In statistics, scaled correlation is a form of a coefficient of correlation applicable to data that have a temporal component such as time series. It is the average short-term correlation. If the signals have multiple components (slow and fast), scaled coefficient of correlation can be computed only for the fast components of the signals, ignoring the contributions of the slow components. This filtering-like operation has the advantages of not having to make assumptions about the sinusoidal nature of the signals.
For example, in the studies of brain signals researchers are often interested in the high-frequency components (beta and gamma range; 25–80 Hz), and may not be interested in lower frequency ranges (alpha, theta, etc.). In that case scaled correlation can be computed only for frequencies higher than 25 Hz by choosing the scale of the analysis, s, to correspond to the period of that frequency (e.g., s = 40 ms for 25 Hz oscillation).
Definition
Scaled correlation between two signals is defined as the average correlation computed across short segments of those signals. First, it is necessary to determine the number of segments that can fit into the total length of the signals for a given scale :
Next, if is Pearson's coefficient of correlation for segment , the scaled correlation across the entire signals is computed as
Efficiency
In a detailed analysis, Nikolić et al. showed that the degree to which the contributions of the slow components will be attenuated depends on three factors, the choice of the scale, the amplitude ratios between the slow and the fast component, and the differences in their oscillation frequencies. The larger the differences in oscillation frequencies, the more efficiently will the contributions of the slow components be removed from the computed correlation coefficient. Similarly, the smaller the power of slow components relative to the fast components, the better will scaled correlation perform.
Application to cross-correlation
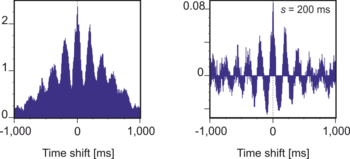
Scaled correlation can be applied to auto- and cross-correlation in order to investigate how correlations of high-frequency components change at different temporal delays. To compute cross-scaled-correlation for every time shift properly, it is necessary to segment the signals anew after each time shift. In other words, signals are always shifted before the segmentation is applied. Scaled correlation has been subsequently used to investigate synchronization hubs in the visual cortex. Scaled correlation can be also used to extract functional networks.
Advantages over filtering methods
Scaled correlation should be in many cases preferred over signal filtering based on spectral methods. The advantage of scaled correlation is that it does not make assumptions about the spectral properties of the signal (e.g., sinusoidal shapes of signals). Nikolić et al. have shown that the use of Wiener–Khinchin theorem to remove slow components is inferior to results obtained by scaled correlation. These advantages become obvious especially when the signals are non-periodic or when they consist of discrete events such as the time stamps at which neuronal action potentials have been detected.
Related methods
A detailed insight into a correlation structure across different scales can be provided by visualization using multiresolution correlation analysis.
Further information on correlation coefficient: EDUindexSee also
- Autocorrelation
- Coherence (signal processing)
- Convolution
- Correlation
- Cross-correlation
- Phase correlation
- Spectral density
- Cross-spectrum
- Wiener–Khinchin theorem
References
- ^ Nikolić D, Muresan RC, Feng W, Singer W (2012) Scaled correlation analysis: a better way to compute a cross-correlogram. European Journal of Neuroscience, pp. 1–21, doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07987.x http://www.danko-nikolic.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/Scaled-correlation-analysis.pdf
- Folias, S.E., S. Yu, A. Snyder, D. Nikolić, and J.E. Rubin (2013) Synchronisation hubs in the visual cortex may arise from strong rhythmic inhibition during gamma oscillations. European Journal of Neuroscience, 38(6): 2864–2883.
- Dolean, S., Dînşoreanu, M., Mureşan, R. C., Geiszt, A., Potolea, R., & Ţincaş, I. (2017, September). A Scaled-Correlation Based Approach for Defining and Analyzing Functional Networks. In International Workshop on New Frontiers in Mining Complex Patterns (pp. 80–92). Springer, Cham.
- Pasanen, L., & Holmström, L. (2016). "Scale space multiresolution correlation analysis for time series data." Computational Statistics, 1–22.
Free sources
- A free source code for computing scaled cross correlation and an interface for MATLAB can be downloaded here: http://www.raulmuresan.ro/sources/corrlib/
- Simple demo code in python: https://github.com/dankonikolic/Scaled-Correlation
 that can fit into the total length
that can fit into the total length  of the signals for a given scale
of the signals for a given scale  :
:

 is
is  , the scaled correlation across the entire signals
, the scaled correlation across the entire signals  is computed as
is computed as
