| Revision as of 17:11, 4 March 2009 view source66.175.164.36 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:03, 15 December 2024 view source Mason7512 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,254 edits Asian people-> Asian ColombiansTag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Country in South America}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| {{About|the country|its predecessor|Gran Colombia|other uses|Colombia (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{distinguish|Columbia}} | |||
| {{Distinguish|Columbia (disambiguation){{!}}Columbia|Colombo}} | |||
| {{otheruses}} | |||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Infobox Country | |||
| {{Use American English|date=November 2021}} | |||
| |native_name = ''República de Colombia''{{spaces|2}}<small>{{es icon}}</small> | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2024}} | |||
| |conventional_long_name = Republic of Colombia | |||
| {{Infobox country | |||
| |common_name = Colombia | |||
| | |
| coordinates = {{Coord|4|35|N|74|4|W|type:city}} | ||
| | |
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Colombia | ||
| | native_name = {{lang|es|República de Colombia}} (]) | |||
| |image_map = LocationColombia.svg | |||
| | image_flag = Flag of Colombia.svg | |||
| |national_motto = "Libertad y Orden"{{spaces|2}}<small>{{es icon}}</small><br />"Liberty and Order"</small> | |||
| | image_coat = Coat of arms of Colombia.svg | |||
| |national_anthem = "]"{{spaces|2}}<small>{{es icon}}</small> | |||
| | common_name = Colombia | |||
| |capital = ] ] | |||
| | national_motto = {{native phrase|es|"Libertad y Orden"|italics=off|nolink=yes}} | |||
| |latd = 4 | |||
| | |
| englishmotto = "Freedom and Order" | ||
| | national_anthem = {{native phrase|es|]|nolink=yes}}<br />"National Anthem of the Republic of Colombia"<div style="padding-top:0.5em;">{{center|]}}</div> | |||
| |latNS = N | |||
| | |
| image_map = COL orthographic (San Andrés and Providencia special).svg | ||
| | |
| map_caption = {{map caption |location_color=dark green }} | ||
| | |
| capital = ] | ||
| | |
| religion = {{unbulleted list | ||
| | 70.2% ] | |||
| |official_languages = ] | |||
| | 16.8% other ] | |||
| |regional_languages = <small>The languages and dialects of ethnic groups are also official in their territories</small><ref> (Article 10)</ref> | |||
| | 11.1% ] | |||
| |ethnic_groups = 58% ], 20% ], 14% ], 4% ], 3% ], 1% ]<ref name="CIAWFB"> {{cite web | author = CIA world fact book | url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/co.html | title = Colombia | work = CIA |date = 2009-01-22| accessdate = 2009-01-24 }}</ref> | |||
| | 1.9% other | |||
| |demonym = Colombian | |||
| |government_type = ] | |||
| |leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |leader_title2 = ] | |||
| |leader_title3 = ] | |||
| |leader_title4 = ] | |||
| |leader_name1 = ] | |||
| |leader_name2 = ] | |||
| |leader_name3 = ] | |||
| |leader_name4 = ] | |||
| |sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| |sovereignty_note = from Spain | |||
| |established_event1 = Declared | |||
| |established_date1 = July 20, 1810 | |||
| |established_event2 = Recognized | |||
| |established_date2 = August 7, 1819 | |||
| |area_rank = 26th | |||
| |area_magnitude = 1 E12 | |||
| |area_km2 = 1,141,748 | |||
| |area_sq_mi = 440,839 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |percent_water = 8.8 | |||
| |population_estimate = 44,760,630 <!--UN WPP--> | |||
| |population_estimate_rank = 29th | |||
| |population_estimate_year = January 2009 | |||
| |population_census = 42,888,592 | |||
| |population_census_year = 2005 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 40 | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = 104 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |population_density_rank = 168th | |||
| |GNI_per_capita = $2,020 | |||
| |GNI_per_capita = 123rd <!--WorldBank List--> | |||
| |GDP_PPP = $378.624 billion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2004&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=233&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=48&pr.y=9 |title=Colombia|publisher=International Monetary Fund|accessdate=2008-10-09}}</ref> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_rank = 28th | |||
| |GDP_PPP_year = 2007 | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $7,968<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 82nd | |||
| |GDP_nominal = $202.630 billion<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_rank = 37th <!---IMF---> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_year = 2007 | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $4,264<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 82nd <!---IMF---> | |||
| |Gini = 52 | |||
| |Gini_year = 2006 | |||
| |Gini_category = <font color="#e0584e">high</font> | |||
| |HDI = {{decrease}} 0.787 | |||
| |HDI_rank = 80th | |||
| |HDI_year = 2008 | |||
| |HDI_category = <font color="#ffcc00">medium</font> | |||
| |HPI = 67.2 | |||
| |HPI_rank = 2nd | |||
| |HPI_year = 2006 | |||
| |HPI_category = <font color="#ffcc00">high</font> | |||
| |currency = ] | |||
| |currency_code = COP | |||
| |country_code = | |||
| |time_zone = | |||
| |utc_offset = -5 | |||
| |time_zone_DST = | |||
| |utc_offset_DST = | |||
| |drives_on = right | |||
| |cctld = ] | |||
| |calling_code = 57 | |||
| |Happy Planet Index = 2 (by 2007) | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | religion_ref = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://es.statista.com/grafico/28553/las-religiones-mas-comunes-en-latinoamerica/ |title=Catholicism and evangelism: the two most common religions in Latin America |website=Statista |date=26 October 2022 |access-date=18 November 2022 |archive-date=19 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221119004809/https://es.statista.com/grafico/28553/las-religiones-mas-comunes-en-latinoamerica/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | religion_year = 2022 | |||
| | largest_city = capital | |||
| | official_languages = ] | |||
| | recognized_regional_languages = ] (in ])<ref>{{cite web |title=Por la cual se dictan normas especiales para la organización y el funcionamiento del Departamento Archipiélago de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina. |url=http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/ley_0047_1993.html |access-date=18 October 2023 |quote=ARTÍCULO 42. IDIOMA Y LENGUA OFICIAL EN EL DEPARTAMENTO ARCHIPIELAGO. Son oficiales en el Departamento Archipiélago de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina el castellano y el inglés comunmente hablado por las comunidades nativas del Archipiélago. |archive-date=5 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231105153804/http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/ley_0047_1993.html |url-status=live }}</ref><br>]{{ref label|iboxa|a|}} | |||
| | ethnic_groups = {{vunblist | |||
| | {{nowrap|87.58% ]-]{{efn|incl. ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]}}}} | |||
| | 6.84% ] | |||
| | 4.31% ] | |||
| | 0.05% ] | |||
| | 0.01% ] | |||
| | 0.01% ] | |||
| | 1.35% not stated | |||
| }} | |||
| | ethnic_groups_year = 2018 census<ref name="grupos étnicos" /><ref name="ncbi.nlm.nih.gov">{{cite journal| title=Genomic Insights into the Ancestry and Demographic History of South America |year=2015 |pmc=4670080 |last1=Homburger |first1=J. R. |last2=Moreno-Estrada |first2=A. |last3=Gignoux |first3=C. R. |last4=Nelson |first4=D. |last5=Sanchez |first5=E. |last6=Ortiz-Tello |first6=P. |last7=Pons-Estel |first7=B. A. |last8=Acevedo-Vasquez |first8=E. |last9=Miranda |first9=P. |last10=Langefeld |first10=C. D. |last11=Gravel |first11=S. |last12=Alarcón-Riquelme |first12=M. E. |last13=Bustamante |first13=C. D. |journal=PLOS Genetics |volume=11 |issue=12 |pages=e1005602 |doi=10.1371/journal.pgen.1005602 |pmid=26636962 |doi-access=free |issn = 1553-7390}}</ref> | |||
| | demonym = ] | |||
| | government_type = Unitary ] | |||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| | leader_name1 = ] | |||
| | leader_title2 = ] | |||
| | leader_name2 = ] | |||
| | legislature = ] | |||
| | upper_house = ] | |||
| | lower_house = ] | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] {{nobold|from Spain}} | |||
| | established_event1 = ] | |||
| | established_date1 = 20 July 1810 | |||
| | established_event2 = Recognized | |||
| | established_date2 = 7 August 1819 | |||
| | established_event3 = Last unitisation | |||
| | established_date3 = 5 August 1886 | |||
| | established_event4 = Secession of ] | |||
| | established_date4 = 6 November 1903 | |||
| | established_event5 = {{nowrap|]}} | |||
| | established_date5 = 4 July 1991 | |||
| | area_km2 = 1,141,748 | |||
| | area_rank = 25th | |||
| | area_sq_mi = 440,831 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | percent_water = 2.1 (as of 2015)<ref>{{cite web|title=Surface water and surface water change|access-date=11 October 2020|publisher=] (OECD)|url=https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=SURFACE_WATER|archive-date=24 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210324133453/https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=SURFACE_WATER|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | population_estimate = {{IncreaseNeutral}} 52,695,952<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/censo2018/proyecciones-de-poblacion/Nacional/DCD-area-proypoblacion-Nac-2020-2070.xlsx|title=Proyecciones de Población DANE|access-date=10 April 2023|archive-date=10 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230410005852/https://www.dane.gov.co/files/censo2018/proyecciones-de-poblacion/Nacional/DCD-area-proypoblacion-Nac-2020-2070.xlsx|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | population_estimate_year = 2024 | |||
| | population_estimate_rank = 27th | |||
| | population_density_km2 = 46.15 | |||
| | population_density_rank = 174th | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 119.54 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $1.042 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.CO">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/April/weo-report?c=233,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2024 Edition. (Colombia) |publisher=] |website=www.imf.org |date=16 April 2024 |access-date=17 April 2024 |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416235246/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/April/weo-report?c=233,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = 32nd | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $19,770<ref name="IMFWEO.CO" /> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 82nd | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $386.076 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.CO" /> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = 46th | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $7,327<ref name="IMFWEO.CO" /> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 97th | |||
| | Gini = 54.8 <!--number only--> | |||
| | Gini_year = 2022 | |||
| | Gini_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | Gini_ref = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/colombia/#economy |title=Colombia - The World Factbook|access-date=September 23, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI = 0.758 | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=]|date=13 March 2024|access-date=13 March 2024|archive-date=13 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 91st | |||
| | currency = ] | |||
| | currency_code = COP | |||
| | time_zone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = −5{{ref label|iboxb|b|}} | |||
| | date_format = DMY | |||
| | drives_on = right | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | cctld = ] | |||
| | footnote_a = {{note|iboxa}}Although the Colombian Constitution specifies Spanish (''Castellano'') as the ] in all Colombian territory, other languages spoken in the country by ethnic groups – approximately 68 languages – each is also official in its territory.<ref> | |||
| ] of 1991 (Title I – Concerning Fundamental Principles – Article 10)</ref> English is also official in the ].<ref name="LEY47DE1993">{{cite web|url=http://www.alcaldiabogota.gov.co/sisjur/normas/Norma1.jsp?i=2780|title=LEY 47 DE 1993|publisher=alcaldiabogota.gov.co|language=es|access-date=23 February 2014|archive-date=11 January 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111165257/http://www.alcaldiabogota.gov.co/sisjur/normas/Norma1.jsp?i=2780|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | footnote_b = {{note|iboxb}}The official Colombian time<ref>{{cite web|url=http://horalegal.inm.gov.co/|title=The official Colombian time|publisher=horalegal.inm.gov.co|language=es|access-date=23 February 2014|archive-date=9 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140209074753/http://horalegal.inm.gov.co/|url-status=live}}</ref> is controlled and coordinated by the National Institute of Metrology.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/decreto_4175_2011.html |title=Decreto 4175 de 2011, artículo 6, numeral 14 |publisher=Presidencia de la República de Colombia |language=es |access-date=14 March 2016 |archive-date=15 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160415083653/http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/decreto_4175_2011.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Colombia''',{{efn|{{IPAc-en|audio=En-Colombia-pronunciation.ogg|k|ə|ˈ|l|ʌ|m|b|i|ə}} {{respell|kə|LUM|bee|ə}}, {{IPAc-en|-|ˈ|l|ɒ|m|-}} {{respell|-|LOM|-}};<ref>{{cite EPD|18}}</ref> {{IPA|es|koˈlombja|lang|Es-Colombia2.oga}}}} officially the '''Republic of Colombia''',{{efn|{{langx|es|{{audio|Es-republica_de_colombia.ogg|República de Colombia}}}}. IPA transcription of "''República de Colombia''": {{IPA|es|reˈpuβlika ðe koˈlombja}}.}} is a country primarily located in ] with ] in ]. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ] to the north, ] to the east and northeast, ] to the southeast, ] and ] to the south and southwest, the ] to the west, and ] to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 ]. The Capital District of ] is also the ] hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich ]<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 March 2017 |title=Colombia herencia cultural más allá de la colonia |url=https://procolombia.co/archivo/colombia-herencia-cultural-mas-alla-de-la-colonia |access-date=26 February 2023 |website=procolombia.co |language=es |archive-date=26 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230226030316/https://procolombia.co/archivo/colombia-herencia-cultural-mas-alla-de-la-colonia |url-status=live }}</ref>—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a colony, fusing cultural elements brought by ] from ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=News & Events - Irlandeses en Colombia y Antioquia |publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs of Ireland |url=https://www.dfa.ie/irish-embassy/colombia/newsevents/irlandeses-en-colombia-y-antioquia-.html |access-date=7 September 2022 |archive-date=26 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220826014128/https://www.dfa.ie/irish-embassy/colombia/newsevents/irlandeses-en-colombia-y-antioquia-.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=10 June 2019 |title=Estos fueron los primeros alemanes en Colombia |url=https://revistadiners.com.co/cultura/archivo/67972_estos-fueron-los-primero-alemanes-en-colombia/ |access-date=18 December 2021 |newspaper=Revista Diners |language=es |archive-date=5 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221105202158/https://revistadiners.com.co/cultura/archivo/67972_estos-fueron-los-primero-alemanes-en-colombia/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Vidal Ortega |first1=Antonino |last2=D'Amato Castillo |first2=Giuseppe |date=1 December 2015 |title=Los otros, sin patria: italianos en el litoral Caribe de Colombia a comienzos del siglo XX |url=https://journals.openedition.org/caravelle/1822 |journal=Caravelle. Cahiers du monde hispanique et luso-brésilien |language=fr |issue=105 |pages=153–175 |doi=10.4000/caravelle.1822 |issn=1147-6753 |doi-access=free |access-date=26 February 2023 |archive-date=6 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221006231718/https://journals.openedition.org/caravelle/1822 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Salamanca |first1=Helwar Figueroa |last2=Espitia |first2=Julián David Corredor |date=31 July 2019 |title="En una ciudad gris y silenciosa": la migración francesa en Bogotá (1900-1920) |url=https://revistas.uis.edu.co/index.php/anuariohistoria/article/view/9864 |journal=Anuario de Historia Regional y de las Fronteras |language=es |volume=24 |issue=2 |pages=75–100 |doi=10.18273/revanu.v24n2-2019003 |s2cid=203515282 |issn=2145-8499 |doi-access=free |access-date=26 February 2023 |archive-date=6 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230306031553/https://revistas.uis.edu.co/index.php/anuariohistoria/article/view/9864 |url-status=live }}</ref> and the ],<ref name="Posada2">{{cite journal |last1=Fawcett de Posada |first1=Louise |last2=Posada Carbó |first2=Eduardo |date=1992 |title=En la tierra de las oportunidades: los sirio-libaneses en Colombia |trans-title=In the land of opportunity: the Syrian-Lebanese in Colombia |url=https://publicaciones.banrepcultural.org/index.php/boletin_cultural/article/download/2252/2325 |format=PDF |journal=Boletín Cultural y Bibliográfico |language=es |publisher=publicaciones.banrepcultural.org |volume=29 |issue=29 |pages=8–11 |access-date=20 July 2017 |archive-date=2 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160302135545/https://publicaciones.banrepcultural.org/index.php/boletin_cultural/article/download/2252/2325 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=S.A.S |first=Editorial La República |title=Colombia y Medio Oriente |url=https://www.larepublica.co/analisis/simon-gaviria-munoz-401830/colombia-y-medio-oriente-3350223 |access-date=26 February 2023 |website=Diario La República |date=26 April 2022 |language=es |archive-date=24 November 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221124013227/https://www.larepublica.co/analisis/simon-gaviria-munoz-401830/colombia-y-medio-oriente-3350223 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Tiempo |first=Casa Editorial El |date=7 March 2019 |title=Los palestinos que encontraron un segundo hogar en el centro de Bogotá |url=https://www.eltiempo.com/mundo/mas-regiones/los-palestinos-que-encontraron-un-segundo-hogar-en-el-centro-de-bogota-334782 |access-date=26 February 2023 |website=El Tiempo |language=es |archive-date=31 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221031223716/https://www.eltiempo.com/mundo/mas-regiones/los-palestinos-que-encontraron-un-segundo-hogar-en-el-centro-de-bogota-334782 |url-status=live }}</ref> with those brought by the ],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Faucher |first=Nicolás Murillo |date=11 August 2014 |title=La herencia Africana en Colombia |url=https://librepensador.uexternado.edu.co/la-herencia-africana-en-colombia/ |access-date=26 February 2023 |website=Libre Pensador |language=es |archive-date=27 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230227011004/https://librepensador.uexternado.edu.co/la-herencia-africana-en-colombia/ |url-status=live }}</ref> as well as with those of the various ] civilizations that predate colonization.<ref>{{Cite web |title=El patrimonio cultural de seis pueblos indígenas renace con 'Sembrando Nuestros Saberes' en Colombia |url=https://www.aa.com.tr/es/mundo/el-patrimonio-cultural-de-seis-pueblos-ind%C3%ADgenas-renace-con-sembrando-nuestros-saberes-en-colombia/2107884 |access-date=26 February 2023 |website=aa.com.tr |archive-date=26 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230226030314/https://www.aa.com.tr/es/mundo/el-patrimonio-cultural-de-seis-pueblos-ind%C3%ADgenas-renace-con-sembrando-nuestros-saberes-en-colombia/2107884 |url-status=live }}</ref> ] is the ], although ] and ] are recognized regionally. | |||
| Colombia has been home to many ] since at least 12,000 BCE. The Spanish first landed in ] in 1499, and by the mid-16th century, they had colonized much of present-day Colombia, and established the ], with ] as its capital. ] from the ] was achieved in 1819, with what is now Colombia emerging as the ]. The new polity experimented with federalism as the ] (1858) and then the ] (1863), before becoming a republic—the current Republic of Colombia—in 1886. With the backing of the United States and France, ] from Colombia in 1903, resulting in Colombia's present borders. Beginning in the 1960s, the country has suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity ] and political violence, both of which escalated in the 1990s. Since 2005, there has been significant improvement in security, stability, and rule of law, as well as unprecedented economic growth and development.<ref name="Enough Already!" /><ref name="Colombia's GDP growth" /> Colombia is recognized for its ], being the best healthcare in ] according to the ] and 22nd in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=World Health Organization Assesses the World's Health Systems |url=https://www.who.int/news/item/07-02-2000-world-health-organization-assesses-the-world%27s-health-systems |access-date=30 March 2023 |publisher=World Health Organization |language=en |archive-date=9 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190409230742/https://www.who.int/whr/2000/media_centre/press_release/en/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Colombia Healthcare System |url=https://www.internationalinsurance.com/health/systems/colombia.php |access-date=30 March 2023 |website=International Citizens Insurance |language=en-US |archive-date=30 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230330020716/https://www.internationalinsurance.com/health/systems/colombia.php |url-status=live }}</ref> Its ] is the third-largest in South America, with macroeconomic stability and favorable long-term growth prospects.<ref name="GDP" /><ref name="strongmacroeconomicmanagement" /> | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| ] | |||
| Colombia is one of the world's seventeen ]; it has the highest level of ] per square mile in the world and the second-highest level overall.<ref name="Biodiversity of Colombia" /> Its territory encompasses ], ], ] and ]. It is the only country in South America with coastlines (and islands) along both the ] and ] oceans. Colombia is a key member of major global and regional organizations including the ], the ], the ], the ], the ] and the ]; it is also a ] Global Partner<ref>{{cite web |title=NATO - Topic: Relations with Colombia |url=https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_143936.htm |website=Nato.int |access-date=30 August 2022 |archive-date=30 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220830174315/https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_143936.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> and a ] of the ].<ref name=":1">{{cite web |last1=Samuels |first1=Brett |date=10 March 2022 |title=Biden designates Colombia as major non-NATO ally |url=https://thehill.com/latino/597747-biden-designates-colombia-as-major-non-nato-ally |access-date=27 November 2022 |website=The Hill |archive-date=18 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231118223318/https://thehill.com/latino/597747-biden-designates-colombia-as-major-non-nato-ally/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The word "Colombia" comes from the name of ] (Italian: ''Cristoforo Colombo'', Spanish: ''Cristóbal Colón''). It was conceived by the revolutionary ] as a reference to all the ], but especially to those territories and colonies under Spanish and ] rule. The name was later adopted by the ] of 1819, formed out of the territories of the old ] (modern day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela and Ecuador).<ref name="LABLAA5"> {{cite web | author = Carlos Restrepo Piedrahita | url = http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero1992/febrero2.htm | title = EL NOMBRE "COLOMBIA", El único país que lleva el nombre del Descubrimiento | work = Revista Credencial | month = February | year = 1992| accessdate = 2008-02-29 | language = Spanish}}</ref> | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| In 1830, when Venezuela and Ecuador broke away, the ] region that remained became a new country — the ]. In 1858 New Granada officially changed its name to the ], then in 1863 the ], before finally adopting its present name — the Republic of Colombia — in 1886.<ref name="LABLAA5"/> | |||
| The name "Colombia" is derived from the last name of the Italian navigator ] ({{langx|la|Christophorus Columbus}}, {{langx|it|Cristoforo Colombo}}, {{langx|es|link=no|Cristóbal Colón}}). It was conceived as a reference to all of the New World.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.banrepcultural.org/|title=La Red Cultural del Banco de la República|first=Subgerencia Cultural del Banco de la|last=República|website=banrepcultural.org|access-date=20 October 2020|archive-date=1 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210501114213/https://www.banrepcultural.org/|url-status=dead}}</ref> The name was later adopted by the ] of 1819, formed from the territories of the old ] (modern-day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela, Ecuador, and northwest Brazil).<ref name="LABLAA5">{{cite web |author=Carlos Restrepo Piedrahita |url=http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero1992/febrero2.htm |title=El nombre "Colombia", El único país que lleva el nombre del Descubrimiento |work=Revista Credencial |date=February 1992 |access-date=29 February 2008 |language=es |archive-date=5 January 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080105031144/http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero1992/febrero2.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| {{main|Geography of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Natural Regions of Colombia|Geology of Colombia}} | |||
| ] | |||
| When Venezuela, Ecuador, and ] came to exist as independent states, the former ] adopted the name "]". New Granada officially changed its name in 1858 to the ]. In 1863 the name was again changed, this time to ], before finally adopting its present name – the Republic of Colombia – in 1886.<ref name="LABLAA5" /> | |||
| Colombia is the ] in the world and the fourth largest in South America. It is bordered to the east by ] and ]; to the south by ] and ]; to the north by ] and the ]; and to the west by the ]. Colombia is the only country in South America to touch both ] and Pacific oceans. | |||
| To refer to this country, the Colombian government uses the terms {{lang|es|Colombia}} and {{lang|es|República de Colombia}}.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Helena Guedes|first=Maria|title=A Grande Colômbia!|publisher=Clube de Autores|pages=141}}</ref> | |||
| Part of the ], a region of the world subject to ]s and ], Colombia is dominated by the ] mountains. Beyond the ] (in the south-western departments of ] and ]) these are divided into three branches known as ''cordilleras'' (from the ] for "rope"): the '']'', running adjacent to the Pacific coast and including the city of ]; the '']'', running between the ] and ] river valleys (to the west and east respectively) and including the cities of ], ] and ]; and the '']'', extending north east to the ] and including ], ] and ]. Peaks in the ''Cordillera Occidental'' exceed 13,000 ft (4,000 m), and in the ''Cordillera Central'' and ''Cordillera Oriental'' they reach 18,000 ft (5,500 m).<ref name="Tallest Mountains"></ref> At 8,500 ft (2,600 m), Bogotá is the highest city of its size in the world. | |||
| == History == | |||
| East of the Andes lies the ] of the '']'', part of the ], and, in the far south east, the ] of the ]. Together these lowlands comprise over half Colombia's territory, but they contain less than 3% of the population. To the north the ], home to 20% of the population and the location of the major port cities of ] and ], generally consists of low-lying plains, but it also contains the ] mountain range, which includes the country's tallest peaks (] and ]), and the ]. By contrast the narrow and discontinuous ], backed by the ] mountains, are covered in dense vegetation and sparsely populated. The principal Pacific port is ]. | |||
| {{Main|History of Colombia|Timeline of Colombian history}} | |||
| === Pre-Columbian<!--This is NOT a typo. Before Christopher Columbus, not before Colombia --> era === | |||
| Colombian territory also includes a number of ]. | |||
| {{Main|Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Owing to its location, the present territory of Colombia was a corridor of early human civilization from ] and the ] to the ] and ]. The oldest archaeological finds are from the ] and ] sites in the Magdalena Valley {{convert|100|km|mi|sp=us}} southwest of Bogotá.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Correal|first=Urrego G.|title=Nuevas evidencias culturales pleistocenicas y megafauna en Colombia|journal=Boletin de Arqueologia|year=1993|issue=8|pages=3–13}}</ref> These sites date from the ] period (18,000–8000 BCE). At ] and other sites, traces from the ] (~8000–2000 BCE) have been found. Vestiges indicate that there was also early occupation in the regions of ] and ] in ]. The oldest pottery discovered in the Americas, found in ], dates to 5000–4000 BCE.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hoopes|first=John|title=Ford Revisited: A Critical Review of the Chronology and Relationships of the Earliest Ceramic Complexes in the New World, 6000-1500 B.C. (1994)|journal=Journal of World Prehistory|year=1994|volume=8|issue=1|pages=1–50|doi=10.1007/bf02221836|s2cid=161916440|url=https://zenodo.org/record/848786|access-date=6 September 2019|archive-date=21 October 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181021232542/https://zenodo.org/record/848786|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Indigenous people inhabited the territory that is now Colombia by 12,500 BCE. Nomadic ] tribes at the El Abra, ] and Tequendama sites near present-day ] traded with one another and with other cultures from the ] Valley.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Van der Hammen |first1=Thomas |last2=Urrego |first2=Gonzalo Correal |title=Prehistoric man of the Sabana de Bogotá: Data for an ecological prehistory |journal=Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology |date=September 1978 |volume=25 |issue=1–2 |pages=179–190 |doi=10.1016/0031-0182(78)90077-9 |bibcode=1978PPP....25..179V }}</ref> A site including {{Convert|8|mi|0|spell=in|sp=us}} of ] that is under study at Serranía de la Lindosa was revealed in November 2020.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/science/2020/nov/29/sistine-chapel-of-the-ancients-rock-art-discovered-in-remote-amazon-forest |title=Sistine Chapel of the ancients' rock art discovered in remote Amazon forest |last=Alberge |first=Dalya |date=29 November 2020 |website=] |access-date=16 June 2021 |archive-date=30 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201130165841/https://www.theguardian.com/science/2020/nov/29/sistine-chapel-of-the-ancients-rock-art-discovered-in-remote-amazon-forest |url-status=live }}</ref> Their age is suggested as being 12,500 years old (c. 10,480 B.C.) by the anthropologists working on the site, because of extinct fauna depicted. It was during the earliest known human occupation of the area. | |||
| ===Climate=== | |||
| {{main|Climate of Colombia}} | |||
| ], 5,200+ m (17,060 ft).]] | |||
| Between 5000 and 1000 BCE, hunter-gatherer tribes transitioned to agrarian societies; fixed settlements were established, and pottery appeared. Beginning in the 1st millennium BCE, groups of ] including the ], ], ], and ] developed the political system of '']s'' with a pyramidal structure of power headed by ''caciques''. The Muisca inhabited mainly the area of what is now the ] of ] and ] high plateau ('']'') where they formed the ]. They farmed maize, potato, quinoa, and cotton, and traded gold, ], blankets, ceramic handicrafts, coca and especially ] with neighboring nations. The Tairona inhabited northern Colombia in the isolated mountain range of ].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Broadbent |first=Sylvia |year=1965 |title=Los Chibchas: organización socio-polític |journal=Serie Latinoamericana |volume=5 }}</ref> The Quimbaya inhabited regions of the ] Valley between the ] and ] Ranges of the Colombian Andes.<ref>{{cite book|title=Los indios de Colombia|volume=7|author1=Álvaro Chaves Mendoza|author2=Jorge Morales Gómez|publisher=Editorial Abya Yala|isbn=978-9978-04-169-7|year=1995|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=txJH1_qweSMC&pg=PA1|language=es|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233343/https://books.google.com/books?id=txJH1_qweSMC&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> Most of the Amerindians practiced agriculture and the social structure of each indigenous community was different. Some groups of indigenous people such as the Caribs lived in a state of permanent war, but others had less bellicose attitudes.<ref>{{cite web|title=Historia de Colombia: el establecimiento de la dominación española – Los Pueblos Indígenas del Territorio Colombiano|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/hicol/hico3.htm|publisher=banrepcultural.org|language=es|access-date=20 September 2016|archive-date=9 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171109083852/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/hicol/hico3.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> During the 1200s, ]s and ] in Colombia made contact, thereby spreading Native American genetics from Precolonial Colombia to some Pacific Ocean islands.<ref>[https://phys.org/news/2020-07-polynesians-native-americans-contact-european.html Polynesians, Native Americans made contact before European arrival, genetic study finds | |||
| The climate of Colombia is primarily determined by its proximity to the ], with ] and ] climate predominating. Other influences are the ]s and the effect of the ] on precipitation. Colombia is also affected by the ] phenomena. | |||
| by Stanford University Medical Center]</ref><ref></ref> | |||
| === Colonial period === | |||
| Temperatures generally decrease about 3.5°] (2°]) for every 1,000-ft (300-m) increase in altitude above sea level, presenting perpetual snowy peaks to hot river valleys and basins. Rainfall is concentrated in two ]s (roughly corresponding to the spring and autumn of temperate latitudes) but varies considerably by location. Colombia's Pacific coast has one of the highest levels of rainfall in the world, with the south east often drenched by more than 200 in (500 cm) of rain per year. On the other hand rainfall in parts of the ] seldom exceeds 30 in (75 cm) per year. Rainfall in the rest of the country runs between these two extremes. | |||
| {{Main|New Kingdom of Granada|Viceroyalty of New Granada}} | |||
| {{See also|Spanish conquest of New Granada|Spanish conquest of the Muisca|Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spanish Empire}} | |||
| ], founder of ], the first stable European settlement on the continent]] | |||
| ] (who had sailed with Columbus) reached the ] in 1499.<ref name="LABLAA6">{{cite web|author=Nicolás del Castillo Mathieu|url=http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/marzo1992/marzo3.htm|title=La primera vision de las costas Colombianas, Repaso de Historia|work=Revista Credencial|date=March 1992|access-date=29 February 2008|language=es|archive-date=19 October 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071019045321/http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/marzo1992/marzo3.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/o/ojeda.htm|title=Alonso de Ojeda|publisher=biografiasyvidas.com|language=es|access-date=2 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140704180050/http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/o/ojeda.htm|archive-date=4 July 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> Spanish explorers, led by ], made the first exploration of the ] in 1500.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/b/bastidas.htm|title=Rodrigo de Bastidas|publisher=biografiasyvidas.com|language=es|access-date=2 April 2014|archive-date=23 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210423173935/http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/b/bastidas.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> ] navigated near the Caribbean in 1502.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/c/colon_cristobal.htm|title=Cristóbal Colón|publisher=biografiasyvidas.com|language=es|access-date=2 April 2014|archive-date=6 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140306173922/http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/c/colon_cristobal.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1508, ] accompanied an expedition to the territory through the region of ] and they founded the town of ] in 1510, the first stable settlement on the continent. {{efn|Balboa is best known for being the first European to see the Pacific Ocean in 1513, which he called ''Mar del Sur'' (or "Sea of the South") and would facilitate Spanish exploration and settlement of South America.}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/b/balboa.htm|title=Vasco Núñez de Balboa|publisher=biografiasyvidas.com|language=es|access-date=2 April 2014|archive-date=7 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407072547/http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/b/balboa.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> ] was founded in 1525,<ref>{{cite book|title=La gobernación de Santa Marta (1570–1670) Vol. 232|author=Vázquez, Trinidad Miranda|publisher=Editorial CSIC-CSIC Press|isbn=978-84-00-04276-9|year=1976|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m5zI94b6u_4C&pg=PP1|page=3|language=es|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233342/https://books.google.com/books?id=m5zI94b6u_4C&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> and ] in 1533.<ref>{{cite book|title=Cartagena de Indias en el siglo XVI. Vol. 288|author=Plá, María del Carmen Borrego|publisher=Editorial CSIC-CSIC Press|isbn=978-84-00-05440-3|year=1983|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hV-bQJo8wOIC&pg=PP1|pages=3–5|language=es|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233355/https://books.google.com/books?id=hV-bQJo8wOIC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> Spanish ] ] led an expedition to the interior in April 1536, and christened the districts through which he passed "]". In August 1538, he provisionally founded its capital near the Muisca ] of ], and named it "Santa Fe". The name soon acquired a suffix and was called Santa Fe de Bogotá.<ref>{{cite book|title=Invading Colombia: Spanish accounts of the Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada expedition of conquest Vol. 1|editor=Francis, John Michael|publisher=Penn State Press|isbn=978-0-271-02936-8|year=2007|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=P1DEFqZ6c5QC&pg=PP1|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233341/https://books.google.com/books?id=P1DEFqZ6c5QC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="JaramilloUribe1989">{{Cite journal |last=Jaramillo Uribe |first=Jaime |year=1989 |title=Perfil histórico de Bogotá |url=https://revistas.uniandes.edu.co/index.php/hiscrit/article/view/3641 |journal=Historia Crítica |language=es |issue=1 |pages=5–19 |doi=10.7440/histcrit1.1989.01 |issn=0121-1617}}</ref> Two other notable journeys by early conquistadors to the interior took place in the same period. ], conqueror of ], traveled north and founded ], in 1536, and ], in 1537;<ref>{{cite book|title=La encomienda en Popayán: tres estudios|author=Silvia Padilla Altamirano|publisher=Editorial CSIC Press|isbn=978-84-00-03612-6|year=1977|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=785fTqvsPSEC&pg=PP1|pages=4–5|language=es|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233342/https://books.google.com/books?id=785fTqvsPSEC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> from 1536 to 1539, German conquistador ] crossed the ] and went over the ] in a search for ], the "city of gold".<ref>{{cite book|title=El dorado en el pantano|author=Massimo Livi Bacci|publisher=Marcial Pons Historia|isbn=978-84-92820-65-8|year=2012|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tMEp1OPtF7QC&pg=PP1|language=es|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233402/https://books.google.com/books?id=tMEp1OPtF7QC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author1=Ramírez, Natalia |author2=Gutiérrez, Germán |url=http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/5001/ |title=Félix de Azara: Observaciones conductuales en su viaje por el Virreinato del Río de la Plata |journal=Revista de historia de la psicología |volume=31 |issue=4 |year=2010 |pages=52–53 |access-date=17 May 2016 |archive-date=17 June 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160617142800/http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/5001/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> The legend and the gold would play a pivotal role in luring the Spanish and other Europeans to New Granada during the 16th and 17th centuries.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/archaeology/el-dorado/| work=National Geographic| title=El Dorado Legend Snared Sir Walter Raleigh| access-date=23 August 2013| archive-date=13 February 2017| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170213054547/http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/archaeology/el-dorado/| url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ], one of the rainiest regions in the world.]] | |||
| The ] made frequent alliances with the enemies of different indigenous communities. ] were crucial to conquest, as well as to creating and maintaining empire.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://queaprendemoshoy.com/la-conquista-del-nuevo-reino-de-granada-la-interpretacion-de-los-siete-mitos-iii/|title=La Conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada: la interpretación de los siete mitos (III) – RESTALL, Matthew: Los siete mitos de la conquista española, Barcelona, 2004|publisher=queaprendemoshoy.com/|language=es|access-date=21 September 2016|archive-date=9 February 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200209181225/http://queaprendemoshoy.com/la-conquista-del-nuevo-reino-de-granada-la-interpretacion-de-los-siete-mitos-iii/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Indigenous peoples in Colombia experienced a decline in population due to conquest as well as Eurasian diseases, such as ], to which they had no immunity.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.icanh.gov.co/recursos_user/documentos/editores/201/Articulos/SociedadesIndigenas-Reyes2009.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.icanh.gov.co/recursos_user/documentos/editores/201/Articulos/SociedadesIndigenas-Reyes2009.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Las sociedades indígenas del Nuevo Reino de Granada bajo el dominio español|author=Jorge Augusto Gamboa M.|publisher=Instituto Colombiano de Antropología e Historia|language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.colombiaaprende.edu.co/html/productos/1685/articles-242836_proyecto_documento.pdf|title=Las plantas medicinales en la época de la colonia y de la independencia|publisher=colombiaaprende.edu.co|language=es|access-date=7 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140408212640/http://www.colombiaaprende.edu.co/html/productos/1685/articles-242836_proyecto_documento.pdf|archive-date=8 April 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> Regarding the land as deserted, the Spanish Crown sold properties to all persons interested in colonized territories, creating large farms and possession of mines.<ref name="TierrasColonia">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/mayo2002/propdetierras.htm|title=La propiedad de tierras en la Colonia: Mercedes, composición de títulos y resguardos indígenas|author=Mayorga, Fernando|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia|website=banrepcultural.org|year=2002|language=es|access-date=7 April 2014|archive-date=8 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140408213109/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/mayo2002/propdetierras.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="EconomíaColonial">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/economia/histecon/histecon2a.htm|title=Historia económica y órdenes de magnitud, Capítulo 1: La Formación de la Economía Colonial (1500–1740).|author=Germán Colmenares|publisher=banrepcultural.org|language=es|access-date=7 April 2014|archive-date=9 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171109160412/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/economia/histecon/histecon2a.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="políticaeconómica">{{cite web|url=http://admin.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/revistas/revanuario/ancolh11/articul/art5/art5a.pdf |title=La política económica virreinal en el Nuevo Reino de Granada: 1750–1810 |author=Margarita González |publisher=banrepcultural.org |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140408211849/http://admin.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/revistas/revanuario/ancolh11/articul/art5/art5a.pdf |archive-date=8 April 2014 }}</ref> In the 16th century, the ] in Spain reached a great development thanks to numerous scientific figures of the ] and nautical science was an essential pillar of the ].<ref name="Alonso de Santa Cruz">{{cite journal |last1=Domingo |first1=Mariano Cuesta |title=Alonso de Santa Cruz, cartógrafo y fabricante de instrumentos náuticos de la Casa de Contratación |trans-title=Alonso de Santa Cruz, Cartographer and Maker of Nautical Instruments of the Spanish Casa de Contratación |language=es |journal=Revista Complutense de Historia de América |date=2004 |volume=30 |pages=7–40 |url=https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=1086671 |access-date=13 November 2020 |archive-date=3 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210203234102/https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=1086671 |url-status=live }}</ref> In 1542, the region of New Granada, along with all other Spanish possessions in South America, became part of the ], with its capital in ].<ref>{{cite book|title=Empires of the Atlantic World: Britain and Spain in America, 1492–1830|author=John Huxtable Elliott|publisher=Yale University Press|isbn=978-0-300-12399-9|year=2007|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Q6ucuphGA3YC&pg=PA124|pages=124–125|access-date=9 November 2020|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233440/https://books.google.com/books?id=Q6ucuphGA3YC&pg=PA124|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1547, New Granada became a separate captaincy-general within the viceroyalty, with its capital at Santa Fe de Bogota.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Shaw|first=Jeffrey M.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vt-vDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA429|title=Religion and Contemporary Politics: A Global Encyclopedia|year=2019|isbn=9781440839337|pages=429|publisher=Abc-Clio|access-date=19 March 2023|archive-date=15 July 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230715073548/https://books.google.com/books?id=vt-vDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA429|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1549, the ] was created by a royal decree, and New Granada was ruled by the ], which at that time comprised the provinces of Santa Marta, Rio de San Juan, Popayán, Guayana and Cartagena.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.congreso.gob.pe/ntley/Imagenes/LeyIndia/0102015.pdf |title=Law VIII ("Royal Audiencia and Chancery of Santa Fe in the New Kingdom of Granada") of Title XV ("Of the Royal Audiencias and Chanceries of the Indies") of Book II |publisher=congreso.gob.pe |access-date=4 April 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140629092003/http://www.congreso.gob.pe/ntley/Imagenes/LeyIndia/0102015.pdf |archive-date=29 June 2014 }}</ref> But important decisions were taken from the colony to Spain by the ].<ref>{{cite book|url=http://www.archivobogota.gov.co/libreria/pdf/LIBRO_PATRIMONIO_DOCUMENTAL.pdf |title=El patrimonio documental de Bogotá, Siglos XVI – XIX: Instituciones y Archivos |author1=Fernando Mayorga García |author2=Juana M. Marín Leoz |author3=Adelaida Sourdis Nájera |publisher=Subdirección Imprenta Distrital – D.D.D.I |isbn=978-958-717-064-1|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407095333/http://www.archivobogota.gov.co/libreria/pdf/LIBRO_PATRIMONIO_DOCUMENTAL.pdf |archive-date=7 April 2014 |year=2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Encomienda y mita en Nueva Granada en el siglo XVII|author=Julián Bautista Ruiz Rivera|publisher=Editorial CSIC Press|isbn=978-84-00-04176-2|year=1975|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5R0dPbOImsUC&pg=PP1|pages=xxi–xxii|access-date=7 December 2018|archive-date=2 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240202233403/https://books.google.com/books?id=5R0dPbOImsUC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Altitude not only affects temperature but is also one of the most important influences on vegetation patterns. The mountainous parts of the country can be divided into several vegetation zones according to altitude, although the altitude limits of each zone may vary somewhat depending on the latitude. Below 3,300 ft (1,000 m) are the tropical crops of the ] (hot land). The most productive land and the majority of the population can be found in the ] (temperate land, 3,300-6,600 ft or 1,000-2,000 m), which provide the best conditions for the country's ] growers, and the ] (cold land, 6,600-10,500 ft, 2,000-3,200 m), where wheat and potatoes dominate. Beyond this lie the alpine conditions of the ] (forested zone, 10,500-12,800 ft, 3,200-3,900 m) and then the treeless grasslands of the ]s (12,800-15,100 ft, 3,900-4,600 m). Above 15,100 ft (4,600 m), where temperatures are below freezing, is the ], a zone of permanent snow and ice. | |||
| ], a major Spanish victory in the ]<ref name="BattleofCartagena" />]] | |||
| In the 16th century, European slave traders had begun to bring ] to the Americas. Spain was the only European power that did not establish ] in Africa to purchase slaves; the Spanish Empire instead relied on the ] system, awarding merchants from other European nations the license to trade enslaved peoples to their overseas territories.<ref>{{cite book|title=Génesis y desarrollo de la esclavitud en Colombia siglos XVI y XVII|publisher=Universidad del Valle|isbn=978-958-670-338-3|year=2005|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PH_cf27ucZAC&pg=PP1|language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Los místeres de las minas: crónica de la colonia europea más grande de Colombia en el siglo XIX, surgida alrededor de las minas de Marmato, Supía y Riosucio|author=Alvaro Gärtner|publisher=Universidad de Caldas|isbn=978-958-8231-42-6|year=2005|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5cUdM30KwxkC&pg=PP1|access-date=7 December 2018|archive-date=21 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240221121101/https://books.google.com/books?id=5cUdM30KwxkC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> This system brought Africans to Colombia, although many spoke out against the institution.{{efn|A royal decree of 1713 approved the legality of ] founded by runaway slaves as a refuge in the seventeenth century. The people of San Basilio fought against slavery, thereby giving rise to the first free place in the Americas.<ref>{{cite book|title=Palenque, Cartagena y Afro-Caribe: historia y lengua|first1=Yves|last1=Moñino|first2=Armin|last2=Schwegler|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|isbn=978-3-11-096022-8|year=2002|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mv4iAAAAQBAJ&pg=PR1|pages=vii–ix, 21–35|access-date=26 December 2021|archive-date=21 February 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240221121101/https://books.google.com/books?id=mv4iAAAAQBAJ&pg=PR1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref> Its main leader was ], who was born in West Africa.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.urosario.edu.co/Subsitio/Catedra-de-Estudios-Afrocolombianos/Documentos/03-Presentacion-Dossier-Unesco---Palenque-de-San-B.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.urosario.edu.co/Subsitio/Catedra-de-Estudios-Afrocolombianos/Documentos/03-Presentacion-Dossier-Unesco---Palenque-de-San-B.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Palenque de San Basilio |publisher=urosario.edu.co|language=es}}</ref>}}{{efn|] was a Spaniard who traveled to Cartagena in 1610 and was ordained as a ] priest in 1616. Claver cared for African slaves for thirty-eight years, defending their lives and the ].<ref>Proceso de beatificación y canonización de San Pedro Claver. Edición de 1696. Traducción del latín y del italiano, y notas de Anna María Splendiani y Tulio Aristizábal S. J. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana. Universidad Católica del Táchira. 2002.</ref><ref>Valtierra, Ángel. 1964. San Pedro Claver, el santo que liberó una raza.</ref>}} The indigenous peoples could not be enslaved because they were legally ] of the Spanish Crown.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gabrielbernat.es/espana/esclavitud/index.html|title=La esclavitud negra en la América española|publisher=gabrielbernat.es|year=2003|language=es|access-date=20 September 2016|archive-date=26 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161126033717/http://www.gabrielbernat.es/espana/esclavitud/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> To protect the indigenous peoples, several forms of land ownership and regulation were established by the Spanish colonial authorities: ''resguardos'', ''encomiendas'' and ''haciendas''.<ref name="TierrasColonia" /><ref name="EconomíaColonial" /><ref name="políticaeconómica" /> | |||
| Colombian ] and ] also interact with climate zone patterns. Scrub woodland of scattered trees and bushes dominates the semi-arid north-eastern ] and ]. To the south, ] (tropical grassland) vegetation covers the eastern plains, the Colombian portion of the ''Llanos''. The rainy areas in the south east are blanketed by tropical ]. In the mountains, the spotty patterns of precipitation in alpine areas complicate vegetation patterns. The rainy side of a mountain may be lush and green, while the other side, in the rain shadow, may be parched. As a result Colombia is one of the world's 17 ].<ref name = "cwlvaj">{{cite news | first= | last= | coauthors= | title=South America Banks on Regional Strategy to Safeguard Quarter of Earth's Biodiversity | date= | publisher= | url =http://web.archive.org/web/20050310115345/http://www.conservation.org/xp/news/press_releases/2003/091603_andean_eng.xml | work =Conservation International | pages = | accessdate = 2007-06-29 | language = }}</ref> | |||
| However, secret anti-Spanish discontentment was already brewing for Colombians since Spain prohibited direct trade between the ], which included Colombia, and the ], which included the Philippines, the source of Asian products like silk and porcelain which was in demand in the Americas. Illegal trade between Peruvians, Filipinos, and Mexicans continued in secret, as smuggled Asian goods ended up in ], the distribution center for illegal Asian imports, due to the collusion between these peoples against the authorities in Spain. They settled and traded with each other while disobeying the forced Spanish monopoly.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1515/sai-2022-0008 |title=El Galeón de Manila y el comercio de Asia: Encuentro de culturas y sistemas |journal=Interacción Sino-Iberoamericana / Sino-Iberoamerican Interaction |date=March 2022 |volume=2 |issue=1 |pages=85–109 |last1=Villamar |first1=Cuauhtemoc |s2cid=249318172 |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ===Environmental issues=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{main|Environmental issues in Colombia}} | |||
| ] erupted in 1985, causing the ].]] | |||
| The ] was established in 1717, then temporarily removed, and then re-established in 1739. Its capital was Santa Fé de Bogotá. This Viceroyalty included some other provinces of northwestern South America that had previously been under the jurisdiction of the ] or ] and correspond mainly to today's Venezuela, Ecuador, and Panama. Bogotá became one of the principal administrative centers of the Spanish possessions in the New World, along with ] and ], though it remained less developed compared to those two cities in several economic and logistical ways.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://institucional.us.es/tamericanistas/uploads/revista/13/RUIZ-RIVERA..pdf |title=Reformismo local en el nuevo Reino de Granada. Temas americanistas N° 13 |author=Rivera, Julián Bautista Ruiz |year=1997 |pages=80–98 |language=es |access-date=8 April 2014 |archive-date=3 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141103045601/http://institucional.us.es/tamericanistas/uploads/revista/13/RUIZ-RIVERA..pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Transferring Wealth and Power from the Old to the New World: Monetary and Fiscal Institutions in the 17th Through the 19th Centuries – Chapter 12|author1=Jaime U. Jaramillo |author2=Adolfo R. Maisel |author3=Miguel M. Urrutia|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-02727-4|year=1997|url=http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/publicaciones/archivos/borra074.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/publicaciones/archivos/borra074.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The environmental challenges faced by Colombia are caused by both natural hazards and human agency. Many natural hazards result from Colombia's position along the Pacific Ring of Fire and the consequent geological instability. Colombia has ], the eruptions of which have on occasion resulted in substantial loss of life, such as at ], and geological faults that have caused numerous devastating earthquakes, such as the ]. Heavy floods both in mountainous areas and in low-lying watersheds and coastal regions regularly cause deaths and considerable damage to property during the rainy seasons. Rainfall intensities vary with the El Niño Southern Oscillation which occurs in unpredictable cycles, at times causing especially severe flooding. | |||
| ] declared war ] in 1739, and the city of Cartagena quickly became a top target for the British. A massive British expeditionary force was dispatched to capture the city, but, after achieving initial inroads, devastating outbreaks of disease crippled their numbers, and the British were forced to withdraw. The battle became one of Spain's most decisive victories in the conflict, and secured Spanish dominance in the Caribbean until the ].<ref name="BattleofCartagena">{{cite book|title=Conflictos coloniales: la guerra de los nueve años 1739–1748|author=Jorge Cerdá Crespo|publisher=Universidad de Alicante|isbn=978-84-9717-127-4|year=2010|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iHc5HlQpmmUC&pg=PA3|language=es|access-date=7 December 2018|archive-date=29 November 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129012920/https://books.google.com/books?id=iHc5HlQpmmUC&pg=PA3#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite magazine| url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/2015/11/151102-colombia-shipwreck-cartagena-battle-1700s/| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151103233303/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/2015/11/151102-colombia-shipwreck-cartagena-battle-1700s/| url-status=dead| archive-date=3 November 2015|magazine=National Geographic|title=Did This Spanish Shipwreck Change the Course of History?|author=Greshko, Michael}}</ref> The 18th-century priest, botanist, and mathematician ] was delegated by Viceroy ] to conduct an inventory of the nature of New Granada. Started in 1783, this became known as the ]. It classified plants and wildlife, and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fe de Bogotá.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rjb.csic.es/jardinbotanico/jardin/index.php?len=en&Pag=89|title=José Celestino Mutis in New Granada: A life at the service of an Expedition (1760–1808)|publisher=Real Jardín Botánico|access-date=9 April 2014|archive-date=13 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140413125927/http://www.rjb.csic.es/jardinbotanico/jardin/index.php?len=en&Pag=89|url-status=live}}</ref> In July 1801 the Prussian scientist ] reached Santa Fe de Bogotá where he met with Mutis. In addition, historical figures in the process of independence in New Granada emerged from the expedition as the astronomer ], the scientist ], the zoologist ] and the painter ].<ref>{{cite book|title=A Geography of Hard Times: Narratives about Travel to South America, 1780–1849 – Part I: The scholar and the baron: Voyage of the exact sciences|author=Angela Perez-Mejia|publisher=SUNY Press|isbn=978-0-7914-6013-9|year=2004|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1AcBiP9mOmoC&pg=PP1|access-date=7 December 2018|archive-date=29 November 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129012910/https://books.google.com/books?id=1AcBiP9mOmoC&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Francisco José de Caldas: A Scientist at Work in Nueva Granada|author=John Wilton Appel|publisher=American Philosophical Society|isbn=978-0-87169-845-2|year=1994|url=https://archive.org/details/franciscojosedec0000appe|url-access=registration|page=}}</ref> | |||
| ] at ].]] | |||
| === Independence === | |||
| Human induced ] has substantially changed the Andean landscape and is creeping into the rainforests of Amazonia and the Pacific coast. Deforestation is also linked to the conversion of lowland tropical forests to ] plantations. However, compared to neighbouring countries rates of deforestation in Colombia are still relatively low.<ref name="HDR Deforestation"></ref> In urban areas industry, the use of ]s, and other human produced waste have contaminated the local environment, and demand from rapidly expanding cities has placed increasing stress on the water supply as watersheds are affected and ground water tables fall. Participants in the country's ] have also contributed to the pollution of the environment. Illegal armed groups have deforested large areas of land to plant illegal crops, with an estimated 99,000 hectares used for the cultivation of ] in 2007,<ref name="WDR Summary"> | |||
| {{ Accessibility dispute|section|date=November 2024}} | |||
| </ref> while in response the government have ] using hazardous chemicals. Insurgents have also destroyed oil pipelines creating major ecological disasters. | |||
| {{Main|Colombian War of Independence|First Republic of New Granada|Gran Colombia}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Rebellions against Spanish rule had occurred in the empire since the advent of conquest and colonization, but most were either crushed or remained too weak to change the overall situation. The last one that sought outright independence from Spain sprang up around 1810 and culminated in the Colombian Declaration of Independence, issued on 20 July 1810, the day that is now celebrated as the nation's Independence Day.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://elpais.com/internacional/2017/07/20/colombia/1500541945_902382.html |title=Independencia de Colombia: ¿por qué se celebra el 20 de julio? |trans-title=Independence of Colombia: Why is it celebrated on 20 July? |date=20 July 2017 |work=El País |access-date=18 July 2018 |language=es |issn=1134-6582 |archive-date=18 July 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180718205151/https://elpais.com/internacional/2017/07/20/colombia/1500541945_902382.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> This movement followed the independence of ] (present-day Haiti) in 1804, which provided some support to an eventual leader of this rebellion: ]. ] also would play a decisive role.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=McFarlane |first1=Anthony |title=El colapso de la autoridad española y la génesis de la independencia en la Nueva Granada |journal=Revista Desarrollo y Sociedad |date=January 1982 |issue=7 |pages=99–120 |doi=10.13043/dys.7.3 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero2010/socorro.htm|title=La independencia del Socorro en la génesis de la emancipación colombiana.|last=Rodriguez Gómez |first=Juan Camilo|publisher=banrepcultural.org|language=es|access-date=15 April 2017|archive-date=10 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171110174547/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero2010/socorro.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gutiérrez Ardila |first1=Daniel |title=Colombia y Haití: historia de un desencuentro (1819–1831) |trans-title=Colombia and Haití: History of a Misunderstanding (1819–1831) |language=es |journal=Secuencia |date=December 2011 |issue=81 |pages=67–93 |url=http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?pid=S0186-03482011000300003&script=sci_arttext |access-date=28 March 2015 |archive-date=7 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170707192322/http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0186-03482011000300003 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| A movement was initiated by ], who opposed Spanish centralism and led the opposition against the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/29874/1/Antonio%20Nari%C3%B1o-Gutierrez%20Escudero.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/29874/1/Antonio%20Nari%C3%B1o-Gutierrez%20Escudero.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Un precursor de la emancipación americana: Antonio Nariño y Álvarez.|last=Gutiérrez Escudero |first=Antonio|publisher=Araucaria. Revista Iberoamericana de Filosofía, Política y Humanidades 8.13 (2005)|pages=205–220|language=es}}</ref> ] became independent in November 1811.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero2010/caribe.htm|title=Independencia del Caribe colombiano 1810–1821|last=Sourdis Nájera |first=Adelaida|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia – Edición 242|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=9 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171109105253/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero2010/caribe.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> In 1811, the ] were proclaimed, headed by ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/node/88606|title=Confederación de las Provincias Unidas de la Nueva Granada|last=Martínez Garnica |first=Armandao|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia – Edición 244|year=2010|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=24 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624131937/http://www.banrepcultural.org/node/88606|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cervantesvirtual.com/obra-visor-din/acta-de-federacion-de-las-provincias-unidas-de-la-nueva-granada-27-de-noviembre-de-1811--0/html/008e5574-82b2-11df-acc7-002185ce6064_2.html#I_0_|title=Acta de la Federación de las Provincias Unidas de Nueva Granada|year=1811|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=25 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170625133814/http://www.cervantesvirtual.com/obra-visor-din/acta-de-federacion-de-las-provincias-unidas-de-la-nueva-granada-27-de-noviembre-de-1811--0/html/008e5574-82b2-11df-acc7-002185ce6064_2.html#I_0_|url-status=live}}</ref> The emergence of two distinct ideological currents among the patriots (] and ]) gave rise to a period of instability called the ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Ocampo López |first=Javier |author-link=Javier Ocampo López |year=1998 |title=La patria boba. Cuadernillos de historia |publisher=Panamericana Editorial |isbn=978-958-30-0533-6}}</ref> Shortly after the ] ended, ], recently restored to the throne in Spain, unexpectedly decided ] to retake most of northern South America. The viceroyalty was restored under the command of ], whose regime punished those who participated in the patriotic movements, ignoring the political nuances of the ]s.<ref>{{cite web|title=Morillo y la reconquista, 1816–1819|url=http://docencia.udea.edu.co/regionalizacion/irs-406/contenido/morillo.html|publisher=udea.edu.co|language=es|access-date=3 July 2017|archive-date=27 October 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161027064057/http://docencia.udea.edu.co/regionalizacion/irs-406/contenido/morillo.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> The retribution stoked renewed rebellion, which, combined with a weakened Spain, made possible a successful rebellion led by the Venezuelan-born ], who finally proclaimed ] in 1819.<ref name="Historia ilustrada de Colombia">{{cite book |last=Ocampo López |first=Javier |author-link=Javier Ocampo López |year=2006 |title=Historia ilustrada de Colombia – Capítulo VI |publisher=Plaza y Janes Editores Colombia sa |isbn=978-958-14-0370-7 |language=es |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XzgpwLiJs5gC&pg=PA1 |access-date=7 December 2018 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129012918/https://books.google.com/books?id=XzgpwLiJs5gC&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Cartagena de Indias en la independencia |publisher=] |year=2011 |url=http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/publicaciones/archivos/lbr_cartagena_independencia.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/publicaciones/archivos/lbr_cartagena_independencia.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live}}</ref> The ] was defeated in 1822 in the present territory of Colombia and in 1823 in Venezuela.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cervantes.es/lengua_y_ensenanza/hispanismo/independencia_americana/bicentenario_independencia_calendario.htm|title=Cronología de las independencias americanas|publisher=cervantes.es|language=es|access-date=16 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180216202647/http://www.cervantes.es/lengua_y_ensenanza/hispanismo/independencia_americana/bicentenario_independencia_calendario.htm|archive-date=16 February 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=http://revistadeindias.revistas.csic.es/index.php/revistadeindias/article/view/640/706|title=La Constitución de Cádiz en la Provincia de Pasto, Virreinato de Nueva Granada, 1812–1822.|last=Gutiérrez Ramos |first=Jairo|journal=Revista de Indias|publisher=Revista de Indias 68, no. 242|page=222|year=2008|volume=68|issue=242|doi=10.3989/revindias.2008.i242.640|language=es|doi-access=free|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=12 July 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130712040017/http://revistadeindias.revistas.csic.es/index.php/revistadeindias/article/view/640/706|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=La Independencia de Venezuela relatada en clave de paz: las regulaciones pacíficas entre patriotas y realistas (1810–1846).|first1=Alfaro |last1=Pareja |first2=Francisco |last2=José |year=2013|language=es|url=http://repositori.uji.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10234/74784/falfaropareja.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402142358/http://repositori.uji.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10234/74784/falfaropareja.pdf|archive-date=2 April 2015}}</ref> During the Independence War, between 250 and 400 thousand people (12–20% of the pre-war population) died.<ref name="19thcentury">http://necrometrics.com/wars19c.htm {{Webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20150430180518/http://necrometrics.com/wars19c.htm%23Venez1859 |date=30 April 2015}} | "Statistics of Wars, Oppressions and Atrocities of the Nineteenth Century"</ref><ref name="Deremilitari">http://remilitari.com/guias/victimario6.htm {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080509084644/http://remilitari.com/guias/victimario6.htm |date=9 May 2008 }} | In Spanish "De re Militari: muertos en Guerras, Dictaduras y Genocidios. Capítulo VI"</ref><ref>Silvio Arturo Zavala (1971). ''Revista de historia de América''. Números 69-70. Ciudad de México: Instituto Panamericano de Geografía e Historia, pp. 303. "Para el primero, de 1400000 habs. que la futura Colombia tendría en 1809 (entre ellos 78000 negros esclavos), (...) mortaldad que él mismo señala a tal guerra (unos 400 000 muertos para la Gran Colombia, entre ellos, 250 000 venezolanos)."</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|History of Colombia|Timeline of Colombian history|La Violencia|El Bogotazo|National Front (Colombia)|Colombian armed conflict (1964–present)}} | |||
| The territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada became the ], organized as a ] of Colombia, Panama, Ecuador, Venezuela, parts of Guyana and Brazil and north of ].<ref>{{cite book|title=(Gran) Colombia, relación geográfica, topográfica, agrícola, comercial y política de este país: Adaptada para todo lector en general y para el comerciante y colono en particular |volume=1 |first=Alexander |last=Walker|publisher=Banco de la República|year=1822|language=es|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uVZsAAAAMAAJ&pg=PR1}}</ref> The ] in 1821 adopted a ] for the new Republic.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/21805/1/18324-59371-1-PB.pdf|title=Los ciudadanos en la Constitución de Cúcuta – Citizenship in the Constitution of Cúcuta|last=Sosa Abella |first=Guillermo|publisher=Instituto Colombiano de Antropología e Historia (icanh)|year=2009|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=23 September 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923183203/http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/21805/1/18324-59371-1-PB.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/vireco/vireco11.htm|title=El viaje de Gaspard-Théodore Mollien por la República de Colombia en 1823. CAPÍTULO IX|last=Mollien |first=Gaspard-Théodore |publisher=Biblioteca Virtual del Banco de la República|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=9 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171109010323/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/vireco/vireco11.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> Simón Bolívar became the first ], and Francisco de Paula Santander was made ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://docencia.udea.edu.co/regionalizacion/irs-406/contenido/laconstitucion.html|title=Avatares de una Joven República – 2. La Constitución de Cúcuta|publisher=Universidad de Antioquia|language=es|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=4 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304025729/http://docencia.udea.edu.co/regionalizacion/irs-406/contenido/laconstitucion.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> However, the new republic was unstable and the Gran Colombia ultimately collapsed. | |||
| Modern Colombia comes from one of the countries that emerged after the ], the other two being Ecuador and Venezuela.<ref name="EtHisColombia">{{Cite news |date=27 August 2012 |title=Colombia profile - Timeline |publisher=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-19390164 |access-date=14 January 2023 |archive-date=26 September 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190926221001/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-19390164 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="GranColombiaNuevaGranada">{{cite web|url=http://www.unimilitar.edu.co/documents/63968/72398/04.GranColANvaGranada.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.unimilitar.edu.co/documents/63968/72398/04.GranColANvaGranada.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=De la gran Colombia a la Nueva Granada, contexto histórico-político de la transición constitucional|last=Blanco Blanco |first=Jacqueline|publisher=Universidad Militar Nueva Granada|year=2007|language=es}}</ref><ref>{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Colombia|date=12 January 2022}}</ref> Colombia was the first ] in South America,<ref name="HistoriaConstitucional">{{cite web |url=http://unilibrepereira.edu.co/catehortua/posgrados/archivos2/HISTORIA%20CONSTITUCIONAL%20COLOMBIANA.pdf |title=Historia Constitucional Colombiana |first=Edgar |last=Arana |publisher=Universidad Libre Seccional Pereira |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150327033803/http://unilibrepereira.edu.co/catehortua/posgrados/archivos2/HISTORIA%20CONSTITUCIONAL%20COLOMBIANA.pdf |archive-date=27 March 2015}}</ref> and the ] and ] parties, founded in 1848 and 1849, respectively, are two of the oldest surviving political parties in the Americas.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://174.129.218.71/publications/thinking_politics/upload/thinking_politics_sp_chap4.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150327041239/http://174.129.218.71/publications/thinking_politics/upload/thinking_politics_sp_chap4.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=27 March 2015 |year=2009 |title=Partidos políticos y think tanks en Colombia |first=Juan Fernando |last=Londoño |publisher=International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance |page=129 |isbn=978-91-85724-73-4 |language=es }}</ref> ] was abolished in the country in 1851.<ref>{{cite book |last=Aguilera |first=Miguel |year=1965 |title=La Legislación y el derecho en Colombia |series=Historia extensa de Colombia |volume=14 |publisher=Lemer |location=Bogotá |pages=428–442}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=http://revistas.unisinos.br/index.php/historia/article/view/6183 |year=2006 |title=Abolitionist arguments in Colombia |last=Restrepo |first=Eduardo |journal=História Unisinos |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=293–306 |language=es |access-date=28 March 2015 |archive-date=8 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170708173736/http://revistas.unisinos.br/index.php/historia/article/view/6183 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Pre-Columbian era===<!--This spelling is correct, please do not edit it. It originates from "Columbus", not "Colombia"--> | |||
| Internal political and territorial divisions led to the dissolution of ] in 1830.<ref name="EtHisColombia" /><ref name="GranColombiaNuevaGranada" /> The so-called "]" adopted the name "]", which it kept until 1858 when it became the "Confederación Granadina" (]). After a ] in 1863, the ] was created, which became known as the Republic of Colombia in 1886.<ref name="HistoriaConstitucional" /><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/poli/poli57.htm |title=Constituciones que han existido en Colombia |publisher=] |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110807093959/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/poli/poli57.htm |archive-date=7 August 2011}}</ref> Internal divisions remained between the bipartisan political forces, occasionally igniting very bloody civil wars, the most significant being the ] (1899–1902), in which between 100 and 180 thousand Colombians lost their lives when the ], supported by ], ], ], and ] rebelled against the ] and took control of ], ultimately being defeated in 1902 by nationalist forces.<ref>{{cite book |first=Gonzalo |last=España |year=2013 |title=El país que se hizo a tiros |publisher=Penguin Random House |isbn=978-958-8613-90-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IordAgAAQBAJ&pg=PP1 |language=es |access-date=7 December 2018 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129012814/https://books.google.com/books?id=IordAgAAQBAJ&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] used to cover his body in gold and, from his raft, he offered treasures to the ''Guatavita'' goddess in the middle of the sacred lake. This old Muisca tradition became the origin of the ] legend.]] | |||
| === 20th century === | |||
| Approximately 10,000 BC, ] societies existed near present-day Bogotá (at "]" and "Tequendama") which traded with one another and with cultures living in the ] Valley.<ref>Van der Hammen, T. and Correal, G. 1978: "Prehistoric man on the Sabana de Bogotá: data for an ecological prehistory"; Paleography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology 25:179-190</ref> Beginning in the first millennium BC, groups of ]s developed the political system of "]s" with a pyramidal structure of power headed by ]. Within Colombia, the two cultures with the most complex cacicazgo systems were the ]s in the ], and the ]s in the highlands around Bogotá, both of which were of the ] language family. The Muisca people are considered to have had one of the most developed political systems in South America, after the ]s.<ref>Broadbent, Sylvia 1964: Los Chibchas: organización socio-política. Série Latinoamericana 5. Bogotá: Facultad de Sociología, Universidad Nacional de Colombia</ref> | |||
| {{See also|Colombian conflict|La Violencia}} | |||
| The United States of America's intentions to influence the area (especially the ] construction and control)<ref>{{cite news |title=The 1903 Treaty and Qualified Independence |url=http://countrystudies.us/panama/8.htm |publisher=U.S. Library of Congress |access-date=13 September 2020 |archive-date=11 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111011225556/http://countrystudies.us/panama/8.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> led to the ] in 1903 and the establishment of it as a nation.<ref name="SeparationofPanama">{{cite web |author=Beluche, Olmedo |year=2003 |title=The true history of the separation of 1903 – La verdadera historia de la separación de 1903 |publisher=ARTICSA |url=https://9256eada680e78ba56205f2037885261263098bd-www.googledrive.com/host/0B9QeWchRinyLejFzX01XWG9uVkU/La-verdadera-historia-de-la-separacion-de-1903.pdf |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151030020242/https://9256eada680e78ba56205f2037885261263098bd-www.googledrive.com/host/0B9QeWchRinyLejFzX01XWG9uVkU/La-verdadera-historia-de-la-separacion-de-1903.pdf |archive-date=30 October 2015}}</ref> The United States paid Colombia $25,000,000 in 1921, seven years after completion of the canal, for redress of President ]'s role in the creation of Panama, and Colombia recognized Panama under the terms of the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=El tratado Urrutia-Thomson. Dificultades de política interna y exterior retrasaron siete años su ratificación |publisher=Revista Credencial Historia |year=2003 |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/node/86422 |language=es |access-date=30 October 2015 |archive-date=15 November 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171115020147/http://www.banrepcultural.org/node/86422 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Colombia and Peru went to ] because of territory disputes far in the ]. The war ended with a peace deal brokered by the ]. The League finally awarded the disputed area to Colombia in June 1934.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Atehortúa Cruz |author2=Adolfo León |year=2014 |title=El conflicto Colombo-Peruano – Apuntes acerca de su desarrollo e importancia histórica |journal=Historia y Espacio |volume=3 |issue=29 |url=http://cms.univalle.edu.co/revistasunivalle/index.php/historiayespacio/article/view/2750/2637 |pages=51–78 |doi=10.25100/hye.v3i29.1664 |s2cid=252776167 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151030020452/http://cms.univalle.edu.co/revistasunivalle/index.php/historiayespacio/article/view/2750/2637 |archive-date=30 October 2015|hdl=10893/1003 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ] in 1948]] | |||
| Soon after, Colombia achieved some degree of political stability, which was interrupted by a bloody conflict that took place between the late 1940s and the early 1950s, a period known as '']'' ("The Violence"). Its cause was mainly mounting tensions between the two leading political parties, which subsequently ignited after the assassination of the Liberal presidential candidate ] on 9 April 1948.<ref>{{cite book |title=El Bogotazo: Memorias Del Olvido |author=Alape, Arturo |publisher=Fundación Universidad Central |year=1983 |language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Mataron a Gaitán: vida pública y violencia urbana en Colombia |author=Braun, Herbert |publisher=], Centro Editorial |year=1987 |isbn=978-958-17-0006-6 |language=es}}</ref> The ensuing riots in Bogotá, known as ], spread throughout the country and claimed the lives of at least 180,000 Colombians.<ref name="Encarta">{{cite encyclopedia |author1=Charles Bergquist |author2=David J. Robinson |year=1997–2005 |url=http://ca.encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761564636_10/Colombia.html |title=Colombia |encyclopedia=Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2005 |publisher=Microsoft Corporation |access-date=16 April 2006 |archive-date=11 November 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071111194946/http://ca.encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761564636_10/Colombia.html}} ''On 9 April 1948, Gaitán was assassinated outside his law offices in downtown Bogotá. The assassination marked the start of a decade of bloodshed, called ''La Violencia'' (The Violence), which took the lives of an estimated 180,000 Colombians before it subsided in 1958.''</ref> | |||
| ===Spanish discovery, conquest, and colonization=== | |||
| Spanish explorers made the first exploration of the ] littoral in 1499 led by ]. ] navigated near the Caribbean in 1502. In 1508, ] started the conquest of the territory through the region of Urabá. In 1513, he was the first European to discover the ] which he called ''Mar del Sur'' (or "Sea of the South") and which in fact would bring the Spaniards to ] and ]. The territory's main population was made up of hundreds of tribes of the ] and ], currently known as the Caribbean people, whom the ] conquered through warfare and alliances, while resulting disease such as ], and the conquest and ] itself caused a demographic reduction among the indigenous.<ref></ref> In the sixteenth century, ] began to bring slaves from Africa. | |||
| Colombia entered the ] when ] was elected president. It was the only Latin American country to join the war in a direct military role as an ally of the United States. Particularly important was the resistance of the Colombian troops at ].<ref name="Colombia's legacy with Korea">{{cite web |title=Colombia y los Estados Unidos en la Guerra de Corea |author1=Carlos Horacio Urán |publisher=The Kellogg Institute for International Studies |year=1986 |url=http://kellogg.nd.edu/publications/workingpapers/WPS/069.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://kellogg.nd.edu/publications/workingpapers/WPS/069.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |language=es}}</ref> | |||
| ===Independence from Spain=== | |||
| ], ] and other heroes of the Independence of Colombia in the ].]] | |||
| The violence between the two political parties decreased first when ] deposed the ] of Colombia in a coup d'état and negotiated with the guerrillas, and then under the ] of General ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Atehortúa Cruz |first1=Adolfo |title=El golpe de Rojas y el poder de los militares |trans-title=Rojas' coup d'etat and the power of army men |language=es |journal=Folios |date=2 February 2010 |volume=1 |issue=31 |pages=33–48 |doi=10.17227/01234870.31folios33.48 |doi-broken-date=1 November 2024 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Ayala Diago, César Augusto |year=2000 |title=Gustavo Rojas Pinilla, 100 años, 1900–1975 |publisher=] |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/marzo2000/123gustavo.htm |language=es |access-date=24 April 2017 |archive-date=24 April 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424112356/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/marzo2000/123gustavo.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Since the beginning of the periods of Conquest and Colonization, there were several rebel movements under Spanish rule, most of them either being crushed or remaining too weak to change the overall situation. The last one which sought outright independence from Spain sprang up around 1810, following the independence of St. Domingue in 1804 (present day ]), who provided a non-negligible degree of support to the eventual leaders of this rebellion: ] and ]. Simón Bolívar had become the first ], and Francisco de Paula Santander was ]; when Simón Bolívar stepped down, Santander became the second President of Colombia. The rebellion finally succeeded in 1819 when the territory of the ] became the Republic of ] organized as a Confederation along Ecuador and Venezuela (Panama was part of Colombia). | |||
| ] (1964–present)]] | |||
| After Rojas' deposition, the Colombian Conservative Party and the Colombian Liberal Party agreed to create the ], a coalition that would jointly govern the country. Under the deal, the presidency would alternate between conservatives and liberals every 4 years for 16 years; the two parties would have parity in all other elective offices.<ref>{{cite web|title=1957–1974 El Frente Nacional|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia|year=2006|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/septiembre2006/frente.htm|author=Alarcón Núñez, Óscar|language=es|access-date=24 April 2017|archive-date=24 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424072902/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/septiembre2006/frente.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> The National Front ended "La Violencia", and National Front administrations attempted to institute far-reaching social and economic reforms in cooperation with the ].<ref>ROJAS, Diana Marcela. La alianza para el progreso de Colombia. Análisis Político, , v. 23, n. 70, p. 91–124, Sep. 2010. {{ISSN|0121-4705}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Frente Nacional: acuerdo bipartidista y alternación en el poder|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia|year=1999|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/noviembre1999/119frente.htm|author=Ayala Diago, César Augusto|language=es|access-date=24 April 2017|archive-date=5 July 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130705231831/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/noviembre1999/119frente.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> Despite the progress in certain sectors, many social and political problems continued, and guerrilla groups were formally created such as the ], the ] and the ] to fight the government and political apparatus.<ref>{{cite web|title=El Frente Nacional|publisher=banrepcultural.org|year=2006|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/politica/el_frente_nacional|language=es|access-date=24 April 2017|archive-date=24 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424073204/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/politica/el_frente_nacional|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ===Post-independence and republicanism=== | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Since the 1960s, the country has suffered from an ] ] ] between ], ] and ].<ref name="HistoricalCommission">{{cite web|title=Contribution to an Understanding of the Armed Conflict in Colombia|author=Historical Commission on the Conflict and Its Victims (CHCV)|date=February 2015|url=https://www.mesadeconversaciones.com.co/sites/default/files/Informe%20Comisi_n%20Hist_rica%20del%20Conflicto%20y%20sus%20V_ctimas.%20La%20Habana,%20Febrero%20de%202015.pdf|language=es|access-date=6 February 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160121194351/https://www.mesadeconversaciones.com.co/sites/default/files/Informe%20Comisi_n%20Hist_rica%20del%20Conflicto%20y%20sus%20V_ctimas.%20La%20Habana%2C%20Febrero%20de%202015.pdf|archive-date=21 January 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> The conflict escalated in the 1990s,<ref name="Colombian armed conflict">{{cite web|author=Lilian Yaffe|url=http://www.icesi.edu.co/revistas/index.php/revista_cs/article/view/1133/1509|title=Armed conflict in Colombia: analyzing the economic, social, and institutional causes of violent opposition|publisher=icesi.edu.co|date=3 October 2011|language=es|access-date=24 April 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131016063214/http://www.icesi.edu.co/revistas/index.php/revista_cs/article/view/1133/1509|archive-date=16 October 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> mainly in remote rural areas.<ref name="Colombian conflict">{{cite web |url=http://www.centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co/informes/informes-2017/tomas-y-ataques-guerrilleros-1965-2013 |title=Tomas y ataques guerrilleros (1965–2013) |publisher=centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co |date=5 June 2017 |language=es |access-date=16 February 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180826051509/http://www.centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co/informes/informes-2017/tomas-y-ataques-guerrilleros-1965-2013 |archive-date=26 August 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Since the beginning of the armed conflict, ] have fought for the respect for human rights, despite staggering opposition.{{efn|] was a prominent medical doctor, university professor, and human rights leader whose holistic vision of healthcare led him to found the Colombian National School of Public Health. The increasing violence and human rights abuses of the 1970s and 1980s led him to fight for social justice in his community.<ref>{{cite book|title=Oblivion: A Memoir|author=Héctor Abad Faciolince|publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux|isbn=978-0-374-53393-9|year=2006}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wola.org/news/oblivion_a_memior_by_hector_abad_wins_wola_duke_human_rights_book_award|title=Oblivion: a memoir by Hector Abad wins Wola-Duke human rights book award|date=12 October 2012|access-date=27 January 2016|publisher=wola.org|archive-date=7 July 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160707233709/http://www.wola.org/news/oblivion_a_memior_by_hector_abad_wins_wola_duke_human_rights_book_award|url-status=live}}</ref>}}{{efn|] was a ] priest who grew up in war-torn Italy and arrived in Colombia a year after the Bogotazo. He developed a program that has offered more than 40,000 young people the education and moral support they needed to become productive citizens.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iaf.gov/resources/publications/grassroots-development-journal/2013-focus-the-iaf-s-investment-in-young-people/first-class-citizens-father-de-nicol-and-the-street-kids-of-colombia|title=First-class citizens: Father de Nicoló and the street kids of Colombia|access-date=28 March 2016|publisher=iaf.gov|archive-date=28 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160328202748/http://www.iaf.gov/resources/publications/grassroots-development-journal/2013-focus-the-iaf-s-investment-in-young-people/first-class-citizens-father-de-nicol-and-the-street-kids-of-colombia|url-status=dead}}</ref>}} Several guerrillas' organizations decided to demobilize after peace negotiations in 1989–1994.<ref name="Enough Already!">{{cite book|title="Enough Already!" Colombia: Memories of War and Dignity.|author=Historical Memory Group|publisher=The National Center for Historical Memory's (NCHM)|year=2013|isbn=9789585760844|url=http://www.centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co/descargas/informes2013/bastaYa/bastaya-colombia-memorias-de-guerra-y-dignidad-2015.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co/descargas/informes2013/bastaYa/bastaya-colombia-memorias-de-guerra-y-dignidad-2015.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|language=es}}</ref> | |||
| Internal political and territorial divisions led to the secession of Venezuela and Quito (today's Ecuador) in 1830. The so-called "Department of ]" adopted the name "]", which it kept until 1856 when it became the "Confederación Granadina" (]). After a ] in 1863, the "]" was created, lasting until 1886, when the country finally became known as the Republic of Colombia. Internal divisions remained between the bipartisan political forces, occasionally igniting very bloody ]s, the most significant being the ] (1899 - 1902) which together with the United States of America's intentions to influence in the area (especially the ] construction and control) led to the separation of the Department of Panama in 1903 and the establishment of it as a nation. Colombia engulfed in a year long war with Peru over a territorial dispute involving the ] and its capital ]. | |||
| The United States has been heavily involved in the conflict since its beginnings, when in the early 1960s the ] encouraged the Colombian military to attack leftist militias in rural Colombia. This was part of the U.S. fight against communism. ]s and multinational corporations such as ] are some of the international actors that have contributed to the violence of the conflict.<ref name="HistoricalCommission" /><ref name="Enough Already!" /><ref name="colombia-and-us-54">{{cite book|title=Colombia and the United States: war, unrest, and destabilization|author1=Mario A. Murillo|author2=Jesús Rey Avirama|publisher=Seven Stories Press|isbn=978-1-58322-606-3|year=2004|url=https://archive.org/details/colombiaunitedst00muri|url-access=registration|page=}}</ref> | |||
| Soon after, Colombia achieved a relative degree of political stability, which was interrupted by a bloody conflict that took place between the late 1940s and the early 1950s, a period known as '']'' ("The Violence"). Its cause was mainly mounting tensions between the two leading political parties, which subsequently ignited after the assassination of the ] presidential candidate ] on April 9, 1948. This assassination caused riots in Bogotá and became known as ]. The violence from these riots spread through out the country and claimed the lives of at least 180,000 Colombians. From 1953 to 1964 the violence between the two political parties decreased first when ] deposed the President of Colombia in a ] and negotiated with the guerrillas, and then under the ] of General ]. | |||
| Beginning in the mid-1970s Colombian ]s became major producers, processors and exporters of ], primarily ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/drugs/business/inside/colombian.html |title=The Colombian Cartels |publisher=WGBH educational foundation |access-date=25 May 2020 |archive-date=28 July 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130728115548/http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/drugs/business/inside/colombian.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| After Rojas' deposition the two political parties ] and Colombian Liberal Party agreed to the creation of a "National Front", whereby the Liberal and Conservative parties would govern jointly. The presidency would be determined by an alternating conservative and liberal president every 4 years for 16 years; the two parties would have parity in all other elective offices. The National Front ended "La Violencia", and National Front administrations attempted to institute far-reaching social and economic reforms in cooperation with the Alliance for Progress. In the end, the contradictions between each successive Liberal and Conservative administration made the results decidedly mixed. Despite the progress in certain sectors, many social and political problems continued, and guerrilla groups were formally created such as the ], ] and ] to fight the government and political apparatus. These guerrilla groups were dominated by ]. | |||
| On 4 July 1991, a new ] was promulgated. The changes generated by the new constitution are viewed as positive by Colombian society.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/colombia/20-grandes-cambios-genero-constitucion-1991 |title=20 grandes cambios que generó la Constitución de 1991 |access-date=28 March 2013 |publisher=elpais.com.co |language=es |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151211013106/http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/colombia/20-grandes-cambios-genero-constitucion-1991 |archive-date=11 December 2015 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name="Colombian Constitution of 1991">{{cite web |url=http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/index.php/leyes-y-antecedentes/constitucion-y-sus-reformas |title=Colombian Constitution of 1991 |access-date=10 March 2014 |publisher=secretariasenado.gov.co |language=es |archive-date=28 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230328034430/http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/index.php/leyes-y-antecedentes/constitucion-y-sus-reformas |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Emerging in the late 1970s, powerful and violent ]s further developed during the 1980s and 1990s. The Medellín Cartel under ] and the ], in particular, exerted political, economic and social influence in Colombia during this period. These cartels also financed and influenced different illegal armed groups throughout the political spectrum. Some enemies of these allied with the guerrillas and created or influenced ]. | |||
| ===21st century=== | |||
| The new ] was ratified after being drafted by the ]. The constitution included key provisions on political, ethnic, human and gender rights. The new constitution initially prohibited the extradition of Colombian nationals. There were accusations of lobbying by drug cartels in favor of this prohibition. The cartels had previously promoted a violent campaign against extradition, leading to many ] and ] style executions. They also tried to influence the government and political structure of Colombia by means of corruption, as in the case of the ] scandal. | |||
| {{See also|Colombian peace process}} | |||
| ] signing a ]]] | |||
| The administration of President ] (2002–2010) adopted the ] which included an integrated ] and ] campaign.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.eltiempo.com/justicia/desmovilizacion-principal-arma-contra-las-guerrillas_13077339-4 |title=Desmovilización, principal arma contra las guerrillas |trans-title=Demobilization, main weapon against the guerrillas |first=Juan Guillermo |last=Mercado |work=] |language=es |date=22 September 2013 |access-date=26 September 2013 |archive-date=23 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130923064310/http://www.eltiempo.com/justicia/desmovilizacion-principal-arma-contra-las-guerrillas_13077339-4 |url-status=live }}</ref> The government economic plan also promoted confidence in investors.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://som.yale.edu/news/news/former-colombian-president-alvaro-uribe-speaks-yale-som |title=Former Colombian President Alvaro Uribe Speaks at Yale SOM |publisher=Yale School of Management |date=3 December 2012 |access-date=25 June 2016 |archive-date=20 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191220195312/https://som.yale.edu/news/news/former-colombian-president-alvaro-uribe-speaks-yale-som |url-status=dead }}</ref> As part of a controversial peace process, the ] (right-wing paramilitaries) had ceased to function formally as an organization .<ref name="CIAWFB">{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Colombia|access-date=24 September 2015}}</ref> In February 2008, millions of Colombians demonstrated against FARC and other outlawed groups.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.movements.org/case-study/entry/oscar-morales-and-one-million-voices-against-farc/ |title=Oscar Morales and One Million Voices Against FARC |website=Movements.org |date=23 July 2010 |access-date=1 April 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131022220325/http://www.movements.org/case-study/entry/oscar-morales-and-one-million-voices-against-farc/ |archive-date=22 October 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| After peace negotiations in ], the ] of President ] and the ] of the FARC-EP announced a final agreement to end the conflict.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co/mesadeconversaciones/index.html|title=Colombia's peace deals|publisher=altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co|access-date=6 September 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170914085318/http://www.altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co/mesadeconversaciones/index.html|archive-date=14 September 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref> However, a ] to ratify the deal was unsuccessful.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-37537252 |title=Colombia referendum: Voters reject Farc peace deal |publisher=] |date=3 October 2016 |access-date=2 November 2016 |archive-date=30 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180930152644/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-37537252 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Plebiscito 2 octubre 2016 – Boletín Nacional No. 53 |url=http://plebiscito.registraduria.gov.co/99PL/DPLZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ_L1.htm |publisher=Registraduría Nacional de Estado Civil |date=2 October 2016 |access-date=2 November 2016 |archive-date=3 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161003083638/http://plebiscito.registraduria.gov.co/99PL/DPLZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ_L1.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Afterward, the Colombian government and the FARC signed a revised ] in November 2016,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-38096179 |title=Colombia signs new peace deal with Farc |date=24 November 2016 |publisher=] |access-date=21 June 2018 |archive-date=28 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161228195756/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-38096179 |url-status=live }}</ref> which the ] approved.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/the_americas/colombian-congress-approves-historic-peace-deal/2016/11/30/9b2fda92-b5a7-11e6-939c-91749443c5e5_story.html |title=Colombia's congress approves historic peace deal with FARC rebels |date=30 November 2016 |first1=Joshua |last1=Partlow |first2=Nick |last2=Miroff |newspaper=] |access-date=1 December 2016 |archive-date=1 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161201090410/https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/the_americas/colombian-congress-approves-historic-peace-deal/2016/11/30/9b2fda92-b5a7-11e6-939c-91749443c5e5_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2016, President Santos was awarded the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2016/santos-lecture_en.html|title=Nobel Lecture by Juan Manuel Santos, Oslo, 10 December 2016|website=NobelPrize.org|access-date=10 December 2016|archive-date=10 December 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161210204701/https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2016/santos-lecture_en.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The Government began a process of attention and comprehensive reparation for victims of conflict.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unidadvictimas.gov.co/normatividad/LEY+DE+VICTIMAS.pdf |title=The Victims and Land Restitution Law |publisher=unidadvictimas.gov.co |access-date=21 December 2014 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150925110822/http://www.unidadvictimas.gov.co/normatividad/LEY%2BDE%2BVICTIMAS.pdf |archive-date=25 September 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.restituciondetierras.gov.co/inicio |title=the Land Restitution Unit |publisher=restituciondetierras.gov.co |access-date=23 March 2013 |archive-date=4 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160104000003/https://www.restituciondetierras.gov.co/inicio |url-status=dead }}</ref> Colombia shows modest progress in the struggle to defend human rights, as expressed by ].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://colombiareports.co/colombia-has-improved-under-santos-human-rights-watch/ |title=Colombia has improved under Santos: Human Rights Watch |first=Toni |last=Peters |work=] |date=12 October 2011 |access-date=31 March 2015 |archive-date=13 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150413201236/http://colombiareports.co/colombia-has-improved-under-santos-human-rights-watch/ |url-status=live }}</ref> A ] has been created to investigate, clarify, prosecute and punish serious human rights violations and grave breaches of ] which occurred during the armed conflict and to satisfy victims' right to ].<ref>{{cite web|title=ABC Jurisdicción Especial para la Paz|url=http://www.altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co/Documents/informes-especiales/abc-del-proceso-de-paz/abc-jurisdiccion-especial-paz.html|publisher=Oficina del Alto Comisionado para la Paz|access-date=24 August 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161005125954/http://www.altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co/Documents/informes-especiales/abc-del-proceso-de-paz/abc-jurisdiccion-especial-paz.html|archive-date=5 October 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> During his visit to Colombia, ] paid tribute to the victims of the conflict.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://en.radiovaticana.va/news/2017/09/08/pope_at_colombia_prayer_meeting_for_reconciliation_weeps_wit/1335635 |title=Pope at Colombia prayer meeting for reconciliation weeps with victims |date=8 September 2017 |website=radiovaticana.va |access-date=9 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170909034315/http://en.radiovaticana.va/news/2017/09/08/pope_at_colombia_prayer_meeting_for_reconciliation_weeps_wit/1335635 |archive-date=9 September 2017 |url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ] during a field training exercise.]] | |||
| ], the country's first ] president]] | |||
| In June 2018, ], the candidate of the right-wing ] party, won the presidential ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Colombia's president-elect Duque wants to 'unite country' |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-44513368 |publisher=BBC News |date=18 June 2018 |access-date=21 April 2021 |archive-date=18 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180618011841/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-44513368 |url-status=live }}</ref> On 7 August 2018, he was sworn in as the new ] to succeed Juan Manuel Santos.<ref>{{cite news|title=Iván Duque: Colombia's new president sworn into office|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-45107063|publisher=BBC News|date=8 August 2018|access-date=8 July 2021|archive-date=30 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201030105110/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-45107063|url-status=live}}</ref> ] have fluctuated due to ideological differences between the two governments.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-10926003 |title=Colombia and Venezuela restore diplomatic relations |publisher=BBC News |date=11 August 2010 |access-date=21 June 2018 |archive-date=13 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180613030309/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-10926003 |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombia has offered ] with food and medicines to mitigate the shortage of supplies in Venezuela.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://es.presidencia.gov.co/noticia/180111-Colombia-reitera-ofrecimiento-de-ayuda-humanitaria-a-Venezuela |title=Colombia reitera ofrecimiento de ayuda humanitaria a Venezuela |trans-title=Colombia reiterates offer of humanitarian aid to Venezuela |date=11 January 2018 |language=es |website=Presidencia.gov.co |access-date=12 January 2018 |archive-date=12 January 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180112025350/http://es.presidencia.gov.co/noticia/180111-Colombia-reitera-ofrecimiento-de-ayuda-humanitaria-a-Venezuela |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombia's Foreign Ministry said that all efforts to resolve ] should be peaceful.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://es.presidencia.gov.co/noticia/170812-Comunicado-de-prensa-del-Ministerio-de-Relaciones-Exteriores |title=Comunicado de prensa del Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores |trans-title=Press release of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs |date=2 June 2017 |language=es |website=Presidencia.gov.co |access-date=13 August 2017 |archive-date=13 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170813113834/http://es.presidencia.gov.co/noticia/170812-Comunicado-de-prensa-del-Ministerio-de-Relaciones-Exteriores |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombia proposed the idea of the ] and a final document was adopted by the United Nations.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Caballero |first=Paula |author-link=Paula Caballero |date=20 September 2016 |title=A Short History of the SDGS. |url=http://impakter.com/short-history-sdgs/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171008122103/http://impakter.com/short-history-sdgs/ |archive-date=8 October 2017 |access-date=8 October 2017 |website=Impakter.com}}</ref> In February 2019, Venezuelan president ] cut off diplomatic relations with Colombia after Colombian President Ivan Duque had helped Venezuelan opposition politicians deliver humanitarian aid to their country. Colombia recognized Venezuelan opposition leader ] as the country's legitimate president. In January 2020, Colombia rejected Maduro's proposal that the two countries restore diplomatic relations.<ref>{{cite news|title=Colombia rejects Venezuelan proposal to resume diplomatic relations|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-colombia-venezuela-idUSKBN1ZT30R|publisher=Reuters|date=30 January 2020|access-date=8 July 2021|archive-date=21 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210421065909/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-colombia-venezuela-idUSKBN1ZT30R|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In recent years, the country has continued to be plagued by the effects of the ], ] ] like FARC and paramilitary groups such as the ] (later demobilized, though paramilitarism remains active), which along with other minor factions have engaged in a bloody internal ]. President ] and the FARC attempted to negotiate a solution to the conflict between 1998 and 2002 in which the government, more or less like Pakistan negotiations with the Taliban , believed the state could not fight forever and agreed to handle huge quantity of land in return for peace.Pastrana began to implement the ] initiative, with the dual goal of ending the armed conflict and promoting a strong ] strategy. This strategy had huge quantity of land to be officially set as "demilitarize" zones were no soldiers from neither side could reside, but as more and more attacks from the drug cartels persisted on the demilitarize zones the government soon realized the negotiations were a waste of time. | |||
| ] started on 28 April 2021 when the government proposed a tax bill that would greatly expand the range of the 19 percent ].<ref name="nyb220721">{{cite news |last1=Guillermoprieto |first1=Alma |title=Confrontation in Colombia {{!}} by Alma Guillermoprieto {{!}} The New York Review of Books |url=https://www.nybooks.com/articles/2021/07/22/confrontation-in-colombia/ |date=22 July 2021 |access-date=2 July 2021 |language=en |archive-date=1 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210701142820/https://www.nybooks.com/articles/2021/07/22/confrontation-in-colombia/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The 19 June 2022 ] run-off vote ended in a win for former guerrilla, ], taking 50.47% of the vote compared to 47.27% for independent candidate ]. The single-term limit for the country's presidency prevented President Iván Duque from seeking re-election. On 7 August 2022, Petro was sworn in, becoming the country's first leftist president.<ref>{{cite news |title=Former guerrilla Gustavo Petro wins Colombian election to become first leftist president |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jun/20/former-guerrilla-gustavo-petro-wins-colombian-election-to-become-first-leftist-president |work=The Guardian |date=20 June 2022 |language=en |access-date=2 August 2022 |archive-date=2 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220802080758/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jun/20/former-guerrilla-gustavo-petro-wins-colombian-election-to-become-first-leftist-president |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Ex-rebel takes oath as Colombia's first left-wing president |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/8/8/gustavo-petro-ex-rebel-fighter-sworn-in-as-colombias-president |publisher=Al Jazeera |language=en |access-date=8 August 2022 |archive-date=8 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220808091808/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/8/8/gustavo-petro-ex-rebel-fighter-sworn-in-as-colombias-president/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| During the presidency of ], who was elected on the promise of applying military pressure on the FARC and other outlawed groups, with the promise that after nearly half a century of negotiation with no results was a sign that some entities "just cannot be negotiated with". Mostly through military pressure and increased military hardware from the US most security indicators improved, showing a steep decrease in reported ] (from 3,700 in the year 2000 to 800 in 2005) and a decrease of more than 48% in homicides between July 2002 and May 2005. Guerillas have been reduced from 16,900 insurgents to 8,900 insurgents. | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| While some in the UN argue Colombia is violating human rights to achieve peace, most do not argue that increase military pressure has had considerable improvements that have favored economic growth and tourism.<ref> '''The Economist''', June 29, 2006.</ref> The ] emerged from the revelations and judicial implications of past and present links between paramilitary groups, mainly the AUC, and some government officials and many politicians, most of them allied to the governing administration.<ref></ref> | |||
| {{Main|Geography of Colombia|Geology of Colombia}} | |||
| ] of Colombia]] | |||
| The geography of Colombia is characterized by its six main ] that present their unique characteristics, from the ] mountain range region; the ]al region; the Caribbean coastal region; the '']'' (plains); the ] region; to the ], comprising islands in both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.<ref name="Geography of Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia-sa.com/geografia/geografia-in.html|title=Natural regions of Colombia and description of the three branches of the andes cordillera|publisher=colombia-sa.com|access-date=7 March 2014|archive-date=14 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140314043601/http://www.colombia-sa.com/geografia/geografia-in.html|url-status=live}}</ref> It shares its maritime limits with ], ], ], ], ], and the ].<ref name="Maritime borders" /> | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| {{main|Government of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Colombian Constitution of 1991}} | |||
| ]''. The presidential palace in ] houses the ] and head of the ].]] | |||
| Colombia is bordered to the northwest by ], to the east by ] and Brazil, and to the south by ] and ];<ref name="Land borders">{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/politica/fronteras-terrestres|title=The Republic of Colombia shares land borders with five (5) countries|publisher=cancilleria.gov.co|access-date=6 June 2016|archive-date=31 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180731123542/http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/politica/fronteras-terrestres|url-status=live}}</ref> it established its maritime boundaries with neighboring countries through seven agreements on the Caribbean Sea and three on the Pacific Ocean.<ref name="Maritime borders">{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/politica/fronteras-maritimas|title=Maritime borders|publisher=cancilleria.gov.co|access-date=6 June 2016|archive-date=31 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180731123704/http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/politica/fronteras-maritimas|url-status=live}}</ref> It lies between latitudes ] and ] and between longitudes ] and ]. | |||
| The government of Colombia takes place within the framework of a ] ] ] as established in the ]. In accordance with the principle of ], government is divided into three branches: the ]; the ]; and the ]. These operate alongside special ] (the offices of the ] and the ]) and ]. | |||
| East of the Andes lies the ] of the '']'', part of the ] River basin, and in the far southeast, the ] of the ]. Together these lowlands make up over half Colombia's territory, but they contain less than 6% of the population. To the north the ], home to 21.9% of the population and the location of the major port cities of ] and ], generally consists of low-lying plains, but it also contains the ] mountain range, which includes the country's tallest peaks (] and ]), and the ]. By contrast the narrow and discontinuous ], backed by the ] mountains, are sparsely populated and covered in dense vegetation. The principal Pacific port is ].<ref name="Geography of Colombia" /><ref name="populationbyregions" /><ref name="Population density" /> | |||
| The ] serves as both ] and ], followed by the ] and the ]. The president is elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms and is currently limited to a maximum of two such terms (increased from one in 2005). At the provincial level executive power is vested in ], ] and local administrators for smaller administrative subdivisions, such as ''corregidores'' for '']''. | |||
| ] as seen from the ]]] | |||
| The legislative branch of government is represented nationally by the ], a bicameral institution comprising a 166-seat ] (including four seats reserved for the representatives of minority communities and expatriates) and a 102-seat ] (including two seats reserved for the representatives of indigenous communities). Members of both houses are elected two months before the president, also by popular vote and to serve four-year terms. At the provincial level the legislative branch is represented by ] and municipal councils. All regional elections are held one year and five months after the presidential election. | |||
| Part of the ], a region of the world subject to earthquakes and ],<ref name="Ring of Fire">{{cite web|url=http://seisan.ingeominas.gov.co/RSNC/index.php/material-educativo|title=Colombia is part of the Ring of Fire|publisher=seisan.ingeominas.gov.co|access-date=7 March 2014|language=es|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307220211/http://seisan.ingeominas.gov.co/RSNC/index.php/material-educativo|archive-date=7 March 2014}}</ref> in the interior of Colombia the Andes are the prevailing geographical feature. Most of Colombia's population centers are located in these interior highlands. Beyond the ] (in the southwestern departments of ] and ]), these are divided into three branches known as ''cordilleras'' (mountain ranges): the ], running adjacent to the Pacific coast and including the city of ]; the ], running between the ] and ] valleys (to the west and east, respectively) and including the cities of ], ], ], and ]; and the ], extending northeast to the ] and including Bogotá, ], and ].<ref name="Geography of Colombia" /><ref name="populationbyregions" /><ref name="Population density" /> Peaks in the Cordillera Occidental exceed {{convert|4700|m|ft|0|abbr=on|sp=us}}, and in the Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental they reach {{convert|5000|m|ft|0|abbr=on|sp=us}}. At {{convert|2600|m|ft|0|abbr=on|sp=us}}, Bogotá is the highest city of its size in the world.<ref name="Geography of Colombia" /> | |||
| The judicial branch is headed by the ], consisting of 23 judges divided into three chambers (Penal, Civil and Agrarian, and Labour). The judicial branch also includes the ], which has special responsibility for ] and also provides legal advice to the executive, the ], responsible for assuring the integrity of the Colombian constitution, and the ], responsible for auditing the judicial branch. Colombia operates a system of ], which since 2005 has been applied through an ]. | |||
| The main rivers of Colombia are Magdalena, Cauca, ], ], ], ] and ]. Colombia has four main drainage systems: the Pacific drain, the Caribbean drain, the Orinoco Basin and the Amazon Basin. The Orinoco and ] Rivers mark limits with Colombia to Venezuela and Peru respectively.<ref name="Hydrography">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia-sa.com/geografia/geografia-in-2.html|title=Hydrography of Colombia|publisher=colombia-sa.com|access-date=7 March 2014|archive-date=20 September 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130920042242/http://www.colombia-sa.com/geografia/geografia-in-2.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Administrative divisions=== | |||
| {{main|Departments of Colombia|Municipalities of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|List of cities in Colombia|Corregimientos of Colombia}} | |||
| === Climate === | |||
| Colombia is divided into 32 ] and one ], which is treated as a department (Bogotá also serves as the capital of the ]). Departments are subdivided into ], each of which is assigned a municipal seat, and municipalities are in turn subdivided into '']''. Each department has a local government with a governor and assembly directly elected to four-year terms. Each municipality is headed by a mayor and council, and each ''corregimiento'' by an elected ''corregidor'', or local leader. | |||
| {{Main|Climate of Colombia}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The climate of Colombia is characterized for being tropical presenting variations within ] and depending on the altitude, temperature, ], winds and rainfall.<ref name="Thermal floors" /> Colombia has a diverse range of climate zones, including ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s and mountain climates. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is one of the unique features of the Andes and other high altitude reliefs where climate is determined by elevation. Below {{convert|1000|m|ft|0|sp=us}} in elevation is the ], where temperatures are above {{convert|24|°C|°F|1}}. About 82.5% of the country's total area lies in the warm altitudinal zone. The ] located between {{convert|1001|and|2000|m|ft|0|sp=us}} is characterized for presenting an average temperature ranging between {{convert|17|and|24|°C|°F|1}}. The ] is present between {{convert|2001|and|3000|m|ft|0|sp=us}} and the temperatures vary between {{convert|12|and|17|°C|°F|1}}. Beyond lies the alpine conditions of the forested zone and then the treeless grasslands of the ]s. Above {{convert|4000|m|ft|0|sp=us}}, where temperatures are below freezing, the climate is ], a zone of permanent snow and ice.<ref name="Thermal floors">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/economia/colombia/eco1.htm|title=Thermal floors|publisher=banrepcultural.org|access-date=25 February 2014|language=es|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141016033544/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/economia/colombia/eco1.htm|archive-date=16 October 2014}}</ref> | |||
| {| style="background:transparent;" | |||
| === Biodiversity and conservation === | |||
| {{see also|Fauna of Colombia|Flora of Colombia|Deforestation in Colombia}} | |||
| Colombia is one of the ] in ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.inecc.gob.mx/descargas/ai/con199328.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.inecc.gob.mx/descargas/ai/con199328.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Declaración de Cancún de países megadiversos afínes|author=Delegatarios de países megadiversos|publisher=inecc.gob.mx|language=es|access-date=9 March 2014}}</ref> ranking first in ].<ref name="Bird Species">{{cite web|url=http://www.proaves.org/colombia-officially-the-nation-with-the-greatest-diversity-of-birds-and-a-new-world-record/?lang=en|title=Colombia Celebrates over 1,900 Bird Species|date=9 December 2013|publisher=proaves.org|access-date=18 December 2013|archive-date=19 December 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131219125544/http://www.proaves.org/colombia-officially-the-nation-with-the-greatest-diversity-of-birds-and-a-new-world-record/?lang=en|url-status=live}}</ref> Colombia is the country with the planet's highest biodiversity, having the highest rate of species by area as well as the largest number of ]s (species that are not found naturally anywhere else) of any country. About 10% of the species of the Earth live in Colombia, including over 1,900 species of bird, more than in Europe and North America combined. Colombia has 10% of the world's ] species, 14% of the ] species and 18% of the ] species of the world.<ref name="DIVERSITY OF SPECIES IN COLOMBIA">{{cite web|url=http://www.humboldt.org.co/component/k2/item/62-cifras |title=Colombia accounts for around 10% of the flora and fauna of the world. |publisher=humboldt.org.co |access-date=21 July 2013 |url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140309144021/http://www.humboldt.org.co/component/k2/item/62-cifras |archive-date=9 March 2014 }}</ref> | |||
| ] ] '']'', is named for Colombian botanist and physician ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/julio2001/laflor.htm|title=La flor de mayo, Cattleya trianae, flor nacional|language=es|access-date=3 March 2017|publisher=banrepcultural.org|archive-date=9 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171109175958/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/julio2001/laflor.htm|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| As for plants, the country has between 40,000 and 45,000 plant ], equivalent to 10 or 20% of total global species, which is even more remarkable given that Colombia is considered a country of intermediate size.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.parquesnacionales.gov.co/PNN/portel/libreria/php/frame_detalle.php?h_id=5274|title=Flora of Colombia|publisher=parquesnacionales.gov.co|language=es|access-date=18 December 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160125222620/http://www.parquesnacionales.gov.co/PNN/portel/libreria/php/frame_detalle.php?h_id=5274|archive-date=25 January 2016}}</ref> Colombia is the second most biodiverse country in the world, lagging only after Brazil which is approximately 7 times bigger.<ref name="Biodiversity of Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.prodiversitas.bioetica.org/nota63.htm |title=Colombia is the second most biodiverse country in the world |author=Luis Fernando Potes |publisher=prodiversitas.bioetica.org |language=es |access-date=9 March 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029190443/http://www.prodiversitas.bioetica.org/nota63.htm |archive-date=29 October 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| Colombia has about 2,000 species of ] and is the second most diverse country in ]. It is also the country with the most endemic species of ], is first in ] species, and has approximately 7,000 species of ]s. Colombia is second in the number of amphibian species and is the third most diverse country in ] and ]. There are about 1,900 species of ]s and according to estimates there are about 300,000 species of ] in the country. In Colombia there are 32 terrestrial ] and 314 types of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sibcolombia.net/web/sib/cifras|title=System of information about biodiversity of Colombia|publisher=Sistema de Información sobre Biodiversidad de Colombia|language=es|access-date=5 April 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130523121645/http://www.sibcolombia.net/web/sib/cifras|archive-date=23 May 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="humboldt">{{cite web |url=http://www.humboldt.org.co/images/documentos/pdf/documentos/iern-biodiversidad-2010-2011.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.humboldt.org.co/images/documentos/pdf/documentos/iern-biodiversidad-2010-2011.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Informe sobre el estado de los recursos naturales renovables y del ambiente Componente de biodiversidad, 2010–2011 |publisher=humboldt.org.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Protected areas and the "National Park System" cover an area of about {{convert|14268224|ha|km2|sp=us}} and account for 12.77% of the Colombian territory.<ref>{{cite web |language=es |url=http://www.parquesnacionales.gov.co/portal/sistema-de-parques-nacionales-naturales/ |title=Dirección de Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia |access-date=15 November 2015 |archive-date=5 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305033857/http://parquesnacionales.gov.co/portal/sistema-de-parques-nacionales-naturales |url-status=dead }}</ref> Compared to neighboring countries, rates of ] are still relatively low.<ref name="United Nations Deforestation">{{cite web |url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/change-forest-area-19902011 |title=Change in forest area, 1990/2011 (%) |publisher=undp.org |access-date=18 February 2015 |archive-date=15 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150215040216/http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/change-forest-area-19902011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Colombia had a 2018 ] mean score of 8.26/10, ranking it 25th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal|last1=Grantham|first1=H. S.|last2=Duncan|first2=A.|last3=Evans|first3=T. D.|last4=Jones|first4=K. R.|last5=Beyer|first5=H. L.|last6=Schuster|first6=R.|last7=Walston|first7=J.|last8=Ray|first8=J. C.|last9=Robinson|first9=J. G.|last10=Callow|first10=M.|last11=Clements|first11=T.|last12=Costa|first12=H. M.|last13=DeGemmis|first13=A.|last14=Elsen|first14=P. R.|last15=Ervin|first15=J.|last16=Franco|first16=P.|last17=Goldman|first17=E.|last18=Goetz|first18=S.|last19=Hansen|first19=A.|last20=Hofsvang|first20=E.|last21=Jantz|first21=P.|last22=Jupiter|first22=S.|last23=Kang|first23=A.|last24=Langhammer|first24=P.|last25=Laurance|first25=W. F.|last26=Lieberman|first26=S.|last27=Linkie|first27=M.|last28=Malhi|first28=Y.|last29=Maxwell|first29=S.|last30=Mendez|first30=M.|last31=Mittermeier|first31=R.|last32=Murray|first32=N. J.|last33=Possingham|first33=H.|last34=Radachowsky|first34=J.|last35=Saatchi|first35=S.|last36=Samper|first36=C.|last37=Silverman|first37=J.|last38=Shapiro|first38=A.|last39=Strassburg|first39=B.|last40=Stevens|first40=T.|last41=Stokes|first41=E.|last42=Taylor|first42=R.|last43=Tear|first43=T.|last44=Tizard|first44=R.|last45=Venter|first45=O.|last46=Visconti|first46=P.|last47=Wang|first47=S.|last48=Watson|first48=J. E. M.|title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material|journal=Nature Communications|volume=11|issue=1|year=2020|page=5978|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3|pmid=33293507|pmc=7723057|bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G }}</ref> Colombia is the sixth country in the world by magnitude of total renewable freshwater supply, and still has large reserves of freshwater.<ref name=worldwater>{{cite web|url=http://worldwater.org/water-data/|title=Table 1: Total Renewable Freshwater Supply, by Country|publisher=worldwater.org|access-date=1 April 2014|archive-date=31 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180731123429/http://www.worldwater.org/water-data/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| == Government and politics == | |||
| {{Main|Government of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|Colombian Constitution of 1991}} | |||
| ] is the official home and principal workplace of the ].]] | |||
| The government of Colombia takes place within the framework of a ] ] republic as established in the Constitution of 1991.<ref name="Colombian Constitution of 1991" /> In accordance with the principle of ], government is divided into three branches: the executive branch, the legislative branch and the judicial branch.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 113)</ref> | |||
| As the head of the executive branch, the ] serves as both ] and ], followed by the ] and the ]. The president is elected by popular vote to serve a single four-year term (In 2015, Colombia's Congress approved the repeal of a 2004 constitutional amendment that changed the one-term limit for presidents to a two-term limit).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sandiegouniontribune.com/hoy-san-diego/sdhoy-colombian-lawmakers-vote-to-limit-presidents-to-2015jun04-story.html|title=Colombian lawmakers vote to limit presidents to single term|work=The San Diego Union-Tribune|date=4 June 2015|access-date=3 May 2017|archive-date=31 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180731153517/http://www.sandiegouniontribune.com/hoy-san-diego/sdhoy-colombian-lawmakers-vote-to-limit-presidents-to-2015jun04-story.html|url-status=live}}</ref> At the provincial level executive power is vested in ], ] and local administrators for smaller administrative subdivisions, such as '']'' or ''comunas''.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 115)</ref> All regional elections are held one year and five months after the presidential election.<ref name="Government">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/gobierno/gob3a.htm|title=The Government of Colombia|publisher=banrepcultural.org|access-date=14 March 2014|language=es|archive-date=15 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140315042920/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/gobierno/gob3a.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII – Concerning the executive branch)</ref> | |||
| ], seat of the ]]] | |||
| The legislative branch of government is represented nationally by the ], a bicameral institution comprising a 166-seat ] and a 102-seat ].<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 114)</ref><ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Chapter 4 – Concerning the senate – Article 171)</ref> The Senate is elected nationally and the Chamber of Representatives is elected in electoral districts.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Chapter 5 – Concerning the chamber of representatives – Article 176)</ref> Members of both houses are elected to serve four-year terms two months before the president, also by popular vote.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VI – Concerning the legislative branch – Chapter 1 – Concerning its structure and functions – Article 132)</ref> | |||
| ], seat and symbol of the ]]] | |||
| The judicial branch is headed by ],<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII – Concerning the judiciary branch – Chapter 2 – Concerning ordinary jurisdiction – Article 234)</ref> consisting of the ] which deals with penal and civil matters, the ], which has special responsibility for ] and also provides legal advice to the executive, the ], responsible for assuring the integrity of the Colombian constitution, and the ], responsible for auditing the judicial branch.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VIII – Concerning the judiciary branch)</ref> Colombia operates a system of ], which since 1991 has been applied through an ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Landau|first=David|title=Colombian Constitutional Law: Leading Cases|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=2017|isbn=9780190640378|pages=217|quote=The 1991 Constitution moved Colombia away from the inquisitorial criminal system that it has traditionally possessed (and where the judge plays the leading role in the criminal process), and toward an adversarial system more like the American system, where lawyers act for each side as the protagonists.}}</ref> | |||
| Despite a number of controversies, the ] has ensured that former President ] remained popular among Colombian people, with his approval rating peaking at 76%, according to a poll in 2009.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.semana.com/politica/articulo/si-no-uribe-santos/103711-3|title=Si no es Uribe, es Santos|publisher=semana.com|date=1 June 2009|access-date=15 March 2014|author=Ipsos-Napoleon Franco poll|language=es|archive-date=16 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316082009/http://www.semana.com/politica/articulo/si-no-uribe-santos/103711-3|url-status=live}}</ref> However, having served two terms, he was constitutionally barred from seeking re-election in 2010.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Colombian Court Blocks President's Bid for a Third Term|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/02/27/world/americas/27colombia.html|newspaper=The New York Times|date=26 February 2010|access-date=24 October 2015|issn=0362-4331|archive-date=5 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151005070520/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/02/27/world/americas/27colombia.html|url-status=live}}</ref> In the run-off ] on 20 June 2010 the former Minister of Defense ] won with 69% of the vote against the second most popular candidate, ]. A second round was required since no candidate received over the 50% winning threshold of votes.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.registraduria.gov.co/imagenes/escrutinio_seg_vuelta.pdf|title=escrutinio 2ª Vuelta 2010|publisher=registraduria.gov.co|language=es|access-date=20 June 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110718033546/http://www.registraduria.gov.co/imagenes/escrutinio_seg_vuelta.pdf|archive-date=18 July 2011|url-status=dead}}</ref> Santos won re-election with nearly 51% of the vote in second-round ] on 15 June 2014, beating right-wing rival ], who won 45%.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://elecciones.registraduria.gov.co:81/elecciones2014/presidente/2v/99PR2/DPR9999999_L1.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140705010101/https://elecciones.registraduria.gov.co:81/elecciones2014/presidente/2v/99PR2/DPR9999999_L1.htm|title=escrutinio 2ª Vuelta 2014|publisher=registraduria.gov.co|language=es|url-status=dead|archive-date=5 July 2014}}</ref> In 2018, ] won in the second round of the ] with 54% of the vote, against 42% for his left-wing rival, ]. His term as Colombia's president ran for four years, beginning on 7 August 2018.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://presidente2018.registraduria.gov.co/resultados/2html/resultados.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180618010101/https://presidente2018.registraduria.gov.co/resultados/2html/resultados.html|title=2ª Vuelta 2018|publisher=registraduria.gov.co|language=es|url-status=dead|archive-date=18 June 2018}}</ref> In 2022, Colombia ] Gustavo Petro, who became its first leftist leader,<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Woodford |first1=Isabel |last2=Vargas |first2=Carlos |last3=Araujo |first3=Gabriel |date=23 June 2022 |title=Latin America's new 'pink tide' gains pace as Colombia shifts left; Brazil up next |language=en |publisher=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/latin-americas-new-pink-tide-gains-pace-colombia-shifts-left-brazil-up-next-2022-06-22/ |access-date=11 July 2022 |archive-date=28 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220628195416/https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/latin-americas-new-pink-tide-gains-pace-colombia-shifts-left-brazil-up-next-2022-06-22/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and ], who was the first black person elected as vice president.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Turkewitz |first=Julie |date=19 June 2022 |title=Francia Márquez — a former housekeeper and activist — is Colombia's first Black vice president. |language=en-US |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2022/06/19/world/americas/francia-marquez-vice-president-colombia.html |access-date=30 July 2022 |issn=0362-4331 |archive-date=4 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230604134301/https://www.nytimes.com/2022/06/19/world/americas/francia-marquez-vice-president-colombia.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Foreign affairs === | |||
| {{Main|Foreign relations of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|List of diplomatic missions of Colombia}} | |||
| ]: Former President of Colombia, ] is second from the left.]] | |||
| The foreign affairs of Colombia are headed by the President, as head of state, and managed by the ].<ref name="The foreign affairs">{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/ministry/the_ministry |title=The Ministry of Foreign Affairs |publisher=cancilleria.gov.co |access-date=15 March 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140227222556/http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/ministry/the_ministry |archive-date=27 February 2014 }}</ref> Colombia has diplomatic missions in all continents.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/colombian-embassies-and-consulates-abroad|title=Colombian Embassies and Consulates abroad|date=9 November 2015|publisher=cancilleria.gov.co|access-date=19 June 2016|archive-date=22 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220922113608/https://www.cancilleria.gov.co/en/colombian-embassies-and-consulates-abroad|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia was one of the four founding members of the ], which is a political, economic and co-operative integration mechanism that promotes the free circulation of goods, services, capital and persons between the members, as well as a common stock exchange and joint embassies in several countries.<ref name="The Pacific Alliance">{{cite web|url=https://alianzapacifico.net/en/what-is-the-pacific-alliance/#what-is-the-pacific-alliance|title=The Pacific Alliance and its Objectives|publisher=alianzapacifico.net|access-date=19 June 2016|archive-date=11 February 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230211035108/https://alianzapacifico.net/en/what-is-the-pacific-alliance/#what-is-the-pacific-alliance|url-status=live}}</ref> Colombia is also a member of the United Nations, the ], the ], the ], the ], and the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/multilateral|title=Organismos multilaterales|publisher=cancilleria.gov.co|access-date=23 April 2017|archive-date=22 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220922064436/https://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/multilateral|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/consensus |title=Mecanismos de Concertación e Integración Regionales |publisher=cancilleria.gov.co |access-date=23 April 2017 |archive-date=22 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220922020840/https://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/consensus |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/regional |title=Organismos regionales |publisher=cancilleria.gov.co |access-date=23 April 2017 |archive-date=5 December 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221205134936/https://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/regional |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/multilateral/inter-governmental|title=Organismos Intergubernamentales|publisher=cancilleria.gov.co|access-date=23 April 2017|archive-date=22 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220922015849/https://www.cancilleria.gov.co/international/multilateral/inter-governmental|url-status=live}}</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210216004726/http://www.oecd.org/latin-america/countries/colombia/ |date=16 February 2021 }}. oecd.org (25 May 2018).</ref> | |||
| Colombia is a global partner of ]<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170521075718/http://nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_143936.htm?selectedLocale=en |date=21 May 2017 }}. nato.int (19 May 2017).</ref> and a ] of the ].<ref name=":1" /> | |||
| === Military === | |||
| {{Main|Military Forces of Colombia}} | |||
| ] ] ]]] | |||
| The executive branch of government is responsible for managing the defense of Colombia, with the President ] of the armed forces. The ] exercises day-to-day control of the military and the ]. Colombia has 455,461 active military personnel.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://asosec.co/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Logros_Sector_Defensa.pdf|title=Military Personnel – Logros de la Política Integral de Seguridad y Defensa para la Prosperidad|language=es|publisher=mindefensa|access-date=23 June 2017|archive-date=23 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170623061949/http://asosec.co/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Logros_Sector_Defensa.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> In 2016, 3.4% of the country's GDP went towards military expenditure, placing it 24th in the world. Colombia's armed forces are the largest in Latin America, and it is the second largest spender on its military after Brazil.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/Milex-constant-2015-USD.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/Milex-constant-2015-USD.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Military spending|publisher=sipri.org|access-date=22 June 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/Milex-share-of-GDP.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/Milex-share-of-GDP.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Military expenditure (% of GDP)|publisher=sipri.org|access-date=22 June 2017}}</ref> In 2018, Colombia signed the UN ].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |title=Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons |publisher=United Nations Treaty Collection |date=7 July 2017 |access-date=17 November 2019 |archive-date=6 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190806220546/https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The Colombian military is divided into three branches: the ]; the ]; and the ]. The National Police functions as a ], operating independently from the military as the law enforcement agency for the entire country. Each of these operates with their own intelligence apparatus separate from the ] (DNI, in Spanish).<ref name="The Colombian military">{{cite web|title=Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII: The Executive Branch – Chapter VII: The Public Force)|language=es|publisher=banrepcultural.org|access-date=20 May 2017|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/derecho/constitucion-politica-de-colombia-1991/titulo-7-capitulo-7|archive-date=21 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170521193530/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/derecho/constitucion-politica-de-colombia-1991/titulo-7-capitulo-7|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The National Army is formed by divisions, brigades, special brigades, and special units,<ref name="The National Army">{{cite web|url=http://www.ejercito.mil.co/?idcategoria=253869|title=Military units|language=es|publisher=ejercito.mil.co|access-date=10 March 2014|archive-date=3 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140403223436/http://ejercito.mil.co/?idcategoria=253869|url-status=live}}</ref> the Colombian Navy by the ], the Naval Force of the Caribbean, the Naval Force of the Pacific, the Naval Force of the South, the Naval Force of the East, Colombia Coast Guards, Naval Aviation, and the Specific Command of San Andres y Providencia<ref name="the National Armada">{{cite web|url=https://www.armada.mil.co/es/content/fuerzas-y-comandos|title=Forces and commands|language=es|publisher=armada.mil.co|access-date=10 March 2014|archive-date=8 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140208012034/http://armada.mil.co/es/content/fuerzas-y-comandos|url-status=live}}</ref> and the Aerospace Force by 15 air units.<ref name="The Air Force">{{cite web|url=https://www.fac.mil.co/unidades-aereas|title=Air units|language=es|publisher=ejercito.mil.co|access-date=10 March 2014|archive-date=17 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141217104239/http://www.fac.mil.co/unidades-aereas|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Administrative divisions === | |||
| {{Main|Departments of Colombia|Municipalities of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|List of cities in Colombia|Corregimientos of Colombia}} | |||
| Colombia is divided into 32 ] and one ], which is treated as a department (Bogotá also serves as the capital of the ]). Departments are subdivided into ], each of which is assigned a municipal seat, and municipalities are in turn subdivided into '']'' in rural areas and into '']'' in urban areas. Each department has a local government with a governor and assembly directly elected to four-year terms, and each municipality is headed by a mayor and council. There is a popularly elected local administrative board in each of the ''corregimientos'' or ''comunas''.<ref name="Administrative divisions">{{cite web|url=http://www.dane.gov.co/Divipola/|title=Codificación de la División Político-Administrativa de Colombia (Divipola)|language=es|publisher=dane.gov.co|access-date=15 March 2014|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140209012507/http://dane.gov.co/Divipola/|archive-date=9 February 2014}}</ref><ref name="Concerning the territorial organization">Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title XI – Concerning the territorial organization)</ref><ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title XI – Concerning the territorial organization – Chapter 3 – Concerning the municipal regime – Article 318)</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Herrera Llanos |first=W |year=2011 |title=Régimen municipal en Colombia (Continuación del tema sobre Organización Territorial) |journal=Revista de Derecho |publisher=Universidad del Norte |page=27}}</ref> | |||
| In addition to the capital, four other cities have been designated ] (in effect special municipalities), on the basis of special distinguishing features. These are ], ], ] and ]. Some departments have local administrative subdivisions, where towns have a large concentration of population and municipalities are near each other (for example, in Antioquia and Cundinamarca). Where departments have a low population (for example Amazonas, Vaupés and Vichada), special administrative divisions are employed, such as "department ''corregimientos''", which are a hybrid of a municipality and a ''corregimiento''.<ref name="Administrative divisions" /><ref name="Concerning the territorial organization" /> | |||
| <small>Click on a department on the map below to go to its article.</small> | |||
| {{Colombia map clickable}} | |||
| {| | |||
| |- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| | |
|<!--First column:--> | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| {| style="background:transparent;" | |||
| |- | |||
| | || {{spaces|1}}'''Department''' || {{smaller|'''Capital city'''}} | |||
| ! || Department || Capital city | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 2 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 3 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 4 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 5 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 6 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 7 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 8 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 9 || ] ]{{Spaces|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | 10 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 11 || ] ] || ]{{nbsp|6}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | 12 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 13 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 14 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 15 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 16 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| 17 || ] ] || ] | ||
| | '''2''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''3''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''4''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''5''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''6''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''7''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''8''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''9''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}'''{{spaces|2}} || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''10''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''11''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}}{{nbsp|6}} </tr> | |||
| | '''12''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''13''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''14''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''15''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''16''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | '''17''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| | |
|<!--Second column:--> | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| {| style="background:transparent;" | |||
| | || {{spaces|1}}'''Department''' || {{smaller|'''Capital city'''}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! || Department || Capital city | |||
| | '''18''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}'''{{nbsp|2}} || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''19''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}}{{spaces|2}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 18 || ] ]{{nbsp|2}}||{{Smaller|]}} | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''21''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 19 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''23''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 20 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''25''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 21 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''27''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 22 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''29''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 23 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''31''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | |
| 24 || ] ] || ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | '''33''' || ]{{spaces|1}}'''{{smaller|]}}''' || {{smaller|]}} </tr> | |||
| | 25 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 26 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 27 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 28 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 29 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 30 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 31 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 32 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 33 || ] ] || ] | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| == Economy == | |||
| In addition to the capital nine other cities have been designated ] (in effect special municipalities), on the basis of special distinguishing features. These are ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Some departments have local administrative subdivisions, where towns have a large concentration of population and municipalities are near each other (for example in Antioquia and Cundinamarca). Where departments have a low population and there are security problems (for example Amazonas, Vaupés and Vichada), special administrative divisions are employed, such as "department ''corregimientos''", which are a hybrid of a municipality and a ''corregimiento''. | |||
| {{Main|Economy of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|Industry of Colombia}} | |||
| ] of ]'s skyscrapers]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] headquarters in ]]] | |||
| Historically an agrarian economy, Colombia urbanized rapidly in the 20th century, by the end of which just 15.8% of the workforce were employed in agriculture, generating just 6.6% of GDP; 20% of the workforce were employed in industry and 65% in services, responsible for 33% and 60% of GDP respectively.<ref name="GDP Composition">{{cite web |url=http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?source=2&country=COL |publisher=worldbank.org |title=Agriculture, Industry, Services |access-date=24 May 2017 |archive-date=25 May 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525061240/http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?source=2&country=COL |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ilo.org/ilostat/faces/ilostat-home/home?_adf.ctrl-state=19bjkp4nom_96&_afrLoop=655651903358909#! |publisher=ilo.org |title=Employment distribution by economic activity (by sex) |access-date=24 May 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170525061202/http://www.ilo.org/ilostat/faces/ilostat-home/home?_adf.ctrl-state=19bjkp4nom_96&_afrLoop=655651903358909#! |archive-date=25 May 2017 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The country's ] is dominated by its strong ]. ] by households is the largest component of GDP.<ref name="GDPCOLOMBIA">{{cite web|url=http://www.dinero.com/economia/articulo/composicion-economia-colombiana-2015/214054|publisher=dinero.com|title=¿Cómo está compuesta la economía colombiana?|date=29 September 2015|language=es|access-date=29 September 2015|archive-date=20 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200920184555/https://www.dinero.com/economia/articulo/composicion-economia-colombiana-2015/214054|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="GDP">{{cite web|url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/pib/bol_PIB_IVtrim17_oferta.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/pib/bol_PIB_IVtrim17_oferta.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |publisher=dane.gov.co |title=Cuentas Trimestrales – Producto Interno Bruto (PIB) |language=es |access-date=16 February 2018}}</ref><ref name="Colombianeconomy">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/economia/econo106.htm|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Colombian economy|language=es|access-date=16 April 2013|archive-date=12 May 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150512141054/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/economia/econo106.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia's ] grew steadily in the latter part of the 20th century, with gross domestic product (GDP) increasing at an average rate of over 4% per year between 1970 and 1998. The country suffered a ] in 1999 (the first full year of negative growth since the ]), and the recovery was long and painful. However, growth reaching 7% in 2007, one of the ] in Latin America.<ref name="Colombia's GDP growth">{{cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG/countries/CO?display=graph|title=Colombia's GDP growth|publisher=World Bank|access-date=9 March 2014|archive-date=5 July 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140705050710/http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG/countries/CO?display=graph|url-status=live}}</ref> According to ] estimates, in 2023, Colombia's GDP (PPP) was US$1 trillion, ] and third in South America, after Brazil and Argentina. | |||
| ===Foreign affairs=== | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Diplomatic missions of Colombia}} | |||
| Total ] account for 28% of the domestic economy. ] equals 40% of gross domestic product. A strong fiscal climate was reaffirmed by a boost in ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2017/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=52&pr.y=7&sy=2017&ey=2018&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=233&s=GGX_NGDP&grp=0&a=|publisher=imf.org|title=General government total expenditure (Percent of GDP)|access-date=15 January 2018|archive-date=26 September 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210926091539/https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2017/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=52&pr.y=7&sy=2017&ey=2018&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=233&s=GGX_NGDP&grp=0&a=|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/paginas/bdeudax_t.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/paginas/bdeudax_t.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|publisher=banrep.gov.co |title=Deuda Externa de Colombia|access-date=15 January 2018}}</ref><ref name="heritage">{{cite web|url=http://www.heritage.org/index/country/colombia|title=Colombia|publisher=]|work=]|access-date=30 January 2015|archive-date=9 April 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220409002035/https://www.heritage.org/index/country/colombia|url-status=live}}</ref> Annual inflation closed 2017 at 4.09% YoY (vs. 5.75% YoY in 2016).<ref name="Inflation Rate">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrep.gov.co/es/ipc|title=Colombia Inflation Rate|publisher=banrep.gov.co|access-date=15 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180116020027/http://www.banrep.gov.co/es/ipc|archive-date=16 January 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref> The average national ] in 2017 was 9.4%,<ref name="Unemployment Rate">{{cite web|url=http://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/ech/ech/bol_empleo_dic_17.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/ech/ech/bol_empleo_dic_17.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Colombia Unemployment Rate|publisher=dane.gov.co|access-date=31 January 2018}}</ref> although the informality is the biggest problem facing the ] (the income of formal workers climbed 24.8% in 5 years while labor incomes of informal workers rose only 9%).<ref name="informal workers">{{cite web|url=http://www.portafolio.co/economia/ingresos-trabajadores-informales-colombia|title=Incomes of informal workers grow less|publisher=portafolio.co|language=es|access-date=19 December 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131221054526/http://www.portafolio.co/economia/ingresos-trabajadores-informales-colombia|archive-date=21 December 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> Colombia has ]s (FTZ),<ref name="FTZ">{{cite web|url=http://www.investincolombia.com.co/investment-incentives/permanent-free-trade-zone.html|title=Colombia's Permanent Free Trade Zones Directory|publisher=investincolombia.com.co|access-date=19 December 2013|archive-date=29 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200929113346/https://investincolombia.com.co/investment-incentives/permanent-free-trade-zone.html|url-status=live}}</ref> such as Zona Franca del Pacifico, located in the ], one of the most striking areas for foreign investment.<ref name="Zonas Francas"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200528073604/https://www.zonafrancadelpacifico.com/ |date=28 May 2020 }}. zonafrancadelpacifico.com</ref> | |||
| The foreign affairs of Colombia are headed by the President of Colombia and managed by the ]. Colombia has diplomatic missions in all continents and is also represented in multilateral organizations at the following locations: | |||
| * '''Brussels''' (Mission to the ]) | |||
| * '''Geneva''' (Permanent Missions to the ] and other international organizations) | |||
| * '''Montevideo''' (Permanent Missions to the ] and ]) | |||
| * '''Nairobi''' (Permanent Missions to the United Nations and other international organizations) | |||
| * '''New York''' (Permanent Mission to the United Nations) | |||
| * '''Paris''' (Permanent Mission to ]) | |||
| * '''Rome''' (Permanent Mission to the ]) | |||
| * '''Washington DC''' (Permanent Mission to the ]) | |||
| The ] has grown favorably due to good liquidity in the economy, the growth of credit and the positive performance of the Colombian economy.<ref name="strongmacroeconomicmanagement">{{cite web |url=http://www.imf.org/en/news/articles/2018/04/30/pr18154-imf-executive-board-concludes-2018-article-iv-consultation-with-colombia |title=IMF Executive Board Concludes 2018 Article IV Consultation with Colombia |access-date=2 May 2018 |publisher=imf.org |archive-date=4 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220604213121/https://www.imf.org/en/news/articles/2018/04/30/pr18154-imf-executive-board-concludes-2018-article-iv-consultation-with-colombia |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.superfinanciera.gov.co/jsp/loader.jsf?lServicio=Publicaciones&lTipo=publicaciones&lFuncion=loadContenidoPublicacion&id=61066|title=Informe de operaciones|access-date=9 March 2014|publisher=superfinanciera.gov.co|language=es|archive-date=1 June 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220601230140/https://www.superfinanciera.gov.co/jsp/loader.jsf?lServicio=Publicaciones&lTipo=publicaciones&lFuncion=loadContenidoPublicacion&id=61066|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrep.gov.co/reporte-estabilidad-financiera|title=Reporte de Estabilidad Financiera|access-date=9 March 2014|publisher=banrep.gov.co|language=es|archive-date=21 March 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220321200635/https://www.banrep.gov.co/reporte-estabilidad-financiera|url-status=live}}</ref> The ] through the Latin American Integrated Market (]) offers a regional market to trade equities.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mercadomila.com/QuienesSomos|title=The Latin American Integrated Market (MILA)|access-date=14 March 2014|publisher=mercadomila.com|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140315042207/http://www.mercadomila.com/QuienesSomos|archive-date=15 March 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrep.org/series-estadisticas/see_m_bursatil.htm|title=Colombia's Colcap Index|access-date=9 March 2014|publisher=banrep.org|language=es|archive-date=17 July 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170717083555/http://www.banrep.org/series-estadisticas/see_m_bursatil.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Colombia is now one of only three economies with a perfect score on the strength of legal rights index, according to the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.doingbusiness.org/~/media/WBG/DoingBusiness/Documents/Annual-Reports/English/DB17-Report.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.doingbusiness.org/~/media/WBG/DoingBusiness/Documents/Annual-Reports/English/DB17-Report.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=World Bank's 2017 Doing Business ranking|access-date=29 October 2016|publisher=doingbusiness.org}}</ref> | |||
| The foreign relations of Colombia are mostly concentrated on combating the illegal drug trade, the fight against terrorism, improving Colombia's image in the international community, expanding the international market for Colombian products, and environmental issues. Colombia receives special military and commercial co-operation and support in its fight against internal armed groups from the United States, mainly through ], as well as special financial preferences from the European Union in certain products. | |||
| Colombia is rich in natural resources, and it is heavily dependent on energy and mining exports.<ref>{{cite web |title=Is Colombia a poor country? {{!}} – CountryReports |url=https://www.countryreports.org/country/Colombia/economy.htm |website=countryreports.org |access-date=19 January 2022 |archive-date=18 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220318083341/https://www.countryreports.org/country/Colombia/economy.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombia's main exports include mineral fuels, oils, ] products, fruit and other agricultural products, sugars and sugar confectionery, ], plastics, precious stones, metals, forest products, ], ], vehicles, electronic products, electrical equipment, perfumery and cosmetics, machinery, manufactured articles, textile and fabrics, clothing and footwear, glass and glassware, furniture, prefabricated buildings, military products, home and office material, construction equipment, software, among others.<ref name="ITC Colombia Exports">{{cite web|url=http://legacy.intracen.org/appli1/TradeCom/TP_EP_CI.aspx?RP=170&YR=2013|title=International Trade Centre: Colombia Exports|access-date=15 April 2015|publisher=intracen.org|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150413170259/http://legacy.intracen.org/appli1/TradeCom/TP_EP_CI.aspx?RP=170&YR=2013|archive-date=13 April 2015}}</ref> Principal trading partners are the United States, China, the European Union and some Latin American countries.<ref name="Exports">{{cite web|url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/exportaciones/bol_exp_dic17.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/exportaciones/bol_exp_dic17.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Exports – partners|publisher=dane.gov.co|access-date=15 February 2018}}</ref><ref name="Imports">{{cite web|url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/importaciones/bol_impo_dic17.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/boletines/importaciones/bol_impo_dic17.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Imports – partners|publisher=dane.gov.co|access-date=15 February 2018}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia is a member of the ] and the ]. | |||
| Non-traditional exports have boosted the growth of Colombian foreign sales as well as the diversification of destinations of export thanks to new free ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mincit.gov.co/publicaciones.php?id=4930|title=Non-traditional exports|access-date=31 January 2014|publisher=mincit.gov.co|language=es|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140202205854/http://www.mincit.gov.co/publicaciones.php?id=4930|archive-date=2 February 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> Recent economic growth has led to a considerable increase of new millionaires, including the new entrepreneurs, Colombians with a net worth exceeding US$1 billion.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blogs.ft.com/beyond-brics/2013/10/21/colombia-making-many-millionaires/|title=Colombia: making many millionaires|access-date=29 March 2014|work=Financial Times|archive-date=9 July 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150709123707/http://blogs.ft.com/beyond-brics/2013/10/21/colombia-making-many-millionaires/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dinero.com/edicion-impresa/negocios/articulo/pais-ricos/163667 |title=País de ricos |access-date=8 April 2013 |publisher=dinero.com |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140329100504/http://www.dinero.com/edicion-impresa/negocios/articulo/pais-ricos/163667 |archive-date=29 March 2014 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Defense=== | |||
| {{main|Military of Colombia}} | |||
| ] ] frigate.]] | |||
| ] ] fighter aircraft.]] | |||
| In 2017, however, the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) reported that 26.9% of the population were living below the poverty line, of which 7.4% were in "extreme poverty". The multidimensional poverty rate stands at 17.0 percent of the population.<ref name="socio-economic policies">{{cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=CO |title=GINI index (World Bank estimate) – Colombia |publisher=World Bank |access-date=19 June 2021 |archive-date=8 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161108065750/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=CO |url-status=live }}</ref> The Government has also been developing a process of ] within the country's most vulnerable population.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.centerforfinancialinclusion.org/storage/documents/EIU_Microscope_2016_English_web.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.centerforfinancialinclusion.org/storage/documents/EIU_Microscope_2016_English_web.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=Colombia and Peru demonstrate the most conducive environments for financial inclusion|publisher=2016 Global Microscope on Financial Inclusion – The Economist Intelligence Unit|access-date=9 January 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The executive branch of government has responsibility for managing the defense of Colombia, with the President ] of the armed forces. The ] exercises day-to-day control of the ] and the ]. According to UN Human Development Report criteria, Colombia has 209,000 military personnel,<ref name="HDR Military Personnel"></ref> and in 2005 3.7% of the country's GDP went towards military expenditure,<ref name="HDR Military Spend"></ref> both figures placing it 21st in the world. Within Latin America, Colombia's armed forces are the third-largest, behind Brazil and Mexico, and it spends the second-highest proportion of GDP after Chile. Since 2000 the Colombian military has also received substantial support from the United States government through the provisions of Plan Colombia. | |||
| The contribution of ] to GDP was US$5,880.3bn (2.0% of total GDP) in 2016. Tourism generated 556,135 jobs (2.5% of total employment) in 2016.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TTCR_2017_web_0401.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TTCR_2017_web_0401.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2017|page=130|publisher=World Economic Forum}}</ref> Foreign tourist visits were predicted to have risen from 0.6 million in 2007 to 4 million in 2017.<ref>{{cite news|title=UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2018 Edition|year=2018|publisher=unwto.org|doi=10.18111/9789284419876|isbn=9789284419876}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://noticias.lainformacion.com/economia-negocios-y-finanzas/turismo-y-tiempo-libre/la-omt-destaca-crecimiento-del-turismo-en-colombia-en-los-ultimos-diez-anos_Qf0PXwFP6sbVhdnrGcFoe3/|title=La OMT destaca crecimiento del turismo en Colombia en los últimos diez años|publisher=lainformacion.com|date=25 June 2014|language=es|access-date=25 June 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140711233513/http://noticias.lainformacion.com/economia-negocios-y-finanzas/turismo-y-tiempo-libre/la-omt-destaca-crecimiento-del-turismo-en-colombia-en-los-ultimos-diez-anos_Qf0PXwFP6sbVhdnrGcFoe3/|archive-date=11 July 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The Colombian military is divided into three branches: the ]; the ]; and the ]. The National Police functions as a ], operating independently from the military as the law enforcement agency for the entire country. Each of these operates with their own intelligence apparatus separate from the national intelligence agency, the ]. The National Army is formed by divisions, regiments and special units; the National Armada by the ], the ], the ], the ], ], ] and the ]; and the Air Force by 13 air units. The National Police has a presence in all municipalities. | |||
| === Agriculture and natural resources === | |||
| ===Politics=== | |||
| {{ |
{{Main|Agriculture in Colombia|Mining in Colombia}} | ||
| ] is an ], the largest of its type, the largest in Latin America and the tenth biggest in the world.]] | |||
| {{see also|Elections in Colombia|List of political parties in Colombia}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| In agriculture, Colombia is one of the five largest producers in the world of ], ] and ], and one of the 10 largest producers in the world of ], ], ] and ]. The country also has considerable production of ], ] and ]. Although it is not the largest coffee producer in the world (Brazil claims that title), the country has been able to carry out, for decades, a global marketing campaign to add value to the country's product. Colombian palm oil production is one of the most sustainable on the planet, compared to the largest existing producers. Colombia is also among the 20 largest producers in the world of ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/ |title=Agriculture and Livestock in Colombia, by FAO |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=29 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200629173611/http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://revistacafeicultura.com.br/?mat=35160 |title=Juan Valdez, garoto propaganda do Café da Colômbia chega aos 50 anos |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=29 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231129012817/https://revistacafeicultura.com.br/?mat=35160 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://summitagro.estadao.com.br/noticias-do-campo/como-e-possivel-produzir-oleo-de-palma-de-maneira-sustentavel-2/ |title=Como é possível produzir óleo de palma de maneira sustentável |date=6 January 2020 |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=15 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230715073551/https://summitagro.estadao.com.br/noticias-do-campo/como-e-possivel-produzir-oleo-de-palma-de-maneira-sustentavel-2/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombia is also the 2nd largest ] exporter in the world, after the Netherlands.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.negocioscomflores.com.br/noticias/como-funciona-a-industria-de-flores-na-colombia-maior-exportador-mundial/ |title=COMO FUNCIONA A INDUSTRIA DE FLORES NA COLOMBIA – MAIOR EXPORTADOR MUNDIAL |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=15 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230715073552/https://www.negocioscomflores.com.br/noticias/como-funciona-a-industria-de-flores-na-colombia-maior-exportador-mundial/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Colombian agriculture emits 55% of Colombia's ] emissions, mostly from deforestation, over-extensive cattle ranching, land grabbing, and illegal agriculture.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kliefoth |first=Willis |date=2021-10-06 |title=Towards a greener, fairer and more productive land use sector in Colombia |url=https://climatefocus.com/towards-greener-fairer-and-more-productive-land-use-sector-colombia/ |access-date=2024-04-18 |website=Climate Focus |language=en-US |archive-date=18 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240418115650/https://climatefocus.com/towards-greener-fairer-and-more-productive-land-use-sector-colombia/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| For over a century Colombian politics were monopolised by the ] (founded in 1848 on an ], broadly ] and ] platform), and the ] (founded in 1849 espousing ], ], and ]). This culminated in the formation of the ] (1958-1974), which formalised arrangements for an alternation of power between the two parties and excluded non-establishment alternatives (thereby fuelling the nascent ]). | |||
| Colombia is an important exporter of ] and ] – in 2020, more than 40% of the country's exports were based on these two products.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://oec.world/en/profile/country/col |title=Colombian exports, by OEC |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=3 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220603062300/https://oec.world/en/profile/country/col |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2018 it was the 5th largest coal exporter in the world.<ref>{{cite web |title=Primary Coal Exports |url=https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world/coal-and-coke/coal-and-coke-exports |publisher=] |access-date=26 July 2020 |archive-date=13 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200813010028/https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world/coal-and-coke/coal-and-coke-exports |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2019, Colombia was the 20th largest petroleum producer in the world, with 791 thousand barrels/day, exporting a good part of its production – the country was the 19th largest oil exporter in the world in 2020.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world/petroleum-and-other-liquids/annual-petroleum-and-other-liquids-production?pd=5&p=0000000000000000000000000000000000vg&u=0&f=A&v=mapbubble&a=-&i=none&vo=value&&t=C&g=00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001&l=249-ruvvvvvfvtvnvv1vrvvvvfvvvvvvfvvvou20evvvvvvvvvvnvvvs0008&s=94694400000&e=1577836800000| title=EIA 2019 Petroleum production| access-date=14 July 2022| archive-date=15 July 2022| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220715213839/https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world/petroleum-and-other-liquids/annual-petroleum-and-other-liquids-production?pd=5&p=0000000000000000000000000000000000vg&u=0&f=A&v=mapbubble&a=-&i=none&vo=value&&t=C&g=00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001&l=249-ruvvvvvfvtvnvv1vrvvvvfvvvvvvfvvvou20evvvvvvvvvvnvvvs0008&s=94694400000&e=1577836800000| url-status=live}}</ref> In mining, Colombia is the world's largest producer of ],<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/noticias/2012/10/121025_colombia_esmeraldas_ru| title=Colombian emeralds| access-date=14 July 2022| archive-date=21 December 2021| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211221174300/https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/noticias/2012/10/121025_colombia_esmeraldas_ru| url-status=live}}</ref> and in the production of ], between 2006 and 2017, the country produced 15 tons per year until 2007, when its production increased significantly, beating the record of 66.1 tons extracted in 2012. In 2017, it extracted 52.2 tons. Currently, the country is among the 25 largest gold producers in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/colombia/gold-production |title=Colombia Gold Production |access-date=14 July 2022 |archive-date=16 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210816022625/https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/colombia/gold-production |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| By the time of the dissolution of the National Front, traditional political alignments had begun to fragment. This process has continued since, and the consequences of this are exemplified by the results of the last ], held on 28 May 2006, which was won with 62% of the vote by the incumbent, ]. President Uribe is from a Liberal background but he campaigned as part of the ] movement with the support of the Conservative Party, and his hard line on security issues and liberal economics place him on the right of the modern political spectrum. In second place with 22% was ] of the ], a newly formed ] alliance which includes elements of the former ] guerrilla movement. ] of the Liberal Party achieved third place with 12%. Meanwhile in the ] held earlier that year the two traditional parties secured only 93 out of 268 seats available. | |||
| ===Energy and transportation=== | |||
| Despite a number of controversies, most notably the ongoing ], dramatic improvements in security and continued strong economic performance have ensured that President Uribe remains extremely popular among the Colombian people, with his approval rating peaking at 91% in July 2008.<ref name="Uribe Popularity"> | |||
| {{Main|Electricity sector in Colombia|Transport in Colombia}} | |||
| </ref> However, having served two terms, he will be constitutionally barred from seeking re-election in 2010. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The electricity production in Colombia comes mainly from ] sources. 69.93% is obtained from the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.siel.gov.co/Inicio/Generaci%C3%B3n/Estad%C3%ADsticasyvariablesdegeneraci%C3%B3n/tabid/115/Default.aspx|title=Colombian Electricity Market – Evolución Variables de Generación Diciembre de 2016|publisher=Unidad de Planeación Minero Energética de Colombia|language=es|access-date=1 April 2014|archive-date=20 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220520050251/http://www.siel.gov.co/Inicio/Generaci%C3%B3n/Estad%C3%ADsticasyvariablesdegeneraci%C3%B3n/tabid/115/Default.aspx|url-status=live}}</ref> Colombia's commitment to renewable energy was recognized in the 2014 ''Global Green Economy Index (GGEI)'', ranking among the top 10 nations in the world in terms of greening efficiency sectors.<ref name=ggei>{{cite web|title=2014 Global Green Economy Index|url=http://dualcitizeninc.com/GGEI-Report2014.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://dualcitizeninc.com/GGEI-Report2014.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|publisher=Dual Citizen LLC|access-date=20 October 2014}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| {{main|Economy of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Agriculture in Colombia}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| In spite of the difficulties presented by serious internal armed conflict, Colombia's ] steadily in the latter part of the twentieth century, with ] (GDP) increasing at an average rate of over 4% per year between 1970 and 1998. The country suffered a ] in 1999 (the first full year of negative growth since the ]), and the recovery from that recession was long and painful. However in recent years growth has been impressive, reaching 8.2% in 2007, one of the ] in Latin America. Meanwhile the ] climbed from 1,000 points at its creation in July 2001 to over 7,300 points by November 2008.<ref name="BANKREP"></ref> | |||
| Transportation in Colombia is regulated within the functions of the ]<ref name="MTransport">{{cite web|url=https://www.mintransporte.gov.co/publicaciones.php?id=33|title=Ministry of Transport|date=8 May 2011 |publisher=mintransporte.gov.co|language=es|access-date=27 November 2014|archive-date=1 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141201163042/https://www.mintransporte.gov.co/publicaciones.php?id=33|url-status=live}}</ref> and entities such as the National Roads Institute (]) responsible for the ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.invias.gov.co/index.php/informacion-institucional/objetivos-y-funciones|title=INVÍAS – Objectives and Functions|publisher=invias.gov.co|language=es|access-date=27 November 2014|archive-date=6 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141206040650/http://www.invias.gov.co/index.php/informacion-institucional/objetivos-y-funciones|url-status=live}}</ref> the ], responsible for civil aviation and ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aerocivil.gov.co/aerocivil/funciones|title=Aerocivil – Funciones y Deberes|publisher=aerocivil.gov.co|language=es|access-date=27 November 2014|archive-date=9 July 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170709104232/http://www.aerocivil.gov.co/aerocivil/funciones|url-status=live}}</ref> the ], in charge of ] through ]s, for the design, construction, maintenance, operation, and administration of the transport infrastructure,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ani.gov.co/informacion-de-la-ani/quienes-somos|title=ANI – Objectives and Functions|date=24 December 2012|publisher=ani.gov.co|language=es|access-date=27 November 2014|archive-date=24 September 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140924102833/http://www.ani.gov.co/informacion-de-la-ani/quienes-somos|url-status=live}}</ref> the General Maritime Directorate (Dimar) has the responsibility of coordinating maritime traffic control along with the Colombian Navy,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dimar.mil.co/en/content/roles-and-responsibilities|title=the General Maritime Directorate (Dimar)|publisher=dimar.mil.co|access-date=9 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141221203751/http://www.dimar.mil.co/en/content/roles-and-responsibilities|archive-date=21 December 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> among others, and under the supervision of the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.supertransporte.gov.co/index.php/la-entidad/objetivos-y-funciones|title=Superintendency of Ports and Transport- Objectives and Functions|publisher=supertransporte.gov.co|language=es|access-date=27 November 2014|archive-date=19 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141219084606/http://www.supertransporte.gov.co/index.php/la-entidad/objetivos-y-funciones|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| According to ] estimates, in 2007 Colombia's nominal GDP was ]202.6 billion (] and fourth in South America). Adjusted for ], GDP per capita stands at $7,968, placing Colombia ]. However, in practice this is relatively unevenly distributed among the population, and, in common with much of Latin America, Colombia scores poorly according to the ], with UN figures placing it ]. In 2003 the richest 20% of the population had a 62.7% share of income/consumption and the poorest 20% just 2.5%, and 17.8% of Colombians live on ].<ref name="HDR Colombia"></ref> ] is 37.9% of GDP.<ref name="CIAWFB"/> Almost a quarter of this goes towards servicing the country's relatively high ], estimated at 52.8% of GDP in 2007.<ref name="HDR Colombia"/><ref name="CIAWFB"/> Other problems facing the economy include weak domestic and foreign demand, the funding of the country's pension system, and unemployment (10.8% in November 2008<ref name="BANKREP"/>). Inflation has remained relatively low in recent years, standing at 5.5% in 2007.<ref name="CIAWFB"/> | |||
| In 2021, Colombia had {{convert|204389|km|0|abbr=on}} of roads, {{convert|32280|km|0|abbr=on}} of which were paved. At the end of 2017, the country had around {{convert|2100|km|0|abbr=on}} of ].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://colaboracion.dnp.gov.co/CDT/Conpes/Econ%C3%B3micos/4039.pdf |title=Declaración de importancia estratégica de los proyectos de inversión del programa vías |access-date=13 July 2022 |archive-date=6 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220706014411/https://colaboracion.dnp.gov.co/CDT/Conpes/Econ%C3%B3micos/4039.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.larepublica.co/infraestructura/colombia-paso-de-tener-700-km-de-doble-calzada-en-2010-a-2100-km-2573137 |title=Colombia pasó de 700 kilómetros de doble calzada en 2010 a 2.100 |date=22 November 2017 |access-date=13 July 2022 |archive-date=18 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220818210134/https://www.larepublica.co/infraestructura/colombia-paso-de-tener-700-km-de-doble-calzada-en-2010-a-2100-km-2573137 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="transporte">Champin, J., Cortés, R., Kohon, J., & Rodríguez, M. (2016). Desafíos del transporte ferroviario de carga en Colombia</ref> ] in Colombia is dedicated almost entirely to ] and the railway network has a length of 1,700 km of potentially active rails.<ref name="transporte" /> Colombia has 3,960 kilometers of gas pipelines, 4,900 kilometers of ], and 2,990 kilometers of refined-products pipelines.<ref name="transporte" /> | |||
| ], ]. Coffee is Colombia's main ].]] | |||
| The Colombian government aimed to build 7,000 km of roads between 2016 and 2020, which would reduce travel times by an estimated 30 per cent, and transport costs by an estimated 20 per cent. A toll road concession programme will comprise 40 projects, and is part of a larger strategic goal to invest nearly $50 bn in transport infrastructure, including railway systems, making the ] navigable again, improving port facilities, and an expansion of ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/dc5d5fe6-668d-11e4-8bf6-00144feabdc0.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221210/http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/dc5d5fe6-668d-11e4-8bf6-00144feabdc0.html |archive-date=10 December 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|title=Ambitious plans to transform Colombia|work=Financial Times|date=17 November 2014|access-date=27 November 2014|last1=Schipani|first1=Andres}}</ref>{{update inline|date=July 2021}} Colombia is a middle-income country.<ref>{{cite web |title=Colombia |url=https://www.state.gov/countries-areas/colombia/ |publisher=United States Department of State |access-date=18 January 2022 |archive-date=18 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220118182840/https://www.state.gov/countries-areas/colombia/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Historically an agrarian economy, Colombia urbanised rapidly in the twentieth century, by the end of which just 22.7% of the workforce were employed in agriculture, generating just 11.5% of GDP. 18.7% of the workforce are employed in industry and 58.5% in services, responsible for 36% and 52.5% of GDP respectively.<ref name="CIAWFB"/> Colombia is rich in natural resources, and its main exports include ], ], ] and other agricultural produce, and ].<ref name="ITC Colombia Exports"> | |||
| </ref> Unofficially, ] are also a major export, with over 80% of the world's ] produced in Colombia, estimated to account for between 1 and 3% of the country's GDP.<ref>{{cite web |last=Clune |first=Sarah|title= Colombia's illegal drug trade |url=http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/latin_america/colombia/trade.html |accessdate= 2007-11-13}}</ref><ref name="Independent, Drugs War"> | |||
| </ref> Colombia is also known as the world's leading source of ]s,<ref name="ICA"> | |||
| </ref> while over 70% of ] imported by the ] are Colombian.<ref name="Flower Basket"> | |||
| </ref> Principal trading partners are the United States (a controversial ] with the United States is currently awaiting approval by the ]), ] and ].<ref name="CIAWFB"/> All imports, exports, and the overall ] are at record levels, and the inflow of export dollars has resulted in a substantial re-valuation of the ]. | |||
| === Science and technology === | |||
| Economic performance has been aided by ] introduced in the early 1990s and continued during the current presidency of ], whose policies include measures designed to bring the ] below 2.5% of GDP. In 2008, the ] assessed the Colombian economy to be 61.9% ], an increase of 2.3% since 2007, placing it ] and 15th out of 29 countries within the region.<ref name="Heritage Foundation"> | |||
| {{Main|Science and technology in Colombia}} | |||
| </ref> Meanwhile the improvements in security resulting from President Uribe's controversial "]" strategy have engendered an increased sense of confidence in the economy. On 28 May 2007 the American magazine ] published an article naming Colombia "the most extreme emerging market on Earth".<ref> May 28, 2007</ref> | |||
| ] is a Colombian Government agency that supports fundamental and applied research.]] | |||
| Colombia has more than 3,950 research groups in science and technology.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.colciencias.gov.co/sites/default/files/ckeditor_files/informes-anal-2014.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.colciencias.gov.co/sites/default/files/ckeditor_files/informes-anal-2014.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live|title=research groups in science and technology|language=es |publisher=colciencias.gov.co |access-date=9 May 2016}}</ref> iNNpulsa, a government body that promotes entrepreneurship and innovation in the country, provides grants to startups, in addition to other services it and institutions provide. Colombia was ranked 61st in the ] in 2024.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship |url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/ |access-date=2024-11-29 |website=www.wipo.int |language=en}}</ref> Co-working spaces have arisen to serve as communities for startups large and small.<ref name="venturebeat.com">{{cite web |url=https://venturebeat.com/2013/09/29/the-silicon-valleys-of-latin-america-a-tale-of-3-nations/ |publisher=venturebeat.com |title=entrepreneurship and innovation in Colombia |date=29 September 2013 |access-date=1 October 2013 |archive-date=1 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131001122006/http://venturebeat.com/2013/09/29/the-silicon-valleys-of-latin-america-a-tale-of-3-nations/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://apps.co/|title=Colombia Startups|publisher=apps.co|language=es|access-date=14 February 2014|archive-date=9 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140209081806/https://apps.co/|url-status=live}}</ref> Organizations such as the Corporation for Biological Research (CIB) for the support of young people interested in scientific work has been successfully developed in Colombia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://cib.org.co/quienes-somos/|title=Corporation for Biological Research (CIB)|publisher=cib.org.co|language=es|access-date=28 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150413214207/http://cib.org.co/quienes-somos/|archive-date=13 April 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> The ] based in Colombia investigates the increasing challenge of ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ciat.cgiar.org/|title=International Center for Tropical Agriculture|access-date=1 October 2013|archive-date=9 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170609150224/http://ciat.cgiar.org/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Tourism=== | |||
| {{main|Tourism in Colombia}} | |||
| ]city.]] | |||
| ] from ].]] | |||
| Important inventions related to medicine have been made in Colombia, such as the first ], invented by the electrical engineer ], an invention of great importance for those who suffer from heart failure. Also invented in Colombia were the ] and keratomileusis technique, which form the fundamental basis of what now is known as ] (one of the most important techniques for the correction of ]s of vision) and the ] for the treatment of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://listas.20minutos.es/lista/mejores-inventos-colombianos-320000/|title=Inventos colombianos|publisher=20minutos.es|language=es|access-date=1 October 2013|archive-date=4 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131004213902/http://listas.20minutos.es/lista/mejores-inventos-colombianos-320000/|url-status=live}}</ref> Colombia has begun to innovate in military technology for its army and other armies of the world; especially in the design and creation of personal ballistic protection products, military hardware, ]s, ]s, simulators and radar.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://dialogo-americas.com/en/articles/colombian-military-industry-markets-weapons-and-technology-international-stage|title=Colombian military industry markets weapons and technology on international stage|publisher=dialogo-americas.com|access-date=16 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170417045356/https://dialogo-americas.com/en/articles/colombian-military-industry-markets-weapons-and-technology-international-stage|archive-date=17 April 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co/ediciones/103/08.html|title=Robots antiexplosivos|publisher=historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co|access-date=9 May 2016|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160509183603/http://historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co/ediciones/103/08.html|archive-date=9 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| For many years serious internal armed conflict deterred tourists from visiting Colombia, with official ] warning against travel to the country. However in recent years numbers have risen sharply, thanks to improvements in security resulting from President Álvaro Uribe's "democratic security" strategy, which has included significant increases in military strength and police presence throughout the country and pushed rebel groups further away from the major cities, highways and tourist sites likely to attract international visitors. Foreign tourist visits were predicted to have risen from 0.5 million in 2003 to 1.3 million in 2007,<ref name="BBC Tourism"></ref> while ] picked Colombia as one of their top ten world destinations for 2006.<ref>{{cite news |publisher=Christian Science Monitor |title=Hot Destination: Colombia |date=May 9, 2006 |url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0509/p06s01-woam.html}}</ref> The improvements in the country's security were recognised in November 2008 with a revision of the travel advice on Colombia issued by the ].<ref name="FCO Travel Advice"> | |||
| </ref> | |||
| Some leading Colombian scientists are Joseph M. Tohme, researcher recognized for his work on the ] of food, ] who is known for his groundbreaking work on ]s for ], ] who discovered the "Paisa Mutation" or a type of ],<ref name="Francisco Lopera">{{cite web|url=http://www.udea.edu.co/portal/page/portal/bActualidad/Principal_UdeA/News/Tab/AEF4F8549743CF0AE04018C8341F754F|publisher=udea.edu.co|title=Beyond Alzheimer's: the "Paisa Mutation"|access-date=1 October 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131005012618/http://www.udea.edu.co/portal/page/portal/bActualidad/Principal_UdeA/News/Tab/AEF4F8549743CF0AE04018C8341F754F|archive-date=5 October 2013}}</ref> ] known for his study of the intrinsic ]s properties and the theory of a syndrome that had changed the way of understanding the functioning of the brain, Jairo Quiroga Puello recognized for his studies on the characterization of ]s which can be used to fight fungus, ]s, ] and even some viruses and Ángela Restrepo who established accurate ] and treatments to combat the effects of a disease caused by '']''.<ref name="Científicos colombianos">{{cite web|url=http://cienciagora.com.co/galeria_de_cientificos.html|title=Científicos colombianos|publisher=cienciagora.com.co|access-date=28 October 2013|language=es|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029200254/http://cienciagora.com.co/galeria_de_cientificos.html|archive-date=29 October 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="brillantes colombianos">{{cite web|url=http://portal.redcolombiana.com/foros/estos-son-los-8-cientificos-del-pais-mas-consultad|title=científicos del país más consultados|publisher=portal.redcolombiana.com|access-date=28 October 2013|language=es|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029201546/http://portal.redcolombiana.com/foros/estos-son-los-8-cientificos-del-pais-mas-consultad|archive-date=29 October 2013}}</ref><ref name="Científicos destacados">{{cite web|url=http://www.eltiempo.com/archivo/documento/CMS-6672909|title=Estos son los científicos colombianos más destacados en el último lustro|date=25 November 2009|publisher=eltiempo.com|access-date=28 October 2013|language=es|archive-date=17 March 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150317120558/http://www.eltiempo.com/archivo/documento/CMS-6672909|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Popular tourist attractions include the historic ] district of central Bogotá, the walled city and beaches of ], the colonial towns of ], ] and ], and the ] and the ]. Tourists are also drawn to ], including ] ], the ], the ] in ] and the ] in Bogotá. Meanwhile, because of the improved security, Caribbean ]s now stop at Cartagena and ]. | |||
| == Demographics == | |||
| ], one of the main ecotourist destinations.]] | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|List of Colombian departments by population}} | |||
| ] of Colombia in 2013]] | |||
| ] | |||
| With an estimated 50 million people in 2020, Colombia is the ] in Latin America, after Brazil and Mexico.<ref name="PopulationProjections">{{cite web |url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/censo2018/proyecciones-de-poblacion/anexos-proyecciones-pob-dptos-area-grupos-de-edad-2018-2023.xlsx |title=¿Cuántos somos? |publisher=Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE) |access-date=26 March 2020 |archive-date=27 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200327040110/https://www.dane.gov.co/files/censo2018/proyecciones-de-poblacion/anexos-proyecciones-pob-dptos-area-grupos-de-edad-2018-2023.xlsx |url-status=dead }}</ref> At the beginning of the 20th century, Colombia's population was approximately 4 million.<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116145835/http://countrystudies.us/colombia/35.htm |date=16 January 2013 }}". ].</ref> Since the early 1970s Colombia has experienced steady declines in its fertility, mortality, and population growth rates. The population growth rate for 2016 is estimated to be 0.9%.<ref name="Population growth">{{cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.GROW?locations=CO|title=Population growth (annual %)|publisher=World Bank|access-date=15 January 2018|archive-date=16 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180116020705/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.GROW?locations=CO|url-status=live}}</ref> About 26.8% of the population were 15 years old or younger, 65.7% were between 15 and 64 years old, and 7.4% were over 65 years old. The proportion of older persons in the total population has begun to increase substantially.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://profamilia.org.co/docs/Libro%20RESUMEN%20EJECUTIVO.pdf|title=Encuesta Nacional de Demografía y Salud (ENDS)|publisher=profamilia.org.co|access-date=5 May 2017|language=es|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170408150728/http://profamilia.org.co/docs/Libro%20RESUMEN%20EJECUTIVO.pdf|archive-date=8 April 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref> Colombia is projected to have a population of 55.3 million by 2050.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cepal.org/en/long-term-population-estimates-and-projections-1950-2100|title=Long term population estimates and projections 1950–2100|publisher=cepal.org|access-date=17 June 2016|archive-date=18 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160618072643/http://www.cepal.org/en/long-term-population-estimates-and-projections-1950-2100|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The great variety in geography, flora and fauna across Colombia has also resulted in the development of an ] industry, concentrated in the country's ]. Popular ecotourist destinations include: along the Caribbean coast, the ] in the ] mountain range and ] on the tip of the ]; the ], the ] and the ] in the central ]; ] in the ]; and the Pacific islands of ] and ]. Colombia is home to seven ]. | |||
| Estimates for the population of the area that is now Colombia range between 2.5 and 12 million people in 1500; estimates between the extremes include figures of 6<ref name="JaramilloUribe1989" /> and 7 million. With the Spanish conquest, the region's population had collapsed to around 1.2 million people in 1600, for an estimated decrease of 52–90%. By the end of the colonial period, it had declined further to around 800,000; it began rising in the early 19th century to around 1.4 million, where it would drop again in the ] to between 1 and 1.2 million. The country's population did not recover to pre-conquest levels until the 1940s, nearly 450 years after its 16th-century peak.<ref name="PoblacioCol">{{Cite web |url=https://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/paginas/lbr_colonial_graficos3.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=8 February 2024 |archive-date=19 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119200112/https://www.banrep.gov.co/sites/default/files/paginas/lbr_colonial_graficos3.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Transportation=== | |||
| {{main|Transportation in Colombia}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| The population is concentrated in the ] and along the ], also the population densities are generally higher in the Andean region. The nine eastern lowland departments, comprising about 54% of Colombia's area, have less than 6% of the population.<ref name="populationbyregions">{{cite web|url=https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/atlasestadistico/pages/tome01/tm01itm17.html|title=Distribution of the population by regions|publisher=geoportal.dane.gov.co|access-date=17 June 2016|archive-date=17 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160617225957/https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/atlasestadistico/pages/tome01/tm01itm17.html|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Population density">{{cite web|url=https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/atlasestadistico/pages/tome01/tm01itm16.html|title=Population density of Colombia|publisher=geoportal.dane.gov.co|access-date=17 June 2016|archive-date=17 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160617225927/https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/atlasestadistico/pages/tome01/tm01itm16.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> Traditionally a rural society, ] was very heavy in the mid-20th century, and Colombia is now one of the most urbanized countries in Latin America. The urban population increased from 31% of the total in 1938 to nearly 60% in 1973, and by 2014 the figure stood at 76%.<ref name="Country Study">{{cite web |url=http://countrystudies.us/colombia/36.htm |title=Colombia: A Country Study |publisher=Countrystudies.us |access-date=16 May 2010 |archive-date=7 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160407023454/http://countrystudies.us/colombia/36.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/Highlights/WUP2014-Highlights.pdf |title=World Urbanization Prospects |publisher=un.org |access-date=10 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141102043800/http://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/Highlights/WUP2014-Highlights.pdf |archive-date=2 November 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The population of ] alone has increased from just over 300,000 in 1938 to approximately 8 million today.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/agosto2008/bogota.htm|title=Bogotá: de paso por la capital|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia|author=León Soler, Natalia|access-date=17 June 2016|language=es|archive-date=18 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160618004654/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/agosto2008/bogota.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> In total seventy-two cities now have populations of 100,000 or more (2015). {{As of|2012}} Colombia has the world's largest populations of ]s (IDPs), estimated to be up to 4.9 million people.<ref name="UNHCR">{{cite web|url=http://www.unhcr.org/pages/49c3646c23.html|title=Internally Displaced People Figures|publisher=The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees|access-date=18 May 2014|archive-date=18 May 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130518072653/http://www.unhcr.org/pages/49c3646c23.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia has a network of national highways maintained by the '']'' or INVIAS (National Institute of Roadways) government agency under the ]. The ] travels through Colombia, connecting the country with Venezuela to the east and Ecuador to the south. | |||
| The life expectancy was 74.8 years in 2015, and infant mortality was 13.1 per thousand in 2016.<ref name="Life expectancy at birth">{{cite web|title=Life expectancy at birth|url=https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.688|publisher=who.int|access-date=13 July 2021|archive-date=5 March 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130305150130/https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.688|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="infant mortality">{{cite web|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.IMRT.IN|title=Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births)|publisher=World Bank|access-date=15 January 2018|archive-date=21 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171021085117/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.IMRT.IN|url-status=live}}</ref> In 2015, 94.58% of adults and 98.66% of youth are literate and the government spends about 4.49% of its GDP on education.<ref name="UNESCO" /> | |||
| Colombia's principal airport is ] in Bogotá. Several national airlines (], ], ] , ] and ], ), and international airlines (such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]) operate from El Dorado. Because of its central location in Colombia and America, it is preferred by national land transportation providers, as well as national and international air transportation providers. | |||
| === |
===Languages=== | ||
| {{Main|Languages of Colombia}} | |||
| Colombia is discussing current trends and challenges as well as recent international developments in the ]s sector with the intention of contributing to the development of a sustainable and competitive biofuels strategy for Colombia and the region.<ref></ref> | |||
| {{See also|Colombian Spanish}} | |||
| Arturo Infante Villarreal is the National Biofuels Coordinator, which is within the Department of National Planning. | |||
| Around 99.2% of Colombians speak Spanish, also called Castilian; 65 ]s, two ], the ] and ] are also used in the country. ] has official status in the ].<ref name="LEY47DE1993" /><ref name="lenguas indígenas">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/antropologia/lengua/clas2.htm|title=Languages of Colombia|publisher=banrepcultural.org|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|archive-date=29 September 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130929200029/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/antropologia/lengua/clas2.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Languages of Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.ambafrance-co.org/Jon-Landaburu-Especialista-de-las|title=Jon Landaburu, Especialista de las lenguas de Colombia|publisher=ambafrance-co.org|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131216191247/http://www.ambafrance-co.org/Jon-Landaburu-Especialista-de-las|archive-date=16 December 2013}}</ref><ref name="MapofthelanguagesofColombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.lenguasdecolombia.gov.co/mapalenguas/inicio.swf|title=Map of the languages of Colombia|publisher=lenguasdecolombia.gov.co|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|archive-date=10 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010222341/http://www.lenguasdecolombia.gov.co/mapalenguas/inicio.swf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Including Spanish, a total of 101 languages are listed for Colombia in the ] database. The specific number of spoken languages varies slightly since some authors consider as different languages what others consider to be varieties or dialects of the same language. Best estimates recorded 71 languages that are spoken in-country today – most of which belong to the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] language families. There are currently more than 850,000 speakers of native languages.<ref name="ethnologue">{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/country/CO|title=The Languages of Colombia|publisher=Ethnologue.com|access-date=16 May 2010|archive-date=7 March 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130307132656/http://www.ethnologue.com/country/CO|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="nativelanguages">{{cite web|url=http://www.lenguasdecolombia.gov.co/content/ley-de-lenguas-nativas |title=Native languages of Colombia |publisher=lenguasdecolombia.gov.co |language=es |access-date=25 March 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140326080213/https://www.lenguasdecolombia.gov.co/content/ley-de-lenguas-nativas |archive-date=26 March 2014}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| {{main|Demographics of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|List of Colombian Departments by population}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| === Ethnic groups === | |||
| With an estimated 44.6 million people in 2008, Colombia is the ] in Latin America, after Brazil and Mexico. The population increased at a rate of 1.9% between 1975 and 2005, predicted to drop to 1.2% over the next decade. Colombia is projected to have a population of 50.7 million by 2015. These trends are reflected in the country's age profile. In 2005 over 30% of the population was under 15 years old, compared to just 5.1% aged 65 and over. ] at birth in 2005 was 72.3; 2.1% would not reach the age of 5, 9.2% would not reach the age of 40.<ref name="HDR Colombia"/> | |||
| {{main|Race and ethnicity in Colombia}} | |||
| {{Pie chart | |||
| |thumb = right | |||
| |caption = Ethnic groups in Colombia - ''']'''<ref name="grupos étnicos">{{cite web|title=visibilización estadística de los grupos étnicos|url=https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/geovisores/sociedad/cnpv-2018/?lt=4.456007353293281&lg=-73.2781601239999&z=5|work=Censo General 2018|publisher=Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica (DANE)|access-date=10 February 2020|archive-date=16 August 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210816231845/https://geoportal.dane.gov.co/geovisores/sociedad/cnpv-2018/?lt=4.456007353293281&lg=-73.2781601239999&z=5|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| |label1 = ]-] | |||
| The population is concentrated in the ] and along the ]. The nine eastern lowland departments, comprising about 54% of Colombia's area, have less than 3% of the population and a density of less than one person per square kilometer (two persons per square mile). Traditionally a rural society, ] was very heavy in the mid-twentieth century, and Colombia is now one of the most urbanized countries in Latin America. The urban population increased from 31% of the total in 1938 to 60% in 1975, and by 2005 the figure stood at 72.7%.<ref name="Country Study"></ref><ref name="HDR Colombia"/> The population of Bogotá alone has increased from just over 300,000 in 1938 to approximately 7 million today. In total thirty cities now have populations of 100,000 or more. | |||
| |value1 = 87.58 | |||
| |color1 = #008080 | |||
| |label2= ] (includes ]) | |||
| Colombia is ranked second in the world in the ]. | |||
| |value2 = 6.68 | |||
| |color2 = #FFBF00 | |||
| |label3= ] | |||
| ===Ethnic groups=== | |||
| |value3 = 4.31 | |||
| ] Women in Cartagena.]] | |||
| |color3 = #1C39BB | |||
| The census data in Colombia does not record ethnicity, other than that of those identifying themselves as members of particular minority ethnic groups, so overall percentages are essentially estimates from other sources and can vary from one to another.<ref name="Nación Multicultural">{{es icon}} </ref> | |||
| |label4= Not stated | |||
| According to the ], the majority of the population (58%) is ], or of mixed European and Amerindian ancestry. 20% is of ], 14% ] (of mixed European and black African ancestry), 4% of ], and 3% ] (of mixed Amerindian and black African ancestry). ] comprise only 1% of the population.<ref name="CIAWFB"/> The overwhelming majority of Colombians speak ] (see also ]), but in total 101 languages are listed for Colombia in the ] database, of which 80 are spoken today as living languages. Most of these belong to the ]n, ] and ]an linguistic families. The ], spoken by descendants of the ], has also extended northwards into Colombia, mainly in urban centers of the southern highlands. There are currently about 500,000 speakers of indigenous languages.<ref name="ethnologue"></ref> | |||
| |value4 = 1.35 | |||
| |color4 = #008080 | |||
| |label5= ] | |||
| ===Indigenous peoples=== | |||
| |value5 = 0.06 | |||
| {{main|Indigenous peoples in Colombia}} | |||
| |color5 = #FFBF00 | |||
| ] represent the largest indigenous ethnic group in Colombia.<ref name="EPM"> {{cite web | author =EPM | url = http://www.eeppm.com/epmcom/contenido/acercade/infraestructura/generacion/Jepirachi/etnia.htm | title = La etnia Wayuu | work = Empresas Publicas de Medellin | date = 2005| accessdate = 2008-02-29 | language = Spanish}}</ref>]] | |||
| |label6= ] | |||
| Before the Spanish colonization of what is now Colombia, the territory was home to a significant number of indigenous peoples. Many of these were absorbed into the mestizo population, but the remainder currently represents over eighty-five distinct cultures. 567 reserves (''resguardos'') established for indigenous peoples occupy 365,004 square kilometres (over 30% of the country's total) and are inhabited by more than 800,000 people in over 67,000 families.<ref name="Resguardos Indígenas">{{es icon}} </ref> The 1991 constitution established their native languages as official in their territories, and most of them have bilingual education (native and Spanish). | |||
| |value6 = 0.02 | |||
| |color6 = #008080 | |||
| |label7= ] | |||
| Some of the largest indigenous groups are the ],<ref name="EPM"/> the ], the ], the ], the ], the ] and the ]. ], ] and ] have the largest indigenous populations. | |||
| |value7 = 0.01 | |||
| |color7 = #808080 | |||
| }} | |||
| Colombia is ethnically diverse, its people descending from the original ] inhabitants, Spanish conquistadors, ] originally brought to the country as slaves, and 20th-century ] and the ], all contributing to a diverse cultural heritage.<ref name="Colombia is ethnically diverse">{{cite web |url=http://www.pedagogica.edu.co/storage/ps/articulos/pedysab15_09arti.pdf |title=The ethnic and cultural diversity of Colombia |publisher=pedagogica.edu.co |language=es |access-date=26 March 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140327221138/http://www.pedagogica.edu.co/storage/ps/articulos/pedysab15_09arti.pdf |archive-date=27 March 2014 }}</ref> The demographic distribution reflects a pattern that is influenced by colonial history.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co/ediciones/105/15.html |title=Mapa genético de los colombianos |publisher=historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co |language=es |access-date=17 June 2016 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160617204901/http://historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co/ediciones/105/15.html |archive-date=17 June 2016 }}</ref> Whites live all throughout the country, mainly in urban centers and the burgeoning highland and coastal cities. The populations of the major cities also include mestizos. ] ''campesinos'' (people living in rural areas) also live in the Andean highlands where some Spanish conquerors mixed with the women of Amerindian ]. Mestizos include artisans and small tradesmen that have played a major part in the urban expansion of recent decades.<ref>Bushnell & Hudson, pp. 87–88.</ref><ref name="grupos étnicos" /> In a study by the American Journal of Physical Anthropology, Colombians have an average ancestry of 47% Amerindian DNA, 42% European DNA, and 11% African DNA.<ref name=Rojas2010>{{cite journal |last1=Rojas |first1=Winston |last2=Parra |first2=María Victoria |last3=Campo |first3=Omer |last4=Caro |first4=María Antonieta |last5=Lopera |first5=Juan Guillermo |last6=Arias |first6=William |last7=Duque |first7=Constanza |last8=Naranjo |first8=Andrés |last9=García |first9=Jharley |last10=Vergara |first10=Candelaria |last11=Lopera |first11=Jaime |last12=Hernandez |first12=Erick |last13=Valencia |first13=Ana |last14=Caicedo |first14=Yuri |last15=Cuartas |first15=Mauricio |last16=Gutiérrez |first16=Javier |last17=López |first17=Sergio |last18=Ruiz-Linares |first18=Andrés |last19=Bedoya |first19=Gabriel |title=Genetic make up and structure of Colombian populations by means of uniparental and biparental DNA markers |journal=American Journal of Physical Anthropology |date=September 2010 |volume=143 |issue=1 |pages=13–20 |doi=10.1002/ajpa.21270 |pmid=20734436 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45822469 |access-date=13 February 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ===Immigrant groups=== | |||
| {{main|Immigration to Colombia}} | |||
| The ] reported that the "non-ethnic population", consisting of ] and mestizos (those of mixed European and Amerindian ancestry), constituted 87.6% of the national population. 6.7% is of ] ancestry. ] constitute 4.3% of the population. ] people constitute 0.06% of the population. ] people constitute 0.02% of the population. 0.01% of the population are ]. A study by Latinobarómetro in 2023 estimates that 50.3% of the population are ], 26.4% are ], 9.5% are ], 9.0% are ], 4.4% are ], and 0.4% are ], these estimates would equate to around 26 million people being Mestizo, 14 million being White, 5 million being Indigenous, 5 million being Black, 2 million being Mulatto, and 200k being Asian.<ref name="2023est">{{cite web |title=Raza/Etnia a la que pertenece |url=https://www.latinobarometro.org/latOnline.jsp |access-date=13 February 2024 |work=Latinobarómetro 2023 Colombia}}</ref> | |||
| The first and most substantial wave of modern immigration to Colombia consisted of ], following the arrival of Europeans in 1499. However a range of other Europeans (], ], ], ], ], ] and ], also many ]) migrated to the country in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, and, in smaller numbers, ], ], ], ] and ] during and after the Second World War. For example, former Mayor of Bogotá ] is the son of Lithuanian immigrants. | |||
| {{Pie chart | |||
| |thumb = right | |||
| |caption = Ethnic groups of Colombia according to Latinobarómetro 2023<ref name="2023est"/> | |||
| |label1=] | |||
| Many immigrant communities have settled on the Caribbean coast, in particular recent immigrants from the ]. ] (the largest city of the Colombian Caribbean) and other Caribbean cities have the largest populations of ] and ], ], ], and people of Italian, German, and French descent. For example, the singer ], a native of Barranquilla, has both Lebanese and Italian ancestry. There are also important communities of ] and ]. | |||
| |value1 = 50.3 | |||
| |color1 = #2b70a7 | |||
| |label2=] | |||
| ] were brought as ], mostly to the coastal lowlands, beginning early in the sixteenth century and continuing into the nineteenth century. Large Afro-Colombian communities are found today on the Caribbean and Pacific coasts. The population of the ], running along the northern portion of Colombia's Pacific coast, is over 80% black.<ref name="Grupos Étnicos">{{es icon}} </ref> | |||
| |value2 = 26.4 | |||
| |color2 = #008dbf | |||
| |label3=] | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| |value3 = 9.5 | |||
| {{main|Education in Colombia}} | |||
| |color3 = #00a9c1 | |||
| ] campus of the ]. The National University is the largest state-run university in Colombia.]] | |||
| |label4=] | |||
| The educational experience of many Colombian children begins with attendance at a preschool academy until age 6. ] is then free and ]. ] (educación media) begins at age 11 and lasts up to six years, in some cases seven (mostly in private schools, where it is usually ]). Secondary school graduates are awarded the diploma (high-school diploma). However in many rural areas, teachers are poorly qualified, and only the five years of primary schooling are offered. The school year can extend from February to November or from August to June, and in many public schools attendance is split into morning and afternoon "shifts", in order to accommodate the large numbers of children. | |||
| |value4 = 9.0 | |||
| |color4 = #00c2ac | |||
| |label5=] | |||
| Public spending on education as a proportion of ] in 2006 was 4.7% — one of the highest rates in Latin America — as compared with 2.4% in 1991. This represented 14.2% of total government expenditure.<ref name="UNESCO"></ref><ref name="HDR Colombia"/> In 2006, the primary and secondary net enrolment rates stood at 88% and 65% respectively, slightly below the regional average. School life expectancy was 12.4 years.<ref name="UNESCO"/> A total of 92.3% of the population aged 15 and older were recorded as literate, including 97.9% of those aged 15-24, both figures slightly higher than the regional average.<ref name="UNESCO"/> However, literacy levels are considerably lower in rural areas.<ref name="Background Note"></ref> | |||
| |value5 = 4.4 | |||
| |color5 = #18d886 | |||
| |label6=] | |||
| Colombia has ]. These are concentrated in Bogotá, which has become known as "the Athens of South America".<ref name="Athens"></ref> | |||
| |value6 = 0.4 | |||
| |color6 = #9ae758 | |||
| }} | |||
| The ] estimated that the 86% of the population that did not consider themselves part of one of the ethnic groups indicated by the 2006 census, white Colombians are mainly of ] lineage, but there is also a large population of ] descent; in some areas there is a considerable input of ] and ] ancestry.<ref name="The Society and Its Environment">{{cite book|last1=Bushnell |first1=David |last2=Hudson |first2=Rex A. |year=2010 |title=The Society and Its Environment; Colombia: a country study |url=https://www.loc.gov/rr/frd/cs/pdf/CS_Colombia.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.loc.gov/rr/frd/cs/pdf/CS_Colombia.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |pages=87, 92 |publisher=Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, Washington D.C.}}</ref><ref name="grupos étnicos" /> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{main|Religion in Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Freedom of religion in Colombia}} | |||
| Many of the ] experienced a reduction in population during the Spanish rule<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.colombia.com/colombiainfo/nuestrahistoria/esclavista.asp |publisher=colombia.com |title=Society and slavery|language=es|access-date=9 September 2013}}</ref> and many others were absorbed into the mestizo population, but the remainder currently represents over eighty distinct cultures. Reserves (''resguardos'') established for indigenous peoples occupy {{convert|30571640|ha|km2|sp=us}} (27% of the country's total) and are inhabited by more than 800,000 people.<ref name="Resguardos Indígenas">{{cite web|url=https://www.siac.gov.co/Estado_Ecosistemas_Bosque/Resguardos_indigenas1.aspx |title=Resguardos indígenas – Concentra el 43% de los bosques naturales |publisher=siac.gov.co |access-date=27 March 2014 |language=es |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140328011617/https://www.siac.gov.co/Estado_Ecosistemas_Bosque/Resguardos_indigenas1.aspx |archive-date=28 March 2014}}</ref> Some of the largest indigenous groups are the ],<ref name="wayuu">{{cite web|url=http://revistas.ucr.ac.cr/index.php/antropologia/article/view/2006/1973|title=Hostein, N. (2010). El pueblo wayuu de la Guajira colombo-venezolana: un panorama de su cultura. Cuadernos de Antropología, 20(1).|access-date=27 March 2014}}</ref> the ], the Pastos, the ] and the ].<ref name="pueblos indígenas">{{cite web |url=https://www.dnp.gov.co/programas/desarrollo-territorial/Paginas/pueblos-indigenas.aspx |title=Los pueblos indígenas de Colombia en el umbral del nuevo milenio. Población, cultura y territorio: bases para el fortalecimiento social y económico de los pueblos indígenas |publisher=dnp.gov.co |access-date=27 March 2014 |archive-date=12 March 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150312221148/https://www.dnp.gov.co/programas/desarrollo-territorial/Paginas/pueblos-indigenas.aspx |url-status=dead }}</ref> The departments of ], ], ], ] and ] have the largest indigenous populations.<ref name="grupos étnicos" /> | |||
| The ] (DANE) does not collect religious statistics, and accurate reports are difficult to obtain. However, based on various studies, more than 95% of the population adheres to ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.religiousintelligence.co.uk/country/?CountryID=78 |title=Religious Intelligence — Country Profile: Colombia |accessdate=2007-10-03}}</ref> the vast majority of which (between 81% and 90%) are ]. About 1% of Colombians adhere to ] and under 1% to ], ], ], and ]. However, despite high numbers of adherents, around 60% of respondents to a poll by ''El Tiempo'' reported that they did not practice their faith actively.<ref name="Religious Freedom">, by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, U.S. Department of State, November 8, 2005.</ref> | |||
| The ] (ONIC), founded at the first National Indigenous Congress in 1982, is an organization representing the indigenous peoples of Colombia. In 1991, Colombia signed and ratified the current international law concerning indigenous peoples, ].<ref name="Ratifications - ilo.org">{{cite web|url=http://www.ilo.org/dyn/normlex/en/f?p=1000:11200:0::NO:11200:P11200_COUNTRY_ID:102595 |title=Ratifications for Colombia |publisher=ilo.org |access-date=26 March 2014}}</ref> | |||
| While Colombia remains an overwhelmingly Roman Catholic country, the Colombian constitution guarantees freedom and equality of religion.<ref> (Article 19)</ref> Religious groups are readily able to obtain recognition as organized associations, although some smaller ones have faced difficulty in obtaining the additional recognition required to offer chaplaincy services in public facilities and to perform legally recognised marriages.<ref name="Religious Freedom"/> | |||
| ] were brought as ], mostly to the coastal lowlands, beginning early in the 16th century and continuing into the 19th century. Large Afro-Colombian communities are found today on the Pacific Coast.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.dane.gov.co/censo/files/presentaciones/grupos_etnicos.pdf |title=Ethnic groups in Colombia |publisher=dane.gov.co |language=es |access-date=26 March 2014 |archive-date=3 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303233546/http://www.dane.gov.co/censo/files/presentaciones/grupos_etnicos.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> Numerous ] migrated mainly to the islands of San Andres and Providencia. A number of other Europeans and North Americans migrated to the country in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including people from the former ] during and after the ].<ref name="Extranjeros en Colombia">{{cite web |url=http://www.rodriguezuribe.co/histories/Inmigrantes%20a%20Colombia%20-%20Luis%20Alvaro%20Gallo.pdf |title=Inmigrantes a Colombia: Personajes extranjeros llegados a Colombia |author=Luis Álvaro Gallo Martínez |publisher=rodriguezuribe.co |year=2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924091807/http://www.rodriguezuribe.co/histories/Inmigrantes%20a%20Colombia%20-%20Luis%20Alvaro%20Gallo.pdf |archive-date=24 September 2015 }}</ref><ref name="Migraciones Internacionales">{{cite web|url=http://rcientificas.uninorte.edu.co/index.php/investigacion/article/view/2116/2827|title=Las migraciones internacionales en Colombia. Investigación & Desarrollo, 20(1) 142–167.|author1=Wabgou, M. |author2=Vargas, D. |author3=Carabalí, J. A.|publisher=uninorte.edu.co|year=2012|access-date=28 March 2015|archive-date=14 September 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160914172309/http://rcientificas.uninorte.edu.co/index.php/investigacion/article/view/2116/2827|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| {{main|Culture of Colombia}} | |||
| {{see also|Festivals in Colombia|Music of Colombia}} | |||
| ] tradition from ], a ] since 2005.]] | |||
| Many immigrant communities have settled on the Caribbean coast, in particular recent immigrants from the ] and ]. Barranquilla (the largest city of the Colombian Caribbean) and other Caribbean cities have the largest populations of ], ], and other ].<ref name="arab colombians">Vargas Arana, Pilar, and Luz Marina Suaza Vargas. "Los árabes en Colombia: Del rechazo a la integración." (2007).</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nodo50.org/csca/agenda08/misc/arti48.html |title=The Arab immigration to Colombia |publisher=nodo50.org |language=es|access-date=30 January 2014}}</ref> There are also important communities of ] and ].<ref name="Colombia is ethnically diverse" /> There is a major migration trend of ], due to the political and economic situation in Venezuela.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/c80f3a_d2e0a0b4821e4238ae021904026a4459.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/c80f3a_d2e0a0b4821e4238ae021904026a4459.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Características de los migrantes de Venezuela a Colombia |date=14 August 2017 |website=labourosario.com|language=es}}</ref> In August 2019, Colombia offered citizenship to more than 24,000 children of Venezuelan refugees who were born in Colombia.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/05/world/americas/colombia-citizenship-venezuelans.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/05/world/americas/colombia-citizenship-venezuelans.html |archive-date=1 January 2022 |url-access=limited|title=Colombia Offers Citizenship to 24,000 Children of Venezuelan Refugees|last1=Kurmanaev|first1=Anatoly|date=5 August 2019|work=The New York Times|access-date=6 August 2019|last2=González|first2=Jenny Carolina|issn=0362-4331}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia lies at the crossroads of ] and the broader ], and as such has been marked by a wide range of cultural influences. ], ] and other ], ], ], ], and ] influences, as well as other Latin American cultural influences, are all present in Colombia's modern culture. ], ], ], and other political, social and economic changes have also left an impression. | |||
| === Religion === | |||
| Historically, the country's imposing landscape left its various ] largely isolated from one another, resulting in the development of very strong regional identities, in many cases stronger than the national. Modern transport links and means of communication have mitigated this and done much to foster a sense of nationhood, but social and political instability, and in particular fears of armed groups and bandits on intercity highways, have contributed to the maintenance of very clear regional differences. Accent, dress, music, food, politics and general attitude vary greatly between the ] and other residents of the central highlands, the '']'' of ] and the ], the ''costeños'' of the ], the '']s'' of the eastern plains, and the inhabitants of the ] and the vast ] to the south east. | |||
| {{Main|Religion in Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|Freedom of religion in Colombia|Jews in Colombia}} | |||
| ] in the southern Colombian Department of ]]] | |||
| The ] (DANE) does not collect religious statistics, and accurate reports are difficult to obtain. However, based on various studies and a survey, about 90% of the population adheres to Christianity, the majority of which (70.9%–79%) are ], while a significant minority (16.7%) adhere to ] (primarily ]). Some 4.7% of the population is ] or agnostic, while 3.5% claim to believe in God but do not follow a specific religion. 1.8% of Colombians adhere to ] and ] and less than 1% adhere to other religions, such as the ], ], Judaism, ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and spiritual studies. The remaining people either did not respond or replied that they did not know. In addition to the above statistics, 35.9% of Colombians reported that they did not practice their faith actively.<ref name="Religion">{{cite book |url=http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/10780/1/Del%20monopolio%20cat%C3%B3lico%20a%20la%20explosi%C3%B3n%20pentecostal.pdf |title=Del monopolio católico a la explosión pentecostal' |author1=Beltrán Cely |author2=William Mauricio (2013) |publisher=Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Facultad de Ciencias Humanas, Centro de Estudios Sociales (CES), Maestría en Sociología |language=es |isbn=978-958-761-465-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160327173229/http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/10780/1/Del%20monopolio%20cat%C3%B3lico%20a%20la%20explosi%C3%B3n%20pentecostal.pdf |archive-date=27 March 2016 |year=2013 }}</ref><ref name="Religion2">{{cite web |url=http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/8486/1/williammauriciobeltran.2011.pdf |title=Descripción cuantitativa de la pluralización religiosa en Colombia |author1=Beltrán Cely |author2=William Mauricio |author-link=William Mauricio Beltrán Cely |publisher=Universitas humanística 73 (2012): 201–238. – bdigital.unal.edu.co |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140329185722/http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/8486/1/williammauriciobeltran.2011.pdf |archive-date=29 March 2014}}</ref><ref name="Religion in Latin America">{{cite web |title=Religion in Latin America, Widespread Change in a Historically Catholic Region |url=http://www.pewforum.org/2014/11/13/religion-in-latin-america/ |publisher=Pew Research Center |date=13 November 2014}}</ref> 1,519,562 people in Colombia, or around 3% of the population reported following an Indigenous religion. | |||
| While Colombia remains a mostly Roman Catholic country by ] numbers, the 1991 Colombian constitution guarantees freedom of religion and all religious faiths and churches are equally free before the law.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title II – Concerning rights, guarantees, and duties – Chapter I – Concerning fundamental rights – Article 19)</ref> | |||
| ] and daughter ] during a visit to Cartagena, Colombia, where they were greeted by ].]] | |||
| ] in ], ].]] | |||
| ===Health=== | |||
| An inheritance from the ], Colombia remains a deeply ] and maintains a large base of Catholic traditions which provide a point of unity for its multicultural society. Colombia has many ] throughout the year, and the majority are rooted in these Catholic religious traditions. However, many are also infused with a diverse range of other influences. Prominent examples of Colombia's festivals include the ], the ], Medellín's ] and Bogotá's ] | |||
| {{Main|Health care in Colombia}} | |||
| ]'' ranking of the best clinics and hospitals in Latin America.<ref name="Colombian clinics" />]] | |||
| The overall ] in Colombia at birth is 79.3 years (76.7 years for males and 81.9 years for females).<ref name="Life expectancy at birth" /> Healthcare reforms have led to massive improvements in the healthcare systems of the country, with health standards in Colombia improving very much since the 1980s. The new system has widened population coverage by the social and health security system from 21% (pre-1993) to 96% in 2012.<ref>{{cite web|title=Ministra de Salud dice que la cobertura en este sector subió al 96%|url=http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/colombia/noticias/ministra-dice-cobertura-en-salud-fue-96|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140728140425/http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/colombia/noticias/ministra-dice-cobertura-en-salud-fue-96|archive-date=28 July 2014|access-date=18 August 2013|publisher=]|language=es}}</ref> In 2017, the government declared a ] and treatment center as a Project of National Strategic Interest.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://es.presidencia.gov.co/noticia/171012-Luis-Carlos-Sarmiento-Angulo-agradece-apoyo-del-Gobierno-a-moderno-centro-de-tratamiento-del-cancer |title=Centro de Tratamiento e Investigación sobre Cáncer (CTIC) |date=12 October 2017 |language=es|website=presidencia.gov.co}}</ref> | |||
| A 2016 study conducted by '']'' magazine ranked 21 Colombian ] among the top 44 in Latin America, amounting to 48 percent of the total.<ref name="Colombian clinics">{{cite web|url=http://rankings.americaeconomia.com/2016/clinicas/ranking|publisher=America Economia magazine|title=21 Colombian clinics among the best 44 in Latin America|access-date=9 June 2017|archive-date=23 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170623141648/http://rankings.americaeconomia.com/2016/clinicas/ranking|url-status=dead}}</ref> In 2022, 26 Colombian hospitals were among the 61 best in ] (42% total).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Cinco hospitales colombianos en el top 10 de los mejores de Latinoamérica |url=https://www.agenciapi.co/noticia/salud/cinco-hospitales-colombianos-en-el-top-10-de-los-mejores-de-latinoamerica |access-date=30 March 2023 |website=Agenciapi.co |language=es}}</ref> Also in 2023, two Colombian hospitals were among the top 75 of the world.<ref>{{Cite journal |date=2023 |title=Global Top 250 Hospitals 2023 |url=https://brandirectory.com/download-report/brand-finance-amc-hospitals-100-2023-full-report.pdf |journal=Brand Finance |pages=14}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Mosquera |first=Eddy |date=17 February 2023 |title=Tres hospitales colombianos están entre los 100 mejores centros médicos del mundo |url=https://caracol.com.co/2023/02/17/tres-hospitales-colombianos-estan-entre-los-100-mejores-centros-medicos-del-mundo/ |access-date=30 March 2023 |website=Caracol Radio |language=es}}</ref> | |||
| The mixing of various different ethnic traditions is reflected in Colombia's ] and dance. The most well-known Colombian genres are ] and ], the latter now strongly influenced by global ]. A powerful and unifying cultural medium in Colombia is ]. Most famously, the ] ] has gained international success through localized versions in the United States, Mexico, and elsewhere. Television has also played a role in the development of the ]. | |||
| === Education === | |||
| As in many Latin American countries, Colombians have a passion for ] (soccer). The ] is seen as a symbol of unity and national pride, though ] also inspire fierce loyalty and ]. Colombia has "exported" many famous players, such as ], ], ], and ]. Other ] have also achieved success, including ]'s ], ]'s ] and ], and the ]'s ]. | |||
| {{Main|Education in Colombia}} | |||
| The educational experience of many Colombian children begins with attendance at a ] academy until age five (''Educación preescolar''). Basic education (''Educación básica'') is compulsory by law.<ref>Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title II – Concerning rights, guarantees, and duties – Chapter 2 – Concerning social, economic and cultural rights – Article 67)</ref> It has two stages: Primary basic education (''Educación básica primaria'') which goes from first to fifth grade – children from six to ten years old, and Secondary basic education (''Educación básica secundaria''), which goes from sixth to ninth grade. Basic education is followed by Middle vocational education (''Educación media vocacional'') that comprises the tenth and eleventh grades. It may have different vocational training modalities or specialties (academic, technical, business, and so on.) according to the curriculum adopted by each school.<ref name="sistema educativo" /> | |||
| ], designed by ]]] | |||
| After the successful completion of all the basic and middle education years, a ] is awarded. The high-school graduate is known as a ''bachiller'', because secondary basic school and middle education are traditionally considered together as a unit called ''bachillerato'' (sixth to eleventh grade). Students in their final year of middle education take the ] (now renamed Saber 11) to gain access to higher education (''Educación superior''). This higher education includes undergraduate professional studies, technical, technological and intermediate professional education, and post-graduate studies. Technical professional institutions of Higher Education are also opened to students holder of a qualification in Arts and Business. This qualification is usually awarded by the ] after a two years curriculum.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://unevoc.unesco.org/go.php?q=World+TVET+Database&ct=COL|title=UNESCO-UNEVOC World TVET Database|website=unevoc.unesco.org}}</ref> | |||
| Other famous Colombians include the ] winning author ], the artist ], the writers ], ], ] and ], the musicians ], ], ] and ], and the actors ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| ''Bachilleres'' (high-school graduates) may enter into a professional undergraduate career program offered by a university; these programs last up to five years (or less for technical, technological and intermediate professional education, and post-graduate studies), even as much to six to seven years for some careers, such as medicine. In Colombia, there is not an institution such as college; students go directly into a career program at a university or any other educational institution to obtain a professional, technical or technological title. Once graduated from the university, people are granted a (professional, technical or technological) diploma and licensed (if required) to practice the career they have chosen. For some professional career programs, students are required to take the Saber-Pro test, in their final year of undergraduate academic education.<ref name="sistema educativo">{{cite web|url=http://menweb.mineducacion.gov.co/nnormas/normas_basicas_4.swf |title=Ministerio de Educación de Colombia, Estructura del sistema educativo |date=29 June 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070629194012/http://menweb.mineducacion.gov.co/nnormas/normas_basicas_4.swf |archive-date=29 June 2007 }}</ref> | |||
| The ] developed mainly from the food traditions of European countries. ], ] and ] culinary influences can all be seen in Colombian cooking. The cuisine of neighboring ], ], ] and ], as well as the ] of the country's indigenous inhabitants, have all influenced Colombian food. | |||
| Public spending on education as a proportion of gross domestic product in 2015 was 4.49%. This represented 15.05% of total government expenditure. The ] stood at 113.56% and 98.09% respectively. ] was 14.42 years. A total of 94.58% of the population aged 15 and older were recorded as literate, including 98.66% of those aged 15–24.<ref name="UNESCO">{{cite web|url=https://uis.unesco.org/en/country/co|title=UNESCO Institute for Statistics Colombia Profile|access-date=5 May 2017|archive-date=6 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170506052541/http://uis.unesco.org/en/country/co|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Many ], both objects and themes, have arisen from Colombia's diverse cultural traditions and aim to represent what Colombia, and the Colombian people, have in common. Cultural expressions in Colombia are promoted by the government through the ].{{clear}} | |||
| == |
===Crime=== | ||
| ], displayed in ]. A subdivision of the ] for the fight against organized crime and terrorist acts.]] | |||
| {{portal|Colombia|Flag of Colombia.svg}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Excerpt|Crime in Colombia}} | ||
| {{clear}} | |||
| <!-- Please place links to all topics directly related to Colombia in the ] --> | |||
| {{Colombia topics|state=uncollapsed}} | |||
| === Urbanization === | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Colombia is a highly urbanized country with 77.1% of the population living in urban areas. The largest cities in the country are ], with 7,387,400 inhabitants, ], with 2,382,399 inhabitants, ], with 2,172,527 inhabitants, and ], with 1,205,284 inhabitants.<ref>{{cite web|title=Largest cities|url=https://www.dane.gov.co/files/varios/informacion-capital-DANE-2019.pdf|publisher=Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica (DANE)|access-date=10 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| {{Largest cities in Colombia}} | |||
| == |
== Culture == | ||
| {{Main|Culture of Colombia}} | |||
| * {{es icon}} Academia Colombiana de Historia (1986), ''Historia extensa de Colombia'' (41 volumes). Bogotá: Ediciones Lerner, 1965-1986. ISBN 9589501338 (Complete work) | |||
| {{See also|Festivals in Colombia|Colombian folklore}} | |||
| * {{es icon}} Barrios, Luis (1984), ''Historia de Colombia''. Fifth edition, Bogotá: Editorial Cultural | |||
| Colombia lies at the crossroads of ] and the broader American continent, and as such has been hit by a wide range of cultural influences. ], ] and other ], ], ], ], and ] influences, as well as other Latin American cultural influences, are all present in Colombia's modern culture. Urban migration, industrialization, globalization, and other political, social and economic changes have also left an impression.{{citation needed|date=July 2021}} | |||
| * {{es icon}} Bedoya F., Víctor A. (1944), ''Historia de Colombia: independencia y república con bases fundamentales en la colonia''. Colección La Salle, Bogotá: Librería Stella | |||
| * Bushnell, David (1993), ''The Making of Modern Colombia: A Nation in Spite of Itself''. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0520082893 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Caballero Argaez, Carlos (1987), ''50 años de economía: de la crisis del treinta a la del ochenta''. Second edition, Colección Jorge Ortega Torres, Bogotá: Editorial Presencia, Asociación Bancaria de Colombia. ISBN 9589040039 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Cadavid Misas, Roberto (2004), ''Cursillo de historia de Colombia: de la conquista a la independencia''. Bogotá: Intermedio Editores. ISBN 9587091345 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Calderón Schrader, Camilo; Gil, Antonio; Torras, Daniel (2001), ''Enciclopedia de Colombia'' (4 volumes). Barcelona: Céano Grupo Editorial, 2001. ISBN 8449419476 (Complete work) | |||
| * {{es icon}} Calderón Schrader, Camilo (1993), ''Gran enciclopedia de Colombia'' (11 volumes). Bogotá: Círculo de Lectores. ISBN 9582802944 (Complete work) | |||
| * {{es icon}} Cavelier Gaviria, Germán (2003), ''Centenario de Panamá: una historia de la separación de Colombia en 1903''. Bogotá: Universidad Externado de Colombia. ISBN 9586167186 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Forero, Manuel José (1946), ''Historia analítica de Colombia desde los orígenes de la independencia nacional''. Second edition, Bogotá: Librería Voluntad. | |||
| * {{es icon}} Gómez Hoyos, Rafael (1992), ''La independencia de Colombia''. Madrid: Editorial Mapfre, Colecciones Mapfre 1492. ISBN 8471005964 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Granados, Rafael María (1978), ''Historia general de Colombia: prehistoria, conquista, colonia, independencia y Repúbica''. Eighth edition, Bogotá: Imprenta Departamental Antonio Nariño. | |||
| * {{es icon}} Hernández de Alba, Guillermo (2004), ''Como nació la República de Colombia''. Colección Bolsilibros. Bogotá: Academia Colombiana de Historia. ISBN 9588040353 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Hernández Becerra, Augusto (2001), ''Ordenamiento y desarreglo territorial en Colombia''. Bogotá: Universidad Externado de Colombia, ISBN 9586165558 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Hernández Rodríguez, Guillermo (1949), ''De los chibchas a la colonia y a la república''. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Sección de Extensión Cultural. | |||
| * Hylton, Forrest (2006), ''Evil Hour in Colombia''. New York: Verso Books. ISBN 1844675513 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Jaramillo Uribe, Jaime; Tirado Mejía, Álvaro; Calderón Schrader, Camilo (2000), ''Nueva historia de Colombia'' (12 volumes). Bogotá: Planeta Colombiana Editorial. ISBN 9586142515 (Complete work) | |||
| * Kirk, Robin (2004), ''More Terrible Than Death: Drugs, Violence, and America's War in Colombia''. United States: PublicAffairs. ISBN 1586482076 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Ocampo López, Javier (1999), ''El proceso ideológico de la emancipación en Colombia''. Colección La Línea de Horizonte, Bogotá: Editorial Planeta. ISBN 9586147924 | |||
| * Ospina, William (2006), ''Once Upon a Time There Was Colombia''. Colombia: Villegas Asociados. ISBN 9588156645 | |||
| * Palacios, Marco (2006), ''Between Legitimacy and Violence: A History of Colombia, 1875-2002''. United States of America: Duke University Press. ISBN 0822337673 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Reichel-Dolmatoff, Gerardo (1998), ''Colombia indígena''. Medellín: Hola Colina. ISBN 9586382761 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Restrepo, José Manuel (1974), ''Historia de la revolución de la República de Colombia''. Medellín: Editorial Bedout. | |||
| * {{es icon}} Rivadeneira Vargas, Antonio José (2002), ''Historia constitucional de Colombia 1510-2000''. Third edition, Tunja: Editorial Bolivariana Internacional. | |||
| * Simons, Geoff (2004), ''Colombia: A Brutal History''. London: Saqi Books. ISBN 0863567584 | |||
| * Smith, Stephen (1999), ''Cocaine Train: Travels in Colombia''. London: Little, Brown. ISBN 0316647497 | |||
| * {{es icon}} Tovar Pinzón, Hermes (1975), ''El movimiento campesino en Colombia durante los siglos XIX y XX''. Second edition, Bogotá: Ediciones Libres. | |||
| * {{es icon}} Trujillo Muñoz Augusto (2001), ''Descentralización, regionalización y autonomía local''. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional de Colombia. | |||
| * {{es icon}} Vidal Perdomo Jaime (2001), ''La Región en la Organización Territorial del Estado''. Bogotá: Universidad del Rosario. | |||
| Many ], both objects and themes, have arisen from Colombia's diverse cultural traditions and aim to represent what Colombia, and the Colombian people, have in common. Cultural expressions in Colombia are promoted by the government through the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=OECD |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Jcp8EAAAQBAJ&dq=Cultural+expressions+in+Colombia+are+promoted+by+the+government+through+the+Ministry+of+Culture.&pg=PA66 |title=Local Economic and Employment Development (LEED) Culture and the Creative Economy in Colombia Leveraging the Orange Economy: Leveraging the Orange Economy |date=21 July 2022 |publisher=OECD Publishing |isbn=978-92-64-65268-2 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{sisterlinks|Colombia}} | |||
| === Literature === | |||
| ; Government | |||
| {{Main|Colombian literature}} | |||
| * {{es icon}} - Colombia Online Government web site | |||
| ] prize winner ]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/literature/laureates/1982/marquez-lecture.html|title=Gabriel García Márquez – Nobel Lecture|publisher=nobelprize.org |access-date=12 March 2017}}</ref>]] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] | |||
| * - National System of Cultural Information | |||
| * {{es icon}} - Maps of Colombia | |||
| Colombian literature dates back to pre-Columbian era; a notable example of the period is the epic poem known as the ''Legend of Yurupary''.<ref name="The Legend of Yurupary">{{cite book|title=Legend of Yurupary|publisher=Cooperativa Editorial Magisterio|isbn=978-958-20-0836-9|year=2006|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=s_ADFUglHo0C&pg=PP1}}</ref> In Spanish colonial times, notable writers include ] ('']''), Hernando Domínguez Camargo and his epic poem to San Ignacio de Loyola, ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://sites.google.com/site/cursodeliteraturacolombiana/unidad-2/los-cronistas |title=Cronistas del Nuevo Reino de Granada |publisher=ihlc.udea.edu.co |access-date=31 March 2014 |archive-date=28 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200528073604/https://sites.google.com/site/cursodeliteraturacolombiana/unidad-2/los-cronistas |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ; Other | |||
| * {{wikitravel}} | |||
| * at ] | |||
| * {{CIA World Factbook link|co|Colombia}} | |||
| * at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| * {{dmoz|Regional/South_America/Colombia}} | |||
| * {{es icon}} - ] in Colombia | |||
| * - ] | |||
| * - ] | |||
| * - ] | |||
| * - ] | |||
| * | |||
| Post-independence literature linked to Romanticism highlighted ], ], ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co/pdf/8/8_2024432110.pdf |title=Vida, pasión y muerte del romanticismo en Colombia |publisher=biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co |access-date=31 March 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141024064257/http://biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co/pdf/8/8_2024432110.pdf |archive-date=24 October 2014 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://ihlc.udea.edu.co/delc/index.php?tema=484&/Romanticismo |title=Romanticismo – Diccionario electrónico de la literatura colombiana |publisher=ihlc.udea.edu.co |date=5 November 2007 |access-date=1 April 2014 |archive-date=14 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210214043616/https://ihlc.udea.edu.co/delc/index.php?tema=484&/Romanticismo |url-status=dead }}</ref> In the second half of the nineteenth century and early twentieth century the literary genre known as '']'' became popular; great writers of this period were ], ] and ] (the latter of whom wrote notable works of children's literature).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.biblioteca.org.ar/libros/155763.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.biblioteca.org.ar/libros/155763.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Colombian children's literature|publisher=biblioteca.org.ar |date=12 March 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://ihlc.udea.edu.co/delc/index.php?tema=477&/Costumbrismo |title=Costumbrismo – Diccionario electrónico de la literatura colombiana |publisher=ihlc.udea.edu.co |date=5 November 2007 |access-date=1 April 2014 |archive-date=8 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210208045557/https://ihlc.udea.edu.co/delc/index.php?tema=477&/Costumbrismo |url-status=dead }}</ref> Within that period, authors such as ], ], ], ] and ] developed the ] movement.<ref>{{cite book |title=Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. Del siglo XIX al siglo XX: debates sobre la cultura nacional |author1=Jaramillo, M.M. |author2=Osorio, B. |author3=Robledo, A. |year=2000 |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapI.pdf |language=es |access-date=13 March 2017 |archive-date=13 March 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170313044900/http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapI.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>Rodríguez-Arenas, F.M. (2006). Bibliografía de la literatura colombiana del siglo XIX: AL. Stockcero, Inc.</ref><ref>Rodríguez-Arenas, F.M. (2006). Bibliografía de la literatura colombiana del siglo XIX: MZ. Stockcero, Inc.</ref> In 1872, Colombia established the ], the first Spanish language academy in the Americas.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.colombiaaprende.edu.co/html/home/1592/article-130142.html |title=Colombian Academy of Language |publisher=colombiaaprende.edu.co |language=es |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923205543/http://www.colombiaaprende.edu.co/html/home/1592/article-130142.html |archive-date=23 September 2015 |url-status=dead }}</ref> ] wrote the groundbreaking ''Cantos Populares de mi Tierra'' (1877), the first book of poetry by an Afro-Colombian author.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://thecitypaperbogota.com/culture/obeso-poet-of-the-magdalena/ |title=Obeso: Poet of the Magdalena |date=6 March 2014 |publisher=thecitypaperbogota.com |access-date=9 March 2014}}</ref><ref name="Candelario Obeso">{{cite book|title="Chambacú, la historia la escribes tú": ensayos sobre cultura afrocolombiana (Candelario Obeso)|author=Lucía Ortiz|publisher=IBEROAMERICANA|isbn=978-84-8489-266-3|year=2007|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VlfcbtH9EY4C&pg=PP1|pages=47–69|language=es}}</ref> | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| |title = Geographic locale | |||
| Between 1939 and 1940 seven books of poetry were published under the name '']'' in the city of Bogotá that significantly influenced the country; they were edited by the poet Jorge Rojas.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/publicacionesbanrep/boletin/bole69/bolet1a.htm |title=Artículo: Piedra y Cielo a contraluz |publisher=banrepcultural.org |language=es |access-date=18 February 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131106074150/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/publicacionesbanrep/boletin/bole69/bolet1a.htm |archive-date=6 November 2013 }}</ref> In the following decade, ] founded the movement of "]" in response to the violence of the time;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/publicacionesbanrep/boletin/boleti5/bol33/nadais10.htm |title=Gonzalo Arango |publisher=banrepcultural.org |language=es |access-date=18 February 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120119041103/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/publicacionesbanrep/boletin/boleti5/bol33/nadais10.htm |archive-date=19 January 2012 }}</ref> he was influenced by ], ], and the thought of another great Colombian writer: ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.otraparte.org/fernando-gonzalez/vida/biografia.html |title=Fernando González Ochoa |publisher=otraparte.org |date=12 March 2017 |access-date=13 March 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190513161548/https://www.otraparte.org/fernando-gonzalez/vida/biografia.html |archive-date=13 May 2019 |url-status=dead }}</ref> During the ], successful writers emerged, led by ] ] and his magnum opus, '']'', ], ], and ], a writer who was awarded the ] and the ].<ref>{{cite book|title=Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. La nación moderna y sus sistemas simbólicos |author1=Jaramillo, M. M.|author2=Osorio, B. |author3=Robledo, A.|year=2000|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapII.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapII.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. El discurso de la nación moderna: continuidades y rupturas |author1=Jaramillo, M. M.|author2=Osorio, B. |author3=Robledo, A.|year=2000|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapIII.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.banrepcultural.org/sites/default/files/lablaa/literatura/narrativa/Volumen1CapIII.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |language=es}}</ref> | |||
| === Visual arts === | |||
| {{Main|Colombian art}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | direction =vertical | |||
| | width = 160 | |||
| | image1 ="Liegende mit Frucht" Skulptur von Fernando Botero in Bamberg - Deutschland.jpg | |||
| | caption1 = Work by the painter and sculptor ] | |||
| | image2 = Alonso de Narvaez - Our Lady of Chiquinquira,1562.jpg | |||
| | caption2 = Colonial painting ] (1562) by ].<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=U6fOEAAAQBAJ&dq=virgin+of+chiquinquir%C3%A1+alonso+de+narvaez&pg=PA522|title=Hispanic American Religious Cultures|author=]|page=522|isbn=9781598841404|publisher=]|year=2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZXWRgP-0KBkC&dq=virgin+of+chiquinquir%C3%A1+alonso+de+narvaez&pg=PA671|title=Mary in Our Life. Atlas of the Names and Titles of Mary, the Mother of Jesus, and Their Place in Marian Devotion|author=Nicholas J. Santoro|page=671|isbn=9781462040223|publisher=]|year=2011}}</ref> She is the Catholic ] of Colombia. The original canvas is located in the ]. | |||
| | image3 = Santiago Martinez Delgado in the colombian congress.jpg | |||
| | caption3 = Mural by ] | |||
| }} | |||
| Colombian art has over 3,000 years of history. Colombian artists have captured the country's changing political and cultural backdrop using a range of styles and mediums. There is archeological evidence of ceramics being produced earlier in Colombia than anywhere else in the Americas, dating as early as 3,000 BCE.<ref name="donquijote.org">{{cite web| url=http://www.donquijote.org/culture/colombia/art/ |publisher=donquijote.org |title=Colombian Art|access-date=22 August 2013}}</ref><ref name="artecolombiano">{{cite book|title=El arte colombiano. Volume 3 of Selección Cultura colombiana|author=Francisco Gil Tovar|publisher=Plaza y Janes Editores Colombia s.a|isbn=978-958-14-0016-4|year=1985|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fre20PtG-ZAC&pg=PP1|language=es}}</ref> | |||
| The earliest examples of gold craftsmanship have been attributed to the Tumaco people<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/gold-museum/tumaco |publisher=banrepcultural.org |title=Tumaco: People and Gold on the Pacific Coast |access-date=22 August 2013 |archive-date=1 November 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131101233105/http://www.banrepcultural.org/gold-museum/tumaco |url-status=dead }}</ref> of the Pacific coast and date to around 325 BCE. Roughly between 200 BCE and 800 CE, the ], masters of ], entered its "classical period". They erected raised ] centers, ], and large stone ]s depicting ] and ] forms out of ].<ref name="artecolombiano" /><ref name="San Agustín">{{cite web| url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/744|publisher=UNESCO| title=San Agustín Archaeological Park|access-date=22 August 2013}}</ref> | |||
| Colombian art has followed the trends of the time, so during the 16th to 18th centuries, ] had a huge influence on Colombian art, and the popular ] style was replaced with ] when the Bourbons ascended to the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/todaslasartes/ext/ext13.htm#12b|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=El espíritu barroco en el arte colonial|author=Marta Fajardo De Rueda|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|archive-date=14 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171014120713/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/todaslasartes/ext/ext13.htm#12b|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/junio2001/joaquin.htm|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Joaquín Gutiérrez, el "pintor de los virreyes": Expresión del estilo rococó en la Nueva Granada|author=Uribe Restrepo, Fernando|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|archive-date=22 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170422013256/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/junio2001/joaquin.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> During this era, in the Spanish colony, the most important Neogranadine (Colombian) painters were ], ], ], ], ] and ], of which their works are preserved. Also important was ] who, although born in the Province of Seville, spent most of his life in colonial Colombia, also the Italian ], lived in Colombia and Peru, and left works of art preserved in several churches in ] city. | |||
| During the mid-19th century, one of the most remarkable painters was ], who produced a series of good quality paintings depicting the people and their customs of different Colombian regions. Also noteworthy in the 19th century were ], ], ], ], ], ], between many others. | |||
| More recently, Colombian artists ] and ] started the Colombian Murial Movement in the 1940s, featuring the ] features of ].<ref name="donquijote.org" /><ref name="artecolombiano" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/biografias/gomepedr.htm|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Pedro Nel Gómez Agudelo|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|archive-date=9 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160509225510/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/biografias/gomepedr.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Miradas a la plástica colombiana de 1900 a 1950: un debate histórico y estético|author1=Luz Guillermina Sinning Téllez|author2=Ruth Nohemí Acuña Prieto|publisher=U. Externado de Colombia|isbn=978-958-710-748-7|year=2011|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yA5joGlOnIEC&pg=PA7|language=es}}</ref> Since the 1950s, the Colombian art started to have a distinctive point of view, reinventing traditional elements under the concepts of the 20th century. Examples of this are the Greiff ]s by ], showing what the Colombian art could do with the new techniques applied to typical Colombian themes. Carlos Correa, with his ]atic "Naturaleza muerta en silencio" (silent dead nature), combines geometrical ] and ]. ] is often considered as the father of modern Colombian painting, and one of the most influential artist in this period, due to his originality, the painting of Colombian landscapes with ] and ] use of animals, (specially the ]).<ref name="artecolombiano" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iadb.org/EXR/cultural/catalogues/Colombia/spabeggining1.htm|publisher=iadb.org|title=Puntos de partida en el arte contemporáneo de Colombia|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160416052215/http://www.iadb.org/EXR/cultural/catalogues/Colombia/spabeggining1.htm|archive-date=16 April 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/coleccion-de-arte-banco-de-la-republica/cl%C3%A1sicos-experimentales-y-radicales-1950-%E2%80%93-1980|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Clásicos, experimentales y radicales 1950–1980|author1=Carmen María Jaramillo|author2=Sylvia Suárez|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|archive-date=10 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160510001359/http://www.banrepcultural.org/coleccion-de-arte-banco-de-la-republica/cl%C3%A1sicos-experimentales-y-radicales-1950-%E2%80%93-1980|url-status=dead}}</ref> ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] are some of the Colombian artists featured at the international level.<ref name="donquijote.org" /><ref>{{cite book|title=Arte en Colombia, 1981–2006|author=Carlos Arturo Fernández|publisher=Universidad de Antioquia|isbn=978-958-714-017-0|year=2007|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=D8bHJutOqqwC&pg=PP1 |language=es}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Geografía del arte en Colombia. Biblioteca del Gran Cauca: Colección clásicos regionales|author=Eugenio Barney Cabrera|publisher=Universidad del Valle|isbn=978-958-670-450-2 |year=2005|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=r6V2T45r03UC&pg=PP1 |language=es}}</ref><ref name="museorayo">{{cite web|url=http://www.museorayo.co/vidaObraOR.php|title=Omar RayoM|publisher=museorayo.co|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160510001306/http://www.museorayo.co/vidaObraOR.php|archive-date=10 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| The Colombian sculpture from the sixteenth to 18th centuries was mostly devoted to ] of ecclesiastic art, strongly influenced by the Spanish schools of ] sculpture. During the early period of the Colombian republic, the national artists were focused in the production of sculptural portraits of politicians and public figures, in a plain ] trend.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.academia.edu/2074247|publisher=academia.edu|title=Pietro Tenerani y la escultura en Colombia en el siglo XIX|author=Carolina Vanegas Carrasco |language=es|access-date=9 May 2016}}</ref> During the 20th century, the Colombian sculpture began to develop a bold and innovative work with the aim of reaching a better understanding of national sensitivity.<ref name="artecolombiano" /><ref name="Colombian sculptors">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia.com/cultura/resenas/escultura.asp|title=Colombian sculptors|publisher=colombia.com|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150723034605/http://www.colombia.com/cultura/resenas/escultura.asp|archive-date=23 July 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Colombian photography was marked by the arrival of the ]. ] was who brought the daguerreotype process to Colombia in 1841. The Piloto public library has Latin America's largest archive of negatives, containing 1.7 million antique photographs covering Colombia 1848 until 2005.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://colombiareports.co/latin-americas-largest-antique-negative-archive-medellins-public-library/| title=Latin America's largest antique negative archive in Medellín| date=16 December 2013|publisher=colombiareports.co|access-date=16 December 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co/pdf/10/phot-mec-cfa.pdf |title=Apuntes para una cronología de la fotografía en Antioquía |language=es |access-date=22 August 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140812182737/http://biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co/pdf/10/phot-mec-cfa.pdf |archive-date=12 August 2014 }}</ref> | |||
| The Colombian press has promoted the work of the ]s. In recent decades, ]s, internet and ]s have been fundamental to the growth of the comic in Colombia.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.elespectador.com/noticias/cultura/entender-los-comics-colombia-articulo-516194|publisher=elespectador.com|title=Para entender los cómics en Colombia|author=Pablo Guerra |language=es|access-date=9 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bibliotecanacional.gov.co/comic/especial-entre-vi%C3%B1etas-la-historieta-colombiana-en-prensa|publisher=bibliotecanacional.gov.co|title=Especial Entre Viñetas la historieta colombiana en prensa|author=Pablo Guerra|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160510044919/http://www.bibliotecanacional.gov.co/comic/especial-entre-vi%C3%B1etas-la-historieta-colombiana-en-prensa|archive-date=10 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://facartes.unal.edu.co/muvirt/cronologia/index.html|publisher=Facultad de Artes: Universidad Nacional de Colombia|title=Museo Virtual de la Historieta Colombiana – Cronología|language=es|access-date=9 May 2016|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160311233941/http://www.facartes.unal.edu.co/muvirt/cronologia/index.html|archive-date=11 March 2016}}</ref> | |||
| === Architecture === | |||
| {{Main|Architecture of Colombia}} | |||
| {{See also|Muisca architecture}} | |||
| Throughout the times, there have been a variety of ], from those of indigenous peoples to contemporary ones, passing through colonial (military and religious), Republican, transition and modern styles.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/1-introduccion/periodizacion/ |title=Periodización |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210036/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/1-introduccion/periodizacion/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] main plaza, ]]] | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| Ancient habitation areas, longhouses, ], roads as the ], cemeteries, ]s and ]es are all part of the ].<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/2-nivel-formativo-tribal/ |title=Nivel Formativo Tribal. La Casa Comunal |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210203/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/2-nivel-formativo-tribal/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> Some prominent indigenous structures are the ] and ] archaeological site of ],<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/1-nivel-paleoindio/ |title=Nivel Paleoindio. Abrigos rocosos del tequendama |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210129/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/1-nivel-paleoindio/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> ] (a park that contains the largest concentration of ] monumental ]s with side chambers),<ref>{{cite web| url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/743|publisher=UNESCO| title=National Archeological Park of Tierradentro|access-date=9 June 2016}}</ref> the largest collection of religious monuments and ] sculptures in South America, located in ],<ref name="San Agustín" /><ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/3-los-cacicazgos/ |title=Los cacicazgos. Las Aldeas y las Tumbas |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160602122708/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/3-los-cacicazgos/ |archive-date=2 June 2016 }}</ref> ] (an archaeological site with a series of terraces carved into the mountainside, a net of tiled roads, and several circular plazas), and the large villages mainly built with ], wood, cane, and mud.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/4-los-tayrona-y-los-muisca-la-preciudad/ |title=Los Tayrona y los Muisca: La Preciudad |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160602202706/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-i/4-los-tayrona-y-los-muisca-la-preciudad/ |archive-date=2 June 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| Architecture during the period of conquest and colonization is mainly derived of adapting ] to local conditions, and ], especially ]n and ]n, can be easily seen.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/3-la-america-espanola-1730-1810/ |title=La América española. El apasionamiento escenográfico, 1730–1810 |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210625/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/3-la-america-espanola-1730-1810/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> When Europeans founded cities two things were making simultaneously: the dimensioning of geometrical space (], street), and the location of a tangible point of ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/sept2001/fundacio.htm |title=Fundaciones coloniales y republicanas en Colombia: normas, trazado y ritos fundacionales |publisher=Revista Credencial Historia |access-date=10 June 2016 |author=Agustín, José |language=es |archive-date=14 August 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110814065957/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/sept2001/fundacio.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> The construction of ]s was common throughout the Caribbean and in some cities of the interior, because of the dangers posed to Spanish colonial settlements from English, French and Dutch ] and hostile indigenous groups.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/1-la-conquista-1500-1550/ |title=La Conquista. El dominio del territorio, 1500–1550 |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210435/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/1-la-conquista-1500-1550/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> Churches, chapels, schools, and hospitals belonging to ] have a great urban influence.<ref name="1550–1750">{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/2-la-espana-americana-1550-1750/ |title=La España americana. Consolidación de tipologías, 1550–1750 |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210511/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-ii/2-la-espana-americana-1550-1750/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> ] is used in military buildings and public spaces.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/?cat=14304 |title=Arquitectura colonial |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210403/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/?cat=14304 |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> Marcelino Arroyo, ] and Domingo de Petrés were great representatives of ].<ref name="1550–1750" /> | |||
| The ] is a great representative of romanticism.<ref>{{cite book| url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/1-el-capitolio-y-tomas-reed-d-capitulo-iii/| title=El Capitolio y Tomás Reed| publisher=Universidad Nacional| author=Silvia Arango| year=1990| location=Bogotá| isbn=958-17-0061-7| url-status=dead| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210826/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/1-el-capitolio-y-tomas-reed-d-capitulo-iii/| archive-date=10 June 2016| df=dmy-all}}</ref> Wood was extensively used in doors, windows, railings, and ceilings during the colonization of ]. The ] architecture acquires a strong ].<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/2-la-arquitectura-de-la-colonizacion/ |title=La arquitectura de la colonización |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610210907/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/2-la-arquitectura-de-la-colonizacion/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> The ] in Bogotá is a lavish example of architecture from the 19th century.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/3-la-arquitectura-urbana-de-fin-de-siglo/ |title=La arquitectura urbana de fin de siglo |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160506073539/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iii/3-la-arquitectura-urbana-de-fin-de-siglo/ |archive-date=6 May 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The quintas houses with innovations in the ] conception are some of the best examples of the Republican architecture; the Republican action in the city focused on the design of three types of ]: parks with forests, small ]s and ] and the ] was most commonly used for the design of churches.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iv/2-la-generacion-republicana/ |title=La generación republicana |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610211218/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-iv/2-la-generacion-republicana/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| Deco style, ], ] ] and ] ] resources significantly influenced the architecture of Colombia, especially during the transition period.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-v/1-la-persistencia-de-los-estilos/ |title=La persistencia de los estilos |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304211009/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-v/1-la-persistencia-de-los-estilos/ |archive-date=4 March 2016 }}</ref> ] contributed with new construction technologies and new ] (steel, ], glass and synthetic materials) and the ] architecture and ] also have a great influence.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vi/3-primera-fase/ |title=Primera fase: los alardes de la técnica |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610212041/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vi/3-primera-fase/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> The most influential architects of the modern movement were ] and Fernando Martínez Sanabria.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vi/4-segunda-fase/ |title=Segunda fase: la asimilación consiente |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160610212127/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vi/4-segunda-fase/ |archive-date=10 June 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| The ] of Colombia is designed to give greater importance to the ], this architecture takes into account the specific ] and is also an architecture that appeals to the ]s.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vii/3-arquitectura-de-los-sentidos-y-contextualidad/ |title=Arquitectura de los sentidos y contextualidad |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160611005914/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vii/3-arquitectura-de-los-sentidos-y-contextualidad/ |archive-date=11 June 2016 }}</ref> The ] of Colombia has been promoted in recent years.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vii/2-la-recuperacion-del-pasado/ |title=La recuperación del pasado |publisher=Universidad Nacional |author=Silvia Arango |year=1990 |location=Bogotá |isbn=958-17-0061-7 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160611010039/http://aplicaciones.virtual.unal.edu.co/blogs/hacolombia/category/cap-vii/2-la-recuperacion-del-pasado/ |archive-date=11 June 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| === Music === | |||
| {{Main|Music of Colombia}} | |||
| Colombia has a vibrant collage of talent that touches a full spectrum of ]s. It is known as the land of a thousand rhythms, at around 1,024 folk rhythms. Musicians, composers, music producers and singers from Colombia are recognized internationally such as ], ], ] and others.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cromos.com.co/especial-colombia/articulo-147471-personajes-destacados-la-musica-vibra-los-cinco-continentes|publisher=cromos.com.co|title=Colombianos que se destacan: Música que vibra por todo el mundo|language=es|access-date=24 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524214703/http://www.cromos.com.co/especial-colombia/articulo-147471-personajes-destacados-la-musica-vibra-los-cinco-continentes|url-status=dead}}</ref> Colombian music blends European-influenced guitar and song structure with large ] and percussion instruments from the indigenous population, while its percussion structure and dance forms come from Africa. Colombia has a diverse and dynamic musical environment.<ref name="about.com">{{cite web|url=http://latinmusic.about.com/od/countrie1/p/PRO04BASICS.htm|publisher=about.com|title=Colombian music|access-date=22 August 2013|archive-date=2 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131102075148/http://latinmusic.about.com/od/countrie1/p/PRO04BASICS.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ], an important cultural figure in the ], Luis Antonio Calvo and Blas Emilio Atehortúa are some of the greatest exponents of the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://facartes.unal.edu.co/compositores/html/_compositores.html|publisher=facartes.unal.edu.co|title=Colombian composers|language=es|access-date=29 April 2017|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160411030708/http://facartes.unal.edu.co/compositores/html/_compositores.html|archive-date=11 April 2016}}</ref> The ] is one of the most active orchestras in Colombia.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://patrimoniocultural.bogota.unal.edu.co/internas-auditorio/acerca-de-la-ofb.html|publisher=patrimoniocultural.bogota.unal.edu.co|title=Bogotá Philharmonic|language=es|access-date=29 April 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Caribbean music has many vibrant rhythms, such as ] (it is played by the ]s, the drums, the gaitas and ]), ] (it is a monotonous but joyful rhythm), ] (with its fast rhythm and constant ]) and the "]", which originated in the northern part of the ] coast (the rhythm is mainly played by the caja, the guacharaca, and ]).<ref name="Colombian music">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia-sa.com/musica/musica-in.html|title=Colombian music|publisher=colombia-sa.com |access-date=25 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/3|title=Músicas Caribe Occidental|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150806233314/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/3|archive-date=6 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/2|title=Músicas Caribe Oriental|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150807074711/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/2|archive-date=7 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=13&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Bolívar|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=9 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160509175109/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=13&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=20&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Cesar|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524081524/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=20&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The music from the ], such as the ], is characterized by its strong use of drums (instruments such as the native ], the conunos, the ], the ], and the cuatro guasas or tubular rattle). An important rhythm of the south region of the Pacific coast is the ] (it is used in dance shows due to the striking colours of the costumes).<ref name="Colombian music" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=27&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Chocó|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524081612/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=27&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=19&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Cauca|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524081657/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=19&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref> Marimba music, traditional chants and dances from the Colombia South Pacific region are on ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unesco.org/culture/ich/en/RL/marimba-music-traditional-chants-and-dances-from-the-colombia-south-pacific-region-and-esmeraldas-province-of-ecuador-01099|title=Marimba music, traditional chants and dances from the Colombia South Pacific region |publisher=unesco.org |access-date=25 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/9|title=Músicas Pacífico Sur|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808023628/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/9|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/4|title=Músicas Pacífico Norte|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808023619/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/4|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ] of the ] band. The ], along with ], are the two most popular Colombian folk music genres heard in Latin America.]] | |||
| Important musical rhythms of the ] are the ] (dance of Andean folklore arising from the transformation of the European contredance), the ] (it is played with guitar, ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/musica/tiple/indice.htm|title=Los Caminos del tiple|publisher=Bogotá: Ediciones AMP Damel.|year=1988|author=Puerta Zuluaga, D.|access-date=3 May 2017|archive-date=3 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170503084731/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/musica/tiple/indice.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> and ], the rhythm is danced by couples), the ] (a rhythm inspired by the Austrian ] and the Colombian "danza", the lyrics have been composed by well-known poets), the guabina (the ], the ] and the ] are the basic instruments), the ] (it originated in ] and ] Departments, the rhythm is joyful and fast).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=11&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Bogotá|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524082507/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=11&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=73&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos -Tolima|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524082541/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=73&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=41&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Huila|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524082605/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=41&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/5|title=Músicas Andinas Centro-Oriente|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808030945/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/5|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/6|title=Músicas Andinas Nor-Occidente|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808023624/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/6|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> Apart from these traditional rhythms, ] has spread throughout the country, and the city of ] is considered by many salsa singers to be 'The New Salsa Capital of the World'.<ref name="Colombian music" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/7|title=Músicas Andinas Centro-Sur|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708222015/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/7|archive-date=8 July 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/10|title=Músicas Andinas Sur-Occidente|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150812043609/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/10|archive-date=12 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The instruments that distinguish the music of the ] are the ], the ] (a type of four-stringed guitar) and maracas. Important rhythms of this region are the ] (a fast rhythm and there is also tapping as a result of its ] ancestry) and the ] (it is heard a lot while ]s are working).<ref name="Colombian music" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=50&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Meta|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524083313/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=50&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=85&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Casanare|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524083348/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=85&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/8|title=Músicas Llaneras|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808030949/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/8|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The music of the Amazon region is strongly influenced by the indigenous religious practices. Some of the musical instruments used are the manguaré (a musical instrument of ] type, consisting of a pair of large ]s), the ] (melodic instrument), the ], the ]s, ]s, and different types of flutes.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=86&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Putumayo|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524114856/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=86&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=91&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Amazonas|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524114935/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=91&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/11|title=Músicas de Frontera|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808023614/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/11|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The music of the ] is usually accompanied by a ], a ], a ], a guitar and ]s. Some popular archipelago rhythms are the ], the ], the ] and the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/1|title=Músicas Isleñas|publisher=territoriosonoro.org|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150808030939/http://www.territoriosonoro.org/CDM/tradicionales/ejes/visualizar/1|archive-date=8 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=88&COLTEM=222|title=Ritmos – Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina|publisher=sinic.gov.co|language=es|access-date=25 May 2016|archive-date=24 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160524084024/http://www.sinic.gov.co/SINIC/ColombiaCultural/ColCulturalBusca.aspx?AREID=3&SECID=8&IdDep=88&COLTEM=222|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| === Popular culture === | |||
| {{Main|Theater of Colombia|Cinema of Colombia|Media of Colombia}} | |||
| ] is the oldest cinema event in Latin America. The central focus is on films from Ibero-America.<ref name="fiapf" />]] | |||
| Theater was introduced in Colombia during the ] in 1550 through ] companies. Colombian theater is supported by the Ministry of Culture and a number of private and state owned organizations. The ] is the cultural event of the highest importance in Colombia and one of the biggest theater festivals in the world.<ref name="Theater Festival">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia.co/en/this-is-colombia/culture/art/six-surprising-facts-bogotas-ibero-american-theater-festival/|title=Six surprising facts about Bogota's Ibero-American Theater Festival|date=2 March 2016|publisher=colombia.co|access-date=17 November 2017|archive-date=17 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171117141147/http://www.colombia.co/en/this-is-colombia/culture/art/six-surprising-facts-bogotas-ibero-american-theater-festival/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Other important theater events are: The Festival of Puppet The Fanfare (Medellín), The Manizales Theater Festival, The Caribbean Theatre Festival (Santa Marta) and The Art Festival of Popular Culture "Cultural Invasion" (Bogotá).<ref name="Theatre in Colombia">{{cite web| url=http://www.iti-worldwide.org/amt/countries/p_COLOMBIA.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080821123228/http://www.iti-worldwide.org/amt/countries/p_COLOMBIA.html |archive-date=21 August 2008 |publisher=iti-worldwide.org |title=Main performing arts festivals – Theatre History|access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref><ref name="theatrical production">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/colhoy/colo11.htm|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Theater of Colombia|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|archive-date=20 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020050211/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/historia/colhoy/colo11.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="teatro siglo XX">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/revista-80|publisher=Revista Credencial Historia|author=Reyes, Carlos José|title=El teatro en Colombia en el siglo XX|language=es|access-date=22 May 2016|archive-date=22 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522220735/http://www.banrepcultural.org/revista-80|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Although the ] is young as an industry, more recently the film industry was growing with support from the Film Act passed in 2003.<ref name="the Film Act passed in 2003">{{cite web|url=http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/ley_0814_2003.html|publisher=secretariasenado.gov.co|title=the Film Act passed in 2003|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013}}{{Dead link|date=September 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> Many film festivals take place in Colombia, but the two most important are the ], which is the oldest film festival in Latin America, and the ].<ref name="fiapf">{{cite web |url=http://www.fiapf.org/intfilmfestivals_2016_sites02.asp |publisher=fiapf.org |title=Competitive specialised film festivals |access-date=23 May 2016 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20161111113646/http://www.fiapf.org/intfilmfestivals_2016_sites02.asp |archive-date=11 November 2016}}</ref><ref name="film festivals">{{cite web|url=http://www.colombia.co/cultura/ocho-festivales-de-cine-imperdibles-en-colombia.html|publisher=colombia.co|title=Ocho festivales de cine imperdibles en Colombia|language=es|access-date=22 May 2016|archive-date=22 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522201326/http://www.colombia.co/cultura/ocho-festivales-de-cine-imperdibles-en-colombia.html|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ficcifestival.com/internas.php?cod=1$$-1$$-qm4nNEHfJmY0tyUjxz05wAXG3C6fwm|publisher=ficcifestival.com|title=La Corporación Festival Internacional de Cine de Cartagena|language=es|access-date=22 May 2016|archive-date=22 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522201249/http://www.ficcifestival.com/internas.php?cod=1$$-1$$-qm4nNEHfJmY0tyUjxz05wAXG3C6fwm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Some important national circulation newspapers are '']'' and '']''. ] has two privately owned TV networks and three state-owned TV networks with national coverage, as well as six regional TV networks and dozens of local TV stations. Private channels, ] and ] are the highest-rated. The regional channels and regional newspapers cover a department or more and its content is made in these particular areas.<ref name="Television in Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/exhibiciones/historia_tv/television_colombia.htm |publisher=banrepcultural.org |title=Television in Colombia |language=es |access-date=9 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150413231621/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/exhibiciones/historia_tv/television_colombia.htm |archive-date=13 April 2015 }}</ref><ref name="press">{{cite web |url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/un-papel-a-toda-prueba |publisher=banrepcultural.org |title=Un papel a toda prueba. 223 años de prensa diaria en Colombia |language=es |access-date=22 May 2016 |archive-date=22 May 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522183614/http://www.banrepcultural.org/un-papel-a-toda-prueba |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="The press in Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/comunicacion/la_prensa|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=La prensa en Colombia|language=es|access-date=22 May 2016|archive-date=22 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522183517/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/comunicacion/la_prensa|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Colombia has three major national ]: ], a state-run national radio; ] and ], privately owned networks with hundreds of affiliates. There are other national networks, including ], ], and Colmundo. Many hundreds of radio stations are registered with the ].<ref name="Radio in Colombia">{{cite web|url=http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/comunicacion/la_radio_en_colombia|publisher=banrepcultural.org|title=Radio in Colombia|language=es|access-date=22 May 2016|archive-date=22 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522190902/http://www.banrepcultural.org/blaavirtual/ayudadetareas/comunicacion/la_radio_en_colombia|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| === Cuisine === | |||
| {{Main|Colombian cuisine}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Colombia's varied cuisine is influenced by its diverse fauna and flora as well as the cultural traditions of the ethnic groups. Colombian dishes and ingredients vary widely by region. Some of the most common ingredients are: cereals such as rice and maize; tubers such as potato and ]; assorted ]s; meats, including beef, chicken, pork and goat; fish; and seafood.<ref name="Paseo de olla">{{cite web| url=http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo10.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo10.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Paseo de olla. Recetas de las cocinas regionales de Colombia – Biblioteca básica de cocinas tradicionales de Colombia|language=es|access-date=6 July 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo09-2.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo09-2.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Food presentation|language=es|access-date=22 January 2017}}</ref> Colombia cuisine also features a variety of tropical fruits such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], mora (]), ], ] and ].<ref name="Colombian cuisine">{{cite web| url=http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo09.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.mincultura.gov.co/Sitios/patrimonio/bibliotecas-de-cocinas/tomos/tomo09.pdf |archive-date=9 October 2022 |url-status=live |title=Gran libro de la cocina colombiana – Biblioteca básica de cocinas tradicionales de Colombia|language=es|access-date=6 July 2016}}</ref> Colombia is one of the world's largest consumers of fruit juices.<ref>Singh, Gitanjali M., et al. "Global, regional, and national consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, fruit juices, and milk: a systematic assessment of beverage intake in 187 countries." PLoS ONE 10.8 (2015): e0124845.</ref> | |||
| Among the most representative appetizers and soups are ] (fried green plantains), ] de gallina (chicken soup with root vegetables) and ] (potato and corn soup). Representative snacks and breads are ], ]s (corn cakes), ]s (fried sweet plantains with cheese), ] de ], ]s and ]s. Representative main courses are ], ], ], ] and fish dishes (such as ]), especially in coastal regions where ], ], ] and ]s are also eaten. Representative side dishes are papas chorreadas (potatoes with cheese), remolachas rellenas con huevo duro (beets stuffed with ]) and ] (coconut rice).<ref name="Colombian cuisine" /><ref name="Paseo de olla" /> ] is a current trend in big cities, although in general across the country the fruits and veggies are very natural and fresh.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nielsen.com/co/es/insights/news/20151/habitos-consumidores-colombianos.html|title=Hábitos de los consumidores en la tendencia saludable|publisher=nielsen.com|language=es|access-date=24 March 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150831012250/http://www.nielsen.com/co/es/insights/news/20151/habitos-consumidores-colombianos.html|archive-date=31 August 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Colombian Food">{{cite web|url=http://southamericanfood.about.com/od/exploresouthamericanfood/tp/Colombian-Food.htm|publisher=southamericanfood.about.com|title=Colombian Food; A List of Traditional and Modern Colombian Recipes|access-date=30 October 2013|archive-date=2 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131102023313/http://southamericanfood.about.com/od/exploresouthamericanfood/tp/Colombian-Food.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Representative desserts are ]s, ]s, ], ] made of guayaba (guava jelly), ] (coconut balls), casquitos de guayaba (candied guava peels), ]s, ]s, ] de ], ], ], ], dulce de ], dulce de ], ] de mojicón, and esponjado de ]. Typical sauces (salsas) are ] (tomato and onion sauce) and Colombian-style ].<ref name="Colombian cuisine" /><ref name="Paseo de olla" /> | |||
| Some representative beverages are ] (Tinto), ], ], ], ] colombiana, ] juice, ], ], ] and fresh fruit juices (often made with water or milk).<ref name="Colombian cuisine" /><ref name="Paseo de olla" /> | |||
| ===Sports=== | |||
| {{Main|Sport in Colombia}} | |||
| ] is a Colombian cyclist, two-time Olympic gold medalist and ].]] | |||
| ] is Colombia's national sport and is a team sport that involves launching projectiles to hit a target.<ref name="Tejo-Colombia's national sport.">{{cite web| url=http://thecitypaperbogota.com/uncategorized/homepage-featured/tejo-most-muddy-sport/ |publisher=thecitypaperbogota.com |title=Tejo – Colombia's national sport|date=28 August 2013 |access-date=28 August 2013}}</ref> But of all sports in Colombia, ] is the most popular. ] was the champion of the ], in which they set a new record of being undefeated, conceding no goals and winning each match. Colombia has been awarded "]" twice.<ref>. FIFA</ref> | |||
| Colombia is a hub for ]. The national team is a perennial powerhouse at the World Roller Speed Skating Championships.<ref name="Patinaje colombiano">{{cite web |url=http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/deportes/noticias/patinaje-colombiano-ganador-mundo |title=Patinaje colombiano, el más ganador del mundo |publisher=elpais.com.co |language=es |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140326235134/http://www.elpais.com.co/elpais/deportes/noticias/patinaje-colombiano-ganador-mundo |archive-date=26 March 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Colombia has traditionally been very good in ] and a large number of Colombian cyclists have triumphed in major competitions of cycling.<ref name="Colombian cycling">{{cite web|url=http://www.antena2.com.co/noticias/momentos-historicos-del-ciclismo-colombiano-69593|title=Historical moments of the Colombian cycling|publisher=antena2.com.co|language=es|access-date=2 June 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140705225607/http://www.antena2.com.co/noticias/momentos-historicos-del-ciclismo-colombiano-69593|archive-date=5 July 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Baseball is popular in cities like ] and ]. Of those cities have come good players like: ], ], who was champion of the ] in ] and ]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.retrosheet.org/boxesetc/2010/Irente0013352010.htm |title=The 2010 SF N World Series Batting Log for Edgar Renteria |publisher=Retrosheet |access-date=21 March 2011}}</ref> and others who have played in ]. Colombia was ] in 1947 and 1965.<ref name="béisbolglorias">{{cite web|url=http://blogs.eltiempo.com/playball/2010/03/26/recordando-a-nuestras-glorias-del-beisbol/|title=Recordando a nuestras glorias del béisbol|publisher=eltiempo.com|language=es|access-date=9 October 2013|archive-date=8 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140308015531/http://blogs.eltiempo.com/playball/2010/03/26/recordando-a-nuestras-glorias-del-beisbol/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ] is one of the sports that has produced more world champions for Colombia.<ref name="History of boxing">{{cite web|url=http://boxeodecolombia.com/historia-del-boxeo-en-colombia/|title=History of boxing in Colombia|date=13 July 2011|publisher=boxeodecolombia.com|access-date=7 March 2014|language=es|archive-date=7 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307230944/http://boxeodecolombia.com/historia-del-boxeo-en-colombia/|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Boxing champions">{{cite web|url=http://boxeodecolombia.com/nuestros-campeones/|title=Boxing champions|publisher=boxeodecolombia.com|access-date=7 March 2014|language=es|archive-date=7 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307230928/http://boxeodecolombia.com/nuestros-campeones/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ]s also occupies an important place in the sporting preferences of Colombians; ] is a race car driver known for winning 7 Formula One events. Colombia also has excelled in sports such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ], also has a long tradition in ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.semana.com/deportes/articulo/colombia-vive-esplendor-deportivo-inedito-en-su-historia/399243-3|title=Colombia vive esplendor deportivo inédito en su historia| date=18 August 2014 |publisher=semana.com|language=es|access-date=14 June 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.coc.org.co/about-us/office-premises/|title=History of the Colombian Olympic Committee.|publisher=]|language=es|access-date=14 June 2016|archive-date=21 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201021094018/http://www.coc.org.co/about-us/office-premises/|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.reporterosasociados.com.co/2016/04/el-bolo-colombiano-ratifico-su-condicion-de-potencia-continental/|title=El bolo colombiano ratificó su condición de potencia continental |publisher=reporterosasociados.com.co|language=es|access-date=14 June 2016}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{Portal|Colombia}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Sister project links|voy=Colombia}} | |||
| <!---- | |||
| Please only list links of nation-wide relevance here. Consider adding other links to the "External links" section of the sub-articles listed. | |||
| -----> | |||
| ===General information=== | |||
| * at ] | |||
| * {{Cite EB1911|wstitle=Colombia |volume=6 |last1=Lamoureux |first1=Andrew Jackson |author1-link=|last2=Edmundson |first2=George |author2-link=George Edmundson| pages=700–713 |short=1}} | |||
| * at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| * . '']''. ]. | |||
| * from ] | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Dead link|date=April 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} | |||
| * {{in lang|es}} | |||
| ===Government=== | |||
| * {{in lang|es}} | |||
| ===Culture=== | |||
| * {{in lang|es}} | |||
| ===Geography=== | |||
| * {{in lang|es}} | |||
| * {{Wikiatlas|Colombia}} | |||
| {{Colombia topics}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title = Articles related to Colombia | |||
| |list = | |list = | ||
| {{Departments of Colombia}} | {{Departments of Colombia}} | ||
| {{Countries of South America}} | {{Countries of South America}} | ||
| {{Symbols of Colombia}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Organization of American States}} | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| {{Union of South American Nations topics}} | |||
| |title = International membership | |||
| |list = | |||
| {{Latin Union}} | |||
| {{Union of South American Nations (Unasur\Unasul)}} | |||
| {{Andean Community of Nations}} | {{Andean Community of Nations}} | ||
| {{Mercosur |
{{Mercosur}} | ||
| {{Organization of American States (OAS)}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Coord|4|N|72|W|display=title}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|eo}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:03, 15 December 2024
Country in South America This article is about the country. For its predecessor, see Gran Colombia. For other uses, see Colombia (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Columbia or Colombo.
| Republic of ColombiaRepública de Colombia (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: "Libertad y Orden" (Spanish)"Freedom and Order" | |
| Anthem: Himno Nacional de la República de Colombia (Spanish) "National Anthem of the Republic of Colombia" | |
 Location of Colombia (dark green) Location of Colombia (dark green) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Bogotá 4°35′N 74°4′W / 4.583°N 74.067°W / 4.583; -74.067 |
| Official languages | Spanish |
| Recognized regional languages | Creole English (in San Andrés and Providencia) 64 other languages |
| Ethnic groups (2018 census) |
|
| Religion (2022) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Colombian |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| • President | Gustavo Petro |
| • Vice President | Francia Márquez |
| Legislature | Congress |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | Chamber of Representatives |
| Independence from Spain | |
| • Declared | 20 July 1810 |
| • Recognized | 7 August 1819 |
| • Last unitisation | 5 August 1886 |
| • Secession of Panama | 6 November 1903 |
| • Current Constitution | 4 July 1991 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,141,748 km (440,831 sq mi) (25th) |
| • Water (%) | 2.1 (as of 2015) |
| Population | |
| • 2024 estimate | |
| • Density | 46.15/km (119.5/sq mi) (174th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2022) | high inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (91st) |
| Currency | Colombian peso (COP) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (COT) |
| Date format | DMY |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +57 |
| ISO 3166 code | CO |
| Internet TLD | .co |
| |
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a colony, fusing cultural elements brought by immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by the African diaspora, as well as with those of the various Indigenous civilizations that predate colonization. Spanish is the official language, although Creole, English and 64 other languages are recognized regionally.
Colombia has been home to many indigenous peoples and cultures since at least 12,000 BCE. The Spanish first landed in La Guajira in 1499, and by the mid-16th century, they had colonized much of present-day Colombia, and established the New Kingdom of Granada, with Santa Fé de Bogotá as its capital. Independence from the Spanish Empire was achieved in 1819, with what is now Colombia emerging as the United Provinces of New Granada. The new polity experimented with federalism as the Granadine Confederation (1858) and then the United States of Colombia (1863), before becoming a republic—the current Republic of Colombia—in 1886. With the backing of the United States and France, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, resulting in Colombia's present borders. Beginning in the 1960s, the country has suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity armed conflict and political violence, both of which escalated in the 1990s. Since 2005, there has been significant improvement in security, stability, and rule of law, as well as unprecedented economic growth and development. Colombia is recognized for its healthcare system, being the best healthcare in Latin America according to the World Health Organization and 22nd in the world. Its diversified economy is the third-largest in South America, with macroeconomic stability and favorable long-term growth prospects.
Colombia is one of the world's seventeen megadiverse countries; it has the highest level of biodiversity per square mile in the world and the second-highest level overall. Its territory encompasses Amazon rainforest, highlands, grasslands and deserts. It is the only country in South America with coastlines (and islands) along both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Colombia is a key member of major global and regional organizations including the UN, the WTO, the OECD, the OAS, the Pacific Alliance and the Andean Community; it is also a NATO Global Partner and a major non-NATO ally of the United States.
Etymology
The name "Colombia" is derived from the last name of the Italian navigator Christopher Columbus (Latin: Christophorus Columbus, Italian: Cristoforo Colombo, Spanish: Cristóbal Colón). It was conceived as a reference to all of the New World. The name was later adopted by the Republic of Colombia of 1819, formed from the territories of the old Viceroyalty of New Granada (modern-day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela, Ecuador, and northwest Brazil).
When Venezuela, Ecuador, and Cundinamarca came to exist as independent states, the former Department of Cundinamarca adopted the name "Republic of New Granada". New Granada officially changed its name in 1858 to the Granadine Confederation. In 1863 the name was again changed, this time to United States of Colombia, before finally adopting its present name – the Republic of Colombia – in 1886.
To refer to this country, the Colombian government uses the terms Colombia and República de Colombia.
History
Main articles: History of Colombia and Timeline of Colombian historyPre-Columbian era
Main article: Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia
Owing to its location, the present territory of Colombia was a corridor of early human civilization from Mesoamerica and the Caribbean to the Andes and Amazon basin. The oldest archaeological finds are from the Pubenza and El Totumo sites in the Magdalena Valley 100 kilometers (62 mi) southwest of Bogotá. These sites date from the Paleoindian period (18,000–8000 BCE). At Puerto Hormiga and other sites, traces from the Archaic Period (~8000–2000 BCE) have been found. Vestiges indicate that there was also early occupation in the regions of El Abra and Tequendama in Cundinamarca. The oldest pottery discovered in the Americas, found in San Jacinto, dates to 5000–4000 BCE.
Indigenous people inhabited the territory that is now Colombia by 12,500 BCE. Nomadic hunter-gatherer tribes at the El Abra, Tibitó and Tequendama sites near present-day Bogotá traded with one another and with other cultures from the Magdalena River Valley. A site including eight miles (13 km) of pictographs that is under study at Serranía de la Lindosa was revealed in November 2020. Their age is suggested as being 12,500 years old (c. 10,480 B.C.) by the anthropologists working on the site, because of extinct fauna depicted. It was during the earliest known human occupation of the area.
Between 5000 and 1000 BCE, hunter-gatherer tribes transitioned to agrarian societies; fixed settlements were established, and pottery appeared. Beginning in the 1st millennium BCE, groups of Amerindians including the Muisca, Zenú, Quimbaya, and Tairona developed the political system of cacicazgos with a pyramidal structure of power headed by caciques. The Muisca inhabited mainly the area of what is now the Departments of Boyacá and Cundinamarca high plateau (Altiplano Cundiboyacense) where they formed the Muisca Confederation. They farmed maize, potato, quinoa, and cotton, and traded gold, emeralds, blankets, ceramic handicrafts, coca and especially rock salt with neighboring nations. The Tairona inhabited northern Colombia in the isolated mountain range of Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. The Quimbaya inhabited regions of the Cauca River Valley between the Western and Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Most of the Amerindians practiced agriculture and the social structure of each indigenous community was different. Some groups of indigenous people such as the Caribs lived in a state of permanent war, but others had less bellicose attitudes. During the 1200s, Malayo-Polynesians and Native Americans in Colombia made contact, thereby spreading Native American genetics from Precolonial Colombia to some Pacific Ocean islands.
Colonial period
Main articles: New Kingdom of Granada and Viceroyalty of New Granada See also: Spanish conquest of New Granada, Spanish conquest of the Muisca, Spanish colonization of the Americas, and Spanish Empire
Alonso de Ojeda (who had sailed with Columbus) reached the Guajira Peninsula in 1499. Spanish explorers, led by Rodrigo de Bastidas, made the first exploration of the Caribbean coast in 1500. Christopher Columbus navigated near the Caribbean in 1502. In 1508, Vasco Núñez de Balboa accompanied an expedition to the territory through the region of Gulf of Urabá and they founded the town of Santa María la Antigua del Darién in 1510, the first stable settlement on the continent. Santa Marta was founded in 1525, and Cartagena in 1533. Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada led an expedition to the interior in April 1536, and christened the districts through which he passed "New Kingdom of Granada". In August 1538, he provisionally founded its capital near the Muisca cacicazgo of Muyquytá, and named it "Santa Fe". The name soon acquired a suffix and was called Santa Fe de Bogotá. Two other notable journeys by early conquistadors to the interior took place in the same period. Sebastián de Belalcázar, conqueror of Quito, traveled north and founded Cali, in 1536, and Popayán, in 1537; from 1536 to 1539, German conquistador Nikolaus Federmann crossed the Llanos Orientales and went over the Cordillera Oriental in a search for El Dorado, the "city of gold". The legend and the gold would play a pivotal role in luring the Spanish and other Europeans to New Granada during the 16th and 17th centuries.
The conquistadors made frequent alliances with the enemies of different indigenous communities. Indigenous allies were crucial to conquest, as well as to creating and maintaining empire. Indigenous peoples in Colombia experienced a decline in population due to conquest as well as Eurasian diseases, such as smallpox, to which they had no immunity. Regarding the land as deserted, the Spanish Crown sold properties to all persons interested in colonized territories, creating large farms and possession of mines. In the 16th century, the nautical science in Spain reached a great development thanks to numerous scientific figures of the Casa de Contratación and nautical science was an essential pillar of the Iberian expansion. In 1542, the region of New Granada, along with all other Spanish possessions in South America, became part of the Viceroyalty of Peru, with its capital in Lima. In 1547, New Granada became a separate captaincy-general within the viceroyalty, with its capital at Santa Fe de Bogota. In 1549, the Royal Audiencia was created by a royal decree, and New Granada was ruled by the Royal Audience of Santa Fe de Bogotá, which at that time comprised the provinces of Santa Marta, Rio de San Juan, Popayán, Guayana and Cartagena. But important decisions were taken from the colony to Spain by the Council of the Indies.

In the 16th century, European slave traders had begun to bring enslaved Africans to the Americas. Spain was the only European power that did not establish factories in Africa to purchase slaves; the Spanish Empire instead relied on the asiento system, awarding merchants from other European nations the license to trade enslaved peoples to their overseas territories. This system brought Africans to Colombia, although many spoke out against the institution. The indigenous peoples could not be enslaved because they were legally subjects of the Spanish Crown. To protect the indigenous peoples, several forms of land ownership and regulation were established by the Spanish colonial authorities: resguardos, encomiendas and haciendas.
However, secret anti-Spanish discontentment was already brewing for Colombians since Spain prohibited direct trade between the Viceroyalty of Peru, which included Colombia, and the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which included the Philippines, the source of Asian products like silk and porcelain which was in demand in the Americas. Illegal trade between Peruvians, Filipinos, and Mexicans continued in secret, as smuggled Asian goods ended up in Córdoba, Colombia, the distribution center for illegal Asian imports, due to the collusion between these peoples against the authorities in Spain. They settled and traded with each other while disobeying the forced Spanish monopoly.

The Viceroyalty of New Granada was established in 1717, then temporarily removed, and then re-established in 1739. Its capital was Santa Fé de Bogotá. This Viceroyalty included some other provinces of northwestern South America that had previously been under the jurisdiction of the Viceroyalties of New Spain or Peru and correspond mainly to today's Venezuela, Ecuador, and Panama. Bogotá became one of the principal administrative centers of the Spanish possessions in the New World, along with Lima and Mexico City, though it remained less developed compared to those two cities in several economic and logistical ways.
Great Britain declared war on Spain in 1739, and the city of Cartagena quickly became a top target for the British. A massive British expeditionary force was dispatched to capture the city, but, after achieving initial inroads, devastating outbreaks of disease crippled their numbers, and the British were forced to withdraw. The battle became one of Spain's most decisive victories in the conflict, and secured Spanish dominance in the Caribbean until the Seven Years' War. The 18th-century priest, botanist, and mathematician José Celestino Mutis was delegated by Viceroy Antonio Caballero y Góngora to conduct an inventory of the nature of New Granada. Started in 1783, this became known as the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Granada. It classified plants and wildlife, and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fe de Bogotá. In July 1801 the Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt reached Santa Fe de Bogotá where he met with Mutis. In addition, historical figures in the process of independence in New Granada emerged from the expedition as the astronomer Francisco José de Caldas, the scientist Francisco Antonio Zea, the zoologist Jorge Tadeo Lozano and the painter Salvador Rizo.
Independence
| The accessibility of this section is in question. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (November 2024) |

Rebellions against Spanish rule had occurred in the empire since the advent of conquest and colonization, but most were either crushed or remained too weak to change the overall situation. The last one that sought outright independence from Spain sprang up around 1810 and culminated in the Colombian Declaration of Independence, issued on 20 July 1810, the day that is now celebrated as the nation's Independence Day. This movement followed the independence of Saint-Domingue (present-day Haiti) in 1804, which provided some support to an eventual leader of this rebellion: Simón Bolívar. Francisco de Paula Santander also would play a decisive role.
A movement was initiated by Antonio Nariño, who opposed Spanish centralism and led the opposition against the Viceroyalty. Cartagena became independent in November 1811. In 1811, the United Provinces of New Granada were proclaimed, headed by Camilo Torres Tenorio. The emergence of two distinct ideological currents among the patriots (federalism and centralism) gave rise to a period of instability called the Patria Boba. Shortly after the Napoleonic Wars ended, Ferdinand VII, recently restored to the throne in Spain, unexpectedly decided to send military forces to retake most of northern South America. The viceroyalty was restored under the command of Juan de Sámano, whose regime punished those who participated in the patriotic movements, ignoring the political nuances of the juntas. The retribution stoked renewed rebellion, which, combined with a weakened Spain, made possible a successful rebellion led by the Venezuelan-born Simón Bolívar, who finally proclaimed independence in 1819. The pro-Spanish resistance was defeated in 1822 in the present territory of Colombia and in 1823 in Venezuela. During the Independence War, between 250 and 400 thousand people (12–20% of the pre-war population) died.

The territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada became the Republic of Colombia, organized as a union of the current territories of Colombia, Panama, Ecuador, Venezuela, parts of Guyana and Brazil and north of Marañón River. The Congress of Cúcuta in 1821 adopted a constitution for the new Republic. Simón Bolívar became the first President of Colombia, and Francisco de Paula Santander was made Vice President. However, the new republic was unstable and the Gran Colombia ultimately collapsed.
Modern Colombia comes from one of the countries that emerged after the dissolution of Gran Colombia, the other two being Ecuador and Venezuela. Colombia was the first constitutional government in South America, and the Liberal and Conservative parties, founded in 1848 and 1849, respectively, are two of the oldest surviving political parties in the Americas. Slavery was abolished in the country in 1851.
Internal political and territorial divisions led to the dissolution of Gran Colombia in 1830. The so-called "Department of Cundinamarca" adopted the name "New Granada", which it kept until 1858 when it became the "Confederación Granadina" (Granadine Confederation). After a two-year civil war in 1863, the United States of Colombia was created, which became known as the Republic of Colombia in 1886. Internal divisions remained between the bipartisan political forces, occasionally igniting very bloody civil wars, the most significant being the Thousand Days' War (1899–1902), in which between 100 and 180 thousand Colombians lost their lives when the Liberal Party, supported by Venezuela, Ecuador, Nicaragua, and Guatemala rebelled against the Nationalist government and took control of Santander, ultimately being defeated in 1902 by nationalist forces.
20th century
See also: Colombian conflict and La ViolenciaThe United States of America's intentions to influence the area (especially the Panama Canal construction and control) led to the separation of the Department of Panama in 1903 and the establishment of it as a nation. The United States paid Colombia $25,000,000 in 1921, seven years after completion of the canal, for redress of President Roosevelt's role in the creation of Panama, and Colombia recognized Panama under the terms of the Thomson–Urrutia Treaty. Colombia and Peru went to war because of territory disputes far in the Amazon basin. The war ended with a peace deal brokered by the League of Nations. The League finally awarded the disputed area to Colombia in June 1934.

Soon after, Colombia achieved some degree of political stability, which was interrupted by a bloody conflict that took place between the late 1940s and the early 1950s, a period known as La Violencia ("The Violence"). Its cause was mainly mounting tensions between the two leading political parties, which subsequently ignited after the assassination of the Liberal presidential candidate Jorge Eliécer Gaitán on 9 April 1948. The ensuing riots in Bogotá, known as El Bogotazo, spread throughout the country and claimed the lives of at least 180,000 Colombians.
Colombia entered the Korean War when Laureano Gómez was elected president. It was the only Latin American country to join the war in a direct military role as an ally of the United States. Particularly important was the resistance of the Colombian troops at Old Baldy.
The violence between the two political parties decreased first when Gustavo Rojas deposed the President of Colombia in a coup d'état and negotiated with the guerrillas, and then under the military junta of General Gabriel París.

After Rojas' deposition, the Colombian Conservative Party and the Colombian Liberal Party agreed to create the National Front, a coalition that would jointly govern the country. Under the deal, the presidency would alternate between conservatives and liberals every 4 years for 16 years; the two parties would have parity in all other elective offices. The National Front ended "La Violencia", and National Front administrations attempted to institute far-reaching social and economic reforms in cooperation with the Alliance for Progress. Despite the progress in certain sectors, many social and political problems continued, and guerrilla groups were formally created such as the FARC, the ELN and the M-19 to fight the government and political apparatus.
Since the 1960s, the country has suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity armed conflict between government forces, leftist guerrilla groups and right wing paramilitaries. The conflict escalated in the 1990s, mainly in remote rural areas. Since the beginning of the armed conflict, human rights defenders have fought for the respect for human rights, despite staggering opposition. Several guerrillas' organizations decided to demobilize after peace negotiations in 1989–1994.
The United States has been heavily involved in the conflict since its beginnings, when in the early 1960s the U.S. government encouraged the Colombian military to attack leftist militias in rural Colombia. This was part of the U.S. fight against communism. Mercenaries and multinational corporations such as Chiquita Brands International are some of the international actors that have contributed to the violence of the conflict.
Beginning in the mid-1970s Colombian drug cartels became major producers, processors and exporters of illegal drugs, primarily marijuana and cocaine.
On 4 July 1991, a new Constitution was promulgated. The changes generated by the new constitution are viewed as positive by Colombian society.
21st century
See also: Colombian peace process
The administration of President Álvaro Uribe (2002–2010) adopted the democratic security policy which included an integrated counter-terrorism and counter-insurgency campaign. The government economic plan also promoted confidence in investors. As part of a controversial peace process, the AUC (right-wing paramilitaries) had ceased to function formally as an organization . In February 2008, millions of Colombians demonstrated against FARC and other outlawed groups.
After peace negotiations in Cuba, the Colombian government of President Juan Manuel Santos and the guerrillas of the FARC-EP announced a final agreement to end the conflict. However, a referendum to ratify the deal was unsuccessful. Afterward, the Colombian government and the FARC signed a revised peace deal in November 2016, which the Colombian congress approved. In 2016, President Santos was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. The Government began a process of attention and comprehensive reparation for victims of conflict. Colombia shows modest progress in the struggle to defend human rights, as expressed by HRW. A Special Jurisdiction of Peace has been created to investigate, clarify, prosecute and punish serious human rights violations and grave breaches of international humanitarian law which occurred during the armed conflict and to satisfy victims' right to justice. During his visit to Colombia, Pope Francis paid tribute to the victims of the conflict.

In June 2018, Iván Duque, the candidate of the right-wing Democratic Center party, won the presidential election. On 7 August 2018, he was sworn in as the new President of Colombia to succeed Juan Manuel Santos. Colombia's relations with Venezuela have fluctuated due to ideological differences between the two governments. Colombia has offered humanitarian support with food and medicines to mitigate the shortage of supplies in Venezuela. Colombia's Foreign Ministry said that all efforts to resolve Venezuela's crisis should be peaceful. Colombia proposed the idea of the Sustainable Development Goals and a final document was adopted by the United Nations. In February 2019, Venezuelan president Nicolás Maduro cut off diplomatic relations with Colombia after Colombian President Ivan Duque had helped Venezuelan opposition politicians deliver humanitarian aid to their country. Colombia recognized Venezuelan opposition leader Juan Guaidó as the country's legitimate president. In January 2020, Colombia rejected Maduro's proposal that the two countries restore diplomatic relations.
Protests started on 28 April 2021 when the government proposed a tax bill that would greatly expand the range of the 19 percent value-added tax. The 19 June 2022 election run-off vote ended in a win for former guerrilla, Gustavo Petro, taking 50.47% of the vote compared to 47.27% for independent candidate Rodolfo Hernández. The single-term limit for the country's presidency prevented President Iván Duque from seeking re-election. On 7 August 2022, Petro was sworn in, becoming the country's first leftist president.
Geography
Main articles: Geography of Colombia and Geology of Colombia
The geography of Colombia is characterized by its six main natural regions that present their unique characteristics, from the Andes mountain range region; the Pacific Coastal region; the Caribbean coastal region; the Llanos (plains); the Amazon rainforest region; to the insular area, comprising islands in both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It shares its maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
Colombia is bordered to the northwest by Panama, to the east by Venezuela and Brazil, and to the south by Ecuador and Peru; it established its maritime boundaries with neighboring countries through seven agreements on the Caribbean Sea and three on the Pacific Ocean. It lies between latitudes 12°N and 4°S and between longitudes 67° and 79°W.
East of the Andes lies the savanna of the Llanos, part of the Orinoco River basin, and in the far southeast, the jungle of the Amazon rainforest. Together these lowlands make up over half Colombia's territory, but they contain less than 6% of the population. To the north the Caribbean coast, home to 21.9% of the population and the location of the major port cities of Barranquilla and Cartagena, generally consists of low-lying plains, but it also contains the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range, which includes the country's tallest peaks (Pico Cristóbal Colón and Pico Simón Bolívar), and the La Guajira Desert. By contrast the narrow and discontinuous Pacific coastal lowlands, backed by the Serranía de Baudó mountains, are sparsely populated and covered in dense vegetation. The principal Pacific port is Buenaventura.

Part of the Ring of Fire, a region of the world subject to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, in the interior of Colombia the Andes are the prevailing geographical feature. Most of Colombia's population centers are located in these interior highlands. Beyond the Colombian Massif (in the southwestern departments of Cauca and Nariño), these are divided into three branches known as cordilleras (mountain ranges): the Cordillera Occidental, running adjacent to the Pacific coast and including the city of Cali; the Cordillera Central, running between the Cauca and Magdalena River valleys (to the west and east, respectively) and including the cities of Medellín, Manizales, Pereira, and Armenia; and the Cordillera Oriental, extending northeast to the Guajira Peninsula and including Bogotá, Bucaramanga, and Cúcuta. Peaks in the Cordillera Occidental exceed 4,700 m (15,420 ft), and in the Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental they reach 5,000 m (16,404 ft). At 2,600 m (8,530 ft), Bogotá is the highest city of its size in the world.
The main rivers of Colombia are Magdalena, Cauca, Guaviare, Atrato, Meta, Putumayo and Caquetá. Colombia has four main drainage systems: the Pacific drain, the Caribbean drain, the Orinoco Basin and the Amazon Basin. The Orinoco and Amazon Rivers mark limits with Colombia to Venezuela and Peru respectively.
Climate
Main article: Climate of Colombia
The climate of Colombia is characterized for being tropical presenting variations within six natural regions and depending on the altitude, temperature, humidity, winds and rainfall. Colombia has a diverse range of climate zones, including tropical rainforests, savannas, steppes, deserts and mountain climates.
Mountain climate is one of the unique features of the Andes and other high altitude reliefs where climate is determined by elevation. Below 1,000 meters (3,281 ft) in elevation is the warm altitudinal zone, where temperatures are above 24 °C (75.2 °F). About 82.5% of the country's total area lies in the warm altitudinal zone. The temperate climate altitudinal zone located between 1,001 and 2,000 meters (3,284 and 6,562 ft) is characterized for presenting an average temperature ranging between 17 and 24 °C (62.6 and 75.2 °F). The cold climate is present between 2,001 and 3,000 meters (6,565 and 9,843 ft) and the temperatures vary between 12 and 17 °C (53.6 and 62.6 °F). Beyond lies the alpine conditions of the forested zone and then the treeless grasslands of the páramos. Above 4,000 meters (13,123 ft), where temperatures are below freezing, the climate is glacial, a zone of permanent snow and ice.
Biodiversity and conservation
See also: Fauna of Colombia, Flora of Colombia, and Deforestation in ColombiaColombia is one of the megadiverse countries in biodiversity, ranking first in bird species. Colombia is the country with the planet's highest biodiversity, having the highest rate of species by area as well as the largest number of endemisms (species that are not found naturally anywhere else) of any country. About 10% of the species of the Earth live in Colombia, including over 1,900 species of bird, more than in Europe and North America combined. Colombia has 10% of the world's mammals species, 14% of the amphibian species and 18% of the bird species of the world.

As for plants, the country has between 40,000 and 45,000 plant species, equivalent to 10 or 20% of total global species, which is even more remarkable given that Colombia is considered a country of intermediate size. Colombia is the second most biodiverse country in the world, lagging only after Brazil which is approximately 7 times bigger.
Colombia has about 2,000 species of marine fish and is the second most diverse country in freshwater fish. It is also the country with the most endemic species of butterflies, is first in orchid species, and has approximately 7,000 species of beetles. Colombia is second in the number of amphibian species and is the third most diverse country in reptiles and palms. There are about 1,900 species of mollusks and according to estimates there are about 300,000 species of invertebrates in the country. In Colombia there are 32 terrestrial biomes and 314 types of ecosystems.
Protected areas and the "National Park System" cover an area of about 14,268,224 hectares (142,682.24 km) and account for 12.77% of the Colombian territory. Compared to neighboring countries, rates of deforestation in Colombia are still relatively low. Colombia had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.26/10, ranking it 25th globally out of 172 countries. Colombia is the sixth country in the world by magnitude of total renewable freshwater supply, and still has large reserves of freshwater.
Government and politics
Main article: Government of Colombia See also: Colombian Constitution of 1991
The government of Colombia takes place within the framework of a presidential participatory democratic republic as established in the Constitution of 1991. In accordance with the principle of separation of powers, government is divided into three branches: the executive branch, the legislative branch and the judicial branch.
As the head of the executive branch, the President of Colombia serves as both head of state and head of government, followed by the Vice President and the Council of Ministers. The president is elected by popular vote to serve a single four-year term (In 2015, Colombia's Congress approved the repeal of a 2004 constitutional amendment that changed the one-term limit for presidents to a two-term limit). At the provincial level executive power is vested in department governors, municipal mayors and local administrators for smaller administrative subdivisions, such as corregimientos or comunas. All regional elections are held one year and five months after the presidential election.

The legislative branch of government is represented nationally by the Congress, a bicameral institution comprising a 166-seat Chamber of Representatives and a 102-seat Senate. The Senate is elected nationally and the Chamber of Representatives is elected in electoral districts. Members of both houses are elected to serve four-year terms two months before the president, also by popular vote.

The judicial branch is headed by four high courts, consisting of the Supreme Court which deals with penal and civil matters, the Council of State, which has special responsibility for administrative law and also provides legal advice to the executive, the Constitutional Court, responsible for assuring the integrity of the Colombian constitution, and the Superior Council of Judicature, responsible for auditing the judicial branch. Colombia operates a system of civil law, which since 1991 has been applied through an adversarial system.
Despite a number of controversies, the democratic security policy has ensured that former President Álvaro Uribe remained popular among Colombian people, with his approval rating peaking at 76%, according to a poll in 2009. However, having served two terms, he was constitutionally barred from seeking re-election in 2010. In the run-off elections on 20 June 2010 the former Minister of Defense Juan Manuel Santos won with 69% of the vote against the second most popular candidate, Antanas Mockus. A second round was required since no candidate received over the 50% winning threshold of votes. Santos won re-election with nearly 51% of the vote in second-round elections on 15 June 2014, beating right-wing rival Óscar Iván Zuluaga, who won 45%. In 2018, Iván Duque won in the second round of the election with 54% of the vote, against 42% for his left-wing rival, Gustavo Petro. His term as Colombia's president ran for four years, beginning on 7 August 2018. In 2022, Colombia elected Gustavo Petro, who became its first leftist leader, and Francia Marquez, who was the first black person elected as vice president.
Foreign affairs
Main article: Foreign relations of Colombia See also: List of diplomatic missions of Colombia
The foreign affairs of Colombia are headed by the President, as head of state, and managed by the Minister of Foreign Affairs. Colombia has diplomatic missions in all continents.
Colombia was one of the four founding members of the Pacific Alliance, which is a political, economic and co-operative integration mechanism that promotes the free circulation of goods, services, capital and persons between the members, as well as a common stock exchange and joint embassies in several countries. Colombia is also a member of the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the Organization of American States, the Organization of Ibero-American States, and the Andean Community of Nations.
Colombia is a global partner of NATO and a major non-NATO ally of the United States.
Military
Main article: Military Forces of Colombia
The executive branch of government is responsible for managing the defense of Colombia, with the President commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The Ministry of Defence exercises day-to-day control of the military and the Colombian National Police. Colombia has 455,461 active military personnel. In 2016, 3.4% of the country's GDP went towards military expenditure, placing it 24th in the world. Colombia's armed forces are the largest in Latin America, and it is the second largest spender on its military after Brazil. In 2018, Colombia signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Colombian military is divided into three branches: the National Army of Colombia; the Colombian Aerospace Force; and the Colombian Navy. The National Police functions as a gendarmerie, operating independently from the military as the law enforcement agency for the entire country. Each of these operates with their own intelligence apparatus separate from the National Intelligence Directorate (DNI, in Spanish).
The National Army is formed by divisions, brigades, special brigades, and special units, the Colombian Navy by the Naval Infantry, the Naval Force of the Caribbean, the Naval Force of the Pacific, the Naval Force of the South, the Naval Force of the East, Colombia Coast Guards, Naval Aviation, and the Specific Command of San Andres y Providencia and the Aerospace Force by 15 air units.
Administrative divisions
Main articles: Departments of Colombia and Municipalities of Colombia See also: List of cities in Colombia and Corregimientos of ColombiaColombia is divided into 32 departments and one capital district, which is treated as a department (Bogotá also serves as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca). Departments are subdivided into municipalities, each of which is assigned a municipal seat, and municipalities are in turn subdivided into corregimientos in rural areas and into comunas in urban areas. Each department has a local government with a governor and assembly directly elected to four-year terms, and each municipality is headed by a mayor and council. There is a popularly elected local administrative board in each of the corregimientos or comunas.
In addition to the capital, four other cities have been designated districts (in effect special municipalities), on the basis of special distinguishing features. These are Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta and Buenaventura. Some departments have local administrative subdivisions, where towns have a large concentration of population and municipalities are near each other (for example, in Antioquia and Cundinamarca). Where departments have a low population (for example Amazonas, Vaupés and Vichada), special administrative divisions are employed, such as "department corregimientos", which are a hybrid of a municipality and a corregimiento.
Click on a department on the map below to go to its article.
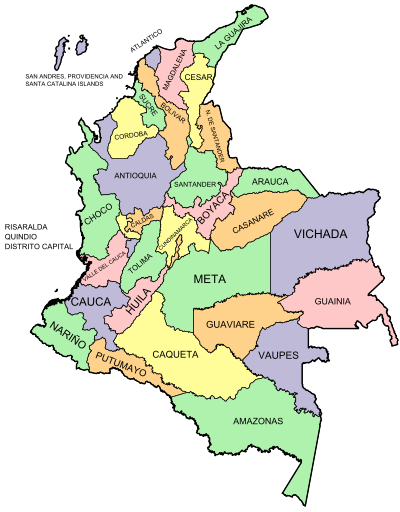
|
|
Economy
Main article: Economy of Colombia See also: Industry of Colombia


Historically an agrarian economy, Colombia urbanized rapidly in the 20th century, by the end of which just 15.8% of the workforce were employed in agriculture, generating just 6.6% of GDP; 20% of the workforce were employed in industry and 65% in services, responsible for 33% and 60% of GDP respectively. The country's economic production is dominated by its strong domestic demand. Consumption expenditure by households is the largest component of GDP.
Colombia's market economy grew steadily in the latter part of the 20th century, with gross domestic product (GDP) increasing at an average rate of over 4% per year between 1970 and 1998. The country suffered a recession in 1999 (the first full year of negative growth since the Great Depression), and the recovery was long and painful. However, growth reaching 7% in 2007, one of the highest in Latin America. According to International Monetary Fund estimates, in 2023, Colombia's GDP (PPP) was US$1 trillion, 32nd in the world and third in South America, after Brazil and Argentina.
Total government expenditures account for 28% of the domestic economy. External debt equals 40% of gross domestic product. A strong fiscal climate was reaffirmed by a boost in bond ratings. Annual inflation closed 2017 at 4.09% YoY (vs. 5.75% YoY in 2016). The average national unemployment rate in 2017 was 9.4%, although the informality is the biggest problem facing the labour market (the income of formal workers climbed 24.8% in 5 years while labor incomes of informal workers rose only 9%). Colombia has free-trade zones (FTZ), such as Zona Franca del Pacifico, located in the Valle del Cauca, one of the most striking areas for foreign investment.
The financial sector has grown favorably due to good liquidity in the economy, the growth of credit and the positive performance of the Colombian economy. The Colombian Stock Exchange through the Latin American Integrated Market (MILA) offers a regional market to trade equities. Colombia is now one of only three economies with a perfect score on the strength of legal rights index, according to the World Bank.
Colombia is rich in natural resources, and it is heavily dependent on energy and mining exports. Colombia's main exports include mineral fuels, oils, distillation products, fruit and other agricultural products, sugars and sugar confectionery, food products, plastics, precious stones, metals, forest products, chemical goods, pharmaceuticals, vehicles, electronic products, electrical equipment, perfumery and cosmetics, machinery, manufactured articles, textile and fabrics, clothing and footwear, glass and glassware, furniture, prefabricated buildings, military products, home and office material, construction equipment, software, among others. Principal trading partners are the United States, China, the European Union and some Latin American countries.
Non-traditional exports have boosted the growth of Colombian foreign sales as well as the diversification of destinations of export thanks to new free trade agreements. Recent economic growth has led to a considerable increase of new millionaires, including the new entrepreneurs, Colombians with a net worth exceeding US$1 billion.
In 2017, however, the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) reported that 26.9% of the population were living below the poverty line, of which 7.4% were in "extreme poverty". The multidimensional poverty rate stands at 17.0 percent of the population. The Government has also been developing a process of financial inclusion within the country's most vulnerable population.
The contribution of tourism to GDP was US$5,880.3bn (2.0% of total GDP) in 2016. Tourism generated 556,135 jobs (2.5% of total employment) in 2016. Foreign tourist visits were predicted to have risen from 0.6 million in 2007 to 4 million in 2017.
Agriculture and natural resources
Main articles: Agriculture in Colombia and Mining in Colombia
In agriculture, Colombia is one of the five largest producers in the world of coffee, avocado and palm oil, and one of the 10 largest producers in the world of sugarcane, banana, pineapple and cocoa. The country also has considerable production of rice, potato and cassava. Although it is not the largest coffee producer in the world (Brazil claims that title), the country has been able to carry out, for decades, a global marketing campaign to add value to the country's product. Colombian palm oil production is one of the most sustainable on the planet, compared to the largest existing producers. Colombia is also among the 20 largest producers in the world of beef and chicken meat. Colombia is also the 2nd largest flower exporter in the world, after the Netherlands. Colombian agriculture emits 55% of Colombia's greenhouse gas emissions, mostly from deforestation, over-extensive cattle ranching, land grabbing, and illegal agriculture.
Colombia is an important exporter of coal and petroleum – in 2020, more than 40% of the country's exports were based on these two products. In 2018 it was the 5th largest coal exporter in the world. In 2019, Colombia was the 20th largest petroleum producer in the world, with 791 thousand barrels/day, exporting a good part of its production – the country was the 19th largest oil exporter in the world in 2020. In mining, Colombia is the world's largest producer of emerald, and in the production of gold, between 2006 and 2017, the country produced 15 tons per year until 2007, when its production increased significantly, beating the record of 66.1 tons extracted in 2012. In 2017, it extracted 52.2 tons. Currently, the country is among the 25 largest gold producers in the world.
Energy and transportation
Main articles: Electricity sector in Colombia and Transport in Colombia
The electricity production in Colombia comes mainly from Renewable energy sources. 69.93% is obtained from the hydroelectric generation. Colombia's commitment to renewable energy was recognized in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index (GGEI), ranking among the top 10 nations in the world in terms of greening efficiency sectors.

Transportation in Colombia is regulated within the functions of the Ministry of Transport and entities such as the National Roads Institute (INVÍAS) responsible for the Highways in Colombia, the Aerocivil, responsible for civil aviation and airports, the National Infrastructure Agency, in charge of concessions through public–private partnerships, for the design, construction, maintenance, operation, and administration of the transport infrastructure, the General Maritime Directorate (Dimar) has the responsibility of coordinating maritime traffic control along with the Colombian Navy, among others, and under the supervision of the Superintendency of Ports and Transport.
In 2021, Colombia had 204,389 km (127,001 mi) of roads, 32,280 km (20,058 mi) of which were paved. At the end of 2017, the country had around 2,100 km (1,305 mi) of duplicated highways. Rail transportation in Colombia is dedicated almost entirely to freight shipments and the railway network has a length of 1,700 km of potentially active rails. Colombia has 3,960 kilometers of gas pipelines, 4,900 kilometers of oil pipelines, and 2,990 kilometers of refined-products pipelines.
The Colombian government aimed to build 7,000 km of roads between 2016 and 2020, which would reduce travel times by an estimated 30 per cent, and transport costs by an estimated 20 per cent. A toll road concession programme will comprise 40 projects, and is part of a larger strategic goal to invest nearly $50 bn in transport infrastructure, including railway systems, making the Magdalena River navigable again, improving port facilities, and an expansion of El Dorado International Airport. Colombia is a middle-income country.
Science and technology
Main article: Science and technology in Colombia
Colombia has more than 3,950 research groups in science and technology. iNNpulsa, a government body that promotes entrepreneurship and innovation in the country, provides grants to startups, in addition to other services it and institutions provide. Colombia was ranked 61st in the Global Innovation Index in 2024. Co-working spaces have arisen to serve as communities for startups large and small. Organizations such as the Corporation for Biological Research (CIB) for the support of young people interested in scientific work has been successfully developed in Colombia. The International Center for Tropical Agriculture based in Colombia investigates the increasing challenge of global warming and food security.
Important inventions related to medicine have been made in Colombia, such as the first external artificial pacemaker with internal electrodes, invented by the electrical engineer Jorge Reynolds Pombo, an invention of great importance for those who suffer from heart failure. Also invented in Colombia were the microkeratome and keratomileusis technique, which form the fundamental basis of what now is known as LASIK (one of the most important techniques for the correction of refractive errors of vision) and the Hakim valve for the treatment of hydrocephalus. Colombia has begun to innovate in military technology for its army and other armies of the world; especially in the design and creation of personal ballistic protection products, military hardware, military robots, bombs, simulators and radar.
Some leading Colombian scientists are Joseph M. Tohme, researcher recognized for his work on the genetic diversity of food, Manuel Elkin Patarroyo who is known for his groundbreaking work on synthetic vaccines for malaria, Francisco Lopera who discovered the "Paisa Mutation" or a type of early-onset Alzheimer's, Rodolfo Llinás known for his study of the intrinsic neurons properties and the theory of a syndrome that had changed the way of understanding the functioning of the brain, Jairo Quiroga Puello recognized for his studies on the characterization of synthetic substances which can be used to fight fungus, tumors, tuberculosis and even some viruses and Ángela Restrepo who established accurate diagnoses and treatments to combat the effects of a disease caused by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Colombia See also: List of Colombian departments by population

With an estimated 50 million people in 2020, Colombia is the third-most populous country in Latin America, after Brazil and Mexico. At the beginning of the 20th century, Colombia's population was approximately 4 million. Since the early 1970s Colombia has experienced steady declines in its fertility, mortality, and population growth rates. The population growth rate for 2016 is estimated to be 0.9%. About 26.8% of the population were 15 years old or younger, 65.7% were between 15 and 64 years old, and 7.4% were over 65 years old. The proportion of older persons in the total population has begun to increase substantially. Colombia is projected to have a population of 55.3 million by 2050.
Estimates for the population of the area that is now Colombia range between 2.5 and 12 million people in 1500; estimates between the extremes include figures of 6 and 7 million. With the Spanish conquest, the region's population had collapsed to around 1.2 million people in 1600, for an estimated decrease of 52–90%. By the end of the colonial period, it had declined further to around 800,000; it began rising in the early 19th century to around 1.4 million, where it would drop again in the Colombian War of Independence to between 1 and 1.2 million. The country's population did not recover to pre-conquest levels until the 1940s, nearly 450 years after its 16th-century peak.
The population is concentrated in the Andean highlands and along the Caribbean coast, also the population densities are generally higher in the Andean region. The nine eastern lowland departments, comprising about 54% of Colombia's area, have less than 6% of the population. Traditionally a rural society, movement to urban areas was very heavy in the mid-20th century, and Colombia is now one of the most urbanized countries in Latin America. The urban population increased from 31% of the total in 1938 to nearly 60% in 1973, and by 2014 the figure stood at 76%. The population of Bogotá alone has increased from just over 300,000 in 1938 to approximately 8 million today. In total seventy-two cities now have populations of 100,000 or more (2015). As of 2012 Colombia has the world's largest populations of internally displaced persons (IDPs), estimated to be up to 4.9 million people.
The life expectancy was 74.8 years in 2015, and infant mortality was 13.1 per thousand in 2016. In 2015, 94.58% of adults and 98.66% of youth are literate and the government spends about 4.49% of its GDP on education.
Languages
Main article: Languages of Colombia See also: Colombian SpanishAround 99.2% of Colombians speak Spanish, also called Castilian; 65 Amerindian languages, two Creole languages, the Romani language and Colombian Sign Language are also used in the country. English has official status in the archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina.
Including Spanish, a total of 101 languages are listed for Colombia in the Ethnologue database. The specific number of spoken languages varies slightly since some authors consider as different languages what others consider to be varieties or dialects of the same language. Best estimates recorded 71 languages that are spoken in-country today – most of which belong to the Chibchan, Tucanoan, Bora–Witoto, Guajiboan, Arawakan, Cariban, Barbacoan, and Saliban language families. There are currently more than 850,000 speakers of native languages.
Ethnic groups
Main article: Race and ethnicity in ColombiaEthnic groups in Colombia - 2018 Census
Mestizo-White (87.58%) Afro-Colombian (includes mixed) (6.68%) Amerindian (4.31%) Not stated (1.35%) Raizal (0.06%) Palenquero (0.02%) Romani (0.01%)Colombia is ethnically diverse, its people descending from the original Native inhabitants, Spanish conquistadors, Africans originally brought to the country as slaves, and 20th-century immigrants from Europe and the Middle East, all contributing to a diverse cultural heritage. The demographic distribution reflects a pattern that is influenced by colonial history. Whites live all throughout the country, mainly in urban centers and the burgeoning highland and coastal cities. The populations of the major cities also include mestizos. Mestizo campesinos (people living in rural areas) also live in the Andean highlands where some Spanish conquerors mixed with the women of Amerindian chiefdoms. Mestizos include artisans and small tradesmen that have played a major part in the urban expansion of recent decades. In a study by the American Journal of Physical Anthropology, Colombians have an average ancestry of 47% Amerindian DNA, 42% European DNA, and 11% African DNA.
The 2018 census reported that the "non-ethnic population", consisting of whites and mestizos (those of mixed European and Amerindian ancestry), constituted 87.6% of the national population. 6.7% is of African ancestry. Indigenous Amerindians constitute 4.3% of the population. Raizal people constitute 0.06% of the population. Palenquero people constitute 0.02% of the population. 0.01% of the population are Roma. A study by Latinobarómetro in 2023 estimates that 50.3% of the population are Mestizo, 26.4% are White, 9.5% are Indigenous, 9.0% are Black, 4.4% are Mulatto, and 0.4% are Asian, these estimates would equate to around 26 million people being Mestizo, 14 million being White, 5 million being Indigenous, 5 million being Black, 2 million being Mulatto, and 200k being Asian.
Ethnic groups of Colombia according to Latinobarómetro 2023
Mestizo (50.3%) White (26.4%) Amerindian (9.5%) Black (9.0%) Mulatto (4.4%) Asian (0.4%)The Federal Research Division estimated that the 86% of the population that did not consider themselves part of one of the ethnic groups indicated by the 2006 census, white Colombians are mainly of Spanish lineage, but there is also a large population of Middle East descent; in some areas there is a considerable input of German and Italian ancestry.
Many of the Indigenous peoples experienced a reduction in population during the Spanish rule and many others were absorbed into the mestizo population, but the remainder currently represents over eighty distinct cultures. Reserves (resguardos) established for indigenous peoples occupy 30,571,640 hectares (305,716.4 km) (27% of the country's total) and are inhabited by more than 800,000 people. Some of the largest indigenous groups are the Wayuu, the Paez, the Pastos, the Emberá and the Zenú. The departments of La Guajira, Cauca, Nariño, Córdoba and Sucre have the largest indigenous populations.
The Organización Nacional Indígena de Colombia (ONIC), founded at the first National Indigenous Congress in 1982, is an organization representing the indigenous peoples of Colombia. In 1991, Colombia signed and ratified the current international law concerning indigenous peoples, Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention, 1989.
Sub-Saharan Africans were brought as slaves, mostly to the coastal lowlands, beginning early in the 16th century and continuing into the 19th century. Large Afro-Colombian communities are found today on the Pacific Coast. Numerous Jamaicans migrated mainly to the islands of San Andres and Providencia. A number of other Europeans and North Americans migrated to the country in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including people from the former USSR during and after the Second World War.
Many immigrant communities have settled on the Caribbean coast, in particular recent immigrants from the Middle East and Europe. Barranquilla (the largest city of the Colombian Caribbean) and other Caribbean cities have the largest populations of Lebanese, Palestinian, and other Levantines. There are also important communities of Romanis and Jews. There is a major migration trend of Venezuelans, due to the political and economic situation in Venezuela. In August 2019, Colombia offered citizenship to more than 24,000 children of Venezuelan refugees who were born in Colombia.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Colombia See also: Freedom of religion in Colombia and Jews in Colombia
The National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) does not collect religious statistics, and accurate reports are difficult to obtain. However, based on various studies and a survey, about 90% of the population adheres to Christianity, the majority of which (70.9%–79%) are Roman Catholic, while a significant minority (16.7%) adhere to Protestantism (primarily Evangelicalism). Some 4.7% of the population is atheist or agnostic, while 3.5% claim to believe in God but do not follow a specific religion. 1.8% of Colombians adhere to Jehovah's Witnesses and Adventism and less than 1% adhere to other religions, such as the Baháʼí Faith, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism, Mormonism, Hinduism, Indigenous religions, Hare Krishna movement, Rastafari movement, Eastern Orthodox Church, and spiritual studies. The remaining people either did not respond or replied that they did not know. In addition to the above statistics, 35.9% of Colombians reported that they did not practice their faith actively. 1,519,562 people in Colombia, or around 3% of the population reported following an Indigenous religion.
While Colombia remains a mostly Roman Catholic country by baptism numbers, the 1991 Colombian constitution guarantees freedom of religion and all religious faiths and churches are equally free before the law.
Health
Main article: Health care in Colombia
The overall life expectancy in Colombia at birth is 79.3 years (76.7 years for males and 81.9 years for females). Healthcare reforms have led to massive improvements in the healthcare systems of the country, with health standards in Colombia improving very much since the 1980s. The new system has widened population coverage by the social and health security system from 21% (pre-1993) to 96% in 2012. In 2017, the government declared a cancer research and treatment center as a Project of National Strategic Interest.
A 2016 study conducted by América Economía magazine ranked 21 Colombian health care institutions among the top 44 in Latin America, amounting to 48 percent of the total. In 2022, 26 Colombian hospitals were among the 61 best in Latin America (42% total). Also in 2023, two Colombian hospitals were among the top 75 of the world.
Education
Main article: Education in ColombiaThe educational experience of many Colombian children begins with attendance at a preschool academy until age five (Educación preescolar). Basic education (Educación básica) is compulsory by law. It has two stages: Primary basic education (Educación básica primaria) which goes from first to fifth grade – children from six to ten years old, and Secondary basic education (Educación básica secundaria), which goes from sixth to ninth grade. Basic education is followed by Middle vocational education (Educación media vocacional) that comprises the tenth and eleventh grades. It may have different vocational training modalities or specialties (academic, technical, business, and so on.) according to the curriculum adopted by each school.

After the successful completion of all the basic and middle education years, a high-school diploma is awarded. The high-school graduate is known as a bachiller, because secondary basic school and middle education are traditionally considered together as a unit called bachillerato (sixth to eleventh grade). Students in their final year of middle education take the ICFES test (now renamed Saber 11) to gain access to higher education (Educación superior). This higher education includes undergraduate professional studies, technical, technological and intermediate professional education, and post-graduate studies. Technical professional institutions of Higher Education are also opened to students holder of a qualification in Arts and Business. This qualification is usually awarded by the SENA after a two years curriculum.
Bachilleres (high-school graduates) may enter into a professional undergraduate career program offered by a university; these programs last up to five years (or less for technical, technological and intermediate professional education, and post-graduate studies), even as much to six to seven years for some careers, such as medicine. In Colombia, there is not an institution such as college; students go directly into a career program at a university or any other educational institution to obtain a professional, technical or technological title. Once graduated from the university, people are granted a (professional, technical or technological) diploma and licensed (if required) to practice the career they have chosen. For some professional career programs, students are required to take the Saber-Pro test, in their final year of undergraduate academic education.
Public spending on education as a proportion of gross domestic product in 2015 was 4.49%. This represented 15.05% of total government expenditure. The primary and secondary gross enrolment ratios stood at 113.56% and 98.09% respectively. School-life expectancy was 14.42 years. A total of 94.58% of the population aged 15 and older were recorded as literate, including 98.66% of those aged 15–24.
Crime

Colombia has a high crime rate due to being a center for the cultivation and trafficking of cocaine. The Colombian conflict began in the mid-1960s and is a low-intensity conflict between Colombian governments, paramilitary groups, crime syndicates, and left-wing guerrillas such as the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), and the National Liberation Army (ELN), fighting each other to increase their influence in Colombian territory. Two of the most important international actors that have contributed to the Colombian conflict are multinational companies and the United States.
Elements of all the armed groups have been involved in drug trafficking. In a country where state capacity has been weak in some regions, the result has been a grinding war on multiple fronts, with the civilian population caught in between and often deliberately targeted for "collaborating". Human rights advocates blame paramilitaries for massacres, "disappearances", and cases of torture and forced displacement. Rebel groups are behind assassinations, kidnapping and extortion.
In 2011, President Juan Manuel Santos launched the "Borders for Prosperity" plan to fight poverty and combat violence from illegal armed groups along Colombia's borders through social and economic development. The plan received praise from the International Crisis Group. Colombia registered a homicide rate of 24.4 per 100,000 in 2016, the lowest since 1974. The 40-year low in murders came the same year the government signed a peace agreement with the FARC. The murder rate further decreased to 22.6 in 2020, though still among the highest in the world, it decreased 73% from 84 in 1991. In the 1980s and 1990s it regularly ranked as number one.
Since the beginning of the crisis in Venezuela and the mass emigration of Venezuelans during the Venezuelan refugee crisis, desperate Venezuelans have been recruited into gangs in order to survive by other Venezuelan gang members. Venezuelan women have also resorted to prostitution in order to make a living in Colombia. Also, many Venezuelan prisoners were released from Venezuelan prisons by Maduro. Gang groups from Venezuela have also migrated to Colombia and other countries.Urbanization
Colombia is a highly urbanized country with 77.1% of the population living in urban areas. The largest cities in the country are Bogotá, with 7,387,400 inhabitants, Medellín, with 2,382,399 inhabitants, Cali, with 2,172,527 inhabitants, and Barranquilla, with 1,205,284 inhabitants.
| Largest cities or towns in Colombia According to the 2018 Census | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Department | Pop. | Rank | Name | Department | Pop. | ||
 Bogotá  Medellín |
1 | Bogotá | Distrito Capital | 7,387,400 | 11 | Ibagué | Tolima | 492,554 |  Cali |
| 2 | Medellín | Antioquia | 2,382,399 | 12 | Villavicencio | Meta | 492,052 | ||
| 3 | Cali | Valle del Cauca | 2,172,527 | 13 | Santa Marta | Magdalena | 455,299 | ||
| 4 | Barranquilla | Atlántico | 1,205,284 | 14 | Valledupar | Cesar | 431,794 | ||
| 5 | Cartagena | Bolívar | 876,885 | 15 | Manizales | Caldas | 405,234 | ||
| 6 | Cúcuta | Norte de Santander | 685,445 | 16 | Montería | Córdoba | 388,499 | ||
| 7 | Soacha | Cundinamarca | 655,025 | 17 | Pereira | Risaralda | 385,838 | ||
| 8 | Soledad | Atlántico | 602,644 | 18 | Neiva | Huila | 335,994 | ||
| 9 | Bucaramanga | Santander | 570,752 | 19 | Pasto | Nariño | 308,095 | ||
| 10 | Bello | Antioquia | 495,483 | 20 | Armenia | Quindío | 287,245 | ||
Culture
Main article: Culture of Colombia See also: Festivals in Colombia and Colombian folkloreColombia lies at the crossroads of Latin America and the broader American continent, and as such has been hit by a wide range of cultural influences. Native American, Spanish and other European, African, American, Caribbean, and Middle Eastern influences, as well as other Latin American cultural influences, are all present in Colombia's modern culture. Urban migration, industrialization, globalization, and other political, social and economic changes have also left an impression.
Many national symbols, both objects and themes, have arisen from Colombia's diverse cultural traditions and aim to represent what Colombia, and the Colombian people, have in common. Cultural expressions in Colombia are promoted by the government through the Ministry of Culture.
Literature
Main article: Colombian literature
Colombian literature dates back to pre-Columbian era; a notable example of the period is the epic poem known as the Legend of Yurupary. In Spanish colonial times, notable writers include Juan de Castellanos (Elegías de varones ilustres de Indias), Hernando Domínguez Camargo and his epic poem to San Ignacio de Loyola, Pedro Simón and Juan Rodríguez Freyle.
Post-independence literature linked to Romanticism highlighted Antonio Nariño, José Fernández Madrid, Camilo Torres Tenorio and Francisco Antonio Zea. In the second half of the nineteenth century and early twentieth century the literary genre known as costumbrismo became popular; great writers of this period were Tomás Carrasquilla, Jorge Isaacs and Rafael Pombo (the latter of whom wrote notable works of children's literature). Within that period, authors such as José Asunción Silva, José Eustasio Rivera, León de Greiff, Porfirio Barba-Jacob and José María Vargas Vila developed the modernist movement. In 1872, Colombia established the Colombian Academy of Language, the first Spanish language academy in the Americas. Candelario Obeso wrote the groundbreaking Cantos Populares de mi Tierra (1877), the first book of poetry by an Afro-Colombian author.
Between 1939 and 1940 seven books of poetry were published under the name Stone and Sky in the city of Bogotá that significantly influenced the country; they were edited by the poet Jorge Rojas. In the following decade, Gonzalo Arango founded the movement of "nothingness" in response to the violence of the time; he was influenced by nihilism, existentialism, and the thought of another great Colombian writer: Fernando González Ochoa. During the boom in Latin American literature, successful writers emerged, led by Nobel laureate Gabriel García Márquez and his magnum opus, One Hundred Years of Solitude, Eduardo Caballero Calderón, Manuel Mejía Vallejo, and Álvaro Mutis, a writer who was awarded the Cervantes Prize and the Prince of Asturias Award for Letters.
Visual arts
Main article: Colombian art Work by the painter and sculptor Fernando Botero
Work by the painter and sculptor Fernando Botero Colonial painting The Virgin of Chiquinquirá (1562) by Alonso de Narváez. She is the Catholic Patroness of Colombia. The original canvas is located in the Basilica of Our Lady of the Rosary of Chiquinquirá.
Colonial painting The Virgin of Chiquinquirá (1562) by Alonso de Narváez. She is the Catholic Patroness of Colombia. The original canvas is located in the Basilica of Our Lady of the Rosary of Chiquinquirá. Mural by Santiago Martínez Delgado
Mural by Santiago Martínez Delgado
Colombian art has over 3,000 years of history. Colombian artists have captured the country's changing political and cultural backdrop using a range of styles and mediums. There is archeological evidence of ceramics being produced earlier in Colombia than anywhere else in the Americas, dating as early as 3,000 BCE.
The earliest examples of gold craftsmanship have been attributed to the Tumaco people of the Pacific coast and date to around 325 BCE. Roughly between 200 BCE and 800 CE, the San Agustín culture, masters of stonecutting, entered its "classical period". They erected raised ceremonial centers, sarcophagi, and large stone monoliths depicting anthropomorphic and zoomorphic forms out of stone.
Colombian art has followed the trends of the time, so during the 16th to 18th centuries, Spanish Catholicism had a huge influence on Colombian art, and the popular baroque style was replaced with rococo when the Bourbons ascended to the Spanish crown. During this era, in the Spanish colony, the most important Neogranadine (Colombian) painters were Gregorio Vásquez de Arce y Ceballos, Gaspar de Figueroa, Baltasar Vargas de Figueroa, Baltasar de Figueroa (the Elder), Antonio Acero de la Cruz and Joaquín Gutiérrez, of which their works are preserved. Also important was Alonso de Narváez who, although born in the Province of Seville, spent most of his life in colonial Colombia, also the Italian Angelino Medoro, lived in Colombia and Peru, and left works of art preserved in several churches in Tunja city.
During the mid-19th century, one of the most remarkable painters was Ramón Torres Méndez, who produced a series of good quality paintings depicting the people and their customs of different Colombian regions. Also noteworthy in the 19th century were Andrés de Santa María, Pedro José Figueroa, Epifanio Garay, Mercedes Delgado Mallarino, José María Espinosa, Ricardo Acevedo Bernal, between many others.
More recently, Colombian artists Pedro Nel Gómez and Santiago Martínez Delgado started the Colombian Murial Movement in the 1940s, featuring the neoclassical features of Art Deco. Since the 1950s, the Colombian art started to have a distinctive point of view, reinventing traditional elements under the concepts of the 20th century. Examples of this are the Greiff portraits by Ignacio Gómez Jaramillo, showing what the Colombian art could do with the new techniques applied to typical Colombian themes. Carlos Correa, with his paradigmatic "Naturaleza muerta en silencio" (silent dead nature), combines geometrical abstraction and cubism. Alejandro Obregón is often considered as the father of modern Colombian painting, and one of the most influential artist in this period, due to his originality, the painting of Colombian landscapes with symbolic and expressionist use of animals, (specially the Andean condor). Fernando Botero, Omar Rayo, Enrique Grau, Édgar Negret, David Manzur, Rodrigo Arenas Betancourt, Oscar Murillo, Doris Salcedo and Oscar Muñoz are some of the Colombian artists featured at the international level.
The Colombian sculpture from the sixteenth to 18th centuries was mostly devoted to religious depictions of ecclesiastic art, strongly influenced by the Spanish schools of sacred sculpture. During the early period of the Colombian republic, the national artists were focused in the production of sculptural portraits of politicians and public figures, in a plain neoclassicist trend. During the 20th century, the Colombian sculpture began to develop a bold and innovative work with the aim of reaching a better understanding of national sensitivity.
Colombian photography was marked by the arrival of the daguerreotype. Jean-Baptiste Louis Gros was who brought the daguerreotype process to Colombia in 1841. The Piloto public library has Latin America's largest archive of negatives, containing 1.7 million antique photographs covering Colombia 1848 until 2005.
The Colombian press has promoted the work of the cartoonists. In recent decades, fanzines, internet and independent publishers have been fundamental to the growth of the comic in Colombia.
Architecture
Main article: Architecture of Colombia See also: Muisca architectureThroughout the times, there have been a variety of architectural styles, from those of indigenous peoples to contemporary ones, passing through colonial (military and religious), Republican, transition and modern styles.



Ancient habitation areas, longhouses, crop terraces, roads as the Inca road system, cemeteries, hypogeums and necropolises are all part of the architectural heritage of indigenous peoples. Some prominent indigenous structures are the preceramic and ceramic archaeological site of Tequendama, Tierradentro (a park that contains the largest concentration of pre-Columbian monumental shaft tombs with side chambers), the largest collection of religious monuments and megalithic sculptures in South America, located in San Agustín, Huila, Lost city (an archaeological site with a series of terraces carved into the mountainside, a net of tiled roads, and several circular plazas), and the large villages mainly built with stone, wood, cane, and mud. Architecture during the period of conquest and colonization is mainly derived of adapting European styles to local conditions, and Spanish influence, especially Andalusian and Extremaduran, can be easily seen. When Europeans founded cities two things were making simultaneously: the dimensioning of geometrical space (town square, street), and the location of a tangible point of orientation. The construction of forts was common throughout the Caribbean and in some cities of the interior, because of the dangers posed to Spanish colonial settlements from English, French and Dutch pirates and hostile indigenous groups. Churches, chapels, schools, and hospitals belonging to religious orders have a great urban influence. Baroque architecture is used in military buildings and public spaces. Marcelino Arroyo, Francisco José de Caldas and Domingo de Petrés were great representatives of neo-classical architecture.
The National Capitol is a great representative of romanticism. Wood was extensively used in doors, windows, railings, and ceilings during the colonization of Antioquia. The Caribbean architecture acquires a strong Arabic influence. The Teatro Colón in Bogotá is a lavish example of architecture from the 19th century. The quintas houses with innovations in the volumetric conception are some of the best examples of the Republican architecture; the Republican action in the city focused on the design of three types of spaces: parks with forests, small urban parks and avenues and the Gothic style was most commonly used for the design of churches.
Deco style, modern neoclassicism, eclecticism folklorist and art deco ornamental resources significantly influenced the architecture of Colombia, especially during the transition period. Modernism contributed with new construction technologies and new materials (steel, reinforced concrete, glass and synthetic materials) and the topology architecture and lightened slabs system also have a great influence. The most influential architects of the modern movement were Rogelio Salmona and Fernando Martínez Sanabria.
The contemporary architecture of Colombia is designed to give greater importance to the materials, this architecture takes into account the specific natural and artificial geographies and is also an architecture that appeals to the senses. The conservation of the architectural and urban heritage of Colombia has been promoted in recent years.
Music
Main article: Music of ColombiaColombia has a vibrant collage of talent that touches a full spectrum of rhythms. It is known as the land of a thousand rhythms, at around 1,024 folk rhythms. Musicians, composers, music producers and singers from Colombia are recognized internationally such as Shakira, Juanes, Carlos Vives and others. Colombian music blends European-influenced guitar and song structure with large gaita flutes and percussion instruments from the indigenous population, while its percussion structure and dance forms come from Africa. Colombia has a diverse and dynamic musical environment.
Guillermo Uribe Holguín, an important cultural figure in the National Symphony Orchestra of Colombia, Luis Antonio Calvo and Blas Emilio Atehortúa are some of the greatest exponents of the art music. The Bogotá Philharmonic Orchestra is one of the most active orchestras in Colombia.
Caribbean music has many vibrant rhythms, such as cumbia (it is played by the maracas, the drums, the gaitas and guacharaca), porro (it is a monotonous but joyful rhythm), mapalé (with its fast rhythm and constant clapping) and the "vallenato", which originated in the northern part of the Caribbean coast (the rhythm is mainly played by the caja, the guacharaca, and accordion).
The music from the Pacific coast, such as the currulao, is characterized by its strong use of drums (instruments such as the native marimba, the conunos, the bass drum, the side drum, and the cuatro guasas or tubular rattle). An important rhythm of the south region of the Pacific coast is the contradanza (it is used in dance shows due to the striking colours of the costumes). Marimba music, traditional chants and dances from the Colombia South Pacific region are on UNESCO's Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.

Important musical rhythms of the Andean Region are the danza (dance of Andean folklore arising from the transformation of the European contredance), the bambuco (it is played with guitar, tiple and mandolin, the rhythm is danced by couples), the pasillo (a rhythm inspired by the Austrian waltz and the Colombian "danza", the lyrics have been composed by well-known poets), the guabina (the tiple, the bandola and the requinto are the basic instruments), the sanjuanero (it originated in Tolima and Huila Departments, the rhythm is joyful and fast). Apart from these traditional rhythms, salsa music has spread throughout the country, and the city of Cali is considered by many salsa singers to be 'The New Salsa Capital of the World'.
The instruments that distinguish the music of the Eastern Plains are the harp, the cuatro (a type of four-stringed guitar) and maracas. Important rhythms of this region are the joropo (a fast rhythm and there is also tapping as a result of its flamenco ancestry) and the galeron (it is heard a lot while cowboys are working).
The music of the Amazon region is strongly influenced by the indigenous religious practices. Some of the musical instruments used are the manguaré (a musical instrument of ceremonial type, consisting of a pair of large cylindrical drums), the quena (melodic instrument), the rondador, the congas, bells, and different types of flutes.
The music of the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina is usually accompanied by a mandolin, a tub-bass, a jawbone, a guitar and maracas. Some popular archipelago rhythms are the Schottische, the Calypso, the Polka and the Mento.
Popular culture
Main articles: Theater of Colombia, Cinema of Colombia, and Media of Colombia
Theater was introduced in Colombia during the Spanish colonization in 1550 through zarzuela companies. Colombian theater is supported by the Ministry of Culture and a number of private and state owned organizations. The Ibero-American Theater Festival of Bogotá is the cultural event of the highest importance in Colombia and one of the biggest theater festivals in the world. Other important theater events are: The Festival of Puppet The Fanfare (Medellín), The Manizales Theater Festival, The Caribbean Theatre Festival (Santa Marta) and The Art Festival of Popular Culture "Cultural Invasion" (Bogotá).
Although the Colombian cinema is young as an industry, more recently the film industry was growing with support from the Film Act passed in 2003. Many film festivals take place in Colombia, but the two most important are the Cartagena Film Festival, which is the oldest film festival in Latin America, and the Bogotá Film Festival.
Some important national circulation newspapers are El Tiempo and El Espectador. Television in Colombia has two privately owned TV networks and three state-owned TV networks with national coverage, as well as six regional TV networks and dozens of local TV stations. Private channels, RCN and Caracol are the highest-rated. The regional channels and regional newspapers cover a department or more and its content is made in these particular areas.
Colombia has three major national radio networks: Radiodifusora Nacional de Colombia, a state-run national radio; Caracol Radio and RCN Radio, privately owned networks with hundreds of affiliates. There are other national networks, including Cadena Super, Todelar, and Colmundo. Many hundreds of radio stations are registered with the Ministry of Information Technologies and Communications.
Cuisine
Main article: Colombian cuisine
Colombia's varied cuisine is influenced by its diverse fauna and flora as well as the cultural traditions of the ethnic groups. Colombian dishes and ingredients vary widely by region. Some of the most common ingredients are: cereals such as rice and maize; tubers such as potato and cassava; assorted legumes; meats, including beef, chicken, pork and goat; fish; and seafood. Colombia cuisine also features a variety of tropical fruits such as cape gooseberry, feijoa, arazá, dragon fruit, mangostino, granadilla, papaya, guava, mora (blackberry), lulo, soursop and passionfruit. Colombia is one of the world's largest consumers of fruit juices.
Among the most representative appetizers and soups are patacones (fried green plantains), sancocho de gallina (chicken soup with root vegetables) and ajiaco (potato and corn soup). Representative snacks and breads are pandebono, arepas (corn cakes), aborrajados (fried sweet plantains with cheese), torta de choclo, empanadas and almojábanas. Representative main courses are bandeja paisa, lechona tolimense, mamona, tamales and fish dishes (such as arroz de lisa), especially in coastal regions where kibbeh, suero, costeño cheese and carimañolas are also eaten. Representative side dishes are papas chorreadas (potatoes with cheese), remolachas rellenas con huevo duro (beets stuffed with hard-boiled egg) and arroz con coco (coconut rice). Organic food is a current trend in big cities, although in general across the country the fruits and veggies are very natural and fresh.
Representative desserts are buñuelos, natillas, Maria Luisa cake, bocadillo made of guayaba (guava jelly), cocadas (coconut balls), casquitos de guayaba (candied guava peels), torta de natas, obleas, flan de mango, roscón, milhoja, manjar blanco, dulce de feijoa, dulce de papayuela, torta de mojicón, and esponjado de curuba. Typical sauces (salsas) are hogao (tomato and onion sauce) and Colombian-style ají.
Some representative beverages are coffee (Tinto), champús, cholado, lulada, avena colombiana, sugarcane juice, aguapanela, aguardiente, hot chocolate and fresh fruit juices (often made with water or milk).
Sports
Main article: Sport in Colombia
Tejo is Colombia's national sport and is a team sport that involves launching projectiles to hit a target. But of all sports in Colombia, football is the most popular. Colombia was the champion of the 2001 Copa América, in which they set a new record of being undefeated, conceding no goals and winning each match. Colombia has been awarded "mover of the year" twice.
Colombia is a hub for roller skaters. The national team is a perennial powerhouse at the World Roller Speed Skating Championships. Colombia has traditionally been very good in cycling and a large number of Colombian cyclists have triumphed in major competitions of cycling.
Baseball is popular in cities like Cartagena and Barranquilla. Of those cities have come good players like: Orlando Cabrera, Édgar Rentería, who was champion of the World Series in 1997 and 2010 and others who have played in Major League Baseball. Colombia was world amateur champion in 1947 and 1965.
Boxing is one of the sports that has produced more world champions for Colombia. Motorsports also occupies an important place in the sporting preferences of Colombians; Juan Pablo Montoya is a race car driver known for winning 7 Formula One events. Colombia also has excelled in sports such as BMX, judo, shooting sport, taekwondo, wrestling, high diving and athletics, also has a long tradition in weightlifting and bowling.
See also
Notes
- incl. Spaniards, Basque, Italians, Germans, French, other Europeans, Arabs and Jews
- /kəˈlʌmbiə/ kə-LUM-bee-ə, /-ˈlɒm-/ -LOM-; Spanish: [koˈlombja]
- Spanish: República de Colombia. IPA transcription of "República de Colombia": Spanish pronunciation: [reˈpuβlika ðe koˈlombja].
- Balboa is best known for being the first European to see the Pacific Ocean in 1513, which he called Mar del Sur (or "Sea of the South") and would facilitate Spanish exploration and settlement of South America.
- A royal decree of 1713 approved the legality of Palenque de San Basilio founded by runaway slaves as a refuge in the seventeenth century. The people of San Basilio fought against slavery, thereby giving rise to the first free place in the Americas. Its main leader was Benkos Biohó, who was born in West Africa.
- Peter Claver was a Spaniard who traveled to Cartagena in 1610 and was ordained as a Jesuit priest in 1616. Claver cared for African slaves for thirty-eight years, defending their lives and the dignity.
- Héctor Abad was a prominent medical doctor, university professor, and human rights leader whose holistic vision of healthcare led him to found the Colombian National School of Public Health. The increasing violence and human rights abuses of the 1970s and 1980s led him to fight for social justice in his community.
- Javier de Nicoló was a Salesian priest who grew up in war-torn Italy and arrived in Colombia a year after the Bogotazo. He developed a program that has offered more than 40,000 young people the education and moral support they needed to become productive citizens.
References
- "Por la cual se dictan normas especiales para la organización y el funcionamiento del Departamento Archipiélago de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina". Archived from the original on 5 November 2023. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
ARTÍCULO 42. IDIOMA Y LENGUA OFICIAL EN EL DEPARTAMENTO ARCHIPIELAGO. Son oficiales en el Departamento Archipiélago de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina el castellano y el inglés comunmente hablado por las comunidades nativas del Archipiélago.
- ^ "visibilización estadística de los grupos étnicos". Censo General 2018. Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica (DANE). Archived from the original on 16 August 2021. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- Homburger, J. R.; Moreno-Estrada, A.; Gignoux, C. R.; Nelson, D.; Sanchez, E.; Ortiz-Tello, P.; Pons-Estel, B. A.; Acevedo-Vasquez, E.; Miranda, P.; Langefeld, C. D.; Gravel, S.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M. E.; Bustamante, C. D. (2015). "Genomic Insights into the Ancestry and Demographic History of South America". PLOS Genetics. 11 (12): e1005602. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005602. ISSN 1553-7390. PMC 4670080. PMID 26636962.
- "Catholicism and evangelism: the two most common religions in Latin America". Statista. 26 October 2022. Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 18 November 2022.
- "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- "Proyecciones de Población DANE". Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2024 Edition. (Colombia)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 16 April 2024. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- "Colombia - The World Factbook". Retrieved 23 September 2024.
- "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title I – Concerning Fundamental Principles – Article 10)
- ^ "LEY 47 DE 1993" (in Spanish). alcaldiabogota.gov.co. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- "The official Colombian time" (in Spanish). horalegal.inm.gov.co. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- "Decreto 4175 de 2011, artículo 6, numeral 14" (in Spanish). Presidencia de la República de Colombia. Archived from the original on 15 April 2016. Retrieved 14 March 2016.
- Jones, Daniel (2011). Roach, Peter; Setter, Jane; Esling, John (eds.). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-15255-6.
- "Colombia herencia cultural más allá de la colonia". procolombia.co (in Spanish). 28 March 2017. Archived from the original on 26 February 2023. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- "News & Events - Irlandeses en Colombia y Antioquia". Department of Foreign Affairs of Ireland. Archived from the original on 26 August 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- "Estos fueron los primeros alemanes en Colombia". Revista Diners (in Spanish). 10 June 2019. Archived from the original on 5 November 2022. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- Vidal Ortega, Antonino; D'Amato Castillo, Giuseppe (1 December 2015). "Los otros, sin patria: italianos en el litoral Caribe de Colombia a comienzos del siglo XX". Caravelle. Cahiers du monde hispanique et luso-brésilien (in French) (105): 153–175. doi:10.4000/caravelle.1822. ISSN 1147-6753. Archived from the original on 6 October 2022. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- Salamanca, Helwar Figueroa; Espitia, Julián David Corredor (31 July 2019). ""En una ciudad gris y silenciosa": la migración francesa en Bogotá (1900-1920)". Anuario de Historia Regional y de las Fronteras (in Spanish). 24 (2): 75–100. doi:10.18273/revanu.v24n2-2019003. ISSN 2145-8499. S2CID 203515282. Archived from the original on 6 March 2023. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- Fawcett de Posada, Louise; Posada Carbó, Eduardo (1992). "En la tierra de las oportunidades: los sirio-libaneses en Colombia" [In the land of opportunity: the Syrian-Lebanese in Colombia] (PDF). Boletín Cultural y Bibliográfico (in Spanish). 29 (29). publicaciones.banrepcultural.org: 8–11. Archived from the original on 2 March 2016. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- S.A.S, Editorial La República (26 April 2022). "Colombia y Medio Oriente". Diario La República (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 24 November 2022. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- Tiempo, Casa Editorial El (7 March 2019). "Los palestinos que encontraron un segundo hogar en el centro de Bogotá". El Tiempo (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 31 October 2022. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- Faucher, Nicolás Murillo (11 August 2014). "La herencia Africana en Colombia". Libre Pensador (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 27 February 2023. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- "El patrimonio cultural de seis pueblos indígenas renace con 'Sembrando Nuestros Saberes' en Colombia". aa.com.tr. Archived from the original on 26 February 2023. Retrieved 26 February 2023.
- ^ Historical Memory Group (2013). "Enough Already!" Colombia: Memories of War and Dignity (PDF) (in Spanish). The National Center for Historical Memory's (NCHM). ISBN 9789585760844. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ "Colombia's GDP growth". World Bank. Archived from the original on 5 July 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "World Health Organization Assesses the World's Health Systems". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 9 April 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- "Colombia Healthcare System". International Citizens Insurance. Archived from the original on 30 March 2023. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ "Cuentas Trimestrales – Producto Interno Bruto (PIB)" (PDF) (in Spanish). dane.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ^ "IMF Executive Board Concludes 2018 Article IV Consultation with Colombia". imf.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2022. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- ^ Luis Fernando Potes. "Colombia is the second most biodiverse country in the world" (in Spanish). prodiversitas.bioetica.org. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "NATO - Topic: Relations with Colombia". Nato.int. Archived from the original on 30 August 2022. Retrieved 30 August 2022.
- ^ Samuels, Brett (10 March 2022). "Biden designates Colombia as major non-NATO ally". The Hill. Archived from the original on 18 November 2023. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- República, Subgerencia Cultural del Banco de la. "La Red Cultural del Banco de la República". banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 1 May 2021. Retrieved 20 October 2020.
- ^ Carlos Restrepo Piedrahita (February 1992). "El nombre "Colombia", El único país que lleva el nombre del Descubrimiento". Revista Credencial (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- Helena Guedes, Maria. A Grande Colômbia!. Clube de Autores. p. 141.
- Correal, Urrego G. (1993). "Nuevas evidencias culturales pleistocenicas y megafauna en Colombia". Boletin de Arqueologia (8): 3–13.
- Hoopes, John (1994). "Ford Revisited: A Critical Review of the Chronology and Relationships of the Earliest Ceramic Complexes in the New World, 6000-1500 B.C. (1994)". Journal of World Prehistory. 8 (1): 1–50. doi:10.1007/bf02221836. S2CID 161916440. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 6 September 2019.
- Van der Hammen, Thomas; Urrego, Gonzalo Correal (September 1978). "Prehistoric man of the Sabana de Bogotá: Data for an ecological prehistory". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 25 (1–2): 179–190. Bibcode:1978PPP....25..179V. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(78)90077-9.
- Alberge, Dalya (29 November 2020). "Sistine Chapel of the ancients' rock art discovered in remote Amazon forest". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- Broadbent, Sylvia (1965). "Los Chibchas: organización socio-polític". Serie Latinoamericana. 5.
- Álvaro Chaves Mendoza; Jorge Morales Gómez (1995). Los indios de Colombia (in Spanish). Vol. 7. Editorial Abya Yala. ISBN 978-9978-04-169-7. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- "Historia de Colombia: el establecimiento de la dominación española – Los Pueblos Indígenas del Territorio Colombiano" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- [https://phys.org/news/2020-07-polynesians-native-americans-contact-european.html Polynesians, Native Americans made contact before European arrival, genetic study finds by Stanford University Medical Center]
- Native American gene flow into Polynesia predating Easter Island settlement by Alexander G. Ioannidis et al.
- Nicolás del Castillo Mathieu (March 1992). "La primera vision de las costas Colombianas, Repaso de Historia". Revista Credencial (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 19 October 2007. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- "Alonso de Ojeda" (in Spanish). biografiasyvidas.com. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- "Rodrigo de Bastidas" (in Spanish). biografiasyvidas.com. Archived from the original on 23 April 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- "Cristóbal Colón" (in Spanish). biografiasyvidas.com. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- "Vasco Núñez de Balboa" (in Spanish). biografiasyvidas.com. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- Vázquez, Trinidad Miranda (1976). La gobernación de Santa Marta (1570–1670) Vol. 232 (in Spanish). Editorial CSIC-CSIC Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-84-00-04276-9. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- Plá, María del Carmen Borrego (1983). Cartagena de Indias en el siglo XVI. Vol. 288 (in Spanish). Editorial CSIC-CSIC Press. pp. 3–5. ISBN 978-84-00-05440-3. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- Francis, John Michael, ed. (2007). Invading Colombia: Spanish accounts of the Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada expedition of conquest Vol. 1. Penn State Press. ISBN 978-0-271-02936-8. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ Jaramillo Uribe, Jaime (1989). "Perfil histórico de Bogotá". Historia Crítica (in Spanish) (1): 5–19. doi:10.7440/histcrit1.1989.01. ISSN 0121-1617.
- Silvia Padilla Altamirano (1977). La encomienda en Popayán: tres estudios (in Spanish). Editorial CSIC Press. pp. 4–5. ISBN 978-84-00-03612-6. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- Massimo Livi Bacci (2012). El dorado en el pantano (in Spanish). Marcial Pons Historia. ISBN 978-84-92820-65-8. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- Ramírez, Natalia; Gutiérrez, Germán (2010). "Félix de Azara: Observaciones conductuales en su viaje por el Virreinato del Río de la Plata". Revista de historia de la psicología. 31 (4): 52–53. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- "El Dorado Legend Snared Sir Walter Raleigh". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 13 February 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- "La Conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada: la interpretación de los siete mitos (III) – RESTALL, Matthew: Los siete mitos de la conquista española, Barcelona, 2004" (in Spanish). queaprendemoshoy.com/. Archived from the original on 9 February 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- Jorge Augusto Gamboa M. "Las sociedades indígenas del Nuevo Reino de Granada bajo el dominio español" (PDF) (in Spanish). Instituto Colombiano de Antropología e Historia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Las plantas medicinales en la época de la colonia y de la independencia" (PDF) (in Spanish). colombiaaprende.edu.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ Mayorga, Fernando (2002). "La propiedad de tierras en la Colonia: Mercedes, composición de títulos y resguardos indígenas". banrepcultural.org (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ Germán Colmenares. "Historia económica y órdenes de magnitud, Capítulo 1: La Formación de la Economía Colonial (1500–1740)" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ Margarita González. "La política económica virreinal en el Nuevo Reino de Granada: 1750–1810" (PDF) (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2014.
- Domingo, Mariano Cuesta (2004). "Alonso de Santa Cruz, cartógrafo y fabricante de instrumentos náuticos de la Casa de Contratación" [Alonso de Santa Cruz, Cartographer and Maker of Nautical Instruments of the Spanish Casa de Contratación]. Revista Complutense de Historia de América (in Spanish). 30: 7–40. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- John Huxtable Elliott (2007). Empires of the Atlantic World: Britain and Spain in America, 1492–1830. Yale University Press. pp. 124–125. ISBN 978-0-300-12399-9. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- Shaw, Jeffrey M. (2019). Religion and Contemporary Politics: A Global Encyclopedia. Abc-Clio. p. 429. ISBN 9781440839337. Archived from the original on 15 July 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- "Law VIII ("Royal Audiencia and Chancery of Santa Fe in the New Kingdom of Granada") of Title XV ("Of the Royal Audiencias and Chanceries of the Indies") of Book II" (PDF). congreso.gob.pe. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 June 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- Fernando Mayorga García; Juana M. Marín Leoz; Adelaida Sourdis Nájera (2011). El patrimonio documental de Bogotá, Siglos XVI – XIX: Instituciones y Archivos (PDF). Subdirección Imprenta Distrital – D.D.D.I. ISBN 978-958-717-064-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 April 2014.
- Julián Bautista Ruiz Rivera (1975). Encomienda y mita en Nueva Granada en el siglo XVII. Editorial CSIC Press. pp. xxi–xxii. ISBN 978-84-00-04176-2. Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ Jorge Cerdá Crespo (2010). Conflictos coloniales: la guerra de los nueve años 1739–1748 (in Spanish). Universidad de Alicante. ISBN 978-84-9717-127-4. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- Génesis y desarrollo de la esclavitud en Colombia siglos XVI y XVII (in Spanish). Universidad del Valle. 2005. ISBN 978-958-670-338-3.
- Alvaro Gärtner (2005). Los místeres de las minas: crónica de la colonia europea más grande de Colombia en el siglo XIX, surgida alrededor de las minas de Marmato, Supía y Riosucio. Universidad de Caldas. ISBN 978-958-8231-42-6. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- Moñino, Yves; Schwegler, Armin (2002). Palenque, Cartagena y Afro-Caribe: historia y lengua. Walter de Gruyter. pp. vii–ix, 21–35. ISBN 978-3-11-096022-8. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- "Palenque de San Basilio" (PDF) (in Spanish). urosario.edu.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Proceso de beatificación y canonización de San Pedro Claver. Edición de 1696. Traducción del latín y del italiano, y notas de Anna María Splendiani y Tulio Aristizábal S. J. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana. Universidad Católica del Táchira. 2002.
- Valtierra, Ángel. 1964. San Pedro Claver, el santo que liberó una raza.
- "La esclavitud negra en la América española" (in Spanish). gabrielbernat.es. 2003. Archived from the original on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- Villamar, Cuauhtemoc (March 2022). "El Galeón de Manila y el comercio de Asia: Encuentro de culturas y sistemas". Interacción Sino-Iberoamericana / Sino-Iberoamerican Interaction. 2 (1): 85–109. doi:10.1515/sai-2022-0008. S2CID 249318172.
- Rivera, Julián Bautista Ruiz (1997). "Reformismo local en el nuevo Reino de Granada. Temas americanistas N° 13" (PDF) (in Spanish). pp. 80–98. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2014.
- Jaime U. Jaramillo; Adolfo R. Maisel; Miguel M. Urrutia (1997). Transferring Wealth and Power from the Old to the New World: Monetary and Fiscal Institutions in the 17th Through the 19th Centuries – Chapter 12 (PDF). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-02727-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Greshko, Michael. "Did This Spanish Shipwreck Change the Course of History?". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 3 November 2015.
- "José Celestino Mutis in New Granada: A life at the service of an Expedition (1760–1808)". Real Jardín Botánico. Archived from the original on 13 April 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- Angela Perez-Mejia (2004). A Geography of Hard Times: Narratives about Travel to South America, 1780–1849 – Part I: The scholar and the baron: Voyage of the exact sciences. SUNY Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-6013-9. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- John Wilton Appel (1994). Francisco José de Caldas: A Scientist at Work in Nueva Granada. American Philosophical Society. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-87169-845-2.
- "Independencia de Colombia: ¿por qué se celebra el 20 de julio?" [Independence of Colombia: Why is it celebrated on 20 July?]. El País (in Spanish). 20 July 2017. ISSN 1134-6582. Archived from the original on 18 July 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- McFarlane, Anthony (January 1982). "El colapso de la autoridad española y la génesis de la independencia en la Nueva Granada". Revista Desarrollo y Sociedad (7): 99–120. doi:10.13043/dys.7.3.
- Rodriguez Gómez, Juan Camilo. "La independencia del Socorro en la génesis de la emancipación colombiana" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- Gutiérrez Ardila, Daniel (December 2011). "Colombia y Haití: historia de un desencuentro (1819–1831)" [Colombia and Haití: History of a Misunderstanding (1819–1831)]. Secuencia (in Spanish) (81): 67–93. Archived from the original on 7 July 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Gutiérrez Escudero, Antonio. "Un precursor de la emancipación americana: Antonio Nariño y Álvarez" (PDF) (in Spanish). Araucaria. Revista Iberoamericana de Filosofía, Política y Humanidades 8.13 (2005). pp. 205–220. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Sourdis Nájera, Adelaida. "Independencia del Caribe colombiano 1810–1821" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia – Edición 242. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Martínez Garnica, Armandao (2010). "Confederación de las Provincias Unidas de la Nueva Granada" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia – Edición 244. Archived from the original on 24 June 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- "Acta de la Federación de las Provincias Unidas de Nueva Granada" (in Spanish). 1811. Archived from the original on 25 June 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Ocampo López, Javier (1998). La patria boba. Cuadernillos de historia. Panamericana Editorial. ISBN 978-958-30-0533-6.
- "Morillo y la reconquista, 1816–1819" (in Spanish). udea.edu.co. Archived from the original on 27 October 2016. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- Ocampo López, Javier (2006). Historia ilustrada de Colombia – Capítulo VI (in Spanish). Plaza y Janes Editores Colombia sa. ISBN 978-958-14-0370-7. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- Cartagena de Indias en la independencia (PDF). Banco de la República. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Cronología de las independencias americanas" (in Spanish). cervantes.es. Archived from the original on 16 February 2018. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- Gutiérrez Ramos, Jairo (2008). "La Constitución de Cádiz en la Provincia de Pasto, Virreinato de Nueva Granada, 1812–1822". Revista de Indias (in Spanish). 68 (242). Revista de Indias 68, no. 242: 222. doi:10.3989/revindias.2008.i242.640. Archived from the original on 12 July 2013. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Pareja, Alfaro; José, Francisco (2013). La Independencia de Venezuela relatada en clave de paz: las regulaciones pacíficas entre patriotas y realistas (1810–1846) (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2015.
- http://necrometrics.com/wars19c.htm Archived 30 April 2015 at archive.today | "Statistics of Wars, Oppressions and Atrocities of the Nineteenth Century"
- http://remilitari.com/guias/victimario6.htm Archived 9 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine | In Spanish "De re Militari: muertos en Guerras, Dictaduras y Genocidios. Capítulo VI"
- Silvio Arturo Zavala (1971). Revista de historia de América. Números 69-70. Ciudad de México: Instituto Panamericano de Geografía e Historia, pp. 303. "Para el primero, de 1400000 habs. que la futura Colombia tendría en 1809 (entre ellos 78000 negros esclavos), (...) mortaldad que él mismo señala a tal guerra (unos 400 000 muertos para la Gran Colombia, entre ellos, 250 000 venezolanos)."
- Walker, Alexander (1822). (Gran) Colombia, relación geográfica, topográfica, agrícola, comercial y política de este país: Adaptada para todo lector en general y para el comerciante y colono en particular (in Spanish). Vol. 1. Banco de la República.
- Sosa Abella, Guillermo (2009). "Los ciudadanos en la Constitución de Cúcuta – Citizenship in the Constitution of Cúcuta" (PDF) (in Spanish). Instituto Colombiano de Antropología e Historia (icanh). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Mollien, Gaspard-Théodore. "El viaje de Gaspard-Théodore Mollien por la República de Colombia en 1823. CAPÍTULO IX" (in Spanish). Biblioteca Virtual del Banco de la República. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- "Avatares de una Joven República – 2. La Constitución de Cúcuta" (in Spanish). Universidad de Antioquia. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ^ "Colombia profile - Timeline". BBC News. 27 August 2012. Archived from the original on 26 September 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2023.
- ^ Blanco Blanco, Jacqueline (2007). "De la gran Colombia a la Nueva Granada, contexto histórico-político de la transición constitucional" (PDF) (in Spanish). Universidad Militar Nueva Granada. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Colombia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. 12 January 2022. (Archived 2022 edition.)
- ^ Arana, Edgar. "Historia Constitucional Colombiana" (PDF) (in Spanish). Universidad Libre Seccional Pereira. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2015.
- Londoño, Juan Fernando (2009). Partidos políticos y think tanks en Colombia (PDF) (in Spanish). International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance. p. 129. ISBN 978-91-85724-73-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2015.
- Aguilera, Miguel (1965). La Legislación y el derecho en Colombia. Historia extensa de Colombia. Vol. 14. Bogotá: Lemer. pp. 428–442.
- Restrepo, Eduardo (2006). "Abolitionist arguments in Colombia". História Unisinos (in Spanish). 10 (3): 293–306. Archived from the original on 8 July 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- "Constituciones que han existido en Colombia" (in Spanish). Banco de la República. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011.
- España, Gonzalo (2013). El país que se hizo a tiros (in Spanish). Penguin Random House. ISBN 978-958-8613-90-1. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- "The 1903 Treaty and Qualified Independence". U.S. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 13 September 2020.
- Beluche, Olmedo (2003). "The true history of the separation of 1903 – La verdadera historia de la separación de 1903" (PDF) (in Spanish). ARTICSA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 October 2015.
- "El tratado Urrutia-Thomson. Dificultades de política interna y exterior retrasaron siete años su ratificación" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. 2003. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- Atehortúa Cruz; Adolfo León (2014). "El conflicto Colombo-Peruano – Apuntes acerca de su desarrollo e importancia histórica". Historia y Espacio (in Spanish). 3 (29): 51–78. doi:10.25100/hye.v3i29.1664. hdl:10893/1003. S2CID 252776167. Archived from the original on 30 October 2015.
- Alape, Arturo (1983). El Bogotazo: Memorias Del Olvido (in Spanish). Fundación Universidad Central.
- Braun, Herbert (1987). Mataron a Gaitán: vida pública y violencia urbana en Colombia (in Spanish). Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Centro Editorial. ISBN 978-958-17-0006-6.
- Charles Bergquist; David J. Robinson (1997–2005). "Colombia". Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2005. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 11 November 2007. Retrieved 16 April 2006. On 9 April 1948, Gaitán was assassinated outside his law offices in downtown Bogotá. The assassination marked the start of a decade of bloodshed, called La Violencia (The Violence), which took the lives of an estimated 180,000 Colombians before it subsided in 1958.
- Carlos Horacio Urán (1986). "Colombia y los Estados Unidos en la Guerra de Corea" (PDF) (in Spanish). The Kellogg Institute for International Studies. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Atehortúa Cruz, Adolfo (2 February 2010). "El golpe de Rojas y el poder de los militares" [Rojas' coup d'etat and the power of army men]. Folios (in Spanish). 1 (31): 33–48. doi:10.17227/01234870.31folios33.48 (inactive 1 November 2024).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Ayala Diago, César Augusto (2000). "Gustavo Rojas Pinilla, 100 años, 1900–1975" (in Spanish). Banco de la República. Archived from the original on 24 April 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- Alarcón Núñez, Óscar (2006). "1957–1974 El Frente Nacional" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 24 April 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ROJAS, Diana Marcela. La alianza para el progreso de Colombia. Análisis Político, , v. 23, n. 70, p. 91–124, Sep. 2010. ISSN 0121-4705
- Ayala Diago, César Augusto (1999). "Frente Nacional: acuerdo bipartidista y alternación en el poder" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 5 July 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- "El Frente Nacional" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. 2006. Archived from the original on 24 April 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ^ Historical Commission on the Conflict and Its Victims (CHCV) (February 2015). "Contribution to an Understanding of the Armed Conflict in Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- Lilian Yaffe (3 October 2011). "Armed conflict in Colombia: analyzing the economic, social, and institutional causes of violent opposition" (in Spanish). icesi.edu.co. Archived from the original on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- "Tomas y ataques guerrilleros (1965–2013)" (in Spanish). centrodememoriahistorica.gov.co. 5 June 2017. Archived from the original on 26 August 2018. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- Héctor Abad Faciolince (2006). Oblivion: A Memoir. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-53393-9.
- "Oblivion: a memoir by Hector Abad wins Wola-Duke human rights book award". wola.org. 12 October 2012. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016. Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- "First-class citizens: Father de Nicoló and the street kids of Colombia". iaf.gov. Archived from the original on 28 March 2016. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- Mario A. Murillo; Jesús Rey Avirama (2004). Colombia and the United States: war, unrest, and destabilization. Seven Stories Press. p. 54. ISBN 978-1-58322-606-3.
- "The Colombian Cartels". WGBH educational foundation. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "20 grandes cambios que generó la Constitución de 1991" (in Spanish). elpais.com.co. Archived from the original on 11 December 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ^ "Colombian Constitution of 1991" (in Spanish). secretariasenado.gov.co. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Mercado, Juan Guillermo (22 September 2013). "Desmovilización, principal arma contra las guerrillas" [Demobilization, main weapon against the guerrillas]. El Tiempo (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 23 September 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- "Former Colombian President Alvaro Uribe Speaks at Yale SOM". Yale School of Management. 3 December 2012. Archived from the original on 20 December 2019. Retrieved 25 June 2016.
- "Colombia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 24 September 2015. (Archived 2015 edition.)
- "Oscar Morales and One Million Voices Against FARC". Movements.org. 23 July 2010. Archived from the original on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
- "Colombia's peace deals". altocomisionadoparalapaz.gov.co. Archived from the original on 14 September 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- "Colombia referendum: Voters reject Farc peace deal". BBC News. 3 October 2016. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- "Plebiscito 2 octubre 2016 – Boletín Nacional No. 53". Registraduría Nacional de Estado Civil. 2 October 2016. Archived from the original on 3 October 2016. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- "Colombia signs new peace deal with Farc". BBC News. 24 November 2016. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- Partlow, Joshua; Miroff, Nick (30 November 2016). "Colombia's congress approves historic peace deal with FARC rebels". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 1 December 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- "Nobel Lecture by Juan Manuel Santos, Oslo, 10 December 2016". NobelPrize.org. Archived from the original on 10 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- "The Victims and Land Restitution Law" (PDF) (in Spanish). unidadvictimas.gov.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- "the Land Restitution Unit". restituciondetierras.gov.co. Archived from the original on 4 January 2016. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- Peters, Toni (12 October 2011). "Colombia has improved under Santos: Human Rights Watch". Colombia Reports. Archived from the original on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "ABC Jurisdicción Especial para la Paz". Oficina del Alto Comisionado para la Paz. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- "Pope at Colombia prayer meeting for reconciliation weeps with victims". radiovaticana.va. 8 September 2017. Archived from the original on 9 September 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- "Colombia's president-elect Duque wants to 'unite country'". BBC News. 18 June 2018. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 21 April 2021.
- "Iván Duque: Colombia's new president sworn into office". BBC News. 8 August 2018. Archived from the original on 30 October 2020. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- "Colombia and Venezuela restore diplomatic relations". BBC News. 11 August 2010. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- "Colombia reitera ofrecimiento de ayuda humanitaria a Venezuela" [Colombia reiterates offer of humanitarian aid to Venezuela]. Presidencia.gov.co (in Spanish). 11 January 2018. Archived from the original on 12 January 2018. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- "Comunicado de prensa del Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores" [Press release of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs]. Presidencia.gov.co (in Spanish). 2 June 2017. Archived from the original on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2017.
- Caballero, Paula (20 September 2016). "A Short History of the SDGS". Impakter.com. Archived from the original on 8 October 2017. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
- "Colombia rejects Venezuelan proposal to resume diplomatic relations". Reuters. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 21 April 2021. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- Guillermoprieto, Alma (22 July 2021). "Confrontation in Colombia | by Alma Guillermoprieto | The New York Review of Books". Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- "Former guerrilla Gustavo Petro wins Colombian election to become first leftist president". The Guardian. 20 June 2022. Archived from the original on 2 August 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- "Ex-rebel takes oath as Colombia's first left-wing president". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- ^ "Natural regions of Colombia and description of the three branches of the andes cordillera". colombia-sa.com. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
- ^ "Maritime borders". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 31 July 2018. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- "The Republic of Colombia shares land borders with five (5) countries". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 31 July 2018. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ^ "Distribution of the population by regions". geoportal.dane.gov.co. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ "Population density of Colombia". geoportal.dane.gov.co. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- "Colombia is part of the Ring of Fire" (in Spanish). seisan.ingeominas.gov.co. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
- "Hydrography of Colombia". colombia-sa.com. Archived from the original on 20 September 2013. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
- ^ "Thermal floors" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
- Delegatarios de países megadiversos. "Declaración de Cancún de países megadiversos afínes" (PDF) (in Spanish). inecc.gob.mx. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "Colombia Celebrates over 1,900 Bird Species". proaves.org. 9 December 2013. Archived from the original on 19 December 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- "Colombia accounts for around 10% of the flora and fauna of the world". humboldt.org.co. Archived from the original on 9 March 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
- "La flor de mayo, Cattleya trianae, flor nacional" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- "Flora of Colombia" (in Spanish). parquesnacionales.gov.co. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- "System of information about biodiversity of Colombia" (in Spanish). Sistema de Información sobre Biodiversidad de Colombia. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- "Informe sobre el estado de los recursos naturales renovables y del ambiente Componente de biodiversidad, 2010–2011" (PDF) (in Spanish). humboldt.org.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2017.
- "Dirección de Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- "Change in forest area, 1990/2011 (%)". undp.org. Archived from the original on 15 February 2015. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- "Table 1: Total Renewable Freshwater Supply, by Country". worldwater.org. Archived from the original on 31 July 2018. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 113)
- "Colombian lawmakers vote to limit presidents to single term". The San Diego Union-Tribune. 4 June 2015. Archived from the original on 31 July 2018. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 115)
- "The Government of Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 15 March 2014. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII – Concerning the executive branch)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title V – Concerning the organization of the state – Chapter 1 – Concerning the structure of the state – Article 114)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Chapter 4 – Concerning the senate – Article 171)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Chapter 5 – Concerning the chamber of representatives – Article 176)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VI – Concerning the legislative branch – Chapter 1 – Concerning its structure and functions – Article 132)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII – Concerning the judiciary branch – Chapter 2 – Concerning ordinary jurisdiction – Article 234)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VIII – Concerning the judiciary branch)
- Landau, David (2017). Colombian Constitutional Law: Leading Cases. Oxford University Press. p. 217. ISBN 9780190640378.
The 1991 Constitution moved Colombia away from the inquisitorial criminal system that it has traditionally possessed (and where the judge plays the leading role in the criminal process), and toward an adversarial system more like the American system, where lawyers act for each side as the protagonists.
- Ipsos-Napoleon Franco poll (1 June 2009). "Si no es Uribe, es Santos" (in Spanish). semana.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- "Colombian Court Blocks President's Bid for a Third Term". The New York Times. 26 February 2010. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 5 October 2015. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- "escrutinio 2ª Vuelta 2010" (PDF) (in Spanish). registraduria.gov.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- "escrutinio 2ª Vuelta 2014" (in Spanish). registraduria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 5 July 2014.
- "2ª Vuelta 2018" (in Spanish). registraduria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018.
- Woodford, Isabel; Vargas, Carlos; Araujo, Gabriel (23 June 2022). "Latin America's new 'pink tide' gains pace as Colombia shifts left; Brazil up next". Reuters. Archived from the original on 28 June 2022. Retrieved 11 July 2022.
- Turkewitz, Julie (19 June 2022). "Francia Márquez — a former housekeeper and activist — is Colombia's first Black vice president". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 4 June 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- "The Ministry of Foreign Affairs". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 27 February 2014. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- "Colombian Embassies and Consulates abroad". cancilleria.gov.co. 9 November 2015. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- "The Pacific Alliance and its Objectives". alianzapacifico.net. Archived from the original on 11 February 2023. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- "Organismos multilaterales". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "Mecanismos de Concertación e Integración Regionales". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "Organismos regionales". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 5 December 2022. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "Organismos Intergubernamentales". cancilleria.gov.co. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- A mutually beneficial relationship Archived 16 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine. oecd.org (25 May 2018).
- Relations with Colombia Archived 21 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine. nato.int (19 May 2017).
- "Military Personnel – Logros de la Política Integral de Seguridad y Defensa para la Prosperidad" (PDF) (in Spanish). mindefensa. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2017. Retrieved 23 June 2017.
- "Military spending" (PDF). sipri.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 22 June 2017.
- "Military expenditure (% of GDP)" (PDF). sipri.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 22 June 2017.
- "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 17 November 2019.
- "Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title VII: The Executive Branch – Chapter VII: The Public Force)" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 21 May 2017. Retrieved 20 May 2017.
- "Military units" (in Spanish). ejercito.mil.co. Archived from the original on 3 April 2014. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- "Forces and commands" (in Spanish). armada.mil.co. Archived from the original on 8 February 2014. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- "Air units" (in Spanish). ejercito.mil.co. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- ^ "Codificación de la División Político-Administrativa de Colombia (Divipola)" (in Spanish). dane.gov.co. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- ^ Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title XI – Concerning the territorial organization)
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title XI – Concerning the territorial organization – Chapter 3 – Concerning the municipal regime – Article 318)
- Herrera Llanos, W (2011). "Régimen municipal en Colombia (Continuación del tema sobre Organización Territorial)". Revista de Derecho. Universidad del Norte: 27.
- "Agriculture, Industry, Services". worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- "Employment distribution by economic activity (by sex)". ilo.org. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- "¿Cómo está compuesta la economía colombiana?" (in Spanish). dinero.com. 29 September 2015. Archived from the original on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- "Colombian economy" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 12 May 2015. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- "General government total expenditure (Percent of GDP)". imf.org. Archived from the original on 26 September 2021. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- "Deuda Externa de Colombia" (PDF). banrep.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- "Colombia". Index of Economic Freedom. The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on 9 April 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- "Colombia Inflation Rate". banrep.gov.co. Archived from the original on 16 January 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- "Colombia Unemployment Rate" (PDF). dane.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
- "Incomes of informal workers grow less" (in Spanish). portafolio.co. Archived from the original on 21 December 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- "Colombia's Permanent Free Trade Zones Directory". investincolombia.com.co. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- Zonas Francas Archived 28 May 2020 at the Wayback Machine. zonafrancadelpacifico.com
- "Informe de operaciones" (in Spanish). superfinanciera.gov.co. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "Reporte de Estabilidad Financiera" (in Spanish). banrep.gov.co. Archived from the original on 21 March 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "The Latin American Integrated Market (MILA)". mercadomila.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2014. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- "Colombia's Colcap Index" (in Spanish). banrep.org. Archived from the original on 17 July 2017. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "World Bank's 2017 Doing Business ranking" (PDF). doingbusiness.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- "Is Colombia a poor country? | – CountryReports". countryreports.org. Archived from the original on 18 March 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- "International Trade Centre: Colombia Exports". intracen.org. Archived from the original on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 15 April 2015.
- "Exports – partners" (PDF). dane.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- "Imports – partners" (PDF). dane.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- "Non-traditional exports" (in Spanish). mincit.gov.co. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 31 January 2014.
- "Colombia: making many millionaires". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 9 July 2015. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- "País de ricos" (in Spanish). dinero.com. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2013.
- "GINI index (World Bank estimate) – Colombia". World Bank. Archived from the original on 8 November 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2021.
- "Colombia and Peru demonstrate the most conducive environments for financial inclusion" (PDF). 2016 Global Microscope on Financial Inclusion – The Economist Intelligence Unit. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- "The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2017" (PDF). World Economic Forum. p. 130. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2018 Edition". unwto.org. 2018. doi:10.18111/9789284419876. ISBN 9789284419876.
- "La OMT destaca crecimiento del turismo en Colombia en los últimos diez años" (in Spanish). lainformacion.com. 25 June 2014. Archived from the original on 11 July 2014. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- "Agriculture and Livestock in Colombia, by FAO". Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Juan Valdez, garoto propaganda do Café da Colômbia chega aos 50 anos". Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Como é possível produzir óleo de palma de maneira sustentável". 6 January 2020. Archived from the original on 15 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "COMO FUNCIONA A INDUSTRIA DE FLORES NA COLOMBIA – MAIOR EXPORTADOR MUNDIAL". Archived from the original on 15 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- Kliefoth, Willis (6 October 2021). "Towards a greener, fairer and more productive land use sector in Colombia". Climate Focus. Archived from the original on 18 April 2024. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- "Colombian exports, by OEC". Archived from the original on 3 June 2022. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Primary Coal Exports". US Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 13 August 2020. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
- "EIA 2019 Petroleum production". Archived from the original on 15 July 2022. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Colombian emeralds". Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Colombia Gold Production". Archived from the original on 16 August 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- "Colombian Electricity Market – Evolución Variables de Generación Diciembre de 2016" (in Spanish). Unidad de Planeación Minero Energética de Colombia. Archived from the original on 20 May 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- "2014 Global Green Economy Index" (PDF). Dual Citizen LLC. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- "Ministry of Transport" (in Spanish). mintransporte.gov.co. 8 May 2011. Archived from the original on 1 December 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "INVÍAS – Objectives and Functions" (in Spanish). invias.gov.co. Archived from the original on 6 December 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "Aerocivil – Funciones y Deberes" (in Spanish). aerocivil.gov.co. Archived from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "ANI – Objectives and Functions" (in Spanish). ani.gov.co. 24 December 2012. Archived from the original on 24 September 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "the General Maritime Directorate (Dimar)". dimar.mil.co. Archived from the original on 21 December 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- "Superintendency of Ports and Transport- Objectives and Functions" (in Spanish). supertransporte.gov.co. Archived from the original on 19 December 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "Declaración de importancia estratégica de los proyectos de inversión del programa vías" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 July 2022. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- "Colombia pasó de 700 kilómetros de doble calzada en 2010 a 2.100". 22 November 2017. Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ Champin, J., Cortés, R., Kohon, J., & Rodríguez, M. (2016). Desafíos del transporte ferroviario de carga en Colombia
- Schipani, Andres (17 November 2014). "Ambitious plans to transform Colombia". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- "Colombia". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 18 January 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- "research groups in science and technology" (PDF) (in Spanish). colciencias.gov.co. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- "Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship". www.wipo.int. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- "entrepreneurship and innovation in Colombia". venturebeat.com. 29 September 2013. Archived from the original on 1 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- "Colombia Startups" (in Spanish). apps.co. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- "Corporation for Biological Research (CIB)" (in Spanish). cib.org.co. Archived from the original on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- "International Center for Tropical Agriculture". Archived from the original on 9 June 2017. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- "Inventos colombianos" (in Spanish). 20minutos.es. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- "Colombian military industry markets weapons and technology on international stage". dialogo-americas.com. Archived from the original on 17 April 2017. Retrieved 16 April 2017.
- "Robots antiexplosivos". historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- "Beyond Alzheimer's: the "Paisa Mutation"". udea.edu.co. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- "Científicos colombianos" (in Spanish). cienciagora.com.co. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- "científicos del país más consultados" (in Spanish). portal.redcolombiana.com. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- "Estos son los científicos colombianos más destacados en el último lustro" (in Spanish). eltiempo.com. 25 November 2009. Archived from the original on 17 March 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- "¿Cuántos somos?". Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE). Archived from the original on 27 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- "Colombia – Population Archived 16 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine". Library of Congress Country Studies.
- "Population growth (annual %)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 16 January 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- "Encuesta Nacional de Demografía y Salud (ENDS)" (PDF) (in Spanish). profamilia.org.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 5 May 2017.
- "Long term population estimates and projections 1950–2100". cepal.org. Archived from the original on 18 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Colombia: A Country Study". Countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on 7 April 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- "World Urbanization Prospects" (PDF). un.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- León Soler, Natalia. "Bogotá: de paso por la capital" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 18 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- "Internally Displaced People Figures". The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Archived from the original on 18 May 2013. Retrieved 18 May 2014.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth". who.int. Archived from the original on 5 March 2013. Retrieved 13 July 2021.
- "Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 21 October 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ "UNESCO Institute for Statistics Colombia Profile". Archived from the original on 6 May 2017. Retrieved 5 May 2017.
- "Languages of Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Jon Landaburu, Especialista de las lenguas de Colombia" (in Spanish). ambafrance-co.org. Archived from the original on 16 December 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Map of the languages of Colombia" (in Spanish). lenguasdecolombia.gov.co. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "The Languages of Colombia". Ethnologue.com. Archived from the original on 7 March 2013. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- "Native languages of Colombia" (in Spanish). lenguasdecolombia.gov.co. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "The ethnic and cultural diversity of Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). pedagogica.edu.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- "Mapa genético de los colombianos" (in Spanish). historico.unperiodico.unal.edu.co. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- Bushnell & Hudson, pp. 87–88.
- Rojas, Winston; Parra, María Victoria; Campo, Omer; Caro, María Antonieta; Lopera, Juan Guillermo; Arias, William; Duque, Constanza; Naranjo, Andrés; García, Jharley; Vergara, Candelaria; Lopera, Jaime; Hernandez, Erick; Valencia, Ana; Caicedo, Yuri; Cuartas, Mauricio; Gutiérrez, Javier; López, Sergio; Ruiz-Linares, Andrés; Bedoya, Gabriel (September 2010). "Genetic make up and structure of Colombian populations by means of uniparental and biparental DNA markers". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 143 (1): 13–20. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21270. PMID 20734436. Retrieved 13 February 2024.
- ^ "Raza/Etnia a la que pertenece". Latinobarómetro 2023 Colombia. Retrieved 13 February 2024.
- Bushnell, David; Hudson, Rex A. (2010). The Society and Its Environment; Colombia: a country study (PDF). Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, Washington D.C. pp. 87, 92. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Society and slavery" (in Spanish). colombia.com. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- "Resguardos indígenas – Concentra el 43% de los bosques naturales" (in Spanish). siac.gov.co. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "Hostein, N. (2010). El pueblo wayuu de la Guajira colombo-venezolana: un panorama de su cultura. Cuadernos de Antropología, 20(1)". Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "Los pueblos indígenas de Colombia en el umbral del nuevo milenio. Población, cultura y territorio: bases para el fortalecimiento social y económico de los pueblos indígenas". dnp.gov.co. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- "Ratifications for Colombia". ilo.org. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- "Ethnic groups in Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). dane.gov.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- Luis Álvaro Gallo Martínez (2011). "Inmigrantes a Colombia: Personajes extranjeros llegados a Colombia" (PDF). rodriguezuribe.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015.
- Wabgou, M.; Vargas, D.; Carabalí, J. A. (2012). "Las migraciones internacionales en Colombia. Investigación & Desarrollo, 20(1) 142–167". uninorte.edu.co. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- Vargas Arana, Pilar, and Luz Marina Suaza Vargas. "Los árabes en Colombia: Del rechazo a la integración." (2007).
- "The Arab immigration to Colombia" (in Spanish). nodo50.org. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- "Características de los migrantes de Venezuela a Colombia" (PDF). labourosario.com (in Spanish). 14 August 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Kurmanaev, Anatoly; González, Jenny Carolina (5 August 2019). "Colombia Offers Citizenship to 24,000 Children of Venezuelan Refugees". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 1 January 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Beltrán Cely; William Mauricio (2013) (2013). Del monopolio católico a la explosión pentecostal' (PDF) (in Spanish). Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Facultad de Ciencias Humanas, Centro de Estudios Sociales (CES), Maestría en Sociología. ISBN 978-958-761-465-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2016.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Beltrán Cely; William Mauricio. "Descripción cuantitativa de la pluralización religiosa en Colombia" (PDF). Universitas humanística 73 (2012): 201–238. – bdigital.unal.edu.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 March 2014.
- "Religion in Latin America, Widespread Change in a Historically Catholic Region". Pew Research Center. 13 November 2014.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title II – Concerning rights, guarantees, and duties – Chapter I – Concerning fundamental rights – Article 19)
- ^ "21 Colombian clinics among the best 44 in Latin America". America Economia magazine. Archived from the original on 23 June 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- "Ministra de Salud dice que la cobertura en este sector subió al 96%" (in Spanish). El País (Colombia). Archived from the original on 28 July 2014. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- "Centro de Tratamiento e Investigación sobre Cáncer (CTIC)". presidencia.gov.co (in Spanish). 12 October 2017.
- "Cinco hospitales colombianos en el top 10 de los mejores de Latinoamérica". Agenciapi.co (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- "Global Top 250 Hospitals 2023" (PDF). Brand Finance: 14. 2023.
- Mosquera, Eddy (17 February 2023). "Tres hospitales colombianos están entre los 100 mejores centros médicos del mundo". Caracol Radio (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- Colombian Constitution of 1991 (Title II – Concerning rights, guarantees, and duties – Chapter 2 – Concerning social, economic and cultural rights – Article 67)
- ^ "Ministerio de Educación de Colombia, Estructura del sistema educativo". 29 June 2007. Archived from the original on 29 June 2007.
- "UNESCO-UNEVOC World TVET Database". unevoc.unesco.org.
- Historical Commission on the Conflict and Its Victims (CHCV) (February 2015). "Contribution to an Understanding of the Armed Conflict in Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- Mario A. Murillo; Jesús Rey Avirama (2004). Colombia and the United States: war, unrest, and destabilization. Seven Stories Press. p. 54. ISBN 978-1-58322-606-3.
- "Understanding Colombia's armed conflict: International actors". colombiareports.com. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- "Q&A: Colombia's civil conflict". BBC News. 23 December 2009. Retrieved 30 April 2010.
- Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores, Colombia. "Borders for Prosperity Plan". Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- International Crisis Group. "Dismantling Colombia's New Illegal Armed Groups: Lessons from a Surrender", CrisisGroup.org. 8 June 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- International Crisis Group. "Corridor of Violence: The Guatemala-Honduras Border". CrisisGroup.org. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- "InSight Crime's 2016 Homicide Round-up". insightcrime.org. 16 January 2017.
- ^ Venezuela: A Mafia State?. Medellin, Colombia: InSight Crime. 2018. pp. 3–84.
- "Largest cities" (PDF). Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica (DANE). Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "Largest cities" (PDF). Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica (DANE). Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- OECD (21 July 2022). Local Economic and Employment Development (LEED) Culture and the Creative Economy in Colombia Leveraging the Orange Economy: Leveraging the Orange Economy. OECD Publishing. ISBN 978-92-64-65268-2.
- "Gabriel García Márquez – Nobel Lecture". nobelprize.org. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- Legend of Yurupary. Cooperativa Editorial Magisterio. 2006. ISBN 978-958-20-0836-9.
- "Cronistas del Nuevo Reino de Granada". ihlc.udea.edu.co. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- "Vida, pasión y muerte del romanticismo en Colombia" (PDF). biblioteca-virtual-antioquia.udea.edu.co. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- "Romanticismo – Diccionario electrónico de la literatura colombiana". ihlc.udea.edu.co. 5 November 2007. Archived from the original on 14 February 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- "Colombian children's literature" (PDF). biblioteca.org.ar. 12 March 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Costumbrismo – Diccionario electrónico de la literatura colombiana". ihlc.udea.edu.co. 5 November 2007. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- Jaramillo, M.M.; Osorio, B.; Robledo, A. (2000). Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. Del siglo XIX al siglo XX: debates sobre la cultura nacional (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 March 2017. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- Rodríguez-Arenas, F.M. (2006). Bibliografía de la literatura colombiana del siglo XIX: AL. Stockcero, Inc.
- Rodríguez-Arenas, F.M. (2006). Bibliografía de la literatura colombiana del siglo XIX: MZ. Stockcero, Inc.
- "Colombian Academy of Language" (in Spanish). colombiaaprende.edu.co. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Obeso: Poet of the Magdalena". thecitypaperbogota.com. 6 March 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- Lucía Ortiz (2007). "Chambacú, la historia la escribes tú": ensayos sobre cultura afrocolombiana (Candelario Obeso) (in Spanish). IBEROAMERICANA. pp. 47–69. ISBN 978-84-8489-266-3.
- "Artículo: Piedra y Cielo a contraluz" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 6 November 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- "Gonzalo Arango" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- "Fernando González Ochoa". otraparte.org. 12 March 2017. Archived from the original on 13 May 2019. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- Jaramillo, M. M.; Osorio, B.; Robledo, A. (2000). Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. La nación moderna y sus sistemas simbólicos (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Jaramillo, M. M.; Osorio, B.; Robledo, A. (2000). Literatura y Cultura: narrativa colombiana del siglo XX. El discurso de la nación moderna: continuidades y rupturas (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Miguel A. De La Torre (2009). Hispanic American Religious Cultures. ABC-CLIO. p. 522. ISBN 9781598841404.
- Nicholas J. Santoro (2011). Mary in Our Life. Atlas of the Names and Titles of Mary, the Mother of Jesus, and Their Place in Marian Devotion. iUniverse. p. 671. ISBN 9781462040223.
- ^ "Colombian Art". donquijote.org. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ^ Francisco Gil Tovar (1985). El arte colombiano. Volume 3 of Selección Cultura colombiana (in Spanish). Plaza y Janes Editores Colombia s.a. ISBN 978-958-14-0016-4.
- "Tumaco: People and Gold on the Pacific Coast". banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ^ "San Agustín Archaeological Park". UNESCO. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- Marta Fajardo De Rueda. "El espíritu barroco en el arte colonial" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Uribe Restrepo, Fernando. "Joaquín Gutiérrez, el "pintor de los virreyes": Expresión del estilo rococó en la Nueva Granada" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 22 April 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- "Pedro Nel Gómez Agudelo" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Luz Guillermina Sinning Téllez; Ruth Nohemí Acuña Prieto (2011). Miradas a la plástica colombiana de 1900 a 1950: un debate histórico y estético (in Spanish). U. Externado de Colombia. ISBN 978-958-710-748-7.
- "Puntos de partida en el arte contemporáneo de Colombia" (in Spanish). iadb.org. Archived from the original on 16 April 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Carmen María Jaramillo; Sylvia Suárez. "Clásicos, experimentales y radicales 1950–1980" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Carlos Arturo Fernández (2007). Arte en Colombia, 1981–2006 (in Spanish). Universidad de Antioquia. ISBN 978-958-714-017-0.
- Eugenio Barney Cabrera (2005). Geografía del arte en Colombia. Biblioteca del Gran Cauca: Colección clásicos regionales (in Spanish). Universidad del Valle. ISBN 978-958-670-450-2.
- "Omar RayoM" (in Spanish). museorayo.co. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- Carolina Vanegas Carrasco. "Pietro Tenerani y la escultura en Colombia en el siglo XIX" (in Spanish). academia.edu. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- "Colombian sculptors" (in Spanish). colombia.com. Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Latin America's largest antique negative archive in Medellín". colombiareports.co. 16 December 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- "Apuntes para una cronología de la fotografía en Antioquía" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- Pablo Guerra. "Para entender los cómics en Colombia" (in Spanish). elespectador.com. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Pablo Guerra. "Especial Entre Viñetas la historieta colombiana en prensa" (in Spanish). bibliotecanacional.gov.co. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- "Museo Virtual de la Historieta Colombiana – Cronología" (in Spanish). Facultad de Artes: Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Periodización. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Nivel Formativo Tribal. La Casa Comunal. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Nivel Paleoindio. Abrigos rocosos del tequendama. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- "National Archeological Park of Tierradentro". UNESCO. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Los cacicazgos. Las Aldeas y las Tumbas. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 2 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Los Tayrona y los Muisca: La Preciudad. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 2 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La América española. El apasionamiento escenográfico, 1730–1810. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Agustín, José. "Fundaciones coloniales y republicanas en Colombia: normas, trazado y ritos fundacionales" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La Conquista. El dominio del territorio, 1500–1550. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- ^ Silvia Arango (1990). La España americana. Consolidación de tipologías, 1550–1750. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Arquitectura colonial. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). El Capitolio y Tomás Reed. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La arquitectura de la colonización. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La arquitectura urbana de fin de siglo. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 6 May 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La generación republicana. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La persistencia de los estilos. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Primera fase: los alardes de la técnica. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Segunda fase: la asimilación consiente. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). Arquitectura de los sentidos y contextualidad. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016.
- Silvia Arango (1990). La recuperación del pasado. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional. ISBN 958-17-0061-7. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016.
- "Colombianos que se destacan: Música que vibra por todo el mundo" (in Spanish). cromos.com.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- "Colombian music". about.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- "Colombian composers" (in Spanish). facartes.unal.edu.co. Archived from the original on 11 April 2016. Retrieved 29 April 2017.
- "Bogotá Philharmonic" (in Spanish). patrimoniocultural.bogota.unal.edu.co. Retrieved 29 April 2017.
- ^ "Colombian music". colombia-sa.com. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Caribe Occidental". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 6 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Caribe Oriental". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 7 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Bolívar" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Cesar" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Chocó" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Cauca" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Marimba music, traditional chants and dances from the Colombia South Pacific region". unesco.org. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Pacífico Sur". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Pacífico Norte". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- Puerta Zuluaga, D. (1988). "Los Caminos del tiple". Bogotá: Ediciones AMP Damel. Archived from the original on 3 May 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2017.
- "Ritmos – Bogotá" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos -Tolima" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Huila" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Andinas Centro-Oriente". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Andinas Nor-Occidente". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Andinas Centro-Sur". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Andinas Sur-Occidente". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 12 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Meta" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Casanare" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Llaneras". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Putumayo" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Amazonas" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas de Frontera". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Músicas Isleñas". territoriosonoro.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- "Ritmos – Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina" (in Spanish). sinic.gov.co. Archived from the original on 24 May 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- ^ "Competitive specialised film festivals". fiapf.org. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- "Six surprising facts about Bogota's Ibero-American Theater Festival". colombia.co. 2 March 2016. Archived from the original on 17 November 2017. Retrieved 17 November 2017.
- "Main performing arts festivals – Theatre History". iti-worldwide.org. Archived from the original on 21 August 2008. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Theater of Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- Reyes, Carlos José. "El teatro en Colombia en el siglo XX" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial Historia. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "the Film Act passed in 2003" (in Spanish). secretariasenado.gov.co. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Ocho festivales de cine imperdibles en Colombia" (in Spanish). colombia.co. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "La Corporación Festival Internacional de Cine de Cartagena" (in Spanish). ficcifestival.com. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "Television in Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Un papel a toda prueba. 223 años de prensa diaria en Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "La prensa en Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "Radio in Colombia" (in Spanish). banrepcultural.org. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ^ "Paseo de olla. Recetas de las cocinas regionales de Colombia – Biblioteca básica de cocinas tradicionales de Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- "Food presentation" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ "Gran libro de la cocina colombiana – Biblioteca básica de cocinas tradicionales de Colombia" (PDF) (in Spanish). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- Singh, Gitanjali M., et al. "Global, regional, and national consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, fruit juices, and milk: a systematic assessment of beverage intake in 187 countries." PLoS ONE 10.8 (2015): e0124845.
- "Hábitos de los consumidores en la tendencia saludable" (in Spanish). nielsen.com. Archived from the original on 31 August 2015. Retrieved 24 March 2015.
- "Colombian Food; A List of Traditional and Modern Colombian Recipes". southamericanfood.about.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- "Tejo – Colombia's national sport". thecitypaperbogota.com. 28 August 2013. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- Top Team and the Best Mover of the Year. FIFA
- "Patinaje colombiano, el más ganador del mundo" (in Spanish). elpais.com.co. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Historical moments of the Colombian cycling" (in Spanish). antena2.com.co. Archived from the original on 5 July 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "The 2010 SF N World Series Batting Log for Edgar Renteria". Retrosheet. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- "Recordando a nuestras glorias del béisbol" (in Spanish). eltiempo.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "History of boxing in Colombia" (in Spanish). boxeodecolombia.com. 13 July 2011. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
- "Boxing champions" (in Spanish). boxeodecolombia.com. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
- "Colombia vive esplendor deportivo inédito en su historia" (in Spanish). semana.com. 18 August 2014. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
- "History of the Colombian Olympic Committee" (in Spanish). Colombian Olympic Committee. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
- "El bolo colombiano ratificó su condición de potencia continental" (in Spanish). reporterosasociados.com.co. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
External links
General information
- Colombia at Britannica.com
- Lamoureux, Andrew Jackson; Edmundson, George (1911). "Colombia" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 6 (11th ed.). pp. 700–713.
- Colombia at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Colombia. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Key Development Forecasts for Colombia from International Futures
- Official investment portal
- Official Colombia Tourism Website
- Study Spanish in Colombia
- (in Spanish) National Administrative Department of Statistics
Government
- (in Spanish) Colombia Online Government website
Culture
- (in Spanish) Ministry of Culture
Geography
- (in Spanish) National parks of Colombia
 Wikimedia Atlas of Colombia
Wikimedia Atlas of Colombia
| Articles related to Colombia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4°N 72°W / 4°N 72°W / 4; -72
Categories: