| Revision as of 08:40, 9 March 2021 editSol505000 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users22,990 edits →Phonemic transcription← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:22, 7 September 2024 edit undo136.57.5.2 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Sounds and pronunciation of the Luxembourgish language}} | |||
| {{selfref|For assistance with IPA transcriptions of Luxembourgish for Misplaced Pages articles, see ]}} | {{selfref|For assistance with IPA transcriptions of Luxembourgish for Misplaced Pages articles, see ]}} | ||
| {{IPA notice}} | |||
| {{Contains special characters|IPA}} | |||
| This article aims to describe the ] and ] of central ], which is regarded as the emerging ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | This article aims to describe the ] and ] of central ], which is regarded as the emerging ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | ||
| ==Consonants== | ==Consonants== | ||
| The consonant inventory of Luxembourgish is quite similar to that of Standard German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | The consonant inventory of Luxembourgish is quite similar to ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
| ! rowspan="2" | ] | ! rowspan="2" | ] | ||
| ! {{small|]}} | ! {{small|]}} | ||
| | ({{IPA link| |
| ({{IPA link|pf}}) | ||
| | {{IPA link| |
| {{IPA link|ts}} | ||
| | {{IPA link| |
| {{IPA link|tʃ}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
| ! {{small|]}} | ! {{small|]}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | ({{IPA link| |
| ({{IPA link|dz}}) | ||
| | ({{IPA link| |
| ({{IPA link|dʒ}}) | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| Line 85: | Line 86: | ||
| * {{IPA|/m, p, b/}} are ], {{IPA|/pf/}} is bilabial-labiodental, whereas {{IPA|/f, v/}} are ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | * {{IPA|/m, p, b/}} are ], {{IPA|/pf/}} is bilabial-labiodental, whereas {{IPA|/f, v/}} are ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | ||
| ** {{IPA|/pf/}} occurs only in loanwords from Standard German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} Just as among many native German-speakers, it tends to be simplified to {{IPA|}} word-initially. For example, |
** {{IPA|/pf/}} occurs only in loanwords from Standard German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} Just as among many native German-speakers, it tends to be simplified to {{IPA|}} word-initially. For example, {{lang|lb|Pflicht}} ('obligation') is pronounced {{IPA|}}, or in careful speech {{IPA|}}. | ||
| ** {{IPA|/v/}} is realized as {{IPAblink|w}} when it occurs after {{IPA|/k, ts, ʃ/}}, e.g. |
** {{IPA|/v/}} is realized as {{IPAblink|w}} when it occurs after {{IPA|/k, ts, ʃ/}}, e.g. {{lang|lb|zwee}} {{IPA|}} ('two').{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=69}} | ||
| * {{IPA|/p, t, k/}} are voiceless fortis {{IPA|}}. They are ] {{IPA|}} in most positions,{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} but not when {{IPA|/s/}} or {{IPA|/ʃ/}} precedes in the same syllable, or when another plosive or affricate follows. The fortis affricates are unaspirated and thus contrast with the lenis ones by voicing alone. | * {{IPA|/p, t, k/}} are voiceless fortis {{IPA|}}. They are ] {{IPA|}} in most positions,{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} but not when {{IPA|/s/}} or {{IPA|/ʃ/}} precedes in the same syllable, or when another plosive or affricate follows. The fortis affricates are unaspirated and thus contrast with the lenis ones by voicing alone. | ||
| ** If followed by a vowel, the fortis stops are ] and voiced to {{IPA|}}; see ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | ** If followed by a vowel, the fortis stops are ] and voiced to {{IPA|}}; see ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | ||
| * {{IPA|/b, d, ɡ/}} are unaspirated lenis, more often voiceless {{IPA|}} than voiced {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} The lenis affricates are truly voiced. | * {{IPA|/b, d, ɡ/}} are unaspirated lenis, more often voiceless {{IPA|}} than voiced {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} The lenis affricates are truly voiced. | ||
| * {{IPA|/ |
* {{IPA|/dz/}} as a phoneme appears only in a few words, such as {{lang|lb|spadséieren}} {{IPA|/ʃpɑˈdzəɪeren/}} ('to go for a walk'). {{IPA|/dʒ/}} as a phoneme occurs only in loanwords from English.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | ||
| ** |
** Phonetic {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}} occur due to voicing of word-final {{IPA|/ts/}} and {{IPA|/tʃ/}}; see ]. | ||
| * {{IPA|/s/}} and {{IPA|/z/}} only contrast between vowels. {{IPA|/s/}} does not occur word-initially except in French and English loanwords. In the oldest loans from French it is often replaced with {{IPA|/ |
* {{IPA|/s/}} and {{IPA|/z/}} only contrast between vowels. {{IPA|/s/}} does not occur word-initially except in French and English loanwords. In the oldest loans from French it is often replaced with {{IPA|/ts/}}. | ||
| * {{IPA|/ŋ, k, ɡ/}} are ], {{IPA|/j/}} is ] whereas {{IPA|/r/}} is ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | * {{IPA|/ŋ, k, ɡ/}} are ], {{IPA|/j/}} is ] whereas {{IPA|/r/}} is ].{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=67}} | ||
| ** {{IPA|/j/}} is frequently realized as {{IPAblink|ʒ}}, e.g. |
** {{IPA|/j/}} is frequently realized as {{IPAblink|ʒ}}, e.g. {{lang|lb|Juni}} {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}} ('June').{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=69}} | ||
| ** The normal realization of {{IPA|/r/}} is more often a ] {{IPAblink|ʀ}} than a fricative {{IPAblink|ʁ}}. The fricative variant is used after short vowels before consonants. If the consonant is voiceless, the fricative is also voiceless, i.e. {{IPAblink|χ}}. Older speakers use the consonantal variant {{IPA|}} also in the word-final position, where younger speakers tend to vocalize the {{IPA|/r/}} to {{IPAblink|ɐ}}, as in German and Danish.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} | ** The normal realization of {{IPA|/r/}} is more often a ] {{IPAblink|ʀ}} than a fricative {{IPAblink|ʁ}}. The fricative variant is used after short vowels before consonants. If the consonant is voiceless, the fricative is also voiceless, i.e. {{IPAblink|χ}}. Older speakers use the consonantal variant {{IPA|}} also in the word-final position, where younger speakers tend to vocalize the {{IPA|/r/}} to {{IPAblink|ɐ}}, as in German and Danish.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} | ||
| * {{IPA|/χ, ʁ/}} have two types of allophones: ] {{IPA|}} and uvular {{IPA|}}. The latter occur after back vowels, whereas the former occur in all other positions.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} | * {{IPA|/χ, ʁ/}} have two types of allophones: ] {{IPA|}} and uvular {{IPA|}}. The latter occur after back vowels, whereas the former occur in all other positions.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} | ||
| ** The {{IPAblink|ʑ}} allophone appears only in a few words intervocalically, e.g. |
** The {{IPAblink|ʑ}} allophone appears only in a few words intervocalically, e.g. {{lang|lb|Spigel}} {{IPA|}} ('mirror'), {{lang|lb|héijen}} {{IPA|}} (inflected form of {{lang|lb|héich}} {{IPA|/ˈhəɪɕ/}} 'high'). An increasing number of speakers do not distinguish between the alveolo-palatal allophones {{IPA|}} and the postalveolar phonemes {{IPA|/ʃ, ʒ/}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|pp=68–69}} | ||
| Morpheme-final {{IPA|/n/}} undergoes both internal and external ]: it is deleted unless followed by a vowel, a ] (i.e. ]) ], i.e. {{IPA|}}, or {{IPA|}}. Furthermore, some unusual consonant clusters may arise post-lexically after ]isation of the ] {{lang|lb|d'}} (for feminine, neuter and plural forms), e.g. {{lang|lb|d'Land}} {{IPA|}} ('the country') or {{lang|lb|d'Kräiz}} {{IPA|}} ('the cross').{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} Due to cluster simplification this article often disappears entirely between consonants. | |||
| ===Word-final obstruents=== | ===Word-final obstruents=== | ||
| In the word-final position the contrast between the voiceless {{IPA|/p, t, tʃ, k, f, s, ʃ, χ/}} on the one hand and the voiced {{IPA|/b, d, dʒ, ɡ, v, z, ʒ, ʁ/}} on the other is neutralized in favor of the former, unless a word-initial vowel follows in which case the obstruent is voiced and are ], that is, moved to the onset of the first syllable of the next word (the same happens with {{IPA|/ts/}}, which becomes {{IPA|}}, and the non-native affricate {{IPA|/pf/}}, which is also voiced to {{IPAblink|bv}}). For instance, {{lang|lb|se'''ch''' eens}} (phonemically {{IPA|/zeχ ˈeːns/}}) is pronounced {{IPA|}},{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|pp=68, 72}} although this article transcribes it {{IPA|}} so that it corresponds more closely to the spelling. Similarly, {{lang|lb|eng interessant Iddi}} is pronounced {{IPA|}} ('an interesting idea'), with a voiced {{IPAblink|d}}. | |||
| ===Pronunciation of the letter ''g''=== | ===Pronunciation of the letter ''g''=== | ||
| In Luxembourgish, the letter ''g'' has no fewer than nine possible pronunciations, depending both on the origin of a word and the phonetic environment. Natively, it is pronounced {{IPA|}} initially and {{IPA|}} elsewhere, the latter being devoiced to {{IPA|}} at the end of a morpheme. Words from French, English and (in a few cases) German have introduced {{IPA|}} (devoiced {{IPA|}}) in other environments, and ]'s ] indicates {{IPA|}} (devoiced {{IPA|}}). By the now very common mergers of {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}}, as well as {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}}, this number may be reduced to seven, however. | In Luxembourgish, the letter ''g'' has no fewer than nine possible pronunciations, depending both on the origin of a word and the phonetic environment. Natively, it is pronounced {{IPA|}} initially and {{IPA|}} elsewhere, the latter being devoiced to {{IPA|}} at the end of a morpheme. Words from French, English and (in a few cases) German have introduced {{IPA|}} (devoiced {{IPA|}}) in other environments, and ]'s ] indicates {{IPA|}} (devoiced {{IPA|}}). By the now very common mergers of {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}}, as well as {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}}, this number may be reduced to seven, however. | ||
| In the unstressed intervocalic position when simultaneously following {{IPA|}} and preceding {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}}, {{IPA|}} may lose its friction and become an approximant {{IPA|}}, as in |
In the unstressed intervocalic position when simultaneously following {{IPA|}} and preceding {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}}, {{IPA|}} may lose its friction and become an approximant {{IPA|}}, as in {{lang|lb|bëllegen}} {{IPA|}} 'cheap (infl.)'. This is generally not obligatory and it happens regardless of whether {{IPA|}} merges with {{IPA|}}, proving that the underlying phoneme is still {{IPA|/ʁ/}} ({{IPA|/ˈbeleʁen/}}). | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 117: | Line 118: | ||
| | native and German<br/>words | | native and German<br/>words | ||
| | stem-initially | | stem-initially | ||
| | {{lang|lb|'''g'''éi|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''géi''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | go | | go | ||
| Line 123: | Line 124: | ||
| | some German words | | some German words | ||
| | stem-internally | | stem-internally | ||
| | {{lang|lb|Dro'''g'''en|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Drogen''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | drugs | | drugs | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | French words | | French words | ||
| | stem-initially and internally before |
| stem-initially and internally before orthographic ''a'', ''o'', ''u'' or consonant | ||
| | {{lang|lb|Ne'''g'''atioun|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Negatioun''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | negation | | negation | ||
| Line 137: | Line 138: | ||
| | French and some<br/>German words | | French and some<br/>German words | ||
| | word-finally | | word-finally | ||
| | {{lang|lb|Dro'''g'''|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Drog''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | drug | | drug | ||
| Line 144: | Line 145: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|ʒ}} | | {{IPAblink|ʒ}} | ||
| | style="text-align: left;" rowspan="2" | French words | | style="text-align: left;" rowspan="2" | French words | ||
| | stem-initially and internally before |
| stem-initially and internally before orthographic ''e'', ''i'', ''y'' | ||
| | {{lang|lb|ori'''g'''inell|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''originell''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | original | | original | ||
| Line 151: | Line 152: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|ʃ}} | | {{IPAblink|ʃ}} | ||
| | word-finally before mute ''e'' | | word-finally before mute ''e'' | ||
| | {{lang|lb|Pla'''g'''e|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Plage''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | beach | | beach | ||
| Line 159: | Line 160: | ||
| | style="text-align: left;" rowspan="5" | native and most<br/>German words | | style="text-align: left;" rowspan="5" | native and most<br/>German words | ||
| | stem-internally after back vowels | | stem-internally after back vowels | ||
| | {{lang|lb|La'''g'''er|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Lager''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | store | | store | ||
| Line 165: | Line 166: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|χ}} | | {{IPAblink|χ}} | ||
| | word-finally after back vowels | | word-finally after back vowels | ||
| | ''' |
| {{lang|lb|Da'''g'''|italic=unset}} | ||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | day | | day | ||
| Line 171: | Line 172: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|ʑ}} | | {{IPAblink|ʑ}} | ||
| | stem-internally after consonants and non-back vowels | | stem-internally after consonants and non-back vowels | ||
| | {{lang|lb|Verfü'''g'''ung|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''Verfügung''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | disposal | | disposal | ||
| Line 177: | Line 178: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|j}} | | {{IPAblink|j}} | ||
| | when both unstressed and intervocalic between {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}} | | when both unstressed and intervocalic between {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}} | ||
| | {{lang|lb|bëlle'''g'''en|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''bëllegen''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | cheap (inflected) | | cheap (inflected) | ||
| Line 183: | Line 184: | ||
| | {{IPAblink|ɕ}} | | {{IPAblink|ɕ}} | ||
| | word-finally after consonants and non-back vowels | | word-finally after consonants and non-back vowels | ||
| | {{lang|lb|bëlle'''g'''|italic=unset}} | |||
| | '''bëlleg''' | |||
| | {{IPA|}} | | {{IPA|}} | ||
| | cheap | | cheap | ||
| Line 282: | Line 283: | ||
| * {{IPA|/i, iː, u, uː, o/}} are close to the corresponding cardinal vowels {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | * {{IPA|/i, iː, u, uː, o/}} are close to the corresponding cardinal vowels {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ||
| ** Some speakers may realize {{IPA|/o/}} as open-mid {{IPAblink|ɔ}}, especially before {{IPA|/r/}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ** Some speakers may realize {{IPA|/o/}} as open-mid {{IPAblink|ɔ}}, especially before {{IPA|/r/}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ||
| * {{IPA|/e/}} is most usually realized as a mid central vowel with slight rounding ({{IPAblink|ə̹}}). Before velars, it is fronted and unrounded to {{IPAblink|e}}, though this is sometimes as open as {{IPAblink|ɛ}}. Contrary to Standard German, the sequence of {{IPA|}} and a sonorant never results in a syllabic sonorant; however, Standard German spoken in Luxembourg often also lacks syllabic sonorants, so that e.g. |
* {{IPA|/e/}} is most usually realized as a mid central vowel with slight rounding ({{IPAblink|ə̹}}). Before velars, it is fronted and unrounded to {{IPAblink|e}}, though this is sometimes as open as {{IPAblink|ɛ}}. Contrary to Standard German, the sequence of {{IPA|}} and a sonorant never results in a syllabic sonorant; however, Standard German spoken in Luxembourg often also lacks syllabic sonorants, so that e.g. {{lang|de|tragen}} is pronounced {{IPA|}}, rather than {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|pp=70–71}}{{sfnp|Dudenredaktion|Kleiner|Knöbl|2015|p=39}} | ||
| * {{IPA|/eː, oː/}} are higher than close-mid {{IPA|}} and may be even as high as {{IPA|/i, u/}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | * {{IPA|/eː, oː/}} are higher than close-mid {{IPA|}} and may be even as high as {{IPA|/i, u/}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ||
| ** Before {{IPA|/r/}}, {{IPA|/eː/}} is realized as open-mid {{IPAblink|ɛː}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ** Before {{IPA|/r/}}, {{IPA|/eː/}} is realized as open-mid {{IPAblink|ɛː}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=70}} | ||
| Line 291: | Line 292: | ||
| * The nasal vowels appear only in loanwords from French, whereas the oral front rounded vowels appear in loans from both French and German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | * The nasal vowels appear only in loanwords from French, whereas the oral front rounded vowels appear in loans from both French and German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | ||
| ** The opposition between close-mid and open-mid vowels does not exist in native Luxembourgish words. In non-native words, there is a marginal contrast between the close-mid {{IPA|/øː/}} and the open-mid {{IPA|/œː/}}. | ** The opposition between close-mid and open-mid vowels does not exist in native Luxembourgish words. In non-native words, there is a marginal contrast between the close-mid {{IPA|/øː/}} and the open-mid {{IPA|/œː/}}. | ||
| ** The short non-native {{IPA|/œ/}} is distinct from {{IPA|/e/}} only on a phonemic level, as the latter is fronted and unrounded to {{IPAblink|e}} before velars (cf. the surname |
** The short non-native {{IPA|/œ/}} is distinct from {{IPA|/e/}} only on a phonemic level, as the latter is fronted and unrounded to {{IPAblink|e}} before velars (cf. the surname {{lang|de|]}} {{IPA|/ˈbœker/}}). In other positions, they are perceived as the same sound, as shown in the spelling of the word {{lang|lb|ëffentlech}} {{IPA|}} 'public' (loaned from German {{lang|de|öffentlich}} {{IPA|}}, meaning the same). For this reason, it is not differentiated from {{IPA|}} in phonetic transcription (so that {{lang|de|Böcker}} is transcribed {{IPA|}}). The long counterpart of this sound is transcribed with {{angbr IPA|œː}} in both types of transcription, which does not imply a difference in quality. | ||
| * The starting points of {{IPA|/əɪ, əʊ/}} are typically schwa-like {{IPAblink|ə}}, but the first element of {{IPA|/əɪ/}} may be more of a centralized front vowel {{IPAblink|e̞|ë̞}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=71}} | * The starting points of {{IPA|/əɪ, əʊ/}} are typically schwa-like {{IPAblink|ə}}, but the first element of {{IPA|/əɪ/}} may be more of a centralized front vowel {{IPAblink|e̞|ë̞}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=71}} | ||
| * The starting points of {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}}, {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}} as well as {{IPA|/iə/}} and {{IPA|/uə/}} are similar to the corresponding short monophthongs {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=71}} | * The starting points of {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}}, {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}} as well as {{IPA|/iə/}} and {{IPA|/uə/}} are similar to the corresponding short monophthongs {{IPA|}}.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=71}} | ||
| Line 298: | Line 299: | ||
| * {{IPA|/oɪ/}} appears only in loanwords from Standard German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | * {{IPA|/oɪ/}} appears only in loanwords from Standard German.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} | ||
| The {{IPA|/æːɪ ~ ɑɪ/}} and {{IPA|/æːʊ ~ ɑʊ/}} contrasts arose from a former lexical tone contrast: the shorter {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}} were used in words with Accent 1, whereas the lengthened {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}} were used in words with Accent 2 (see ].){{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} The contrast between the two sets of diphthongs is only partially encoded in orthography, so that the fronting {{IPA|/ɑɪ, æːɪ/}} are differentiated as {{angbr|ei}} or {{angbr|ai}} vs. {{angbr|äi}}, whereas {{angbr|au}} can stand for either {{IPA|/ɑʊ/}} or {{IPA|/æːʊ/}}. The difference is phonemic in both cases and there are minimal pairs such as |
The {{IPA|/æːɪ ~ ɑɪ/}} and {{IPA|/æːʊ ~ ɑʊ/}} contrasts arose from a former lexical tone contrast: the shorter {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}} were used in words with Accent 1, whereas the lengthened {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}} were used in words with Accent 2 (see | ||
| ].){{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=72}} The contrast between the two sets of diphthongs is only partially encoded in orthography, so that the fronting {{IPA|/ɑɪ, æːɪ/}} are differentiated as {{angbr|ei}} or {{angbr|ai}} vs. {{angbr|äi}}, whereas {{angbr|au}} can stand for either {{IPA|/ɑʊ/}} or {{IPA|/æːʊ/}}. The difference is phonemic in both cases and there are minimal pairs such as {{lang|lb|fein}} {{IPA|/fɑɪn/}} 'elevated' vs. {{lang|lb|fäin}} {{IPA|/fæːɪn/}} 'decent' and {{lang|lb|faul}} {{IPA|/fɑʊl/}} 'rotten' vs. {{lang|lb|faul}} {{IPA|/fæːʊl/}} 'lazy'. The diphthongs contrast mainly in monosyllabics. In penultimate syllables, the short {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}} occur mainly before voiced consonants and in hiatus, whereas the long {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}} occur mainly before voiceless consonants (including phonetically voiceless consonants that are voiced in their underlying form). The last traces of the dative forms of nouns show a shortening from {{IPA|/æːɪ, æːʊ/}} to {{IPA|/ɑɪ, ɑʊ/}}; compare the nominative forms {{lang|lb|Läif}} {{IPA|/læːɪv/}} 'body' and {{lang|lb|Haus}} {{IPA|/hæːʊz/}} 'house' with the corresponding dative forms {{lang|lb|Leif}} {{IPA|/lɑɪv/}} and {{lang|lb|Haus}} {{IPA|/hɑʊz/}}.{{sfnp|Keller|1961|pp=260–261}} | |||
| Additional phonetic diphthongs {{IPA|}} arise after vocalisation of {{IPA|/r/}} after long vowels. In loanwords from Standard German (such as |
Additional phonetic diphthongs {{IPA|}} arise after vocalisation of {{IPA|/r/}} after long vowels. In loanwords from Standard German (such as {{lang|de|]}} and {{lang|de|]}}) {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}} also occur. The sequence {{IPA|/aːr/}} is monophthongized to {{IPAblink|aː}}, unless a vowel follows within the same word. It is also sporadically retained in the environments where it is vocalized after other long vowels, which is why the merger with the monophthong {{IPAblink|aː}} is assumed to be phonetic, rather than phonemic.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|pp=68, 71}} This variation is not encoded in transcriptions in this article, where the phonetic output of {{IPA|/aːr/}} is consistently written with {{angbr IPA|aː}}. | ||
| {{IPA|/r/}} after short vowels is not vocalized but fricativized to {{IPAblink|ʁ}} or {{IPAblink|χ}}, depending on the voicing of the following sound (the lenis stops count as ''voiced'' despite their being unaspirated with variable voicing). The fricativization and devoicing to {{IPAblink|χ}} also occurs whenever the non-prevocalic {{IPA|/r/}} is retained between {{IPA|/aː/}} and a fortis consonant, as in |
{{IPA|/r/}} after short vowels is not vocalized but fricativized to {{IPAblink|ʁ}} or {{IPAblink|χ}}, depending on the voicing of the following sound (the lenis stops count as ''voiced'' despite their being unaspirated with variable voicing). The fricativization and devoicing to {{IPAblink|χ}} also occurs whenever the non-prevocalic {{IPA|/r/}} is retained between {{IPA|/aː/}} and a fortis consonant, as in {{lang|lb|schwaarz}} {{IPA|}} 'black', alternatively pronounced {{IPA|}}. Thus, before {{IPA|/r/}}, {{IPA|/aː/}} behaves more like a short vowel than a long one. When the following consonant is lenis or the {{IPA|/r/}} occurs before a pause, it is unclear whether the more common consonantal realization of {{IPA|/r/}} is a fricative or a trill.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=68}} | ||
| ==Sample== | ==Sample== | ||
| Line 308: | Line 310: | ||
| ===Phonemic transcription=== | ===Phonemic transcription=== | ||
| {{IPA|/ɑn der ˈtsæːɪt |
{{IPA|/ɑn der ˈtsæːɪt hun zeχ den ˈnordvɑnd ɑn ˈdzon ɡeˈʃtriden viə fun hinen ˈtsveː vuəl ˈməɪ ʃtaːrk viːr vəɪ en ˈvɑnderer deːn ɑn en ˈvaːrmen ˈmɑntel ˈɑnɡepaːk vaːr ivert den ˈveː kəʊm/}} | ||
| ===Phonetic transcription=== | ===Phonetic transcription=== | ||
| Line 314: | Line 316: | ||
| ===Orthographic version=== | ===Orthographic version=== | ||
| An der Zäit hunn sech den Nordwand an d'Sonn gestridden, wie vun hinnen zwee wuel méi staark wier, wéi e Wanderer, deen an ee waarme Mantel agepak war, iwwert de Wee koum.{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=73}} | {{lang|lb|An der Zäit hunn sech den Nordwand an d'Sonn gestridden, wie vun hinnen zwee wuel méi staark wier, wéi e Wanderer, deen an ee waarme Mantel agepak war, iwwert de Wee koum.|italic=unset}}{{sfnp|Gilles|Trouvain|2013|p=73}} | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 350: | Line 352: | ||
| |doi=10.1017/S0025100312000278 | |doi=10.1017/S0025100312000278 | ||
| |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/3C9FB295A261FD6F28D694252B06B4A3/S0025100312000278a.pdf/luxembourgish.pdf | |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/3C9FB295A261FD6F28D694252B06B4A3/S0025100312000278a.pdf/luxembourgish.pdf | ||
| |doi-access=free | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{Citation | * {{Citation | ||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 7 September 2024
Sounds and pronunciation of the Luxembourgish language For assistance with IPA transcriptions of Luxembourgish for Misplaced Pages articles, see Help:IPA/Luxembourgish This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between , / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters.This article aims to describe the phonology and phonetics of central Luxembourgish, which is regarded as the emerging standard.
Consonants
The consonant inventory of Luxembourgish is quite similar to that of Standard German.
| Labial | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Dorsal | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||
| Plosive | fortis | p | t | k | ||
| lenis | b | d | ɡ | |||
| Affricate | fortis | (pf) | ts | tʃ | ||
| lenis | (dz) | (dʒ) | ||||
| Fricative | fortis | f | s | ʃ | χ | h |
| lenis | v | z | ʒ | ʁ | ||
| Approximant | j | |||||
| Liquid | l | r | ||||
- /m, p, b/ are bilabial, /pf/ is bilabial-labiodental, whereas /f, v/ are labiodental.
- /pf/ occurs only in loanwords from Standard German. Just as among many native German-speakers, it tends to be simplified to word-initially. For example, Pflicht ('obligation') is pronounced , or in careful speech .
- /v/ is realized as [w] when it occurs after /k, ts, ʃ/, e.g. zwee ('two').
- /p, t, k/ are voiceless fortis . They are aspirated in most positions, but not when /s/ or /ʃ/ precedes in the same syllable, or when another plosive or affricate follows. The fortis affricates are unaspirated and thus contrast with the lenis ones by voicing alone.
- If followed by a vowel, the fortis stops are moved to the onset of the following syllable and voiced to ; see below.
- /b, d, ɡ/ are unaspirated lenis, more often voiceless than voiced . The lenis affricates are truly voiced.
- /dz/ as a phoneme appears only in a few words, such as spadséieren /ʃpɑˈdzəɪeren/ ('to go for a walk'). /dʒ/ as a phoneme occurs only in loanwords from English.
- Phonetic and occur due to voicing of word-final /ts/ and /tʃ/; see below.
- /s/ and /z/ only contrast between vowels. /s/ does not occur word-initially except in French and English loanwords. In the oldest loans from French it is often replaced with /ts/.
- /ŋ, k, ɡ/ are velar, /j/ is palatal whereas /r/ is uvular.
- /j/ is frequently realized as [ʒ], e.g. Juni or ('June').
- The normal realization of /r/ is more often a trill [ʀ] than a fricative [ʁ]. The fricative variant is used after short vowels before consonants. If the consonant is voiceless, the fricative is also voiceless, i.e. [χ]. Older speakers use the consonantal variant also in the word-final position, where younger speakers tend to vocalize the /r/ to [ɐ], as in German and Danish.
- /χ, ʁ/ have two types of allophones: alveolo-palatal and uvular . The latter occur after back vowels, whereas the former occur in all other positions.
- The [ʑ] allophone appears only in a few words intervocalically, e.g. Spigel ('mirror'), héijen (inflected form of héich /ˈhəɪɕ/ 'high'). An increasing number of speakers do not distinguish between the alveolo-palatal allophones and the postalveolar phonemes /ʃ, ʒ/.
Morpheme-final /n/ undergoes both internal and external sandhi: it is deleted unless followed by a vowel, a homorganic (i.e. apical) noncontinuant, i.e. , or . Furthermore, some unusual consonant clusters may arise post-lexically after cliticisation of the definite article d' (for feminine, neuter and plural forms), e.g. d'Land ('the country') or d'Kräiz ('the cross'). Due to cluster simplification this article often disappears entirely between consonants.
Word-final obstruents
In the word-final position the contrast between the voiceless /p, t, tʃ, k, f, s, ʃ, χ/ on the one hand and the voiced /b, d, dʒ, ɡ, v, z, ʒ, ʁ/ on the other is neutralized in favor of the former, unless a word-initial vowel follows in which case the obstruent is voiced and are resyllabified, that is, moved to the onset of the first syllable of the next word (the same happens with /ts/, which becomes , and the non-native affricate /pf/, which is also voiced to [bv]). For instance, sech eens (phonemically /zeχ ˈeːns/) is pronounced , although this article transcribes it so that it corresponds more closely to the spelling. Similarly, eng interessant Iddi is pronounced ('an interesting idea'), with a voiced [d].
Pronunciation of the letter g
In Luxembourgish, the letter g has no fewer than nine possible pronunciations, depending both on the origin of a word and the phonetic environment. Natively, it is pronounced initially and elsewhere, the latter being devoiced to at the end of a morpheme. Words from French, English and (in a few cases) German have introduced (devoiced ) in other environments, and French orthography's "soft g" indicates (devoiced ). By the now very common mergers of and , as well as and , this number may be reduced to seven, however.
In the unstressed intervocalic position when simultaneously following and preceding or , may lose its friction and become an approximant , as in bëllegen 'cheap (infl.)'. This is generally not obligatory and it happens regardless of whether merges with , proving that the underlying phoneme is still /ʁ/ (/ˈbeleʁen/).
| Phoneme | Allophone | Applies in | Phonetic environment | Example | IPA | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /ɡ/ | [ɡ] | native and German words |
stem-initially | géi | go | |
| some German words | stem-internally | Drogen | drugs | |||
| French words | stem-initially and internally before orthographic a, o, u or consonant | Negatioun | negation | |||
| [k] | French and some German words |
word-finally | Drog | drug | ||
| /ʒ/ | [ʒ] | French words | stem-initially and internally before orthographic e, i, y | originell | original | |
| [ʃ] | word-finally before mute e | Plage | beach | |||
| /ʁ/ | [ʁ] | native and most German words |
stem-internally after back vowels | Lager | store | |
| [χ] | word-finally after back vowels | Dag | day | |||
| [ʑ] | stem-internally after consonants and non-back vowels | Verfügung | disposal | |||
| [j] | when both unstressed and intervocalic between and | bëllegen | cheap (inflected) | |||
| [ɕ] | word-finally after consonants and non-back vowels | bëlleg | cheap |
Vowels


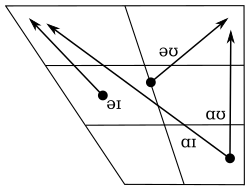
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- /i, iː, u, uː, o/ are close to the corresponding cardinal vowels .
- Some speakers may realize /o/ as open-mid [ɔ], especially before /r/.
- /e/ is most usually realized as a mid central vowel with slight rounding ([ə̹]). Before velars, it is fronted and unrounded to [e], though this is sometimes as open as [ɛ]. Contrary to Standard German, the sequence of and a sonorant never results in a syllabic sonorant; however, Standard German spoken in Luxembourg often also lacks syllabic sonorants, so that e.g. tragen is pronounced , rather than .
- /eː, oː/ are higher than close-mid and may be even as high as /i, u/.
- Before /r/, /eː/ is realized as open-mid [ɛː].
- The quality of /æ/ matches the prototypical IPA value of the ⟨æ⟩ symbol ([æ]).
- [ɐ] is the realization of a non-prevocalic, unstressed sequence /er/.
- /ɑ/ is near-open [ɑ̝].
- /aː/, a phonological back vowel (the long counterpart of /ɑ/), is phonetically near-front [a̠ː]. Sometimes, it may be as front and as high as /æ/ ([æː]), though without losing its length.
- The nasal vowels appear only in loanwords from French, whereas the oral front rounded vowels appear in loans from both French and German.
- The opposition between close-mid and open-mid vowels does not exist in native Luxembourgish words. In non-native words, there is a marginal contrast between the close-mid /øː/ and the open-mid /œː/.
- The short non-native /œ/ is distinct from /e/ only on a phonemic level, as the latter is fronted and unrounded to [e] before velars (cf. the surname Böcker /ˈbœker/). In other positions, they are perceived as the same sound, as shown in the spelling of the word ëffentlech 'public' (loaned from German öffentlich , meaning the same). For this reason, it is not differentiated from in phonetic transcription (so that Böcker is transcribed ). The long counterpart of this sound is transcribed with ⟨œː⟩ in both types of transcription, which does not imply a difference in quality.
- The starting points of /əɪ, əʊ/ are typically schwa-like [ə], but the first element of /əɪ/ may be more of a centralized front vowel [ë̞].
- The starting points of /æːɪ, æːʊ/, /ɑɪ, ɑʊ/ as well as /iə/ and /uə/ are similar to the corresponding short monophthongs .
- The first elements of /æːɪ, æːʊ/ may be phonetically short in fast speech or in unstressed syllables.
- The centering diphthongs end in the mid central unrounded area [ə].
- /oɪ/ appears only in loanwords from Standard German.
The /æːɪ ~ ɑɪ/ and /æːʊ ~ ɑʊ/ contrasts arose from a former lexical tone contrast: the shorter /ɑɪ, ɑʊ/ were used in words with Accent 1, whereas the lengthened /æːɪ, æːʊ/ were used in words with Accent 2 (see Pitch-accent language.) The contrast between the two sets of diphthongs is only partially encoded in orthography, so that the fronting /ɑɪ, æːɪ/ are differentiated as ⟨ei⟩ or ⟨ai⟩ vs. ⟨äi⟩, whereas ⟨au⟩ can stand for either /ɑʊ/ or /æːʊ/. The difference is phonemic in both cases and there are minimal pairs such as fein /fɑɪn/ 'elevated' vs. fäin /fæːɪn/ 'decent' and faul /fɑʊl/ 'rotten' vs. faul /fæːʊl/ 'lazy'. The diphthongs contrast mainly in monosyllabics. In penultimate syllables, the short /ɑɪ, ɑʊ/ occur mainly before voiced consonants and in hiatus, whereas the long /æːɪ, æːʊ/ occur mainly before voiceless consonants (including phonetically voiceless consonants that are voiced in their underlying form). The last traces of the dative forms of nouns show a shortening from /æːɪ, æːʊ/ to /ɑɪ, ɑʊ/; compare the nominative forms Läif /læːɪv/ 'body' and Haus /hæːʊz/ 'house' with the corresponding dative forms Leif /lɑɪv/ and Haus /hɑʊz/.
Additional phonetic diphthongs arise after vocalisation of /r/ after long vowels. In loanwords from Standard German (such as Lürmann and Röhr) and also occur. The sequence /aːr/ is monophthongized to [aː], unless a vowel follows within the same word. It is also sporadically retained in the environments where it is vocalized after other long vowels, which is why the merger with the monophthong [aː] is assumed to be phonetic, rather than phonemic. This variation is not encoded in transcriptions in this article, where the phonetic output of /aːr/ is consistently written with ⟨aː⟩.
/r/ after short vowels is not vocalized but fricativized to [ʁ] or [χ], depending on the voicing of the following sound (the lenis stops count as voiced despite their being unaspirated with variable voicing). The fricativization and devoicing to [χ] also occurs whenever the non-prevocalic /r/ is retained between /aː/ and a fortis consonant, as in schwaarz 'black', alternatively pronounced . Thus, before /r/, /aː/ behaves more like a short vowel than a long one. When the following consonant is lenis or the /r/ occurs before a pause, it is unclear whether the more common consonantal realization of /r/ is a fricative or a trill.
Sample
The sample text is a reading of the first sentence of The North Wind and the Sun. The transcription is based on a recording of a 26-year-old male speaker of Central Luxembourgish.
Phonemic transcription
/ɑn der ˈtsæːɪt hun zeχ den ˈnordvɑnd ɑn ˈdzon ɡeˈʃtriden viə fun hinen ˈtsveː vuəl ˈməɪ ʃtaːrk viːr vəɪ en ˈvɑnderer deːn ɑn en ˈvaːrmen ˈmɑntel ˈɑnɡepaːk vaːr ivert den ˈveː kəʊm/
Phonetic transcription
Orthographic version
An der Zäit hunn sech den Nordwand an d'Sonn gestridden, wie vun hinnen zwee wuel méi staark wier, wéi e Wanderer, deen an ee waarme Mantel agepak war, iwwert de Wee koum.
References
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 67.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 72.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 69.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 68.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 68–69.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 68, 72.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 70.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 70–71.
- Dudenredaktion, Kleiner & Knöbl (2015), p. 39.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 68, 70–71.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 71.
- Keller (1961), pp. 260–261.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 68, 71.
- Gilles & Trouvain (2013), pp. 72–73.
- ^ Gilles & Trouvain (2013), p. 73.
Bibliography
- Dudenredaktion; Kleiner, Stefan; Knöbl, Ralf (2015) , Das Aussprachewörterbuch (in German) (7th ed.), Berlin: Dudenverlag, ISBN 978-3-411-04067-4
- Gilles, Peter; Trouvain, Jürgen (2013), "Luxembourgish" (PDF), Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 43 (1): 67–74, doi:10.1017/S0025100312000278
- Keller, Rudolf Ernst (1961), German dialects: phonology and morphology, with selected texts, Manchester: Manchester University Press, ISBN 0-7190-0762-3
Further reading
- Tamura, Kenichi (2011), "The Wiltz Dialect in a Luxembourgish Drama for Children: Analysis of the Script for "Den Zauberer vun Oz" (2005)" (PDF), Bulletin of Aichi University of Education, 60: 11–21, archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04
| Phonologies of the world's languages | |
|---|---|
| |
| A–E | |
| F–L | |
| M–S | |
| T–Z | |