| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Semi-major and semi-minor axes" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Part of a series on |
| Astrodynamics |
|---|
| Orbital mechanics |
| Orbital elements |
|
Types of two-body orbits by eccentricity Transfer orbit |
| Equations |
| Celestial mechanics |
| Gravitational influences |
| N-body orbitsLagrangian points |
| Engineering and efficiency |
| Preflight engineering |
| Efficiency measures |
| Propulsive maneuvers |
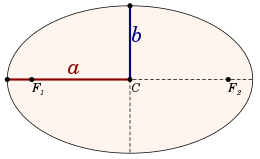
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longest semidiameter or one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (minor semiaxis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle.
The length of the semi-major axis a of an ellipse is related to the semi-minor axis's length b through the eccentricity e and the semi-latus rectum , as follows:
The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches. Thus it is the distance from the center to either vertex of the hyperbola.
A parabola can be obtained as the limit of a sequence of ellipses where one focus is kept fixed as the other is allowed to move arbitrarily far away in one direction, keeping fixed. Thus a and b tend to infinity, a faster than b.
The major and minor axes are the axes of symmetry for the curve: in an ellipse, the minor axis is the shorter one; in a hyperbola, it is the one that does not intersect the hyperbola.
Ellipse
The equation of an ellipse is
where (h, k) is the center of the ellipse in Cartesian coordinates, in which an arbitrary point is given by (x, y).
The semi-major axis is the mean value of the maximum and minimum distances and of the ellipse from a focus — that is, of the distances from a focus to the endpoints of the major axis

In astronomy these extreme points are called apsides.
The semi-minor axis of an ellipse is the geometric mean of these distances:
The eccentricity of an ellipse is defined as
so
Now consider the equation in polar coordinates, with one focus at the origin and the other on the direction:
The mean value of and , for and is
In an ellipse, the semi-major axis is the geometric mean of the distance from the center to either focus and the distance from the center to either directrix.
The semi-minor axis of an ellipse runs from the center of the ellipse (a point halfway between and on the line running between the foci) to the edge of the ellipse. The semi-minor axis is half of the minor axis. The minor axis is the longest line segment perpendicular to the major axis that connects two points on the ellipse's edge.
The semi-minor axis b is related to the semi-major axis a through the eccentricity e and the semi-latus rectum , as follows:
A parabola can be obtained as the limit of a sequence of ellipses where one focus is kept fixed as the other is allowed to move arbitrarily far away in one direction, keeping fixed. Thus a and b tend to infinity, a faster than b.
The length of the semi-minor axis could also be found using the following formula:
where f is the distance between the foci, p and q are the distances from each focus to any point in the ellipse.
Hyperbola
The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches; if this is a in the x-direction the equation is:
In terms of the semi-latus rectum and the eccentricity, we have
The transverse axis of a hyperbola coincides with the major axis.
In a hyperbola, a conjugate axis or minor axis of length , corresponding to the minor axis of an ellipse, can be drawn perpendicular to the transverse axis or major axis, the latter connecting the two vertices (turning points) of the hyperbola, with the two axes intersecting at the center of the hyperbola. The endpoints of the minor axis lie at the height of the asymptotes over/under the hyperbola's vertices. Either half of the minor axis is called the semi-minor axis, of length b. Denoting the semi-major axis length (distance from the center to a vertex) as a, the semi-minor and semi-major axes' lengths appear in the equation of the hyperbola relative to these axes as follows:
The semi-minor axis is also the distance from one of focuses of the hyperbola to an asymptote. Often called the impact parameter, this is important in physics and astronomy, and measure the distance a particle will miss the focus by if its journey is unperturbed by the body at the focus.
The semi-minor axis and the semi-major axis are related through the eccentricity, as follows:
Note that in a hyperbola b can be larger than a.
Astronomy
Orbital period
In astrodynamics the orbital period T of a small body orbiting a central body in a circular or elliptical orbit is:
where:
a is the length of the orbit's semi-major axis, is the standard gravitational parameter of the central body.Note that for all ellipses with a given semi-major axis, the orbital period is the same, disregarding their eccentricity.
The specific angular momentum h of a small body orbiting a central body in a circular or elliptical orbit is
where:
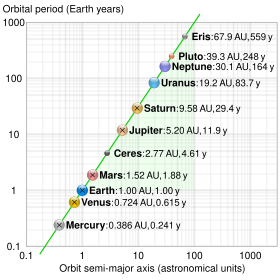
a and are as defined above, e is the eccentricity of the orbit.In astronomy, the semi-major axis is one of the most important orbital elements of an orbit, along with its orbital period. For Solar System objects, the semi-major axis is related to the period of the orbit by Kepler's third law (originally empirically derived):
where T is the period, and a is the semi-major axis. This form turns out to be a simplification of the general form for the two-body problem, as determined by Newton:
where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the central body, and m is the mass of the orbiting body. Typically, the central body's mass is so much greater than the orbiting body's, that m may be ignored. Making that assumption and using typical astronomy units results in the simpler form Kepler discovered.
The orbiting body's path around the barycenter and its path relative to its primary are both ellipses. The semi-major axis is sometimes used in astronomy as the primary-to-secondary distance when the mass ratio of the primary to the secondary is significantly large (); thus, the orbital parameters of the planets are given in heliocentric terms. The difference between the primocentric and "absolute" orbits may best be illustrated by looking at the Earth–Moon system. The mass ratio in this case is 81.30059. The Earth–Moon characteristic distance, the semi-major axis of the geocentric lunar orbit, is 384,400 km. (Given the lunar orbit's eccentricity e = 0.0549, its semi-minor axis is 383,800 km. Thus the Moon's orbit is almost circular.) The barycentric lunar orbit, on the other hand, has a semi-major axis of 379,730 km, the Earth's counter-orbit taking up the difference, 4,670 km. The Moon's average barycentric orbital speed is 1.010 km/s, whilst the Earth's is 0.012 km/s. The total of these speeds gives a geocentric lunar average orbital speed of 1.022 km/s; the same value may be obtained by considering just the geocentric semi-major axis value.
Average distance
It is often said that the semi-major axis is the "average" distance between the primary focus of the ellipse and the orbiting body. This is not quite accurate, because it depends on what the average is taken over. The time- and angle-averaged distance of the orbiting body can vary by 50-100% from the orbital semi-major axis, depending on the eccentricity.
- averaging the distance over the eccentric anomaly indeed results in the semi-major axis.
- averaging over the true anomaly (the true orbital angle, measured at the focus) results in the semi-minor axis .
- averaging over the mean anomaly (the fraction of the orbital period that has elapsed since pericentre, expressed as an angle) gives the time-average .
The time-averaged value of the reciprocal of the radius, , is .
Energy; calculation of semi-major axis from state vectors
In astrodynamics, the semi-major axis a can be calculated from orbital state vectors:
for an elliptical orbit and, depending on the convention, the same or
for a hyperbolic trajectory, and
(specific orbital energy) and
(standard gravitational parameter), where:
- v is orbital velocity from velocity vector of an orbiting object,
- r is a cartesian position vector of an orbiting object in coordinates of a reference frame with respect to which the elements of the orbit are to be calculated (e.g. geocentric equatorial for an orbit around Earth, or heliocentric ecliptic for an orbit around the Sun),
- G is the gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of the gravitating body, and
- is the specific energy of the orbiting body.
Note that for a given amount of total mass, the specific energy and the semi-major axis are always the same, regardless of eccentricity or the ratio of the masses. Conversely, for a given total mass and semi-major axis, the total specific orbital energy is always the same. This statement will always be true under any given conditions.
Semi-major and semi-minor axes of the planets' orbits
Planet orbits are always cited as prime examples of ellipses (Kepler's first law). However, the minimal difference between the semi-major and semi-minor axes shows that they are virtually circular in appearance. That difference (or ratio) is based on the eccentricity and is computed as , which for typical planet eccentricities yields very small results.
The reason for the assumption of prominent elliptical orbits lies probably in the much larger difference between aphelion and perihelion. That difference (or ratio) is also based on the eccentricity and is computed as . Due to the large difference between aphelion and perihelion, Kepler's second law is easily visualized.
| Eccentricity | Semi-major axis a (AU) | Semi-minor axis b (AU) | Difference (%) | Perihelion (AU) | Aphelion (AU) | Difference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 0.206 | 0.38700 | 0.37870 | 2.2 | 0.307 | 0.467 | 52 |
| Venus | 0.007 | 0.72300 | 0.72298 | 0.002 | 0.718 | 0.728 | 1.4 |
| Earth | 0.017 | 1.00000 | 0.99986 | 0.014 | 0.983 | 1.017 | 3.5 |
| Mars | 0.093 | 1.52400 | 1.51740 | 0.44 | 1.382 | 1.666 | 21 |
| Jupiter | 0.049 | 5.20440 | 5.19820 | 0.12 | 4.950 | 5.459 | 10 |
| Saturn | 0.057 | 9.58260 | 9.56730 | 0.16 | 9.041 | 10.124 | 12 |
| Uranus | 0.046 | 19.21840 | 19.19770 | 0.11 | 18.330 | 20.110 | 9.7 |
| Neptune | 0.010 | 30.11000 | 30.10870 | 0.004 | 29.820 | 30.400 | 1.9 |
1 AU (astronomical unit) equals 149.6 million km.
References
- ^ Lissauer, Jack J.; de Pater, Imke (2019). Fundamental Planetary Sciences: physics, chemistry, and habitability. New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 24–31. ISBN 9781108411981.
- "Major / Minor axis of an ellipse", Math Open Reference, 12 May 2013.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Ellipse". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2024-08-20.
- "7.1 Alternative Characterization". www.geom.uiuc.edu. Archived from the original on 2018-10-24. Retrieved 2007-09-06.
- "The Geometry of Orbits: Ellipses, Parabolas, and Hyperbolas". www.bogan.ca.
- "7.1 Alternative Characterization". Archived from the original on 2018-10-24. Retrieved 2007-09-06.
- Williams, Darren M. (November 2003). "Average distance between a star and planet in an eccentric orbit". American Journal of Physics. 71 (11): 1198–1200. Bibcode:2003AmJPh..71.1198W. doi:10.1119/1.1578073.
External links
- Semi-major and semi-minor axes of an ellipse With interactive animation
| Gravitational orbits | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types |
| ||||||||
| Parameters |
| ||||||||
| Maneuvers | |||||||||
| Orbital mechanics |
| ||||||||
 , as follows:
, as follows:


 and
and  of the ellipse from a focus — that is, of the distances from a focus to the endpoints of the major axis
of the ellipse from a focus — that is, of the distances from a focus to the endpoints of the major axis




 direction:
direction:

 and
and  , for
, for  is
is





 , corresponding to the minor axis of an ellipse, can be drawn perpendicular to the transverse axis or major axis, the latter connecting the two
, corresponding to the minor axis of an ellipse, can be drawn perpendicular to the transverse axis or major axis, the latter connecting the two  of the minor axis lie at the height of the asymptotes over/under the hyperbola's vertices. Either half of the minor axis is called the semi-minor axis, of length b. Denoting the semi-major axis length (distance from the center to a vertex) as a, the semi-minor and semi-major axes' lengths appear in the equation of the hyperbola relative to these axes as follows:
of the minor axis lie at the height of the asymptotes over/under the hyperbola's vertices. Either half of the minor axis is called the semi-minor axis, of length b. Denoting the semi-major axis length (distance from the center to a vertex) as a, the semi-minor and semi-major axes' lengths appear in the equation of the hyperbola relative to these axes as follows:



 is the
is the 


 ); thus, the orbital parameters of the planets are given in heliocentric terms. The difference between the primocentric and "absolute" orbits may best be illustrated by looking at the Earth–Moon system. The mass ratio in this case is 81.30059. The Earth–Moon characteristic distance, the semi-major axis of the geocentric lunar orbit, is 384,400 km. (Given the lunar orbit's eccentricity e = 0.0549, its semi-minor axis is 383,800 km. Thus the Moon's orbit is almost circular.) The barycentric lunar orbit, on the other hand, has a semi-major axis of 379,730 km, the Earth's counter-orbit taking up the difference, 4,670 km. The Moon's average barycentric orbital speed is 1.010 km/s, whilst the Earth's is 0.012 km/s. The total of these speeds gives a geocentric lunar average orbital speed of 1.022 km/s; the same value may be obtained by considering just the geocentric semi-major axis value.
); thus, the orbital parameters of the planets are given in heliocentric terms. The difference between the primocentric and "absolute" orbits may best be illustrated by looking at the Earth–Moon system. The mass ratio in this case is 81.30059. The Earth–Moon characteristic distance, the semi-major axis of the geocentric lunar orbit, is 384,400 km. (Given the lunar orbit's eccentricity e = 0.0549, its semi-minor axis is 383,800 km. Thus the Moon's orbit is almost circular.) The barycentric lunar orbit, on the other hand, has a semi-major axis of 379,730 km, the Earth's counter-orbit taking up the difference, 4,670 km. The Moon's average barycentric orbital speed is 1.010 km/s, whilst the Earth's is 0.012 km/s. The total of these speeds gives a geocentric lunar average orbital speed of 1.022 km/s; the same value may be obtained by considering just the geocentric semi-major axis value.
 .
. .
. , is
, is  .
.




 is the specific energy of the orbiting body.
is the specific energy of the orbiting body. , which for typical planet eccentricities yields very small results.
, which for typical planet eccentricities yields very small results.
 . Due to the large difference between aphelion and perihelion,
. Due to the large difference between aphelion and perihelion,