| Revision as of 08:21, 23 October 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified and watched fields - updated 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 08:04, 11 August 2024 edit undo2a00:23c6:19a8:f401:d1e2:e98f:2b02:7f18 (talk) Fixed typo, this is an antiemetic not an antisemeticTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Antiemetic medication}} | |||
| {{Drugbox | {{Drugbox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| | verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 470615098 | ||
| | IUPAC_name = ''N''-{methyl}-<br>3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzamide | | IUPAC_name = ''N''-{methyl}-<br>3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzamide | ||
| | image = |
| image = Trimethobenzamide2DACS.svg | ||
| | image2 = Trimethobenzamidefinal.png | |||
| | width = 250px | | width = 250px | ||
| <!--Clinical data--> | <!--Clinical data--> | ||
| | tradename = Tigan | | tradename = Tigan, Tebamide | ||
| | Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|trimethobenzamide-hydrochloride}} | | Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|trimethobenzamide-hydrochloride}} | ||
| | MedlinePlus = a682693 | | MedlinePlus = a682693 | ||
| | pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | | pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | ||
| | pregnancy_US = |
| pregnancy_US = C | ||
| | legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S4 / S8 --> | | legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S4 / S8 --> | ||
| | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> | | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> | ||
| | legal_US = Rx-only | | legal_US = Rx-only | ||
| | routes_of_administration = Oral, rectal, ] | | routes_of_administration = Oral, rectal, ] | ||
| <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| | bioavailability = 60-100% | |||
| | elimination_half-life = 7 to 9 hours (mean) | | elimination_half-life = 7 to 9 hours (mean) | ||
| | excretion = urine (30-50%), faeces | |||
| <!--Identifiers--> | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| | IUPHAR_ligand = 7614 | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| | CAS_number = 138-56-7 | | CAS_number = 138-56-7 | ||
| | ATC_prefix = |
| ATC_prefix = R06 | ||
| | ATC_suffix = AA10 | |||
| | PubChem = 5577 | | PubChem = 5577 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| | DrugBank = |
| DrugBank = DB00662 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 5375 | | ChemSpiderID = 5375 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| | UNII = W2X096QY97 | | UNII = W2X096QY97 | ||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite| |
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEBI = 27796 | | ChEBI = 27796 | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEMBL = 1201256 | | ChEMBL = 1201256 | ||
| <!--Chemical data--> | <!--Chemical data--> | ||
| | C=21 | H=28 | N=2 | O=5 |
| C=21 | H=28 | N=2 | O=5 | ||
| | molecular_weight = 388.458 g/mol | |||
| | smiles = O=C(c1cc(OC)c(OC)c(OC)c1)NCc2ccc(OCCN(C)C)cc2 | | smiles = O=C(c1cc(OC)c(OC)c(OC)c1)NCc2ccc(OCCN(C)C)cc2 | ||
| | InChI = 1/C21H28N2O5/c1-23(2)10-11-28-17-8-6-15(7-9-17)14-22-21(24)16-12-18(25-3)20(27-5)19(13-16)26-4/h6-9,12-13H,10-11,14H2,1-5H3,(H,22,24) | |||
| | InChIKey = FEZBIKUBAYAZIU-UHFFFAOYAO | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C21H28N2O5/c1-23(2)10-11-28-17-8-6-15(7-9-17)14-22-21(24)16-12-18(25-3)20(27-5)19(13-16)26-4/h6-9,12-13H,10-11,14H2,1-5H3,(H,22,24) | | StdInChI = 1S/C21H28N2O5/c1-23(2)10-11-28-17-8-6-15(7-9-17)14-22-21(24)16-12-18(25-3)20(27-5)19(13-16)26-4/h6-9,12-13H,10-11,14H2,1-5H3,(H,22,24) | ||
| Line 50: | Line 48: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Trimethobenzamide''' ('''Tebamide''', '''Tigan''') is an ] used to prevent ] and ] |
'''Trimethobenzamide''' (trade names '''Tebamide''', '''Tigan''') is an ] used to prevent ] and ]. | ||
| == Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
| Trimethobenzamide is an ] of the ].<ref name="Smith2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Smith HS, Cox LR, Smith BR | title = Dopamine receptor antagonists | journal = Ann Palliat Med | volume = 1 | issue = 2 | pages = 137–42 | year = 2012 | pmid = 25841474 | doi = 10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2012.07.09 }}</ref> It is believed to affect the ] (CTZ) of the ] to suppress ] and ]. | |||
| Although the specific mechanism through which trimethobenzamide functions is unknown, it is believed to affect the ] (CTZ) of the ]. | |||
| == Side effects == | == Side effects == | ||
| Possible side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, headache |
Possible side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, muscle cramps, and blurred vision. More serious adverse effects include skin rash, tremors, ], and ]. | ||
| == Formulations == | == Formulations == | ||
| Trimethobenzamide is marketed under the brand names '''Tebamide''' and '''Tigan''', manufactured by ] and ], respectively. It is available as oral capsules and injectable formulations. |
Trimethobenzamide is marketed under the brand names '''Tebamide''' and '''Tigan''', manufactured by ] and ], respectively. It is available as oral capsules and injectable formulations. | ||
| Trimethobenzamide was also available as a rectal ], but such formulations were banned by the U.S. ] on April 6, 2007 due to unproven efficacy.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/554812 | title = FDA Bans Suppositories With Trimethobenzamide | last = Waknine | first = Yael | date = April 6, 2007 | |
Trimethobenzamide was also available as a rectal ], but such formulations were banned by the U.S. ] on April 6, 2007, due to unproven efficacy.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/554812 | title = FDA Bans Suppositories With Trimethobenzamide | last = Waknine | first = Yael | date = April 6, 2007 | access-date = 2007-04-06 | publisher = ]}}{{dead link|date=September 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> | ||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
| ], {{US patent|2879293}} (1959).]] | |||
| Alkylation of the sodium salt of ''p''-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1) with 2-dimethylaminoethyl chloride affords the ether (2). Reductive amination of the aldehyde in the presence of ammonia gives diamine (3). Acylation of that product with 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloride affords trimethobenzamide (4). | |||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| Line 73: | Line 75: | ||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| * |
* | ||
| * (manufacturer's website) |
* (manufacturer's website) | ||
| {{Antiemetics}} | {{Antiemetics}} | ||
| {{Dopaminergics}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:04, 11 August 2024
Antiemetic medication Pharmaceutical compound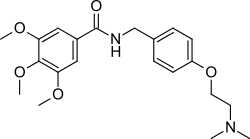 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tigan, Tebamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682693 |
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60-100% |
| Elimination half-life | 7 to 9 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | urine (30-50%), faeces |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.848 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H28N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 388.464 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Trimethobenzamide (trade names Tebamide, Tigan) is an antiemetic used to prevent nausea and vomiting.
Mechanism of action
Trimethobenzamide is an antagonist of the D2 receptor. It is believed to affect the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) of the medulla oblongata to suppress nausea and vomiting.
Side effects
Possible side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, muscle cramps, and blurred vision. More serious adverse effects include skin rash, tremors, parkinsonism, and jaundice.
Formulations
Trimethobenzamide is marketed under the brand names Tebamide and Tigan, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline and King Pharmaceuticals, respectively. It is available as oral capsules and injectable formulations.
Trimethobenzamide was also available as a rectal suppository, but such formulations were banned by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 6, 2007, due to unproven efficacy.
Synthesis

Alkylation of the sodium salt of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1) with 2-dimethylaminoethyl chloride affords the ether (2). Reductive amination of the aldehyde in the presence of ammonia gives diamine (3). Acylation of that product with 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloride affords trimethobenzamide (4).
See also
References
- Smith HS, Cox LR, Smith BR (2012). "Dopamine receptor antagonists". Ann Palliat Med. 1 (2): 137–42. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2012.07.09. PMID 25841474.
- Waknine, Yael (April 6, 2007). "FDA Bans Suppositories With Trimethobenzamide". Medscape. Retrieved 2007-04-06.