| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Testicular artery | |
|---|---|
 The abdominal aorta and its branches (internal spermatic vessels labeled at right) The abdominal aorta and its branches (internal spermatic vessels labeled at right) | |
 Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts (internal spermatic artery labeled vertically at center) Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts (internal spermatic artery labeled vertically at center) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Abdominal aorta |
| Vein | Testicular vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria testicularis |
| TA98 | A12.2.12.086M |
| TA2 | 4288 |
| FMA | 14758 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The testicular artery (the male gonadal artery, also called the internal spermatic arteries in older texts) is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.
It is the male equivalent of the ovarian artery. Because the testis is found in a different location than that of its female equivalent, it has a different course than the ovarian artery.
They are two slender vessels of considerable length, and arise from the front of the aorta a little below the renal arteries.
Each passes obliquely downward and lateralward behind the peritoneum, resting on the psoas major, the right lying in front of the inferior vena cava and behind the middle colic and ileocolic arteries and the terminal part of the ileum, the left behind the left colic and sigmoid arteries and the iliac colon.
Each crosses obliquely over the ureter and the lower part of the external iliac artery to reach the abdominal inguinal ring, through which it passes, and accompanies the other constituents of the spermatic cord along the inguinal canal to the scrotum, where it becomes tortuous, and divides into several branches.
Two or three of these accompany the ductus deferens, and supply the epididymis, anastomosing with the artery of the ductus deferens; others pierce the back part of the tunica albuginea, and supply the substance of the testicle.
The internal spermatic artery supplies one or two small branches to the ureter, and in the inguinal canal gives one or two twigs to the cremaster.
Clinical significance
The testicular artery may be damaged during inguinal hernia repair, possibly resulting in insiduous testicular atrophy - but not necessarily accompanied by testicular necrosis due to collateral arterial supply via the inferior epigastric, prostatic, vesical, and scrotal arteries.
Additional images
-
 Spermatic vessels
Spermatic vessels
-
 Testicular artery of a bull (steer).
Testicular artery of a bull (steer).
-
 The veins of the right half of the male pelvis.
The veins of the right half of the male pelvis.
-
 Spermatic veins.
Spermatic veins.
-
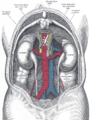 The relations of the viscera and large vessels of the abdomen (posterior view).
The relations of the viscera and large vessels of the abdomen (posterior view).
-
 Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis.
Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis.
-
 Testis, spermatic vessels and vas deferens
Testis, spermatic vessels and vas deferens
-
Testicular artery and vein
See also
References
- Schwartz's Principles of Surgery (11th ed.). 2019. p. 1620.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 611 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 611 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:36:07-0303 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Layers of the Spermatic Cord"
- inguinalregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (spermaticcord)