| Revision as of 19:53, 23 December 2011 editNableezy (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers56,176 edits Undid revision 467386714 by Nableezy (talk) self-rv, somebody else revert this tho← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:08, 8 January 2025 edit undoTimrollpickering (talk | contribs)Administrators353,825 editsm →Bedouin variety: remove needless piping, replaced: Palestine → PalestineTag: AWB | ||
| (526 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Dialect of Arabic spoken in the State of Palestine}} | |||
| {{no footnotes|date=December 2010}} | |||
| {{multiple issues| | |||
| {{more footnotes needed|date=December 2010}} | |||
| {{cleanup lang|date=May 2019}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
| |name=Palestinian Arabic | | name = Palestinian Arabic | ||
| | nativename = اللهجة الفلسطينية | |||
| |states='']'', ] | |||
| | states = ], ] | |||
| |familycolor=Afro-Asiatic | |||
| | region = ] | |||
| |fam2=] | |||
| | speakers = {{sigfig|4.270000|2}} million | |||
| |fam3=] | |||
| | date = 2021 | |||
| |fam4=] | |||
| | ref = e26 | |||
| |fam5=] | |||
| | familycolor = Afroasiatic | |||
| |script=] | |||
| | fam2 = ] | |||
| |iso3=ajp | |||
| | fam3 = ] | |||
| |notice=IPA}} | |||
| | fam4 = ] | |||
| '''Palestinian Arabic''' is a ] dialect subgroup spoken by ] and the majority of ]. Rural varieties of this dialect exhibit several distinctive features; particularly the pronunciation of ''qaf'' as ''kaf'', which distinguish them from other Arabic varieties. Palestinian urban dialects more closely resemble northern Levantine Arabic dialects, that is, the colloquial variants of ] and ]. | |||
| | fam5 = ] | |||
| | fam6 = ] | |||
| | listclass = hlist | |||
| | dia1 = Fellahi<br>Madani<br>] | |||
| | script = ] | |||
| | iso3comment = (covered by ]) | |||
| | iso3 = none | |||
| | isoexception = dialect | |||
| | glotto = sout3123 | |||
| | glottorefname = South Levantine Arabic | |||
| | notice = IPA | |||
| | map = Levantine Arabic 2022.svg | |||
| | mapcaption = {{legend|#800080|]}} | |||
| | ietf = apc-PS | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Contains special characters|Levantine}} | |||
| '''Palestinian Arabic''' (also known as simply '''Palestinian''') is a ] comprising various mutually intelligible varieties of ] spoken by ] in ], which includes the ], ], and the ].<ref name="asianabsolute">{{cite web |date=2016-01-19 |title=How to Reach your Audience with the Right Dialect of Arabic |url=https://asianabsolute.co.uk/blog/2016/01/19/arabic-language-dialects/ |access-date=2020-06-24 |work=Asian Absolute}}</ref><ref name="daytranslations">{{cite web |date=2015-10-16 |title=Arabic Language: Tracing its Roots, Development and Varied Dialects |url=https://www.daytranslations.com/blog/arabic-language-dialects/ |access-date=2020-06-24 |work=Day Translations}}</ref> | |||
| The Arabic dialects spoken in the region of Palestine and Transjordan do not form a homogeneous linguistic unit; rather, they encompass a diverse range of dialects influenced by geographical, historical, and socioeconomic factors.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Palva |first1=H. |date=1984 |title=A general classification for the Arabic dialects spoken in Palestine and Transjordan |journal=Studia Orientalia Electronica |volume=55 |pages=357–376}}</ref> Comparative studies of Arabic dialects indicate that Palestinian Arabic is among the closest dialects to ],<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Kwaik |first1=K. |last2=Saad |first2=M. |last3=Chatzikyriakidis |first3=S. |last4=Dobnik |first4=S. |year=2018 |title=A Lexical Distance Study of Arabic Dialects |journal=Procedia Computer Science |series=The 4th International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics (ACLing) |language=en |publication-date=15 November 2018 |volume=143 |pages=1, 3 |doi=10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.456 |issn=1877-0509 |doi-access=free}}</ref> particularly the dialect spoken in the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Harrat |first1=S. |title=Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing. Gelbukh, Alexander (Ed.) |last2=Meftouh |first2=K. |last3=Abbas |first3=M. |last4=Jamoussi |first4=S. |last5=Saad |first5=M. |last6=Smaili |first6=K. |publisher=Springer, Cham. |year=2015 |isbn=978-3-319-18110-3 |series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science |volume=9041 |publication-date=April 14–20, 2015 |pages=3, 6 |language=en |chapter=Cross-Dialectal Arabic Processing |doi=10.1007/978-3-319-18111-0_47 |access-date=29 November 2022 |chapter-url=https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18111-0_47 |s2cid=5978068}}</ref> Additional distinctions can be made within Palestinian Arabic, such as the dialects spoken in the northern ] and the ] area, which exhibit similarities to those spoken by descendants of ]. | |||
| ==Differences from other forms of Levantine Arabic== | |||
| {{see also|Timeline of the name Palestine}} | |||
| Until relatively recently the Arabic spoken in the Ottoman sanjak of Syria was considered a single Syrian dialect, as for example advised by F. E. Crow in his 1901 ''Arabic manual: a colloquial handbook in the Syrian dialect, for the use of visitors to Syria and Palestine, containing a simplified grammar, a comprehensive English and Arabic vocabulary and dialogues.'' printed in London by Luzac & co. | |||
| Palestinian Arabic dialects reflect a historical layering of languages previously spoken in the region, including ], ] (both ] and ]), ] (especially ]), ], ], and ]. Furthermore, during the early modern period, these dialects were influenced by ] and various ]. Since the establishment of Israel in 1948, Palestinian Arabic has also been shaped by ] influences.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Bassal |first=Ibrahim |date=2012 |title=Hebrew and Aramaic Substrata in Spoken Palestinian Arabic |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.13173/medilangrevi.19.2012.0085 |journal=Mediterranean Language Review |volume=19 |pages=85–104 |issn=0724-7567 |jstor=10.13173/medilangrevi.19.2012.0085}}</ref> | |||
| There are noticeable differences between Palestinian Arabic and other forms of Levantine Arabic such as ] and ]. However, none of these is invariable, given the differences of dialect within Palestinian Arabic itself. | |||
| == History == | |||
| One typical feature of Palestinian dialects is the pronunciation of ]ted verbs with an 'o'-like vowel in the imperfect. For example, in {{Unicode|]}} the imperfect of اكل ''akala'' 'eat' is آكل '''ākulu'': the common equivalent in Palestinian dialect is بوكل ''bōkel''. (The ''b'' prefix marks a present indicative meaning.) Thus, in the Galilee, the colloquial for the verbal expression, "I am eating" or "I eat" is ''ana bōkel'', rather than ''ana bākəl'' used in Syrian dialect. However, ''ana bākul'' is used by the Bedouin in the south. | |||
| Prior to their adoption of the Arabic language from the seventh century onwards, most of the ] spoke varieties of ] (], ], ]) as a native language. ] was used among the Hellenized elite and aristocracy, and ] for liturgical purposes. | |||
| The ] was under the rule of the ] for the greater part of ], and included settlements such as Mahoza and ] where ]n and ] populations lived in alongside each other, as documented by the ] archive which dates to the second century. The earliest ] inscription most resembling of ] is found in ], being a poem dedicated to King ], known for defeating the ] ]. Its date is estimated between 79 and 120 CE, but no later than 150 CE at most.<ref>{{Cite web |title=A First/Second Century Arabic Inscription Of 'En 'Avdat |url=https://www.islamic-awareness.org/history/islam/inscriptions/avdat |access-date=2024-06-15 |website=www.islamic-awareness.org}}</ref> | |||
| Palestinian Arabic also shares some features with ], distinguishing it from the northern Levantine dialects: | |||
| The Nabataeans tended to adopt Aramaic as a written language as shown in the ] texts of ],<ref name=":2" /> as well as a ]. ] and ] dialects would both have been thought of as “Aramaic”, and almost certainly have been mutually comprehensible. Additionally, occasional Arabic ]s can be found in the Jewish Aramaic documents of the ].<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Macdonald|first=Michael C. A.|title=How much can we know about language and literacy in Roman Judaea? A review|url=https://www.academia.edu/38960413|journal=Journal of Roman Archaeology|year=2017 |volume=30|pages=832–842|doi=10.1017/S1047759400074882|s2cid=232343804|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| *In vocabulary: 'like' (prep.) is زي ''zayy'' for some regions in the Palestinian Territories as it is in Egypt. However, مثل ''mitl'', as found in Syrian and Lebanese Arabic, is also used by Palestinians in other regions. | |||
| *In grammar: the Palestinian dialects (except for the dialect of Palestinian Bedouins), like Egyptian, typically suffix (ش -sh, IPA: {{IPA|/ʃ/}}) to form the negative of verbs and pseudo-verbal prepositional pronouns. | |||
| {{Palestinians}} | |||
| The ] among the local population occurred most probably in several waves. After the ] Arabians took control of the area, so as to maintain their regular activity, the upper classes had to quickly become fluent in the language of the new rulers who most probably were only few. The prevalence of Northern Levantine features in the urban dialects until the early 20th century, as well as in the dialect of ] in ] (with systematic imala of /a:/) tends to show that a first layer of Arabization of urban upper classes could have led to what is now urban Levantine. Then, the main phenomenon could have been the slow countryside shift of Aramaic-speaking villages to Arabic under the influence of Arabized elites, leading to the emergence of the rural Palestinian dialects{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}}. This scenario is consistent with several facts. | |||
| ==Sub-dialects of Palestinian Arabic== | |||
| * The rural forms can be correlated with features also observed in the few Syrian villages where use of Aramaic has been retained up to this day. Palatalisation of /k/ (but of /t/ too), pronunciation of /q/ for instance. Note that the first also exists in ] and ], but is limited to palatal contexts (/k/ followed by i or a). Moreover, those Eastern dialects have or for /q/ {{Citation needed|date=July 2013}}. | |||
| Palestinian Arabic falls into three groups: | |||
| * The less-evolutive urban forms can be explained by a limitation owed to the contacts urban trader classes had to maintain with Arabic speakers of other towns in Syria or Egypt. | |||
| *Urban Palestinian, | |||
| * The Negev Bedouin dialect shares a number of features with Bedouin Hejazi dialects (unlike Urban Hejazi). | |||
| *Rural Palestinian | |||
| *] Palestinian. | |||
| == Features == | |||
| Of these, the urban dialect is the closest to northern Levantine Arabic of Syria and Lebanon. Meanwhile, the Bedouin dialect is nearer to varieties of Arabic spoken in ] itself, the Bedouins being more certainly known to be ]s not only in culture, language and customs but also by ] traceable outside Palestine/Israel (as opposed to being locals whose ethnic identity - Aramaic, Jewish, Greek - had shifted to an Arab ethnic identity following the process of cultural and linguistic ] over the centuries). | |||
| ] | |||
| The dialects spoken Arabic-speakers in the ], form a group of dialects known as ]. Arabic manuals for the "Syrian dialect" were produced in the early 20th century,<ref>Crow, F.E., ''Arabic manual: a colloquia handbook in the Syrian dialect, for the use of visitors to Syria and Palestine, containing a simplified grammar, a comprehensive English and Arabic vocabulary and dialogues'', Luzac & co, London, 1901</ref> and in 1909 a specific "Palestinian Arabic" manual was published in Jerusalem for ]. | |||
| Palestinian Arabic is a variant of Levantine Arabic because its dialects display characteristic Levantine features: | |||
| Notable differences in the varieties of Palestinian Arabic are as follows: | |||
| * A conservative stress pattern, closer to Classical Arabic than anywhere else in the Arab world. | |||
| * The indicative imperfect with a b- prefix | |||
| * A very frequent ] of the feminine ending in front consonant context (names in -eh). | |||
| * A realisation of /q/ in the cities, and a realisation of /q/ by the ]{{citation needed|date=July 2021}}{{dubious|date=December 2018}}, and more variants (including ) in the countryside. | |||
| * A shared lexicon | |||
| The noticeable differences between southern and northern forms of Levantine Arabic, such as ] and ], are stronger in non-urban dialects. The main differences between Palestinian and northern Levantine Arabic are as follows: | |||
| *The pronunciation of ''qāf'' serves as a ] to distinguish the three main Palestinian dialects: it becomes a ] in most cities, a ] ''k'' in smaller villages and the countryside, in some areas a (non-pharyngealized) ''k'', and ''g'' in the far south and among ] speakers. In a number of villages in the Galilee (e.g. Maghār), especially but not only among the ], the ''qāf'' is actually pronounced ''qāf'' as in Classical Arabic and other previous semitic languages of the area. | |||
| *In dialects where ''qāf'' is pronounced as ''k'', a true ''kāf'' is often pronounced {{IPA|/tʃ/}}, as in some dialects of ]. This is generally a feature of more conservative ]s. This pronunciation of ''kāf'' also happens in the northern West Bank and adjacent Palestinian populated areas in Israel, known as "]". This pronunciation is often stigmatised by urban Palestinians and some villagers who refrain from that pronunciation. | |||
| *In addition, a feminine ] ''-a'' rather than the more common Levantine ''-i'' or ''-é'' is fairly widespread, particularly in the south of the area. However, the "-i" or something approximating it is in use in the "triangle" while the Westbank and the Galilee mostly use ''-é''. | |||
| *Another interesting sub-dialectical marker is the word used for the preposition "here". The urban dialect favours "hōn". The Negev Bedouin, on the other hand, tend to use "hiniyye" or even "hiniyante". | |||
| *In the Negev, the -sh form is not used in negating the past or present. Instead, the Bedouin dialect uses only the "mā" particle to negate. | |||
| * Phonetically, Palestinian dialects differ from Lebanese regarding the classical diphthongs /aj/ and /aw/, which have simplified to and in Palestinian dialects as in Western Syrian, while in Lebanese they have retained a diphthongal pronunciation: and . | |||
| In general, the rural dialects are somewhat stigmatised and urban pronunciations are gaining ground, as is the case in other Arabic dialect groups. In contrast, Bedouin dialect use remains quite common, even among university educated Bedouins. While stigmatized by other ], the basic characteristics of the Bedouin dialect (e.g. the ''qāf'' pronounced as a ''g'') are used very widely in all informal contexts by Bedouin speakers, including those who are university-educated. Thus, a phenomenon similar to the disappearance of the {{IPA|/tʃ/}} for the ''kāf'' - as seen in the "triangle" - has yet to be witnessed in the Negev. This is not the case, however, with Bedouin from the Negev who moved to Lod and Ramle in the 1960s and show more of a tendency to adopt a standard urban dialect. | |||
| * Palestinian dialects differ from Western Syrian as far as short stressed /i/ and /u/ are concerned: in Palestinian they keep a more or less open and pronunciation, and are not neutralised to as in Syrian. | |||
| * The Lebanese and Syrian dialects are more prone to ] of /aː/ than the Palestinian dialects are. For instance شتا 'winter' is in Palestinian but in Lebanese and Western Syrian. Some Palestinian dialects ignore imāla totally (e.g. Gaza). Those dialects that prominently demonstrate imāla of /aː/ (e.g. Nablus) are distinct among Palestinian dialects. | |||
| * In morphology, the plural personal pronouns are إحنا 'we', همه also hunne 'they', كم- 'you', هم- هني 'them' in Palestinian, while they are in Syria/Lebanon نحنا 'we', هنه 'they', كن- 'you', هن- 'them'. The variants كو 'you', ـهن 'them', and هنه 'they' are used in Northern Palestinian. | |||
| * The conjugation of the imperfect 1st and 3rd person masculine has different prefix vowels. Palestinians say بَكتب 'I write' بَشوف 'I see' where Lebanese and Syrians say بِكتب and بْشوف . In the 3rd person masculine, Palestinians say بِكتب 'He writes' where Lebanese and Western Syrians say بيَكتب . | |||
| * Hamza-initial verbs commonly have an prefix sound in the imperfect in Palestinian. For example, Classical Arabic has اكل /akala/ 'to eat' in the perfect tense, and آكل /aːkulu/ with sound in the first person singular imperfect. The common equivalent in Palestinian Arabic is اكل /akal/ in the perfect, with imperfect 1st person singular بوكل /boːkel/ (with the indicative b- prefix.) Thus, in the Galilee and Northern West Bank, the colloquial for the verbal expression, "I am eating" or "I eat" is commonly / , rather than used in the Western Syrian dialect. Note however that or even are used in the South of Palestine. | |||
| * The conjugation of the imperative is different too. 'Write!' is اكتب in Palestinian, but كتوب , with different stress and vowel and length, in Lebanese and Western Syrian. | |||
| * For the ] of verbs and prepositional pseudo-verbs, Palestinian, like Egyptian, typically suffixes ش on top of using the preverb negation /ma/, e.g. 'I don't write' is مابكتبش in Palestinian, but مابكتب in Northern Levantine (although some areas in southern Lebanon utilise the ش suffix). However, unlike Egyptian, Palestinian allows for ش without the preverb negation /ma/ in the present tense, e.g. بكتبش . | |||
| * In vocabulary, Palestinian is closer to Lebanese than to Western Syrian, e.g. 'is not' is مش in both Lebanese and Palestinian (although in a few villages مهوش and مهيش , which are found in Maltese and North African dialects, are used) while it is مو in Syrian; 'How?' is كيف in Lebanese and Palestinian while it is شلون in Syrian (though كيف is also used) . However, Palestinian also shares items with ], e.g. 'like' (prep.) is زي in Palestinian in addition to مثل , as found in Syrian and Lebanese Arabic. | |||
| There are also typical Palestinian words that are ]s compared to other ] dialects : | |||
| ==Other Differences from Modern Standard/Classical Arabic== | |||
| * The usage of إشي 'thing, something', as opposed to شي in Lebanon and Syria as an indefinite pronoun. | |||
| ===Restrictive Clause=== | |||
| * Besides common Levantine هلق 'now', Central Rural dialects around Jerusalem and Ramallah use هالقيت (although is used in some cities such as Tulkarm, Hebron, and Nablus alongside هلق (both from هالوقت /halwaqt/ ) and northern Palestinians use إسا , إساع , and هسة (from الساعة/ɪsːɑːʕɑ/). Villagers in the southern West Bank also use هالحين or هالحينة (both from هذا الحين ) | |||
| *Some villagers use بقى (meaning 'remained' in MSA) as a verb to be alongside the standard كان ( in MSA) | |||
| ==Social and geographic dialect structuration== | |||
| As in most forms of colloquial Arabic, the clause markers of ] الذي، التي، اللذان، اللتان، الذين and اللاتي are replaced by the single form إللي {{IPA|/ʔilːi/}} | |||
| As is very common in Arabic-speaking countries, the ] spoken by a person depends on both the region of origin, and socio-economic class. The ], a form of women's oral literature inscribed to UNESCO's list of ], is recited in both the urban and rural dialects of Palestinian Arabic.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last=Rivoal |first=Isabelle |date=2001-01-01 |title=Susan Slyomovics, The Object of Memory. Arabs and Jews Narrate the Palestinian Village |url=https://journals.openedition.org/lhomme/6701 |journal=L'Homme. Revue française d'anthropologie |language=fr |issue=158–159 |pages=478–479 |doi=10.4000/lhomme.6701 |issn=0439-4216|doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Timothy |first=Dallen J. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XRypDwAAQBAJ&dq=%22Palestinian+hikaye%22+-wikipedia&pg=PT123 |title=Routledge Handbook on Tourism in the Middle East and North Africa |date=2018-12-07 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-317-22923-0 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === |
===Urban varieties === | ||
| The Urban ('madani') dialects resemble closely northern Levantine Arabic dialects, that is, the colloquial variants of western ] and ].<ref name="Sociolinguistics/Soziolinguistik 3: An International Handbook">{{cite book|last=Ammon|first=Ulrich|title=Sociolinguistics/Soziolinguistik 3: An International Handbook of the Science|year=2006|pages=1922|publisher=Walter de Gruyter |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LMZm0w0k1c4C&q=levantine%20arabic%20influences&pg=PR4|isbn=9783110184181}}</ref> This fact, that makes the urban dialects of the Levant remarkably homogeneous, is probably due to the trading network among cities in ], or to an older Arabic dialect layer closer to the ] (the 'qeltu dialects"). | |||
| Urban dialects are characterised by the (]) pronunciation of {{lang|ar|ق}} ], the simplification of interdentals as dentals plosives, i.e. {{lang|ar|ث}} as , {{lang|ar|ذ}} as and both {{lang|ar|ض}} and {{lang|ar|ظ}} as . In borrowings from ], these interdental consonants are realised as dental sibilants, i.e. {{lang|ar|ث}} as , {{lang|ar|ذ}} as and ظ as but {{lang|ar|ض}} is kept as . The Druzes have a dialect that may be classified with the Urban ones,{{dubious|date=December 2018}} with the difference that they keep the uvular pronunciation of {{lang|ar|ق}} qaf as . The urban dialects also ignore the difference between masculine and feminine in the plural pronouns انتو is both 'you' (masc. plur.) and 'you' (fem. plur.), and is both 'they' (masc.) and 'they' (fem.) | |||
| The particle ''li-'' has fused with the preceding stem as an indicator of an indirect object. Thus MSA ''qultu lahû'' {{IPA|/qultu lahuː/}} is expressed as '''ultillo'' {{IPA|/ʔultilˈlo/}}, ''qultillo'' {{IPA|/qultilˈlo/}} or ''kultillo'' {{IPA|/kultilˈlo/}} and MSA ''Katabtu lahâ'' {{IPA|/katabtu lahaː/}} is translated in Palestinian Arabic as ''Katabtilha'' {{IPA|/katabtilˈha/}}. | |||
| === |
==== Sephardi variety ==== | ||
| {{Main|Modern Palestinian Judeo-Arabic}} | |||
| As ] were ] after the conclusion of the ], they established ] in Ottoman Palestine in Jerusalem and Galilee under the invitation of Sultan ]. Their ] ] dialect mixed with Palestinian Arabic. It peaked at 10,000 speakers and thrived alongside ] among ] until the widespread adoption of ] among the ] following its revival in the ]. | |||
| Today it is nearly extinct, with only 5 speakers remaining in the Galilee.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Judeo-Arabic |url=https://www.jewishlanguages.org/judeo-arabic |access-date=2024-01-25 |website=Jewish Languages |language=en}}</ref> It contained influence from ] and influence ] and ].<ref>{{Citation |last=Geva-Kleinberger |first=Aharon |title=Languages in Jewish Communities, Past and Present |date=2018-11-05 |pages=569–580 |access-date=2024-01-25 |chapter=Judeo-Arabic in the Holy Land and Lebanon |chapter-url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9781501504631-021/html |publisher=De Gruyter Mouton |language=en |doi=10.1515/9781501504631-021 |isbn=978-1-5015-0463-1 |s2cid=134826368}}</ref> | |||
| ===Rural varieties=== | |||
| Rural (']') variety is retaining the interdental consonants, and is closely related with rural dialects in ] and the sedentary population east of the ]. They keep the distinction between masculine and feminine plural pronouns, e.g. انتو is 'you' (masc.) while انتن is 'you' (fem.), and همه is 'they' (masc.) while هنه is 'they' (fem.). The three rural groups in the region are the following: | |||
| * North Galilean rural dialect – does not feature the k > tʃ ], and many of them have kept the realisation of ق (e.g. Maghār, Tirat Carmel). In the very north, they announce dialect thats is more closely to the Northern Levantine dialects with n-ending pronouns such as كن- 'you', هن- 'them' (Tarshiha, etc.). | |||
| * Central rural Palestinian (From Nazareth to Bethlehem, including Jaffa countryside) exhibits a very distinctive feature with pronunciation of ك 'kaf' as 'tshaf' (e.g. كفية 'keffieh' as ) and ق 'qaf' as ] /k/ i.e. 'kaf' (e.g. قمح 'wheat' as ). This k > tʃ sound change is not conditioned by the surrounding sounds in Central Palestinian. This combination is unique in the whole Arab world, but could be related to the 'qof' transition to 'kof' in the ] in ], north of ]. | |||
| * Southern outer rural Levantine Arabic (to the south of an Isdud/]-] line) has k > tʃ only in presence of front vowels (ديك 'rooster' is in the singular but the plural ديوك 'roosters' is because u prevents /k/ from changing to ). In this dialect ق is not pronounced as but instead as . This dialect is actually very similar to northern Jordanian (], ]) and the dialects of Syrian ]. In Southern rural Palestinian, the feminine ending often remains . | |||
| ===Bedouin variety=== | |||
| The Bedouins of Southern Levant use two different (']') dialects in ] and the ]. The Negev desert Bedouins, who are also present in ] and ] use a dialect closely related to those spoken in the Hijaz, and in the Sinai. Unlike them, the Bedouins of Galilee speak a dialect related to those of the ] and ], which indicates their arrival to the region is relatively recent. The ]s, who ended up around Hebron and Jerusalem after the ] have a specific vocabulary, where they maintain the interdental consonants, do not use the ش- negative suffix, always realise ك /k/ as and ق /q/ as , and distinguish plural masculine from plural feminine pronouns, but with different forms as the rural speakers. | |||
| ===Current evolutions=== | |||
| On the urban dialects side, the current trend is to have urban dialects getting closer to their rural neighbours, thus introducing some variability among cities in the Levant. For instance, Jerusalem used to say as Damascus ("we") and ("they") at the beginning of the 20th century, and this has moved to the more rural and nowadays.<ref>U. Seeger, Mediterranean Language Review '''10''' (1998), pp. 89-145.</ref> This trend was probably initiated by the partition of the Levant of several states in the course of the 20th century. | |||
| The Rural description given above is moving nowadays with two opposite trends. On the one hand, urbanisation gives a strong influence power to urban dialects. As a result, villagers may adopt them at least in part, and Beduin maintain a two-dialect practice. On the other hand, the individualisation that comes with urbanisation make people feel more free to choose the way they speak than before, and in the same way as some will use typical Egyptian or Lebanese features as for , others may use typical rural features such as the rural realisation of ق as a pride reaction against the stigmatisation of this pronunciation. | |||
| == Phonology == | |||
| === Consonants === | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" | | |||
| ! colspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" | ]/] | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | ] | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | ] | |||
| |- style="font-size: 80%;" | |||
| !plain | |||
| !] | |||
| ! plain | |||
| ! ] | |||
| ! plain | |||
| ! ] | |||
| ! plain | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="text-align: left;" | ] | |||
| | {{IPA link|m}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|mˤ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|n}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="text-align: left;" | ] | |||
| ! style="text-align: left; font-size: 80%;" | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|t}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|tˤ}} | |||
| | ({{IPA link|t͡ʃ}}) | |||
| | {{IPA link|k}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|kˤ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|ʔ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="text-align: left; font-size: 80%;" | ] | |||
| | {{IPA link|b}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|bˤ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|d}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|dˤ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|d͡ʒ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ɡ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | ({{IPA link|ɢ}}) | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="text-align: left;" | ] | |||
| ! style="text-align: left; font-size: 80%;" | ] | |||
| | {{IPA link|f}} | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|θ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|s}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|sˤ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ʃ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|χ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ħ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|h}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="text-align: left; font-size: 80%;" | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|ð}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ðˤ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|z}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|zˤ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ʒ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|ʁ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|ʕ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="text-align: left;" | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | ({{IPA link|r}}) | |||
| | {{IPA link|ˤ|rˤ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="text-align: left;" | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPA link|l}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|lˤ}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|j}} | |||
| | {{IPA link|w}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |} | |||
| * Sounds {{IPA|/θ, ð, ðˤ, t͡ʃ, d͡ʒ/}} are mainly heard in both the rural and Bedouin dialects. Sounds {{IPA|/zˤ/}} and /{{IPA|ʒ/}} are mainly heard in the urban dialects. {{IPA|/kˤ/}} is heard in the rural dialects. | |||
| * {{IPA|/ɡ/}} is heard in the Bedouin dialects, and may also be heard as a uvular {{IPA|}}. | |||
| * {{IPA|}} mainly occurs as a palatalization of {{IPA|/k/}}, and is only heard in a few words as phonemic. In some rural dialects {{IPA|}} has replaced {{IPA|/k/}} as a phoneme. | |||
| * {{IPA|/rˤ/}} may de-pharyngealize as {{IPA|}} in certain phonetic environments. | |||
| * {{IPA|/ʁ/}} can also be heard as velar {{IPA|}} among some rural dialects. | |||
| * {{IPA|/b/}} can be heard as {{IPA|}} within devoiced positions. | |||
| === Vowels === | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| ! | |||
| !] | |||
| !] | |||
| !] | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPA link|i}} {{IPA link|iː}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|u}} {{IPA link|uː}} | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPA link|e}} {{IPA link|eː}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|o}} {{IPA link|oː}} | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !] | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|a}} {{IPA link|aː}} | |||
| | | |||
| |} | |||
| * The short vowel {{IPA|/a/}} is typically heard as {{IPA|}}, when in unstressed form. | |||
| * {{IPA|/a, aː/}} are heard as {{IPA|}} when following and preceding a pharyngealized consonant. The short vowel {{IPA|/a/}} as {{IPA|}}, can also be raised as {{IPA|}} in lax form within closed syllables. | |||
| * {{IPA|/i, u/}} can be lowered to {{IPA|}} when in lax form, or within the position of a post-velar consonant.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Shahin |first=Kimary N. |title=Palestinian Arabic |publisher=Leiden: Brill |year=2019 |isbn=978-90-04-17702-4 |location=In Kees Versteegh (ed.), Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics, Vol. II |pages=526–538}}</ref> | |||
| ==Vocabulary== | |||
| As Palestinian Arabic originated in the heartland of the Semitic languages, it has kept many regular Semitic words. For this reason, it is simple to speculate how ] words map onto Palestinian Arabic Words. The ''Swadesh'' list of basic words of Palestinian Arabic available on the Wiktionary (see ''external links'' below) may be used for this. However, some words are not transparent mappings from MSA, and deserve a description. This is due either to meaning changes in Arabic along the centuries – while MSA keeps the ] meanings – or to the adoption of non-Arabic words (see below). Note that this section focuses on Urban Palestinian unless otherwise specified. | |||
| === Prepositional pseudo verbs === | |||
| The words used in Palestinian to express the basic verbs 'to want', 'to have', 'there is/are' are called prepositional pseudo verbs because they share all the features of verbs but are constructed with a preposition and a suffix pronoun. | |||
| * ''there is, there are'' is فيه in the imperfect, and كان فيه in the perfect. | |||
| * To want is formed with bɪdd + suffix pronouns and to have is formed with ʕɪnd + suffix pronouns. In the imperfect they are | |||
| {| class = "wikitable" | {| class = "wikitable" | ||
| ! |
!Person || To want || To have | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |I | |||
| |لماذا <i>Limāðā<i> | |||
| |بدي | |||
| |ليش {{IPA|/ˈleʃ/}} | |||
| |عندي | |||
| |Why | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |You (sing. masc.) | |||
| |ماذا ''māðā'' | |||
| |بدك | |||
| |ايش {{IPA|/ˈʔeʃ/}} or شو {{IPA|/ˈʃu/}} | |||
| |عندك | |||
| |What | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |You (sing. fem.) | |||
| |كيف ''Kayfa'' | |||
| |بدك | |||
| |كيف ''Kīf'' {{IPA|/ˈkif ~ ˈkef/}} | |||
| |عندك | |||
| |How | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |He | |||
| |متى ''matā'' | |||
| |بده | |||
| |إيمتى ''ēmtā'' {{IPA|/ˈʔemta ~ ˈʔɛmta/}} or وينتى {{IPA|/ˈwenta/}} | |||
| |عنده | |||
| |When | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |She | |||
| |اين ''ayna'' | |||
| |بدها | |||
| |وين {{IPA|/ˈwen/}} | |||
| |عندها | |||
| |Where | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |We | |||
| |من ''man'' | |||
| |بدنا | |||
| |مين {{IPA|/ˈmin/}} | |||
| |عندنا | |||
| |Who | |||
| |- | |||
| |You (plur.) | |||
| |بدكم | |||
| |عندكم | |||
| |- | |||
| |They | |||
| |بدهم | |||
| |عندهم | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| In the perfect, they are preceded by كان , e.g. ''we wanted'' is كان بدنا . | |||
| === Determiners === | |||
| ==Influence of other languages== | |||
| '''Relative clause''' | |||
| As in most forms of colloquial Arabic, the relative clause markers of ] (الذي، التي، اللذان، اللتان، الذين and اللاتي) have been simplified to a single form إللي . | |||
| The variations between dialects reflect the different historical steps of arabization of the Palestinian. Until the 7th Century, the area used to speak predominantly Aramaic (as witnessed e.g. in the Jewish Aramaic and Judeo Christian Aramaic literature), as well as Greek (probably in upper or trader social classes) and some traces of Hebrew. At that time, Arabic speaking people living in the Jordan desert beyond Zarqa, Amman or Karak had no significant influence - on the contrary they tended to adopt Aramaic as a written language as shown in Nabatean texts of Petra or Palmyrenian documents of Tadmor. | |||
| Arabization of the population occurred most probably in several waves. After the Arabs took control of the area, so as to maintain their regular activity, the upper classes had quickly to get fluency in the language of the new masters who most probably were only few. The main phenomenon could have been the slow shift of Aramaic-speaking villages to Arabic under the influence of Arabicized elites. | |||
| '''Interrogatives pronouns''' | |||
| This scenario is consistent with several facts. | |||
| * The rural forms can be correlated with features also observed in the few Syrian villages where use of Aramaic has been retained up to this day. Palatalization of /k/, pronunciation of /q/ for instance. Note that the first also exists in Najdi and Gulf Arabic, but limited to palatal contexts (k followed by i or e). Moreover those eastern dialects have or for /q/. | |||
| * The less-evolutive urban forms can be explained by a limitation owed to the contacts urban trader classes had to maintain with Arabic speakers of other towns in Syria or Egypt. | |||
| * The Bedouins dialect shares a number of features with Hijazi dialects. | |||
| The main Palestinian interrogative pronouns (with their Modern Standard Arabic counterparts) are the following ones. | |||
| This scenario may also be consistent with the fact that the rural dialects of Palestinian Arabic contain features that appear to resemble their classical Hebrew counterparts. | |||
| {| class = "wikitable" | |||
| * The clearest example is the second and third person plural pronouns. ''hemme'' (they masc.) and ''henne'' (they fem.) resembles Hebrew ''hēm'' / ''hēn'' as against Classical Arabic ''hum''/''hunna'', Aramaic ''hennōn''/''hennēn'' and general Levantine Arabic ''hunne''. Similarly the suffixes ''-kem'' (you or your, masc.) and ''-ken'' observed in Bīr-Zēt resembles Hebrew ''-khem'' / ''-khen'' as against Classical Arabic ''-kum'' and ''-kunna'' and Aramaic ''-kōn'' / ''-kēn'' and northern Levantine Arabic ''-kon''. | |||
| !Meaning || Palestinian Arabic || MSA | |||
| * A less clear example is the transformation of glottal stop followed by long alif (alif madda) into an "o" sound, as in the form ''Ana bokel (أنا بوكل)'' noted above. This certainly occurs in the future forms of Hebrew verbs with an ''aleph'' as the first consonant of their root. However, it is equally characteristic of Aramaic. | |||
| |- | |||
| |Why? | |||
| |ليش | |||
| |لماذا | |||
| |- | |||
| |What? | |||
| |ايش or شو | |||
| |ماذا | |||
| |- | |||
| |How? | |||
| |كيف | |||
| |كيف | |||
| |- | |||
| |When? | |||
| |إيمتى or وينتى | |||
| |متى | |||
| |- | |||
| |Where? | |||
| |وين | |||
| |اين | |||
| |- | |||
| |Who? | |||
| |مين | |||
| |من | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| Note that it is tempting to consider the long in مين 'who?' as an influence of ancient Hebrew מי on Classical Arabic من , but it could be as well an analogy with the long vowels of the other interrogatives. | |||
| ===Palestinian-Hebrew Arabic=== | |||
| ] have adopted Hebrew loanwords, like {{transl|he|yesh}} {{script/Hebrew|יֶשׁ}} ("we did it!" - used as sports cheer) which cannot be translated literally into Arabic. According to social linguist Dr. David Mendelson from ], there is an adoption of words from Hebrew in Arabic spoken in Israel which contain alternative native terms. According to linguist Mohammed Omara, of ] some researchers call the Arabic spoken by Israeli Arabs '''''Arabrew'''''. The list of words adopted contain: | |||
| * {{transl|he|ramzor}} {{script/Hebrew|רַמְזוֹר}} (traffic light) | |||
| * {{transl|he|shamenet}} {{script/Hebrew|שַׁמֶּנֶת}} (sour cream) | |||
| * {{transl|he|beseder}} {{script/Hebrew|בְּסֵדֶר}} (O.K, alright) | |||
| * {{transl|he|kohavit}} {{script/Hebrew|כּוֹכָבִית}} (asterisk) | |||
| '''Marking Indirect Object''' | |||
| Palestinians in the Palestinian territories refer to their brethren in Israel with ] "the b'seder Arabs" because of their adoption of the Hebrew word for O.K, However words like {{transl|he|ramzor}} {{script/Hebrew|רַמְזוֹר}} (traffic light) and {{transl|he|maḥsom}} {{script/Hebrew|מַחְסוֹם}} (roadblock) became a part of Palestinian ]. Such borrowings are often "Arabized" to reflect not only ] but the phonology of Hebrew as spoken by Arabs.<ref name="Stern, Yoav">{{cite web|last=Stern|first=Yoav|title=The 'b'seder' Arabs|url=http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/features/the-b-seder-arabs-1.244919|publisher=]|accessdate=13 December 2011}}</ref> | |||
| In Classical Arabic, the indirect object was marked with the particle /li-/ ('for', 'to'). For instance 'I said to him' was قلت له and 'I wrote to her' was كتبت لها . In Palestinian Arabic, the Indirect Object marker is still based on the consonant /l/, but with more complex rules, and two different vocal patterns. The basic form before pronouns is a clitic , that always bears the stress, and to which person pronouns are suffixed. The basic form before nouns is . For instance | |||
| The 2009 film '']'' is mostly spoken in Palestinian-Hebrew Arabic. | |||
| * ... قلت لإمك 'I told your mother ...' | |||
| * ...اعطينا المكتوب لمدير البنك 'We gave the letter to the bank manager' | |||
| * ... قلت إله 'I told him ...' | |||
| * ... قلت إلها 'I told her ...' | |||
| * ... كتبت إلّي 'You wrote me ...' | |||
| === Vowel harmony === | |||
| The most often cited example of ] in Palestinian Arabic is in the ] ]s of verbs. If the root vowel is ], then the roundness spreads to other high vowels in the ]. Vowel harmony in PA is also found in the ] verbal domain. ]es are immune to rounding harmony, and vowels left of the stressed ] do not have vowel harmony.<ref>Kenstowicz, Michael. 1981. Vowel Harmony in Palestinian Arabic: A Suprasegmental Analysis. Linguistics 19:449-465.</ref> | |||
| Palestinian Arabic has a regressive vowel harmony for these present tense conjugations: if the verb stem's main vowel is /u/, then the vowel in the prefix is also /u/, else the vowel is /i/. This is compared with ] (which can be seen as representative of other Arabic dialects), where the vowel in the prefix is consistently /a/.<ref>Abu-Salim, Issam. 1987. Vowel Harmony in Palestinian Arabic: A Metrical Perspective. Journal of Linguistics 23:1-24.</ref> | |||
| Examples: | |||
| *‘he understands’: PA ‘''b'''i'''fh'''a'''m''’ (MSA, or standard Arabic, ‘''yafhamu''’) | |||
| *‘he studies’: PA ‘''b'''u'''dr'''u'''s''’ (MSA, ‘''yadrusu''’) | |||
| *‘she wears’: PA ‘''bt'''i'''lb'''i'''s''’ (MSA, ‘''talbisu''’) | |||
| *‘she writes’: PA ‘''bt'''u'''kt'''u'''b''’ (MSA, ‘''taktubu''’) | |||
| *‘oven’: PA ‘''f'''u'''r'''u'''n’ (MSA, ‘''furn''’) | |||
| *‘wedding’: PA ‘'''''U'''r'''u'''s''’ (MSA,‘'urs'’) | |||
| === Substratum and Loanwords === | |||
| The ], as well as their ] successors, have either retained words from the original languages spoken in ], or borrowed them from other cultures and various imperial rulers they contacted or interacted with throughout history. | |||
| ==== Semitic ==== | |||
| ===== Biblical Hebrew ===== | |||
| * {{lang|ar|سفل}} ''sifil'' (bowl, mug) may be a Canaanite/Hebrew substrate.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| * {{lang|ar|جرجير}} ] is regionally used in the sense of shrivelled olive. The Hebrew Bible uses it to refer to a grain (berry), while Mishnaic Hebrew used it to refer to both berries and shriveled olives.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| ===== Western Aramaic ===== | |||
| Most prominently ] by the ]. For instance there are mountains known as جبل الطور where طور is just the Aramaic טור for 'mountain', as well as agricultural terms.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| ===== Modern Hebrew ===== | |||
| From Hebrew, especially the ] have adopted many ]s, like {{transl|he|yesh}} {{script/Hebrew|יֵשׁ}} ("we did it!" – used as sports cheer) which has no real equivalent in Arabic. According to sociolinguist David Mendelson from ], there is an adoption of words from Hebrew in Arabic spoken in Israel where alternative native terms exist. According to linguist Mohammed Omara, of ] some researchers call the Arabic spoken by Israeli Arabs ''Arabrew'' (in Hebrew, ערברית ''"Aravrit''"). The list of words adopted contain: | |||
| * رمزور from {{script/Hebrew|רַמְזוֹר}} 'traffic light' | |||
| * شمنيت from {{script/Hebrew|שַׁמֶּנֶת}} 'sour cream' | |||
| * بسدر from {{script/Hebrew|בְּסֵדֶר}} 'O.K, alright' | |||
| * كوخفيت from {{script/Hebrew|כּוֹכָבִית}} 'asterisk' | |||
| * بلفون from {{script/Hebrew|פֶּלֶאפוֹן}} 'cellular phone'. | |||
| Palestinians in the ] sometimes refer to ] as "the b'seder Arabs"{{Citation needed|date=December 2024}} because of their adoption of the Hebrew word בְּסֵדֶר for 'O.K.', (while Arabic is ماشي ). However words like {{transl|he|ramzor}} {{script/Hebrew|רַמְזוֹר}} 'traffic light' and {{transl|he|maḥsom}} {{script/Hebrew|מַחְסוֹם}} 'roadblock' have become a part of the general Palestinian vernacular. | |||
| Interpretations of "Arabrew" are often colored by non-linguistic political and cultural factors,<ref name="Hawker">{{cite journal |author=Hawker |first=Nancy |year=2018 |title=The mirage of 'Arabrew': Ideologies for understanding Arabic-Hebrew contact |url=https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:0f99963f-8877-45d5-a9e8-85e72f18ca9e |journal=Language in Society |volume=47 |issue=2 |pages=219–244 |doi=10.1017/S0047404518000015 |s2cid=148862120}}</ref> but how contact with Hebrew is realized has been studied, and has been described in linguistic terms and in terms of how it varies. "Arabrew" as spoken by Palestinians and more generally Arab citizens of Israel has been described as classical ] without much structural effect<ref name="Kheir">{{cite journal |author=Afifa Eve Kheir |year=2019 |title=The Matrix Language Turnover Hypothesis: The Case of the Druze Language in Israel |journal=Journal of Language Contact |volume=12 |issue=2 |pages=479–512 |doi=10.1163/19552629-01202008 |s2cid=202246511 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="Hawker" /> While the codeswitching by the majority of Arab or Palestinian citizens of Israel who are Christian or Muslim from the North or the Triangle is described as limited, more intense codeswitching is seen among Arabs who live in Jewish-majority settlements as well as Bedouin (in the South) who serve in the army, although this variety can still be called codeswitching, and does not involve any significant structural change deviating from the non-Hebrew influenced norm.<ref name="Kheir" /> For the most part among all Christian and Muslim Arabs in Israel, the impact of Hebrew contact on Palestinian Arabic is limited to borrowing of nouns, mostly for specialist vocabulary, plus a few discourse markers.<ref name="Hawker" /> However, this does not apply to the Arabic spoken by the Israeli Druze, which has been documented as manifesting much more intense contact effects, including the mixture of Arabic and Hebrew words within syntactic clauses, such as the use of a Hebrew preposition for an Arabic element and vice versa, and the adherence to gender and number agreement between Arabic and Hebrew elements (i.e. a Hebrew possessive adjective must agree with the gender of the Arabic noun it describes).<ref name="Kheir" /> While Hebrew definite articles can only be used for Hebrew nouns, Arabic definite articles are used for Hebrew nouns and are, in fact, the most common DP structure.<ref name="Kheir" /> | |||
| ==== Non-Semitic ==== | |||
| ===== Turkic ===== | |||
| * ''Oda'' (اوضا), from Turkish '']'' (Room) | |||
| *''Kundara'' (كندرة) from Turkish '']'' (Shoe) | |||
| * ''Dughri'' (دُغْرِيّ) from Turkish '']'' (Straight; forward) | |||
| * A -ji Suffix (جي-), used to denote professions or characteristics. Examples include ''kahwaji'' (café waiter) from Turkish ''kahveci''. And ''sufraji'', ''sabonji'', etc. | |||
| ==== Indo-European ==== | |||
| *] such as قصر , from '']'' (Castle), and قلم from '']'' (Reed Pens) which are also known in MSA, but also words such as طاولة from '']'' (Table), which are known in the Arab world. | |||
| *] such as بندورة , from ''']''' (Tomato). | |||
| * ] such as كتو\غتو , '<nowiki/>'']''' (Cake). | |||
| * ] such as بنشر , a reference to tools used to replace ]s such as tire irons and lug wrenches. | |||
| ==Media== | |||
| The ] was published in Palestinian Arabic in 1940,<ref>{{Cite book|title=Gospel of St. Mark in South Levantine Spoken Arabic.|last1=Bishop|first1=E. F. F|last2=George|first2=Surayya|date=1940|location=Cairo|language=ar|oclc = 77662380}}</ref> with the ] and the ] published in 1946.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://gochristianhelps.com/iccm/arabic/othehist.htm|title=Arabic--Other Bible History|website=gochristianhelps.com|access-date=2018-10-15}}</ref> | |||
| ] which are of ] often use Palestinian Arabic as the main language. | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| == |
==Further reading== | ||
| *P. Behnstedt, Wolfdietrich Fischer and Otto Jastrow, ''Handbuch der Arabischen Dialekte''. 2nd ed. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz 1980 (ISBN |
*P. Behnstedt, Wolfdietrich Fischer and Otto Jastrow, ''Handbuch der Arabischen Dialekte''. 2nd ed. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz 1980 ({{ISBN|3-447-02039-3}}) | ||
| *Haim Blanc, ''Studies in North Palestinian Arabic: linguistic inquiries among the Druzes of Western Galilee and Mt. Carmel''. Oriental notes and studies, no. 4. Jerusalem: Typ. Central Press 1953. | *Haim Blanc, ''Studies in North Palestinian Arabic: linguistic inquiries among the Druzes of Western Galilee and Mt. Carmel''. Oriental notes and studies, no. 4. Jerusalem: Typ. Central Press 1953. | ||
| *J. Blau, "Syntax des palästinensischen Bauerndialektes von Bir-Zet: auf Grund der Volkserzahlungen aus Palastina von Hans Schmidt und Paul kahle". Walldorf-Hessen: Verlag fur Orientkunde H. Vorndran 1960. | *J. Blau, "Syntax des palästinensischen Bauerndialektes von Bir-Zet: auf Grund der Volkserzahlungen aus Palastina von Hans Schmidt und Paul kahle". Walldorf-Hessen: Verlag fur Orientkunde H. Vorndran 1960. | ||
| Line 131: | Line 437: | ||
| *R. L. Cleveland, "Notes on an Arabic Dialect of Southern Palestine", in: ''Bulletin of the American Society of Oriental Research'' 185 (1967), pp. 43–57. | *R. L. Cleveland, "Notes on an Arabic Dialect of Southern Palestine", in: ''Bulletin of the American Society of Oriental Research'' 185 (1967), pp. 43–57. | ||
| *Olivier Durand, ''Grammatica di arabo palestinese: il dialetto di Gerusalemme'', Rome: Università di Roma La Sapienza 1996. | *Olivier Durand, ''Grammatica di arabo palestinese: il dialetto di Gerusalemme'', Rome: Università di Roma La Sapienza 1996. | ||
| *Yohanan Elihai, ''Dictionnaire de l’arabe |
*Yohanan Elihai, ''Dictionnaire de l’arabe parlé palestinien: français-arabe''. Jerusalem: Typ. Yanetz 1973. | ||
| *Yohanan Elihai, ''The olive tree dictionary: a transliterated dictionary of conversational Eastern Arabic (Palestinian)''. Washington, DC: Kidron Pub. 2004 (ISBN |
*Yohanan Elihai, ''The olive tree dictionary: a transliterated dictionary of conversational Eastern Arabic (Palestinian)''. Washington, DC: Kidron Pub. 2004 ({{ISBN|0-9759726-0-X}}) | ||
| *Elias N. Haddad, "Manual of Palestinian Arabic". Jerusalem: Syrisches Weisenhaus 1909. | *Elias N. Haddad, "Manual of Palestinian Arabic". Jerusalem: Syrisches Weisenhaus 1909. | ||
| *Moin Halloun, ''A Practical Dictionary of the Standard Dialect Spoken in Palestine''. Bethlehem University 2000. | *Moin Halloun, ''A Practical Dictionary of the Standard Dialect Spoken in Palestine''. Bethlehem University 2000. | ||
| *Moin Halloun, ''Lehrbuch ds Palästinensisch-Arabischen''. Heidelberg 2001. | |||
| *Moin Halloun, ''Spoken Arabic for Foreigners. An Introduction to the Palestinian Dialect''. Vol. 1 & 2. Jerusalem 2003. | *Moin Halloun, ''Spoken Arabic for Foreigners. An Introduction to the Palestinian Dialect''. Vol. 1 & 2. Jerusalem 2003. | ||
| *Arye Levin, ''A Grammar of the Arabic Dialect of Jerusalem'' ]]. Jerusalem: Magnes Press 1994 (ISBN |
*Arye Levin, ''A Grammar of the Arabic Dialect of Jerusalem'' ]]. Jerusalem: Magnes Press 1994 ({{ISBN|965-223-878-3}}) | ||
| *M. Piamenta, ''Studies in the Syntax of Palestinian Arabic''. Jerusalem 1966. | *M. Piamenta, ''Studies in the Syntax of Palestinian Arabic''. Jerusalem 1966. | ||
| *Frank A. Rice and Majed F. Sa'ed, ''Eastern Arabic: an introduction to the spoken Arabic of Palestine, Syria and Lebanon''. Beirut: Khayat's 1960. | *Frank A. Rice and Majed F. Sa'ed, ''Eastern Arabic: an introduction to the spoken Arabic of Palestine, Syria and Lebanon''. Beirut: Khayat's 1960. | ||
| *Frank A. Rice, ''Eastern Arabic-English, English-Eastern Arabic: dictionary and phrasebook for the spoken Arabic of Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine/Israel and Syria''. New York: Hippocrene Books 1998 (ISBN |
*Frank A. Rice, ''Eastern Arabic-English, English-Eastern Arabic: dictionary and phrasebook for the spoken Arabic of Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine/Israel and Syria''. New York: Hippocrene Books 1998 ({{ISBN|0-7818-0685-2}}) | ||
| *H. Schmidt & P. E. Kahle, "Volkserzählungen aus Palaestina, gesammelt bei den Bauern von Bir-Zet". Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht 1918. | *H. Schmidt & P. E. Kahle, "Volkserzählungen aus Palaestina, gesammelt bei den Bauern von Bir-Zet". Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht 1918. | ||
| * {{cite journal|first=Ulrich |last=Seeger|language=de|title=Wörterbuch Palästinensisch – Deutsch|location= | |||
| *Kimary N. Shahin, ''Palestinian Rural Arabic (Abu Shusha dialect)''. 2nd ed. University of British Columbia. LINCOM Europa, 2000 (ISBN 3-89586-960-0) | |||
| Wiesbaden|publisher= Harrassowitz Verlag|year= 2022|journal=Semitica Viva|volume=XVII|issue=61}} | |||
| *Kimary N. Shahin, ''Palestinian Rural Arabic (Abu Shusha dialect)''. 2nd ed. University of British Columbia. LINCOM Europa, 2000 ({{ISBN|3-89586-960-0}}) | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Wikibooks|Levantine Arabic}} | |||
| {{external links|date=December 2011}} | |||
| {{Wiktionary category|category=South Levantine Arabic language}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * "", Dissertation Proposal by Uri Horesh, Philadelphia, December 12, 2003 (]) | |||
| * , project description by Otto Jastrow. | |||
| * (from Wiktionary's ) | |||
| * {{cite web|url=https://sites.google.com/nyu.edu/palestine-lexicon|title=The Open Palestinian Arabic Lexicon "Maknuune"|website=CAMeL Lab, New York University Abu Dhabi}} | |||
| {{Varieties of Arabic}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * "", Dissertation Proposal by Uri Horesh, Philadelphia, December 12, 2003 (]) | |||
| * , project description by Otto Jastrow. | |||
| {{Levantine Arabic}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Varieties of Arabic}}{{Palestine topics}}{{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:08, 8 January 2025
Dialect of Arabic spoken in the State of PalestineThis article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Palestinian Arabic | |
|---|---|
| اللهجة الفلسطينية | |
| Native to | State of Palestine, Israel |
| Region | Palestine |
| Native speakers | 4.3 million (2021) |
| Language family | Afro-Asiatic |
| Dialects |
|
| Writing system | Arabic alphabet |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | (covered by apc) |
| Glottolog | sout3123 |
| IETF | apc-PS |
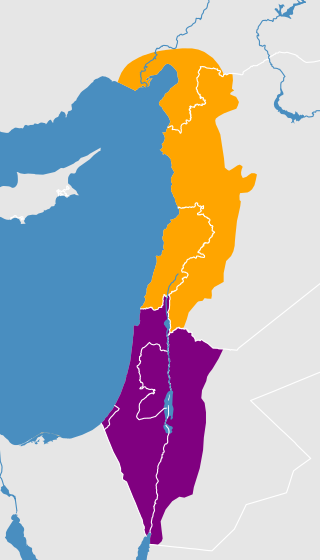 South Levantine South Levantine | |
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |
{ font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma; }
.
Palestinian Arabic (also known as simply Palestinian) is a dialect continuum comprising various mutually intelligible varieties of Levantine Arabic spoken by Palestinians in Palestine, which includes the State of Palestine, Israel, and the Palestinian diaspora.
The Arabic dialects spoken in the region of Palestine and Transjordan do not form a homogeneous linguistic unit; rather, they encompass a diverse range of dialects influenced by geographical, historical, and socioeconomic factors. Comparative studies of Arabic dialects indicate that Palestinian Arabic is among the closest dialects to Modern Standard Arabic, particularly the dialect spoken in the Gaza Strip. Additional distinctions can be made within Palestinian Arabic, such as the dialects spoken in the northern West Bank and the Hebron area, which exhibit similarities to those spoken by descendants of Palestinian refugees.
Palestinian Arabic dialects reflect a historical layering of languages previously spoken in the region, including Canaanite, Hebrew (both Biblical and Mishnaic), Aramaic (especially Western Aramaic), Persian, Greek, and Latin. Furthermore, during the early modern period, these dialects were influenced by Turkish and various European languages. Since the establishment of Israel in 1948, Palestinian Arabic has also been shaped by Modern Hebrew influences.
History
Prior to their adoption of the Arabic language from the seventh century onwards, most of the inhabitants of Palestine spoke varieties of Palestinian Aramaic (Jewish, Christian, Samaritan) as a native language. Koine Greek was used among the Hellenized elite and aristocracy, and Mishanic Hebrew for liturgical purposes.
The Negev desert was under the rule of the Nabatean Kingdom for the greater part of Classical antiquity, and included settlements such as Mahoza and Ein-Gedi where Judean and Nabatean populations lived in alongside each other, as documented by the Babatha archive which dates to the second century. The earliest Old Arabic inscription most resembling of Classical Arabic is found in Ayn Avadat, being a poem dedicated to King Obodas I, known for defeating the Hasmonean Alexander Jannaeus. Its date is estimated between 79 and 120 CE, but no later than 150 CE at most.
The Nabataeans tended to adopt Aramaic as a written language as shown in the Nabataean language texts of Petra, as well as a Lingua Franca. Nabatean and Palestinian Aramaic dialects would both have been thought of as “Aramaic”, and almost certainly have been mutually comprehensible. Additionally, occasional Arabic loanwords can be found in the Jewish Aramaic documents of the Dead Sea Scrolls.
The adoption of Arabic among the local population occurred most probably in several waves. After the Early Muslim Arabians took control of the area, so as to maintain their regular activity, the upper classes had to quickly become fluent in the language of the new rulers who most probably were only few. The prevalence of Northern Levantine features in the urban dialects until the early 20th century, as well as in the dialect of Samaritans in Nablus (with systematic imala of /a:/) tends to show that a first layer of Arabization of urban upper classes could have led to what is now urban Levantine. Then, the main phenomenon could have been the slow countryside shift of Aramaic-speaking villages to Arabic under the influence of Arabized elites, leading to the emergence of the rural Palestinian dialects. This scenario is consistent with several facts.
- The rural forms can be correlated with features also observed in the few Syrian villages where use of Aramaic has been retained up to this day. Palatalisation of /k/ (but of /t/ too), pronunciation of /q/ for instance. Note that the first also exists in Najdi Arabic and Gulf Arabic, but is limited to palatal contexts (/k/ followed by i or a). Moreover, those Eastern dialects have or for /q/ .
- The less-evolutive urban forms can be explained by a limitation owed to the contacts urban trader classes had to maintain with Arabic speakers of other towns in Syria or Egypt.
- The Negev Bedouin dialect shares a number of features with Bedouin Hejazi dialects (unlike Urban Hejazi).
Features

The dialects spoken Arabic-speakers in the Eastern Mediterranean, form a group of dialects known as Levantine Arabic. Arabic manuals for the "Syrian dialect" were produced in the early 20th century, and in 1909 a specific "Palestinian Arabic" manual was published in Jerusalem for Western travelers.
Palestinian Arabic is a variant of Levantine Arabic because its dialects display characteristic Levantine features:
- A conservative stress pattern, closer to Classical Arabic than anywhere else in the Arab world.
- The indicative imperfect with a b- prefix
- A very frequent Imāla of the feminine ending in front consonant context (names in -eh).
- A realisation of /q/ in the cities, and a realisation of /q/ by the Druze, and more variants (including ) in the countryside.
- A shared lexicon
The noticeable differences between southern and northern forms of Levantine Arabic, such as Syrian Arabic and Lebanese Arabic, are stronger in non-urban dialects. The main differences between Palestinian and northern Levantine Arabic are as follows:
- Phonetically, Palestinian dialects differ from Lebanese regarding the classical diphthongs /aj/ and /aw/, which have simplified to and in Palestinian dialects as in Western Syrian, while in Lebanese they have retained a diphthongal pronunciation: and .
- Palestinian dialects differ from Western Syrian as far as short stressed /i/ and /u/ are concerned: in Palestinian they keep a more or less open and pronunciation, and are not neutralised to as in Syrian.
- The Lebanese and Syrian dialects are more prone to imāla of /aː/ than the Palestinian dialects are. For instance شتا 'winter' is in Palestinian but in Lebanese and Western Syrian. Some Palestinian dialects ignore imāla totally (e.g. Gaza). Those dialects that prominently demonstrate imāla of /aː/ (e.g. Nablus) are distinct among Palestinian dialects.
- In morphology, the plural personal pronouns are إحنا 'we', همه also hunne 'they', كم- 'you', هم- هني 'them' in Palestinian, while they are in Syria/Lebanon نحنا 'we', هنه 'they', كن- 'you', هن- 'them'. The variants كو 'you', ـهن 'them', and هنه 'they' are used in Northern Palestinian.
- The conjugation of the imperfect 1st and 3rd person masculine has different prefix vowels. Palestinians say بَكتب 'I write' بَشوف 'I see' where Lebanese and Syrians say بِكتب and بْشوف . In the 3rd person masculine, Palestinians say بِكتب 'He writes' where Lebanese and Western Syrians say بيَكتب .
- Hamza-initial verbs commonly have an prefix sound in the imperfect in Palestinian. For example, Classical Arabic has اكل /akala/ 'to eat' in the perfect tense, and آكل /aːkulu/ with sound in the first person singular imperfect. The common equivalent in Palestinian Arabic is اكل /akal/ in the perfect, with imperfect 1st person singular بوكل /boːkel/ (with the indicative b- prefix.) Thus, in the Galilee and Northern West Bank, the colloquial for the verbal expression, "I am eating" or "I eat" is commonly / , rather than used in the Western Syrian dialect. Note however that or even are used in the South of Palestine.
- The conjugation of the imperative is different too. 'Write!' is اكتب in Palestinian, but كتوب , with different stress and vowel and length, in Lebanese and Western Syrian.
- For the negation of verbs and prepositional pseudo-verbs, Palestinian, like Egyptian, typically suffixes ش on top of using the preverb negation /ma/, e.g. 'I don't write' is مابكتبش in Palestinian, but مابكتب in Northern Levantine (although some areas in southern Lebanon utilise the ش suffix). However, unlike Egyptian, Palestinian allows for ش without the preverb negation /ma/ in the present tense, e.g. بكتبش .
- In vocabulary, Palestinian is closer to Lebanese than to Western Syrian, e.g. 'is not' is مش in both Lebanese and Palestinian (although in a few villages مهوش and مهيش , which are found in Maltese and North African dialects, are used) while it is مو in Syrian; 'How?' is كيف in Lebanese and Palestinian while it is شلون in Syrian (though كيف is also used) . However, Palestinian also shares items with Egyptian Arabic, e.g. 'like' (prep.) is زي in Palestinian in addition to مثل , as found in Syrian and Lebanese Arabic.
There are also typical Palestinian words that are shibboleths compared to other Levantine Arabic dialects :
- The usage of إشي 'thing, something', as opposed to شي in Lebanon and Syria as an indefinite pronoun.
- Besides common Levantine هلق 'now', Central Rural dialects around Jerusalem and Ramallah use هالقيت (although is used in some cities such as Tulkarm, Hebron, and Nablus alongside هلق (both from هالوقت /halwaqt/ ) and northern Palestinians use إسا , إساع , and هسة (from الساعة/ɪsːɑːʕɑ/). Villagers in the southern West Bank also use هالحين or هالحينة (both from هذا الحين )
- Some villagers use بقى (meaning 'remained' in MSA) as a verb to be alongside the standard كان ( in MSA)
Social and geographic dialect structuration
As is very common in Arabic-speaking countries, the Arabic dialect spoken by a person depends on both the region of origin, and socio-economic class. The hikaye, a form of women's oral literature inscribed to UNESCO's list of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Palestine, is recited in both the urban and rural dialects of Palestinian Arabic.
Urban varieties
The Urban ('madani') dialects resemble closely northern Levantine Arabic dialects, that is, the colloquial variants of western Syria and Lebanon. This fact, that makes the urban dialects of the Levant remarkably homogeneous, is probably due to the trading network among cities in Ottoman Syria, or to an older Arabic dialect layer closer to the North Mesopotamian Arabic (the 'qeltu dialects").
Urban dialects are characterised by the (hamza) pronunciation of ق qaf, the simplification of interdentals as dentals plosives, i.e. ث as , ذ as and both ض and ظ as . In borrowings from Modern Standard Arabic, these interdental consonants are realised as dental sibilants, i.e. ث as , ذ as and ظ as but ض is kept as . The Druzes have a dialect that may be classified with the Urban ones, with the difference that they keep the uvular pronunciation of ق qaf as . The urban dialects also ignore the difference between masculine and feminine in the plural pronouns انتو is both 'you' (masc. plur.) and 'you' (fem. plur.), and is both 'they' (masc.) and 'they' (fem.)
Sephardi variety
Main article: Modern Palestinian Judeo-ArabicAs Sephardic Jews were expelled after the conclusion of the Reconquista, they established communities in Ottoman Palestine in Jerusalem and Galilee under the invitation of Sultan Bayezid II. Their Maghrebi Judeo-Arabic dialect mixed with Palestinian Arabic. It peaked at 10,000 speakers and thrived alongside Yiddish among Ashkenazis until the widespread adoption of Modern Hebrew among the Yishuv following its revival in the late 19th century.
Today it is nearly extinct, with only 5 speakers remaining in the Galilee. It contained influence from Judeo-Moroccan Arabic and influence Judeo-Lebanese Arabic and Judeo-Syrian Arabic.
Rural varieties
Rural ('fallahi') variety is retaining the interdental consonants, and is closely related with rural dialects in Southern Lebanon and the sedentary population east of the Jordan river. They keep the distinction between masculine and feminine plural pronouns, e.g. انتو is 'you' (masc.) while انتن is 'you' (fem.), and همه is 'they' (masc.) while هنه is 'they' (fem.). The three rural groups in the region are the following:
- North Galilean rural dialect – does not feature the k > tʃ palatalization, and many of them have kept the realisation of ق (e.g. Maghār, Tirat Carmel). In the very north, they announce dialect thats is more closely to the Northern Levantine dialects with n-ending pronouns such as كن- 'you', هن- 'them' (Tarshiha, etc.).
- Central rural Palestinian (From Nazareth to Bethlehem, including Jaffa countryside) exhibits a very distinctive feature with pronunciation of ك 'kaf' as 'tshaf' (e.g. كفية 'keffieh' as ) and ق 'qaf' as pharyngealised /k/ i.e. 'kaf' (e.g. قمح 'wheat' as ). This k > tʃ sound change is not conditioned by the surrounding sounds in Central Palestinian. This combination is unique in the whole Arab world, but could be related to the 'qof' transition to 'kof' in the Aramaic dialect spoken in Ma'loula, north of Damascus.
- Southern outer rural Levantine Arabic (to the south of an Isdud/Ashdod-Bethlehem line) has k > tʃ only in presence of front vowels (ديك 'rooster' is in the singular but the plural ديوك 'roosters' is because u prevents /k/ from changing to ). In this dialect ق is not pronounced as but instead as . This dialect is actually very similar to northern Jordanian (Ajloun, Irbid) and the dialects of Syrian Hauran. In Southern rural Palestinian, the feminine ending often remains .
Bedouin variety
The Bedouins of Southern Levant use two different ('badawi') dialects in Galilee and the Negev. The Negev desert Bedouins, who are also present in Palestine and Gaza Strip use a dialect closely related to those spoken in the Hijaz, and in the Sinai. Unlike them, the Bedouins of Galilee speak a dialect related to those of the Syrian Desert and Najd, which indicates their arrival to the region is relatively recent. The Negev Bedouins, who ended up around Hebron and Jerusalem after the 1948 Palestine War have a specific vocabulary, where they maintain the interdental consonants, do not use the ش- negative suffix, always realise ك /k/ as and ق /q/ as , and distinguish plural masculine from plural feminine pronouns, but with different forms as the rural speakers.
Current evolutions
On the urban dialects side, the current trend is to have urban dialects getting closer to their rural neighbours, thus introducing some variability among cities in the Levant. For instance, Jerusalem used to say as Damascus ("we") and ("they") at the beginning of the 20th century, and this has moved to the more rural and nowadays. This trend was probably initiated by the partition of the Levant of several states in the course of the 20th century.
The Rural description given above is moving nowadays with two opposite trends. On the one hand, urbanisation gives a strong influence power to urban dialects. As a result, villagers may adopt them at least in part, and Beduin maintain a two-dialect practice. On the other hand, the individualisation that comes with urbanisation make people feel more free to choose the way they speak than before, and in the same way as some will use typical Egyptian or Lebanese features as for , others may use typical rural features such as the rural realisation of ق as a pride reaction against the stigmatisation of this pronunciation.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Interdental | Dental/Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | emph. | plain | emph. | plain | emph. | plain | emph. | ||||||
| Nasal | m | mˤ | n | ||||||||||
| Stop | voiceless | t | tˤ | (t͡ʃ) | k | kˤ | ʔ | ||||||
| voiced | b | bˤ | d | dˤ | d͡ʒ | ɡ | (ɢ) | ||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | θ | s | sˤ | ʃ | χ | ħ | h | ||||
| voiced | ð | ðˤ | z | zˤ | ʒ | ʁ | ʕ | ||||||
| Trill | (r) | rˤ | |||||||||||
| Approximant | l | lˤ | j | w | |||||||||
- Sounds /θ, ð, ðˤ, t͡ʃ, d͡ʒ/ are mainly heard in both the rural and Bedouin dialects. Sounds /zˤ/ and /ʒ/ are mainly heard in the urban dialects. /kˤ/ is heard in the rural dialects.
- /ɡ/ is heard in the Bedouin dialects, and may also be heard as a uvular .
- mainly occurs as a palatalization of /k/, and is only heard in a few words as phonemic. In some rural dialects has replaced /k/ as a phoneme.
- /rˤ/ may de-pharyngealize as in certain phonetic environments.
- /ʁ/ can also be heard as velar among some rural dialects.
- /b/ can be heard as within devoiced positions.
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i iː | u uː | |
| Mid | e eː | o oː | |
| Open | a aː |
- The short vowel /a/ is typically heard as , when in unstressed form.
- /a, aː/ are heard as when following and preceding a pharyngealized consonant. The short vowel /a/ as , can also be raised as in lax form within closed syllables.
- /i, u/ can be lowered to when in lax form, or within the position of a post-velar consonant.
Vocabulary
As Palestinian Arabic originated in the heartland of the Semitic languages, it has kept many regular Semitic words. For this reason, it is simple to speculate how Modern Standard Arabic words map onto Palestinian Arabic Words. The Swadesh list of basic words of Palestinian Arabic available on the Wiktionary (see external links below) may be used for this. However, some words are not transparent mappings from MSA, and deserve a description. This is due either to meaning changes in Arabic along the centuries – while MSA keeps the Classical Arabic meanings – or to the adoption of non-Arabic words (see below). Note that this section focuses on Urban Palestinian unless otherwise specified.
Prepositional pseudo verbs
The words used in Palestinian to express the basic verbs 'to want', 'to have', 'there is/are' are called prepositional pseudo verbs because they share all the features of verbs but are constructed with a preposition and a suffix pronoun.
- there is, there are is فيه in the imperfect, and كان فيه in the perfect.
- To want is formed with bɪdd + suffix pronouns and to have is formed with ʕɪnd + suffix pronouns. In the imperfect they are
| Person | To want | To have |
|---|---|---|
| I | بدي | عندي |
| You (sing. masc.) | بدك | عندك |
| You (sing. fem.) | بدك | عندك |
| He | بده | عنده |
| She | بدها | عندها |
| We | بدنا | عندنا |
| You (plur.) | بدكم | عندكم |
| They | بدهم | عندهم |
In the perfect, they are preceded by كان , e.g. we wanted is كان بدنا .
Determiners
Relative clause
As in most forms of colloquial Arabic, the relative clause markers of Classical Arabic (الذي، التي، اللذان، اللتان، الذين and اللاتي) have been simplified to a single form إللي .
Interrogatives pronouns
The main Palestinian interrogative pronouns (with their Modern Standard Arabic counterparts) are the following ones.
| Meaning | Palestinian Arabic | MSA |
|---|---|---|
| Why? | ليش | لماذا |
| What? | ايش or شو | ماذا |
| How? | كيف | كيف |
| When? | إيمتى or وينتى | متى |
| Where? | وين | اين |
| Who? | مين | من |
Note that it is tempting to consider the long in مين 'who?' as an influence of ancient Hebrew מי on Classical Arabic من , but it could be as well an analogy with the long vowels of the other interrogatives.
Marking Indirect Object
In Classical Arabic, the indirect object was marked with the particle /li-/ ('for', 'to'). For instance 'I said to him' was قلت له and 'I wrote to her' was كتبت لها . In Palestinian Arabic, the Indirect Object marker is still based on the consonant /l/, but with more complex rules, and two different vocal patterns. The basic form before pronouns is a clitic , that always bears the stress, and to which person pronouns are suffixed. The basic form before nouns is . For instance
- ... قلت لإمك 'I told your mother ...'
- ...اعطينا المكتوب لمدير البنك 'We gave the letter to the bank manager'
- ... قلت إله 'I told him ...'
- ... قلت إلها 'I told her ...'
- ... كتبت إلّي 'You wrote me ...'
Vowel harmony
The most often cited example of vowel harmony in Palestinian Arabic is in the present tense conjugations of verbs. If the root vowel is rounded, then the roundness spreads to other high vowels in the prefix. Vowel harmony in PA is also found in the nominal verbal domain. Suffixes are immune to rounding harmony, and vowels left of the stressed syllable do not have vowel harmony.
Palestinian Arabic has a regressive vowel harmony for these present tense conjugations: if the verb stem's main vowel is /u/, then the vowel in the prefix is also /u/, else the vowel is /i/. This is compared with standard Arabic (which can be seen as representative of other Arabic dialects), where the vowel in the prefix is consistently /a/.
Examples:
- ‘he understands’: PA ‘bifham’ (MSA, or standard Arabic, ‘yafhamu’)
- ‘he studies’: PA ‘budrus’ (MSA, ‘yadrusu’)
- ‘she wears’: PA ‘btilbis’ (MSA, ‘talbisu’)
- ‘she writes’: PA ‘btuktub’ (MSA, ‘taktubu’)
- ‘oven’: PA ‘furun’ (MSA, ‘furn’)
- ‘wedding’: PA ‘Urus’ (MSA,‘'urs'’)
Substratum and Loanwords
The Ancient peoples of Palestine, as well as their Palestinian successors, have either retained words from the original languages spoken in the land, or borrowed them from other cultures and various imperial rulers they contacted or interacted with throughout history.
Semitic
Biblical Hebrew
- سفل sifil (bowl, mug) may be a Canaanite/Hebrew substrate.
- جرجير "arugula" is regionally used in the sense of shrivelled olive. The Hebrew Bible uses it to refer to a grain (berry), while Mishnaic Hebrew used it to refer to both berries and shriveled olives.
Western Aramaic
Most prominently place names preserved by the inhabitants through the centuries. For instance there are mountains known as جبل الطور where طور is just the Aramaic טור for 'mountain', as well as agricultural terms.
Modern Hebrew
From Hebrew, especially the Arab citizens of Israel have adopted many Hebraisms, like yesh יֵשׁ ("we did it!" – used as sports cheer) which has no real equivalent in Arabic. According to sociolinguist David Mendelson from Givat Haviva's Jewish-Arab Center for Peace, there is an adoption of words from Hebrew in Arabic spoken in Israel where alternative native terms exist. According to linguist Mohammed Omara, of Bar-Ilan University some researchers call the Arabic spoken by Israeli Arabs Arabrew (in Hebrew, ערברית "Aravrit"). The list of words adopted contain:
- رمزور from רַמְזוֹר 'traffic light'
- شمنيت from שַׁמֶּנֶת 'sour cream'
- بسدر from בְּסֵדֶר 'O.K, alright'
- كوخفيت from כּוֹכָבִית 'asterisk'
- بلفون from פֶּלֶאפוֹן 'cellular phone'.
Palestinians in the Palestinian territories sometimes refer to Israeli Arabs as "the b'seder Arabs" because of their adoption of the Hebrew word בְּסֵדֶר for 'O.K.', (while Arabic is ماشي ). However words like ramzor רַמְזוֹר 'traffic light' and maḥsom מַחְסוֹם 'roadblock' have become a part of the general Palestinian vernacular.
Interpretations of "Arabrew" are often colored by non-linguistic political and cultural factors, but how contact with Hebrew is realized has been studied, and has been described in linguistic terms and in terms of how it varies. "Arabrew" as spoken by Palestinians and more generally Arab citizens of Israel has been described as classical codeswitching without much structural effect While the codeswitching by the majority of Arab or Palestinian citizens of Israel who are Christian or Muslim from the North or the Triangle is described as limited, more intense codeswitching is seen among Arabs who live in Jewish-majority settlements as well as Bedouin (in the South) who serve in the army, although this variety can still be called codeswitching, and does not involve any significant structural change deviating from the non-Hebrew influenced norm. For the most part among all Christian and Muslim Arabs in Israel, the impact of Hebrew contact on Palestinian Arabic is limited to borrowing of nouns, mostly for specialist vocabulary, plus a few discourse markers. However, this does not apply to the Arabic spoken by the Israeli Druze, which has been documented as manifesting much more intense contact effects, including the mixture of Arabic and Hebrew words within syntactic clauses, such as the use of a Hebrew preposition for an Arabic element and vice versa, and the adherence to gender and number agreement between Arabic and Hebrew elements (i.e. a Hebrew possessive adjective must agree with the gender of the Arabic noun it describes). While Hebrew definite articles can only be used for Hebrew nouns, Arabic definite articles are used for Hebrew nouns and are, in fact, the most common DP structure.
Non-Semitic
Turkic
- Oda (اوضا), from Turkish oda (Room)
- Kundara (كندرة) from Turkish kundura (Shoe)
- Dughri (دُغْرِيّ) from Turkish doğru (Straight; forward)
- A -ji Suffix (جي-), used to denote professions or characteristics. Examples include kahwaji (café waiter) from Turkish kahveci. And sufraji, sabonji, etc.
Indo-European
- Latin such as قصر , from Castrum (Castle), and قلم from Calamus (Reed Pens) which are also known in MSA, but also words such as طاولة from Tabula (Table), which are known in the Arab world.
- Italian such as بندورة , from Pomodoro (Tomato).
- French such as كتو\غتو , 'Gâteau' (Cake).
- English such as بنشر , a reference to tools used to replace flat tires such as tire irons and lug wrenches.
Media
The Gospel of Mark was published in Palestinian Arabic in 1940, with the Gospel of Matthew and the Letter of James published in 1946.
Films which are of Palestinian production often use Palestinian Arabic as the main language.
See also
- Palestinian Music
- Levantine Arabic
- Varieties of Arabic
- Demographic history of Palestine (region)
- Arabization
- Arabic language in Israel
References
- Palestinian Arabic at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)

- "How to Reach your Audience with the Right Dialect of Arabic". Asian Absolute. 2016-01-19. Retrieved 2020-06-24.
- "Arabic Language: Tracing its Roots, Development and Varied Dialects". Day Translations. 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2020-06-24.
- Palva, H. (1984). "A general classification for the Arabic dialects spoken in Palestine and Transjordan". Studia Orientalia Electronica. 55: 357–376.
- Kwaik, K.; Saad, M.; Chatzikyriakidis, S.; Dobnik, S. (2018). "A Lexical Distance Study of Arabic Dialects". Procedia Computer Science. The 4th International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics (ACLing). 143 (published 15 November 2018): 1, 3. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.456. ISSN 1877-0509.
- Harrat, S.; Meftouh, K.; Abbas, M.; Jamoussi, S.; Saad, M.; Smaili, K. (2015). "Cross-Dialectal Arabic Processing". Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing. Gelbukh, Alexander (Ed.). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 9041. Springer, Cham. (published April 14–20, 2015). pp. 3, 6. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-18111-0_47. ISBN 978-3-319-18110-3. S2CID 5978068. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ Bassal, Ibrahim (2012). "Hebrew and Aramaic Substrata in Spoken Palestinian Arabic". Mediterranean Language Review. 19: 85–104. ISSN 0724-7567. JSTOR 10.13173/medilangrevi.19.2012.0085.
- "A First/Second Century Arabic Inscription Of 'En 'Avdat". www.islamic-awareness.org. Retrieved 2024-06-15.
- ^ Macdonald, Michael C. A. (2017). "How much can we know about language and literacy in Roman Judaea? A review". Journal of Roman Archaeology. 30: 832–842. doi:10.1017/S1047759400074882. S2CID 232343804.
- Crow, F.E., Arabic manual: a colloquia handbook in the Syrian dialect, for the use of visitors to Syria and Palestine, containing a simplified grammar, a comprehensive English and Arabic vocabulary and dialogues, Luzac & co, London, 1901
- Rivoal, Isabelle (2001-01-01). "Susan Slyomovics, The Object of Memory. Arabs and Jews Narrate the Palestinian Village". L'Homme. Revue française d'anthropologie (in French) (158–159): 478–479. doi:10.4000/lhomme.6701. ISSN 0439-4216.
- Timothy, Dallen J. (2018-12-07). Routledge Handbook on Tourism in the Middle East and North Africa. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-22923-0.
- Ammon, Ulrich (2006). Sociolinguistics/Soziolinguistik 3: An International Handbook of the Science. Walter de Gruyter. p. 1922. ISBN 9783110184181.
- "Judeo-Arabic". Jewish Languages. Retrieved 2024-01-25.
- Geva-Kleinberger, Aharon (2018-11-05), "Judeo-Arabic in the Holy Land and Lebanon", Languages in Jewish Communities, Past and Present, De Gruyter Mouton, pp. 569–580, doi:10.1515/9781501504631-021, ISBN 978-1-5015-0463-1, S2CID 134826368, retrieved 2024-01-25
- U. Seeger, Mediterranean Language Review 10 (1998), pp. 89-145.
- Shahin, Kimary N. (2019). Palestinian Arabic. In Kees Versteegh (ed.), Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics, Vol. II: Leiden: Brill. pp. 526–538. ISBN 978-90-04-17702-4.
- Kenstowicz, Michael. 1981. Vowel Harmony in Palestinian Arabic: A Suprasegmental Analysis. Linguistics 19:449-465.
- Abu-Salim, Issam. 1987. Vowel Harmony in Palestinian Arabic: A Metrical Perspective. Journal of Linguistics 23:1-24.
- ^ Hawker, Nancy (2018). "The mirage of 'Arabrew': Ideologies for understanding Arabic-Hebrew contact". Language in Society. 47 (2): 219–244. doi:10.1017/S0047404518000015. S2CID 148862120.
- ^ Afifa Eve Kheir (2019). "The Matrix Language Turnover Hypothesis: The Case of the Druze Language in Israel". Journal of Language Contact. 12 (2): 479–512. doi:10.1163/19552629-01202008. S2CID 202246511.
- Bishop, E. F. F; George, Surayya (1940). Gospel of St. Mark in South Levantine Spoken Arabic (in Arabic). Cairo. OCLC 77662380.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Arabic--Other Bible History". gochristianhelps.com. Retrieved 2018-10-15.
Further reading
- P. Behnstedt, Wolfdietrich Fischer and Otto Jastrow, Handbuch der Arabischen Dialekte. 2nd ed. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz 1980 (ISBN 3-447-02039-3)
- Haim Blanc, Studies in North Palestinian Arabic: linguistic inquiries among the Druzes of Western Galilee and Mt. Carmel. Oriental notes and studies, no. 4. Jerusalem: Typ. Central Press 1953.
- J. Blau, "Syntax des palästinensischen Bauerndialektes von Bir-Zet: auf Grund der Volkserzahlungen aus Palastina von Hans Schmidt und Paul kahle". Walldorf-Hessen: Verlag fur Orientkunde H. Vorndran 1960.
- J. Cantineau, "Remarques sur les parlés de sédentaires syro-libano-palestiniens", in: Bulletin de la Société de Linguistique de Paris 40 (1938), pp. 80–89.
- R. L. Cleveland, "Notes on an Arabic Dialect of Southern Palestine", in: Bulletin of the American Society of Oriental Research 185 (1967), pp. 43–57.
- Olivier Durand, Grammatica di arabo palestinese: il dialetto di Gerusalemme, Rome: Università di Roma La Sapienza 1996.
- Yohanan Elihai, Dictionnaire de l’arabe parlé palestinien: français-arabe. Jerusalem: Typ. Yanetz 1973.
- Yohanan Elihai, The olive tree dictionary: a transliterated dictionary of conversational Eastern Arabic (Palestinian). Washington, DC: Kidron Pub. 2004 (ISBN 0-9759726-0-X)
- Elias N. Haddad, "Manual of Palestinian Arabic". Jerusalem: Syrisches Weisenhaus 1909.
- Moin Halloun, A Practical Dictionary of the Standard Dialect Spoken in Palestine. Bethlehem University 2000.
- Moin Halloun, Lehrbuch ds Palästinensisch-Arabischen. Heidelberg 2001.
- Moin Halloun, Spoken Arabic for Foreigners. An Introduction to the Palestinian Dialect. Vol. 1 & 2. Jerusalem 2003.
- Arye Levin, A Grammar of the Arabic Dialect of Jerusalem . Jerusalem: Magnes Press 1994 (ISBN 965-223-878-3)
- M. Piamenta, Studies in the Syntax of Palestinian Arabic. Jerusalem 1966.
- Frank A. Rice and Majed F. Sa'ed, Eastern Arabic: an introduction to the spoken Arabic of Palestine, Syria and Lebanon. Beirut: Khayat's 1960.
- Frank A. Rice, Eastern Arabic-English, English-Eastern Arabic: dictionary and phrasebook for the spoken Arabic of Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine/Israel and Syria. New York: Hippocrene Books 1998 (ISBN 0-7818-0685-2)
- H. Schmidt & P. E. Kahle, "Volkserzählungen aus Palaestina, gesammelt bei den Bauern von Bir-Zet". Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht 1918.
- Seeger, Ulrich (2022). "Wörterbuch Palästinensisch – Deutsch". Semitica Viva (in German). XVII (61). Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Kimary N. Shahin, Palestinian Rural Arabic (Abu Shusha dialect). 2nd ed. University of British Columbia. LINCOM Europa, 2000 (ISBN 3-89586-960-0)
External links
- "The Open Palestinian Arabic Lexicon "Maknuune"". CAMeL Lab, New York University Abu Dhabi.
- The Arabic dialect of central Palestine
- Arabic in Jordan (Palestinian dialect)
- "Phonological change and variation in Palestinian Arabic as spoken inside Israel", Dissertation Proposal by Uri Horesh, Philadelphia, December 12, 2003 (PDF)
- The Corpus of Spoken Palestinian Arabic (CoSPA), project description by Otto Jastrow.
| Levantine Arabic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Overview |  | |
| Dialects | ||
| Related varieties | ||
| Arabic language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overviews | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scripts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Varieties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Academic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguistics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calligraphy · Script | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||