and the subsequent growth of the small waves has been modeled by Miles, also in 1957.

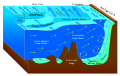
In linear plane waves of one wavelength in deep water, parcels near the surface move not plainly up and down but in circular orbits: forward above and backward below (compared to the wave propagation direction). As a result, the surface of the water forms not an exact sine wave, but more a trochoid with the sharper curves upwards—as modeled in trochoidal wave theory. Wind waves are thus a combination of transversal and longitudinal waves.
When waves propagate in shallow water, (where the depth is less than half the wavelength) the particle trajectories are compressed into ellipses.
In reality, for finite values of the wave amplitude (height), the particle paths do not form closed orbits; rather, after the passage of each crest, particles are displaced slightly from their previous positions, a phenomenon known as Stokes drift.
As the depth below the free surface increases, the radius of the circular motion decreases. At a depth equal to half the wavelength λ, the orbital movement has decayed to less than 5% of its value at the surface. The phase speed (also called the celerity) of a surface gravity wave is—for pure periodic wave motion of small-amplitude waves—well approximated by
where
- c = phase speed;
- λ = wavelength;
- d = water depth;
- g = acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface.
In deep water, where , so and the hyperbolic tangent approaches , the speed approximates
In SI units, with in m/s, , when is measured in metres. This expression tells us that waves of different wavelengths travel at different speeds. The fastest waves in a storm are the ones with the longest wavelength. As a result, after a storm, the first waves to arrive on the coast are the long-wavelength swells.
For intermediate and shallow water, the Boussinesq equations are applicable, combining frequency dispersion and nonlinear effects. And in very shallow water, the shallow water equations can be used.
If the wavelength is very long compared to the water depth, the phase speed (by taking the limit of c when the wavelength approaches infinity) can be approximated by
On the other hand, for very short wavelengths, surface tension plays an important role and the phase speed of these gravity-capillary waves can (in deep water) be approximated by
where
- S = surface tension of the air-water interface;
- = density of the water.
When several wave trains are present, as is always the case in nature, the waves form groups. In deep water, the groups travel at a group velocity which is half of the phase speed. Following a single wave in a group one can see the wave appearing at the back of the group, growing, and finally disappearing at the front of the group.
As the water depth decreases towards the coast, this will have an effect: wave height changes due to wave shoaling and refraction. As the wave height increases, the wave may become unstable when the crest of the wave moves faster than the trough. This causes surf, a breaking of the waves.
The movement of wind waves can be captured by wave energy devices. The energy density (per unit area) of regular sinusoidal waves depends on the water density , gravity acceleration and the wave height (which, for regular waves, is equal to twice the amplitude, ):
The velocity of propagation of this energy is the group velocity.
Models
Surfers are very interested in the wave forecasts. There are many websites that provide predictions of the surf quality for the upcoming days and weeks. Wind wave models are driven by more general weather models that predict the winds and pressures over the oceans, seas, and lakes.
Wind wave models are also an important part of examining the impact of shore protection and beach nourishment proposals. For many beach areas there is only patchy information about the wave climate, therefore estimating the effect of wind waves is important for managing littoral environments.
A wind-generated wave can be predicted based on two parameters: wind speed at 10 m above sea level and wind duration, which must blow over long periods of time to be considered fully developed. The significant wave height and peak frequency can then be predicted for a certain fetch length.
Seismic signals
Main article: MicroseismOcean water waves generate seismic waves that are globally visible on seismographs. There are two principal constituents of the ocean wave-generated seismic microseism. The strongest of these is the secondary microseism which is created by ocean floor pressures generated by interfering ocean waves and has a spectrum that is generally between approximately 6–12 s periods, or at approximately half of the period of the responsible interfering waves. The theory for microseism generation by standing waves was provided by Michael Longuet-Higgins in 1950 after in 1941 Pierre Bernard suggested this relation with standing waves on the basis of observations. The weaker primary microseism, also globally visible, is generated by dynamic seafloor pressures of propagating waves above shallower (less than several hundred meters depth) regions of the global ocean. Microseisms were first reported in about 1900, and seismic records provide long-term proxy measurements of seasonal and climate-related large-scale wave intensity in Earth's oceans including those associated with anthropogenic global warming.
See also
- Airy wave theory – Fluid dynamics theory on the propagation of gravity waves
- Breakwater (structure) – Coastal defense structure
- Boussinesq approximation (water waves) – Approximation valid for weakly non-linear and fairly long waves
- Clapotis – Non-breaking standing wave pattern
- Cross sea – Sea state with two wave systems traveling at oblique angles
- Gravity wave – Wave where gravity is the main restoring force
- Internal wave – Type of gravity waves that oscillate within a fluid medium
- Luke's variational principle – Mathematics of surface waves on a fluid
- Mild-slope equation – Physics phenomenon and formula
- Rogue wave – Unexpectedly large transient ocean surface wave
- Shallow water equations – Set of partial differential equations that describe the flow below a pressure surface in a fluid
- Tsunami – Series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water
- Wave power – Transport of energy by wind waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work
- Wave radar – Technology for measuring surface waves on water
- Wave setup – The increase in mean water level due to the presence of breaking waves
- Waves and shallow water – Effect of shallow water on a surface gravity wave
References
- Tolman, H. L. (23 June 2010). Mahmood, M.F. (ed.). CBMS Conference Proceedings on Water Waves: Theory and Experiment (PDF). Howard University, US, 13–18 May 2008: World Scientific Publications. ISBN 978-981-4304-23-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Holthuijsen (2007), page 5.
- Lorenz, R. D.; Hayes, A. G. (2012). "The Growth of Wind-Waves in Titan's Hydrocarbon Seas". Icarus. 219 (1): 468–475. Bibcode:2012Icar..219..468L. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2012.03.002.
- Barnes, Jason W.; Sotin, Christophe; Soderblom, Jason M.; Brown, Robert H.; Hayes, Alexander G.; Donelan, Mark; Rodriguez, Sebastien; Mouélic, Stéphane Le; Baines, Kevin H.; McCord, Thomas B. (2014-08-21). "Cassini/VIMS observes rough surfaces on Titan's Punga Mare in specular reflection". Planetary Science. 3 (1): 3. Bibcode:2014PlSci...3....3B. doi:10.1186/s13535-014-0003-4. ISSN 2191-2521. PMC 4959132. PMID 27512619.
- Heslar, Michael F.; Barnes, Jason W.; Soderblom, Jason M.; Seignovert, Benoît; Dhingra, Rajani D.; Sotin, Christophe (2020-08-14). "Tidal Currents Detected in Kraken Mare Straits from Cassini VIMS Sun Glitter Observations". The Planetary Science Journal. 1 (2): 35. arXiv:2007.00804. Bibcode:2020PSJ.....1...35H. doi:10.3847/PSJ/aba191. ISSN 2632-3338. S2CID 220301577.
- Young, I. R. (1999). Wind generated ocean waves. Elsevier. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-08-043317-2.
- Weisse, Ralf; von Storch, Hans (2008). Marine climate change: Ocean waves, storms and surges in the perspective of climate change. Springer. p. 51. ISBN 978-3-540-25316-7.
- ^ Phillips, O. M. (2006). "On the generation of waves by turbulent wind". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 2 (5): 417. Bibcode:1957JFM.....2..417P. doi:10.1017/S0022112057000233 (inactive 1 November 2024). S2CID 116675962.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Miles, John W. (2006). "On the generation of surface waves by shear flows". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 3 (2): 185. Bibcode:1957JFM.....3..185M. doi:10.1017/S0022112057000567 (inactive 1 November 2024). S2CID 119795395.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - "Chapter 16, Ocean Waves". Archived from the original on 2016-05-11. Retrieved 2013-11-12.
- Hasselmann, K.; et al. (1973). "Measurements of wind-wave growth and swell decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP)". Ergnzungsheft zur Deutschen Hydrographischen Zeitschrift Reihe A. 8 (12): 95. hdl:10013/epic.20654.
- Pierson, Willard J.; Moskowitz, Lionel (15 December 1964). "A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii". Journal of Geophysical Research. 69 (24): 5181–5190. Bibcode:1964JGR....69.5181P. doi:10.1029/JZ069i024p05181.
- "Know the risks: Waves". Royal National Lifeboat Institution. Retrieved 31 August 2024.
- Holliday, Naomi P.; Yelland, Margaret J.; Pascal, Robin; Swail, Val R.; Taylor, Peter K.; Griffiths, Colin R.; Kent, Elizabeth (2006). "Were extreme waves in the Rockall Trough the largest ever recorded?". Geophysical Research Letters. 33 (L05613). Bibcode:2006GeoRL..33.5613H. doi:10.1029/2005GL025238.
- P. C. Liu; H. S. Chen; D.-J. Doong; C. C. Kao; Y.-J. G. Hsu (11 June 2008). "Monstrous ocean waves during typhoon Krosa". Annales Geophysicae. 26 (6): 1327–1329. Bibcode:2008AnGeo..26.1327L. doi:10.5194/angeo-26-1327-2008.
- Munk, Walter H. (1950). "Proceedings 1st International Conference on Coastal Engineering". Coastal Engineering Proceedings (1). Long Beach, California: ASCE: 1–4. doi:10.9753/icce.v1.1.
- Tom Garrison (2009). Oceanography: An Invitation to Marine Science (7th ed.). Yolanda Cossio. ISBN 978-0495391937.
- International Towing Tank Conference (ITTC), retrieved 11 November 2010
- International Ship and Offshore Structures Congress
- Pierson, W. J.; Moscowitz, L. (1964), "A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S A Kitaigorodskii", Journal of Geophysical Research, 69 (24): 5181–5190, Bibcode:1964JGR....69.5181P, doi:10.1029/JZ069i024p05181
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaros, K.; Vandemark, D. (July 15, 1997). "A unified directional spectrum for long and short wind-driven waves" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 102 (C7): 15781–15796. Bibcode:1997JGR...10215781E. doi:10.1029/97jc00467.
- Jefferys, E. R. (1987), "Directional seas should be ergodic", Applied Ocean Research, 9 (4): 186–191, Bibcode:1987AppOR...9..186J, doi:10.1016/0141-1187(87)90001-0
- Longuet-Higgins, M. S.; Stewart, R. W. (1964). "Radiation stresses in water waves; a physical discussion, with applications". Deep-Sea Research. 11 (4): 529–562. Bibcode:1964DSRA...11..529L. doi:10.1016/0011-7471(64)90001-4.
- Gulrez, Tauseef; Hassanien, Aboul Ella (2011-11-13). Advances in Robotics and Virtual Reality. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783642233630.
- R.J. Dean and R.A. Dalrymple (2002). Coastal processes with engineering applications. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-60275-4. p. 96–97.
- Phillips, O. M. (1957). "On the generation of waves by turbulent wind". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 2 (5): 417–445. Bibcode:1957JFM.....2..417P. doi:10.1017/S0022112057000233 (inactive 1 November 2024). S2CID 116675962.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Miles, J. W. (1957). "On the generation of surface waves by shear flows". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 3 (2): 185–204. Bibcode:1957JFM.....3..185M. doi:10.1017/S0022112057000567 (inactive 1 November 2024). S2CID 119795395.
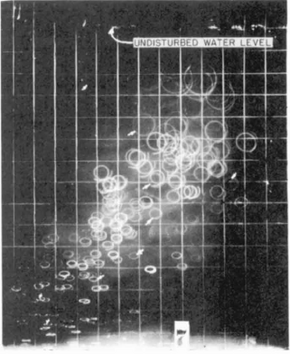
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Figure 6 from: Wiegel, R. L.; Johnson, J. W. (1950). "Proceedings 1st International Conference on Coastal Engineering". Coastal Engineering Proceedings (1). Long Beach, California: ASCE: 5–21. doi:10.9753/icce.v1.2.
- For the particle trajectories within the framework of linear wave theory, see for instance:
Phillips (1977), page 44.
Lamb, H. (1994). Hydrodynamics (6th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-45868-9. Originally published in 1879, the 6th extended edition appeared first in 1932. See §229, page 367.
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz (1986). Fluid mechanics. Course of Theoretical Physics. Vol. 6 (Second revised ed.). Pergamon Press. ISBN 978-0-08-033932-0. See page 33. - A good illustration of the wave motion according to linear theory is given by Prof. Robert Dalrymple's Java applet Archived 2017-11-14 at the Wayback Machine.
- For nonlinear waves, the particle paths are not closed, as found by George Gabriel Stokes in 1847, see the original paper by Stokes. Or in Phillips (1977), page 44: "To this order, it is evident that the particle paths are not exactly closed ... pointed out by Stokes (1847) in his classical investigation".
- Solutions of the particle trajectories in fully nonlinear periodic waves and the Lagrangian wave period they experience can for instance be found in:
J. M. Williams (1981). "Limiting gravity waves in water of finite depth". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 302 (1466): 139–188. Bibcode:1981RSPTA.302..139W. doi:10.1098/rsta.1981.0159. S2CID 122673867.
J. M. Williams (1985). Tables of progressive gravity waves. Pitman. ISBN 978-0-273-08733-5. - Carl Nordling, Jonny Östermalm (2006). Physics Handbook for Science and Engineering (Eight ed.). Studentliteratur. p. 263. ISBN 978-91-44-04453-8.
- In deep water, the group velocity is half the phase velocity, as is shown here. Another reference is Archived 2000-03-12 at the Wayback Machine.
- Wood, AMM & Fleming, CA 1981, Coastal hydraulics, John Wiley & Sons, New York
- "Peter Bormann. Seismic Signals and Noise" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2012-03-08.
- Ardhuin, Fabrice, Lucia Gualtieri, and Eleonore Stutzmann. "How ocean waves rock the Earth: two mechanisms explain seismic noise with periods 3 to 300 s." Geophys. Res. Lett. 42 (2015).
- Bernard, P. (1941). "Sur certaines proprietes de la boule etudiees a l'aide des enregistrements seismographiques". Bulletin de l'Institut Océanographique de Monaco. 800: 1–19.
- Longuet-Higgins, M. S. (1950). "A theory of the origin of microseisms". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 243 (857): 1–35. Bibcode:1950RSPTA.243....1L. doi:10.1098/rsta.1950.0012. S2CID 31828394.
- Reguero, Borja; Losada, Inigo J.; Mendez, Fernand J. (2019). "A recent increase in global wave power as a consequence of oceanic warming". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 205. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10..205R. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08066-0. PMC 6331560. PMID 30643133.
- Aster, Richard C.; McNamara, Daniel E.; Bromirski, Peter D. (2008). "Multidecadal climate-induced variability in microseisms". Seismological Research Letters. 79 (2): 94–202. Bibcode:2008SeiRL..79..194A. doi:10.1785/gssrl.79.2.194.
- Bromirski, Peter (2023). "Climate-Induced Decadal Ocean Wave Height Variability From Microseisms: 1931–2021". Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 128 (8): e2023JC019722. Bibcode:2023JGRC..12819722B. doi:10.1029/2023JC019722.
- Aster, Richard C.; Ringler, Adam T.; Anthony, Robert E.; Lee, Thomas A. (2023). "Increasing ocean wave energy observed in Earth's seismic wavefield since the late 20th century". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 6984. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-42673-w. PMC 10620394. PMID 37914695.
Scientific
- G. G. Stokes (1880). Mathematical and Physical Papers, Volume I. Cambridge University Press. pp. 197–229.
- Phillips, O. M. (1977). The dynamics of the upper ocean (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29801-8.
- Holthuijsen, Leo H. (2007). Waves in oceanic and coastal waters. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-86028-4.
- Janssen, Peter (2004). The interaction of ocean waves and wind. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-46540-3.
Other
- Rousmaniere, John (1989). The Annapolis Book of Seamanship (2nd revised ed.). Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-67447-2.
- Carr, Michael (October 1998). "Understanding Waves". Sail. pp. 38–45.
External links
| Underwater diving | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 of the wavelength on the period (the
of the wavelength on the period (the 


 . It is composed of a wave height spectrum (WHS)
. It is composed of a wave height spectrum (WHS)  and a wave direction spectrum (WDS)
and a wave direction spectrum (WDS)  . Many interesting properties about the sea state can be found from the wave spectra.
. Many interesting properties about the sea state can be found from the wave spectra.
 .
The relationship between the spectrum
.
The relationship between the spectrum  and the wave amplitude
and the wave amplitude  for a wave component
for a wave component  is:
is:






 is the wave elevation,
is the wave elevation,  is uniformly distributed between 0 and
is uniformly distributed between 0 and  , and
, and  is randomly drawn from the directional distribution function
is randomly drawn from the directional distribution function 


 , so
, so  and the hyperbolic tangent approaches
and the hyperbolic tangent approaches  , the speed
, the speed  approximates
approximates

 in m/s,
in m/s,  , when
, when  is measured in metres.
This expression tells us that waves of different wavelengths travel at different speeds. The fastest waves in a storm are the ones with the longest wavelength. As a result, after a storm, the first waves to arrive on the coast are the long-wavelength swells.
is measured in metres.
This expression tells us that waves of different wavelengths travel at different speeds. The fastest waves in a storm are the ones with the longest wavelength. As a result, after a storm, the first waves to arrive on the coast are the long-wavelength swells.


 =
=  decreases towards the
decreases towards the  and the wave height
and the wave height  (which, for regular waves, is equal to twice the
(which, for regular waves, is equal to twice the  ):
):