 | |
| Original author(s) | Dr. Fred Tracy |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Flownet software |
| License | Free |
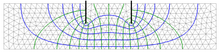
SEEP2D is a 2D seepage analysis program written by Dr. Fred Tracy of the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The program is used to analyze water seepage, typically through dams and levees or under sheet piles. "The model is internationally known in the engineering community as a model for complicated seepage analysis of dams and levees." It has been shown to have acceptable accuracy compared with experimental results.
Features
SEEP2D has the following features:
- Steady-state
- 2D profiles (XZ)
- Finite-element unstructured mesh
- Confined or unconfined models
- Automatic mesh truncation on phreatic surface (optional)
- Flow modeling in both saturated and unsaturated regions (optional)
- Support for nonhomogeneous and anisotropic soil conditions
- Output of total head, flow vectors
- Output of everything necessary to create a flownet

Related software
- GMS - has a pre and post processor for SEEP2D.
- UTEXAS - slope stability analysis software that can use SEEP2D results.
References
- Corcoran, Maureen K. (July 2011), Initial Research into the Effects of Woody Vegetation on Levees (PDF), vol. III of V (Numerical Model Simulation ed.), US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center
- Bahzad MA, Noori; Ismaeel, Khaleel S. (February 2011), Evaluation of Seepage and Stability of Duhok Dam (PDF), University of Duhok College of Engineering
- Jones, Norman L. (1999), SEEP2D Primer, Environmental Modeling Research Laboratory, Brigham Young University
| Geotechnical engineering | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offshore geotechnical engineering | |||||||
| Investigation and instrumentation | |||||||
| Soil |
| ||||||
| Structures (Interaction) |
| ||||||
| Mechanics |
| ||||||
| Numerical analysis software | |||||||
| Related fields | |||||||