| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Parallel slowdown" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
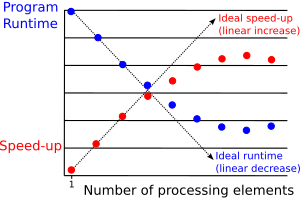
Parallel slowdown is a phenomenon in parallel computing where parallelization of a parallel algorithm beyond a certain point causes the program to run slower (take more time to run to completion).
Parallel slowdown is typically the result of a communications bottleneck. As more processor nodes are added, each processing node spends progressively more time doing communication than useful processing. At some point, the communications overhead created by adding another processing node surpasses the increased processing power that node provides, and parallel slowdown occurs.
Parallel slowdown occurs when the algorithm requires significant communication, particularly of intermediate results. Some problems, known as embarrassingly parallel problems, do not require such communication, and thus are not affected by slowdown.
This computer science article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
| Parallel computing | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Levels | |
| Multithreading | |
| Theory | |
| Elements | |
| Coordination | |
| Programming | |
| Hardware | |
| APIs | |
| Problems | |
References
- Kukanov, Alexey (2008-03-04). "Why a simple test can get parallel slowdown". Retrieved 2015-02-15.
See also
- Mythical man month, an analogous situation for a team programmers where productivity is affected by human communication.