| Revision as of 22:09, 19 June 2005 edit82.38.178.64 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 13:18, 19 December 2024 edit undoJochen Burghardt (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users23,691 edits →Formal definition: the name is defined right here, so we don't need a wikilink for it | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Computation model defining an abstract machine}} | |||
| The '''Turing machine''' is an ] introduced in ] by ] to give a mathematically precise definition of ] or 'mechanical procedure'. | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| As such it is still widely used | |||
| ] | |||
| === '''Informal description''' === | |||
| {{Turing}} | |||
| {{Automata theory}} | |||
| A '''Turing machine''' is a ] describing an ]<ref>Minsky 1967:107 "In his 1936 paper, A. M. Turing defined the class of abstract machines that now bear his name. A Turing machine is a finite-state machine associated with a special kind of environment -- its tape -- in which it can store (and later recover) sequences of symbols," also Stone 1972:8 where the word "machine" is in quotation marks.</ref> that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules.<ref>Stone 1972:8 states "This "machine" is an abstract mathematical model", also cf. Sipser 2006:137ff that describes the "Turing machine model". Rogers 1987 (1967):13 refers to "Turing's characterization", Boolos Burgess and Jeffrey 2002:25 refers to a "specific kind of idealized machine".</ref> Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any ].<ref>Sipser 2006:137 "A Turing machine can do everything that a real computer can do".</ref> | |||
| A Turing machine is a ] made more powerful by relaxing the last-in-first-out requirement of its stack. (Interestingly, this seemingly minor relaxation enables the Turing machine to perform such a wide variety of computations that it can serve as a model for the computational capabilities of all modern computer software.) | |||
| The machine operates on an infinite<ref>Cf. Sipser 2002:137. Also, Rogers 1987 (1967):13 describes "a paper tape of infinite length in both directions". Minsky 1967:118 states "The tape is regarded as infinite in both directions". Boolos Burgess and Jeffrey 2002:25 include the possibility of "there is someone stationed at each end to add extra blank squares as needed".</ref> memory tape divided into ] cells,<ref>Cf. Rogers 1987 (1967):13. Other authors use the word "square" e.g. Boolos Burgess Jeffrey 2002:35, Minsky 1967:117, Penrose 1989:37.</ref> each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a ] of symbols called the ] of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right,<ref>Boolos Burgess Jeffry 2002:25 illustrate the machine as moving along the tape. Penrose 1989:36-37 describes himself as "uncomfortable" with an infinite tape observing that it "might be hard to shift!"; he "prefer to think of the tape as representing some external environment through which our finite device can move" and after observing that the " 'movement' is a convenient way of picturing things" and then suggests that "the device receives all its input from this environment. Some variations of the Turing machine model also allow the head to stay in the same position instead of moving or halting.</ref> or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write, which direction to move the head, and whether to halt is based on a finite table that specifies what to do for each combination of the current state and the symbol that is read. Like a real computer program, it is possible for a Turing machine to go into an ] which will never halt. | |||
| More precisely, a Turing machine consists of: | |||
| # A ''tape'' which is divided into cells, one next to the other. Each cell contains a symbol from some finite alphabet. The alphabet contains a special ''blank'' symbol (here written as '0') and one or more other symbols. The tape is assumed to be arbitrarily extendible to the left and to the right, i.e., the Turing machine is always supplied with as much tape as it needs for its computation. Cells that have not been written to before are assumed to be filled with the blank symbol. | |||
| # A ''head'' that can read and write symbols on the tape and move left and right. | |||
| # A ''state register'' that stores the state of the Turing machine. The number of different states is always finite and there is one special ''start state'' with which the state register is initialized. | |||
| # An ''action table'' (or ''transition function'') that tells the machine what symbol to write, how to move the head ('L' for one step left, and 'R' for one step right) and what its new state will be, given the symbol it has just read on the tape and the state it is currently in. If there is no entry in the table for the current combination of symbol and state then the machine will halt. | |||
| Note that every part of the machine is finite; it is the potentially unlimited amount of tape that gives it an unbounded amount of storage space. | |||
| The Turing machine was invented in 1936 by ],<ref name=Hodges-2012>{{cite book |first=Andrew | last=Hodges |author-link =Andrew Hodges |year = 2012 |title =Alan Turing: The Enigma |publisher =] |isbn=978-0-691-15564-7 |edition=The Centenary }}</ref><ref>The idea came to him in mid-1935 (perhaps, see more in the History section) after a question posed by ] in his lectures: "Was there a definite method, or as Newman put it, a "mechanical process" which could be applied to a mathematical statement, and which would come up with the answer as to whether it was provable" (Hodges 1983:93). Turing submitted his paper on 31 May 1936 to the London Mathematical Society for its ''Proceedings'' (cf. Hodges 1983:112), but it was published in early 1937 and offprints were available in February 1937 (cf. Hodges 1983:129).</ref> who called it an "a-machine" (automatic machine).<ref>See footnote in Davis 2000:151.</ref> It was Turing's doctoral advisor, ], who later coined the term "Turing machine" in a review.<ref name="mitpress.mit.edu">see note in forward to The Collected Works of Alonzo Church ({{Cite book |url=https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/collected-works-alonzo-church |title=The Collected Works of Alonzo Church |date=2019-04-23 |publisher=MIT Press |isbn=978-0-262-02564-5 |editor-last=Burge |editor-first=Tyler |location=Cambridge, MA, US |language=en |editor-last2=Enderton |editor-first2=Herbert}})</ref> With this model, Turing was able to answer two questions in the negative: | |||
| === Formal definition === | |||
| * Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape is "circular" (e.g., freezes, or fails to continue its computational task)? | |||
| ==== One-tape Turing machine ==== | |||
| * Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape ever prints a given symbol?<ref name="The Undecidable' page 119">Turing 1936 in ''The Undecidable'' 1965:132-134; Turing's definition of "circular" is found on page 119.</ref><ref name="Turing 1937 230–265">{{cite journal |first=Alan Mathison |last=Turing |title=On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the ''Entscheidungsproblem'' |journal=Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society |series=Series 2 |volume=42 |number=1 |pages=230–265 |year=1937 | doi=10.1112/plms/s2-42.1.230 |s2cid=73712 }}</ref> | |||
| More formally, a (one-tape) Turing machine is usually defined as a 6-] <math>M=(Q, \Gamma, s, b, F, \delta)</math>, where | |||
| Thus by providing a mathematical description of a very simple device capable of arbitrary computations, he was able to prove properties of computation in general—and in particular, the ] of the '']'' ('decision problem').<ref name="ReferenceA">Turing 1936 in ''The Undecidable'' 1965:145</ref> | |||
| Turing machines proved the existence of fundamental limitations on the power of mechanical computation.<ref>Sipser 2006:137 observes that "A Turing machine can do everything that a real computer can do. Nevertheless, even a Turing machine cannot solve certain problems. In a very real sense, these problems are beyond the theoretical limits of computation."</ref> While they can express arbitrary computations, their minimalist design makes them too slow for computation in practice: real-world ]s are based on different designs that, unlike Turing machines, use ]. | |||
| *<math>Q</math> is a finite set of states | |||
| *<math>\Gamma</math> is a finite set of the tape alphabet | |||
| *<math>s \in Q</math> is the initial state | |||
| *<math>b \in \Gamma</math> is the blank symbol (the only symbol allowed to occur on the tape infinitely often at any step during the computation) | |||
| *<math>F \subseteq Q</math> is the set of final or accepting states | |||
| *<math>\delta: Q \times \Gamma \rightarrow Q \times \Gamma \times \{L,R\}</math> is a ] called the transition function, where L is left shift, R is right shift. | |||
| ] is the ability for a ] or a system of instructions to simulate a Turing machine. A programming language that is Turing complete is theoretically capable of expressing all tasks accomplishable by computers; nearly all programming languages are Turing complete if the limitations of finite memory are ignored. | |||
| Definitions in the literature sometimes differ slightly, to make arguments or proofs easier or clearer, but this is always done in such a way that the resulting machine has the same computational power. For example, changing the set <math>\{L,R\}</math> to <math>\{L,R,S\}</math>, where ''S'' would allow the machine to stay on the same tape cell instead of moving left or right, does not increase the machine's computational power. | |||
| ==Overview== | |||
| ==== k-tape Turing machine ==== | |||
| A Turing machine is an idealised model of a ] (CPU) that controls all data manipulation done by a computer, with the canonical machine using sequential memory to store data. Typically, the sequential memory is represented as a tape of infinite length on which the machine can perform read and write operations. | |||
| A k-tape Turing machine can similarly be described as a 6-tuple <math>M=(Q, \Gamma, s, b, F, \delta)</math>, where | |||
| In the context of ] theory, a Turing machine (]) is capable of ] some arbitrary subset of valid strings of an ]. A set of strings which can be enumerated in this manner is called a ]. The Turing machine can equivalently be defined as a model that recognises valid input strings, rather than enumerating output strings. | |||
| *<math>Q</math> is a finite set of states | |||
| *<math>\Gamma</math> is a finite set of the tape alphabet | |||
| *<math>s \in Q</math> is the initial state | |||
| *<math>b \in \Gamma</math> is the blank symbol | |||
| *<math>F \subseteq Q</math> is the set of final or accepting states | |||
| *<math>\delta: Q \times \Gamma^k \rightarrow Q \times (\Gamma \times \{L,R,S\})^k</math> is a partial function called the transition function, where L is left shift, R is right shift, S is no shift. | |||
| Given a Turing machine ''M'' and an arbitrary string ''s'', it is generally not possible to decide whether ''M'' will eventually produce ''s''. This is due to the fact that the ] is unsolvable, which has major implications for the theoretical limits of computing. | |||
| Note that a k-tape Turing Machine is no more powerful than a standard Turing Machine. | |||
| The Turing machine is capable of processing an ], which further implies that it is capable of robustly evaluating ] in an infinite number of ways. This is famously demonstrated through ]. | |||
| == Example == | |||
| The following Turing machine has an alphabet {'0', '1'}, with 0 being the blank symbol. It expects a series of 1s on the tape, with the head initially on the leftmost 1, and doubles the 1s with a 0 in between, i.e., "111" becomes "1110111". | |||
| The set of states is {s1, s2, s3, s4, s5} and the start state is s1. | |||
| The action table is as follows. | |||
| A Turing machine that is able to simulate any other Turing machine is called a ] (UTM, or simply a universal machine). Another mathematical formalism, ], with a similar "universal" nature was introduced by ]. Church's work intertwined with Turing's to form the basis for the ]. This thesis states that Turing machines, lambda calculus, and other similar formalisms of ] do indeed capture the informal notion of ]s in ] and ] and thus provide a model through which one can reason about an ] or "mechanical procedure" in a mathematically precise way without being tied to any particular formalism. Studying the ] of Turing machines has yielded many insights into ], ], and ]. | |||
| Old Read Wr. New Old Read Wr. New | |||
| St. Sym. Sym. Mv. St. St. Sym. Sym. Mv. St. | |||
| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - | |||
| s1 1 -> 0 R s2 s4 1 -> 1 L s4 | |||
| s2 1 -> 1 R s2 s4 0 -> 0 L s5 | |||
| s2 0 -> 0 R s3 s5 1 -> 1 L s5 | |||
| s3 0 -> 1 L s4 s5 0 -> 1 R s1 | |||
| s3 1 -> 1 R s3 | |||
| ===Physical description=== | |||
| A computation of this Turing machine might for example be: | |||
| In his 1948 essay, "Intelligent Machinery", Turing wrote that his machine consists of: | |||
| (the position of the head is indicated by displaying the cell in bold face) | |||
| {{blockquote|...an unlimited memory capacity obtained in the form of an infinite tape marked out into squares, on each of which a symbol could be printed. At any moment there is one symbol in the machine; it is called the scanned symbol. The machine can alter the scanned symbol, and its behavior is in part determined by that symbol, but the symbols on the tape elsewhere do not affect the behavior of the machine. However, the tape can be moved back and forth through the machine, this being one of the elementary operations of the machine. Any symbol on the tape may therefore eventually have an innings.<ref>See the definition of "]" on ]</ref>|Turing 1948, p. 3<ref> | |||
| Step State Tape Step State Tape | |||
| {{cite report | |||
| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - | |||
| | title=Intelligent Machinery | |||
| 1 s1 '''1'''1 9 s2 10'''0'''1 | |||
| | author=A.M. Turing | |||
| 2 s2 0'''1''' 10 s3 100'''1''' | |||
| | date= Jul 1948 | |||
| 3 s2 01'''0''' 11 s3 1001'''0''' | |||
| | url=http://www.alanturing.net/Turing_archive/archive/l/l32/L32-004.html | |||
| 4 s3 010'''0''' 12 s4 100'''1'''1 | |||
| | institution=National Physical Laboratory | |||
| 5 s4 01'''0'''1 13 s4 10'''0'''11 | |||
| }} Here: p.3-4 | |||
| 6 s5 0'''1'''01 14 s5 1'''0'''011 | |||
| </ref>}} | |||
| 7 s5 '''0'''101 15 s1 11'''0'''11 | |||
| 8 s1 1'''1'''01 -- halt -- | |||
| ==Description== | |||
| The behavior of this machine can be described as a loop: | |||
| {{for|examples of Turing machines|Turing machine examples}} | |||
| it starts out in s1, replaces the first 1 with a 0, then uses s2 to move to the right, skipping over 1s and the first 0 encountered. S3 then skips over the next sequence of 1s (initially there are none) and replaces the first 0 it finds with a 1. S4 moves back to the left, skipping over 1s until it finds a 0 and switches to s5. s5 then moves to the left, skipping over 1s until it finds the 0 that was originally written by s1. | |||
| It replaces that 0 with a 1, moves one position to the right and enters s1 again for another round of the loop. | |||
| This continues until s1 finds a 0 (this is the 0 right in the middle between the two strings of 1s) at which time the machine halts. | |||
| The Turing machine mathematically models a machine that mechanically operates on a tape. On this tape are symbols, which the machine can read and write, one at a time, using a tape head. Operation is fully determined by a finite set of elementary instructions such as "in state 42, if the symbol seen is 0, write a 1; if the symbol seen is 1, change into state 17; in state 17, if the symbol seen is 0, write a 1 and change to state 6;" etc. In the original article ("]", see also ]), Turing imagines not a mechanism, but a person whom he calls the "computer", who executes these deterministic mechanical rules slavishly (or as Turing puts it, "in a desultory manner"). | |||
| == Deterministic and non-deterministic Turing machines == | |||
| If the action table has at most one entry for each combination of symbol and state then the machine is a '''deterministic Turing machine''' (DTM). If the action table contains multiple entries for a combination of symbol and state then the machine is a ''']''' (NDTM or NTM). | |||
| ] | |||
| == Universal Turing machines == | |||
| ] | |||
| Every Turing machine computes a certain fixed ] ] from the input strings over its alphabet. In that sense it behaves like a computer with a fixed program. However, as Alan Turing already described, we can encode the action table of any Turing machine in a string. Thus we might try to construct a Turing machine that expects on its tape a string describing an action table followed by a string describing the input tape, and then computes the tape that the encoded Turing machine would have computed. | |||
| As Turing showed, such a Turing machine is indeed possible and since it is able to simulate any other Turing machine it is called a ''universal Turing machine''. | |||
| More explicitly, a Turing machine consists of: | |||
| With this encoding of action tables as strings, it becomes possible in principle | |||
| * A ''tape'' divided into cells, one next to the other. Each cell contains a symbol from some finite alphabet. The alphabet contains a special blank symbol (here written as '0') and one or more other symbols. The tape is assumed to be arbitrarily extendable to the left and to the right, so that the Turing machine is always supplied with as much tape as it needs for its computation. Cells that have not been written before are assumed to be filled with the blank symbol. In some models the tape has a left end marked with a special symbol; the tape extends or is indefinitely extensible to the right. | |||
| for Turing machines to answer questions about the behavior of other Turing machines. | |||
| * A ''head'' that can read and write symbols on the tape and move the tape left and right one (and only one) cell at a time. In some models the head moves and the tape is stationary. | |||
| Most of these questions, however, are undecidable, meaning that the function in question cannot be calculated by any Turing machine. | |||
| * A ''state register'' that stores the state of the Turing machine, one of finitely many. Among these is the special ''start state'' with which the state register is initialised. These states, writes Turing, replace the "state of mind" a person performing computations would ordinarily be in. | |||
| For instance, the problem of determining whether a particular Turing machine will halt on a particular input, or on all inputs, known as the ], was shown to be undecidable in Turing's original paper. | |||
| * A finite ''table''<ref>Occasionally called an ''action table'' or '']''.</ref> of instructions<ref>Usually quintuples : q<sub>i</sub>a<sub>j</sub>→q<sub>i1</sub>a<sub>j1</sub>d<sub>k</sub>, but sometimes quadruples .</ref> that, given the ''state''(q<sub>i</sub>) the machine is currently in ''and'' the ''symbol''(a<sub>j</sub>) it is reading on the tape (the symbol currently under the head), tells the machine to do the following ''in sequence'' (for the 5-] models): | |||
| ] shows that any nontrivial question about the behavior or output of a Turing machine is undecidable. | |||
| # Either erase or write a symbol (replacing a<sub>j</sub> with a<sub>j1</sub>). | |||
| # Move the head (which is described by d<sub>k</sub> and can have values: 'L' for one step left ''or'' 'R' for one step right ''or'' 'N' for staying in the same place). | |||
| # Assume the same or a ''new state'' as prescribed (go to state q<sub>i1</sub>). | |||
| In the 4-tuple models, erasing or writing a symbol (a<sub>j1</sub>) and moving the head left or right (d<sub>k</sub>) are specified as separate instructions. The table tells the machine to (ia) erase or write a symbol ''or'' (ib) move the head left or right, ''and then'' (ii) assume the same or a new state as prescribed, but not both actions (ia) and (ib) in the same instruction. In some models, if there is no entry in the table for the current combination of symbol and state, then the machine will halt; other models require all entries to be filled. | |||
| Every part of the machine (i.e. its state, symbol-collections, and used tape at any given time) and its actions (such as printing, erasing and tape motion) is ''finite'', ''discrete'' and ''distinguishable''; it is the unlimited amount of tape and runtime that gives it an unbounded amount of ]. | |||
| If we broaden the definition to include any Turing machine that simulates some Turing-complete computational model, not just Turing machines that directly simulate other Turing machines, a universal Turing machine can be fairly simple, using just a few states and a few symbols. For example, only 2 states are needed, since a 2×18 (meaning 2 states, 18 symbols) universal Turing machine is known. | |||
| A complete list of the smallest known universal Turing machines is: 2×18, 3×10, 4×6, 5×5, 7×4, 10×3, 22×2. | |||
| These simulate a computational model called ]. | |||
| ==Formal definition== | |||
| A universal Turing machine is ]. | |||
| Following {{harvtxt|Hopcroft|Ullman|1979|p=148}}, a (one-tape) Turing machine can be formally defined as a 7-] <math>M = \langle Q, \Gamma, b, \Sigma, \delta, q_0, F \rangle</math> where | |||
| It can calculate any ], decide any ], and accept any ]. | |||
| * <math>\Gamma</math> is a finite, non-empty set of ''tape alphabet symbols''; | |||
| According to the Church-Turing thesis, the problems solvable by a universal Turing machine are exactly those problems solvable by an ''algorithm'' or an ''effective method of computation'', for any reasonable definition of those terms. | |||
| * <math>b \in \Gamma</math> is the ''blank symbol'' (the only symbol allowed to occur on the tape infinitely often at any step during the computation); | |||
| * <math>\Sigma\subseteq\Gamma\setminus\{b\}</math> is the set of ''input symbols'', that is, the set of symbols allowed to appear in the initial tape contents; | |||
| * <math>Q</math> is a finite, non-empty set of ''states''; | |||
| * <math>q_0 \in Q</math> is the ''initial state''; | |||
| * <math>F \subseteq Q</math> is the set of ''final states'' or ''accepting states''. The initial tape contents is said to be ''accepted'' by <math>M</math> if it eventually halts in a state from <math>F</math>. | |||
| * <math>\delta: (Q \setminus F) \times \Gamma \rightharpoonup Q \times \Gamma \times \{L,R\}</math> is a ] called the ''transition function'', where L is left shift, R is right shift. If <math>\delta</math> is not defined on the current state and the current tape symbol, then the machine halts;<ref>p.149; in particular, Hopcroft and Ullman assume that <math>\delta</math> is undefined on all states from <math>F</math></ref> intuitively, the transition function specifies the next state transited from the current state, which symbol to overwrite the current symbol pointed by the head, and the next head movement. | |||
| ] | |||
| A variant allows "no shift", say N, as a third element of the set of directions <math>\{L,R\}</math>. | |||
| The 7-tuple for the 3-state ] looks like this (see more about this busy beaver at ]): | |||
| * <math>Q = \{ \mbox{A}, \mbox{B}, \mbox{C}, \mbox{HALT} \}</math> (states); | |||
| * <math>\Gamma = \{ 0, 1 \}</math> (tape alphabet symbols); | |||
| * <math>b = 0</math> (blank symbol); | |||
| * <math>\Sigma = \{ 1 \}</math> (input symbols); | |||
| * <math>q_0 = \mbox{A}</math> (initial state); | |||
| * <math>F = \{ \mbox{HALT} \}</math> (final states); | |||
| * <math>\delta =</math> see state-table below (transition function). | |||
| Initially all tape cells are marked with <math>0</math>. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |+ State table for 3-state, 2-symbol busy beaver | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | Tape symbol | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state A | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state B | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state C | |||
| |- style="font-size:9pt" | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| |- | |||
| | 0 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | R | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''A''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''C''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | R | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | R | |||
| | '''HALT''' | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Additional details required to visualise or implement Turing machines== | |||
| In the words of van Emde Boas (1990), p. 6: "The set-theoretical object provides only partial information on how the machine will behave and what its computations will look like." | |||
| For instance, | |||
| * There will need to be many decisions on what the symbols actually look like, and a failproof way of reading and writing symbols indefinitely. | |||
| * The shift left and shift right operations may shift the tape head across the tape, but when actually building a Turing machine it is more practical to make the tape slide back and forth under the head instead. | |||
| * The tape can be finite, and automatically extended with blanks as needed (which is closest to the mathematical definition), but it is more common to think of it as stretching infinitely at one or both ends and being pre-filled with blanks except on the explicitly given finite fragment the tape head is on (this is, of course, not implementable in practice). The tape ''cannot'' be fixed in length, since that would not correspond to the given definition and would seriously limit the range of computations the machine can perform to those of a ] if the tape was proportional to the input size, or ] if it was strictly fixed-length. | |||
| ===Alternative definitions=== | |||
| Definitions in literature sometimes differ slightly, to make arguments or proofs easier or clearer, but this is always done in such a way that the resulting machine has the same computational power. For example, the set could be changed from <math>\{L,R\}</math> to <math>\{L,R,N\}</math>, where ''N'' ("None" or "No-operation") would allow the machine to stay on the same tape cell instead of moving left or right. This would not increase the machine's computational power. | |||
| The most common convention represents each "Turing instruction" in a "Turing table" by one of nine 5-tuples, per the convention of Turing/Davis (Turing (1936) in ''The Undecidable'', p. 126–127 and Davis (2000) p. 152): | |||
| : (definition 1): '''(q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>/E/N, L/R/N, q<sub>m</sub>)''' | |||
| :: '''(''' current state '''q<sub>i</sub>''' ''',''' symbol scanned '''S<sub>j</sub>''' ''',''' print symbol '''S<sub>k</sub>'''/erase '''E'''/none '''N''' ''',''' move_tape_one_square left '''L'''/right '''R'''/none '''N''' ''',''' new state '''q<sub>m</sub>''' ''')''' | |||
| Other authors (Minsky (1967) p. 119, Hopcroft and Ullman (1979) p. 158, Stone (1972) p. 9) adopt a different convention, with new state '''q<sub>m</sub>''' listed immediately after the scanned symbol S<sub>j</sub>: | |||
| : (definition 2): '''(q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, q<sub>m</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>/E/N, L/R/N)''' | |||
| :: '''(''' current state '''q<sub>i</sub>''' ''',''' symbol scanned '''S<sub>j</sub>''' ''',''' new state '''q<sub>m</sub>''' ''',''' print symbol '''S<sub>k</sub>'''/erase '''E'''/none '''N''' ''',''' move_tape_one_square left '''L'''/right '''R'''/none '''N''' ''')''' | |||
| For the remainder of this article "definition 1" (the Turing/Davis convention) will be used. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center" | |||
| |+ Example: state table for the 3-state 2-symbol busy beaver reduced to 5-tuples | |||
| ! Current state | |||
| ! Scanned symbol | |||
| ! Print symbol | |||
| ! Move tape | |||
| ! Final (i.e. next) state | |||
| ! 5-tuples | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''A''' | |||
| | 0 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | R | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | ('''A''', 0, 1, R, '''B''') | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''A''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''C''' | |||
| | ('''A''', 1, 1, L, '''C''') | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | 0 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''A''' | |||
| | ('''B''', 0, 1, L, '''A''') | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | R | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | ('''B''', 1, 1, R, '''B''') | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''C''' | |||
| | 0 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | L | |||
| | '''B''' | |||
| | ('''C''', 0, 1, L, '''B''') | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''C''' | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | 1 | |||
| | N | |||
| | '''H''' | |||
| | ('''C''', 1, 1, N, '''H''') | |||
| |} | |||
| In the following table, Turing's original model allowed only the first three lines that he called N1, N2, N3 (cf. Turing in ''The Undecidable'', p. 126). He allowed for erasure of the "scanned square" by naming a 0th symbol S<sub>0</sub> = "erase" or "blank", etc. However, he did not allow for non-printing, so every instruction-line includes "print symbol S<sub>k</sub>" or "erase" (cf. footnote 12 in Post (1947), ''The Undecidable'', p. 300). The abbreviations are Turing's (''The Undecidable'', p. 119). Subsequent to Turing's original paper in 1936–1937, machine-models have allowed all nine possible types of five-tuples: | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! | |||
| ! Current m-configuration<br />(Turing state) | |||
| ! Tape symbol | |||
| ! Print-operation | |||
| ! Tape-motion | |||
| ! Final m-configuration<br />(Turing state) | |||
| ! 5-tuple | |||
| ! 5-tuple comments | |||
| ! 4-tuple | |||
| |- | |||
| | N1 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Print(S<sub>k</sub>) | |||
| | Left L | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>, L, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | {{CEmpty}} "blank" = S<sub>0</sub>, 1=S<sub>1</sub>, etc. | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | N2 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Print(S<sub>k</sub>) | |||
| | Right R | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>, R, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | {{CEmpty}} "blank" = S<sub>0</sub>, 1=S<sub>1</sub>, etc. | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | N3 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Print(S<sub>k</sub>) | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>, N, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | {{CEmpty}} "blank" = S<sub>0</sub>, 1=S<sub>1</sub>, etc. | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, S<sub>k</sub>, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| |- | |||
| | 4 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | Left L | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, N, L, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, L, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| |- | |||
| | 5 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | Right R | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, N, R, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, R, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| |- | |||
| | 6 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, N, N, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | Direct "jump" | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, N, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| |- | |||
| | 7 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Erase | |||
| | Left L | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, E, L, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | 8 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Erase | |||
| | Right R | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, E, R, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | 9 | |||
| | q<sub>i</sub> | |||
| | S<sub>j</sub> | |||
| | Erase | |||
| | {{CNone|None N}} | |||
| | q<sub>m</sub> | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, E, N, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| | | |||
| | (q<sub>i</sub>, S<sub>j</sub>, E, q<sub>m</sub>) | |||
| |} | |||
| Any Turing table (list of instructions) can be constructed from the above nine 5-tuples. For technical reasons, the three non-printing or "N" instructions (4, 5, 6) can usually be dispensed with. For examples see ]. | |||
| Less frequently the use of 4-tuples are encountered: these represent a further atomization of the Turing instructions (cf. Post (1947), Boolos & Jeffrey (1974, 1999), Davis-Sigal-Weyuker (1994)); also see more at ]. | |||
| ===The "state"=== | |||
| The word "state" used in context of Turing machines can be a source of confusion, as it can mean two things. Most commentators after Turing have used "state" to mean the name/designator of the current instruction to be performed—i.e. the contents of the state register. But Turing (1936) made a strong distinction between a record of what he called the machine's "m-configuration", and the machine's (or person's) "state of progress" through the computation—the current state of the total system. What Turing called "the state formula" includes both the current instruction and ''all'' the symbols on the tape: | |||
| {{blockquote|Thus the state of progress of the computation at any stage is completely determined by the note of instructions and the symbols on the tape. That is, the ''state of the system'' may be described by a single expression (sequence of symbols) consisting of the symbols on the tape followed by Δ (which is supposed to not to appear elsewhere) and then by the note of instructions. This expression is called the "state formula".|''The Undecidable'', pp. 139–140, emphasis added}} | |||
| Earlier in his paper Turing carried this even further: he gives an example where he placed a symbol of the current "m-configuration"—the instruction's label—beneath the scanned square, together with all the symbols on the tape (''The Undecidable'', p. 121); this he calls "the ''complete configuration''" (''The Undecidable'', p. 118). To print the "complete configuration" on one line, he places the state-label/m-configuration to the ''left'' of the scanned symbol. | |||
| A variant of this is seen in Kleene (1952) where ] shows how to write the ] of a machine's "situation": he places the "m-configuration" symbol q<sub>4</sub> over the scanned square in roughly the center of the 6 non-blank squares on the tape (see the Turing-tape figure in this article) and puts it to the ''right'' of the scanned square. But Kleene refers to "q<sub>4</sub>" itself as "the machine state" (Kleene, p. 374–375). Hopcroft and Ullman call this composite the "instantaneous description" and follow the Turing convention of putting the "current state" (instruction-label, m-configuration) to the ''left'' of the scanned symbol (p. 149), that is, the instantaneous description is the composite of non-blank symbols to the left, state of the machine, the current symbol scanned by the head, and the non-blank symbols to the right. | |||
| ''Example: total state of 3-state 2-symbol busy beaver after 3 "moves"'' (taken from example "run" in the figure below): | |||
| :: 1'''A'''1 | |||
| This means: after three moves the tape has ... 000110000 ... on it, the head is scanning the right-most 1, and the state is ''A''. Blanks (in this case represented by "0"s) can be part of the total state as shown here: ''B''01; the tape has a single 1 on it, but the head is scanning the 0 ("blank") to its left and the state is ''B''. | |||
| "State" in the context of Turing machines should be clarified as to which is being described: the current instruction, or the list of symbols on the tape together with the current instruction, or the list of symbols on the tape together with the current instruction placed to the left of the scanned symbol or to the right of the scanned symbol. | |||
| Turing's biographer Andrew Hodges (1983: 107) has noted and discussed this confusion. | |||
| ==="State" diagrams=== | |||
| {|class="wikitable" | |||
| |+ The table for the 3-state busy beaver ("P" = print/write a "1") | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Tape symbol | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state A | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state B | |||
| ! colspan="3" | Current state C | |||
| |- | |||
| | | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| | Write symbol | |||
| | Move tape | |||
| | Next state | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''0'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | R | |||
| | ''B'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | L | |||
| | ''A'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | L | |||
| | ''B'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''1'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | L | |||
| | ''C'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | R | |||
| | ''B'' | |||
| | P | |||
| | R | |||
| | ''HALT'' | |||
| |} | |||
| ]. Each circle represents a "state" of the table—an "m-configuration" or "instruction". "Direction" of a state ''transition'' is shown by an arrow. The label (e.g. ''0/P,R'') near the outgoing state (at the "tail" of the arrow) specifies the scanned symbol that causes a particular transition (e.g. ''0'') followed by a slash ''/'', followed by the subsequent "behaviors" of the machine, e.g. "''P'' ''print''" then move tape "''R'' ''right''". No general accepted format exists. The convention shown is after McClusky (1965), Booth (1967), Hill, and Peterson (1974).]] | |||
| To the right: the above table as expressed as a "state transition" diagram. | |||
| Usually large tables are better left as tables (Booth, p. 74). They are more readily simulated by computer in tabular form (Booth, p. 74). However, certain concepts—e.g. machines with "reset" states and machines with repeating patterns (cf. Hill and Peterson p. 244ff)—can be more readily seen when viewed as a drawing. | |||
| Whether a drawing represents an improvement on its table must be decided by the reader for the particular context. | |||
| ] | |||
| The reader should again be cautioned that such diagrams represent a snapshot of their table frozen in time, ''not'' the course ("trajectory") of a computation ''through'' time and space. While every time the busy beaver machine "runs" it will always follow the same state-trajectory, this is not true for the "copy" machine that can be provided with variable input "parameters". | |||
| The diagram "progress of the computation" shows the three-state busy beaver's "state" (instruction) progress through its computation from start to finish. On the far right is the Turing "complete configuration" (Kleene "situation"<!-- Stuation? Not Situation? Is that the right word? Yes, it is, cf. page 375 for example "The Godel number of the stiuation..." and then he shows a tape, etc. This usage runs throughout the chapter. wvbailey~~~~ --><!--So is it "stuation" or "stiuation"?-->, Hopcroft–Ullman "instantaneous description") at each step. If the machine were to be stopped and cleared to blank both the "state register" and entire tape, these "configurations" could be used to rekindle a computation anywhere in its progress (cf. Turing (1936) ''The Undecidable'', pp. 139–140). | |||
| ==Equivalent models== | |||
| {{See also|Turing machine equivalents|Register machine|Post–Turing machine}} | |||
| Many machines that might be thought to have more computational capability than a simple universal Turing machine can be shown to have no more power (Hopcroft and Ullman p. 159, cf. Minsky (1967)). They might compute faster, perhaps, or use less memory, or their instruction set might be smaller, but they cannot compute more powerfully (i.e. more mathematical functions). (The ] ''hypothesises'' this to be true for any kind of machine: that anything that can be "computed" can be computed by some Turing machine.) | |||
| A Turing machine is equivalent to a single-stack ] (PDA) that has been made more flexible and concise by relaxing the ] (LIFO) requirement of its stack. In addition, a Turing machine is also equivalent to a two-stack PDA with standard LIFO semantics, by using one stack to model the tape left of the head and the other stack for the tape to the right. | |||
| At the other extreme, some very simple models turn out to be ], i.e. to have the same computational power as the Turing machine model. | |||
| Common equivalent models are the ], ], machines with input and output, and the ] (NDTM) as opposed to the ''deterministic'' Turing machine (DTM) for which the action table has at most one entry for each combination of symbol and state. | |||
| ] are equivalent to ] (as well as ] by conversion using the ] algorithm). | |||
| For practical and didactic intentions, the equivalent ] can be used as a usual ] ]. | |||
| A relevant question is whether or not the computation model represented by concrete programming languages is Turing equivalent. While the computation of a real computer is based on finite states and thus not capable to simulate a Turing machine, programming languages themselves do not necessarily have this limitation. Kirner et al., 2009 have shown that among the general-purpose programming languages some are Turing complete while others are not. For example, ] is not Turing complete, as all instantiations of ANSI C (different instantiations are possible as the standard deliberately leaves certain behaviour undefined for legacy reasons) imply a finite-space memory. This is because the size of memory reference data types, called ''pointers'', is accessible inside the language. However, other programming languages like ] do not have this feature, which allows them to be Turing complete in principle. | |||
| It is just Turing complete in principle, as ] in a programming language is allowed to fail, which means the programming language can be Turing complete when ignoring failed memory allocations, but the compiled programs executable on a real computer cannot. | |||
| ==Choice c-machines, oracle o-machines== | |||
| Early in his paper (1936) Turing makes a distinction between an "automatic machine"—its "motion ... completely determined by the configuration" and a "choice machine": | |||
| {{blockquote|...whose motion is only partially determined by the configuration ... When such a machine reaches one of these ambiguous configurations, it cannot go on until some arbitrary choice has been made by an external operator. This would be the case if we were using machines to deal with axiomatic systems.|''The Undecidable'', p. 118}} | |||
| Turing (1936) does not elaborate further except in a footnote in which he describes how to use an a-machine to "find all the provable formulae of the calculus" rather than use a choice machine. He "suppose that the choices are always between two possibilities 0 and 1. Each proof will then be determined by a sequence of choices i<sub>1</sub>, i<sub>2</sub>, ..., i<sub>n</sub> (i<sub>1</sub> = 0 or 1, i<sub>2</sub> = 0 or 1, ..., i<sub>n</sub> = 0 or 1), and hence the number 2<sup>n</sup> + i<sub>1</sub>2<sup>n-1</sup> + i<sub>2</sub>2<sup>n-2</sup> + ... +i<sub>n</sub> completely determines the proof. The automatic machine carries out successively proof 1, proof 2, proof 3, ..." (Footnote ‡, ''The Undecidable'', p. 138) | |||
| This is indeed the technique by which a deterministic (i.e., a-) Turing machine can be used to mimic the action of a ]; Turing solved the matter in a footnote and appears to dismiss it from further consideration. | |||
| An ] or o-machine is a Turing a-machine that pauses its computation at state "'''o'''" while, to complete its calculation, it "awaits the decision" of "the oracle"—an entity unspecified by Turing "apart from saying that it cannot be a machine" (Turing (1939), ''The Undecidable'', p. 166–168). | |||
| ==Universal Turing machines== | |||
| {{Main|Universal Turing machine}} | |||
| ] | |||
| As Turing wrote in ''The Undecidable'', p. 128 (italics added): | |||
| {{blockquote|It is possible to invent a ''single machine'' which can be used to compute ''any'' computable sequence. If this machine '''U''' is supplied with the tape on the beginning of which is written the string of quintuples separated by semicolons of some computing machine '''M''', then '''U''' will compute the same sequence as '''M'''.}} | |||
| This finding is now taken for granted, but at the time (1936) it was considered astonishing.{{citation needed|date=December 2021}} The model of computation that Turing called his "universal machine"—"'''U'''" for short—is considered by some (cf. Davis (2000)) to have been the fundamental theoretical breakthrough that led to the notion of the ]. | |||
| {{blockquote|Turing's paper ... contains, in essence, the invention of the modern computer and some of the programming techniques that accompanied it.|Minsky (1967), p. 104}} | |||
| In terms of ], a multi-tape universal Turing machine need only be slower by ]ic factor compared to the machines it simulates. This result was obtained in 1966 by F. C. Hennie and ]. (Arora and Barak, 2009, theorem 1.9) | |||
| ==Comparison with real machines== | ==Comparison with real machines== | ||
| ] pieces]] | |||
| Turing machines are more powerful than some other kinds of automata, such as ]s and ]. According to the ], they are as powerful as real machines, and are able to execute any operation that a real program can. What is neglected in this statement is that, because a real machine can only have a finite number of ''configurations'', it is nothing but a finite-state machine, whereas a Turing machine has an unlimited amount of storage space available for its computations. | |||
| There are a number of ways to explain why Turing machines are useful models of real computers: | |||
| It's often said that Turing machines, unlike simpler automata, are as powerful as real machines, and are able to execute any operation that a real program can. What is missed in this statement is that almost any particular program running on ''a particular machine'' and given a finite amount of input is in fact nothing but a ], since the machine it runs on can only be in finitely many ''configurations''. Turing machines would actually only be equivalent to a machine that had an unlimited amount of storage space. We might ask, then, why Turing machines are useful models of real computers. There are a number of ways to answer this: | |||
| # The difference lies only with the ability of a Turing machine to manipulate an unbounded amount of data. However, given a finite amount of time, a Turing machine (like a real machine) can only manipulate a finite amount of data. | |||
| # Like a Turing machine, a real machine can have its storage space enlarged as needed, by acquiring more disks or other storage media. If the supply of these runs short, the Turing machine may become less useful as a model. But the fact is that neither Turing machines nor real machines need astronomical amounts of storage space in order to do most of the computations people actually want done. The processing time required is usually much more of a problem. | |||
| # Real machines are much more complex than a Turing machine. For example, a Turing machine describing an algorithm may have a few hundred states, while the equivalent DFA on a given real machine has quadrillions. | |||
| # Turing machines describe algorithms independent of how much memory they utilize. There is a maximum to the amount of memory that any machine which we know of has, but this limit can rise arbitrarily in time. Turing machines allow us to make statements about algorithms which will (theoretically) hold forever, regardless of advances in ''conventional'' computing machine architecture. | |||
| # Turing machines simplify the statement of algorithms. Algorithms running on Turing-equivalent abstract machines are usually more general than their counterparts running on real machines, because they have arbitrary-precision datatypes available and never have to deal with unexpected conditions (including, but not limited to, running out of memory). | |||
| * Anything a real computer can compute, a Turing machine can also compute. For example: "A Turing machine can simulate any type of subroutine found in programming languages, including recursive procedures and any of the known parameter-passing mechanisms" (Hopcroft and Ullman p. 157). A large enough FSA can also model any real computer, disregarding IO. Thus, a statement about the limitations of Turing machines will also apply to real computers. | |||
| One way in which Turing machines are a poor model for programs is that many real programs, such as ]s and ]s, are written to receive unbounded input over time, and therefore do not halt. Turing machines do not model such ongoing computation well (but can still model portions of it, such as individual procedures). | |||
| * The difference lies only with the ability of a Turing machine to manipulate an unbounded amount of data. However, given a finite amount of time, a Turing machine (like a real machine) can only manipulate a finite amount of data. | |||
| * Like a Turing machine, a real machine can have its storage space enlarged as needed, by acquiring more disks or other storage media. | |||
| * Descriptions of real machine programs using simpler abstract models are often much more complex than descriptions using Turing machines. For example, a Turing machine describing an algorithm may have a few hundred states, while the equivalent deterministic finite automaton (DFA) on a given real machine has quadrillions. This makes the DFA representation infeasible to analyze. | |||
| * Turing machines describe algorithms independent of how much memory they use. There is a limit to the memory possessed by any current machine, but this limit can rise arbitrarily in time. Turing machines allow us to make statements about algorithms which will (theoretically) hold forever, regardless of advances in ''conventional'' computing machine architecture. | |||
| * Algorithms running on Turing-equivalent abstract machines can have arbitrary-precision data types available and never have to deal with unexpected conditions (including, but not limited to, running ]). | |||
| ] | |||
| Another limitation of Turing Machines is that they do not model the strengths of a particular arrangement well. For instance, modern computers are actually instances of a more specific form of computing machine, known as the ]. The primary difference between this machine and the Turing Machine is that the Turing Machine uses an infinite tape, while the random access machine uses a numerically indexed sequence (typically an integer field). The upshot of this distinction is that there are computational optimizations that can be performed based on the memory indices, which are not possible in a general Turing Machine; thus when Turing Machines are used as the basis for bounding running times, a 'false lower bound' can be proven on certain algorithms' running times (due to the false simplifying assumption of a Turing Machine). An example of this is ], which seemingly violates the <math>\theta(n\log{n})</math> ] on ]. | |||
| ===Limitations=== | |||
| == A physical Turing machine == | |||
| ====Computational complexity theory==== | |||
| It is not difficult to simulate a Turing machine on a modern computer | |||
| {{further|Computational complexity theory}} | |||
| (except for the limited memory of actually existing computers). | |||
| A limitation of Turing machines is that they do not model the strengths of a particular arrangement well. For instance, modern stored-program computers are actually instances of a more specific form of ] known as the ] or RASP machine model. Like the universal Turing machine, the RASP stores its "program" in "memory" external to its finite-state machine's "instructions". Unlike the universal Turing machine, the RASP has an infinite number of distinguishable, numbered but unbounded "registers"—memory "cells" that can contain any integer (cf. Elgot and Robinson (1964), Hartmanis (1971), and in particular Cook-Rechow (1973); references at ]). The RASP's finite-state machine is equipped with the capability for indirect addressing (e.g., the contents of one register can be used as an address to specify another register); thus the RASP's "program" can address any register in the register-sequence. The upshot of this distinction is that there are computational optimizations that can be performed based on the memory indices, which are not possible in a general Turing machine; thus when Turing machines are used as the basis for bounding running times, a "false lower bound" can be proven on certain algorithms' running times (due to the false simplifying assumption of a Turing machine). An example of this is ], an algorithm that can be shown to perform more quickly when using the RASP model of computation rather than the Turing machine model. | |||
| It is also possible to build a Turing machine on a purely mechanical basis. | |||
| The mathematician ] did indeed build such a machine in ] | |||
| using metal and plastic construction sets, and some wood. | |||
| The 1.5 meter high machine uses the pulling of strings to read, move and | |||
| write the data (which is represented using ball ]s). | |||
| ====Interaction==== | |||
| The machine is now exhibited in the entrance of the Department of Computer | |||
| In the early days of computing, computer use was typically limited to ], i.e., non-interactive tasks, each producing output data from given input data. Computability theory, which studies computability of functions from inputs to outputs, and for which Turing machines were invented, reflects this practice. | |||
| Science of the ], ]. | |||
| Since the 1970s, ] use of computers became much more common. In principle, it is possible to model this by having an external agent read from the tape and write to it at the same time as a Turing machine, but this rarely matches how interaction actually happens; therefore, when describing interactivity, alternatives such as ] are usually preferred. | |||
| Also, using a few hundred mirrors, one can build an optical universal Turing machine in one's backyard, using the ]. This is based on a work by ]. | |||
| == Comparison with the arithmetic model of computation == | |||
| The concept of a Turing machine was used as an educational tool in the ] novel '']'' (1995), by ]. The main character, Nell, possesses an interactive book which teaches her creative thinking and logic by presenting puzzles in a story as Turing machines which become more and more complex as the story progresses. They begin as a simple chain-fed clockwork device and progresses to abstract economic processes, trades, and finally the interaction of entire fictional kingdoms. | |||
| The ] differs from the Turing model in two aspects:<ref name=":0">{{Cite Geometric Algorithms and Combinatorial Optimization}}</ref>{{Rp|page=32}} | |||
| * In the arithmetic model, every real number requires a single memory cell, whereas in the Turing model the storage size of a real number depends on the number of bits required to represent it. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * In the arithmetic model, every basic arithmetic operation on real numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) can be done in a single step, whereas in the Turing model the run-time of each arithmetic operation depends on the length of the operands. | |||
| * ], a simple two-dimensional analogue of the Turing machine. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], which says Turing machines can perform any computation that can be performed. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], any computing system or language which, like the Turing machine, is not only Turing-complete but also useless for practical computing. | |||
| * ]'s ] | |||
| Some algorithms run in polynomial time in one model but not in the other one. For example: | |||
| == References == | |||
| *]: ''The Universal Turing Machine - A Half-Century Survey'', Springer Verlag, ISBN 3-211-82637-8 | |||
| *]: ''Turing and the Computer - The big idea'', Anchor Books/Doubleday, ISBN 0-385-49243-X | |||
| * , Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, Series 2, Volume 42, 1936; reprinted in M. David (ed.), ''The Undecidable'', Hewlett, NY: Raven Press, 1965; | |||
| * Boolos, G. and Jeffrey, R., ''Computability and Logic'', 2nd ed., Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1980. | |||
| * , ''Romanian Journal Of Information Science and Technology'', 1(3), 259-265, 1998. (surveys known results about small universal Turing machines) | |||
| * The ] runs in polynomial time in the Turing model, but not in the arithmetic model. | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * The algorithm that reads ''n'' numbers and then computes <math>2^{2^n}</math> by ] runs in polynomial time in the Arithmetic model, but not in the Turing model. This is because the number of bits required to represent the outcome is exponential in the input size. | |||
| * | |||
| * (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy) | |||
| * | |||
| However, if an algorithm runs in polynomial time in the arithmetic model, and in addition, the binary length of all involved numbers is polynomial in the length of the input, then it is always polynomial-time in the Turing model. Such an algorithm is said to run in ]. | |||
| == Simulators == | |||
| * (free software for Windows). | |||
| * (java applet). | |||
| * (free software). | |||
| * (free software). | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * - A working Turing machine built out of scale trains. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{See also|Algorithm|Church–Turing thesis}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Historical background: computational machinery=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] (1919–1995)—a student of Alan Turing (1912–1954), and his lifelong friend—traces the lineage of the notion of "calculating machine" back to ] (circa 1834) and actually proposes "Babbage's Thesis": | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{blockquote|''That the whole of development and operations of analysis are now capable of being executed by machinery''.|(italics in Babbage as cited by Gandy, p. 54)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Gandy's analysis of Babbage's ] describes the following five operations (cf. p. 52–53): | |||
| ] | |||
| # The arithmetic functions +, −, ×, where − indicates "proper" subtraction: {{nowrap|''x'' − ''y'' {{=}} 0}} if {{nowrap|''y'' ≥ ''x''}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| # Any sequence of operations is an operation. | |||
| ] | |||
| # Iteration of an operation (repeating n times an operation P). | |||
| ] | |||
| # Conditional iteration (repeating n times an operation P conditional on the "success" of test T). | |||
| ] | |||
| # Conditional transfer (i.e., conditional "]"). | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Gandy states that "the functions which can be calculated by (1), (2), and (4) are precisely those which are ]." (p. 53). He cites other proposals for "universal calculating machines" including those of ] (1909), ] (1914),<ref name="LTQ1914es">L. Torres Quevedo. ''Ensayos sobre Automática – Su definicion. Extension teórica de sus aplicaciones,'' Revista de la Academia de Ciencias Exacta, Revista 12, pp. 391–418, 1914.</ref><ref name="LTQ1915fr">Torres Quevedo. L. (1915). , ''Revue Génerale des Sciences Pures et Appliquées'', vol. 2, pp. 601–611.</ref> ] (1922), ] (1933), ] (1936), ] (1937). However: | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{blockquote|… the emphasis is on programming a fixed iterable sequence of arithmetical operations. The fundamental importance of conditional iteration and conditional transfer for a general theory of calculating machines is not recognized…|Gandy p. 55}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===The Entscheidungsproblem (the "decision problem"): Hilbert's tenth question of 1900=== | |||
| ] | |||
| With regard to ] posed by the famous mathematician ] in 1900, an aspect of ] had been floating about for almost 30 years before it was framed precisely. Hilbert's original expression for No. 10 is as follows: | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{blockquote|''10. Determination of the solvability of a Diophantine equation''. Given a ] with any number of unknown quantities and with rational integral coefficients: To devise a process according to which it can be determined in a finite number of operations whether the equation is solvable in rational integers. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The Entscheidungsproblem ]] is solved when we know a procedure that allows for any given logical expression to decide by finitely many operations its validity or satisfiability ... The Entscheidungsproblem must be considered the main problem of mathematical logic.|quoted, with this translation and the original German, in Dershowitz and Gurevich, 2008}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| By 1922, this notion of "]" had developed a bit, and ] stated that | |||
| {{blockquote|... most general form of the Entscheidungsproblem as follows: | |||
| <blockquote>A quite definite generally applicable prescription is required which will allow one to decide in a finite number of steps the truth or falsity of a given purely logical assertion ...</blockquote>|Gandy p. 57, quoting Behmann}} | |||
| {{blockquote|Behmann remarks that ... the general problem is equivalent to the problem of deciding which mathematical propositions are true.|''ibid.''}} | |||
| {{blockquote|If one were able to solve the Entscheidungsproblem then one would have a "procedure for solving many (or even all) mathematical problems".|''ibid.'', p. 92}} | |||
| By the 1928 international congress of mathematicians, Hilbert "made his questions quite precise. First, was mathematics '']'' ... Second, was mathematics '']'' ... And thirdly, was mathematics '']''?" (Hodges p. 91, Hawking p. 1121). The first two questions were answered in 1930 by ] at the very same meeting where Hilbert delivered his retirement speech (much to the chagrin of Hilbert); the third—the Entscheidungsproblem—had to wait until the mid-1930s. | |||
| The problem was that an answer first required a precise definition of "definite general applicable prescription", which Princeton professor ] would come to call "]", and in 1928 no such definition existed. But over the next 6–7 years ] developed his definition of a worker moving from room to room writing and erasing marks per a list of instructions (Post 1936), as did Church and his two students ] and ] by use of Church's lambda-calculus and Gödel's ] (1934). Church's paper (published 15 April 1936) showed that the Entscheidungsproblem was indeed "undecidable"<ref>The narrower question posed in ], about ]s, remains unresolved until 1970, when the relationship between ]s and ]s is finally laid bare.</ref> and beat Turing to the punch by almost a year (Turing's paper submitted 28 May 1936, published January 1937). In the meantime, Emil Post submitted a brief paper in the fall of 1936, so Turing at least had priority over Post. While Church refereed Turing's paper, Turing had time to study Church's paper and add an Appendix where he sketched a proof that Church's lambda-calculus and his machines would compute the same functions. | |||
| {{blockquote|But what Church had done was something rather different, and in a certain sense weaker. ... the Turing construction was more direct, and provided an argument from first principles, closing the gap in Church's demonstration.|Hodges p. 112}} | |||
| And Post had only proposed a definition of ] and criticised Church's "definition", but had proved nothing. | |||
| ===Alan Turing's a-machine=== | |||
| In the spring of 1935, Turing as a young Master's student at ], took on the challenge; he had been stimulated by the lectures of the logician ] "and learned from them of Gödel's work and the Entscheidungsproblem ... Newman used the word 'mechanical' ... In his obituary of Turing 1955 Newman writes: | |||
| {{blockquote|To the question 'what is a "mechanical" process?' Turing returned the characteristic answer 'Something that can be done by a machine' and he embarked on the highly congenial task of analysing the general notion of a computing machine.|Gandy, p. 74}} | |||
| Gandy states that: | |||
| {{blockquote|I suppose, but do not know, that Turing, right from the start of his work, had as his goal a proof of the undecidability of the Entscheidungsproblem. He told me that the 'main idea' of the paper came to him when he was lying in Grantchester meadows in the summer of 1935. The 'main idea' might have either been his analysis of computation or his realization that there was a universal machine, and so a ] to prove unsolvability.|''ibid.'', p. 76}} | |||
| While Gandy believed that Newman's statement above is "misleading", this opinion is not shared by all. Turing had a lifelong interest in machines: "Alan had dreamt of inventing typewriters as a boy; Mrs. Turing had a typewriter; and he could well have begun by asking himself what was meant by calling a typewriter 'mechanical'" (Hodges p. 96). While at Princeton pursuing his PhD, Turing built a Boolean-logic multiplier (see below). His PhD thesis, titled "]", contains the following definition of "a computable function": | |||
| {{blockquote|It was stated above that 'a function is effectively calculable if its values can be found by some purely mechanical process'. We may take this statement literally, understanding by a purely mechanical process one which could be carried out by a machine. It is possible to give a mathematical description, in a certain normal form, of the structures of these machines. The development of these ideas leads to the author's definition of a computable function, and to an identification of computability with effective calculability. It is not difficult, though somewhat laborious, to prove that these three definitions are equivalent.|Turing (1939) in ''The Undecidable'', p. 160}} | |||
| Alan Turing invented the "a-machine" (automatic machine) in 1936.<ref name=Hodges-2012/> Turing submitted his paper on 31 May 1936 to the London Mathematical Society for its ''Proceedings'' (cf. Hodges 1983:112), but it was published in early 1937 and offprints were available in February 1937 (cf. Hodges 1983:129) It was Turing's doctoral advisor, ], who later coined the term "Turing machine" in a review.<ref name="mitpress.mit.edu"/> With this model, Turing was able to answer two questions in the negative: | |||
| * Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape is "circular" (e.g., freezes, or fails to continue its computational task)? | |||
| * Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape ever prints a given symbol?<ref name="The Undecidable' page 119"/><ref name="Turing 1937 230–265"/> | |||
| Thus by providing a mathematical description of a very simple device capable of arbitrary computations, he was able to prove properties of computation in general—and in particular, the ] of the '']'' ('decision problem').<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| When Turing returned to the UK he ultimately became jointly responsible for breaking the German secret codes created by encryption machines called "The Enigma"; he also became involved in the design of the ACE (]), " ACE proposal was effectively self-contained, and its roots lay not in the ] , but in his own universal machine" (Hodges p. 318). Arguments still continue concerning the origin and nature of what has been named by Kleene (1952) ]. But what Turing ''did prove'' with his computational-machine model appears in his paper "]" (1937): | |||
| {{blockquote| the Hilbert Entscheidungsproblem can have no solution ... I propose, therefore to show that there can be no general process for determining whether a given formula U of the functional calculus K is provable, i.e. that there can be no machine which, supplied with any one U of these formulae, will eventually say whether U is provable.|from Turing's paper as reprinted in ''The Undecidable'', p. 145}} | |||
| Turing's example (his second proof): If one is to ask for a general procedure to tell us: "Does this machine ever print 0", the question is "undecidable". | |||
| ===1937–1970: The "digital computer", the birth of "computer science"=== | |||
| In 1937, while at Princeton working on his PhD thesis, Turing built a digital (Boolean-logic) multiplier from scratch, making his own electromechanical ] (Hodges p. 138). "Alan's task was to embody the logical design of a Turing machine in a network of relay-operated switches ..." (Hodges p. 138). While Turing might have been just initially curious and experimenting, quite-earnest work in the same direction was going in Germany (] (1938)), and in the United States (]) and ] (1937); the fruits of their labors were used by both the Axis and Allied militaries in ] (cf. Hodges p. 298–299). In the early to mid-1950s ] and ] reduced the Turing machine to a simpler form (a precursor to the ] of ]); simultaneously European researchers were reducing the new-fangled ] to a computer-like theoretical object equivalent to what was now being called a "Turing machine". In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the coincidentally parallel developments of Melzak and Lambek (1961), Minsky (1961), and Shepherdson and Sturgis (1961) carried the European work further and reduced the Turing machine to a more friendly, computer-like abstract model called the ]; Elgot and Robinson (1964), Hartmanis (1971), Cook and Reckhow (1973) carried this work even further with the ] and ] models—but basically all are just multi-tape Turing machines with an arithmetic-like instruction set. | |||
| ===1970–present: as a model of computation=== | |||
| Today, the counter, register and random-access machines and their sire the Turing machine continue to be the models of choice for theorists investigating questions in the ]. In particular, ] makes use of the Turing machine: | |||
| {{blockquote|Depending on the objects one likes to manipulate in the computations (numbers like nonnegative integers or alphanumeric strings), two models have obtained a dominant position in machine-based complexity theory: | |||
| <blockquote>''the off-line multitape Turing machine''..., which represents the standard model for string-oriented computation, and | |||
| the ''random access machine (RAM)'' as introduced by Cook and Reckhow ..., which models the idealised Von Neumann-style computer.</blockquote>|van Emde Boas 1990:4}} | |||
| {{blockquote|Only in the related area of analysis of algorithms this role is taken over by the RAM model.|van Emde Boas 1990:16}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{divcol|colwidth=22em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], showing the impossibility of infinite-tape Turing machines of finite size and bounded energy | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] or ] for information relating to the halting problem | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], a Turing-complete cellular automaton | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'', a famous book that discusses, among other topics, the Church–Turing thesis | |||
| * ], for more references | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] and ]s, simple two-dimensional analogues of the Turing machine | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], another leading thinker in information theory | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], any computing system or language that, despite being Turing complete, is generally considered useless for practical computing | |||
| * ], for Turing's very early ideas on neural networks | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{divcol-end}} | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| <references responsive="0" /> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{citation style|date=November 2019}}<!--mix of footnotes plus inline Harvard references--> | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ===Primary literature, reprints, and compilations=== | |||
| * B. ] ed. (2004), ''The Essential Turing: Seminal Writings in Computing, Logic, Philosophy, Artificial Intelligence, and Artificial Life plus The Secrets of Enigma,'' Clarendon Press (Oxford University Press), Oxford UK, {{isbn|0-19-825079-7}}. Contains the Turing papers plus a draft letter to ] re his criticism of "Turing's convention", and Donald W. Davies' ''Corrections to Turing's Universal Computing Machine'' | |||
| * ] (ed.) (1965), ''The Undecidable'', Raven Press, Hewlett, NY. | |||
| * Emil Post (1936), "Finite Combinatory Processes—Formulation 1", ''Journal of Symbolic Logic'', 1, 103–105, 1936. Reprinted in ''The Undecidable'', pp. 289ff. | |||
| * Emil Post (1947), "Recursive Unsolvability of a Problem of Thue", ''Journal of Symbolic Logic'', vol. 12, pp. 1–11. Reprinted in ''The Undecidable'', pp. 293ff. In the Appendix of this paper Post comments on and gives corrections to Turing's paper of 1936–1937. In particular see the footnotes 11 with corrections to the universal computing machine coding and footnote 14 with comments on ]. | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last= Turing | first= A.M. | publication-date = 1937 | year = 1936 | title = On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem | url=https://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/activities/ieg/e-library/sources/tp2-ie.pdf|journal = Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society | series = 2 | volume = 42 | pages = 230–265 | doi= 10.1112/plms/s2-42.1.230 | s2cid= 73712 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last = Turing | first = A.M. | publication-date = 1937 | title = On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem: A correction | journal = Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society | series = 2 | volume = 43 | pages = 544–6 | doi = 10.1112/plms/s2-43.6.544 | year = 1938 | issue = 6 }} Reprinted in ''The Undecidable'', pp. 115–154. | |||
| * Alan Turing, 1948, "Intelligent Machinery." Reprinted in "Cybernetics: Key Papers." Ed. C.R. Evans and A.D.J. Robertson. Baltimore: University Park Press, 1968. p. 31. Reprinted in {{Cite journal | doi = 10.1093/philmat/4.3.256| title = Intelligent Machinery, A Heretical Theory| journal = Philosophia Mathematica| volume = 4| issue = 3| pages = 256–260| year = 1996| last1 = Turing | first1 = A. M.| doi-access = free}} | |||
| * F. C. Hennie and ]. ''Two-tape simulation of multitape Turing machines''. ], 13(4):533–546, 1966. | |||
| ===Computability theory=== | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Boolos | first = George |author2=Richard Jeffrey | title = Computability and Logic | url = https://archive.org/details/computabilitylog0000bool_r8y9 | url-access = registration | edition = 3rd | publisher = Cambridge University Press | location = Cambridge UK | orig-year = 1989| year = 1999| isbn = 0-521-20402-X }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Boolos | first = George |author2=John Burgess |author3=Richard Jeffrey | title = Computability and Logic | edition = 4th | publisher = Cambridge University Press | location = Cambridge UK | year = 2002 | isbn = 0-521-00758-5 }} Some parts have been significantly rewritten by Burgess. Presentation of Turing machines in context of Lambek "abacus machines" (cf. ]) and ], showing their equivalence. | |||
| * ] (1967), ''Sequential Machines and Automata Theory'', John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. Graduate level engineering text; ranges over a wide variety of topics, Chapter IX ''Turing Machines'' includes some recursion theory. | |||
| * {{cite book|author = Martin Davis | year = 1958| title = Computability and Unsolvability| publisher = McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc, New York | author-link = Martin Davis (mathematician)}}. On pages 12–20 he gives examples of 5-tuple tables for Addition, The Successor Function, Subtraction (x ≥ y), Proper Subtraction (0 if x < y), The Identity Function and various identity functions, and Multiplication. | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Davis| first = Martin |author2=Ron Sigal |author3=Elaine J. Weyuker|author3-link=Elaine Weyuker | title = Computability, Complexity, and Languages and Logic: Fundamentals of Theoretical Computer Science | edition = 2nd | publisher = Academic Press, Harcourt, Brace & Company| location = San Diego | year = 1994 | isbn = 0-12-206382-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last =Hennie |first = Fredrick | year = 1977| title = Introduction to Computability| publisher = Addison–Wesley, Reading, Mass|id=QA248.5H4 1977 }}. On pages 90–103 Hennie discusses the UTM with examples and flow-charts, but no actual 'code'. | |||
| * {{cite book|last1 = Hopcroft | first1 = John | author-link1 = John Hopcroft | last2 = Ullman | first2 = Jeffrey | author-link2 = Jeffrey Ullman | year = 1979| title = Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation| title-link = Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation| publisher = Addison–Wesley, Reading Mass| edition = 1st | isbn = 0-201-02988-X}} Centered around the issues of machine-interpretation of "languages", NP-completeness, etc. | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Hopcroft | first = John E.|author2=Rajeev Motwani |author3=Jeffrey D. Ullman | title = Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation| edition = 2nd | publisher = Addison–Wesley | location = Reading Mass | year = 2001 | isbn = 0-201-44124-1}} | |||
| * ] (1952), ''Introduction to Metamathematics'', North–Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam Netherlands, 10th impression (with corrections of 6th reprint 1971). Graduate level text; most of Chapter XIII ''Computable functions'' is on Turing machine proofs of computability of recursive functions, etc. | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Knuth | first = Donald E. | author-link = Donald Knuth | title = Volume 1/Fundamental Algorithms: The Art of computer Programming| edition = 2nd | publisher = Addison–Wesley Publishing Company| location = Reading, Mass.| year = 1973 }}. With reference to the role of Turing machines in the development of computation (both hardware and software) see 1.4.5 ''History and Bibliography'' pp. 225ff and 2.6 ''History and Bibliography''pp. 456ff. | |||
| * ], 1974, '']''. Reprinted, Dover, 2003. {{isbn|978-0-486-43238-0}} | |||
| * ], ''Computation: Finite and Infinite Machines'', Prentice–Hall, Inc., N.J., 1967. See Chapter 8, Section 8.2 "Unsolvability of the Halting Problem." | |||
| * {{cite book|author = Christos Papadimitriou | year = 1993 | title = Computational Complexity | publisher = Addison Wesley | edition = 1st | isbn = 0-201-53082-1| author-link = Christos Papadimitriou }} Chapter 2: Turing machines, pp. 19–56. | |||
| * ], ''Theory of Recursive Functions and Effective Computability'', The MIT Press, Cambridge MA, paperback edition 1987, original McGraw-Hill edition 1967, {{isbn|0-262-68052-1}} (pbk.) | |||
| * {{cite book | author = Michael Sipser | year = 1997 | title = Introduction to the Theory of Computation | publisher = PWS Publishing | isbn = 0-534-94728-X | url = https://archive.org/details/introductiontoth00sips | author-link = Michael Sipser }} Chapter 3: The Church–Turing Thesis, pp. 125–149. | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Stone | first = Harold S. | title = Introduction to Computer Organization and Data Structures| edition = 1st | publisher = McGraw–Hill Book Company | location = New York | year = 1972 | isbn = 0-07-061726-0 }} | |||
| * ] 1990, ''Machine Models and Simulations'', pp. 3–66, in ], ed., ''Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science, Volume A: Algorithms and Complexity'', The MIT Press/Elsevier, , {{isbn|0-444-88071-2}} (Volume A). QA76.H279 1990. | |||
| ===Church's thesis=== | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Nachum Dershowitz |author2=Yuri Gurevich |date=September 2008 |title=A natural axiomatization of computability and proof of Church's Thesis |journal=Bulletin of Symbolic Logic |volume=14 |issue=3 |url=http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/gurevich/Opera/188.pdf |access-date=2008-10-15}} | |||
| * {{cite book|author = Roger Penrose | orig-year = 1989| year = 1990 | title = The Emperor's New Mind | publisher = Oxford University Press, New York| edition = 2nd | isbn = 0-19-851973-7| author-link = Roger Penrose}} | |||
| ===Small Turing machines=== | |||
| * Rogozhin, Yurii, 1998, "", ''Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology'', 1(3), 259–265, 1998. (surveys known results about small universal Turing machines) | |||
| * ], 2002, , Wolfram Media, {{isbn|1-57955-008-8}} | |||
| * Brunfiel, Geoff, , ''Nature'', October 24. 2007. | |||
| * Jim Giles (2007), , New Scientist, October 24, 2007. | |||
| * Alex Smith, , Submission for the Wolfram 2, 3 Turing Machine Research Prize. | |||
| * Vaughan Pratt, 2007, "", FOM email list. October 29, 2007. | |||
| * Martin Davis, 2007, "", and FOM email list. October 26–27, 2007. | |||
| * Alasdair Urquhart, 2007 "", FOM email list. October 26, 2007. | |||
| * Hector Zenil (Wolfram Research), 2007 "", FOM email list. October 29, 2007. | |||
| * Todd Rowland, 2007, "", Wolfram Science message board, October 30, 2007. | |||
| * Olivier and Marc RAYNAUD, 2014, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160114140003/http://machinedeturing.com/ang_default.asp |date=2016-01-14 }}" LIMOS Laboratory of Blaise Pascal University (Clermont-Ferrand in France). | |||
| ===Other=== | |||
| * {{cite book|author = Martin Davis | year = 2000| title = Engines of Logic: Mathematicians and the origin of the Computer| publisher = W. W. Norton & Company, New York| edition = 1st | isbn = 978-0-393-32229-3| author-link = Martin Davis (mathematician)}} | |||
| * ], "The Confluence of Ideas in 1936", pp. 51–102 in ], see below. | |||
| * ] (editor), 2005, ''God Created the Integers: The Mathematical Breakthroughs that Changed History'', Running Press, Philadelphia, {{isbn|978-0-7624-1922-7}}. Includes Turing's 1936–1937 paper, with brief commentary and biography of Turing as written by Hawking. | |||
| * {{cite book | author = Rolf Herken | title = The Universal Turing Machine—A Half-Century Survey | publisher = Springer Verlag | isbn = 978-3-211-82637-9 | year = 1995}} | |||
| * ], '']'', ], New York. Cf. Chapter "The Spirit of Truth" for a history leading to, and a discussion of, his proof. | |||
| * {{cite book|author = Ivars Peterson | year = 1988| title = The Mathematical Tourist: Snapshots of Modern Mathematics|url = https://archive.org/details/mathematicaltour00pete |url-access = registration | publisher = W. H. Freeman and Company, New York| edition = 1st | isbn = 978-0-7167-2064-5 | author-link = Ivars Peterson}} | |||
| * ], ''The Emperor's New Mind: Concerning Computers, Minds, and the Laws of Physics'', ], Oxford and New York, 1989 (1990 corrections), {{isbn|0-19-851973-7}}. | |||
| * {{cite book | author = Paul Strathern | title = Turing and the Computer—The Big Idea | publisher = Anchor Books/Doubleday | isbn = 978-0-385-49243-0 | year = 1997 | url = https://archive.org/details/turingcomputer00stra | author-link = Paul Strathern }} | |||
| * ], "A variant to Turing's theory of computing machines", ''Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery'' (JACM) 4, 63–92 (1957). | |||
| * ], , John Wiley & Sons, Inc., {{isbn|0-470-22905-5}} | |||
| * Arora, Sanjeev; Barak, Boaz, , Cambridge University Press, 2009, {{isbn|978-0-521-42426-4}}, section 1.4, "Machines as strings and the universal Turing machine" and 1.7, "Proof of theorem 1.9" | |||
| * {{cite journal |title=A note on turing machine computability of rule driven systems |date=December 1, 2005 |doi=10.1145/1107523.1107525 |issue=4 |volume=36 |pages=109–110 |journal=] |first=Isaiah Pinchas |last=Kantorovitz|s2cid=31117713 }} | |||
| * Kirner, Raimund; Zimmermann, Wolf; Richter, Dirk: , In 15. Kolloquium Programmiersprachen und Grundlagen der Programmierung (KPS'09), Maria Taferl, Austria, Oct. 2009. | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons category|Turing machines}} | |||
| * {{springer|title=Turing machine|id=p/t094460}} | |||
| * – ] | |||
| * by Enrique Zeleny as part of the ]. | |||
| {{Formal languages and grammars}} | |||
| {{Mathematical logic}} | |||
| {{Alan Turing}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Turing machine}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:18, 19 December 2024
Computation model defining an abstract machine For other uses, see Turing machine (disambiguation).

A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm.
The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write, which direction to move the head, and whether to halt is based on a finite table that specifies what to do for each combination of the current state and the symbol that is read. Like a real computer program, it is possible for a Turing machine to go into an infinite loop which will never halt.
The Turing machine was invented in 1936 by Alan Turing, who called it an "a-machine" (automatic machine). It was Turing's doctoral advisor, Alonzo Church, who later coined the term "Turing machine" in a review. With this model, Turing was able to answer two questions in the negative:
- Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape is "circular" (e.g., freezes, or fails to continue its computational task)?
- Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape ever prints a given symbol?
Thus by providing a mathematical description of a very simple device capable of arbitrary computations, he was able to prove properties of computation in general—and in particular, the uncomputability of the Entscheidungsproblem ('decision problem').
Turing machines proved the existence of fundamental limitations on the power of mechanical computation. While they can express arbitrary computations, their minimalist design makes them too slow for computation in practice: real-world computers are based on different designs that, unlike Turing machines, use random-access memory.
Turing completeness is the ability for a computational model or a system of instructions to simulate a Turing machine. A programming language that is Turing complete is theoretically capable of expressing all tasks accomplishable by computers; nearly all programming languages are Turing complete if the limitations of finite memory are ignored.
Overview
A Turing machine is an idealised model of a central processing unit (CPU) that controls all data manipulation done by a computer, with the canonical machine using sequential memory to store data. Typically, the sequential memory is represented as a tape of infinite length on which the machine can perform read and write operations.
In the context of formal language theory, a Turing machine (automaton) is capable of enumerating some arbitrary subset of valid strings of an alphabet. A set of strings which can be enumerated in this manner is called a recursively enumerable language. The Turing machine can equivalently be defined as a model that recognises valid input strings, rather than enumerating output strings.
Given a Turing machine M and an arbitrary string s, it is generally not possible to decide whether M will eventually produce s. This is due to the fact that the halting problem is unsolvable, which has major implications for the theoretical limits of computing.
The Turing machine is capable of processing an unrestricted grammar, which further implies that it is capable of robustly evaluating first-order logic in an infinite number of ways. This is famously demonstrated through lambda calculus.
A Turing machine that is able to simulate any other Turing machine is called a universal Turing machine (UTM, or simply a universal machine). Another mathematical formalism, lambda calculus, with a similar "universal" nature was introduced by Alonzo Church. Church's work intertwined with Turing's to form the basis for the Church–Turing thesis. This thesis states that Turing machines, lambda calculus, and other similar formalisms of computation do indeed capture the informal notion of effective methods in logic and mathematics and thus provide a model through which one can reason about an algorithm or "mechanical procedure" in a mathematically precise way without being tied to any particular formalism. Studying the abstract properties of Turing machines has yielded many insights into computer science, computability theory, and complexity theory.
Physical description
In his 1948 essay, "Intelligent Machinery", Turing wrote that his machine consists of:
...an unlimited memory capacity obtained in the form of an infinite tape marked out into squares, on each of which a symbol could be printed. At any moment there is one symbol in the machine; it is called the scanned symbol. The machine can alter the scanned symbol, and its behavior is in part determined by that symbol, but the symbols on the tape elsewhere do not affect the behavior of the machine. However, the tape can be moved back and forth through the machine, this being one of the elementary operations of the machine. Any symbol on the tape may therefore eventually have an innings.
— Turing 1948, p. 3
Description
For examples of Turing machines, see Turing machine examples.The Turing machine mathematically models a machine that mechanically operates on a tape. On this tape are symbols, which the machine can read and write, one at a time, using a tape head. Operation is fully determined by a finite set of elementary instructions such as "in state 42, if the symbol seen is 0, write a 1; if the symbol seen is 1, change into state 17; in state 17, if the symbol seen is 0, write a 1 and change to state 6;" etc. In the original article ("On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem", see also references below), Turing imagines not a mechanism, but a person whom he calls the "computer", who executes these deterministic mechanical rules slavishly (or as Turing puts it, "in a desultory manner").


More explicitly, a Turing machine consists of:
- A tape divided into cells, one next to the other. Each cell contains a symbol from some finite alphabet. The alphabet contains a special blank symbol (here written as '0') and one or more other symbols. The tape is assumed to be arbitrarily extendable to the left and to the right, so that the Turing machine is always supplied with as much tape as it needs for its computation. Cells that have not been written before are assumed to be filled with the blank symbol. In some models the tape has a left end marked with a special symbol; the tape extends or is indefinitely extensible to the right.
- A head that can read and write symbols on the tape and move the tape left and right one (and only one) cell at a time. In some models the head moves and the tape is stationary.
- A state register that stores the state of the Turing machine, one of finitely many. Among these is the special start state with which the state register is initialised. These states, writes Turing, replace the "state of mind" a person performing computations would ordinarily be in.
- A finite table of instructions that, given the state(qi) the machine is currently in and the symbol(aj) it is reading on the tape (the symbol currently under the head), tells the machine to do the following in sequence (for the 5-tuple models):
- Either erase or write a symbol (replacing aj with aj1).
- Move the head (which is described by dk and can have values: 'L' for one step left or 'R' for one step right or 'N' for staying in the same place).
- Assume the same or a new state as prescribed (go to state qi1).
In the 4-tuple models, erasing or writing a symbol (aj1) and moving the head left or right (dk) are specified as separate instructions. The table tells the machine to (ia) erase or write a symbol or (ib) move the head left or right, and then (ii) assume the same or a new state as prescribed, but not both actions (ia) and (ib) in the same instruction. In some models, if there is no entry in the table for the current combination of symbol and state, then the machine will halt; other models require all entries to be filled.
Every part of the machine (i.e. its state, symbol-collections, and used tape at any given time) and its actions (such as printing, erasing and tape motion) is finite, discrete and distinguishable; it is the unlimited amount of tape and runtime that gives it an unbounded amount of storage space.
Formal definition
Following Hopcroft & Ullman (1979, p. 148), a (one-tape) Turing machine can be formally defined as a 7-tuple where
- is a finite, non-empty set of tape alphabet symbols;
- is the blank symbol (the only symbol allowed to occur on the tape infinitely often at any step during the computation);
- is the set of input symbols, that is, the set of symbols allowed to appear in the initial tape contents;
- is a finite, non-empty set of states;
- is the initial state;
- is the set of final states or accepting states. The initial tape contents is said to be accepted by if it eventually halts in a state from .
- is a partial function called the transition function, where L is left shift, R is right shift. If is not defined on the current state and the current tape symbol, then the machine halts; intuitively, the transition function specifies the next state transited from the current state, which symbol to overwrite the current symbol pointed by the head, and the next head movement.

A variant allows "no shift", say N, as a third element of the set of directions .
The 7-tuple for the 3-state busy beaver looks like this (see more about this busy beaver at Turing machine examples):
- (states);
- (tape alphabet symbols);
- (blank symbol);
- (input symbols);
- (initial state);
- (final states);
- see state-table below (transition function).
Initially all tape cells are marked with .
| Tape symbol | Current state A | Current state B | Current state C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | |
| 0 | 1 | R | B | 1 | L | A | 1 | L | B |
| 1 | 1 | L | C | 1 | R | B | 1 | R | HALT |
Additional details required to visualise or implement Turing machines
In the words of van Emde Boas (1990), p. 6: "The set-theoretical object provides only partial information on how the machine will behave and what its computations will look like."
For instance,
- There will need to be many decisions on what the symbols actually look like, and a failproof way of reading and writing symbols indefinitely.
- The shift left and shift right operations may shift the tape head across the tape, but when actually building a Turing machine it is more practical to make the tape slide back and forth under the head instead.
- The tape can be finite, and automatically extended with blanks as needed (which is closest to the mathematical definition), but it is more common to think of it as stretching infinitely at one or both ends and being pre-filled with blanks except on the explicitly given finite fragment the tape head is on (this is, of course, not implementable in practice). The tape cannot be fixed in length, since that would not correspond to the given definition and would seriously limit the range of computations the machine can perform to those of a linear bounded automaton if the tape was proportional to the input size, or finite-state machine if it was strictly fixed-length.
Alternative definitions
Definitions in literature sometimes differ slightly, to make arguments or proofs easier or clearer, but this is always done in such a way that the resulting machine has the same computational power. For example, the set could be changed from to , where N ("None" or "No-operation") would allow the machine to stay on the same tape cell instead of moving left or right. This would not increase the machine's computational power.
The most common convention represents each "Turing instruction" in a "Turing table" by one of nine 5-tuples, per the convention of Turing/Davis (Turing (1936) in The Undecidable, p. 126–127 and Davis (2000) p. 152):
- (definition 1): (qi, Sj, Sk/E/N, L/R/N, qm)
- ( current state qi , symbol scanned Sj , print symbol Sk/erase E/none N , move_tape_one_square left L/right R/none N , new state qm )
Other authors (Minsky (1967) p. 119, Hopcroft and Ullman (1979) p. 158, Stone (1972) p. 9) adopt a different convention, with new state qm listed immediately after the scanned symbol Sj:
- (definition 2): (qi, Sj, qm, Sk/E/N, L/R/N)
- ( current state qi , symbol scanned Sj , new state qm , print symbol Sk/erase E/none N , move_tape_one_square left L/right R/none N )
For the remainder of this article "definition 1" (the Turing/Davis convention) will be used.
| Current state | Scanned symbol | Print symbol | Move tape | Final (i.e. next) state | 5-tuples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 1 | R | B | (A, 0, 1, R, B) |
| A | 1 | 1 | L | C | (A, 1, 1, L, C) |
| B | 0 | 1 | L | A | (B, 0, 1, L, A) |
| B | 1 | 1 | R | B | (B, 1, 1, R, B) |
| C | 0 | 1 | L | B | (C, 0, 1, L, B) |
| C | 1 | 1 | N | H | (C, 1, 1, N, H) |
In the following table, Turing's original model allowed only the first three lines that he called N1, N2, N3 (cf. Turing in The Undecidable, p. 126). He allowed for erasure of the "scanned square" by naming a 0th symbol S0 = "erase" or "blank", etc. However, he did not allow for non-printing, so every instruction-line includes "print symbol Sk" or "erase" (cf. footnote 12 in Post (1947), The Undecidable, p. 300). The abbreviations are Turing's (The Undecidable, p. 119). Subsequent to Turing's original paper in 1936–1937, machine-models have allowed all nine possible types of five-tuples:
| Current m-configuration (Turing state) |
Tape symbol | Print-operation | Tape-motion | Final m-configuration (Turing state) |
5-tuple | 5-tuple comments | 4-tuple | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | qi | Sj | Print(Sk) | Left L | qm | (qi, Sj, Sk, L, qm) | "blank" = S0, 1=S1, etc. | |
| N2 | qi | Sj | Print(Sk) | Right R | qm | (qi, Sj, Sk, R, qm) | "blank" = S0, 1=S1, etc. | |
| N3 | qi | Sj | Print(Sk) | None N | qm | (qi, Sj, Sk, N, qm) | "blank" = S0, 1=S1, etc. | (qi, Sj, Sk, qm) |
| 4 | qi | Sj | None N | Left L | qm | (qi, Sj, N, L, qm) | (qi, Sj, L, qm) | |
| 5 | qi | Sj | None N | Right R | qm | (qi, Sj, N, R, qm) | (qi, Sj, R, qm) | |
| 6 | qi | Sj | None N | None N | qm | (qi, Sj, N, N, qm) | Direct "jump" | (qi, Sj, N, qm) |
| 7 | qi | Sj | Erase | Left L | qm | (qi, Sj, E, L, qm) | ||
| 8 | qi | Sj | Erase | Right R | qm | (qi, Sj, E, R, qm) | ||
| 9 | qi | Sj | Erase | None N | qm | (qi, Sj, E, N, qm) | (qi, Sj, E, qm) |
Any Turing table (list of instructions) can be constructed from the above nine 5-tuples. For technical reasons, the three non-printing or "N" instructions (4, 5, 6) can usually be dispensed with. For examples see Turing machine examples.
Less frequently the use of 4-tuples are encountered: these represent a further atomization of the Turing instructions (cf. Post (1947), Boolos & Jeffrey (1974, 1999), Davis-Sigal-Weyuker (1994)); also see more at Post–Turing machine.
The "state"
The word "state" used in context of Turing machines can be a source of confusion, as it can mean two things. Most commentators after Turing have used "state" to mean the name/designator of the current instruction to be performed—i.e. the contents of the state register. But Turing (1936) made a strong distinction between a record of what he called the machine's "m-configuration", and the machine's (or person's) "state of progress" through the computation—the current state of the total system. What Turing called "the state formula" includes both the current instruction and all the symbols on the tape:
Thus the state of progress of the computation at any stage is completely determined by the note of instructions and the symbols on the tape. That is, the state of the system may be described by a single expression (sequence of symbols) consisting of the symbols on the tape followed by Δ (which is supposed to not to appear elsewhere) and then by the note of instructions. This expression is called the "state formula".
— The Undecidable, pp. 139–140, emphasis added
Earlier in his paper Turing carried this even further: he gives an example where he placed a symbol of the current "m-configuration"—the instruction's label—beneath the scanned square, together with all the symbols on the tape (The Undecidable, p. 121); this he calls "the complete configuration" (The Undecidable, p. 118). To print the "complete configuration" on one line, he places the state-label/m-configuration to the left of the scanned symbol.
A variant of this is seen in Kleene (1952) where Kleene shows how to write the Gödel number of a machine's "situation": he places the "m-configuration" symbol q4 over the scanned square in roughly the center of the 6 non-blank squares on the tape (see the Turing-tape figure in this article) and puts it to the right of the scanned square. But Kleene refers to "q4" itself as "the machine state" (Kleene, p. 374–375). Hopcroft and Ullman call this composite the "instantaneous description" and follow the Turing convention of putting the "current state" (instruction-label, m-configuration) to the left of the scanned symbol (p. 149), that is, the instantaneous description is the composite of non-blank symbols to the left, state of the machine, the current symbol scanned by the head, and the non-blank symbols to the right.
Example: total state of 3-state 2-symbol busy beaver after 3 "moves" (taken from example "run" in the figure below):
- 1A1
This means: after three moves the tape has ... 000110000 ... on it, the head is scanning the right-most 1, and the state is A. Blanks (in this case represented by "0"s) can be part of the total state as shown here: B01; the tape has a single 1 on it, but the head is scanning the 0 ("blank") to its left and the state is B.
"State" in the context of Turing machines should be clarified as to which is being described: the current instruction, or the list of symbols on the tape together with the current instruction, or the list of symbols on the tape together with the current instruction placed to the left of the scanned symbol or to the right of the scanned symbol.
Turing's biographer Andrew Hodges (1983: 107) has noted and discussed this confusion.
"State" diagrams
| Tape symbol | Current state A | Current state B | Current state C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | Write symbol | Move tape | Next state | |
| 0 | P | R | B | P | L | A | P | L | B |
| 1 | P | L | C | P | R | B | P | R | HALT |

To the right: the above table as expressed as a "state transition" diagram.
Usually large tables are better left as tables (Booth, p. 74). They are more readily simulated by computer in tabular form (Booth, p. 74). However, certain concepts—e.g. machines with "reset" states and machines with repeating patterns (cf. Hill and Peterson p. 244ff)—can be more readily seen when viewed as a drawing.
Whether a drawing represents an improvement on its table must be decided by the reader for the particular context.
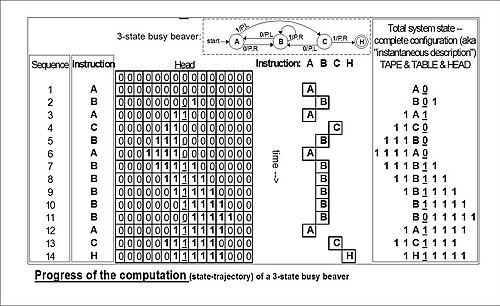
The reader should again be cautioned that such diagrams represent a snapshot of their table frozen in time, not the course ("trajectory") of a computation through time and space. While every time the busy beaver machine "runs" it will always follow the same state-trajectory, this is not true for the "copy" machine that can be provided with variable input "parameters".
The diagram "progress of the computation" shows the three-state busy beaver's "state" (instruction) progress through its computation from start to finish. On the far right is the Turing "complete configuration" (Kleene "situation", Hopcroft–Ullman "instantaneous description") at each step. If the machine were to be stopped and cleared to blank both the "state register" and entire tape, these "configurations" could be used to rekindle a computation anywhere in its progress (cf. Turing (1936) The Undecidable, pp. 139–140).
Equivalent models
See also: Turing machine equivalents, Register machine, and Post–Turing machineMany machines that might be thought to have more computational capability than a simple universal Turing machine can be shown to have no more power (Hopcroft and Ullman p. 159, cf. Minsky (1967)). They might compute faster, perhaps, or use less memory, or their instruction set might be smaller, but they cannot compute more powerfully (i.e. more mathematical functions). (The Church–Turing thesis hypothesises this to be true for any kind of machine: that anything that can be "computed" can be computed by some Turing machine.)
A Turing machine is equivalent to a single-stack pushdown automaton (PDA) that has been made more flexible and concise by relaxing the last-in-first-out (LIFO) requirement of its stack. In addition, a Turing machine is also equivalent to a two-stack PDA with standard LIFO semantics, by using one stack to model the tape left of the head and the other stack for the tape to the right.
At the other extreme, some very simple models turn out to be Turing-equivalent, i.e. to have the same computational power as the Turing machine model.
Common equivalent models are the multi-tape Turing machine, multi-track Turing machine, machines with input and output, and the non-deterministic Turing machine (NDTM) as opposed to the deterministic Turing machine (DTM) for which the action table has at most one entry for each combination of symbol and state.
Read-only, right-moving Turing machines are equivalent to DFAs (as well as NFAs by conversion using the NFA to DFA conversion algorithm).
For practical and didactic intentions, the equivalent register machine can be used as a usual assembly programming language.
A relevant question is whether or not the computation model represented by concrete programming languages is Turing equivalent. While the computation of a real computer is based on finite states and thus not capable to simulate a Turing machine, programming languages themselves do not necessarily have this limitation. Kirner et al., 2009 have shown that among the general-purpose programming languages some are Turing complete while others are not. For example, ANSI C is not Turing complete, as all instantiations of ANSI C (different instantiations are possible as the standard deliberately leaves certain behaviour undefined for legacy reasons) imply a finite-space memory. This is because the size of memory reference data types, called pointers, is accessible inside the language. However, other programming languages like Pascal do not have this feature, which allows them to be Turing complete in principle. It is just Turing complete in principle, as memory allocation in a programming language is allowed to fail, which means the programming language can be Turing complete when ignoring failed memory allocations, but the compiled programs executable on a real computer cannot.
Choice c-machines, oracle o-machines
Early in his paper (1936) Turing makes a distinction between an "automatic machine"—its "motion ... completely determined by the configuration" and a "choice machine":
...whose motion is only partially determined by the configuration ... When such a machine reaches one of these ambiguous configurations, it cannot go on until some arbitrary choice has been made by an external operator. This would be the case if we were using machines to deal with axiomatic systems.
— The Undecidable, p. 118
Turing (1936) does not elaborate further except in a footnote in which he describes how to use an a-machine to "find all the provable formulae of the calculus" rather than use a choice machine. He "suppose that the choices are always between two possibilities 0 and 1. Each proof will then be determined by a sequence of choices i1, i2, ..., in (i1 = 0 or 1, i2 = 0 or 1, ..., in = 0 or 1), and hence the number 2 + i12 + i22 + ... +in completely determines the proof. The automatic machine carries out successively proof 1, proof 2, proof 3, ..." (Footnote ‡, The Undecidable, p. 138)
This is indeed the technique by which a deterministic (i.e., a-) Turing machine can be used to mimic the action of a nondeterministic Turing machine; Turing solved the matter in a footnote and appears to dismiss it from further consideration.
An oracle machine or o-machine is a Turing a-machine that pauses its computation at state "o" while, to complete its calculation, it "awaits the decision" of "the oracle"—an entity unspecified by Turing "apart from saying that it cannot be a machine" (Turing (1939), The Undecidable, p. 166–168).
Universal Turing machines
Main article: Universal Turing machine
As Turing wrote in The Undecidable, p. 128 (italics added):
It is possible to invent a single machine which can be used to compute any computable sequence. If this machine U is supplied with the tape on the beginning of which is written the string of quintuples separated by semicolons of some computing machine M, then U will compute the same sequence as M.
This finding is now taken for granted, but at the time (1936) it was considered astonishing. The model of computation that Turing called his "universal machine"—"U" for short—is considered by some (cf. Davis (2000)) to have been the fundamental theoretical breakthrough that led to the notion of the stored-program computer.
Turing's paper ... contains, in essence, the invention of the modern computer and some of the programming techniques that accompanied it.
— Minsky (1967), p. 104
In terms of computational complexity, a multi-tape universal Turing machine need only be slower by logarithmic factor compared to the machines it simulates. This result was obtained in 1966 by F. C. Hennie and R. E. Stearns. (Arora and Barak, 2009, theorem 1.9)
Comparison with real machines

Turing machines are more powerful than some other kinds of automata, such as finite-state machines and pushdown automata. According to the Church–Turing thesis, they are as powerful as real machines, and are able to execute any operation that a real program can. What is neglected in this statement is that, because a real machine can only have a finite number of configurations, it is nothing but a finite-state machine, whereas a Turing machine has an unlimited amount of storage space available for its computations.
There are a number of ways to explain why Turing machines are useful models of real computers:
- Anything a real computer can compute, a Turing machine can also compute. For example: "A Turing machine can simulate any type of subroutine found in programming languages, including recursive procedures and any of the known parameter-passing mechanisms" (Hopcroft and Ullman p. 157). A large enough FSA can also model any real computer, disregarding IO. Thus, a statement about the limitations of Turing machines will also apply to real computers.
- The difference lies only with the ability of a Turing machine to manipulate an unbounded amount of data. However, given a finite amount of time, a Turing machine (like a real machine) can only manipulate a finite amount of data.
- Like a Turing machine, a real machine can have its storage space enlarged as needed, by acquiring more disks or other storage media.
- Descriptions of real machine programs using simpler abstract models are often much more complex than descriptions using Turing machines. For example, a Turing machine describing an algorithm may have a few hundred states, while the equivalent deterministic finite automaton (DFA) on a given real machine has quadrillions. This makes the DFA representation infeasible to analyze.
- Turing machines describe algorithms independent of how much memory they use. There is a limit to the memory possessed by any current machine, but this limit can rise arbitrarily in time. Turing machines allow us to make statements about algorithms which will (theoretically) hold forever, regardless of advances in conventional computing machine architecture.
- Algorithms running on Turing-equivalent abstract machines can have arbitrary-precision data types available and never have to deal with unexpected conditions (including, but not limited to, running out of memory).

Limitations
Computational complexity theory
Further information: Computational complexity theoryA limitation of Turing machines is that they do not model the strengths of a particular arrangement well. For instance, modern stored-program computers are actually instances of a more specific form of abstract machine known as the random-access stored-program machine or RASP machine model. Like the universal Turing machine, the RASP stores its "program" in "memory" external to its finite-state machine's "instructions". Unlike the universal Turing machine, the RASP has an infinite number of distinguishable, numbered but unbounded "registers"—memory "cells" that can contain any integer (cf. Elgot and Robinson (1964), Hartmanis (1971), and in particular Cook-Rechow (1973); references at random-access machine). The RASP's finite-state machine is equipped with the capability for indirect addressing (e.g., the contents of one register can be used as an address to specify another register); thus the RASP's "program" can address any register in the register-sequence. The upshot of this distinction is that there are computational optimizations that can be performed based on the memory indices, which are not possible in a general Turing machine; thus when Turing machines are used as the basis for bounding running times, a "false lower bound" can be proven on certain algorithms' running times (due to the false simplifying assumption of a Turing machine). An example of this is binary search, an algorithm that can be shown to perform more quickly when using the RASP model of computation rather than the Turing machine model.
Interaction
In the early days of computing, computer use was typically limited to batch processing, i.e., non-interactive tasks, each producing output data from given input data. Computability theory, which studies computability of functions from inputs to outputs, and for which Turing machines were invented, reflects this practice.
Since the 1970s, interactive use of computers became much more common. In principle, it is possible to model this by having an external agent read from the tape and write to it at the same time as a Turing machine, but this rarely matches how interaction actually happens; therefore, when describing interactivity, alternatives such as I/O automata are usually preferred.
Comparison with the arithmetic model of computation
The arithmetic model of computation differs from the Turing model in two aspects:
- In the arithmetic model, every real number requires a single memory cell, whereas in the Turing model the storage size of a real number depends on the number of bits required to represent it.
- In the arithmetic model, every basic arithmetic operation on real numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) can be done in a single step, whereas in the Turing model the run-time of each arithmetic operation depends on the length of the operands.
Some algorithms run in polynomial time in one model but not in the other one. For example:
- The Euclidean algorithm runs in polynomial time in the Turing model, but not in the arithmetic model.
- The algorithm that reads n numbers and then computes by repeated squaring runs in polynomial time in the Arithmetic model, but not in the Turing model. This is because the number of bits required to represent the outcome is exponential in the input size.
However, if an algorithm runs in polynomial time in the arithmetic model, and in addition, the binary length of all involved numbers is polynomial in the length of the input, then it is always polynomial-time in the Turing model. Such an algorithm is said to run in strongly polynomial time.
History
See also: Algorithm and Church–Turing thesisHistorical background: computational machinery
Robin Gandy (1919–1995)—a student of Alan Turing (1912–1954), and his lifelong friend—traces the lineage of the notion of "calculating machine" back to Charles Babbage (circa 1834) and actually proposes "Babbage's Thesis":
That the whole of development and operations of analysis are now capable of being executed by machinery.
— (italics in Babbage as cited by Gandy, p. 54)
Gandy's analysis of Babbage's analytical engine describes the following five operations (cf. p. 52–53):
- The arithmetic functions +, −, ×, where − indicates "proper" subtraction: x − y = 0 if y ≥ x.
- Any sequence of operations is an operation.
- Iteration of an operation (repeating n times an operation P).
- Conditional iteration (repeating n times an operation P conditional on the "success" of test T).
- Conditional transfer (i.e., conditional "goto").
Gandy states that "the functions which can be calculated by (1), (2), and (4) are precisely those which are Turing computable." (p. 53). He cites other proposals for "universal calculating machines" including those of Percy Ludgate (1909), Leonardo Torres Quevedo (1914), Maurice d'Ocagne (1922), Louis Couffignal (1933), Vannevar Bush (1936), Howard Aiken (1937). However:
… the emphasis is on programming a fixed iterable sequence of arithmetical operations. The fundamental importance of conditional iteration and conditional transfer for a general theory of calculating machines is not recognized…
— Gandy p. 55
The Entscheidungsproblem (the "decision problem"): Hilbert's tenth question of 1900
With regard to Hilbert's problems posed by the famous mathematician David Hilbert in 1900, an aspect of problem #10 had been floating about for almost 30 years before it was framed precisely. Hilbert's original expression for No. 10 is as follows:
10. Determination of the solvability of a Diophantine equation. Given a Diophantine equation with any number of unknown quantities and with rational integral coefficients: To devise a process according to which it can be determined in a finite number of operations whether the equation is solvable in rational integers. The Entscheidungsproblem is solved when we know a procedure that allows for any given logical expression to decide by finitely many operations its validity or satisfiability ... The Entscheidungsproblem must be considered the main problem of mathematical logic.
— quoted, with this translation and the original German, in Dershowitz and Gurevich, 2008
By 1922, this notion of "Entscheidungsproblem" had developed a bit, and H. Behmann stated that
... most general form of the Entscheidungsproblem as follows:
— Gandy p. 57, quoting BehmannA quite definite generally applicable prescription is required which will allow one to decide in a finite number of steps the truth or falsity of a given purely logical assertion ...
Behmann remarks that ... the general problem is equivalent to the problem of deciding which mathematical propositions are true.
— ibid.
If one were able to solve the Entscheidungsproblem then one would have a "procedure for solving many (or even all) mathematical problems".
— ibid., p. 92
By the 1928 international congress of mathematicians, Hilbert "made his questions quite precise. First, was mathematics complete ... Second, was mathematics consistent ... And thirdly, was mathematics decidable?" (Hodges p. 91, Hawking p. 1121). The first two questions were answered in 1930 by Kurt Gödel at the very same meeting where Hilbert delivered his retirement speech (much to the chagrin of Hilbert); the third—the Entscheidungsproblem—had to wait until the mid-1930s.
The problem was that an answer first required a precise definition of "definite general applicable prescription", which Princeton professor Alonzo Church would come to call "effective calculability", and in 1928 no such definition existed. But over the next 6–7 years Emil Post developed his definition of a worker moving from room to room writing and erasing marks per a list of instructions (Post 1936), as did Church and his two students Stephen Kleene and J. B. Rosser by use of Church's lambda-calculus and Gödel's recursion theory (1934). Church's paper (published 15 April 1936) showed that the Entscheidungsproblem was indeed "undecidable" and beat Turing to the punch by almost a year (Turing's paper submitted 28 May 1936, published January 1937). In the meantime, Emil Post submitted a brief paper in the fall of 1936, so Turing at least had priority over Post. While Church refereed Turing's paper, Turing had time to study Church's paper and add an Appendix where he sketched a proof that Church's lambda-calculus and his machines would compute the same functions.
But what Church had done was something rather different, and in a certain sense weaker. ... the Turing construction was more direct, and provided an argument from first principles, closing the gap in Church's demonstration.
— Hodges p. 112
And Post had only proposed a definition of calculability and criticised Church's "definition", but had proved nothing.
Alan Turing's a-machine
In the spring of 1935, Turing as a young Master's student at King's College, Cambridge, took on the challenge; he had been stimulated by the lectures of the logician M. H. A. Newman "and learned from them of Gödel's work and the Entscheidungsproblem ... Newman used the word 'mechanical' ... In his obituary of Turing 1955 Newman writes:
To the question 'what is a "mechanical" process?' Turing returned the characteristic answer 'Something that can be done by a machine' and he embarked on the highly congenial task of analysing the general notion of a computing machine.
— Gandy, p. 74
Gandy states that:
I suppose, but do not know, that Turing, right from the start of his work, had as his goal a proof of the undecidability of the Entscheidungsproblem. He told me that the 'main idea' of the paper came to him when he was lying in Grantchester meadows in the summer of 1935. The 'main idea' might have either been his analysis of computation or his realization that there was a universal machine, and so a diagonal argument to prove unsolvability.
— ibid., p. 76
While Gandy believed that Newman's statement above is "misleading", this opinion is not shared by all. Turing had a lifelong interest in machines: "Alan had dreamt of inventing typewriters as a boy; Mrs. Turing had a typewriter; and he could well have begun by asking himself what was meant by calling a typewriter 'mechanical'" (Hodges p. 96). While at Princeton pursuing his PhD, Turing built a Boolean-logic multiplier (see below). His PhD thesis, titled "Systems of Logic Based on Ordinals", contains the following definition of "a computable function":
It was stated above that 'a function is effectively calculable if its values can be found by some purely mechanical process'. We may take this statement literally, understanding by a purely mechanical process one which could be carried out by a machine. It is possible to give a mathematical description, in a certain normal form, of the structures of these machines. The development of these ideas leads to the author's definition of a computable function, and to an identification of computability with effective calculability. It is not difficult, though somewhat laborious, to prove that these three definitions are equivalent.
— Turing (1939) in The Undecidable, p. 160
Alan Turing invented the "a-machine" (automatic machine) in 1936. Turing submitted his paper on 31 May 1936 to the London Mathematical Society for its Proceedings (cf. Hodges 1983:112), but it was published in early 1937 and offprints were available in February 1937 (cf. Hodges 1983:129) It was Turing's doctoral advisor, Alonzo Church, who later coined the term "Turing machine" in a review. With this model, Turing was able to answer two questions in the negative:
- Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape is "circular" (e.g., freezes, or fails to continue its computational task)?
- Does a machine exist that can determine whether any arbitrary machine on its tape ever prints a given symbol?
Thus by providing a mathematical description of a very simple device capable of arbitrary computations, he was able to prove properties of computation in general—and in particular, the uncomputability of the Entscheidungsproblem ('decision problem').
When Turing returned to the UK he ultimately became jointly responsible for breaking the German secret codes created by encryption machines called "The Enigma"; he also became involved in the design of the ACE (Automatic Computing Engine), " ACE proposal was effectively self-contained, and its roots lay not in the EDVAC , but in his own universal machine" (Hodges p. 318). Arguments still continue concerning the origin and nature of what has been named by Kleene (1952) Turing's Thesis. But what Turing did prove with his computational-machine model appears in his paper "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem" (1937):
the Hilbert Entscheidungsproblem can have no solution ... I propose, therefore to show that there can be no general process for determining whether a given formula U of the functional calculus K is provable, i.e. that there can be no machine which, supplied with any one U of these formulae, will eventually say whether U is provable.
— from Turing's paper as reprinted in The Undecidable, p. 145
Turing's example (his second proof): If one is to ask for a general procedure to tell us: "Does this machine ever print 0", the question is "undecidable".
1937–1970: The "digital computer", the birth of "computer science"
In 1937, while at Princeton working on his PhD thesis, Turing built a digital (Boolean-logic) multiplier from scratch, making his own electromechanical relays (Hodges p. 138). "Alan's task was to embody the logical design of a Turing machine in a network of relay-operated switches ..." (Hodges p. 138). While Turing might have been just initially curious and experimenting, quite-earnest work in the same direction was going in Germany (Konrad Zuse (1938)), and in the United States (Howard Aiken) and George Stibitz (1937); the fruits of their labors were used by both the Axis and Allied militaries in World War II (cf. Hodges p. 298–299). In the early to mid-1950s Hao Wang and Marvin Minsky reduced the Turing machine to a simpler form (a precursor to the Post–Turing machine of Martin Davis); simultaneously European researchers were reducing the new-fangled electronic computer to a computer-like theoretical object equivalent to what was now being called a "Turing machine". In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the coincidentally parallel developments of Melzak and Lambek (1961), Minsky (1961), and Shepherdson and Sturgis (1961) carried the European work further and reduced the Turing machine to a more friendly, computer-like abstract model called the counter machine; Elgot and Robinson (1964), Hartmanis (1971), Cook and Reckhow (1973) carried this work even further with the register machine and random-access machine models—but basically all are just multi-tape Turing machines with an arithmetic-like instruction set.
1970–present: as a model of computation
Today, the counter, register and random-access machines and their sire the Turing machine continue to be the models of choice for theorists investigating questions in the theory of computation. In particular, computational complexity theory makes use of the Turing machine:
Depending on the objects one likes to manipulate in the computations (numbers like nonnegative integers or alphanumeric strings), two models have obtained a dominant position in machine-based complexity theory:
— van Emde Boas 1990:4the off-line multitape Turing machine..., which represents the standard model for string-oriented computation, and the random access machine (RAM) as introduced by Cook and Reckhow ..., which models the idealised Von Neumann-style computer.
Only in the related area of analysis of algorithms this role is taken over by the RAM model.
— van Emde Boas 1990:16
See also
- Arithmetical hierarchy
- Bekenstein bound, showing the impossibility of infinite-tape Turing machines of finite size and bounded energy
- BlooP and FlooP
- Chaitin's constant or Omega (computer science) for information relating to the halting problem
- Chinese room
- Conway's Game of Life, a Turing-complete cellular automaton
- Digital infinity
- The Emperor's New Mind
- Enumerator (in theoretical computer science)
- Genetix
- Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid, a famous book that discusses, among other topics, the Church–Turing thesis
- Halting problem, for more references
- Harvard architecture
- Imperative programming
- Langton's ant and Turmites, simple two-dimensional analogues of the Turing machine
- List of things named after Alan Turing
- Modified Harvard architecture
- Quantum Turing machine
- Claude Shannon, another leading thinker in information theory
- Turing machine examples
- Turing tarpit, any computing system or language that, despite being Turing complete, is generally considered useless for practical computing
- Unorganised machine, for Turing's very early ideas on neural networks
- Von Neumann architecture
Notes
- Minsky 1967:107 "In his 1936 paper, A. M. Turing defined the class of abstract machines that now bear his name. A Turing machine is a finite-state machine associated with a special kind of environment -- its tape -- in which it can store (and later recover) sequences of symbols," also Stone 1972:8 where the word "machine" is in quotation marks.
- Stone 1972:8 states "This "machine" is an abstract mathematical model", also cf. Sipser 2006:137ff that describes the "Turing machine model". Rogers 1987 (1967):13 refers to "Turing's characterization", Boolos Burgess and Jeffrey 2002:25 refers to a "specific kind of idealized machine".
- Sipser 2006:137 "A Turing machine can do everything that a real computer can do".
- Cf. Sipser 2002:137. Also, Rogers 1987 (1967):13 describes "a paper tape of infinite length in both directions". Minsky 1967:118 states "The tape is regarded as infinite in both directions". Boolos Burgess and Jeffrey 2002:25 include the possibility of "there is someone stationed at each end to add extra blank squares as needed".
- Cf. Rogers 1987 (1967):13. Other authors use the word "square" e.g. Boolos Burgess Jeffrey 2002:35, Minsky 1967:117, Penrose 1989:37.
- Boolos Burgess Jeffry 2002:25 illustrate the machine as moving along the tape. Penrose 1989:36-37 describes himself as "uncomfortable" with an infinite tape observing that it "might be hard to shift!"; he "prefer to think of the tape as representing some external environment through which our finite device can move" and after observing that the " 'movement' is a convenient way of picturing things" and then suggests that "the device receives all its input from this environment. Some variations of the Turing machine model also allow the head to stay in the same position instead of moving or halting.
- ^ Hodges, Andrew (2012). Alan Turing: The Enigma (The Centenary ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15564-7.
- The idea came to him in mid-1935 (perhaps, see more in the History section) after a question posed by M. H. A. Newman in his lectures: "Was there a definite method, or as Newman put it, a "mechanical process" which could be applied to a mathematical statement, and which would come up with the answer as to whether it was provable" (Hodges 1983:93). Turing submitted his paper on 31 May 1936 to the London Mathematical Society for its Proceedings (cf. Hodges 1983:112), but it was published in early 1937 and offprints were available in February 1937 (cf. Hodges 1983:129).
- See footnote in Davis 2000:151.
- ^ see note in forward to The Collected Works of Alonzo Church (Burge, Tyler; Enderton, Herbert, eds. (2019-04-23). The Collected Works of Alonzo Church. Cambridge, MA, US: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-02564-5.)
- ^ Turing 1936 in The Undecidable 1965:132-134; Turing's definition of "circular" is found on page 119.
- ^ Turing, Alan Mathison (1937). "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem". Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. Series 2. 42 (1): 230–265. doi:10.1112/plms/s2-42.1.230. S2CID 73712.
- ^ Turing 1936 in The Undecidable 1965:145
- Sipser 2006:137 observes that "A Turing machine can do everything that a real computer can do. Nevertheless, even a Turing machine cannot solve certain problems. In a very real sense, these problems are beyond the theoretical limits of computation."
- See the definition of "innings" on Wiktionary
- A.M. Turing (Jul 1948). Intelligent Machinery (Report). National Physical Laboratory. Here: p.3-4
- Occasionally called an action table or transition function.
- Usually quintuples : qiaj→qi1aj1dk, but sometimes quadruples .
- p.149; in particular, Hopcroft and Ullman assume that is undefined on all states from
- Grötschel, Martin; Lovász, László; Schrijver, Alexander (1993), Geometric algorithms and combinatorial optimization, Algorithms and Combinatorics, vol. 2 (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-78240-4, ISBN 978-3-642-78242-8, MR 1261419
- L. Torres Quevedo. Ensayos sobre Automática – Su definicion. Extension teórica de sus aplicaciones, Revista de la Academia de Ciencias Exacta, Revista 12, pp. 391–418, 1914.
- Torres Quevedo. L. (1915). "Essais sur l'Automatique - Sa définition. Etendue théorique de ses applications", Revue Génerale des Sciences Pures et Appliquées, vol. 2, pp. 601–611.
- The narrower question posed in Hilbert's tenth problem, about Diophantine equations, remains unresolved until 1970, when the relationship between recursively enumerable sets and Diophantine sets is finally laid bare.
References
| This article has an unclear citation style. The references used may be made clearer with a different or consistent style of citation and footnoting. (November 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Primary literature, reprints, and compilations
- B. Jack Copeland ed. (2004), The Essential Turing: Seminal Writings in Computing, Logic, Philosophy, Artificial Intelligence, and Artificial Life plus The Secrets of Enigma, Clarendon Press (Oxford University Press), Oxford UK, ISBN 0-19-825079-7. Contains the Turing papers plus a draft letter to Emil Post re his criticism of "Turing's convention", and Donald W. Davies' Corrections to Turing's Universal Computing Machine
- Martin Davis (ed.) (1965), The Undecidable, Raven Press, Hewlett, NY.
- Emil Post (1936), "Finite Combinatory Processes—Formulation 1", Journal of Symbolic Logic, 1, 103–105, 1936. Reprinted in The Undecidable, pp. 289ff.
- Emil Post (1947), "Recursive Unsolvability of a Problem of Thue", Journal of Symbolic Logic, vol. 12, pp. 1–11. Reprinted in The Undecidable, pp. 293ff. In the Appendix of this paper Post comments on and gives corrections to Turing's paper of 1936–1937. In particular see the footnotes 11 with corrections to the universal computing machine coding and footnote 14 with comments on Turing's first and second proofs.
- Turing, A.M. (1936). "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem" (PDF). Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. 2. 42 (published 1937): 230–265. doi:10.1112/plms/s2-42.1.230. S2CID 73712.
- Turing, A.M. (1938). "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem: A correction". Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. 2. 43 (6) (published 1937): 544–6. doi:10.1112/plms/s2-43.6.544. Reprinted in The Undecidable, pp. 115–154.
- Alan Turing, 1948, "Intelligent Machinery." Reprinted in "Cybernetics: Key Papers." Ed. C.R. Evans and A.D.J. Robertson. Baltimore: University Park Press, 1968. p. 31. Reprinted in Turing, A. M. (1996). "Intelligent Machinery, A Heretical Theory". Philosophia Mathematica. 4 (3): 256–260. doi:10.1093/philmat/4.3.256.
- F. C. Hennie and R. E. Stearns. Two-tape simulation of multitape Turing machines. JACM, 13(4):533–546, 1966.
Computability theory
- Boolos, George; Richard Jeffrey (1999) . Computability and Logic (3rd ed.). Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-20402-X.
- Boolos, George; John Burgess; Richard Jeffrey (2002). Computability and Logic (4th ed.). Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-00758-5. Some parts have been significantly rewritten by Burgess. Presentation of Turing machines in context of Lambek "abacus machines" (cf. Register machine) and recursive functions, showing their equivalence.
- Taylor L. Booth (1967), Sequential Machines and Automata Theory, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. Graduate level engineering text; ranges over a wide variety of topics, Chapter IX Turing Machines includes some recursion theory.
- Martin Davis (1958). Computability and Unsolvability. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc, New York.. On pages 12–20 he gives examples of 5-tuple tables for Addition, The Successor Function, Subtraction (x ≥ y), Proper Subtraction (0 if x < y), The Identity Function and various identity functions, and Multiplication.
- Davis, Martin; Ron Sigal; Elaine J. Weyuker (1994). Computability, Complexity, and Languages and Logic: Fundamentals of Theoretical Computer Science (2nd ed.). San Diego: Academic Press, Harcourt, Brace & Company. ISBN 0-12-206382-1.
- Hennie, Fredrick (1977). Introduction to Computability. Addison–Wesley, Reading, Mass. QA248.5H4 1977.. On pages 90–103 Hennie discusses the UTM with examples and flow-charts, but no actual 'code'.
- Hopcroft, John; Ullman, Jeffrey (1979). Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation (1st ed.). Addison–Wesley, Reading Mass. ISBN 0-201-02988-X. Centered around the issues of machine-interpretation of "languages", NP-completeness, etc.
- Hopcroft, John E.; Rajeev Motwani; Jeffrey D. Ullman (2001). Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation (2nd ed.). Reading Mass: Addison–Wesley. ISBN 0-201-44124-1.
- Stephen Kleene (1952), Introduction to Metamathematics, North–Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam Netherlands, 10th impression (with corrections of 6th reprint 1971). Graduate level text; most of Chapter XIII Computable functions is on Turing machine proofs of computability of recursive functions, etc.
- Knuth, Donald E. (1973). Volume 1/Fundamental Algorithms: The Art of computer Programming (2nd ed.). Reading, Mass.: Addison–Wesley Publishing Company.. With reference to the role of Turing machines in the development of computation (both hardware and software) see 1.4.5 History and Bibliography pp. 225ff and 2.6 History and Bibliographypp. 456ff.
- Zohar Manna, 1974, Mathematical Theory of Computation. Reprinted, Dover, 2003. ISBN 978-0-486-43238-0
- Marvin Minsky, Computation: Finite and Infinite Machines, Prentice–Hall, Inc., N.J., 1967. See Chapter 8, Section 8.2 "Unsolvability of the Halting Problem."
- Christos Papadimitriou (1993). Computational Complexity (1st ed.). Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-201-53082-1. Chapter 2: Turing machines, pp. 19–56.
- Hartley Rogers, Jr., Theory of Recursive Functions and Effective Computability, The MIT Press, Cambridge MA, paperback edition 1987, original McGraw-Hill edition 1967, ISBN 0-262-68052-1 (pbk.)
- Michael Sipser (1997). Introduction to the Theory of Computation. PWS Publishing. ISBN 0-534-94728-X. Chapter 3: The Church–Turing Thesis, pp. 125–149.
- Stone, Harold S. (1972). Introduction to Computer Organization and Data Structures (1st ed.). New York: McGraw–Hill Book Company. ISBN 0-07-061726-0.
- Peter van Emde Boas 1990, Machine Models and Simulations, pp. 3–66, in Jan van Leeuwen, ed., Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science, Volume A: Algorithms and Complexity, The MIT Press/Elsevier, , ISBN 0-444-88071-2 (Volume A). QA76.H279 1990.
Church's thesis
- Nachum Dershowitz; Yuri Gurevich (September 2008). "A natural axiomatization of computability and proof of Church's Thesis" (PDF). Bulletin of Symbolic Logic. 14 (3). Retrieved 2008-10-15.
- Roger Penrose (1990) . The Emperor's New Mind (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press, New York. ISBN 0-19-851973-7.
Small Turing machines
- Rogozhin, Yurii, 1998, "A Universal Turing Machine with 22 States and 2 Symbols", Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology, 1(3), 259–265, 1998. (surveys known results about small universal Turing machines)
- Stephen Wolfram, 2002, A New Kind of Science, Wolfram Media, ISBN 1-57955-008-8
- Brunfiel, Geoff, Student snags maths prize, Nature, October 24. 2007.
- Jim Giles (2007), Simplest 'universal computer' wins student $25,000, New Scientist, October 24, 2007.
- Alex Smith, Universality of Wolfram's 2, 3 Turing Machine, Submission for the Wolfram 2, 3 Turing Machine Research Prize.
- Vaughan Pratt, 2007, "Simple Turing machines, Universality, Encodings, etc.", FOM email list. October 29, 2007.
- Martin Davis, 2007, "Smallest universal machine", and Definition of universal Turing machine FOM email list. October 26–27, 2007.
- Alasdair Urquhart, 2007 "Smallest universal machine", FOM email list. October 26, 2007.
- Hector Zenil (Wolfram Research), 2007 "smallest universal machine", FOM email list. October 29, 2007.
- Todd Rowland, 2007, "Confusion on FOM", Wolfram Science message board, October 30, 2007.
- Olivier and Marc RAYNAUD, 2014, A programmable prototype to achieve Turing machines Archived 2016-01-14 at the Wayback Machine" LIMOS Laboratory of Blaise Pascal University (Clermont-Ferrand in France).
Other
- Martin Davis (2000). Engines of Logic: Mathematicians and the origin of the Computer (1st ed.). W. W. Norton & Company, New York. ISBN 978-0-393-32229-3.
- Robin Gandy, "The Confluence of Ideas in 1936", pp. 51–102 in Rolf Herken, see below.
- Stephen Hawking (editor), 2005, God Created the Integers: The Mathematical Breakthroughs that Changed History, Running Press, Philadelphia, ISBN 978-0-7624-1922-7. Includes Turing's 1936–1937 paper, with brief commentary and biography of Turing as written by Hawking.
- Rolf Herken (1995). The Universal Turing Machine—A Half-Century Survey. Springer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-211-82637-9.
- Andrew Hodges, Alan Turing: The Enigma, Simon and Schuster, New York. Cf. Chapter "The Spirit of Truth" for a history leading to, and a discussion of, his proof.
- Ivars Peterson (1988). The Mathematical Tourist: Snapshots of Modern Mathematics (1st ed.). W. H. Freeman and Company, New York. ISBN 978-0-7167-2064-5.
- Roger Penrose, The Emperor's New Mind: Concerning Computers, Minds, and the Laws of Physics, Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, 1989 (1990 corrections), ISBN 0-19-851973-7.
- Paul Strathern (1997). Turing and the Computer—The Big Idea. Anchor Books/Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-49243-0.
- Hao Wang, "A variant to Turing's theory of computing machines", Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery (JACM) 4, 63–92 (1957).
- Charles Petzold, The Annotated Turing, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ISBN 0-470-22905-5
- Arora, Sanjeev; Barak, Boaz, "Complexity Theory: A Modern Approach", Cambridge University Press, 2009, ISBN 978-0-521-42426-4, section 1.4, "Machines as strings and the universal Turing machine" and 1.7, "Proof of theorem 1.9"
- Kantorovitz, Isaiah Pinchas (December 1, 2005). "A note on turing machine computability of rule driven systems". SIGACT News. 36 (4): 109–110. doi:10.1145/1107523.1107525. S2CID 31117713.
- Kirner, Raimund; Zimmermann, Wolf; Richter, Dirk: "On Undecidability Results of Real Programming Languages", In 15. Kolloquium Programmiersprachen und Grundlagen der Programmierung (KPS'09), Maria Taferl, Austria, Oct. 2009.
External links
- "Turing machine", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Turing Machine – Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Turing Machine Causal Networks by Enrique Zeleny as part of the Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
| Automata theory: formal languages and formal grammars | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Each category of languages, except those marked by a , is a proper subset of the category directly above it. Any language in each category is generated by a grammar and by an automaton in the category in the same line. | |||||||||
| Mathematical logic | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||
| Theorems (list) and paradoxes | |||||||||
| Logics |
| ||||||||
| Set theory |
| ||||||||
| Formal systems (list), language and syntax |
| ||||||||
| Proof theory | |||||||||
| Model theory | |||||||||
| Computability theory | |||||||||
| Related | |||||||||
| Alan Turing | |
|---|---|
| Publications |
|
| Related | |
 where
where
 is a finite, non-empty set of tape alphabet symbols;
is a finite, non-empty set of tape alphabet symbols; is the blank symbol (the only symbol allowed to occur on the tape infinitely often at any step during the computation);
is the blank symbol (the only symbol allowed to occur on the tape infinitely often at any step during the computation); is the set of input symbols, that is, the set of symbols allowed to appear in the initial tape contents;
is the set of input symbols, that is, the set of symbols allowed to appear in the initial tape contents; is a finite, non-empty set of states;
is a finite, non-empty set of states; is the initial state;
is the initial state; is the set of final states or accepting states. The initial tape contents is said to be accepted by
is the set of final states or accepting states. The initial tape contents is said to be accepted by  if it eventually halts in a state from
if it eventually halts in a state from  .
. is a
is a  is not defined on the current state and the current tape symbol, then the machine halts; intuitively, the transition function specifies the next state transited from the current state, which symbol to overwrite the current symbol pointed by the head, and the next head movement.
is not defined on the current state and the current tape symbol, then the machine halts; intuitively, the transition function specifies the next state transited from the current state, which symbol to overwrite the current symbol pointed by the head, and the next head movement. .
.
 (states);
(states); (tape alphabet symbols);
(tape alphabet symbols); (blank symbol);
(blank symbol); (input symbols);
(input symbols); (initial state);
(initial state); (final states);
(final states); see state-table below (transition function).
see state-table below (transition function). .
.
 , where N ("None" or "No-operation") would allow the machine to stay on the same tape cell instead of moving left or right. This would not increase the machine's computational power.
, where N ("None" or "No-operation") would allow the machine to stay on the same tape cell instead of moving left or right. This would not increase the machine's computational power.
 by
by